Strip base or slab?
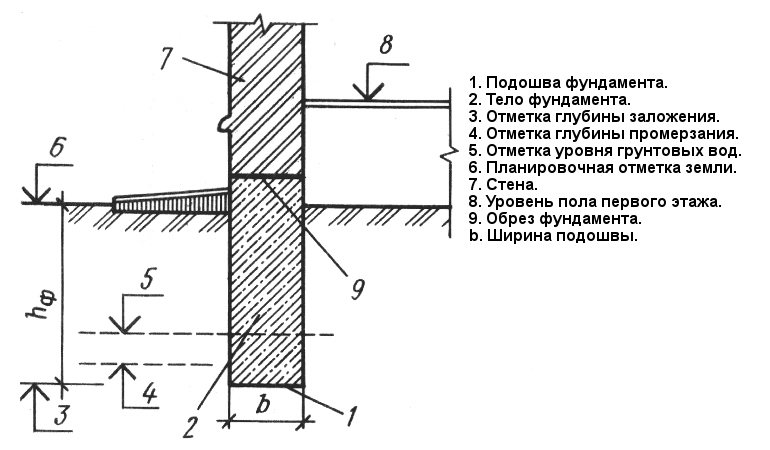
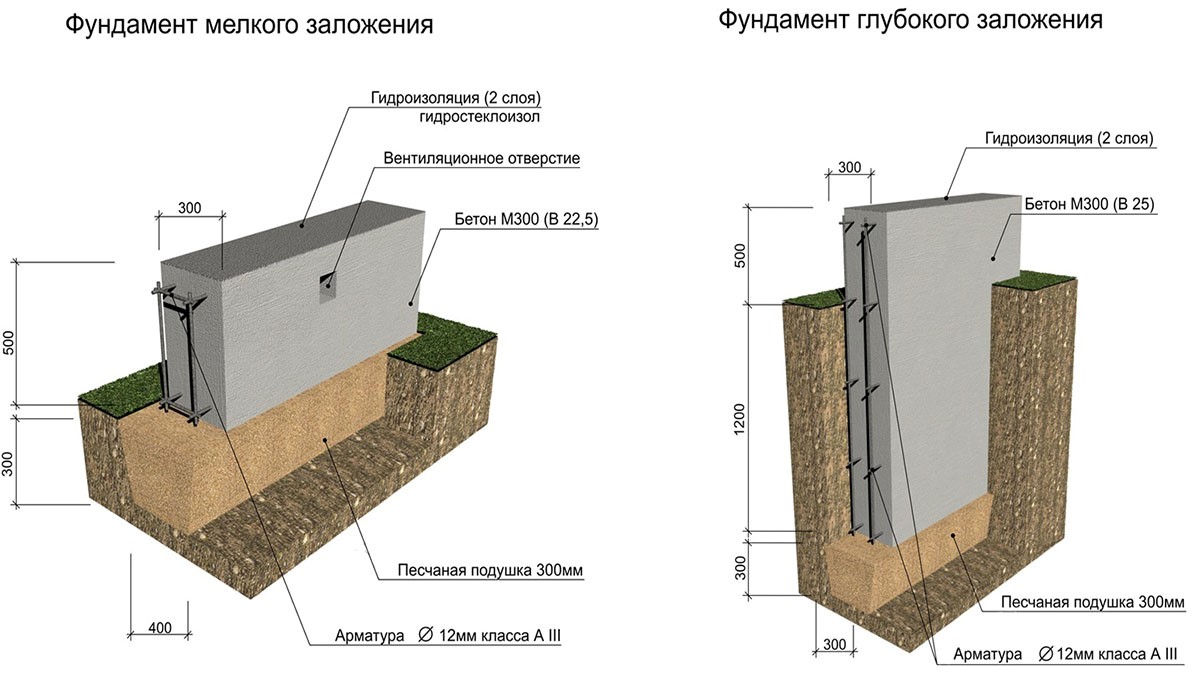
A building with a basement or cellar needs a recessed base
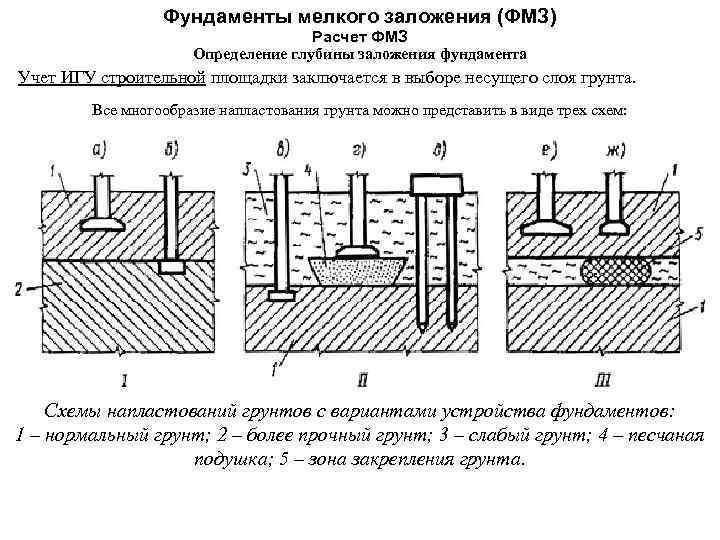
When determining the required depth, it is important to take into account not only the characteristics of the house, but also factors such as the level of groundwater and the characteristics of the soil. Such calculations are usually carried out by professional builders.
When all the calculations have been made, a choice is made in favor of one or another version of the foundation.
The most popular options for houses with a basement are:
- Strip foundation. It is convenient in that it can be erected from various building materials, prefabricated structures or a monolith. To select certain materials, an accurate calculation of the foundation is carried out, taking into account such a parameter as the load from the house.
- Reinforced slab base. The strip foundation has a serious disadvantage - it is unable to correctly distribute the load coming from the bearing walls on some types of soil. If you are building a house on problem ground, you should give preference to a slab base. It can be poured entirely on a selected area or equipped with individual slabs.
The strip and slab foundations differ not only in the materials used, but also in the price. The latter has a higher cost, which is fully justified when building a house with a basement on difficult ground. Peat bogs, clay and heaving soils are considered problematic. They are characterized by instability and high groundwater content. Because of this, they are subject to natural shrinkage and periodic movement. A regular foundation will not be able to provide the necessary protection to the house, while a slab foundation has a large area for load distribution and guarantees the stability of the building.
This is especially important for a home with a basement.
Future basement.
How to build a foundation with a basement with your own hands?
A phased plan for the construction of a base with a residential basement consists of the following points:
- Cleaning and marking the construction site.
- Arrangement of a pit and trenches for engineering communications.
- Arrangement of drainage bedding under the sole of the future foundation.
- Arrangements for waterproofing the foundation soles.
- Construction of the sole of the base.
- Base wall construction.
- Waterproofing and thermal insulation of base walls.
- Backfilling of soil with the obligatory arrangement of a drainage layer under the base wall.
- Arrangement of the blind area and front finishing of the basement of the building.
The first four stages are carried out according to generally accepted technologies used in the construction of a conventional strip or slab foundation. That is, before making the foundation for a house with a basement, the site is cleared of fertile soil (it will come in handy in flower beds), mark the upper border of the pit and start earthworks.
Digging of the pit is carried out in stages, by selecting 50-centimeter layers of soil. As a result, the walls of the pit have a stepped structure, and only the bottom of the excavation coincides with the dimensions of the future foundation.
The filling of the drainage layer is arranged by placing a 15 or 20 cm layer of sand and fine gravel at the bottom of the pit. On top of this sandwich, roll waterproofing (membrane film or roofing material) is laid.
But work on the construction of the sole and walls of the base is carried out according to an individual technology, which is characteristic only for the construction of monolithic foundations with a basement. Therefore, we will consider the construction of the sole and walls separately.
Fill the sole of the base
The construction of the basement base involves the pouring of a classic foundation slab, along the perimeter of which reinforcing outlets are left. That is, a removable formwork is laid along the perimeter of the last step of the pit, inside which a reinforcing cage is equipped with vertical posts towering above the edge of the deck.
However, when independently arranging a deep basement, a labor-intensive solid foundation sole is not built.Instead of a monolithic slab, you can get by with a wide tape, the dimensions of which exceed the thickness of the foundation walls by 40-50 centimeters (20-25 centimeters from each edge). Such a sole will work no worse than a monolith, increasing the bearing capacity of the soil.
Well, the floor of the future basement can be poured over the crushed stone bedding, laid directly on the waterproofing layer.
As a result, the least time-consuming process of filling the sole is as follows:
- A classic, double-walled formwork is built along the contour of the walls, equipped with an overlap of 20-25 centimeters on each side of the wall.
- Decks are reinforced with cross braces and side scaffolding.
- In the inner part of the formwork, grids of 12-mm reinforcement are laid, which are connected to vertical, outrigger pins.
- The formwork body is filled with M300 or M400 concrete.
After the concrete hardens, the formwork is dismantled, and the side edges of the sole are coated with moisture-repellent mastic.
How to fill a foundation with a basement - stages of work
Having completed the construction of the base of the base, you can proceed to the construction of the foundation walls. Moreover, the fastest and most reliable way to build such walls is to pour it into a fixed formwork made of foam or hollow formwork blocks.
By using formwork blocks, you can save time on the construction of labor-intensive panel formwork, the deck height of which will be 2-2.5 meters. However, panel formwork is cheaper than the block version.
The construction of block formwork resembles the assembly of a wall from blocks of a child's construction set.
In practice, this process looks like this:
- Blocks fit into special grooves, which eliminates the possibility of distortion of the wall of the future foundation. In addition, block formwork does not need support scaffolding.
- The reinforcing frame is laid between the blocks, on transverse screeds laid inside the formwork.
- The vertical pins of the reinforcement are joined to the outsole outlets and are located in the inner cavities of the blocks.
The concrete is poured in layers, the depth of which should not exceed 30 centimeters. The foundation grillage is the upper edge of the monolithic fill.
The construction of panel formwork involves the assembly of a double-walled structure from metal or wooden decks, the height of which is equal to the height of the foundation wall. Such a structure requires sophisticated support scaffolding to anchor the decks while the foundation wall is being poured. Filling is carried out according to the same layer-by-layer principle.
Approximate calculation of the depth of the strip foundation
Craftsmen who are engaged in the construction of houses use different methods for calculating the depth of the strip base. Very often, a simple formula is used to determine the depth of the strip base for a one-story house:
Hp = m * tm * Hh,
where m - denotes the coefficient of working conditions, it is in most cases equal to 1.1; tm is the coefficient of thermal impact on the soil, the value of which ranges from 0.7 to 1;
Hh - depth of soil freezing.
For example, we can consider the option in which the level of soil freezing is 1.6 meters, and the thermal effect is determined by the value 0.6: 1.1 * 0.6 * 1.8 = 1.188.
Therefore, taking into account such parameters, the foundation strip can be buried 1.2 meters. But such a formula is used only in cases where the soil on the site has a good density.
To calculate the depth of laying under buildings of several floors, they use another method: the number of floors is multiplied by 0.8. This means that a house with two floors requires laying a base tape to a depth of 1.6 meters. This definition also only works on solid ground.
To determine the most accurate result, professional calculation formulas are used, which have their own calculation feature.They can be found in the relevant regulatory document, namely SNiP No. 2.02.01-83 "Foundations of houses and structures" dated 09.11.1985.
Calculation of belt depth
The next step is to figure out how all of the above factors affect the choice of the type of foundation. As you remember, there are only three of them.
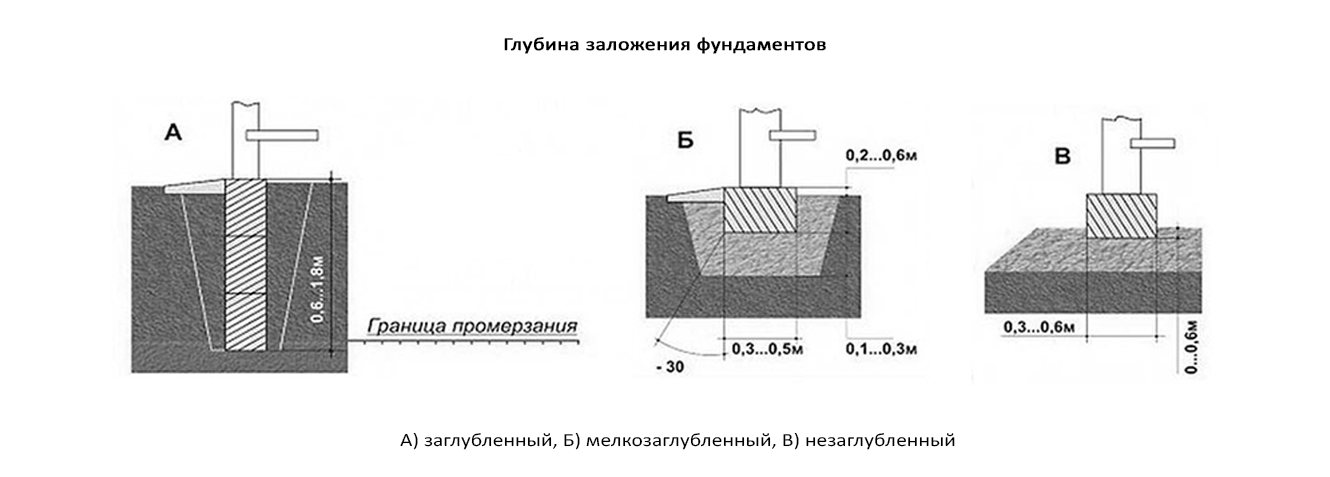
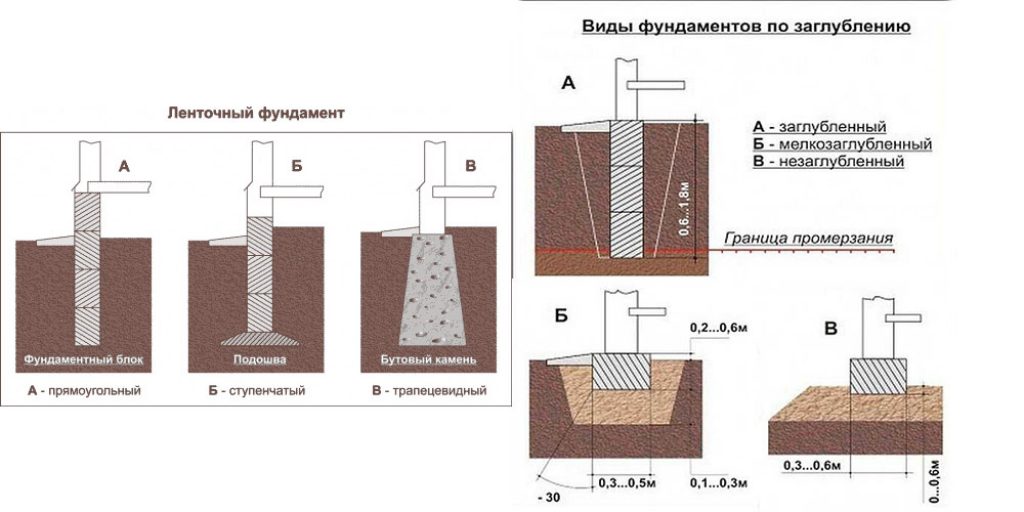
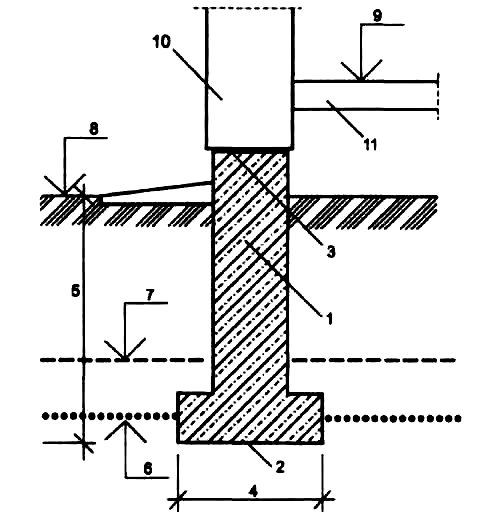
 Strip foundation. Depth views.
Strip foundation. Depth views.
This type of foundation tape is not able to withstand heavy weight loads and therefore is used very rarely. It is completely located on the surface of the ground, and only the sand and gravel cushion is buried. Therefore, the concept of laying depth for this type of foundations can only be applied conditionally. The main advantage of this design is that the heaving force does not act on the side concrete walls.
The shallow foundation base can only be mounted on dense, stable soils. For its device, the top layer of soil is removed to a depth of 30-40 cm. After that, a mixture of sand and gravel is poured into the trench and compacted well with spilling water. The formwork is installed, the reinforcing cage is assembled and the concrete mixture is poured. The height of the foundation, or rather the basement, is 50-60 cm, width 30-40 cm. Therefore, the width of the pillow should be 40-50 cm.
A shallow foundation perceives heaving loads and, at the same time, is not as reliable as a buried foundation. It is done above the freezing point of the soil. Therefore, the extent of its deepening depends on such factors as the type of soil, the depth of freezing and the level of groundwater. Where to get this data, it was indicated above. Tables of dependences of the depth of the shallow-buried strip foundation are given in SNIP 2.02.01-83 and above in the text of the article.
If the groundwater level is below the GP, usually there is no heaving from the process. An exception is the presence of a layer of clay, which can trap and accumulate rain and melt water. In any case, even for a one-story house, the rule applies here - the depth of the tape should be at least half the position of the freezing point. And if in your settlement the GP is at around 1.8 m, then the foundation should be deepened by 0.9 m.
Is it possible to reduce the depth of the laying
It often happens that the calculations performed show the need for large dimensions and the cost of erecting the tape becomes too significant. Especially if the depth of the strip foundation is calculated for a two-story house. Then the question immediately arises of how to reduce the overall dimensions of the foundation structure.
There are three options:
- reduce GP;
- lowering the groundwater level;
- buffer cushion device.
It is impossible to change the climate, but using insulation, it is possible to reduce the depth of soil freezing. For this, the outer wall of the tape is covered with expanded polystyrene plates. Also, the insulation must be laid under the blind area for its entire width. As a result, the GPU will decrease and the foundation can be made smaller.
The drainage of groundwater below the GP is carried out by laying an effective drainage system. It must be mounted below the freezing depth of the soil. This is a large amount of earthworks, a lot of materials and wells, but the effect will be excellent.
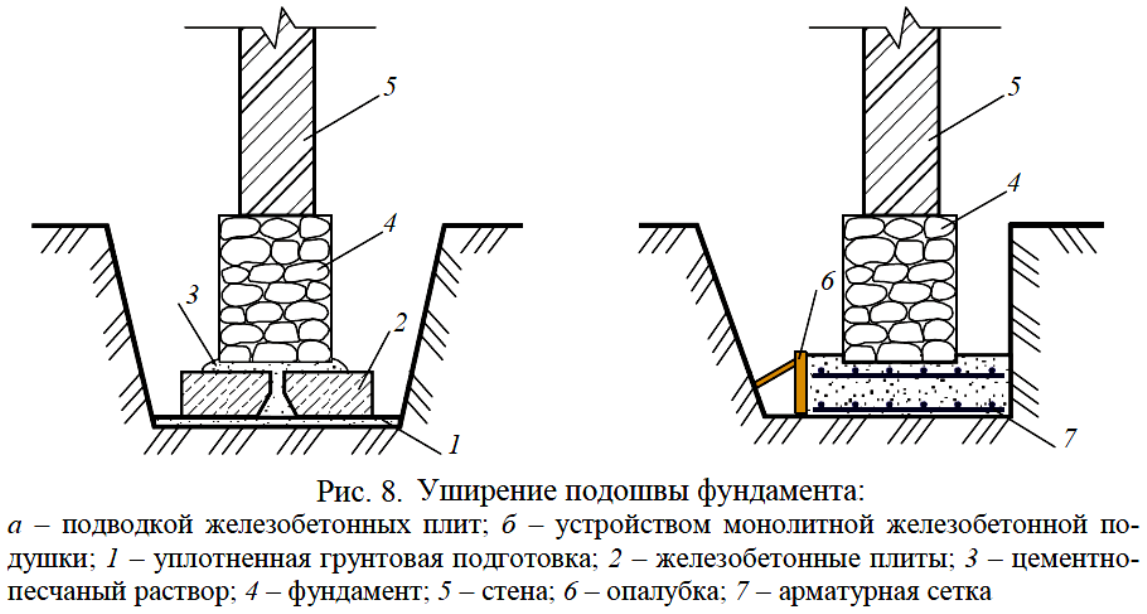
With a large layer of heaving or swampy soils, the foundation will have to be laid deep. To avoid this, unstable soil simply needs to be replaced with bulk materials. To do this, a trench about a meter wide is dug from the outside of the tape and covered with sand and gravel. A pillow under the foundation is also required.
 Pillow under the strip foundation.
Pillow under the strip foundation.
Calculation and design of foundations
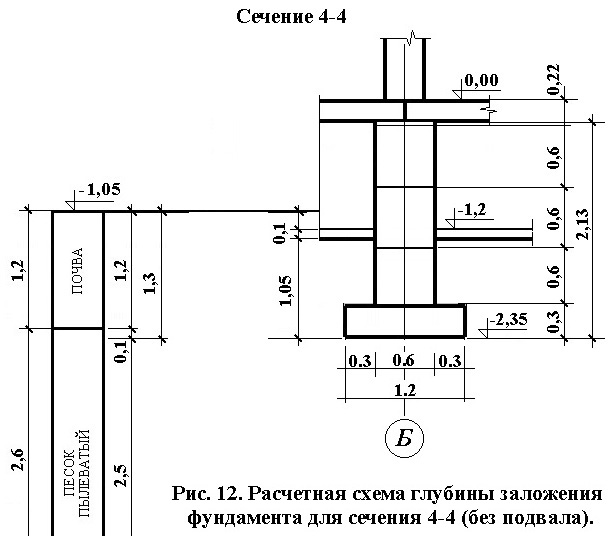
Calculation of the foundation for the outer wall along the axes 1, 10 with a basement
Load per 1 m of foundation length Fv - 6.625 kN. The level of the layout is 1.05 m. The depth of the foundation d is 2.22 m.The floor in the basement is concrete on the ground with a thickness of 0.1 m. The specific gravity of the floor material = 18kN / m3. According to Table 1 of Appendix 1 [] - the design soil resistance of the base Ro = 200kPa. The foot area of an eccentrically loaded foundation.
A = Fv x 1.1 / (Ro - Vav x d) = 6.625 x 1.1 / (200 - 22.5 x 2.22) = 0.05 m.
Required foundation width b = A / 1 = 0.05 m.
Since the foundation is designed for the outer wall of a building with a basement
d1 = 0.17 + 0.1 x 18 / 18.2 = 0.87 m.
dv = 2.5 - 1.05 = 1.45 m.
The values are calculated:
V2 = (18.2 x (11.7 - 2.25) + 3.5 X 20.5 + 4 x 20.7) / (11.7 - 2.25 + 3.5 + 4.0) = 19 , 26 kN / m3;
V2? = 18.2 kN / m3.
According to tables 4 and 5 of Appendix 1, the values of the coefficients are determined:
Vc1 = 1.3; Vc2 = 1; MO = 1.55; Mq = 7.71; Mwith = 9.58; R = 1; R2 = 0,7.
the calculated soil resistance at the base of the foundation with a width of - 0.05 m is determined;
R = 1.3 x 1 (1.55 x 0.7 x 0.05 x 19.29 + 7.71 x 0.87 x 18.2 + 6.71 x 1.45 x 18.2 + 9, 58 x 2) / 1 = 319.4 kPa.
Since the discrepancy between the values of R and Rо:
100 (319.4 - 200) / 319.4 = 37% exceeds 10%, the width of the foundation is recalculated.
A = 6.625 x 1.1 / (319.4 - 22.5 x 2.22) = 0.03 m2, b = 0.03 m.
Design support of the soil at the base of the foundation with a width of h = 0.03 m.
R? = 1.3 (1.55 x 0.7 x 0.03 x 19.26 + 7.71 x 0.87 x 18.2 + 6.71 x 1.45 x 18.2 + 9.58 x 2 ) = 414.5 kPa.
Discrepancy between R and R ?:
100 (414.5 - 319.4) / 414.5 = 23%> 10% - the calculation is repeated.
A = 6.625 x 1.1 / (414.5 - 22.5 x 2.22) = 0.02 m2, b = 0.02 m.
Design soil resistance at the base of the foundation with a width of = 0.02 m.
R? = 1.3 (1.55 x 0.7 x 0.02 x 19.26 + 7.71 x 0.87 x 18.2 + 6.71 x 1.45 x 18.2 + 9.58 x 2 ) = 414.3 kPa.
The discrepancy between R? R ?:
100 (414.5 - 414.3) / 414.5 = 3% does not exceed 10%, the calculation by the method of successive approximation ends.
According to the tables in Appendix 3 [], standard foundation structures are accepted: plate of the FL brand - 6.24 (L = 2.38 m, h = 0.6 m, K - 0.3 m, weight - 10.4 kN); foundation blocks of the FBS 24.6.6 brand (L - 2.38 m, h = 0.6 m, K = 0.6 m, weight = 19.6 kN).
The foundation is being constructed. Foundation weight 1 m long:
Gf = 10.4 / 2.38 + 2x 19.6 / 2.38 = 20.84 kN.
The weight of the soil on the edges of the foundation is Ggr = 0.
Load at the level of the foot of the foundation
N = Fq + Gf + Ggr = 20.84 + 6.625 = 27.47 kN.
Gа1 = q + tq2 (45 - 2 / 2) = 10 x tq2 (45o - 35o / 2) = 2.7kPa
where q is the load from the blind area, taken by q - 10 kPa.
The magnitude of the active soil pressure at the level of the base of the foundation
Ga2 = V2? x H x tq2 (45o - 2 / 2) = 18.2 x 2.77 x tq2 (45o - 35o / 2) = 13.66 kPa,
where Н = d + q (2? = 2.22 + 10 / 18.2 = 2.77 m.
Active lateral pressure force per 1 m of foundation.
Ea = (Ga1 + Ga2) / 3 (Ga1 + Ga2) = 2.22 (13.66 + 2 x 2.7) / 3 (2.7 + 13.66) = 0.74 m
The shoulder of the force Ea relative to the center of the sole of the foundation:
Lа = d (Ga2 + 2Ga1) / 3 (Ga1 + Ga2) = 2.22 (13.06 + 2 x 2.7) / 3 (2.7 + 13.66) = 0.74 m.
Moment of active force of lateral pressure
Me = Ea x La = 18.16 x 0.74 = 13.44 kN m.
The total moment is M = Me = 13.44 kN m.
Edge pressures under the foot of the foundation
where W = Lw2 / 6 = 1 x 0.62 / 6 = 0.06 m3
Pmax = 27.47 / 0.6 x 1 + 13.44 / 0.06 = 269.78 kPa
Pmin = 27.47 / 0.6 x 1 - 13.44 / 0.06 = 178.22 kPa.
Average pressure under the foot of the foundation
P = (Pmax + Pmin) / 2 = (269.78 + 178.22) / 2 = 224 kPa.
The condition is checked
Pmax ? 1.2 R 269.78
Pmin ? 0 178.22 kPa> 0;
P? R 224
The conditions are met. Section designed with load
100 (414.3 - 224) / 414.3 = 46% - uneconomical, a reasonable solution is to use intermittent foundations.
Spacing between slabs
WITHmax = (W / in - 1) Lt
where Lt is the length of the foundation slab, Lt = 2.38 m;
W - accepted standard pillow width W = 0.6 m;
c - the required width of the pillow, c = 0.02 m.
Cmax = (0.6 / 0.02 - 1) x 2.38 = 69.02 m, but
WITH
Determines the number of slabs in a discontinuous foundation
n = (L + C) / (L + C) = (30.62 + 1.15) / (2.38 + 1.15) = 8.98.
Accepted n = 9 pieces
The value of C is specified.
С = (L - n x L) / (n - 1) = (30.62 - 9 x 2.38) / (9 - 1) = 1.15 m.
Average pressure under the bottom of the slabs
P = N x L / L x n = 27.47 x 30.62 / 2.38 x 9 = 263.27 kPa.
Condition P? R:
257,1
The section underload when using an intermittent foundation is reduced to
100 (414,3 — 257,1) / 414,3 = 36%
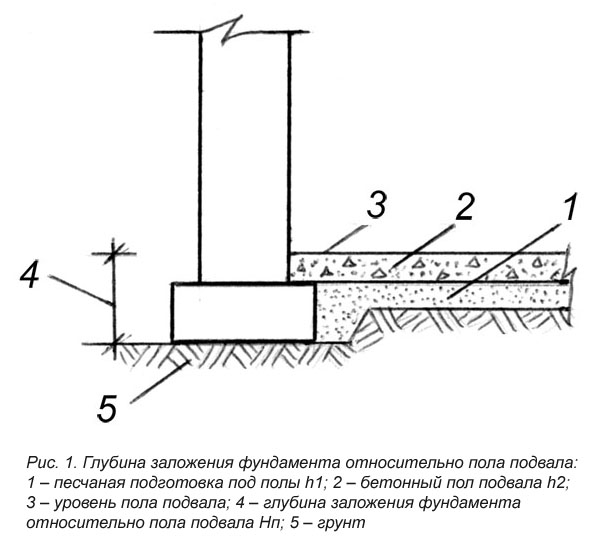
Basement with basement
Now you need to understand the issue of determining the depth of the foundation with a basement.

Basement with basement
The soil is considered the basis for the equipment of any foundation and must have a sufficient strength indicator. Be that as it may, not all types of soil have the necessary quality characteristics.
In winter, climatic conditions determine the depth of rock freezing. After freezing, heaving soils can settle unevenly, often this process becomes the cause of the formation of cracks on the foundation. To prevent anything like this from happening, the foundation must be deepened to such an extent that the soil froze above the concrete structure.
In most of the regions of our country, the soil freezing depth is at the level of 1.2 m, so a 1.5 m foundation can be equipped without any particular fears. The basis for the foundation should always be only the continental soil, which has managed to be compacted over the years.
Determination of the depth of the foundation
The choice of depth for laying the foundation begins with calculating the depth of freezing of the ground on the site, taking into account the heating mode.Calculations are carried out using the formula:
Df = k × Dfn, here:
- Dfn - standard indicator of freezing depth
- Df - calculated index of freezing depth
- Kn - coefficient related to the heating mode of the building (according to SNiP 2.02.01-83)
Then determine the properties of the soil directly at the site of the foundation. It is enough to dig a hole and take soil samples.

The soil can be selected even after independent (but thorough) study in the field. It is enough to take the earth in the palm of your hand, knead it, roll it up with a cord, try to make a ring out of it and look at the result: a whole ring speaks of clay soil, disintegrating - about loam, crumbling during the rolling process - the soil is most likely from sandy loam. But the most optimal method is to consult a specialist.
Then they determine at what depth the groundwater passes - for this they drill a hole up to 3 meters deep, lower a pipe made of metal or plastic into it, measure the water level at different times of the year - it is important to understand whether the water is capable of rising above 2 meters to the freezing level land.
The data obtained allows you to determine what depth to make the strip foundation. Usually, table 2 SNiP 2.02.01-83 is used for calculations. Provided that the groundwater level is 2 (or more) meters below the freezing point of the earth, the foundation is laid at a certain depth in accordance with the type of soil.
Optimum foundation depth:
- Gravel, medium / coarse sands - 50 centimeters
- Fine sands, sandy loam - at least 50 centimeters
- Loams, clays, coarse-grained soils - minimum 0.5 Df
In the case when the groundwater is located closer than 2 meters to the freezing boundary Df, the base is designed at a depth of the minimum value of Df.
Basement walls made of blocks
Regardless of the fact that the basement under the house can be built from monolithic concrete or brick, the most common is the use of basement concrete blocks - GOST.
Walls basement from blocks
The installation of a basement from blocks is distinguished by its speed. The main document that determines the construction of basements is GOST 13579 - 78. Number 78 indicates the year that GOST was put into effect.
Foundation blocks
For the installation of basements, solid blocks of GOST are used:
- solid foundation block (FBS);
- foundation block with a cutout (FBV);
- hollow foundation block (FBP).
FBS is the most common and is used in all types of construction. These blocks can be of several sizes. The most used one has dimensions of length, width and height 2380x300x580 mm, respectively. It can be 400, 500 or 600 mm wide at the specified length and height. GOST FBS has an additional block of the same dimensions, but with a height of 280 mm. It can be 1180 or 880 mm long.
Stacking FBS blocks
FBV differs from FBS with a cut that runs along its entire length. This allows you to lay door ceilings and communication lines on the walls during installation. FBV has a length of 880 mm and the same width and height dimensions as FBS.
Installation of blocks
FBP has voids open at the top and bottom. Thanks to such voids, the amount of concrete for their production is reduced and the weight of the blocks is much lower. This type of block has a length and height of 2380 and 580 mm, respectively, and can be 400, 500 or 600 mm wide. Additional FBP blocks are not produced.
Strip foundation from blocks
GOST 13579 - 78 defines the alphanumeric designation of foundation blocks, which indicates the brand of the block, its rounded dimensions in decimeters, the type of concrete. For example, GOST 13579 - 78 defines the brand of the block "ФБП 24.4.6 - С". This means that we have a hollow foundation block with dimensions of 2380x400x580 mm, made of silicate concrete. The marking T or L can be used, which means heavy or light concrete. GOST 78 defines the strength class of concrete for foundation blocks.Blocks made of light or heavy concrete have a strength class of B 3.5, and their silicate concrete is B 12.5.
FBS type blocks
FBS are manufactured without internal filling with reinforcement. GOST defines in such blocks the presence of a mounting loop of a special shape made of metal of class 8AI and higher. The hinges can be installed on the surface of the block or located in a technological recess at a distance of 25-30 cm from the edges of the block. If the block has a minimum length of 880 mm, then GOST allows the manufacture of such products without loops.
Foundation blocks FBS
Installation of a basement wall from blocks
FBS is used in the construction of houses with strip foundations. They are installed after laying the foundation cushion and horizontal waterproofing.
Installation of basement walls from blocks
The process of installing a foundation wall under the house has its own technology:
- Roofing material is laid between the bottom row of blocks and the concrete surface using bitumen-polymer mastic. Depending on the density of the soil, a cement solution is laid, 25-30 cm thick, which will be a leveling base for the blocks.
- To connect blocks and joints between them, a cement mortar with waterproof and frost-resistant additives is used.
- Installation of blocks must be carried out using special geodetic equipment for the axial breakdown of the building.
- First of all, beacon blocks are installed. They are mounted at the corners and at the junction of the outer walls with the inner ones. If the house is long, then the installation of beacon blocks is carried out every 20-25 meters. When the beacon blocks are installed, a mounting thread is pulled between them to install other blocks.
- For the installation of the blocks, special equipment is required, since one FBS 2380x300x580 block weighs 980 kg.
- 6. Before assembling the next row, the upper part of the previous row of blocks is treated with water, after which the cement mixture is laid and leveled on it.
- The next row of blocks is mounted with the movement of the vertical seam within 30 cm. For this, marking is carried out on the lower row of blocks.
- The correctness of the installation is checked by the beacon blocks and the assembly thread.
- Minor displacements are eliminated on site. Raise the slab, remove excess cement mixture or add the required amount.
- When the plate has taken the required position, it is freed from the assembly slings. The excess solution, which has come out, is removed and placed in a vertical seam. The same seam is then completely filled with mortar to avoid voids and prevent water from penetrating into the basement.
How to build a foundation from FBS blocks
Truth and myths about the depth of the foundation
 If the house is being built with your own hands, then the correct calculation of the depth of the foundation is one of the most difficult moments.
If the house is being built with your own hands, then the correct calculation of the depth of the foundation is one of the most difficult moments.
If the house is being built with your own hands, then the correct calculation of the depth of the foundation is one of the most difficult moments. But first of all, it is necessary to decide on the material and design of the base, since the depth of the foundation also depends on this.
Most often, they build a one-story house with their own hands, so we will consider the types of bases suitable for this building:
- If the wall structures of the future house are planned to be made of brick, natural stone or reinforced concrete, then the only option for a suitable base is a buried monolithic strip foundation or a foundation made of foundation blocks (FBS). Sometimes combined structures are used, when a monolithic tape belt is made as a sole, and the rest of the foundation is made of FBS.
- For houses, from light wall blocks, for example, aerated concrete, logs, timber and other light materials, you can make shallow foundations. Also, such bases can be made for frame and frame-panel houses. In this case, you can use the following types of shallow foundations:
- shallow columnar foundation made of pipes, concrete blocks, logs, bricks or concrete with a depth of 0.7-0.8 m;
- shallow belt structures made of FBS and reinforced concrete with a depth of 0.6-0.7 m;
- slab foundation with a depth of 0.5-0.6 m.
Shallow foundations can be used for houses made of aerated concrete, logs, beams, light wall blocks made of other materials, as well as for frame structures erected on solid rocky ground. Shallow foundation can also be strip, slab and columnar
When calculating such bases, it is very important to provide for additional fixation of the structure.
According to the joint venture, most often a deep foundation is made for a capital structure (at least 1.2 m), since several forces act on underground structures:
- the severity of the building (it will not be so large for buildings made of aerated concrete, timber, logs and other light wall blocks);
- horizontal ground movements;
- heaving forces arising in winter in clay and loamy soils saturated with moisture;
- underground and surface waters.
Some builders and designers believe that the deeper the foundation, the better. In fact, this is not the case, because too deep foundation depth can lead to unreasonably high costs for the construction of this part of the structure:
- the volume of earthworks is increasing;
- material consumption increases;
- labor costs become more;
- the construction time of the base increases.