Creating a new one: what to consider?
It is necessary to understand in order to build a solid brick house with your own hands - the mass of a single floor made of this material can exceed a couple of tiers of timber. It is categorically unacceptable not only belts with shallow deepening, but also pillars in the form of steel pipes.
It is recommended at all stages of construction - from design to roof and finishing of walls - to be guided by the provisions of SNiP. This means that even when doing all the work on your own, you need to order professional calculations. The construction of a brick building in a swamp must take into account not only the weakening of the bearing capacity during the warm season, but also the likelihood of frost heaving in the cold months.

Shrinkage
It is necessary to calculate the shrinkage even before the start of detailed design, when the general parameters of the future house have already been fully determined. In the most difficult cases, the shrinkage process takes up to 8 years, but it may take “only” two or three years. Therefore, for the entire period, until this is over, it is imperative to preserve expansion joints. A sand pillow helps to compensate for the negative impact on the foundation. It is also recommended to prepare drainage to absorb additional damage.


Wall mass
The severity of the walls of houses directly affects the depth of the foundation. Bearing capacity 1 sq. see this:
- for fine and medium sand - 2 - 2.5 kg;
- for dusty wet sand - 1 kg;
- for gravel from 4 to 5 kg.
For homogeneous sand or clay of low moisture, the bearing capacity indicator reaches approximately 2 kg per 1 cm2
With regard to the load acting on the base, the highest specific gravity of the building material is taken into account. The stress created by the walls is determined by their total area, multiplied by the mass of the brick
The load created by the basement and attic floors, the roof and the interior of the dwelling is also added to the severity of the wall blocks. Additionally, the calculation includes estimates of the average snow load and the severity of the projected foundation itself.


Construction stages
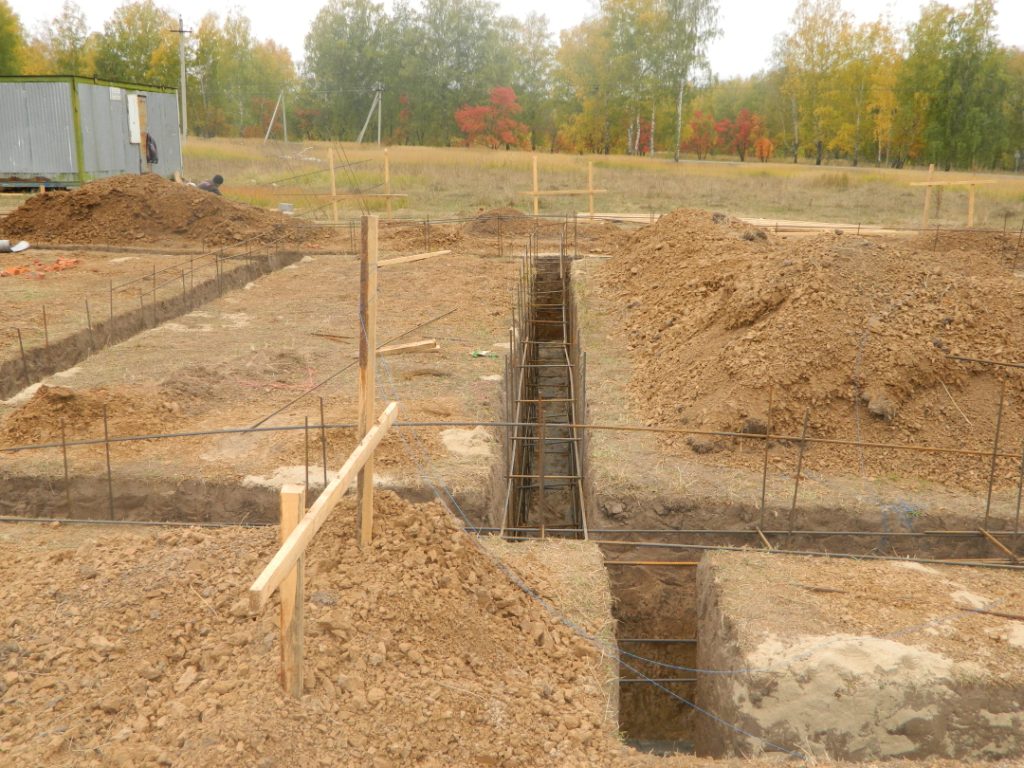
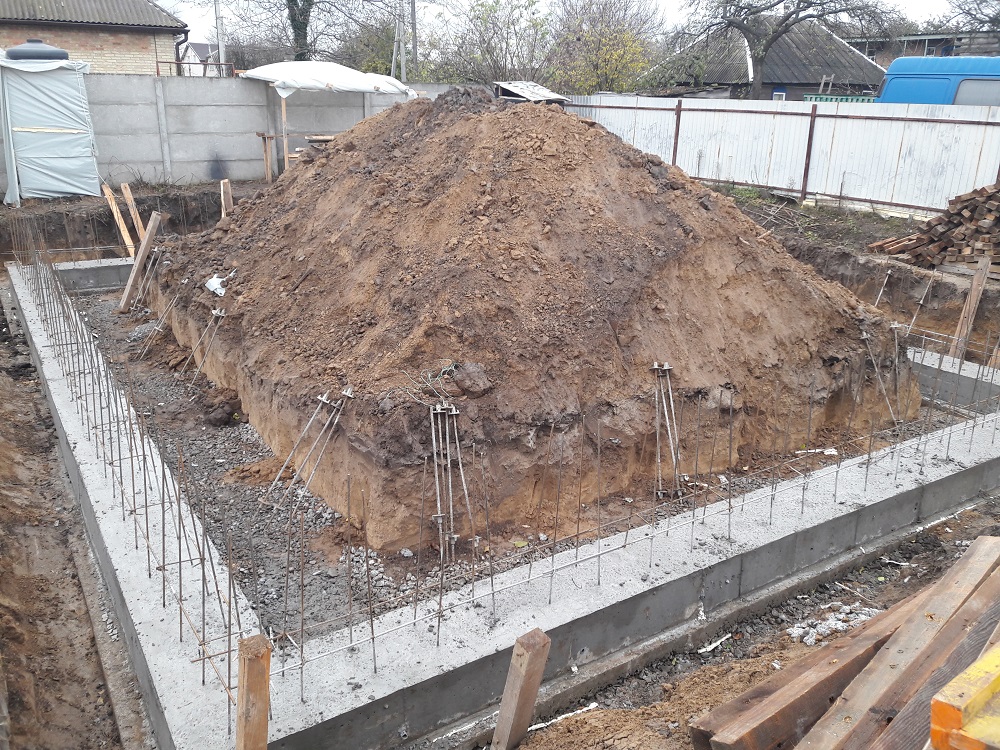
The first step is design, and without geodetic and geophysical surveys, it will not be possible to achieve an optimal result. At the same time, estimate documentation is being prepared, the desired dimensions and architectural nuances of the dwelling are laid. This is how professionals work. Without doing all this, it makes no sense for a private developer to start marking the future foundation of the dwelling. When the marking is completed, holes are drilled, a foundation pit or a trench is dug.
Gravel (sand) is used as a bedding: these layers will help to increase the strength and reliability of the block being created. Pits can be made with fixed or free walls. It must be remembered that under the action of the mechanisms developing the soil and when the natural load (overlying layer) is removed, the upper section of the bearing layer turns out to be less dense.
The extent to which this will be expressed will be influenced by:
- waiting time between soil removal and concrete pouring;
- dynamics of groundwater;
- wetting the soil from atmospheric precipitation;
- the severity of freezing in the winter months during construction, and so on.
The longer the pit is open, the more the clayey rocks swell from water. When wet from atmospheric precipitation, the overall strength is noticeably reduced. If the walls of the pit are sandy, you need to take into account other possible problems - a change in density with rapid soaking. That is why, in any case, they strive to complete the primary stage as soon as possible. Outside, in any case, waterproofing is equipped.


Options for creating a foundation of different types
As a rule, when building a brick house, the creation of three types is used:
- Tape.
- Pile.
- Plate.
The creation of each of them has its own characteristics.
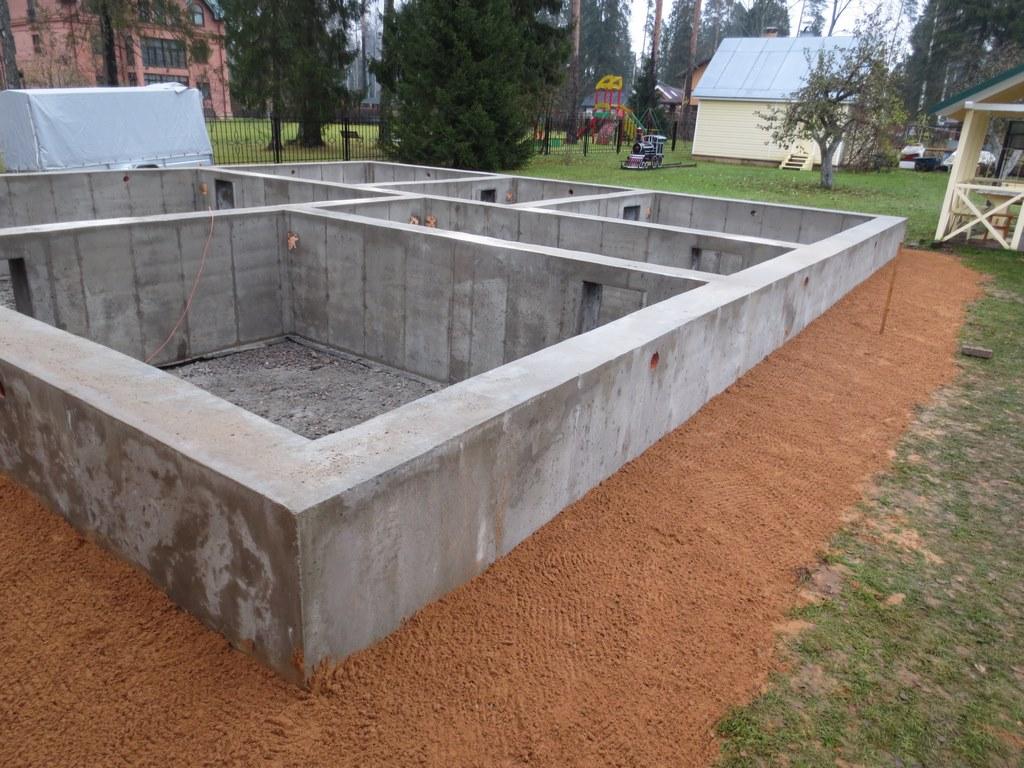
The procedure for creating a strip foundation for the implementation of a future brick building
Using this base option for building a brick house is one of the most common and frequently used options.
 This design is characterized by a high degree of reliability. It runs both under the load-bearing and under the interior walls. Depending on the type of building chosen, several types of strip base can be used to create a house.
This design is characterized by a high degree of reliability. It runs both under the load-bearing and under the interior walls. Depending on the type of building chosen, several types of strip base can be used to create a house.
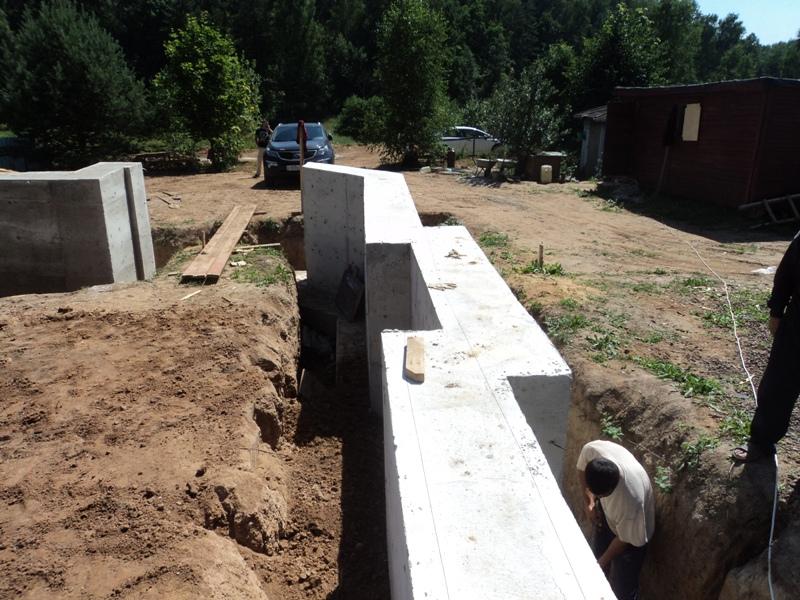
- The large width of the foundation is distinguished by the monolithic version. It is a stand-alone structure made of reinforced concrete. The disadvantages include a long hardening period.
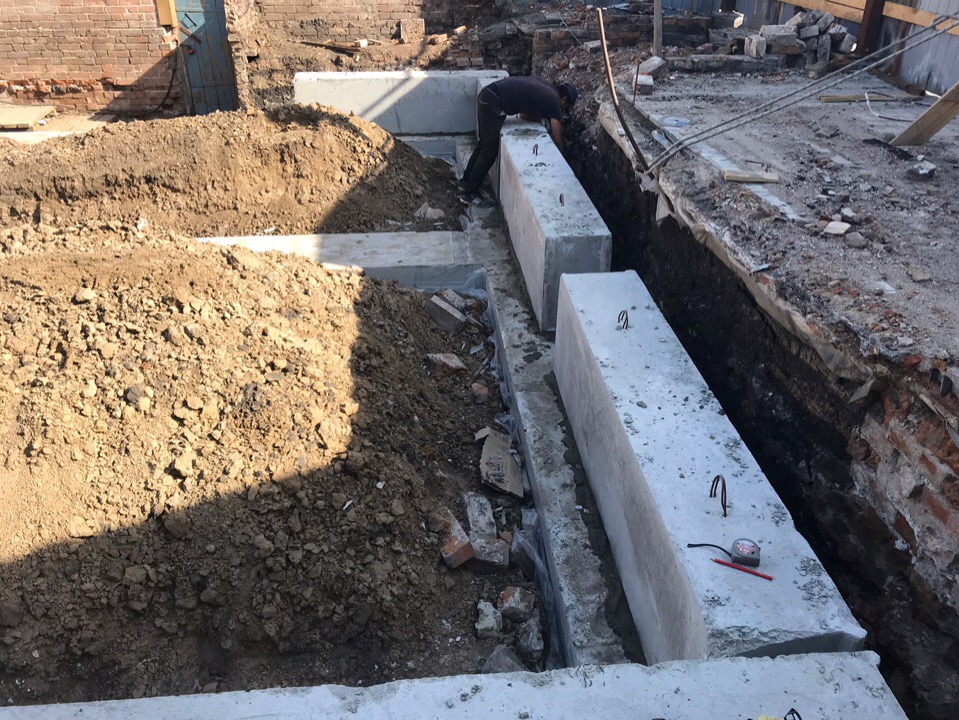
- The prefabricated version of the foundation for a strip-type brick house is made of stone or reinforced concrete blocks. It is difficult to carry out it on your own, since the use of specialized equipment and additional working hands is required.
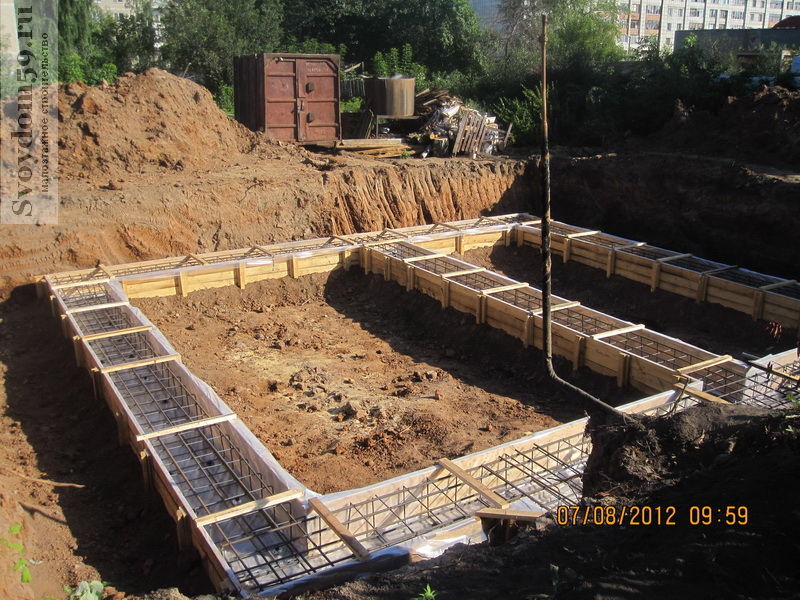
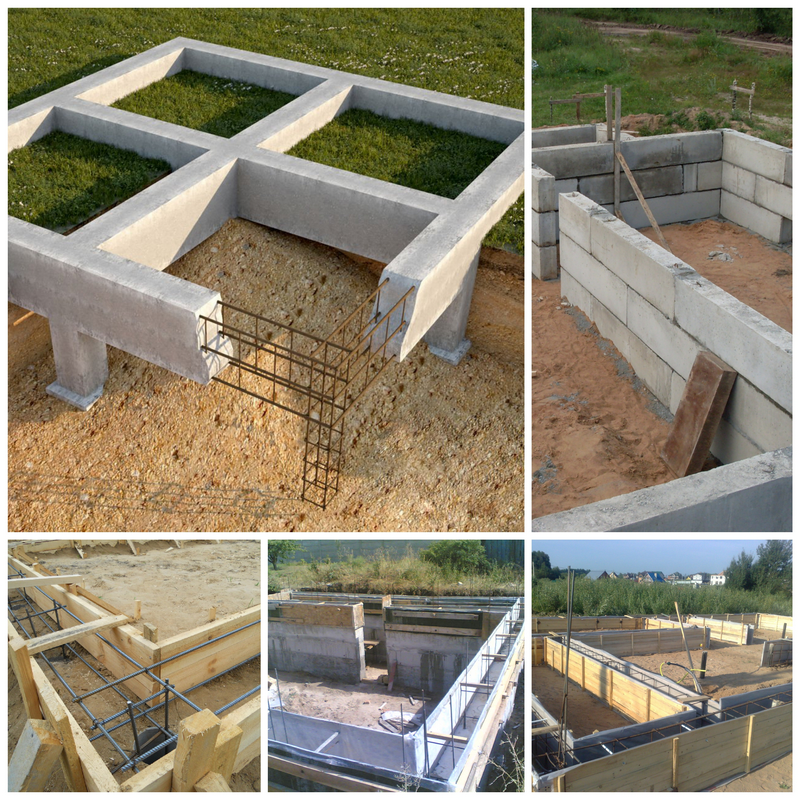
The work procedure includes:
- Preparing the site for creating the foundation for the house
- Alignment of the corners of the future structure
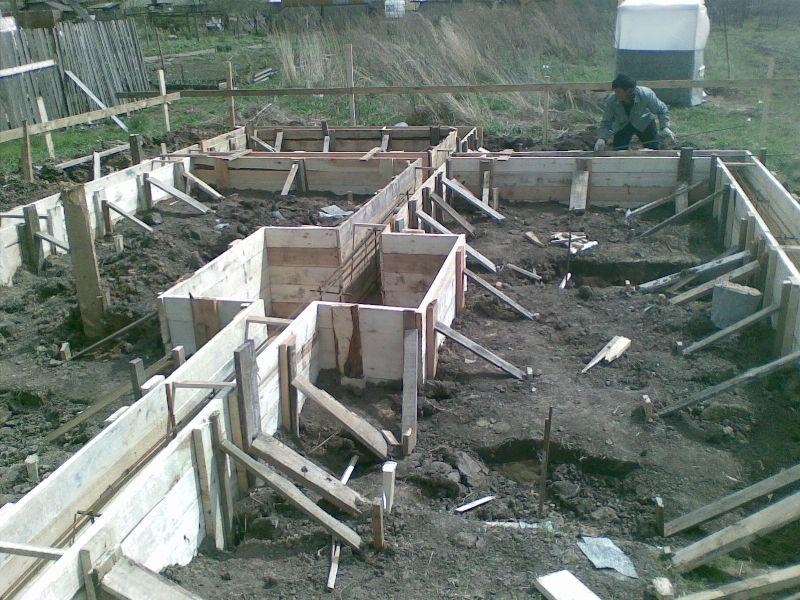
- Digging a trench or foundation pit, taking into account an additional two meters from the planned width of the foundation for placing the formwork
- Depth alignment with theodolite
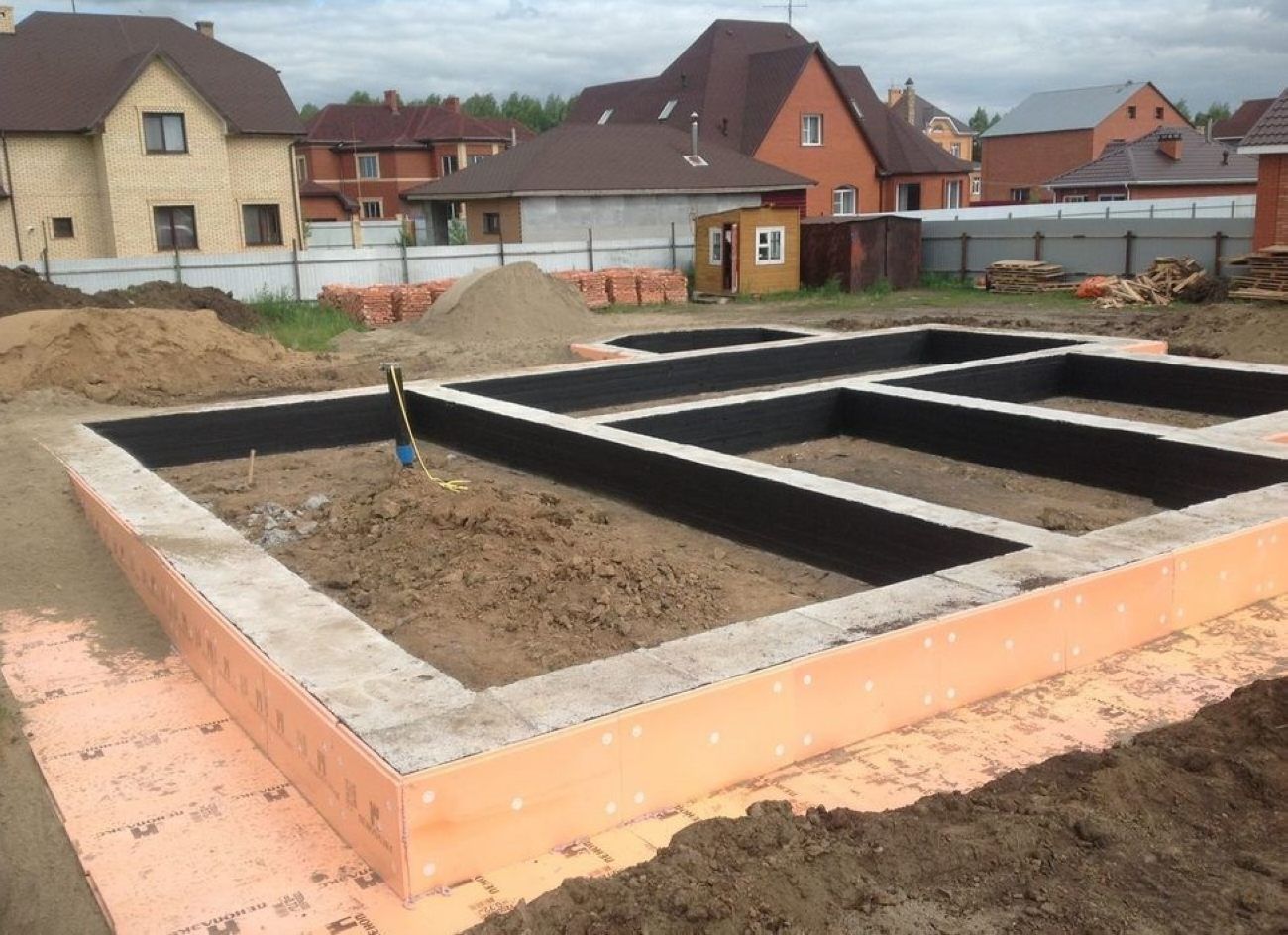
- Backfilling of a sand cushion with a height of about 20 centimeters
- Placement of a layer of waterproofing, which will also provide insulation of the foundation
- Backfill tamping using a vibrating plate
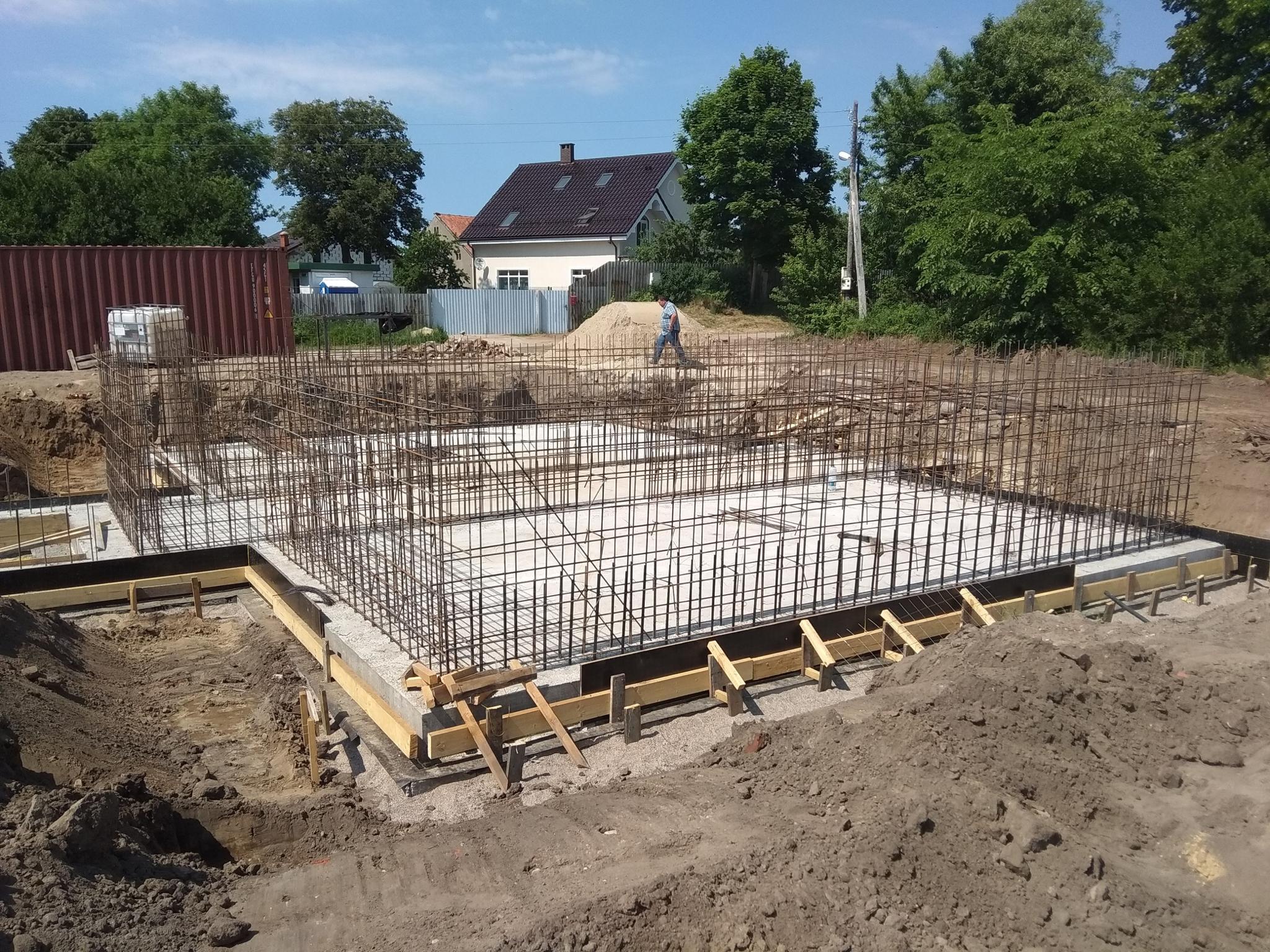
- Formation of the frame from reinforcement, performed outside the trench, the finished structure is lowered into the trench
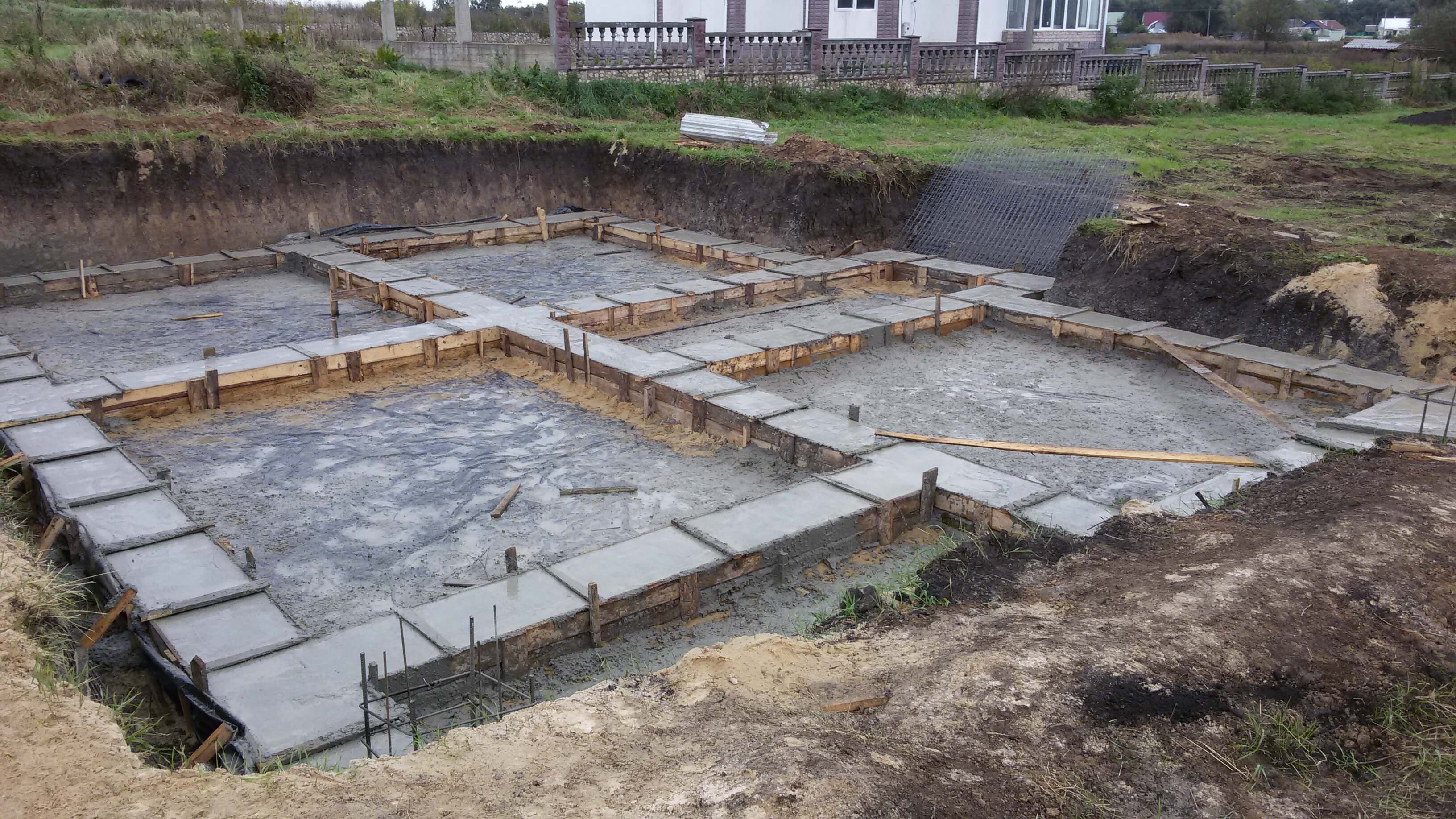
- Concrete pouring
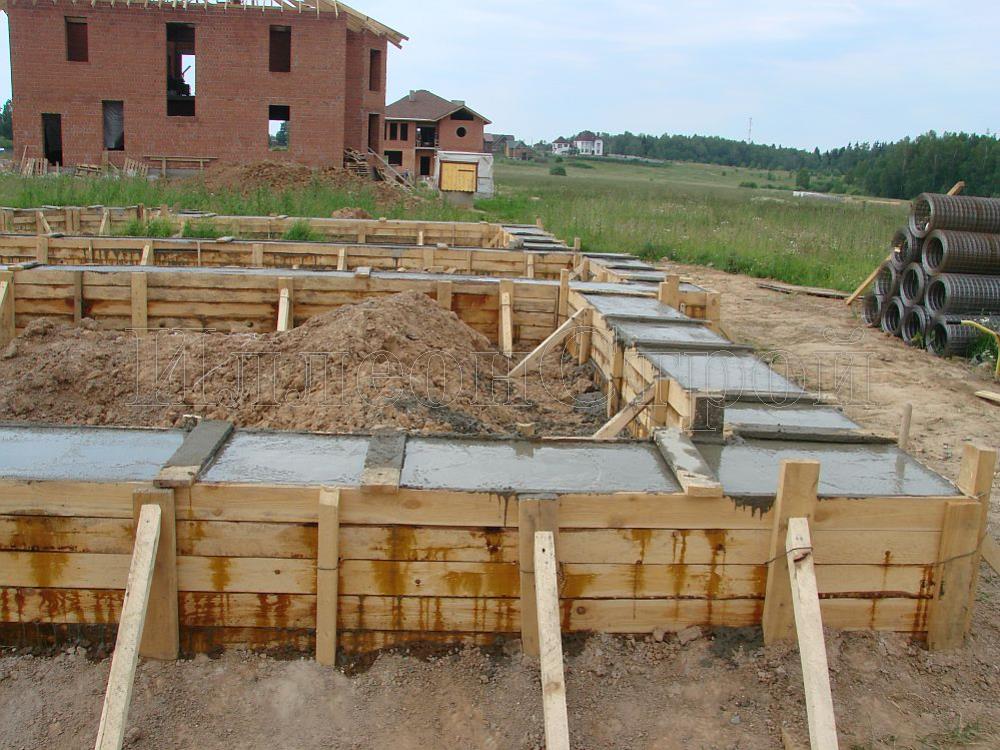
Filling is best done in layers. It is best to choose a shovel to free each layer of concrete from the resulting voids. Each layer must be carefully tamped. A completely filled foundation will dry out for about a month. It is advisable to moisten its surface with water at this time, so as not to cover the cracked base with a brick. Further, a layer of roofing material is laid, which will also provide insulation of the foundation.
The work on the creation of a prefabricated type of foundation is carried out in approximately the same way. An important difference is that it is necessary to carry out additional compaction in the places where the blocks are located. It is advisable to choose blocks of the same size.
Creation of a pile-grillage base for a brick structure
A reliable and solid brick house can be placed even in areas with crumbling soil. Such a structure may have a basement and two or three floors. When performing an underground floor or basement, it is advisable to carry out additional insulation of the foundation.
 In this case, the walls of the building rest on both piles and a grillage that reliably supports the walls. This option is convenient to choose when designing a building in a hilly area. Piles connected by a grillage make the structure durable and make it possible to build a house even on rough terrain.
In this case, the walls of the building rest on both piles and a grillage that reliably supports the walls. This option is convenient to choose when designing a building in a hilly area. Piles connected by a grillage make the structure durable and make it possible to build a house even on rough terrain.
A feature of creating this base for a brick structure is the need to use special equipment to create holes for installing supports.
If there is a need to build a structure with a large number of storeys and areas, for a correct and reliable structure, it is advisable to use the installation of intermediate piles of the required diameter, which are installed about two meters from each other.
Another difference is the connection of the pile frame with reinforcement. At this stage, it is possible to use heaters and thermal insulation. Further, the structure is poured with concrete. Laying bricks is possible, as in the case of creating a strip foundation in about a month.
The procedure for forming a slab foundation
A good slab foundation does not require a lot of effort.For this, the simplest foundation, you will need to place a solid slab on the site, on which the brick structure will be placed in the future. Such a base is chosen when performing work in areas with subsidence or ground movement.
 Such a base for a house can be located at different depths. It's easy to do it yourself. To create a reliable foundation for the structure, insulation of the foundation is required and the use of materials for the implementation of thermal insulation. To form such a foundation of the house, a sand and gravel pillow is laid out on the cleared area, which is then simply poured with concrete. You can also start laying bricks in a month.
Such a base for a house can be located at different depths. It's easy to do it yourself. To create a reliable foundation for the structure, insulation of the foundation is required and the use of materials for the implementation of thermal insulation. To form such a foundation of the house, a sand and gravel pillow is laid out on the cleared area, which is then simply poured with concrete. You can also start laying bricks in a month.
The thickness of the foundation for a brick house
If we talk about calculating the thickness (width) of the foundation tape for a brick house, then it comes down to calculating the required support area for the house, where everything is taken into account, starting from the weight of the house itself, ending with all soil parameters at the construction site. Also, the thickness of the walls plays an important role in determining the width of the foundation.
It would be logical to assume that the wider the monolithic tape is, the stronger it will be and the more support it will have on the ground, but by doing so we significantly increase the costs of the foundation as a whole. Therefore, the thickness must be optimal. In other words, the width of the foundation must be selected in such a way that there is sufficient strength, support on the ground, and also, it is necessary to minimize the cost of concrete, which is the most expensive material for a strip foundation.
I already wrote about how to calculate the foundation for a house in one of the previous articles, so in order not to repeat myself, who is interested, you can take a look. In this calculation, you will learn how to determine the load on the foundation, what should be its support area on the ground, and much more.
Well, if your soil on the site is not very bad, and the terrain is not swampy, then, in principle, the width of the foundation tape can be chosen from the thickness of your external load-bearing walls. So that later there would be no problems with a large overhang of the material from which the walls will be built.
It also plays a huge role in what the basement of the house will be built from. If, for example, made of bricks, then the thickness of the foundation, for expediency, should be a multiple of the width of the brick, i.e. 38 cm, 51 cm, etc. Well, as a rule, for even counting, the width is chosen a multiple of 10 cm, i.e. 40cm, 50cm, etc.
In addition, we can say that with a foundation width of 40 cm and a basement width of 38 cm, it will be easier to correct the errors in marking the foundation and erect the basement with greater geometric accuracy.
The width of our foundation will be 40 cm, which is kind of a "standard" for our area, and most strip foundations are done in the same way.
Despite the fact that the walls of our house will be about 50 cm, in order to save money, you can leave the thickness of the foundation for our brick house 40 cm, this will be enough for support and reliability. The basement will also be about 40 cm, and on top of the basement we will immediately fill the concrete floor with a solid monolithic slab, which will help compensate for the difference in the width of the foundation and the thickness of the walls.
Types of foundations
After familiarizing yourself with the main criteria for choosing load-bearing bases, you should consider in more detail the technical features of a particular foundation for a brick house. In this capacity, three types of bases are most often used:
- Tape.
- Pile.
- Plate.
To understand how to make the right foundation, you should familiarize yourself with the technological nuances of its construction.
Tape base
Strip foundation for a brick house
Strip foundations for a brick house are the most common type.Among the advantages of this option is its simplicity and the ability to withstand very heavy loads, which is especially important for massive buildings, for example, for a two-story brick house. Base-tapes, depending on the design features, are divided into two types:
- Monolithic.
- National teams.
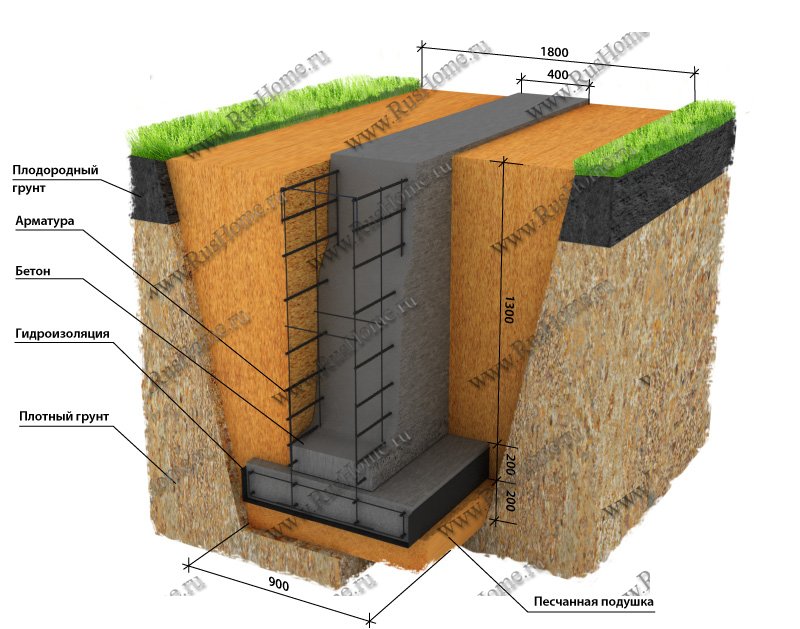
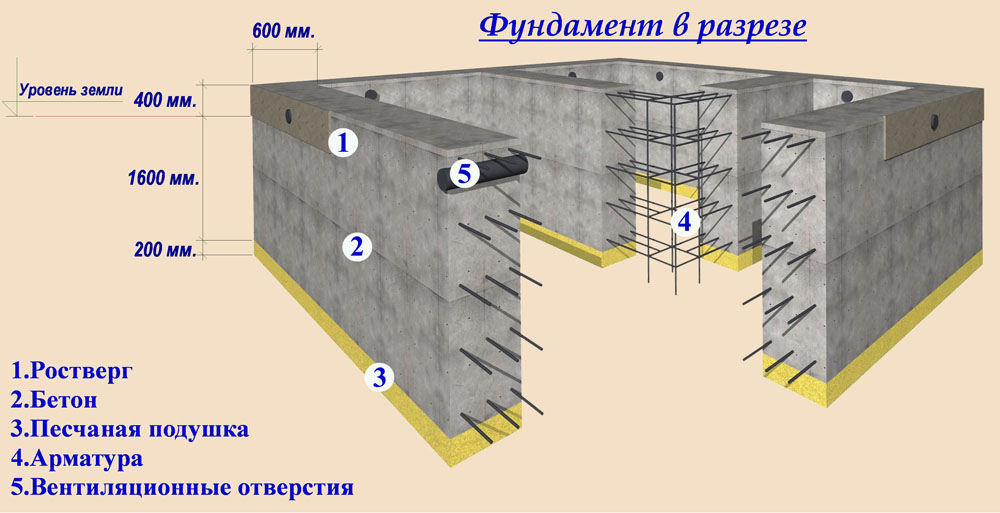
Monolithic bases are cast directly at the construction site from concrete mortar. Before starting concreting, formwork is built and a reinforcing frame is assembled in it. Prefabricated belt structures are assembled from blocks using lifting equipment. Structurally, the foundation tape is a concrete strip running under all the supporting walls of the building, both external and internal.
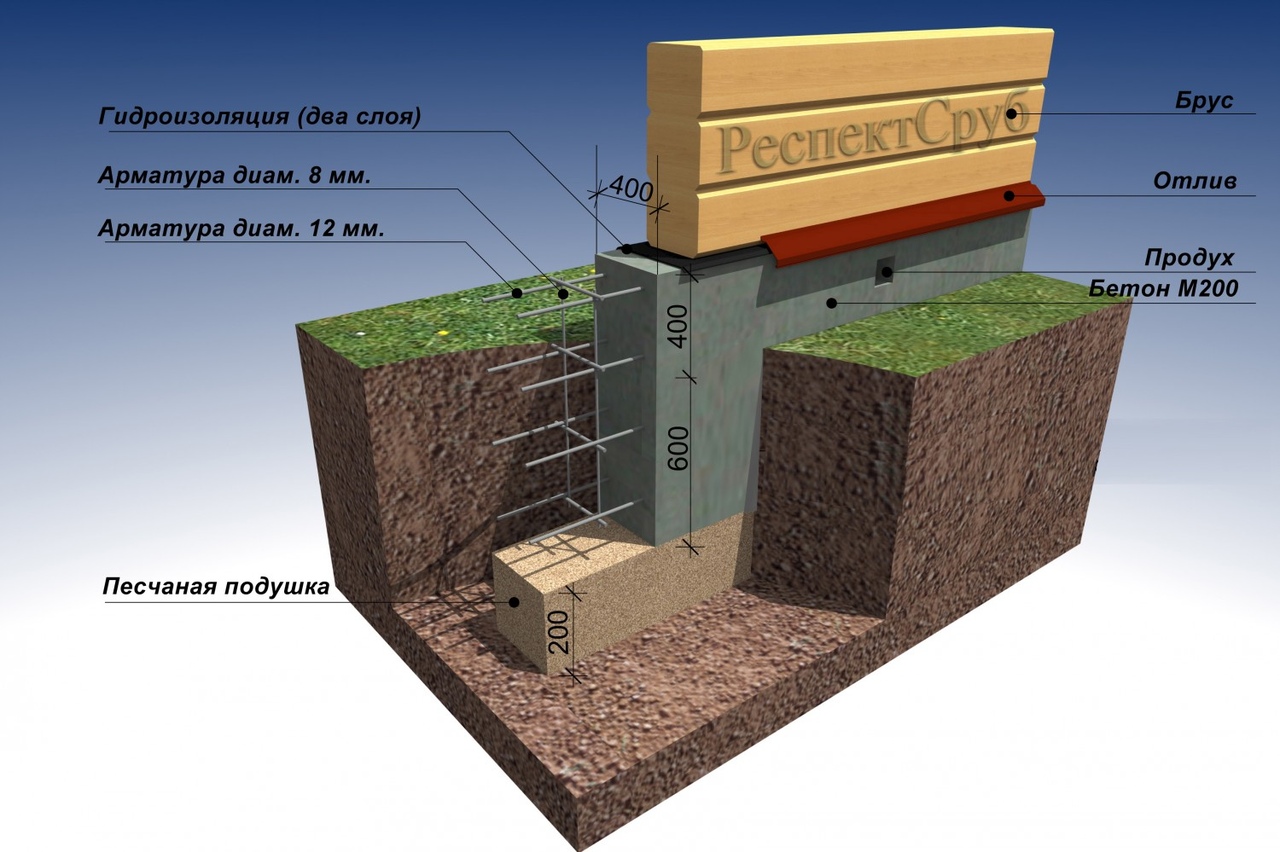
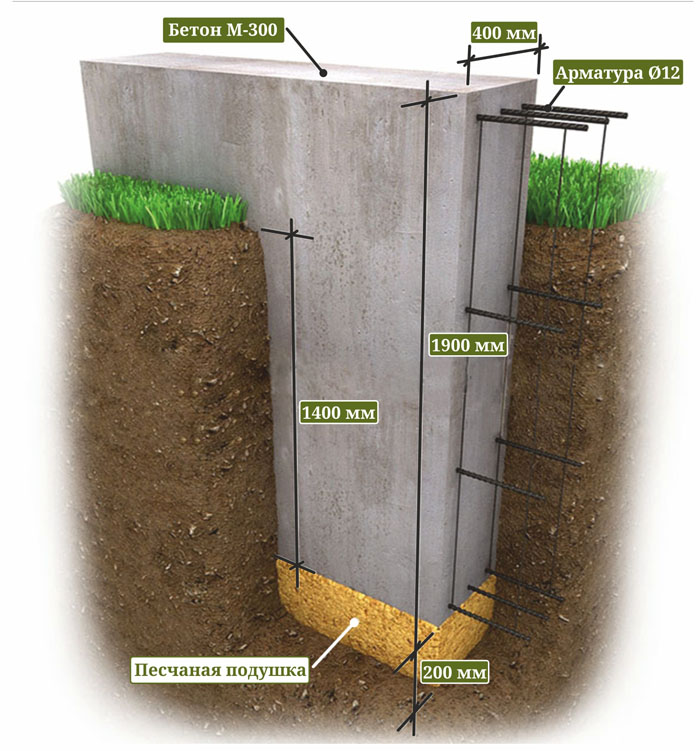
The width of the strip foundation can vary from 30 to 60 cm: it is this size of monolithic foundation slabs that is regulated by construction GOSTs. If the width of the strip foundation for relatively small and light brick buildings can be 300 mm, then the thickness of the foundation for a two-story house should be at least 400 mm.
Pile foundations
A similar version of the foundation is usually used when erecting a building on weak, swampy or heaving soils. A feature of construction on such soils is the need for a solid foundation, which can ensure the stability of the building. For these purposes, the base of the foundation must be buried down to solid rocks, excluding the shrinkage of the building. Or the bottom of the base should be below the level of soil freezing in the cold season. This will exclude it from being squeezed out of the ground by the forces of frost heaving.
Pile foundation for a brick house
In this case, the most optimal technology is the method of driving or twisting piles into the ground. This saves a lot of effort, time and money that would be needed to excavate and fill a monolithic tape of similar depth. There are three technologies for constructing a pile foundation:
- Hammering.
- Bored
- Screw.
Driving method consists in burying the pile into the ground using a special pile hammer. It can be mechanical, suspended from a crane or excavator. In private construction, a manual headframe, powered by the muscular strength of people, can also be used. Bored technology provides for drilling a well of the required depth in the ground, after which it is reinforced and poured with monolithic concrete.
With the screw technique, special piles with a spiral tip are used for the construction of the bearing base. They are deepened with mechanical or manual twists, and the whole process resembles the twisting of a self-tapping screw or a corkscrew.
Slab foundation
Slab foundation
A relatively rarely used technology in residential construction. The classic slab foundation is a reinforced monolithic slab cast on a sand and gravel bed. The low prevalence of this option is associated with a number of operational disadvantages. Firstly, the base-slab excludes the construction of a basement, basement or underground under the house. Secondly, such a foundation is used only in the construction of buildings that are small in weight and size.
The slab foundation of a two-story brick house can be too expensive for the developer due to the large volume of concrete pouring.
Therefore, the base-slab in brick private construction is used only in case of emergency. For example, if the construction is carried out on fragile soils. In this case, a large area of the base plate will prevent the building from sinking, reducing its specific pressure on the ground.
The slab technology can also be used on dense soils, when it is necessary to combine the foundation and subfloors to optimize the work. Such a need may arise during the construction of baths, garages or warehouses.
Having familiarized himself with the features of various foundation structures and the criteria for their selection, a private developer can independently mount a high-quality foundation for his brick house.
The best choice for a two-story house
The choice of the most optimal technology for mounting the base is the key to trouble-free durable construction
At this stage, it is extremely important to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the features of a particular object.
In this case, it is necessary to take into account the maximum permissible values of the loads on the supporting structure.
To resolve the dilemma of which foundation is better, one should turn to statistics. The wide practice of using various types of foundations for a two-story brick house makes it possible to state with confidence that tape technology in this case acts as the most priority direction.
 Manor
Manor
For example, the foundation for a two-story house made of foam blocks based on this technology has already gained popularity among many happy owners. The prerequisites for choosing the presented method are based on the optimal combination of various criteria of a technical, material and operational nature.
The advantages of this method are as follows:
- high level of bearing capacity;
- high performance indicators;
- resistance to deformation and tearing;
- ease of installation;
- low level of material costs;
- ease of maintenance;
- the ability to choose different types of layouts;
- minimum of technical equipment.
 Formwork installation
Formwork installation
It should be noted that all the positive aspects of the recommended technique will manifest themselves only under the condition of strict compliance with the requirements in the presence of good-quality materials.
Choosing the type of foundation for a brick house
Brick houses, even if they are built in 1-2 floors, are classified as heavy structures. Only a few types of foundations can be used as a foundation for such buildings, namely:
- Tape;
- Plate;
- Pile.
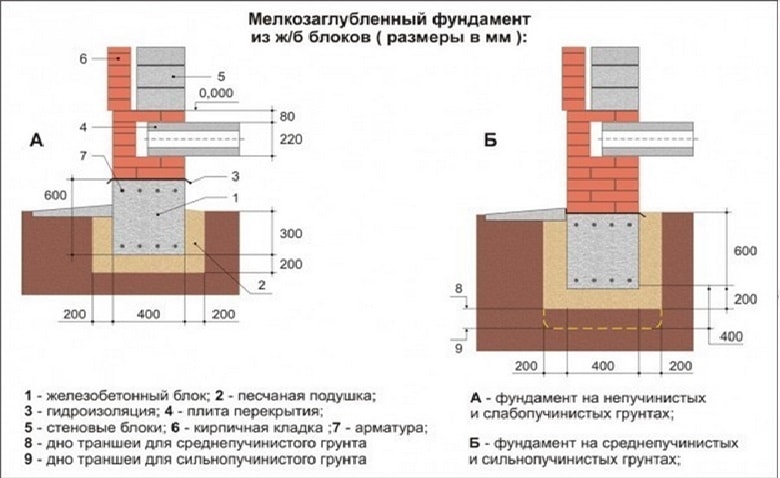
The most economically profitable type of foundation is a shallow strip foundation - however, its use is possible only in non-porous soils, which are extremely scarce in the Moscow Region.

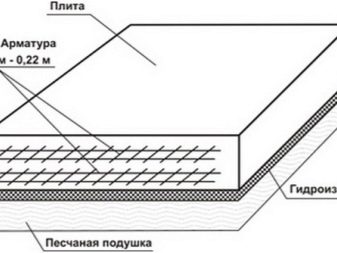
Rice. 1.1: Scheme of a shallow strip foundation The most reliable foundation with high bearing characteristics is a foundation made of a monolithic slab, which is also the most expensive, due to the large amount of materials required for the arrangement.
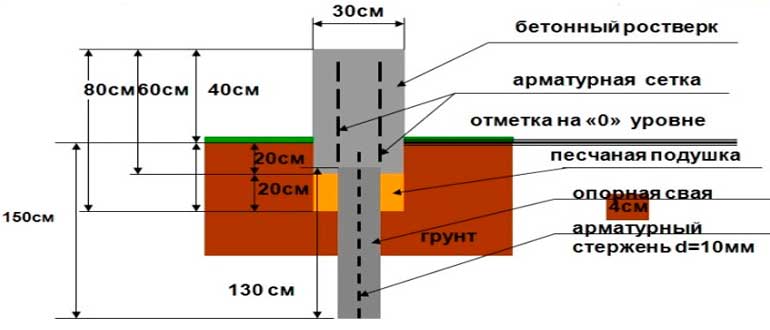
Pile foundations are the "golden mean", with the correct configuration, the foundations on driven piles are not inferior, and in certain types of soils they surpass the bearing properties of slab foundations, work on their arrangement is performed faster and they cost less.
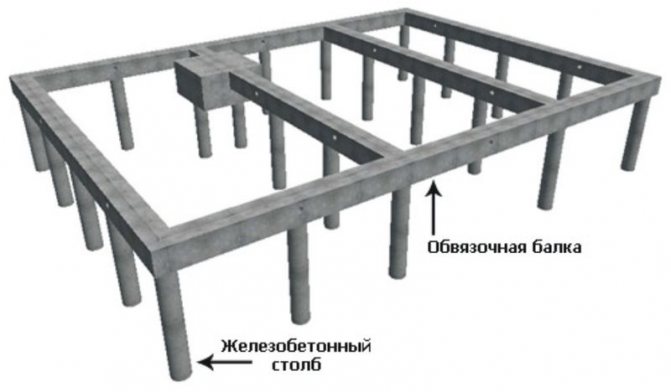
Rice
1.2: Diagram of the pile foundation Important: the economic component is only an insignificant criterion when choosing a foundation for a brick house. First of all, it is necessary to be guided by the standards for the correspondence of foundations to a specific type of soil and weight and size characteristics of the building being erected.
The main factors that determine the type of foundation on which a brick house should be built are as follows:
- Type of soil on the construction site;
- The depth of soil freezing;
- Groundwater level;
- The mass and number of storeys of the structure.
To obtain information about the characteristics of the soil, it makes sense to use the service of a geodetic survey of the site, since without the availability of special equipment it is impossible to collect all the necessary data, namely, they have the maximum weight in the design of any foundation.
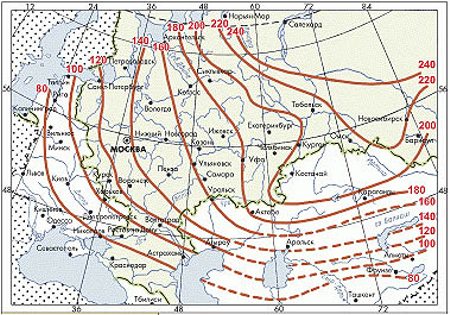
Rice. 1.3: Map of the depth of soil freezing on the territory of Russia Consider the relationship between the type of soil and the type of foundation for a brick house:
- Tape bases - are erected on dry cohesive soils and sandy soil, they are subject to the effects of heaving forces, therefore, when laying in heaving soil, they must submerge below the depth of its freezing;
- Slab foundations - suitable for problem soils prone to shear and subsiding soil, have high resistance to soil heaving;
- Pile foundations are a universal option for all types of soil, except for rocky soil.
Based on the weight and size characteristics of the building being erected, the choice of the foundation is as follows:
- Tape - suitable for 1-2 storey brick houses, allow you to equip a basement or basement;
- Slabs are used for the construction of 1-3-storey houses from timber, brick and felling. On such foundations, houses of a standard rectangular shape are built, since it is problematic to fill in a monolithic slab of a complex configuration. If it is necessary to equip the basement floor, the foundation slab is equipped at the bottom of the pit;
- Pile foundations - with the appropriate design of the pile foundation, any houses, including multi-storey buildings, can be erected on it. Such a foundation does not provide for the possibility of arranging a basement.

Rice. 1.4: Houses with a pile foundation on a difficult area of the relief Strip and slab foundations are subject to the effects of frost heaving of the soil and groundwater, depending on which the required depth of the foundation is determined:
| Expert advice! If calculations show that, due to the large depth of the foundation, it is not economically profitable to erect such foundations, the pile foundation remains the only rational type of foundation for a brick house. |
Features of brick as a building material
A brick house can be characterized by two features that affect the supporting structures.
- strong susceptibility of all stone houses to shrinkage (even small);
- great weight.
Susceptibility to shrinkage
This problem is relevant for any buildings made of small-piece materials. In addition, the brick works well in compression, but it breaks when stretched or bent. Uneven shrinkage of the foundation is especially terrible for the structure, since they lead to the following problems:
- vertical cracks;
- oblique cracks.
These defects reduce the strength and reliability of the structure. There is only one reason for the appearance - uneven shrinkage of the foundation, distortion or tilt of the house. The following deformations can lead to distortion:
- Excessive shrinkage of individual parts of the foundation. The reason for this phenomenon may be a violation of construction technology or insufficient study of the geological conditions of the site. Subsidence of the foundation can be caused by the presence of a lens of weak or water-saturated soil, insufficient soil compaction and bedding at the place of the problem.
- Bulging of individual parts. Here, everything happens the other way around: the problem area is not moving down, but up. The reasons may be an increase in the level of groundwater at the site, insufficient deepening of the foot of the foundation (on heaving ones, it should be located not less than the freezing depth, calculated according to the joint venture "Foundations of buildings and structures").
The above problems can be eliminated only by strengthening the supports and strengthening the soil. These measures are quite costly, so it is better to choose the correct type of foundation for a brick house at the stage of designing an object and carefully observe the technology during the construction process.
Wall mass
Brick is the most problematic material when it comes to density. Only reinforced concrete weighs more than it, but it is practically not used for the construction of walls in its pure form. Many types of foundations are not suitable for brick construction because they cannot cope with the load applied. For comparison, the masses of walls made of various materials are considered below.
| Wall material | Optimal thickness (for heating engineering, without insulation) | The mass of a running meter of the outer wall of one floor, with a height of 3 meters. |
| Wood | 300 mm | 470 kg |
| Foam concrete | 500 mm | 1350 kg |
| Brick | 640 mm | 3460 kg |
It can be seen from the table that the thickness of the brick wall is greater than when it is made from other materials (the calculations are made for ceramic bricks), in addition, the density of the stone is two times higher than that of foam concrete and more than three times the value for wood.
Such a load imposes serious restrictions on what the foundation should be for a brick house.
The main indicators of the soil
To determine the depth of the foundation for a two-story brick house, you must have the following data:
- type of soil;
- the depth of freezing of the soil;
- the depth of finding groundwater.
 Determine the soil type before laying the foundation
Determine the soil type before laying the foundation
The soil water level is located at a great distance from the freezing level (more than 2 meters). For this reason, building a foundation will not be expensive.
The type of soil is one of the important factors affecting the depth and choice of material to fill the foundation. From the influence of weather conditions, the soil changes its volume, therefore, by determining its properties, it is possible to determine the classification of the type of soil. They are divided into:
- rocky ones are reliable, strong enough;
- coarse - a combination of sand and various solid particles, the base is reliable;
- sandy - they contain sand of different densities, they are perfectly permeable to water, they are not subject to heaving, but shrink under load;
- clayey - the main percentage consists of clay, they retain water, can shrink or erode, are exposed to frost heaving;
- loamy - a soil containing from 10 to 30% loam with sand, retain moisture, which contributes to severe freezing and an increase in volume;
- peat - a mixture of clay, sand and other organic impurities, compacted unevenly under load.
Ground water level
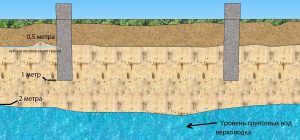 Groundwater level diagram
Groundwater level diagram
The level of groundwater is an indicator that helps to establish the depth of the foundation, which is necessary for this particular type of structure. If the level indicators are high, then it is better not to use this site for construction.
This can lead to high costs and incorrect design decisions, and additional waterproofing must be done afterwards.
All the necessary information should be found out even before the start of construction. This can be done without special surveying: ask neighbors, visit real estate agencies, or use the help of a company that conducted tests in the area.
The amount of soil freezing
 If the soil is not collapsed, then the amount of soil freezing will not affect the foundation
If the soil is not collapsed, then the amount of soil freezing will not affect the foundation
Many firms engaged in construction use a simplified version of determining the depth of laying the foundation, since they consider the main criterion on which it depends is winter freezing of the soil.
To some extent, this is the right decision, but on the other hand, this method can increase the cost of work several times.
If the soil is not collapsed, then the amount of frost will not have a great influence on the foundation, no matter how deep it is laid. But be that as it may, this factor must be taken into account.
What you need to know when determining the size of the foundation
To choose the required optimal size of the foundation, ensuring the reliability of the entire structure, you need to know:
- soil composition at the site;
- the height of the groundwater;
- the depth of soil freezing in a given region;
- the weight of the building itself, i.e. loads on the foundation from the weight of walls, floors, and roofs.
The overhang of the walls above the foundation by a width of 10-13 cm is allowed, but no more.This is due to the fact that reinforced concrete has a high strength, much higher than the strength of wall materials, therefore it can withstand the load from a wider wall, and a narrow foundation can reduce the consumption of concrete and reinforcement.
Determining the bottom of the foundation
The calculation of the width of the foundation is determined depending on the width of its base, which is calculated based on the loads pressing on the foundation. The foundation, in turn, exerts pressure on the ground.
As a result, in order to correctly calculate the size of the foundation, it is necessary to know the properties of the soil at the construction site.
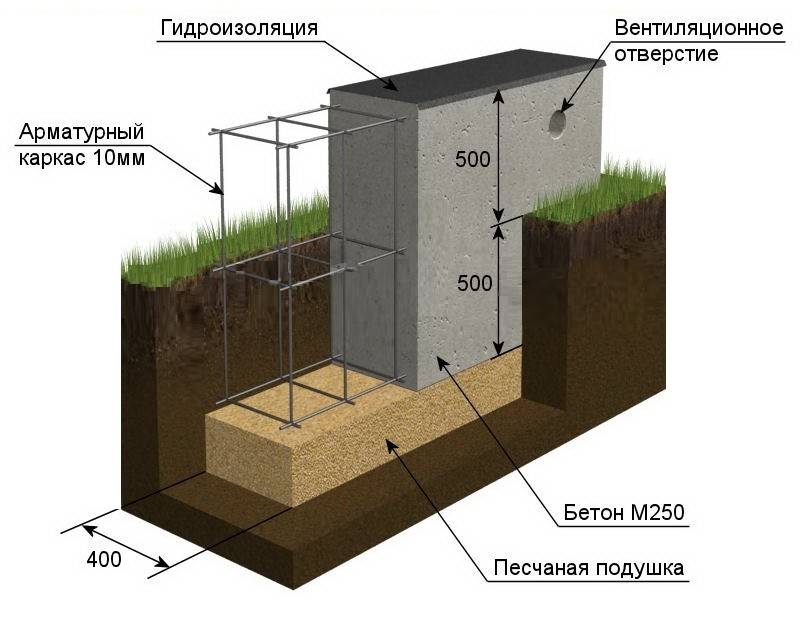
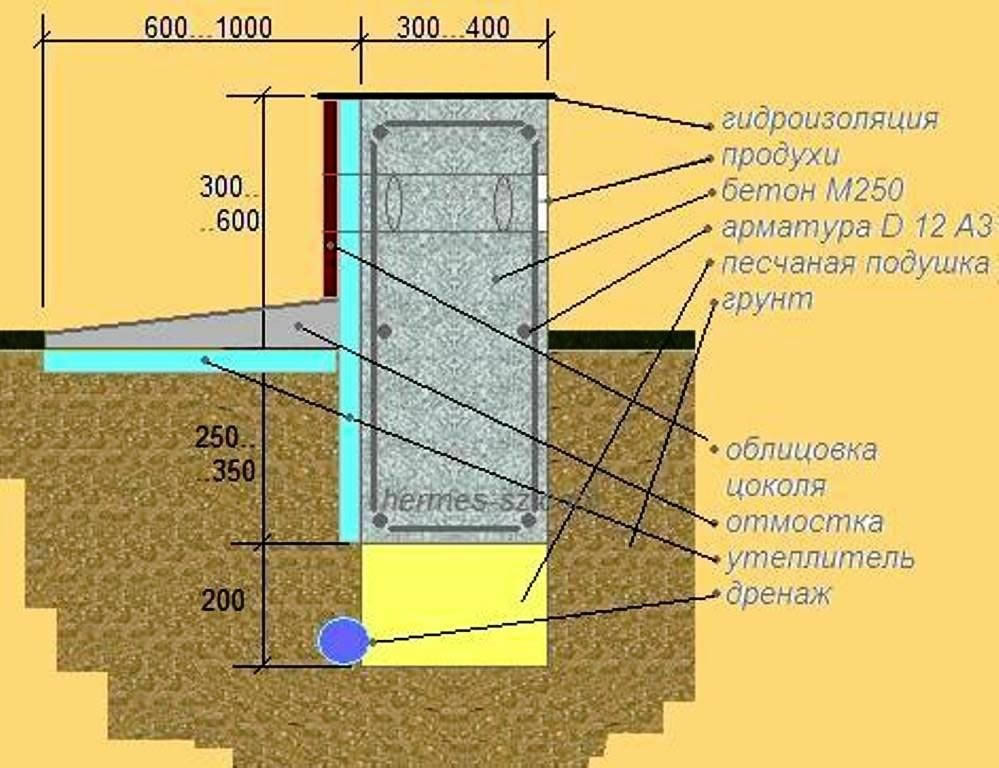
If the soil on the site is heaving, and the house is supposed to be built from bricks or concrete blocks, then the best option for choosing a foundation would be deepened. And since foundations of this type are arranged below the level of soil freezing, the height of the strip foundation for the house will be within 1–2.5 m to ground level.

Laying the foundation on heaving soil
For small buildings - a bathhouse, a garage or a country house, a shallow foundation with a height from base to top within 60-80 cm is quite suitable.In this case, there will be 40-50 cm of foundation height in the ground, the rest will protrude above the soil level and be the basement of the building. Despite the low height, the strength of the foundation will be guaranteed by the properties of concrete and reinforcing cage.
Before calculating the width of the strip foundation, it is necessary to calculate the loads that can be easily determined knowing the dimensions of all wall structures, roofs and the specific gravity of the materials used. To these loads is added the weight of people and everything that will be in the house - furniture, household equipment and others.
The dimensions of the strip footing are calculated in such a way that the load on the base does not exceed the permissible loads on the ground at the given construction site.
When calculating the strip foundation, we find out the height and width, after which we determine:
- the amount of concrete required for pouring,
- number of fittings,
- material for formwork.
As you can see, the dimensions of the foundation allow you to learn a lot for the device of a reliable foundation.
The first step is to determine the depth of the buried tape foundation. To do this, you need to know the depth of soil freezing in your region in the winter. All this can be found in construction guides.
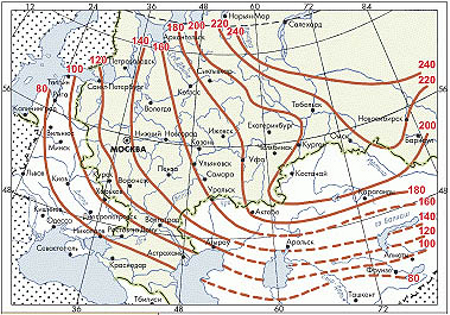
The depth of soil freezing in different regions
When making a calculation, first set the preliminary dimensions of the foundation (width of the sole, height), focusing on the design features of the house. If the bearing capacity of the soil is greater than the pressure of the building on the ground, then the selected dimensions are left unchanged, otherwise, the dimensions are selected so that the calculated soil resistance is not less than the specific pressure of the building weight.
And if, among other things, there is reason to believe that the site has a high level of groundwater, then the calculation of the foundation and the assessment of the soil is best ordered from specialists so as not to risk the money invested in the construction. Because heaving soils can change their properties over time under the influence of some factors, such as, for example, a change in the level of groundwater.
You can independently find out the height of the strip foundation above the ground using the online calculator, where the program itself will calculate both the area of the base of the foundation, its height, and the thickness of the sand cushion based on data about your soil.