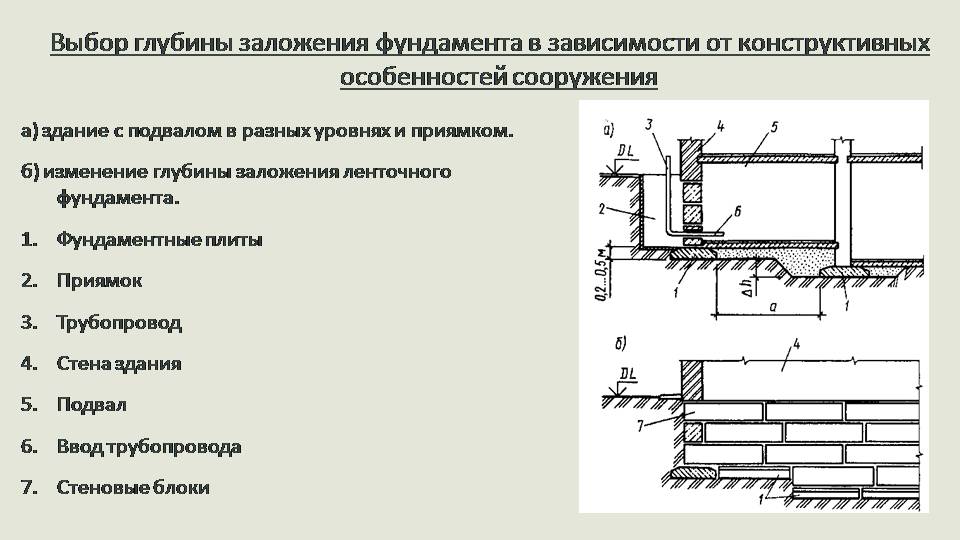
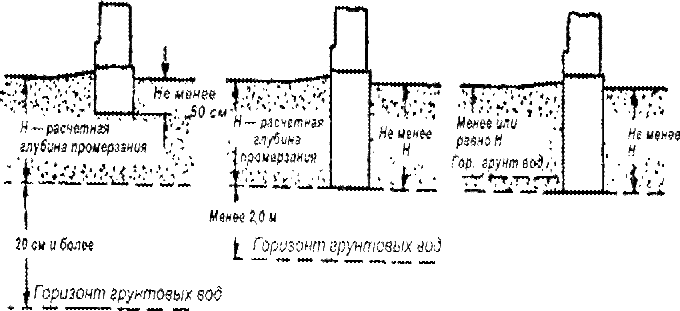Foundation laying methods
The building must evenly transfer the load to its base, which, in turn, imposes it on the ground in a measured manner. So, in order to avoid the above errors, it is advisable to take into account all the factors in order to understand what depth of the strip foundation is most optimal for your case.
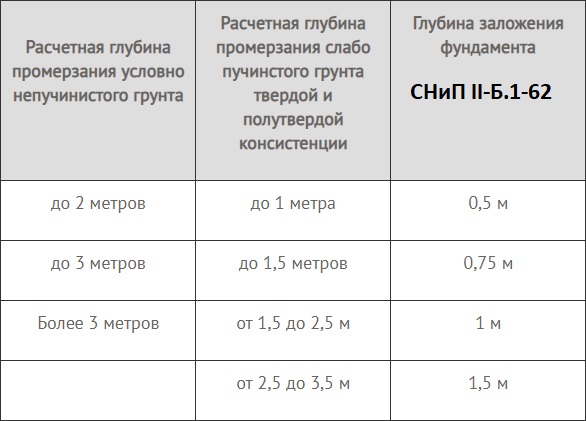
- Soil properties. This includes the type of soil, its heaving, the level and thickness of the freezing depth.
- Ground water level.
- The approximate load of the building on the foundation, its heaviness.
It is believed that in Russia it is necessary to lay the foundation to a minimum depth of 0.5 meters.
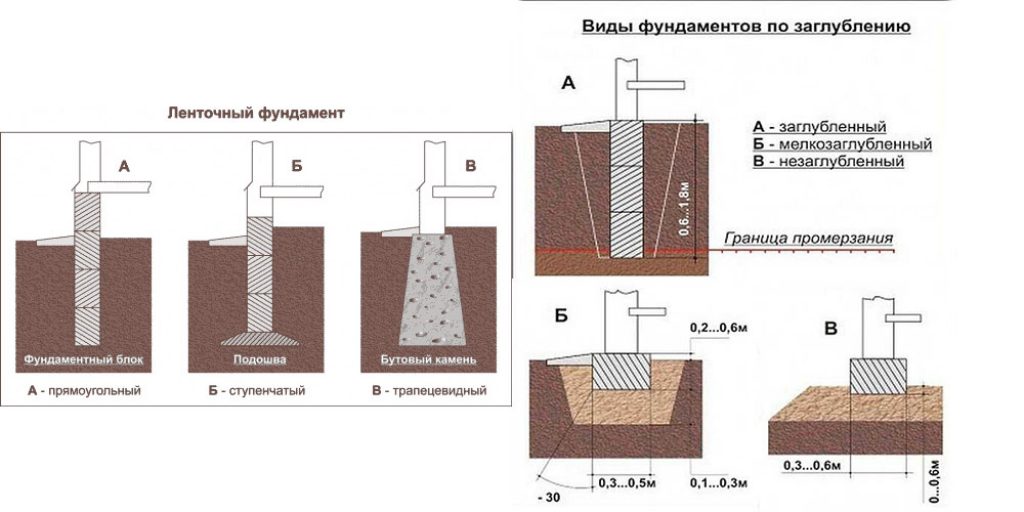
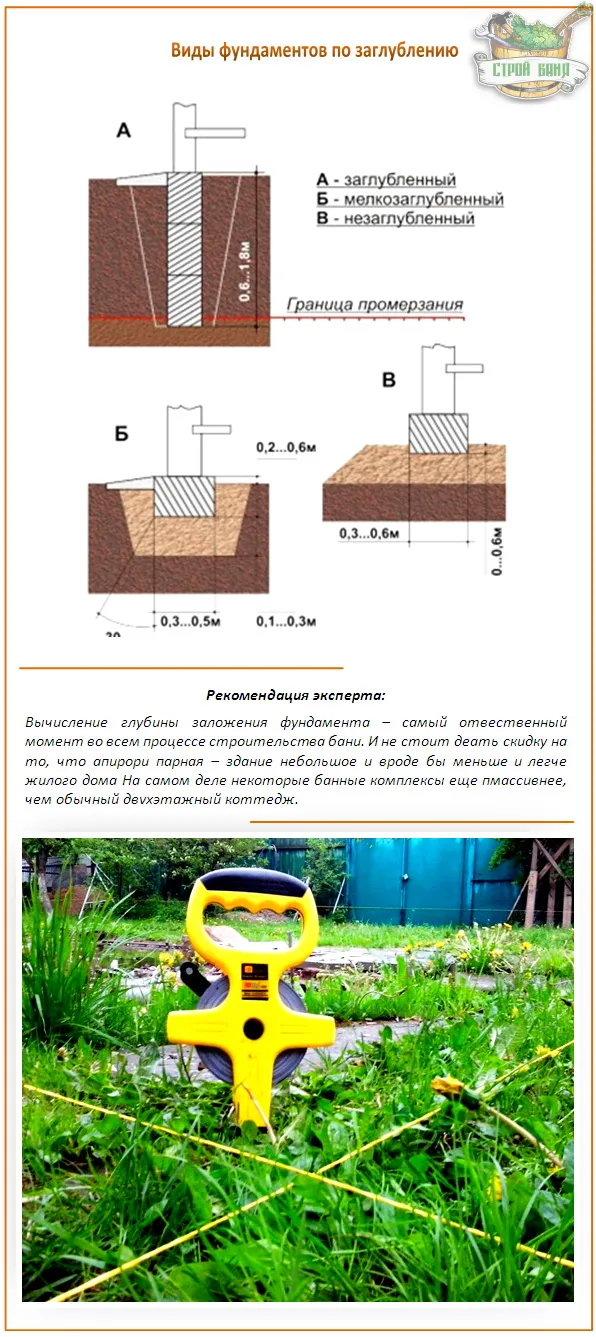
Depending on the type of soil and the material from which it is planned to create a house, strip foundations can be distinguished

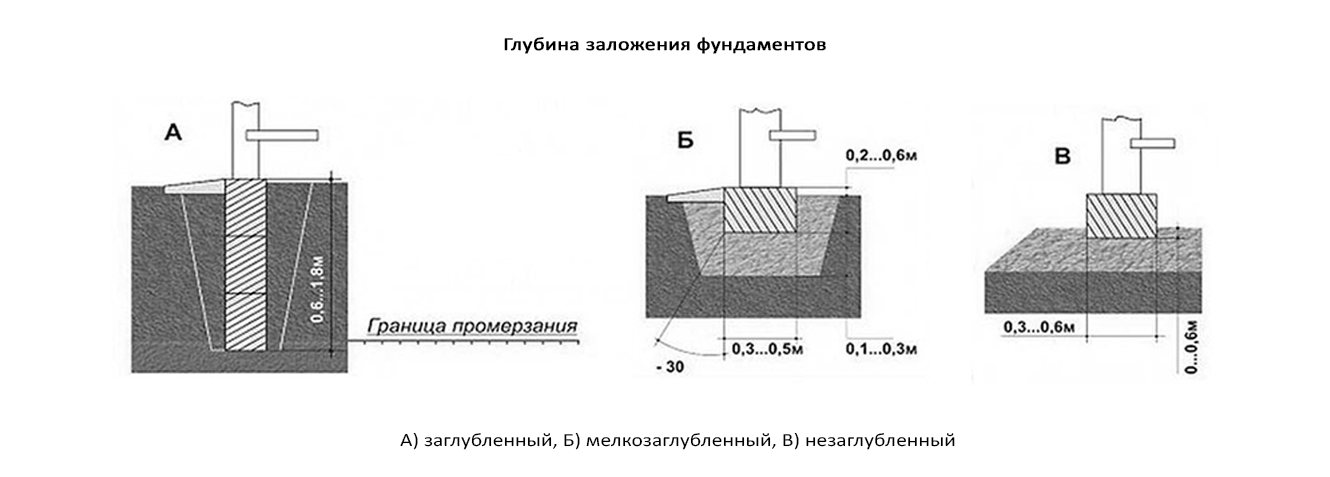
Shallow
The ability not to go too deep into the ground is determined by the fact that the soil layer capable of regularly bearing a considerable load, which does not significantly change its properties under the influence of factors acting on it, is close to the surface, while the possibility of the appearance of factors that will cause the bearing layer to deform is excluded. This is possible only with non-porous and slightly porous types of soils (sands, for example). A slight deepening is possible due to the fact that the soil either does not heave at all, or it happens evenly, which is safe for the integrity of your building.
Such a base is more suitable for light buildings - wooden, small brick, foam concrete and the like. The presence of groundwater near the surface is also unacceptable. If all these conditions are met, then you are lucky! You have a chance to save time, money and effort. You do not need to take into account the level of freezing of the ground below you, calculate the level of groundwater and carry out other computational activities. The main thing is to remove the vegetative layer of the earth, get to a strong, hardy layer and load it with the embodiment of your creativity - the foundation, and then the building.
The depth of such a strip foundation ranges from 50 to 70 centimeters.
If the surface is rocky, without the possibility of deepening, the foundation is laid on the upper found strong bearing layer of soil.
Recessed
If you live on heaving soil (clay, loam, sandy loam, etc.), you are going to build a rather heavy building with massive elements, you want to equip a basement (not necessarily all at once), then the best option for you is a buried strip foundation.
Here, things are a little more complicated. But don't despair! After some calculations, you will find your ideal depth.
First you need to do a little investigation. You need to find out the depth of soil freezing and the height of the groundwater. This will be the determining factor.
The depth of freezing can be determined by books and tablets that will tell you its meaning for any region of the Fatherland. The groundwater level will have to be measured independently. To do this, you need to drill a well of 2.5-3 meters and lower the pipe there. During the year it is necessary to observe how much the waters can rise.
If they are constantly below the freezing depth of the soil by more than 2 meters, then the trenches under the base of the house should be deepened by at least 3/4 of the calculated freezing depth, from 70 centimeters.
If the groundwater exceeds this mark, then it is worth laying the strip foundation to the freezing depth plus 20-30 centimeters.
The depth of the trenches under the inner walls may differ from the depth for the outer contour. There is nothing wrong with that.
Burial types
First, let's say about what the depth of the foundation depends on. The main factors are divided into:
- Features of the soil (freezing depth, level of groundwater, relief, soil type).
- Structural features of the building (presence of a basement, heating, number of floors, etc.).
It depends on these points how deeply you need to dig a trench or foundation pit. Their value may be different, but in general, the grounds for this criterion are divided into:
- Recessed.
- Shallow.
- Shallow.
Each of these types is suitable in specific cases. In which ones - we'll figure it out further.
Not buried
Such grounds are resorted to in the following cases:
- When light buildings are being erected on heaving soil.
- When constructing buildings of heavy material (eg stone) on rocky ground.
- When erecting buildings on highly heaving soils or soils with weak subsidence.
These include:
- Tape.
- Columnar.
- Lattice (a type of slab foundation).
This type has a couple of good advantages. Firstly, you do not need to spend a lot of money on an unburied foundation. If the share of other foundations in the total estimate is 28 - 45%, then in this case it reaches about 8%. Secondly, a large depth of the foundation is not provided here; therefore, in most cases, it will take a little time to dig a pit, even on clay soil. True, if you want to build a columnar base, it will take longer to tinker.
The tape type is chosen quite often. But the other two also have their place in the unburied system. So, a slab-lattice base allows you to save concrete in cases where you can not pour a solid base. After all, in fact, these are several small plates, between which a space is left. Columnar supports can also boast of rationality, however, in two cases: if a light building is being built on soft soil or a heavy building on very hard soil.
What is the importance of soil freezing
The depth of soil freezing should be discussed separately. The main problem in the construction of foundations, in particular, for example, a shallowly buried belt-type structure, is the presence of the influence of forces acting at the moment of frost heaving of the soil. They form in the soil above the freezing point.


Most of the territory of Russia has soils, where soil freezing varies within 2 x meters. That is, it becomes necessary to deduce the depth of the pit under the foundation precisely in these parameters and lay the concrete base to a depth of 0.5 m below the freezing point.

Foundation depth: dispelling myths
Yes, the simplest solution seems to be to bury the same bathhouse deeper, and it will last a hundred years. In fact, this is not so, and today there are many myths among builders about the depth of the foundation.
The deeper the better?
Even among fairly experienced architects, there is a myth that the deeper the foundation, the stronger it is. Of course, you can understand the customer's desire to save money, as well as the foreman who is trying to convey to the fact that with the foundation "at random" - will not work. But to bury deeper does not mean that it will be stronger.
So, the depth of the zero level is determined by many parameters - and it is better to entrust this issue to specialists. Engineering and geological surveys are being done, the type of soil is being investigated, the level of groundwater and its freezing are measured. A lot is also decided by the constructive feature of the building: the number of floors, superstructures, wall material - and a bathhouse in this parameter is just less demanding on the power of the base than a residential building. More details about determining the depth of the foundation can be found in a small interesting book by V.S. Sazhin "Do not bury the foundations deep".
Does depth really always "save"?
But it is far from always necessary to strive to make the foundation deeper if the soil is restless - in fact, there are methods of how to compact and make any soil more solid. And therefore, if the bathhouse is not built at all massive, it makes no sense, as the builders like to say, “to bury money in the ground”.
So, first you need to study the problem well. For example, if water is often visible on the surface or close to it, competent drainage around the foundation will save. After all, it is pointless to strengthen the foundation in this case by increasing the support - the zero level will continue to "walk", and a lot of money will be spent on such a method. There really is a need for depth here.
But if landslides are observed along the perimeter, the foundation is undermined and even somewhere already begins to sag - it is not it that needs to be strengthened, but the soil. So, for sandy soil, silicatization is good - the soil around the foundation is watered with a mixture of liquid glass and water, one to one, and the resulting wet sand is compacted well. Or they use chemical reagents: small-diameter wells are drilled, and special resin compositions are pumped into them. It is durable and inexpensive, and for soft soils - what you need.
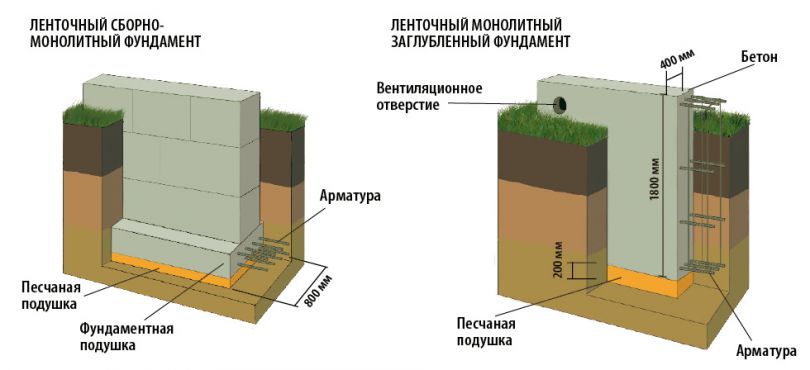
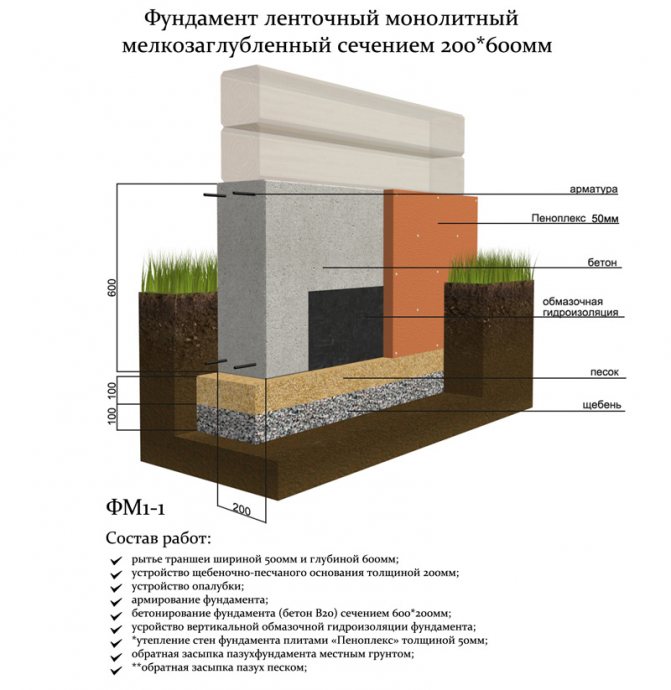
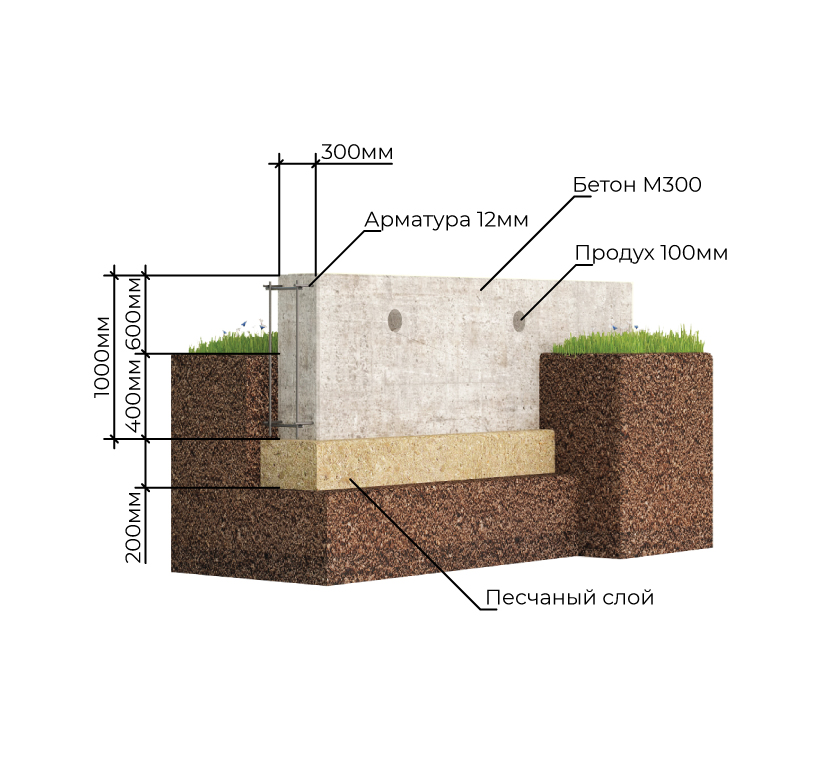
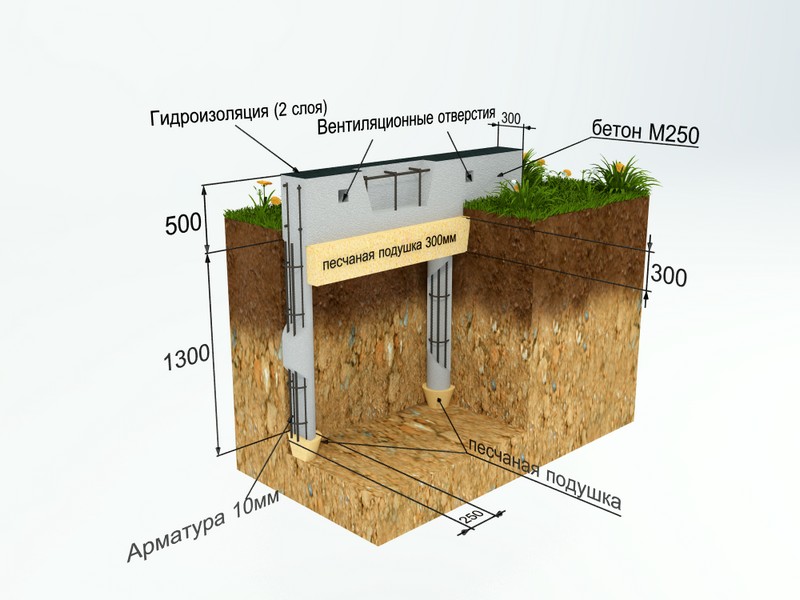
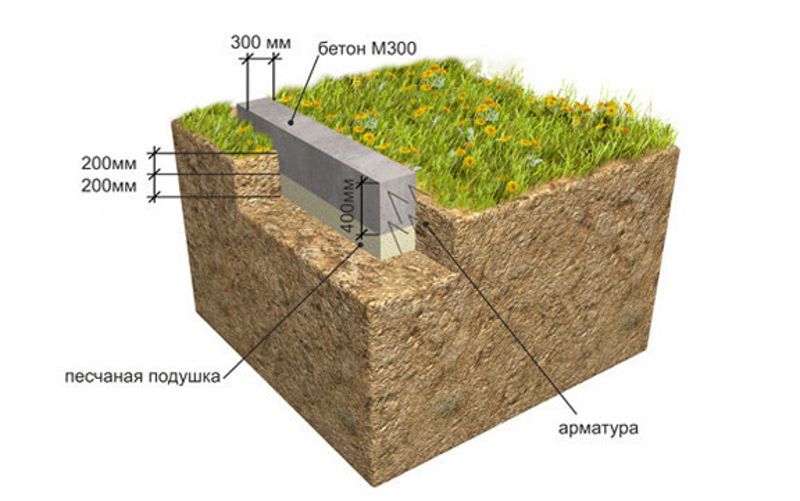
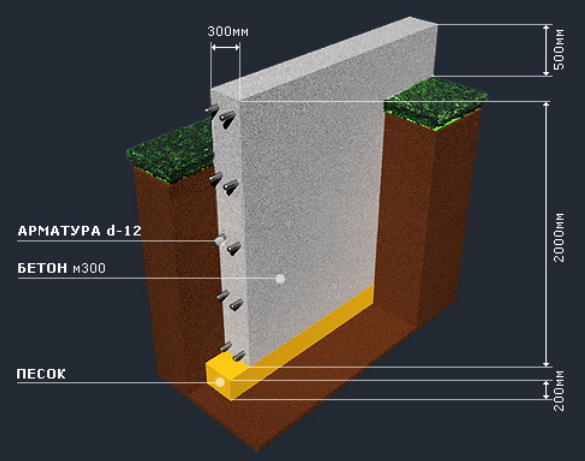
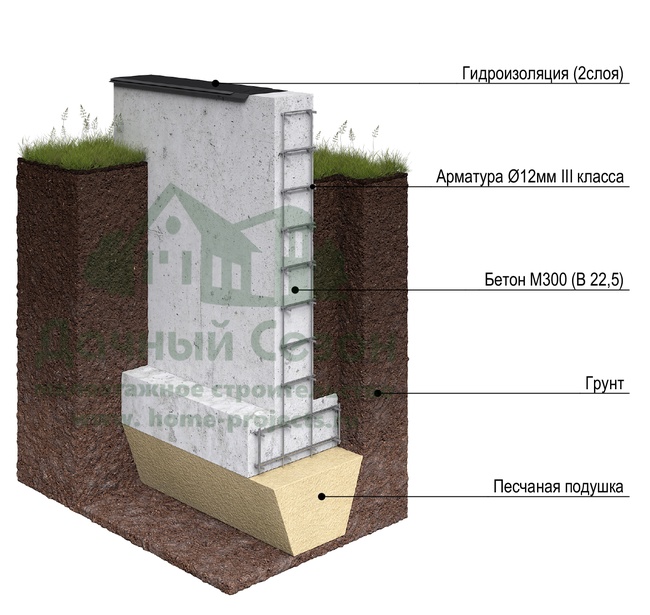
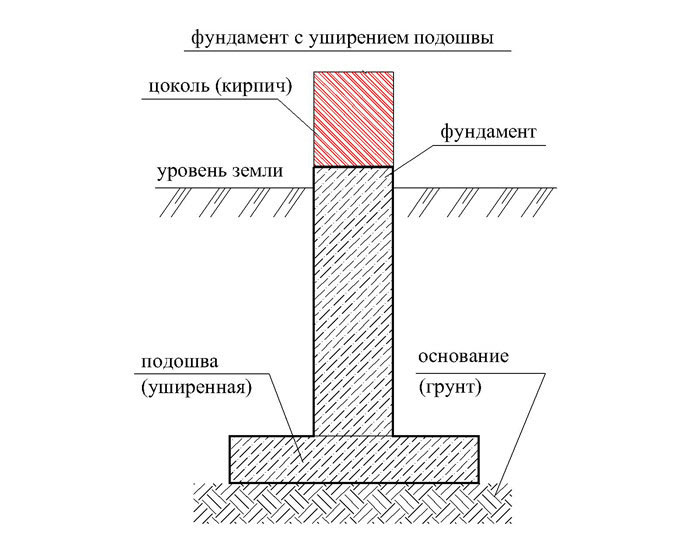
Laying the strip foundation
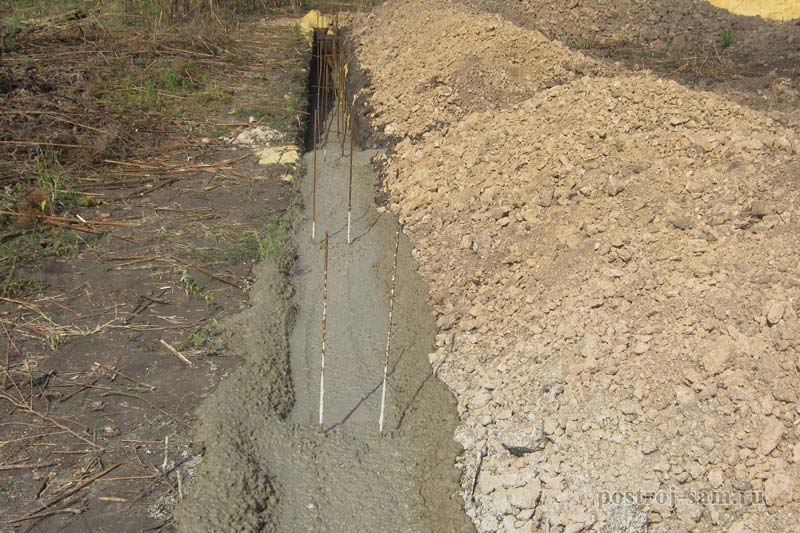
To lay the strip foundation, it is not at all necessary to dig the entire foundation pit, it is enough just to restrict ourselves to trenches for the foundation blocks. At the same time, the quality of the foundation does not depend in any way on the chosen approach. The main load from the building is borne by the soil, and the denser it is, the better for the building as a whole.
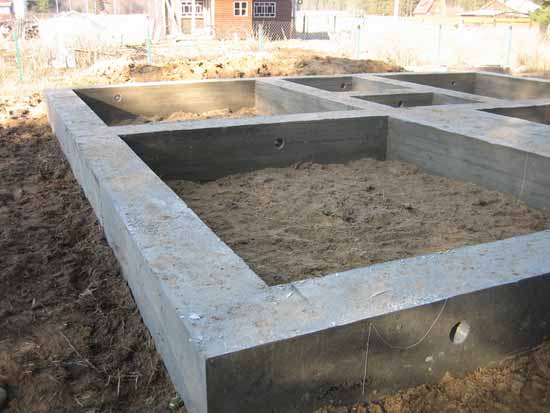

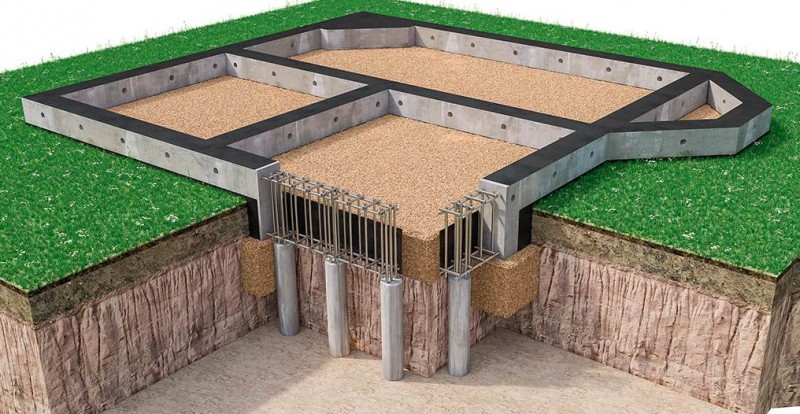
Figure: Deep foundation strip
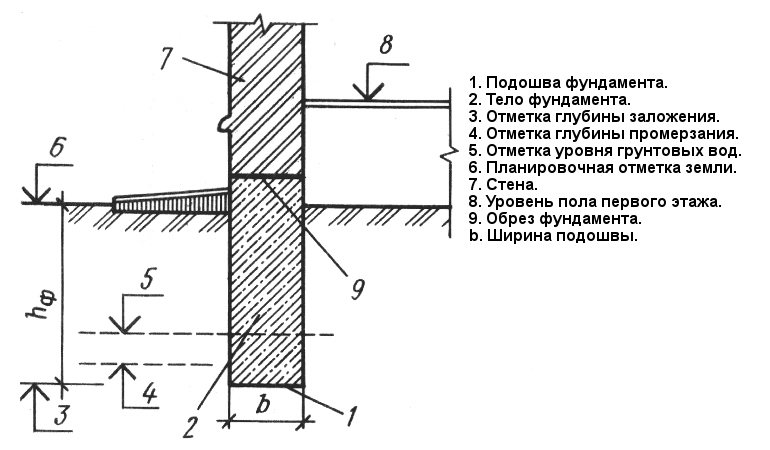
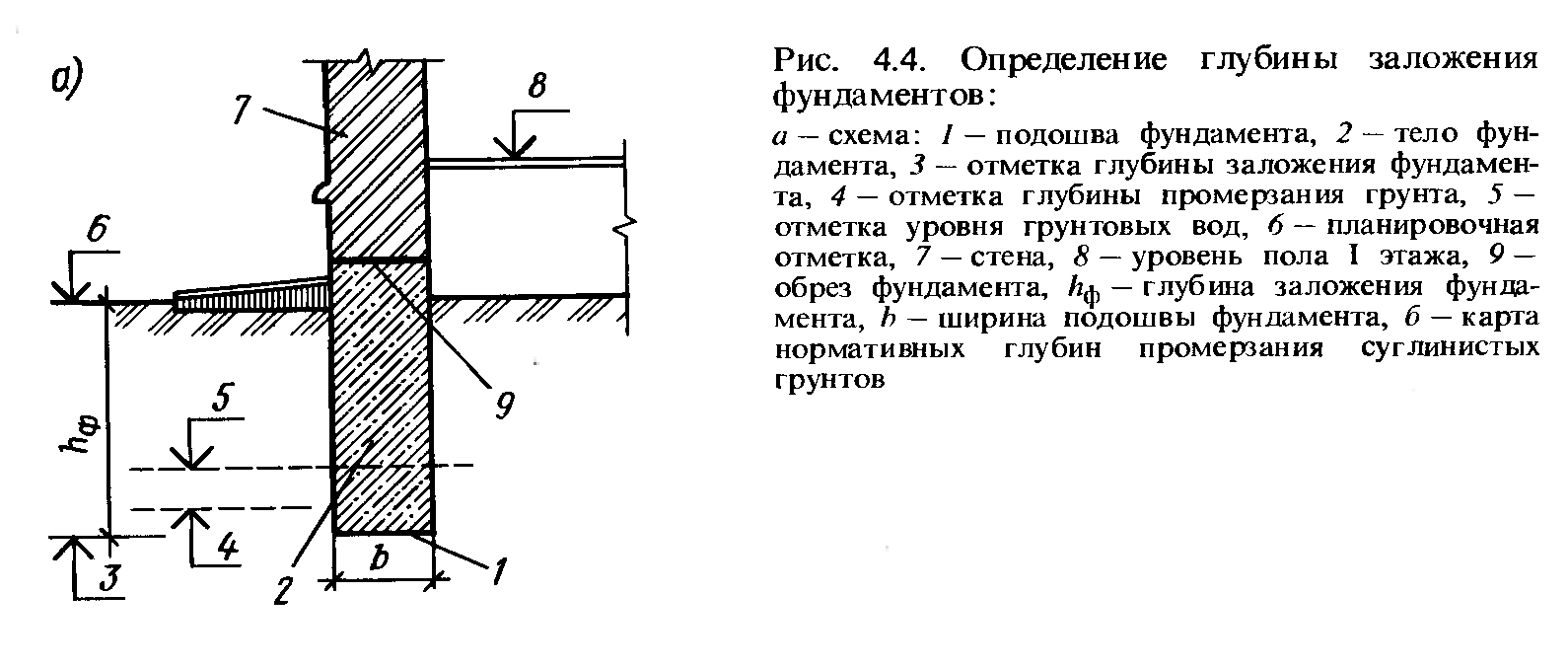
Practical work on laying a strip foundation should be preceded by a base design stage. The calculation of the foundation involves identifying the required depth of its foundation, which is determined on the basis of the depth of soil freezing, the level of groundwater, geodesy of the construction site and the technical characteristics of the building being erected.
Work on laying a strip foundation to a great depth is carried out in the following sequence:
Site preparation;
The construction site is cleared of surface vegetation, the fertile soil layer is removed to a depth of 10-20 cm (one shovel bayonet). If necessary, the area is leveled.
Markup;
The marking of the future strip foundation begins with the mark of the bearing wall of the building, then the perpendicular walls are marked and the correctness of the right angles is checked using the Egyptian triangle method. The foundation strip is marked both along the outer and inner contours. Fig .: Scheme of checking the corners of the foundation marking
Excavation;
Digging a trench under the foundation is performed manually or mechanically. Since the depth of the trench is large enough, digging can be accompanied by shedding of its walls.

Figure: Scheme of strengthening the walls of the trench
| Expert advice! To avoid shedding the soil, the walls of the trench are reinforced with plywood or fiberboard shields, which are installed using horizontal struts. |
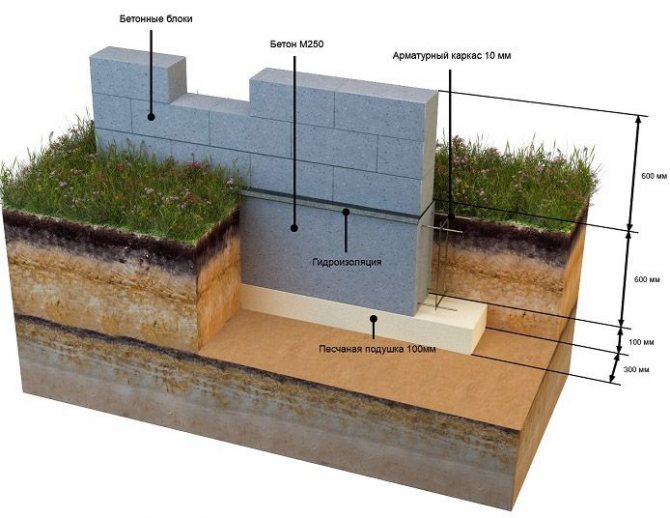
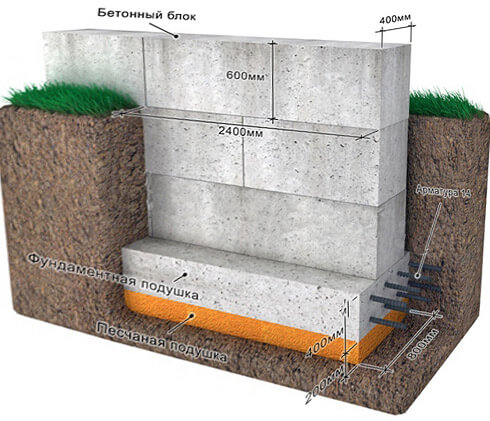
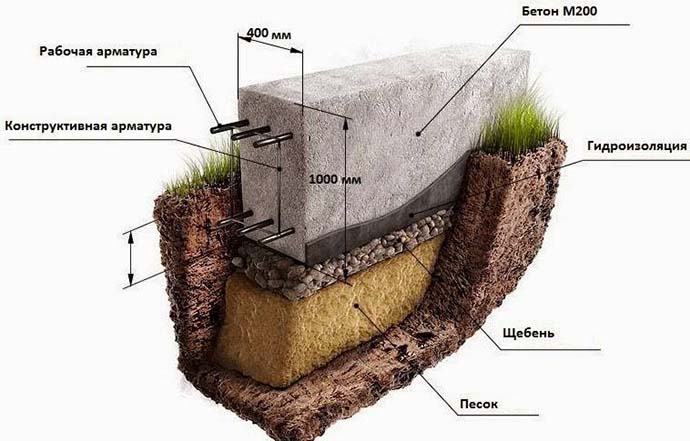
Dumping the sealing pad;
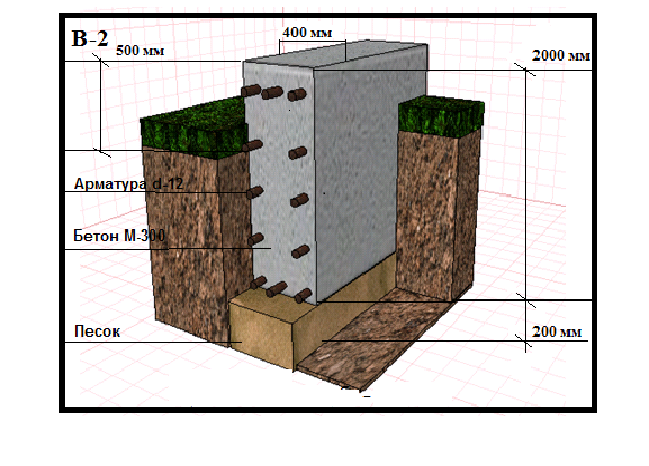
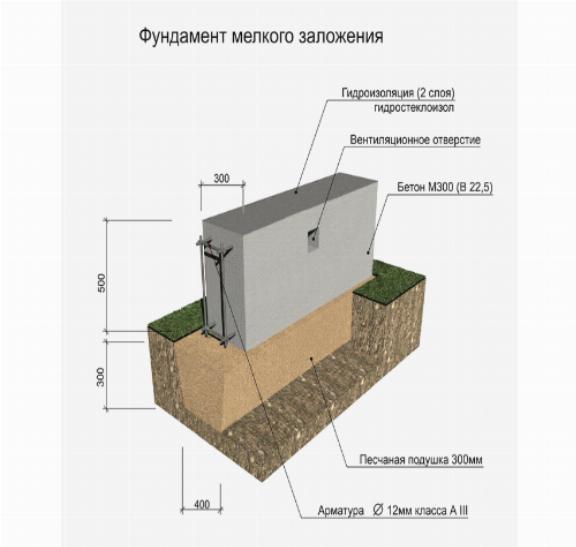
To create a compacting pad, sand and fine gravel or crushed stone are used. The thickness of the layers is the same, as a rule, it is 10-15 centimeters. The sand is the first layer, after filling it is poured with water and carefully compacted.
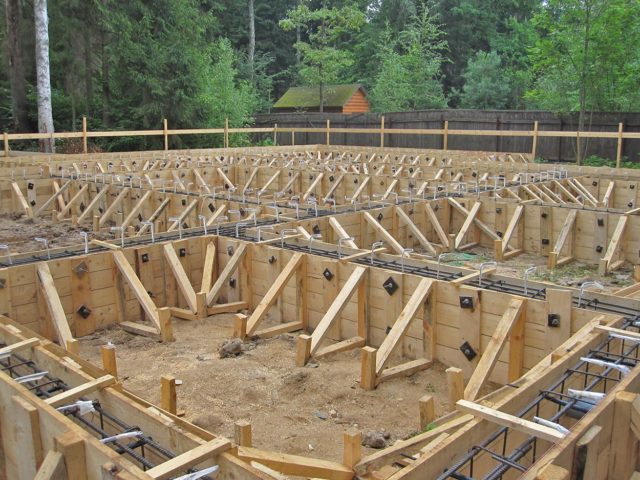
Formwork creation;
Formwork for pouring with concrete is made of planed boards with a thickness of 2-3 centimeters. The boards are connected by means of vertical strips and fastened with nails or self-tapping screws.
Important! The height of the formwork should be greater than the depth of the trench, as the foundation tape will also form the base of the house. Fig .: Scheme of the formwork for the strip foundation After installation, the formwork is covered from the inside with a waterproofing material, which is needed to prevent concrete from flowing into the gaps between the boards
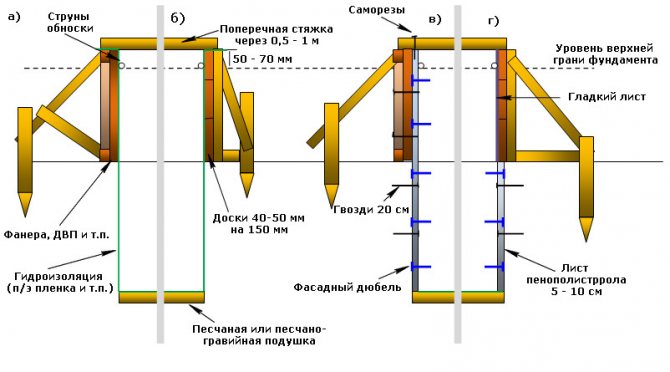
Fig .: Scheme of the formwork for the strip foundation After installation, the formwork is covered from the inside with waterproofing material, which is needed to prevent concrete from flowing into the gaps between the boards.
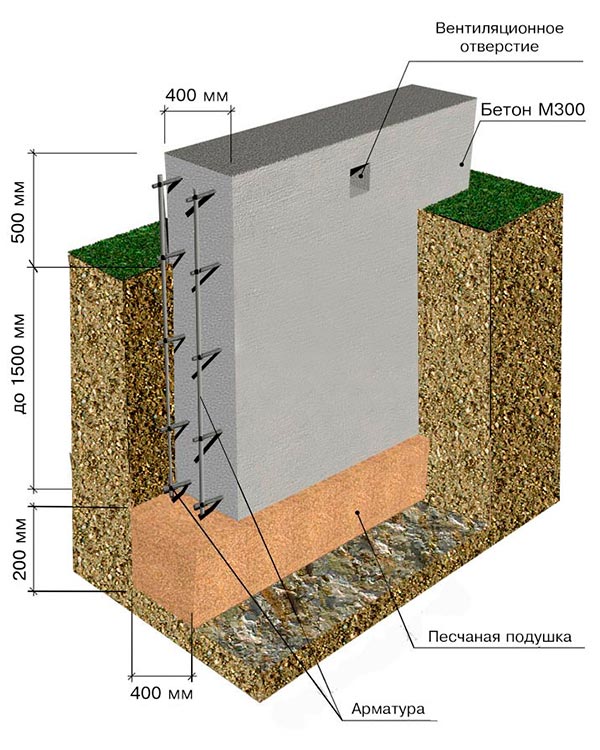
Reinforcement;
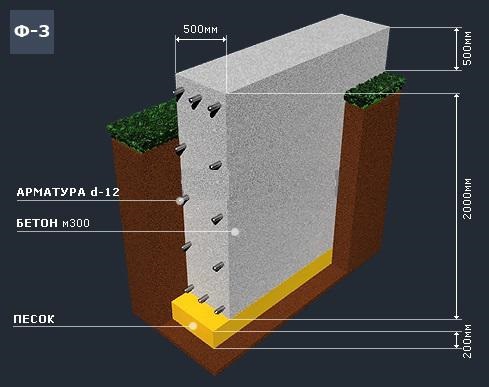
For the reinforcement of the strip foundation, a double-circuit reinforcement cage is used, consisting of vertical rods and horizontal lintels.
| Expert advice! The thickness of the reinforcement rods for the vertical contour should be 12-14 mm, for vertical connecting elements smooth reinforcement with a diameter of 8-10 mm can be used. |
Fig .: Scheme of the reinforcement cage for the strip foundation
The reinforcement cage is connected using a knitting wire or welding. The first option is more preferable, since when welded, the structure loses its elasticity and the concrete tape is less resistant to bending loads.
Concreting;
The strip foundation is poured simultaneously or in layers (provided that a new portion of concrete will be poured out before the previous layer has set). For pouring, heavy concrete from M300-M400 cement is used.
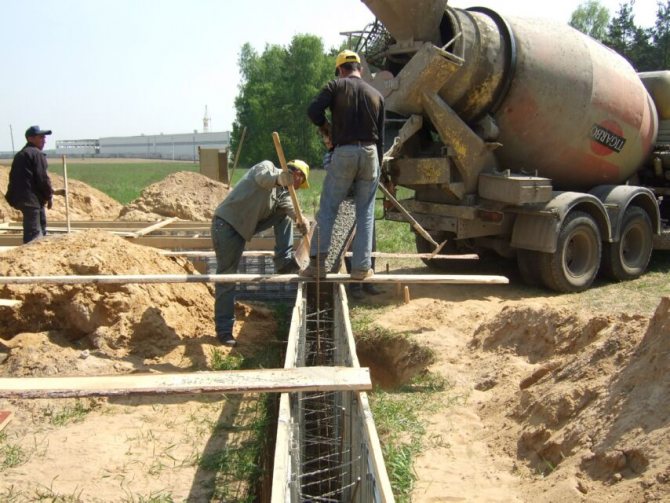

Fig .: Concreting a deep strip foundation
Compaction of concrete with vibration compactors or bayonet with reinforcing rods is mandatory.
| Expert advice! If the construction is carried out in the warm season, the ripening concrete must be covered with oilcloth and regularly moistened, since when the concrete dries, the surface of the foundation tape may become covered with microcracks. |
Payment
As already mentioned, several criteria affect the calculation of the depth of the foundation. The main ones are the following:
- The level of soil freezing.
- The location of groundwater.
- Base type.
These three points affect the determination of the depth of the foundation the most. Therefore, in each case, the distance from the soil surface to the bottom of the trench will be different. So, the depth of the foundation for a particular one-story house can be either large or practically absent. To make it clearer, consider the above criteria in order.
Depending on the degree of soil freezing
This factor influencing the depth of any foundation is often mentioned in the first place. If you are going to dig a trench for a buried foundation, this indicator should be known to you first. Filling the tape without taking into account the depth of freezing, it is possible to destroy the building with displacements in the ground caused by the transformation of water into ice.
Let's talk about how to find out how much the soil freezes. There are tables and maps with the average level of soil freezing in a particular area. If you need an accurate indicator, you need to take data from ten years of research on a flat, non-snowy area. But usually they are absent.
Then you can calculate the approximate depth yourself. To do this, you need to contact the nearest hydrometeorological center and find out the average temperature for the month. If you provide everyday data, you can calculate it yourself (add up the indicators and divide by their number). Then the square root is extracted from this figure, which is multiplied by the coefficient of the type of soil (can be found on the Internet). That's it, you have an approximate level of freezing depth.
From the water table
Water is one of the most dangerous enemies of foundations. The foundations are erected, as a rule, of concrete, be it a monolith or FBS. If the water table is too high, moisture enters the pores through the sole. With the onset of cold weather, the water freezes and begins to destroy the concrete. At best, everything can end in cracks, and at worst, the building will simply collapse.
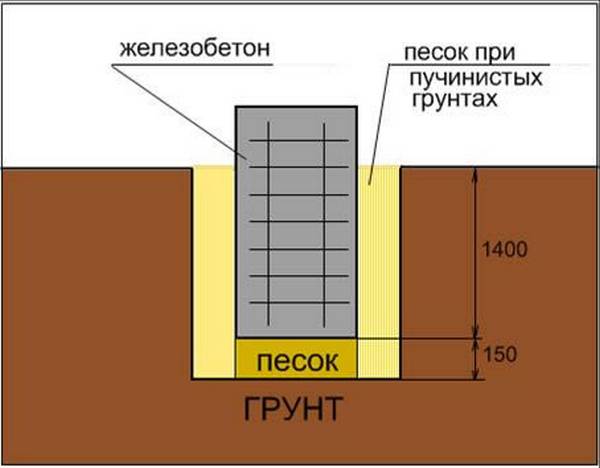
To prevent this, the necessary measures are taken: the sub-base is properly arranged (using sand of the required fraction), a drainage system is being built, etc. In addition, freezing, moisture puffs up the soil.Therefore, if there are fine or silty sands under the sole, and the groundwater is at a level higher than two meters, only a buried foundation should be built.
Thus, the choice of the depth of laying a particular foundation also depends on the groundwater.
Therefore, it is important to know where they are. Determining the depth of water at the site is actually not difficult. You need to select several points at the place where you are going to build a house
In this case, one of them should be at the bottom of the site. Wells are made at the designated points. In a day, you can start measuring. It is best to determine the location of groundwater in spring, when the soil moisture saturation is maximum.
It is also possible to determine the GWL using a well located in the immediate vicinity of the construction site (if any). The fact is that it is groundwater that serves as a source for them. Therefore, the distance from the soil surface to the water surface is the same level. It is worth remembering that the well should be as full as possible (that is, there is no need to check the level after taking water, especially in large quantities).
From the choice of the type of foundation
Of course, the ground matters a lot. But, besides this, the depth of the foundation depends on itself. In this case, we are talking about the form. The depth of occurrence of a particular foundation can be described in a few words:
- Tape and columnar bases depend on groundwater and the depth of soil freezing;
- The depth of the pile foundation is determined using its bearing capacity;
- The slab base is deepened by about 40 - 50 cm.
Factors affecting the determination of the depth of the foundation
To determine the depth of the strip base, three main factors are taken as a basis.
Geological conditions of the site
To obtain more accurate data, it is necessary to conduct geotechnical surveys. Such work is carried out by specialized companies that take soil samples from the site and examine them in laboratory conditions. The analysis results in the following data:
- Type of soil, its density and bearing capacity.
- Groundwater level.
After the analysis, a dense layer is determined on which the foundation will directly rest. To do this, you should familiarize yourself with the bearing properties of different types of soil:
- Rocky soil is the most dense type, as it has a welded and cemented structure. Among the advantages of this type are resistance to freezing and compression. However, the development of such a soil is very difficult.
- Coarse soil consists of crystalline and sedimentary rocks, therefore it has a low degree of compressibility and, as a result, a high bearing capacity. It is rather difficult to develop such soil.
- The sand is characterized by its volume retention after rapid compression and therefore has a good bearing capacity.
- Sandy loam with high humidity becomes mobile, therefore it is better not to build a foundation at all on such soil.
- Loam differs in that it can be washed out by water, but under heavy load it can compress.
- Clay is a good foundation soil, but you should be aware that the increased moisture content in such soil leads to heaving.
Having decided on the bearing capacity of the soil, it should be remembered that it is not recommended to build a strip base on heaving and deep-freezing soils.
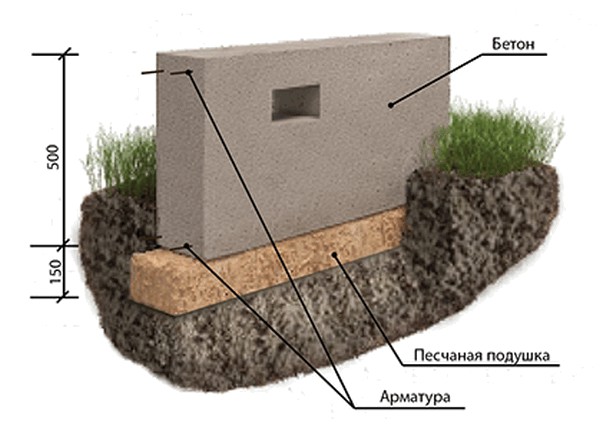
In addition, there are standard rules for laying the foundation:
- The laying depth should not be less than 50 cm.
- The deepening into the bearing layer should be 10-20 cm.
- If possible, lay above the water table to reduce excavation costs.
Climatic conditions
In many ways, the depth of laying the foundation depends on the level of freezing and thawing of the soil.Some types of soil, when frozen, are prone to heaving, that is, to an increase in volume. When building on sites with a predominance of such soils, it is not recommended to equip the base of the foundation above the freezing level.

Environmental conditions
Also in this situation, it is worth paying attention to the groundwater level. The depth of the foundation is determined by the level of freezing of the soil, prone to heaving, only if the groundwater lies at a depth of more than 2 meters from the freezing point
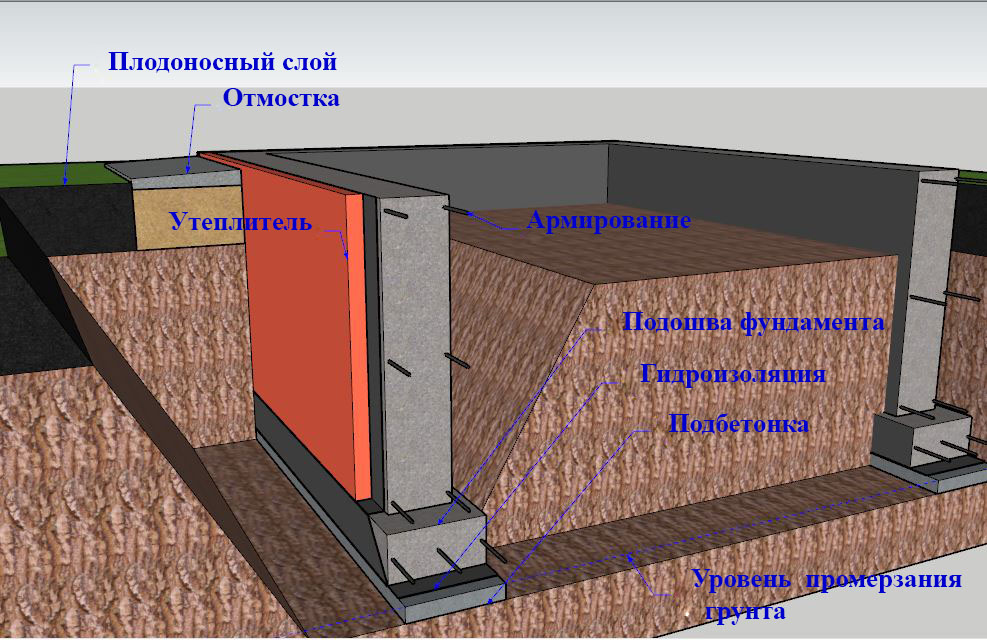
Structural design features
The depth of the strip foundation is largely determined by the design features of the building being erected. In particular, we are talking about the following:
- Proposed construction of a basement, basement or other underground space.
- Pits or bases for equipment.
- Existing underground communications and the depth of their laying.
- Foundation design.
- Estimated loads on the base of the structure.
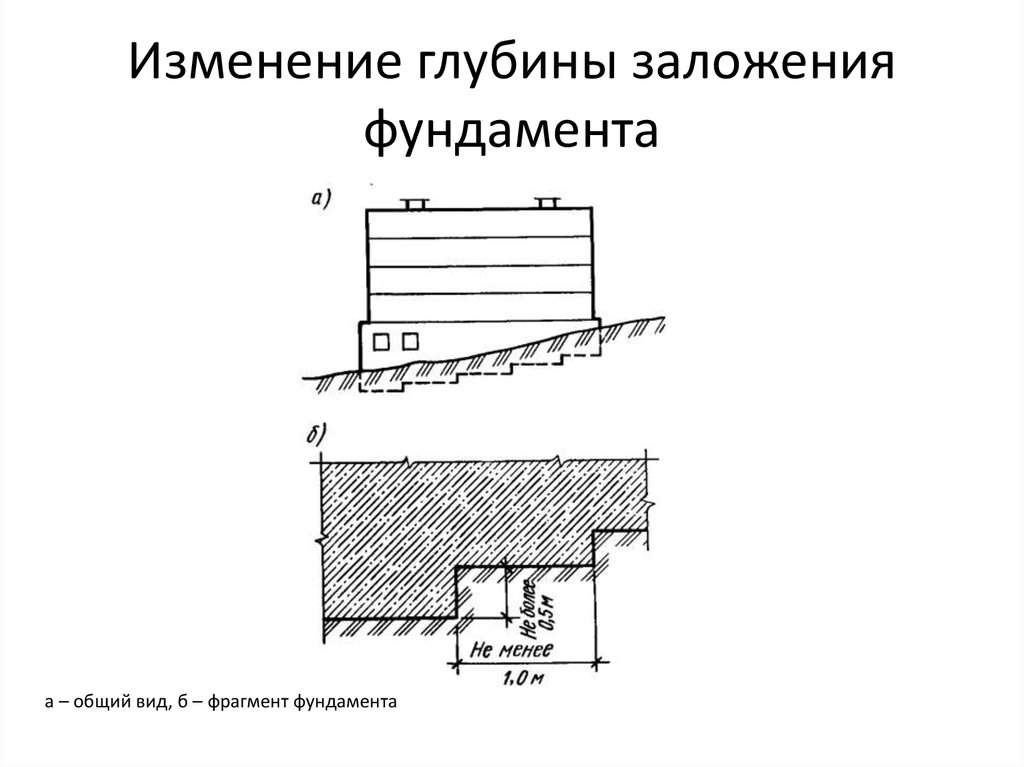
The deepening of the tape in most cases is carried out 50 cm below the base of the underground room.
When calculating the depth of the foundation for the listed factors, the maximum value of three is selected and taken as a basis.
Types and structure of foundations.
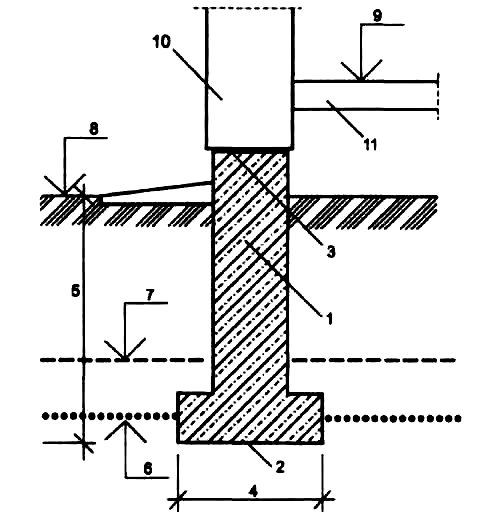
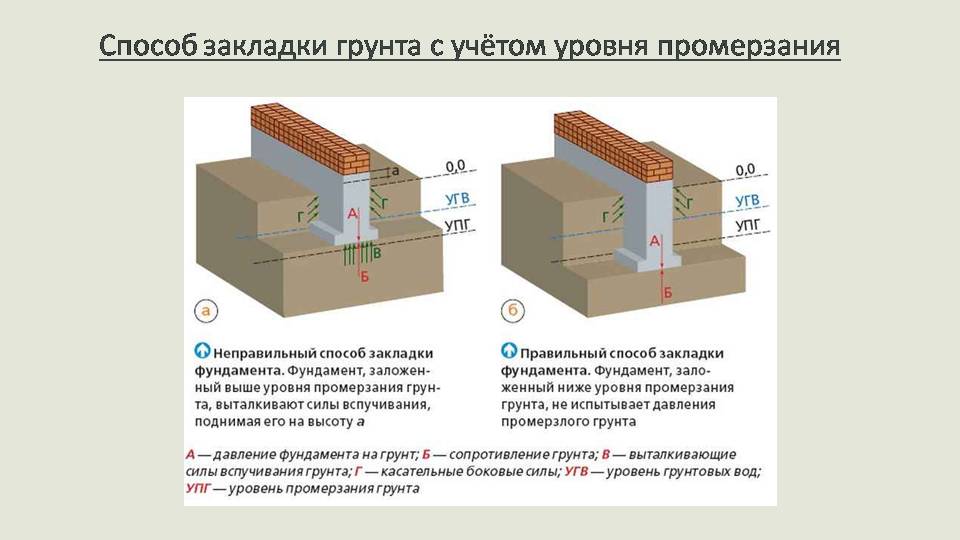
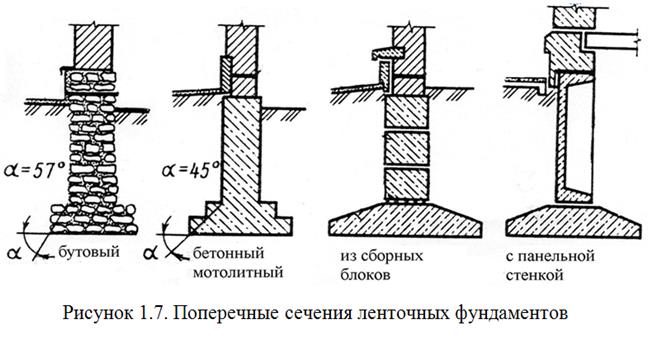
The opinion is erroneous that the lower the depth of the foundation in the soils prone to heaving, the more reliable it is and provides the structure with high stability. Yes, it lies below the freezing line and buoyant forces do not act on it, but tangential forces will easily lift the entire foundation structure along with the frozen soil. These forces will tear it apart, forming the upper and lower parts, especially if the structure is light and the foundation is not monolithic and without a reinforcing frame. Whatever this happens, the foundation should be laid below the depth of freezing soil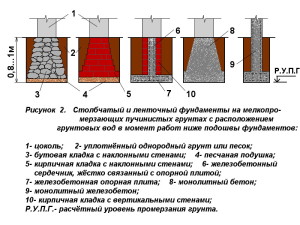
 and with a broadened sole in the form of an anchor. For greater rigidity, a reinforcement frame is laid in the foundation body. If the foundation is made of stones or bricks and without reinforcement, then it is made in the form of a trapezoid with a narrowed foundation body at the top. This configuration, with a necessarily smoothed surface, is not exposed to buoyancy forces in heaving soils (Fig. 2). To reduce the effect of tangential forces, sliding materials are used to cover the walls of the foundation, for example, polyethylene film, bitumen.
and with a broadened sole in the form of an anchor. For greater rigidity, a reinforcement frame is laid in the foundation body. If the foundation is made of stones or bricks and without reinforcement, then it is made in the form of a trapezoid with a narrowed foundation body at the top. This configuration, with a necessarily smoothed surface, is not exposed to buoyancy forces in heaving soils (Fig. 2). To reduce the effect of tangential forces, sliding materials are used to cover the walls of the foundation, for example, polyethylene film, bitumen.
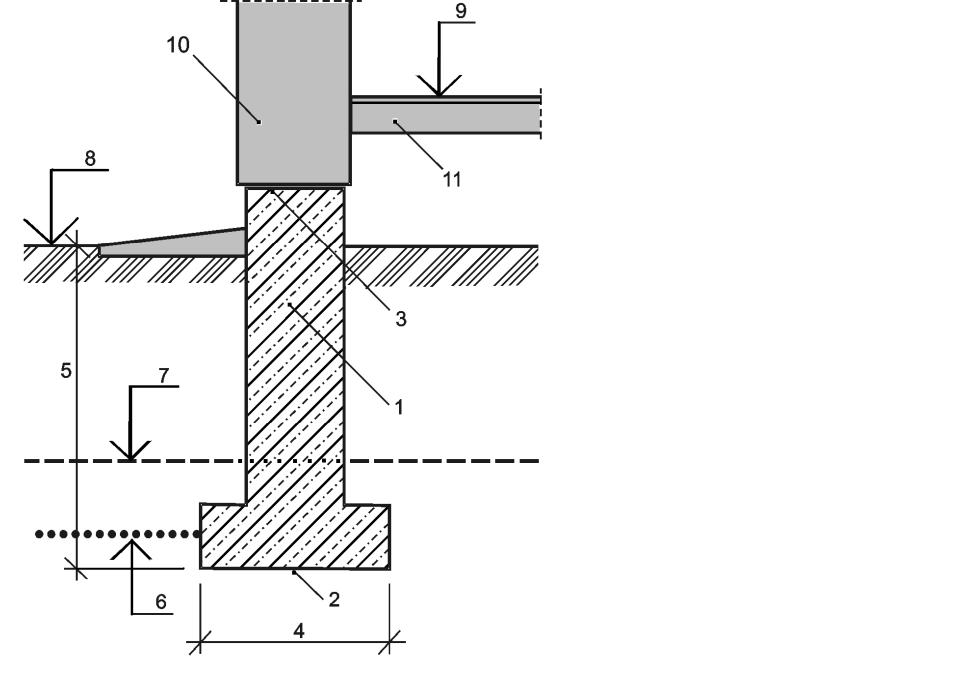
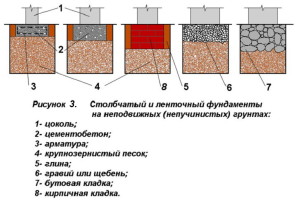
If the ground is motionless, i.e. not subject to heaving, in low-rise construction it is advisable to use the simplest foundations on a sand cushion (Fig. 3). In such structures, the upper part can be made of inorganic material - crushed stone, concrete, brick, stone, and the lower, the base, of coarse sand. Foundations of this type are quite reliable and durable, provided that they are protected from rain and flood waters. They can be used for any type of low-rise buildings and with any depth of soil freezing. The groundwater level (GWL) should not be higher than the soil freezing boundary. If the water rises above this mark, then the soil will become abyssal, and the foundation will be mobile, which will entail the destruction of the integrity of the walls of the structure.
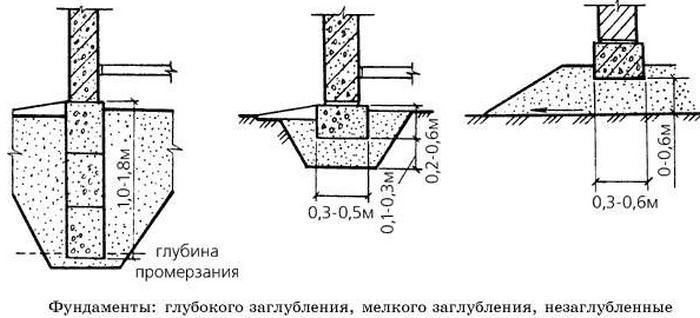
In soils subject to heaving, the foundations are designed taking into account the action of the pushing tangential forces of frost heaving. (Fig. 2) shows the types of structures that can be made in soils with shallow freezing and in the absence of water in trenches and pits at the time of work.
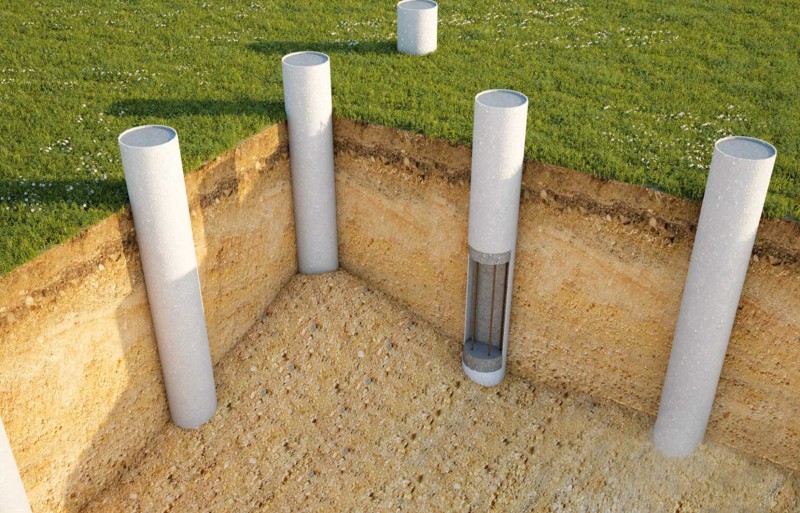
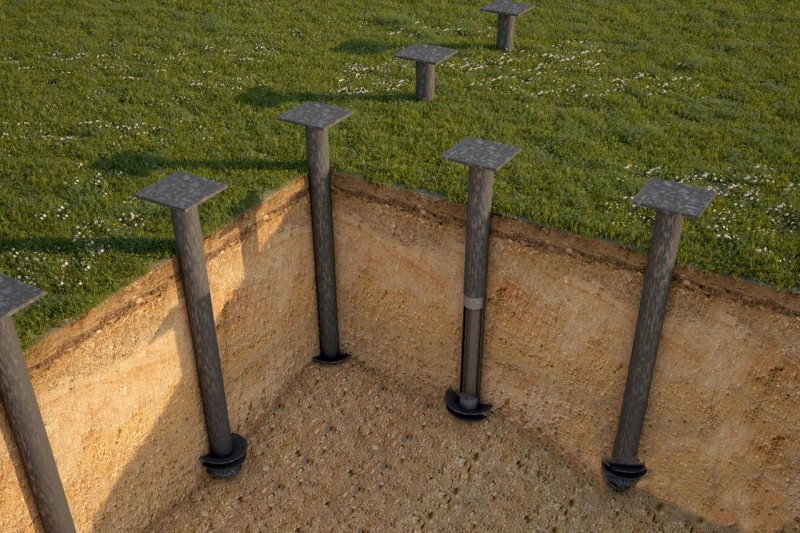
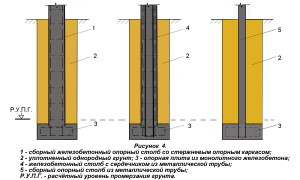 For structures with a foundation depth of more than 1 m, the use of a tape type (unless, of course, you are building a basement) is not economically viable. Here it is recommended to use foundation pillars made of monolithic reinforced concrete, metal or asbestos-cement pipes, (Fig. 4). If there is no ground water in the pit, then monolithic concrete is laid on the bottom in the form of a slab just before the installation of the pillars, while the ends of the pillars must have reinforcement outlets that will be sunk into the concrete.
For structures with a foundation depth of more than 1 m, the use of a tape type (unless, of course, you are building a basement) is not economically viable. Here it is recommended to use foundation pillars made of monolithic reinforced concrete, metal or asbestos-cement pipes, (Fig. 4). If there is no ground water in the pit, then monolithic concrete is laid on the bottom in the form of a slab just before the installation of the pillars, while the ends of the pillars must have reinforcement outlets that will be sunk into the concrete. 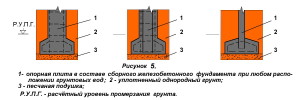 If the groundwater level is higher than the lower part of the foundation, then its installation is carried out with pillars that are pre-made together with the support plate, Figure 5.
If the groundwater level is higher than the lower part of the foundation, then its installation is carried out with pillars that are pre-made together with the support plate, Figure 5.
The groundwater level can be determined as follows: a well is drilled near the construction site in autumn or at the beginning of winter and the groundwater level is determined by the depth of the standing water.
It is necessary to pay attention to the stability of the soil, its resistance to bursting. In low-rise construction, the subsidence of the strip foundation due to the action of loads from the building is a rare phenomenon, because
the supporting area of the foundation structure is much larger than the calculated one. If the building is being erected on weak unstable soils (subject to subsidence from its own weight or the weight of the building structure with increasing humidity - loess, clay, some types of sandy loam, clayey fill soils, industrial waste, ash deposits, etc.) or use foundation pillars in buildings with heavy walls, it is recommended to check the area of contact of the sole with the ground in places of concentration of loads by calculation. If necessary, you can increase the area of the base of the foundation, widen it, and in columnar ones also reduce the distance between the posts.
Interesting Facts
All bumblebees are represented by the genus Bombus, which, like a honey bee, belongs to the Apidae family. The extraction of nectar and flights continue even at 0 C, so the species Bombus Polaris lives in the Arctic Circle.
Species of individuals
A bumblebee family may not only consist of a male and a female. Since spring, working individuals are hatched in it, that is, females that are not able to reproduce. And in autumn males collect nectar from late honey plants.
The number of individuals in a bumblebee family cannot exceed 200-300. For northern species, the number is limited to 2. Usually the speed of a bumblebee in flight reaches 12 km / h. But already at T = 35 ° C flight will not be possible due to overheating.
- For wintering, a female bumblebee digs a mink. But when nesting, it seems to forget about this ability and uses ready-made holes in the ground for the nest.
- In the predawn hours, a so-called bumblebee appears in the bumblebee's nest — a trumpeter, which hums very much. It was believed that in this way he raises relatives to work. But, later it turned out that in the early morning hours, when the air at the surface of the soil is significantly cooled, the insect is simply trying to warm up with the help of intensive work of the pectoral muscles.
- There is a branch of agriculture - bumblebee breeding. Bumblebee breeding is practiced in order to increase the yield of agricultural crops.
- Previously, it was believed that according to the laws of aerodynamics, a bumblebee should not fly. But physicist Zheng Jane Wang from Cornell University in the USA proved that the bumblebee does not fly contrary to the laws of physics, and the information of the beginning of the 20th century was a delusion.
Preparatory work before pouring the foundation
Creating an unburied strip foundation with your own hands, first of all, they prepare the site selected for construction. It is necessary to remove a layer of fertile soil, level the surface. Then the markup is performed according to the project.
According to the markings, it is necessary to dig a trench, which should pass under all the walls of the building. The width and depth of the trench should correspond to the design parameters of the foundation cushion. A sand and gravel mixture is poured into the trench and compacted tightly. If the pillow is tamped correctly, an adult with an average build will walk over it without leaving any marks.
The next stage is the installation of the formwork. It must be mounted as a whole, to the calculated height of the foundation, so that the tape is monolithic. Cold seams drastically reduce the bearing capacity of an unburied base, which is already low.
The walls of the formwork are rigidly fastened to each other, otherwise the structure is deformed during pouring. Especially high quality should be fastened to the corners - they have a maximum load. The cracks between the formwork boards should be reliably drilled so that the cement “milk” does not flow away - this will reduce the strength of the concrete.

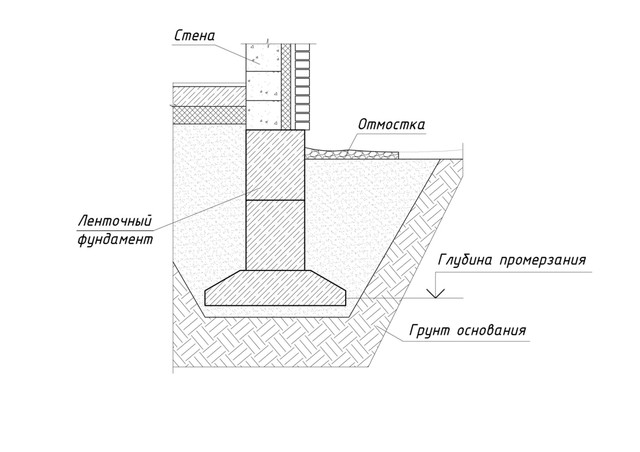
The depth of soil freezing
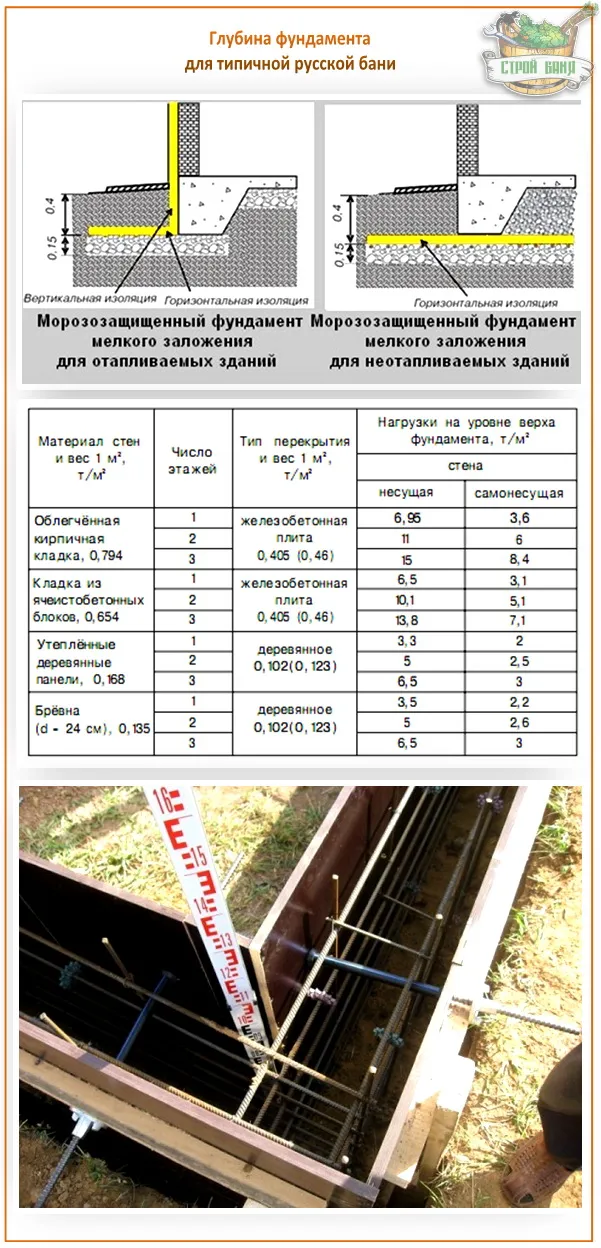
For a strip foundation, this parameter is decisive.On any type of soil - heaving, non-heaving or loose - the base of the structure should be located either below the level of the frozen layer, or within its central part. Since deformation of the formation occurs during freezing, it is recommended to arrange the foundations in such a way that they rest on a strong non-freezing layer.
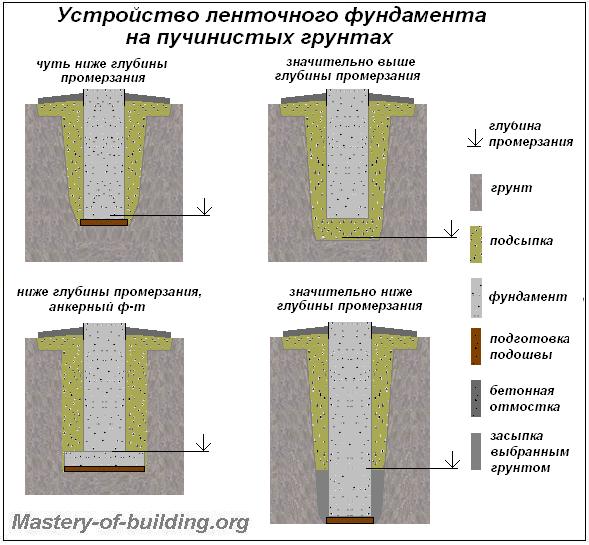
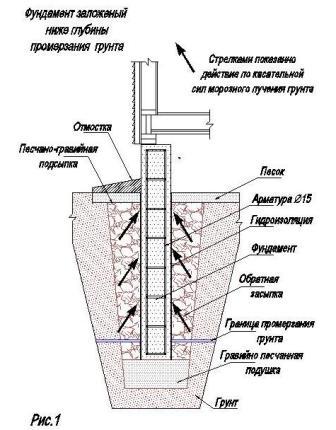
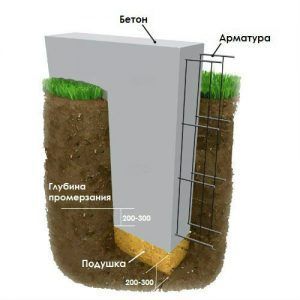 Laying the foundation below the depth of soil freezing
Laying the foundation below the depth of soil freezing
The base of the strip shallow foundation is located within the freezing zone, since the loads on a structure of this type are insignificant and the factor of soil freezing does not significantly affect the stability of the structure
For deep strip foundations, it is important to build trenches deeper than the freezing soil layer is located
Data on the average depth of soil freezing in a certain region are freely available on the Internet or the corresponding SNiPs. At the same time, the maximum depth of the strip shallow foundation is 700 mm, and the minimum elevation of the base of deep foundations depends on the region of construction, but must be at least 0.7 meters.
Geological surveys
 For greater confidence in the reliability and capital nature of the building or structure being erected, activities related to the study of the geology of the site are carried out. Geology must be studied in order to find out the condition of the soil foundations, the type of soil, and also to make sure that the selected type of foundation structures is rational.
For greater confidence in the reliability and capital nature of the building or structure being erected, activities related to the study of the geology of the site are carried out. Geology must be studied in order to find out the condition of the soil foundations, the type of soil, and also to make sure that the selected type of foundation structures is rational.
It is not recommended to arrange monolithic foundations on highly heaving, loose and subsiding soils, and in general, tape rigidly fixed structures - in this case, pile structures are preferable. Information about the condition of the soil in this case can save you from significant problems during operation. Based on the survey results, the contractor also receives data on the location of a reliable bearing layer and the level of groundwater.
Ground water
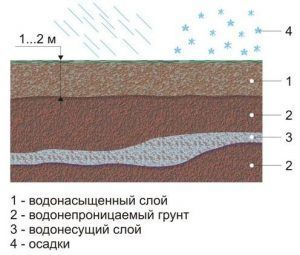 Groundwater layout
Groundwater layout
According to the data on the water table, the depth of the trench can vary significantly. Moreover, changes can be both in the direction of increasing, and in the direction of decreasing the depth of laying. For a shallow strip foundation, this factor is not so critical, since groundwater is rarely less than 700 mm.
In any case, this indicator should be taken into account, since even waterproofing of foundation structures will not be able to create their full-fledged protection against corrosion due to interaction with groundwater.