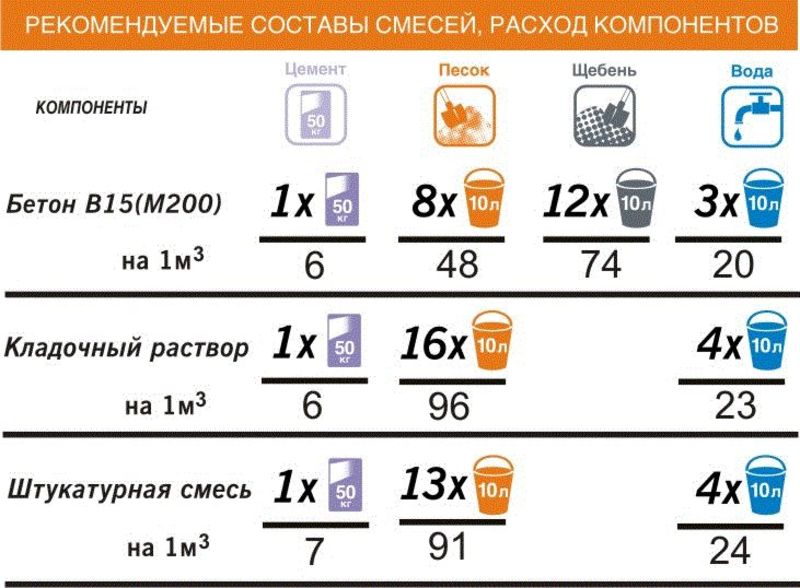
Fillers: sand and granite
Versatile auxiliary components interact with cement to create a durable structure. Regardless of the brand and type of dry product, the composition of the concrete mass includes:
- crushed stone is a strong frost-resistant stone without harmful impurities and components. To increase the hardness of the concrete mixture, granite is used, with fractions from 10 to 40 mm. Good performance properties determine the high cost and popularity of the building material.
- Sand is a sedimentary solid. Correctly selected grade of sand helps to reduce the consumption of expensive limestone. For foundations, open pit sand of medium grain size from 1.2 mm to 3.5 mm is in demand. The permissible amount of impurities should not exceed 5% of the total volume of sand.
Water is added to the solution in portions until a mixture of a homogeneous consistency is obtained. When mixing the constituent elements, it is imperative to correctly determine their proportions. The resulting voids between gravel grains, if incorrectly filled, will subject the base to rapid deformation.
How to calculate cement for a foundation
The method for calculating the required amount of cement is quite simple. The main role, of course, is assigned to concrete, which is planned to be obtained from this building material. Having studied the proportions of concrete for the foundation, it is easy to calculate how much cement will be required to build the base of the house. The calculation is usually carried out in bags that can hold a kg of binder.

How much cement is approximately required for the construction of the foundation
The sequence of calculation can be represented as follows, in stages:
- first, we calculate the volume of concrete that will go to the construction of the foundation. We wrote how to do this in the article "Calculation of concrete for a foundation." At this stage, it all comes down to the summation of the volumes of individual base structures, or the usual volume calculation, which is important for a slab foundation;
- further we determine the composition of the concrete mass. Depending on the loads on the basement of the house, as well as the composition of the soil, the concrete grade is determined. The percentage of cement per unit of volume depends on the grade of the concrete mixture (as a rule, it is calculated per cubic meter). At the same time, an analysis is carried out - is it necessary to introduce different additives into concrete to simplify the work in specific conditions;
- at the last stage, the required amount of binder and aggregates (sand, crushed stone, etc.) is calculated. We will talk about what kind of sand is needed for the foundation in one of the following articles.
Below we have presented a table, using which you can calculate the approximate number of bags of cement for concrete for the foundation. Minor adjustments are possible both upward and downward. If you plan to strengthen the foundations by cementation (we are talking mostly about the restoration of the old base, when a new one is additionally attached to it), then, accordingly, the volume of the required cement must be adjusted already for a cement mortar, and not a concrete mixture.
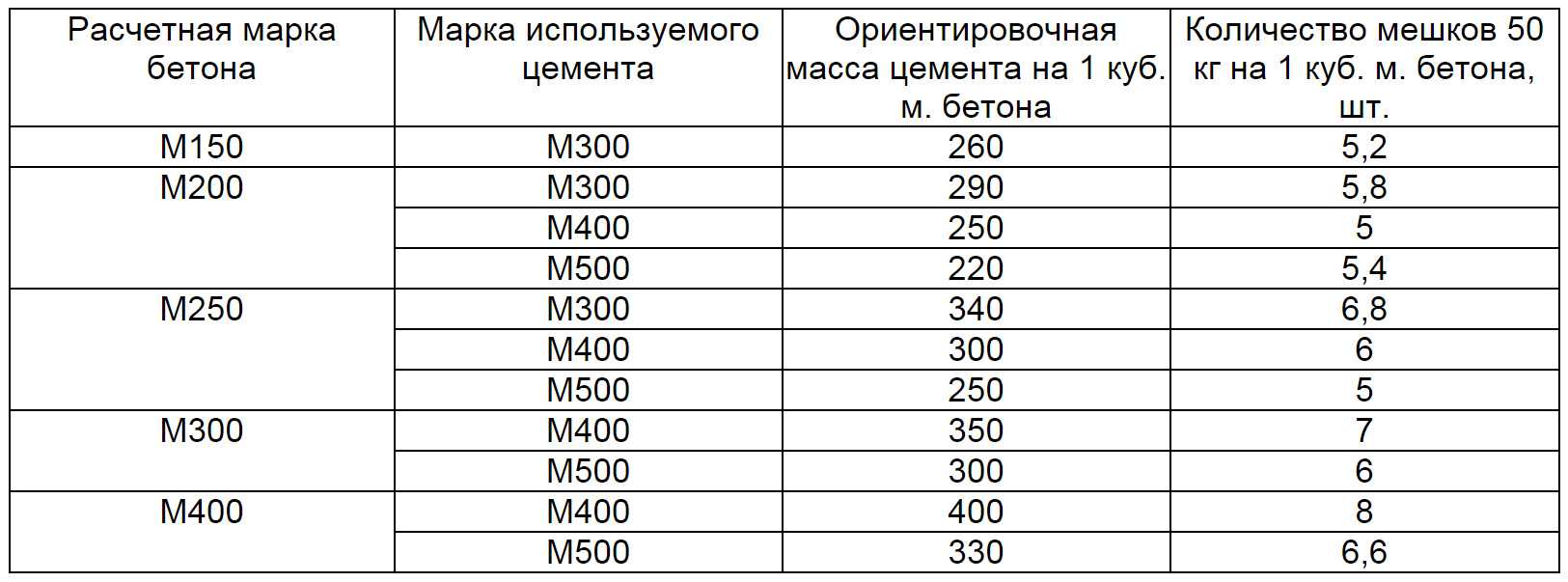
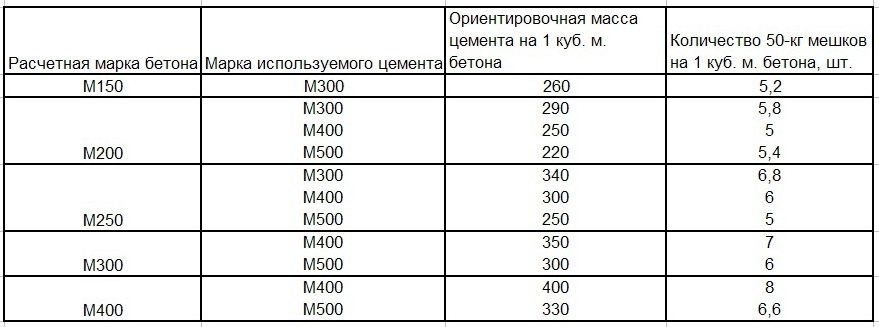
Estimated grade of concrete Grade of cement used Approximate weight of cement per 1 cu. m. of concrete Number of bags 50 kg per 1 cu. m. of concrete, pcs.
| M150 | M300 | 260 | 5,2 |
| M200 | M300 | 290 | 5,8 |
| M400 | 250 | 5 | |
| M500 | 220 | 5,4 | |
| M250 | M300 | 340 | 6,8 |
| M400 | 300 | 6 | |
| M500 | 250 | 5 | |
| M300 | M400 | 350 | 7 |
| M500 | 300 | 6 | |
| M400 | M400 | 400 | 8 |
| M500 | 330 | 6,6 |
It turns out that calculating the volume of cement for the foundation is not particularly difficult.
It is only important to know the volume of concrete required for the construction of a specific type of base for a house, as well as the ratio of the components that make up the concrete mixture
Approximate tabular data
The approximate consumption of cement per cube of concrete for the foundation, depending on the grade used, is presented in the tables:
mixture prepared on the basis of M300
| Concrete grade | M250 | M300 |
| Required mass of cement, kg | 340 | 300 |
based on M400
| Concrete grade | M300 | M400 |
| Required mass of cement, kg | 350 | 300 |
When the amount of cement of a particular brand in the composition changes, the brand of concrete changes. The values indicated in the table depend on the quality of the soil and the size of the crushed stone, therefore, during the calculations, they can change up or down.
Does it make sense to use the M500 for a foundation?
Using the arithmetic method or tables, it is not difficult to find out, for example, how much cement M 500 is needed per 1 cube of concrete for a foundation. At least 8 bags or 400 kg to obtain M400 mortar, used for the construction of foundations in professional construction.

The use of M500 in small construction does not make sense
It is not desirable that 1 cube of concrete contains more than 350 kg of cement. An oversaturated foundation, after the final evaporation of moisture, will be subject to severe cracking. Therefore, it is not advisable to use the M500 grade for placing concrete under the foundation. This material is for other purposes.
Calculation of materials: without the invention of the bicycle
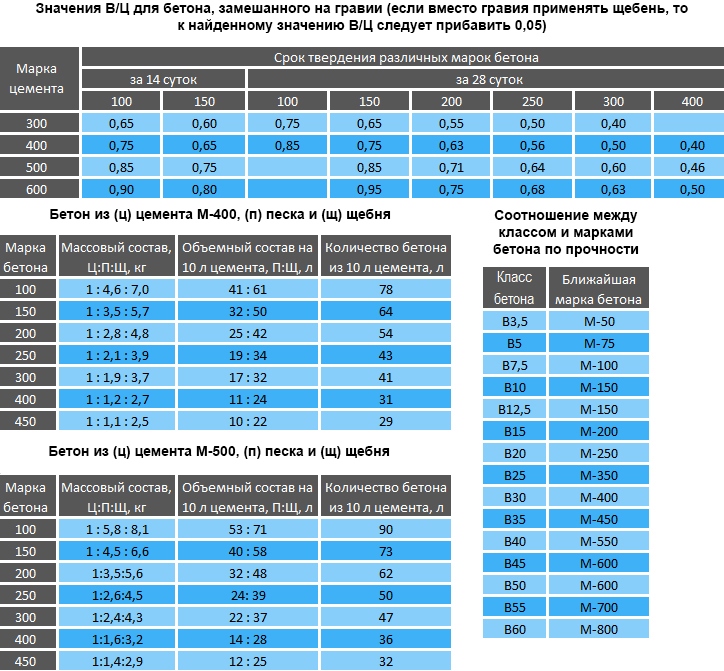
How to calculate the cement for the foundation? For the accuracy of the results, it is necessary to take into account the brands of concrete and cement, as well as the ratio of water and cement, which is called for short - VC. The table below is illustrative and does not require a person to have a degree in mathematics.
The table is easy to use. For example, we need to prepare 2 m3 of M250 grade concrete:
- It needs M500 cement, which means we multiply 297 kg by 2, we get - 594 kg. Now this number must be divided by 50, since this is the weight of one bag of cement: 594/50 = 11.88. The result is rounded up towards a larger value - we get 12 bags of M500 cement.
- Crushed stone with a grain of 20 mm for our concrete will be calculated as follows: multiply 1188 by 2, we get 2376 kg. If you chose a different faction, then all calculations will have to be done again.
- Sand is calculated in the same way as crushed stone: 1188 * 2 = 2376 kg.
- We find water like this: we multiply 205 liters by 2, we get 410 liters as a result.
Indeed, the calculations should not cause any difficulties, you just need to decide on the required characteristics of your raw materials. If plasticizers are used for the foundation, then adjustments must be made to the calculations, the coefficients can easily be found in reference books.
Calculation of cement for 1 cubic meter of concrete (m³)
The proportional ratio of cement to other binders affects the flowability of the concrete mix. In order to prepare high-quality building materials, the following ratios should be adhered to:
- cement up to 1 kg;
- sand up to 3 kg;
- crushed stone up to 5 kg.
Failure to comply with all component ratios leads to a decrease in the strength characteristics of the future building coating. This will lead to rapid wear and surface cracking. Quantitative consumption of cement per 1 m³ of mortar directly depends on the brand of concrete mixture planned by the manufacturer. Under different climatic conditions and construction zones, different grades of material are used.
Concrete marking classifier
Table of the ratio of classes and grades of concrete.
With various requirements for the stability and reliability of a building object, the following marking classifier of concrete mixtures is mainly used:
- M100. It is used at the initial (preparatory) stage of construction work.
- M200. Has a wider range of applications. Most often used when pouring fundamental surfaces.
- M300. This building material has great strength characteristics. Fundamental laying with such a concrete monolith is used in industrial construction.
- M400. It is used in the construction of structures of a hydraulic nature. It has high strength and differs from other grades of concrete by its fast hardening.
Decoding of building material: the letter M with a number that indicates the arithmetic mean of the strength characteristics of the sample, for compression in kgf / cm².
How many cubes of concrete are needed for a foundation?
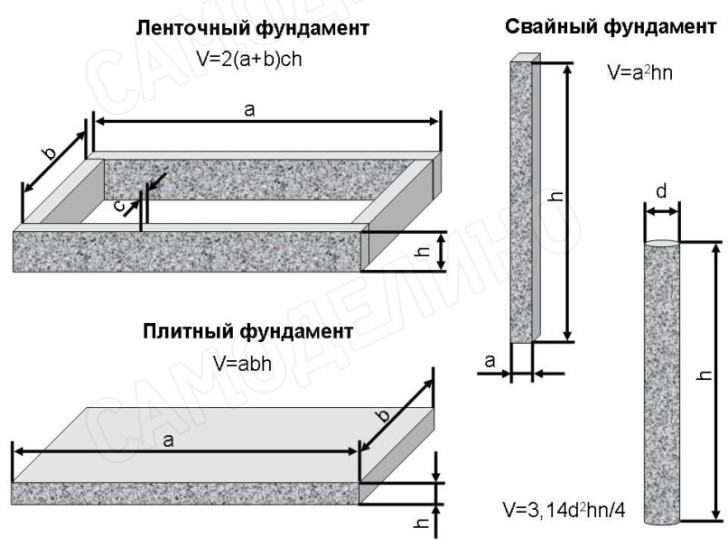
When building a civil or industrial facility, two types of fundamental coatings are used: strip and slab bases. For the convenience of the calculated indicators, a reinforced concrete (reinforced concrete) foundation 10 by 10 is taken:
- Strip foundation. The required amount of mortar is determined by the total volume of the base. The calculation is carried out by multiplying the metric values: height, length and width of reinforced concrete tape. Initial data: height - 1.5 m, width - 0.5 m, total length of the tape - 55 m. Multiplying the values and rounding the value to an integer, we get 41 cubic meters of concrete.
- Slab base. The amount of concrete mix is determined very simply for a slab foundation. For example, the thickness of the slab is 40 cm. Multiplying the initial data, we get: 10 mx 10 mx 0.4 m = 40 m³.
Weight of 1 m³ of concrete mix
The specific gravity of the binder building material is variable.
The mass of concrete weighs differently, depending on its structural components, that is, on the type of aggregate. In civil and industrial construction, a heavy type of concrete monolith is usually used. Gravel and crushed stone of large fractions are used as filler. Thanks to this basis, the fundamental coating has a special strength and stable surface. The weight of one cubic meter of concrete mix is from 1.7 to 2.5 tons.
Determine how much cement, sand, gravel and water is in a cube of concrete.
4 June, 2013 - 12:35 Concrete is one of the most demanded materials in construction. Such popularity of concrete is explained by its excellent properties: compressive strength, ease of forming and laying, waterproofing, water resistance, low price.
For the manufacture of concrete, cement, water and so-called aggregates are used, which can be coarse (crushed stone) or fine (sand). Builders often face the question of how to mix concrete correctly. It is at this stage that it is usually required to determine how much cement is in a cube of concrete.
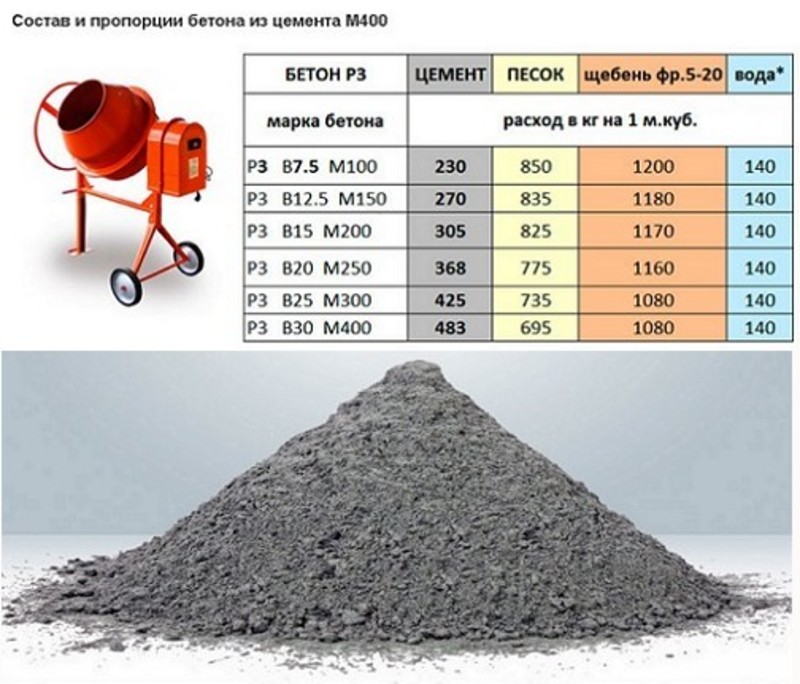
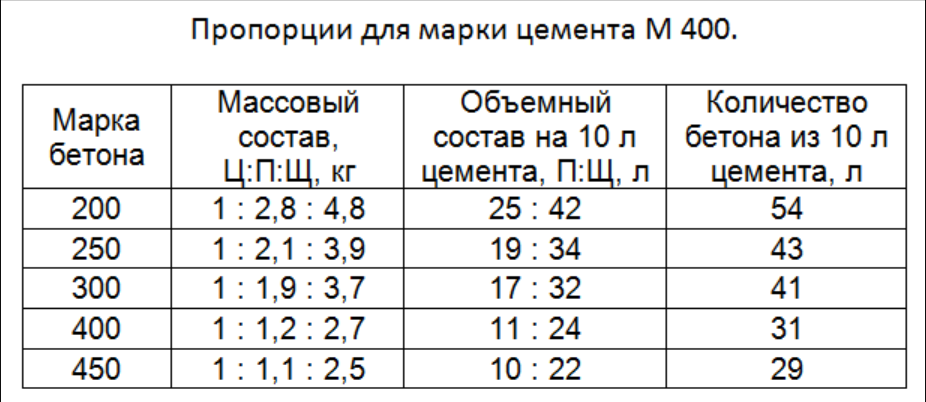
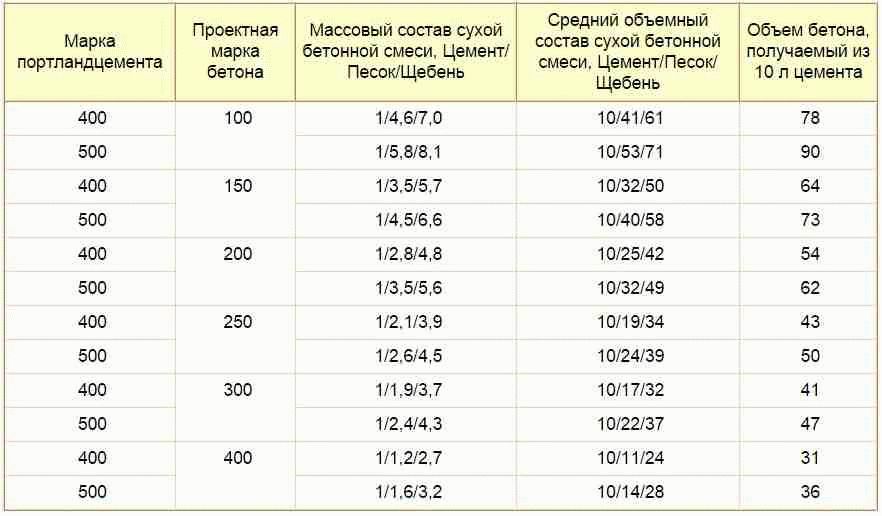
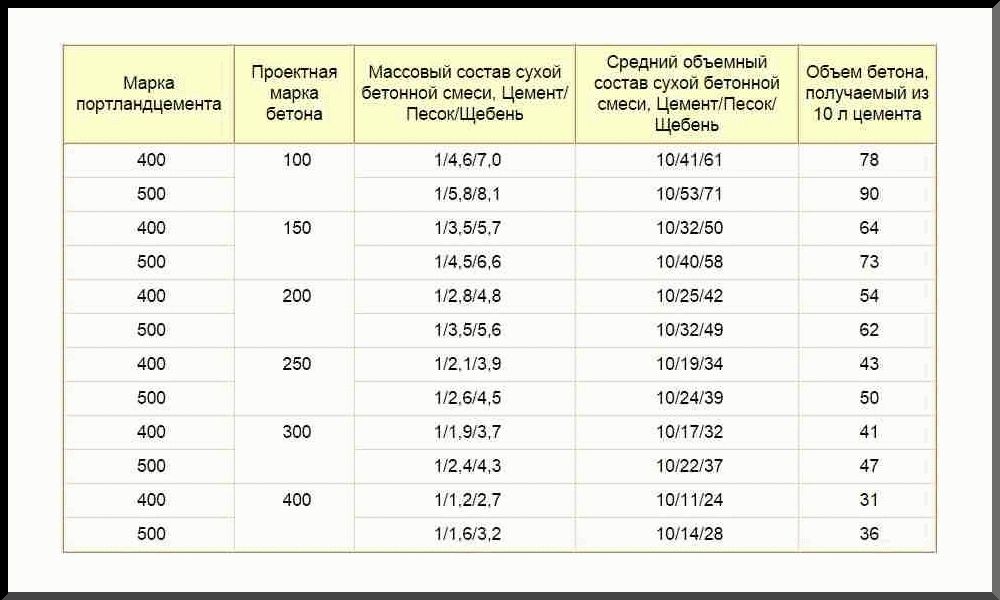
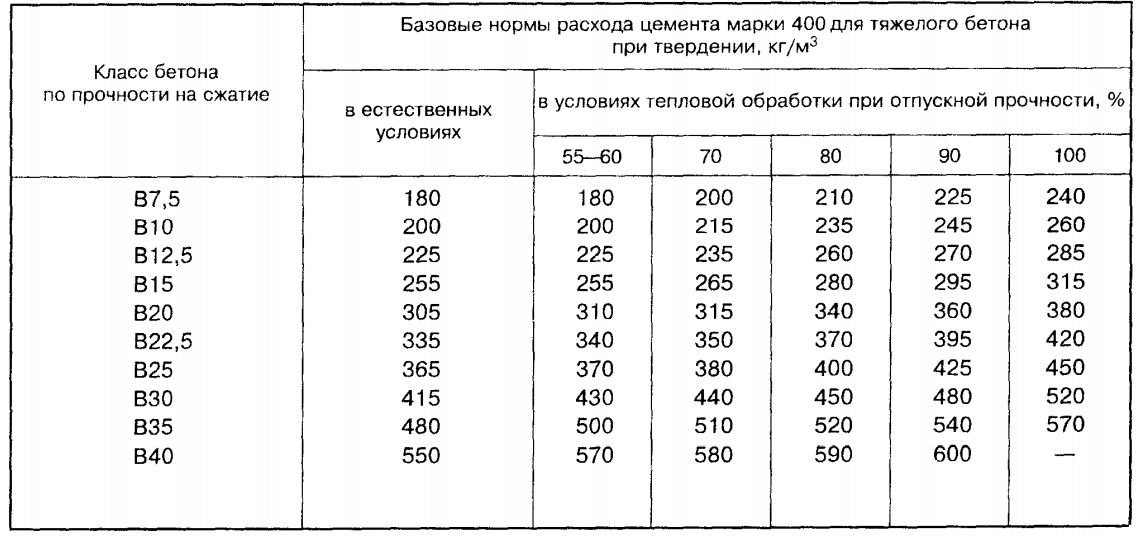
Today, there are a large number of concrete grades that differ in their composition, or rather, in the volume or mass ratio of its constituent components. For example, to create 1 cubic meter of 100 grade concrete, 200 kg of cement is required, to create 1 cube of 400 grade concrete, 360 kg of cement is required.
There are special tables from which you can understand not only how much cement per cube of concrete is required, but also the percentage of other concrete components in the finished composition.
So, for example, for the most running grade 300 concrete, it is necessary to mix 382 kg of M400 cement, 705 kg of sand, 1080 kg of crushed stone and 220 liters of water. For concrete of 100 brands, you will need 214 kg of cement (M400), 870 kg of sand, 1080 kg of crushed stone and 210 liters of water.
In general terms, you can determine how much sand is in a cube of concrete, according to the following scheme:
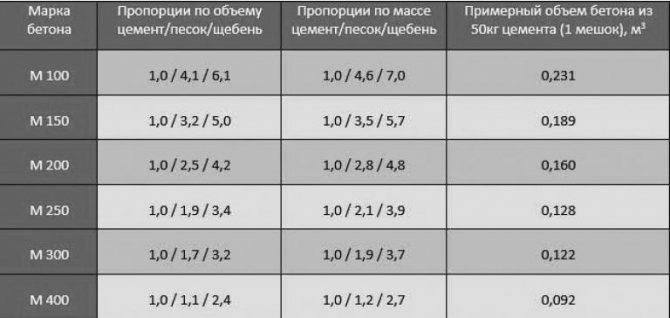
1 volume fraction of cement in grade 100 concrete accounts for 4.1 shares of sand and 6.1 shares of crushed stone; for concrete grade 150, the ratio of cement (M400), sand and crushed stone is 1 to 3.2 and to 5.0; for concrete M200 - 1 to 2.5 and to 4.2; for М250 - 1 to 1.9 and to 3.4 (cement: sand: crushed stone); for 300 1 to 1.7 and to 3, "; for 340 1 to 1.1 and to 2.4.
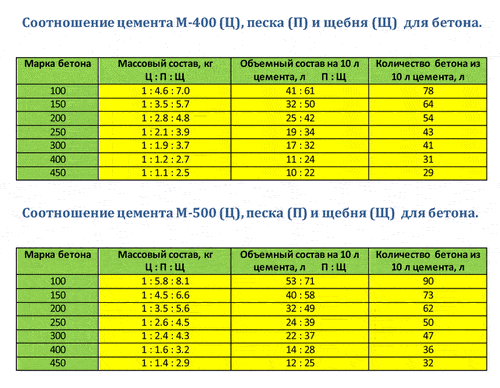
Table 1. Proportions of cement, sand and crushed stone by concrete grades
| Concrete grade | proportions cement: sand: crushed stone | |
| cement grade 400 | cement grade 500 | |
| 100 | 1,0 : 4,1 : 6,1 | 1,0 : 5,3 : 7,1 |
| 150 | 1,0 : 3,2 : 5,0 | 1,0 : 4,0 : 5,8 |
| 200 | 1,0 : 2,5 : 4,2 | 1,0 : 3,2 : 4,9 |
| 250 | 1,0 : 1,9 : 3,4 | 1,0 : 2,4 : 3,9 |
| 300 | 1,0 : 1,7 : 3,2 | 1,0 : 2,2 : 3,7 |
| 400 | 1,0 : 1,1 : 2,4 | 1,0 : 1,4 : 2,8 |
| 450 | 1,0 : 1,0 : 2,2 | 1,0 : 1,2 : 2,5 |
Knowing these proportions, you can not only easily find out, for example, how much rubble is in a cube of concrete, but also knead absolutely any amount of high-quality concrete without much difficulty.
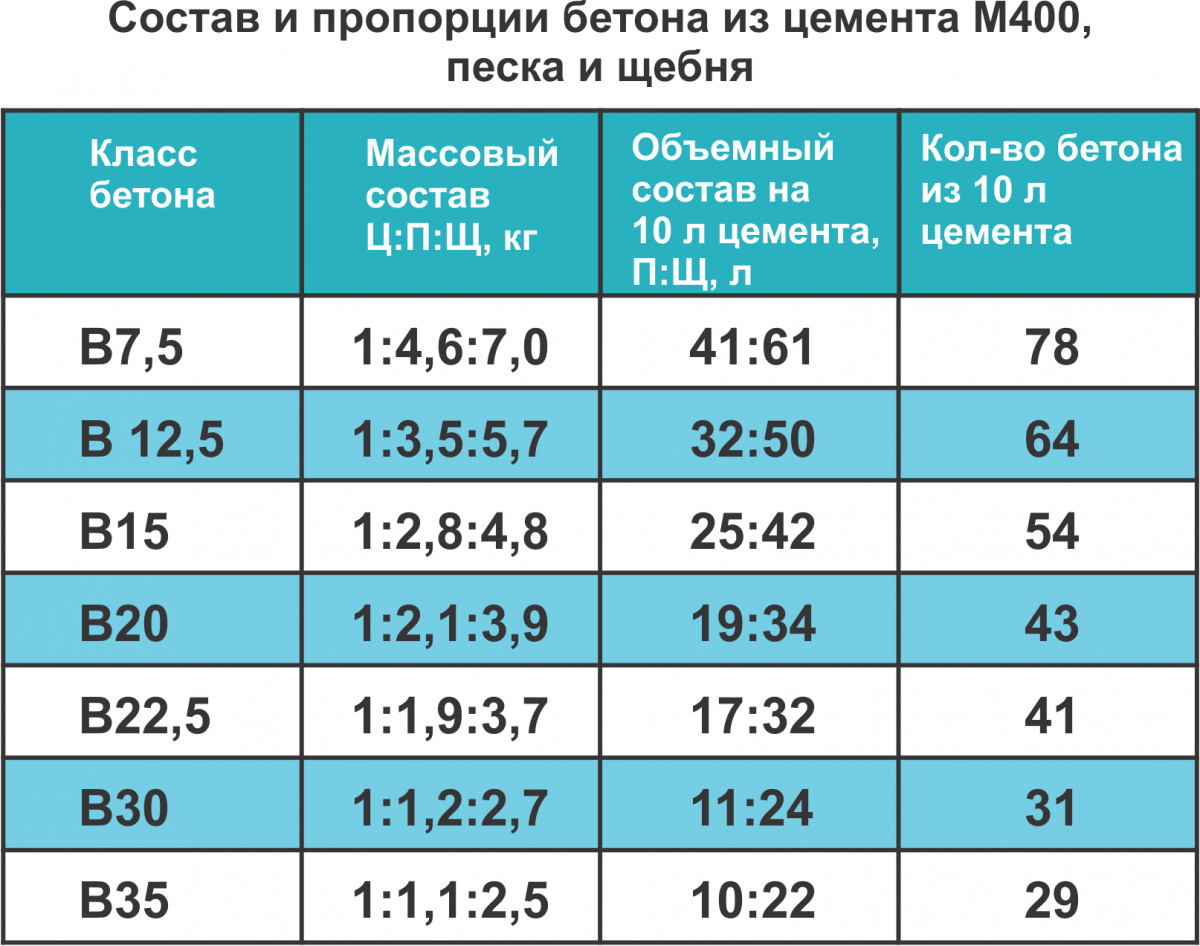
Table 2. Relationships between the class and concrete grades in terms of strength.
| Brand | Class | Strength, kg / cm2 |
| M-100 | B7.5 | 98,2 |
| M-150 | AT 10 | 131,0 |
| M-150 | B12.5 | 163,7 |
| M-200 | B15 | 196,5 |
| M-250 | B20 | 261,9 |
| M-350 | B25 | 327,4 |
| M-400 | B30 | 392,9 |
| M-450 | B35 | 458,4 |
| M-500 | B40 | 532,9 |
It is important to note that the physical and mechanical properties of the concrete will depend on the grade of cement used to make concrete. So, if instead of cement M400 add cement M500, the grade of concrete will increase (say, instead of 200, it will become 350)
In order to get good concrete, you should choose crushed stone, the grade of which will exceed the grade of concrete that we want to get by 2 times.
Simple concrete mixing scheme
If for construction you do not need factory accuracy, and there is no need to strictly maintain the grade of concrete, you can use a simplified scheme: take 0.5 parts of water, 2 parts of sand and 4 parts of crushed stone for 1 part of cement. For the manufacture of 1 cubic meter of concrete, the weight fractions of the components at this ratio will be as follows: cement - 330 kg (0.25 cubic meters), water 180 l (0.18 cubic meters), sand 600 kg (0.43 cubic meters), crushed stone 1, 25 tons (0.9 cubic meters).
How much cement, sand, gravel (crushed stone) and water is needed to get a cube of concrete:
M50 concrete
- Portland cement M400 - 380 kg. (1)
- Gravel - 608 kg. (1.59)
- Sand - 645 kg. (1.69)
- Water - 210 l. (0.55)
M75 concrete
- Portland cement M300 - 175 kg. (1)
- Crushed stone - 1053 kg. (6.02)
- Sand - 945 kg. (5.4)
- Water - 210 l. (1,2)
M100 concrete
- Portland cement M300 - 214 kg. (1)
- Crushed stone - 1080 kg. (5.05)
- Sand - 870 kg. (4.07)
- Water - 210 l. (0.98)
M150 concrete
- Portland cement M400 - 235 kg. (1)
- Crushed stone - 1080 kg. (4.6)
- Sand - 855 kg. (3.64)
- Water - 210 l. (0.89)
M200 concrete
- Portland cement M400 - 286 kg. (1)
- Crushed stone - 1080 kg. (3.78)
- Sand - 795 kg. (2.78)
- Water - 210 l. (0.74)
M250 concrete
- Portland cement M400 - 332 kg. (1)
- Crushed stone - 1080 kg. (3.25)
- Sand - 750 kg. (2.26)
- Water - 215 l. (0.65)
M300 concrete
- Portland cement M400 - 382 kg. (1)
- Crushed stone - 1080 kg. (2.83)
- Sand - 705 kg. (1.85)
- Water - 220 l. (0.58)
M350 concrete
- Portland cement M400 - 428 kg. (1)
- Crushed stone - 1080 kg. (2.5)
- Sand - 660 kg. (1.54)
- Water - 220 l. (0.51)
p.s. The sequence of laying materials in a concrete mixer affects the quality of concrete.
Calculation of materials for concrete
Before starting construction, every developer always asks the question: how much raw material will be required for the final product and how to determine this?
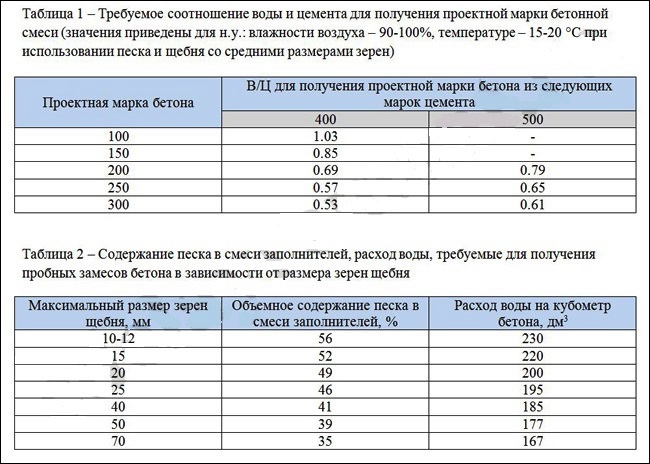
It is easy to calculate the consumption. For example, if for the preparation of one cube of the finished binder product, 325 kg is required, and the VC is 0.63, then 325 * 0.63 = 205 liters of water is needed. And here there is no need to "reinvent the wheel". These calculations are very well summarized in the following table:

Using such data, you can easily and quickly determine the need for raw materials for the preparation of, say, three cubes of the finished M200 product for the foundation:
cement M400 - 302 kg * 3 = 906 kg; it comes to the distribution network packaged in 50-kilogram bags, so you need to find out how many such bags are required - 906 kg / 50 kg = 18.12 pieces; since the value is fractional, it is rounded up, that is, you need to purchase 19 bags of M400 cement;
crushed stone of an average fraction of 20 mm - 1208 kg * 3 = 3624 kg; you should pay attention to the fact that when using a different fraction of crushed stone, the consumption of all materials for obtaining a cube of concrete will change and the entire composition must be re-calculated;
sand - 1208 kg * 3 = 3624 kg:
water - 205 l * 3 = 615 liters.
 Plasticizing additives can significantly improve the quality of concrete
Plasticizing additives can significantly improve the quality of concrete
Thus, knowing the initial characteristics of raw materials, it is possible to accurately calculate and determine exactly how much materials will be required for the needs of building a foundation or any other structures.
It must be remembered that when using plasticizing additives or using a fast-hardening binder, the calculation must be adjusted. It is not necessary to independently calculate the coefficients, there are ready-made consumption data in the reference books.
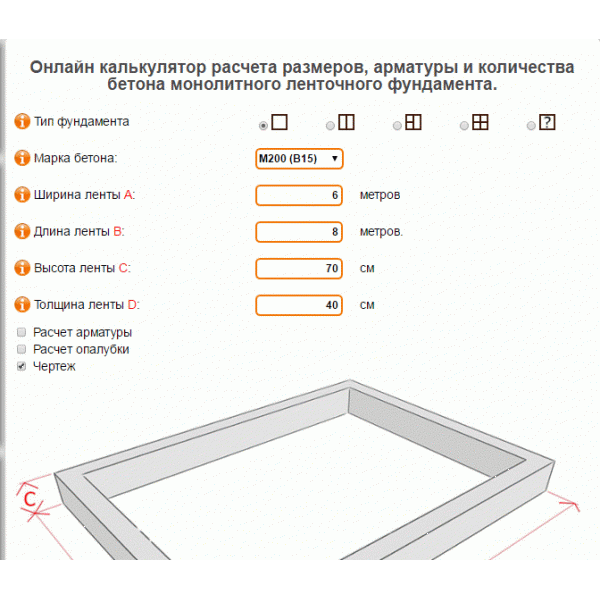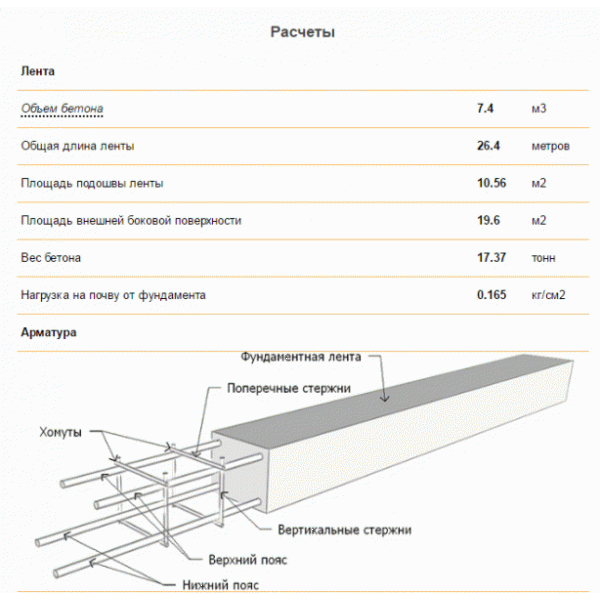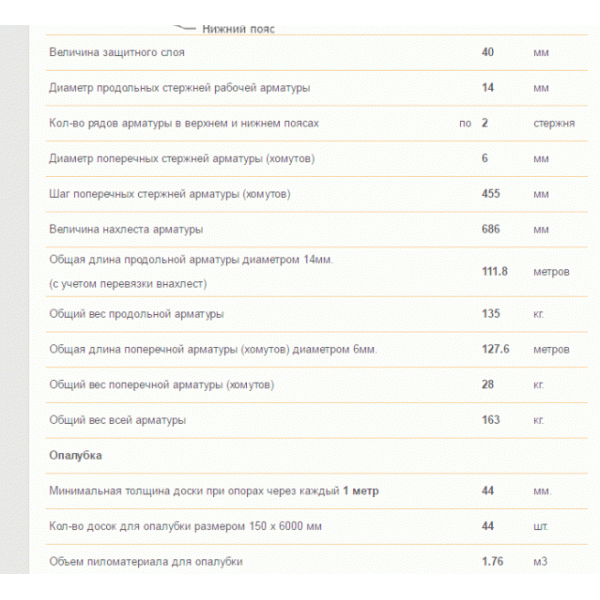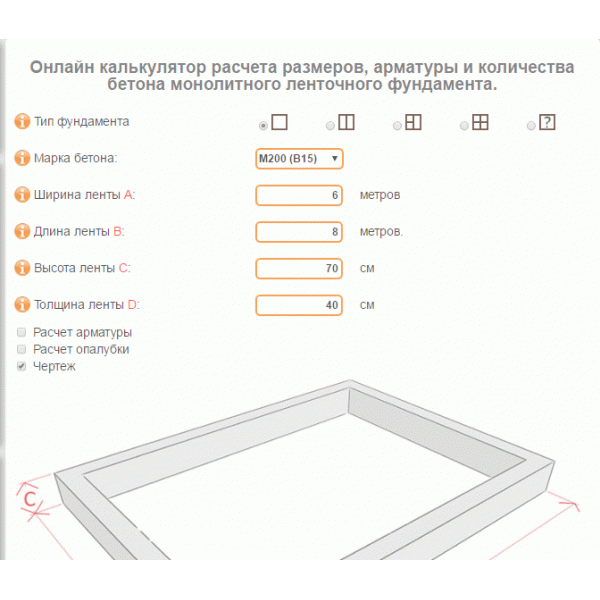
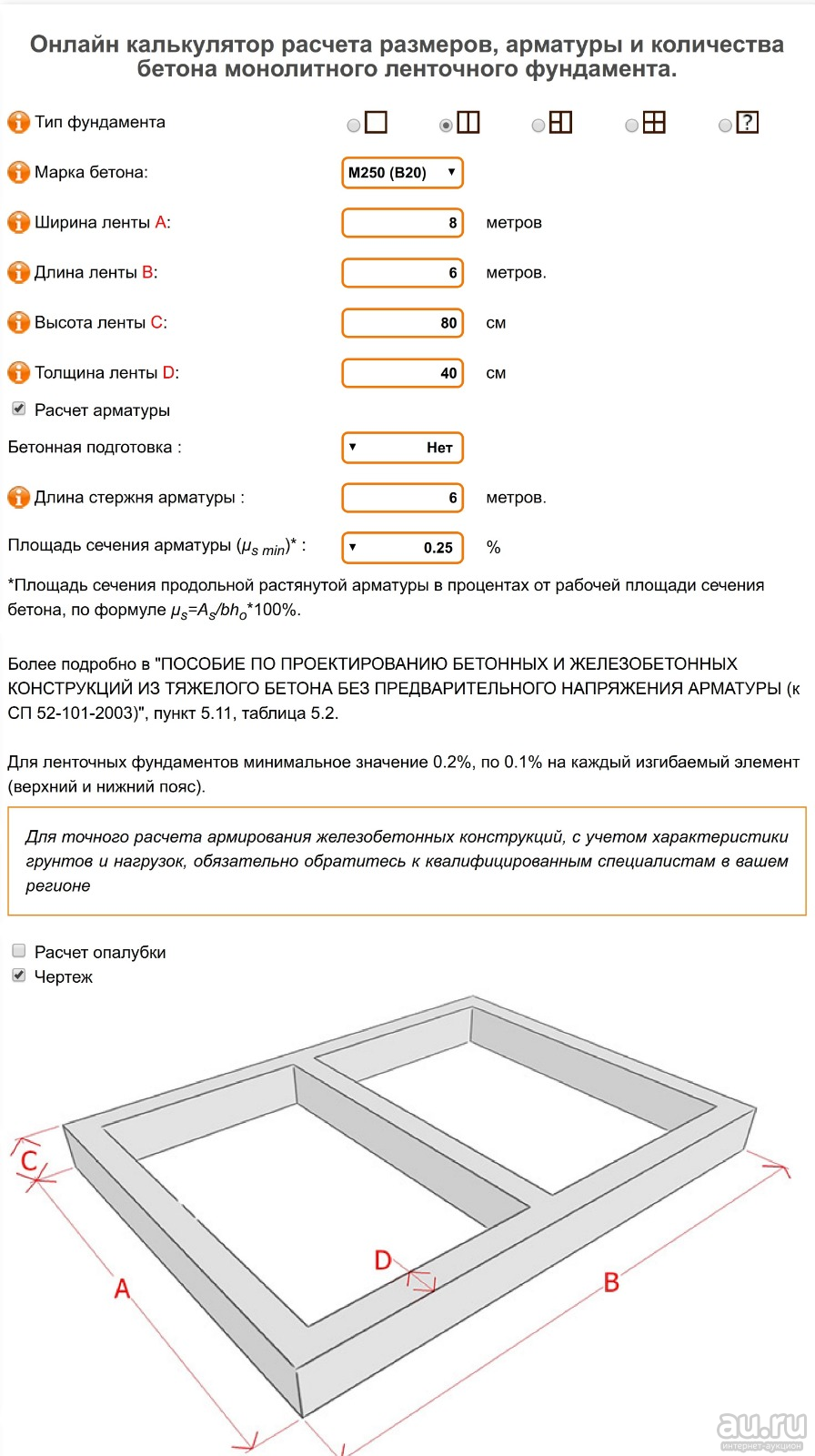
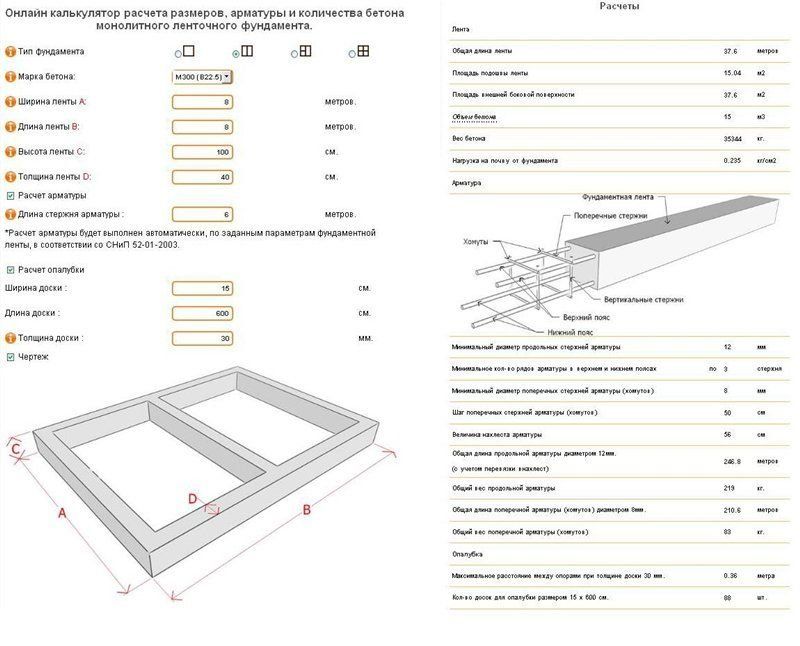
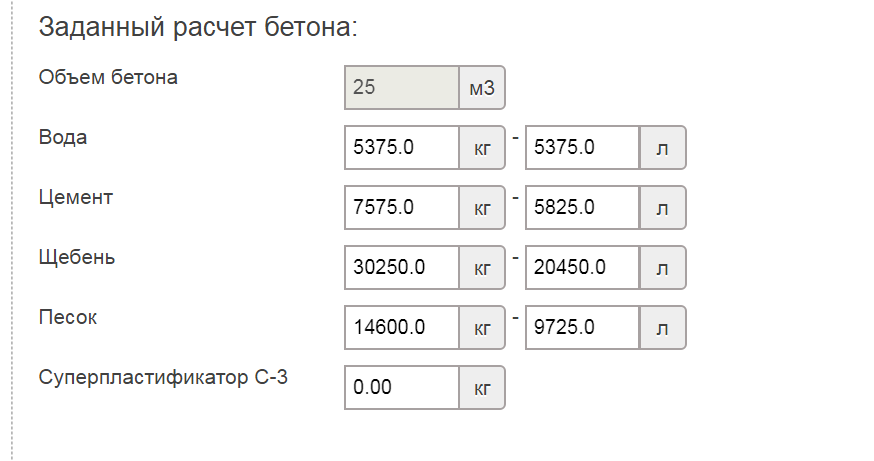
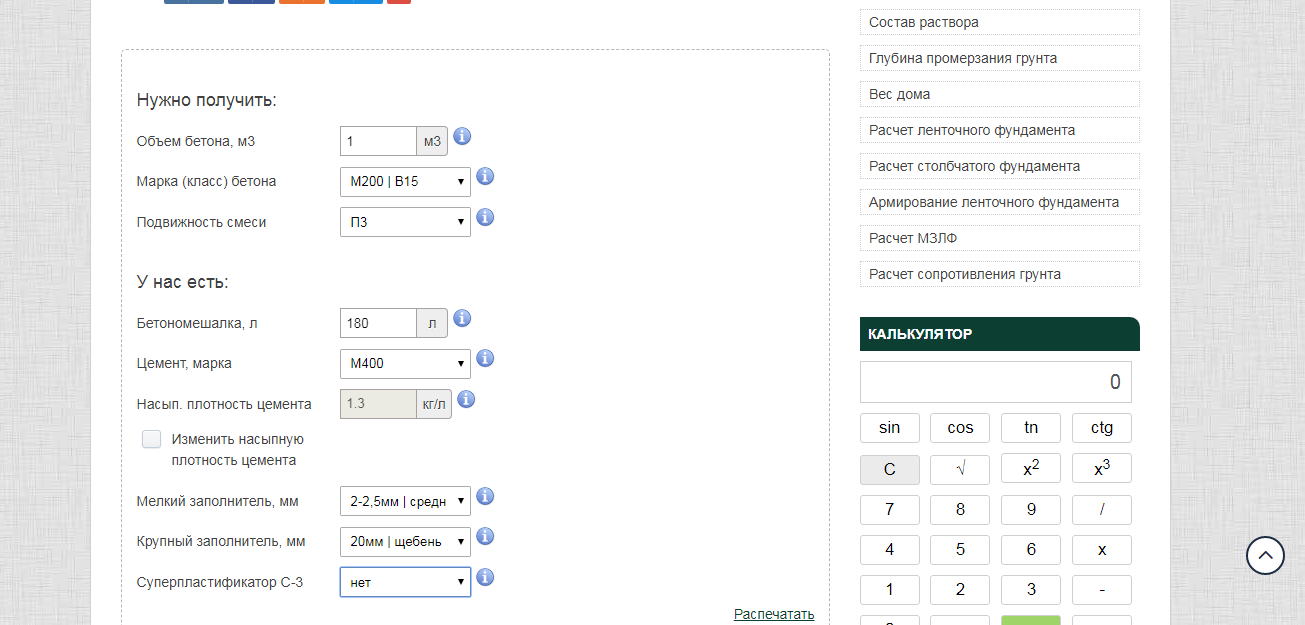
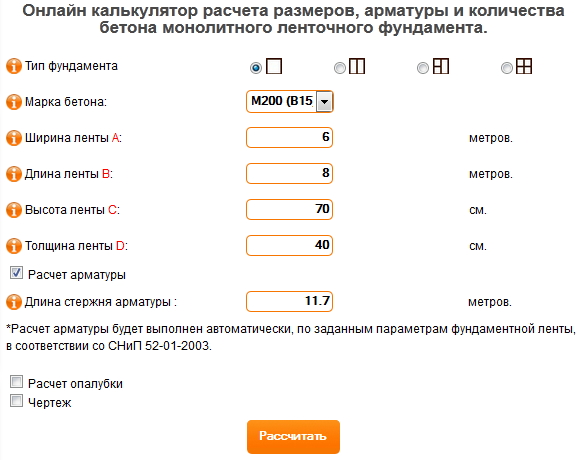
Online calculators: tricky will not go uphill

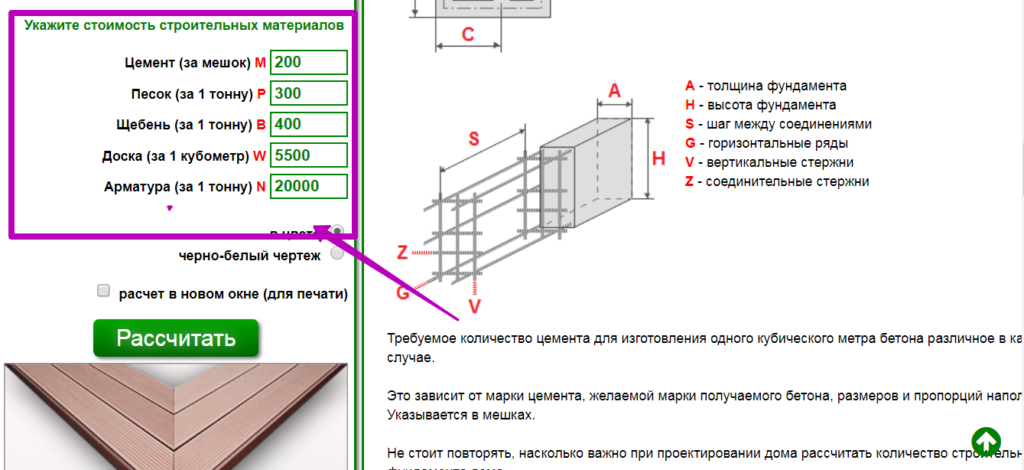
The easiest way to calculate cement is to trust the software. With its help, you can not only draw a project of a future object, but also calculate the required building material. These online calculators are attractive in that the procedure is subject to everyone: in order to determine the desired numbers, you just need to enter some data. In this case, this is the following:
- concrete and cement grades;
- dimensions of the foundation;
- number of belts of reinforcement.
You won't have to wait long for the result, it will be issued almost instantly. But you need to tell about a couple of fly in the ointment that lie in wait for you in this easy task. Problems will arise with accuracy, since the programs determine only the approximate amount of necessary materials, and for private construction, which requires a lot of funds for only one foundation (sometimes up to 30% of all costs), this is an unaffordable luxury.
Features of the guidance of the solution
When building small private houses, the concrete mix is often prepared independently.The procedure involves the gradual introduction of water into the dry composition, followed by thorough and constant stirring of the solution to prevent hardening. For this purpose, it is recommended to use a concrete mixer. Filling work should be carried out in a short time, until the induced solution has lost the required viscosity.
Component quality requirements:
- Cement fractions from 5 to 20 mm are separated by sifting through a sieve. Dry, loose cement is suitable.
- The sand should not contain unnecessary impurities. After sieving, sand is isolated with fractions from 1.5 to 5 mm.
- Gravel or crushed stone is of medium size, in the range of 8-35 mm.
- Water should not contain an increased amount of unnecessary chemical elements, be heavily contaminated.
In a humid environment, cement quickly damp, lumps form. With this in mind, purchase it immediately before use. In the absence of experience, medium or large crushed stone should be selected. Large stones provide a denser concrete structure and prevent air bubbles from forming.

Guiding solution
High-quality pouring of the foundation requires the removal of air bubbles or cavities from the concrete mass, which always appear during the pouring work. For this purpose, the concrete mass is compacted using specialized vibrating machines for construction.
Concrete mix composition
 For the manufacture of high-quality concrete, it is necessary to use only proven materials.
For the manufacture of high-quality concrete, it is necessary to use only proven materials.
No construction is complete without concrete. Today it is one of the main building materials for prefabricated, monolithic concrete and reinforced concrete structures. Large construction sites receive concrete mix centrally from manufacturing plants.
At the same time, in private housing construction, hardly anyone will order a ready-made mixture - this is both expensive and pointless. A small quantity will not be accepted into an order, and a large one has nowhere to use. It is much cheaper and more reliable to purchase the necessary materials and prepare the concrete mixture in batches at the construction site.
The finished product is a hardened concrete mass, for the preparation of which you need: a binder, crushed stone, sand and water. The main characteristic of concrete is compressive strength. Its marking depends on this: M200, M300, M400, M500. For the construction of the foundation, the following types M200, M300 are used. For convenience, the calculation of the consumption of materials is not made for the entire amount, but for 1 cubic meter of concrete.
How much concrete is needed for the foundation
The prepared structure is poured with concrete mixture, and its quantity is determined in cubic meters.
To calculate the volume of concrete for the construction of the foundation, first check for the ability to carry the design load, taking into account the characteristics of the soil at the construction site. To bring the projected base into compliance with the specified parameters and to comply with the standards, its geometric dimensions (depth, width) and the reinforcement scheme are changed. The resulting dimensions are substituted into the calculation formulas and calculate how many cubes of concrete are needed.
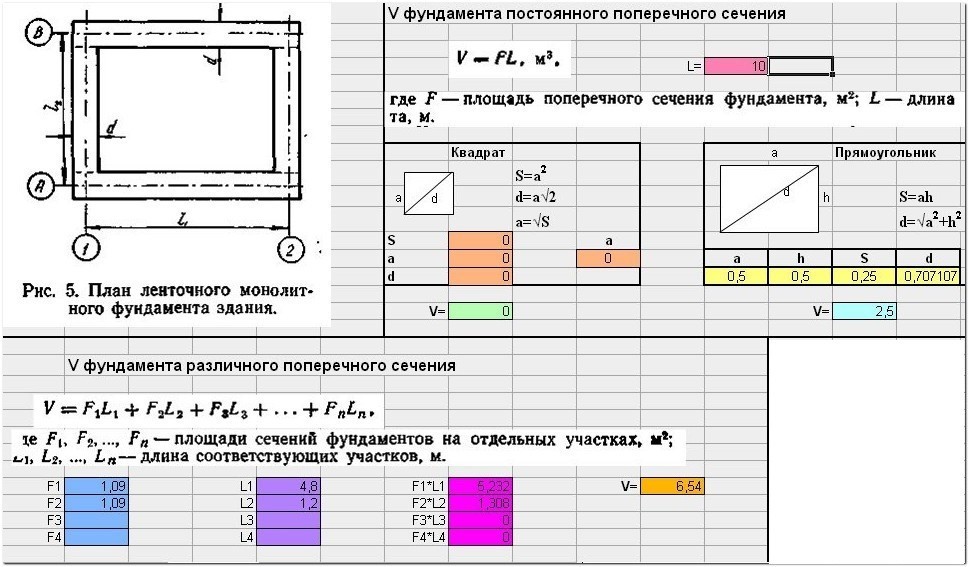
Tape
When calculating concrete for a strip foundation, the following parameters are required: the length of the strip, its width and height. The height is taken as the distance from the sole to the edge. Usually the sawn-off edge is located 50-60 cm above the ground.
With the depth of the sole (the part located underground) of 160 cm and the size of its part above the ground at 60 cm, the total will be 220 cm.The depth of the monolithic strip base is determined depending on the properties of the soil and on the grade of concrete.
The width of the tape depends on the weight of the building, the thickness of the walls and the soil. In accordance with the load, the required number of longitudinal reinforcement rods of the required diameter is installed in the design of the tape, the pitch and diameter of the clamps are determined.
The length of the tape is the sum of the lengths of all external and internal load-bearing walls of the house. For a cottage measuring 8x10 m with an internal load-bearing wall 10 m long, it will be 46 meters:
(10 m + 10 m + 8 m + 8 m = 36 m) + (10 m) = 46 meters.
Concrete consumption for the base of such a house with a tape width of 0.5 m and a height of 2.2 m:
46 (L) x 0.5 (W) x 2.2 (H) = 50.6 cubic meters.
Platen
To calculate the concrete volume for this type of foundation, the total volume of the slab is determined. This will be the desired value and is equal to the product of the area of the slab base by its thickness.
The area of the cottage is 8x10 meters equal to 80 sq.m. For example, the thickness of the slab is 25 cm.Thus, the consumption of the mixture will be:
(80 sqm) x (thickness: 0.25 m) = 20 cubic meters.
When calculating, it is important to take into account the weight of the building. With a heavy load, you need to either increase the thickness of the slab, or add stiffeners
They are made along load-bearing walls (including internal ones), or they are formed into square cells ranging in size from 1.5 m to 2 m - it depends on the operating conditions. In the second case, the plate has increased rigidity and strength.
The filling of the stiffener structure will be an additional value that is added to the total flow rate and is determined as follows:
(cross-sectional area of stiffener) x (total length of ribs).
Columnar
Represents pillars located at a certain pitch below the anchor points. To calculate the concrete for such a foundation, the values for one support are determined and multiplied by their number.
The volume of one column, since it is, in fact, a cylinder, corresponds to the product of the cross-sectional area and length.
Let the diameter of the pillar be taken as 40 cm. S = ¼πd² = ¼ x 3.14 x 0.4² = 0.13 sq. M. At a height of 2.2 m, the required value is 0.29 m³.
For the final determination of the consumption of concrete mixture for a columnar base, the resulting value is multiplied by the number of pillars.
The results obtained, despite the simplicity of the formulas, are quite accurate. This will help avoid unnecessary costs and order or prepare the optimal amount of concrete for pouring the foundation. However, during preparatory earthworks, transportation and unloading, soil shrinkage, etc., an additional increase in the final figure by 3-10% is possible.
Determination of the amount of rubble
There are several ways to determine the volume of rubble and other components in a cube of concrete. Each of them has certain advantages and disadvantages, and is relevant for a specific type of work.
The composition of concrete grades and the ratio of sand, cement and crushed stone
For different types of concrete mortar, different types of crushed stone are used as filler. So, standard large crushed stone is added to the composition of concretes of grades M100-M300. assumes the use of washed gravel or crushed stone of a coarse fraction without additional impurities (of better quality).
For an indicator of strength within M500-M600, granite crushed stone or dense limestone of a fine fraction is taken. All components are thoroughly checked beforehand. Basic concrete mixes require certain proportions of the constituents. For example, consider the brands M400 and M500.
The ratio of fillers for cement grade M400:
- Grade: consumption of crushed stone 6.1 and 4.1 sand
- М150: 5 rubble and 3.2 sand
- М200: 4.2 rubble and 2.5 sand
- М250: 3.4 rubble and 1.9 sand
- М300: 3.2 rubble and 1.7 sand
- М400: 2.4 rubble and 1.1 sand
- М450: 2.2 rubble and 1 sand
The ratio of fillers for the cement grade M500:
- Concrete grade M100: 7.1 crushed stone and 5.3 sand
- М150: 5.8 rubble and 4 sand
- М200: 4.9 rubble and 3.2 sand
- М250: 3.9 rubble and 2.4 sand
- М300: 3.7 rubble and 2.2 sand
- М400: 2.8 rubble and 1.4 sand
- М450: 2.5 rubble and 1.2 sand
Experimental calculation
You can determine how much rubble goes to a cube of concrete using a special formula:
Crushed stone = 1000 / (α * V void.sh / y embankment.u + 1 y uh), here:
- α - denotes the sliding factor
- V void.sh - void weight, measured in kg / l
- y embankment. u - bulk weight, measured in kg / l
- y u - material density, measured in kg / l
So, if you need to prepare a solution of M 200 and calculate the volume of the filler for one cube, take the cement M400 and the filler in a volume that is calculated in accordance with its technical characteristics.In the example, the parameters of crushed stone are as follows: density 2.5 kg / l, fraction 20 millimeters, bulk density equal to 1.3 kg / l, void weight equal to 0.49 kg / l.
It should be taken into account that the coefficient α for all brands above M400 is approximately 1.05-1.15, usually 1.1 is taken. For other grades of concrete, the coefficient is found in special tables .. Calculation of the volume: U = 1000 / (1.1 * 0.49 / 1.3 + ½.5) = 1227 kg / m³
Thus, to obtain a cube of solution, you need to take 1227 kilograms of crushed stone with the specified characteristics. This method is effective, but in everyday life, simpler methods of calculations are usually used.
Volume calculation: W = 1000 / (1.1 * 0.49 / 1.3 + ½.5) = 1227 kg / m³. Thus, to obtain a cube of solution, you need to take 1227 kilograms of crushed stone with the specified characteristics. This method is effective, but in everyday life, simpler methods of calculations are usually used.
Practical calculation
equal to approximately 1700-2500 kilograms. The final figure is influenced by the characteristics of the components. Usually the recipe for preparing the mixture is as follows: 200-400 kilograms of cement, 500-700 kilograms of sand, 1100-1300 kilograms of crushed stone, 100-200 liters of water.
In practice, the calculations are performed as follows: the amount of gravel should be equal to the volume of the solution. So, to obtain a cubic meter of concrete, the same amount of filler is taken.
Proportions for home kneading:
- Cement - 0.3 cubic meters
- Crushed stone - cubic meter (1300 kilograms)
- Water - 180 liters
- Sand - 650 kilograms
This recipe allows you to get a high-quality concrete solution. If you increase the volume of sand and crushed stone, you can noticeably deteriorate the properties of the material and significantly reduce the strength indicator.
Determining how much crushed stone is needed for one cube of concrete, you can use several different methods. It is best to entrust the execution of the calculations to the master, which will guarantee the correctness of the calculations and the quality of the resulting mixture.
The need for materials for the solution
The foundation can be not only concrete or reinforced concrete, there is also a version of the rubble concrete base. In this case, rubble stone is poured into the prepared trench and filled with cement-sand mortar.
It is undesirable to use concrete, since, due to the crushed stone-gravel component, it may not envelop stones tightly enough, leave voids. This will certainly negatively affect the strength of the entire structure. Over time, it can collapse.
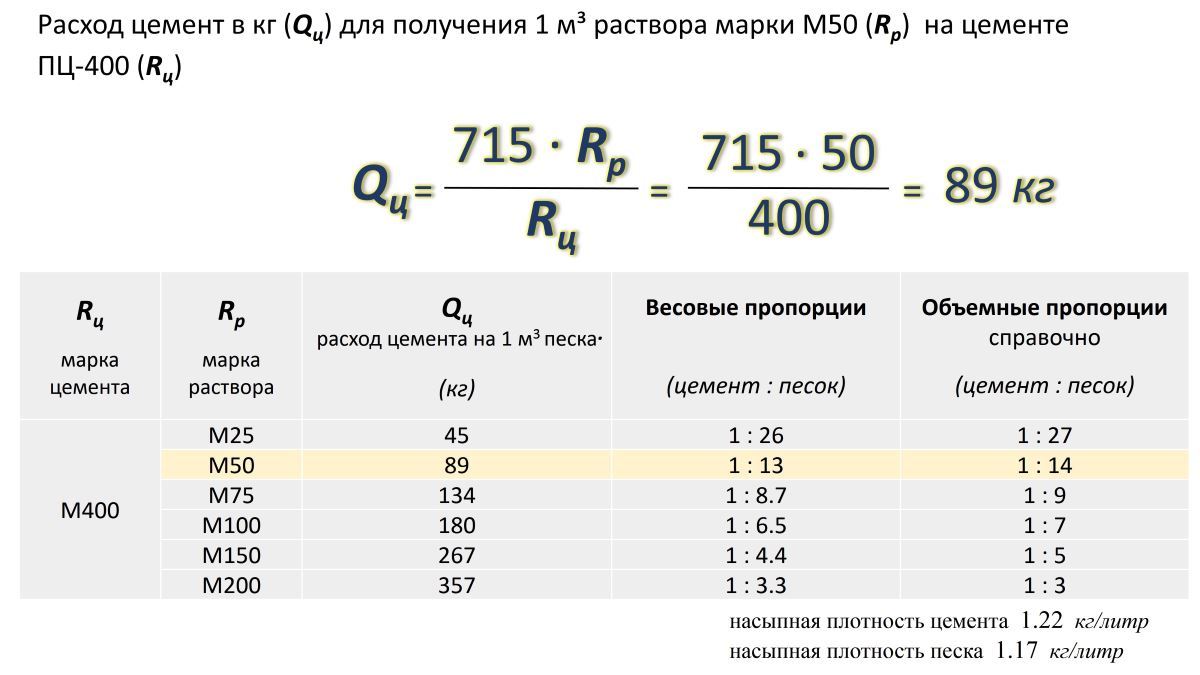
The consumption of sand and binder for the preparation of a solution of a certain brand is usually performed in relation to one component to another in parts. You can calculate the amount using the ratios from the table:
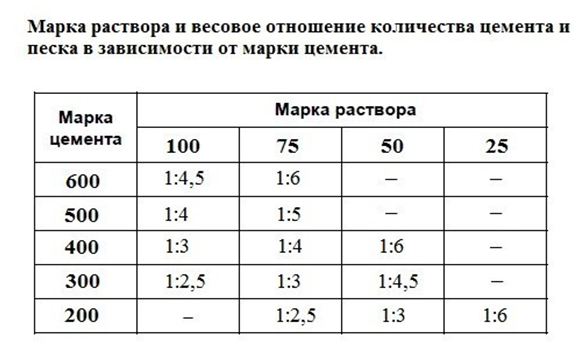
This is not difficult. Suppose that for pouring a rubble foundation you need two cubes of grade 100 mortar. It was decided to buy cement grade 400. To prepare a heavy M100 solution, you need 300 kg of M400 binder per one cube of the mixture (reference data). How much sand is required?
According to the table, the ratio is 1: 3, which means 900 kg of sand is needed. Two cubes - twice as much. The sand is thoroughly mixed with cement and only then is it poured with water. Water must be added until then, constantly stirring the solution so that it turns out to be plastic and freely pours into the foundation, enveloping rubble stones. If the use of any additives is provided, then they are first dissolved in water, and only then added to the dry composition.
We recommend watching a video on how to properly mix the solution at home.
Conclusion
At first glance, it is not difficult to prepare concrete for the foundation. However, this is the most important part of the work in the construction of a residential building, mistakes in pouring the foundation will affect further work and during operation. The cement calculator for the foundation, although it will help to calculate the amount of concrete, will be inaccurate figures, and you can not guess much with the proportions, especially if you have not seen building materials before. In many cases, it is advisable to contact professional craftsmen.
Number of blocks: 18 | Total number of characters: 22789
Number of donors used: 5
Information for each donor: