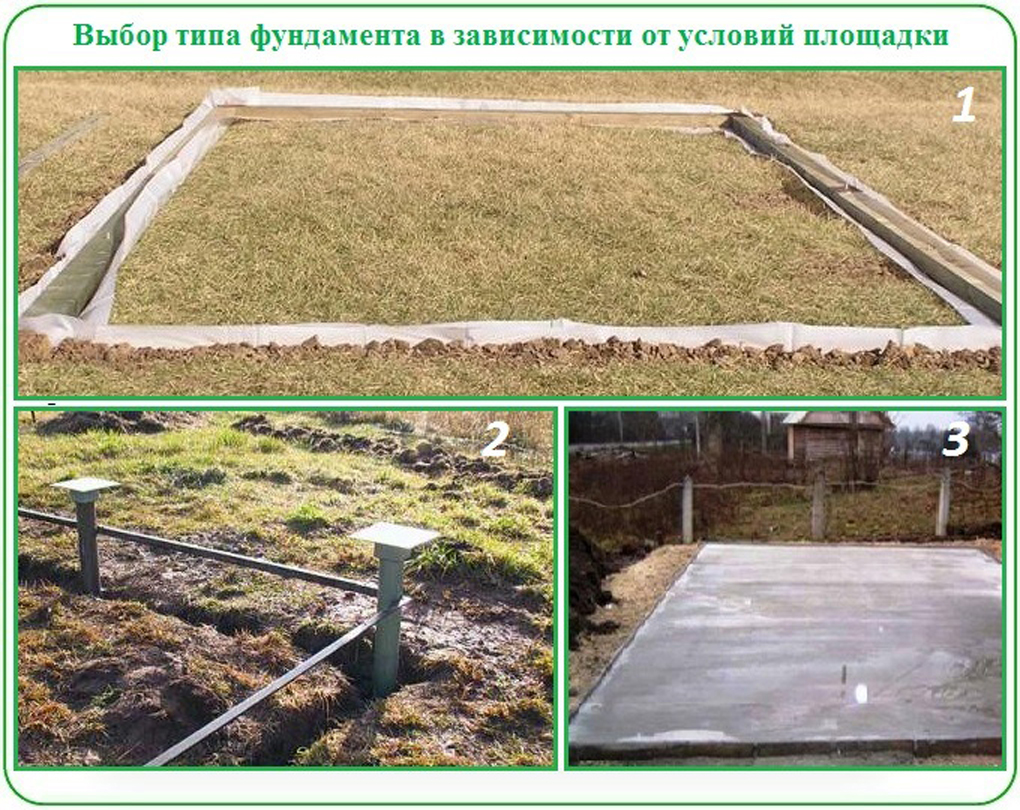
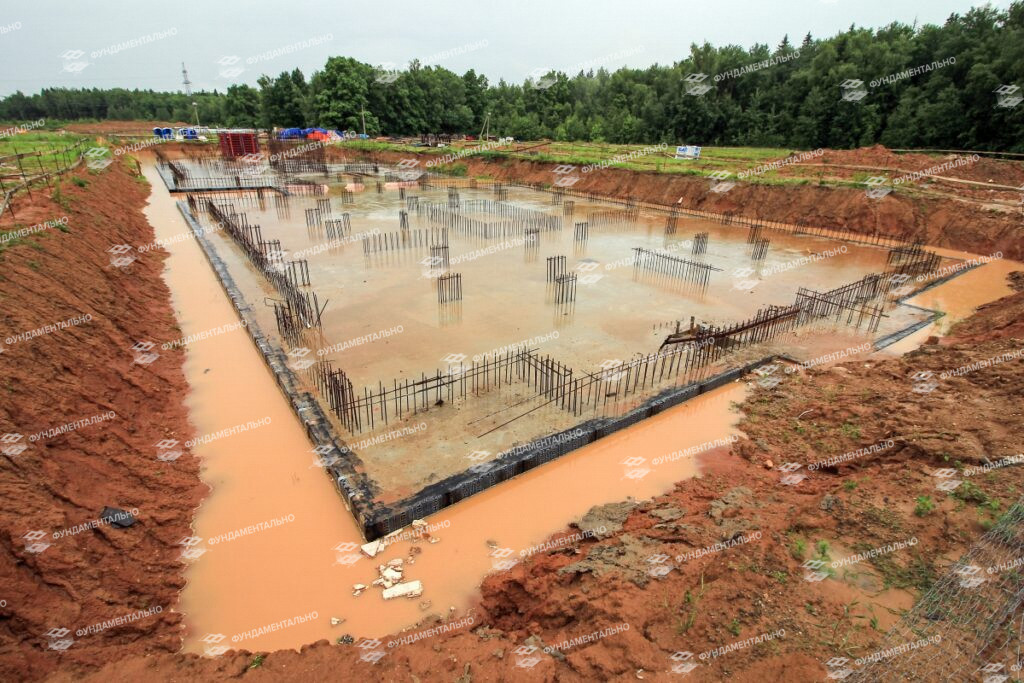
Foundation monolithic slab for a house in a swamp
The figure below shows the device of an artificial soil foundation and slab foundation for a stone house on a weak swampy ground.
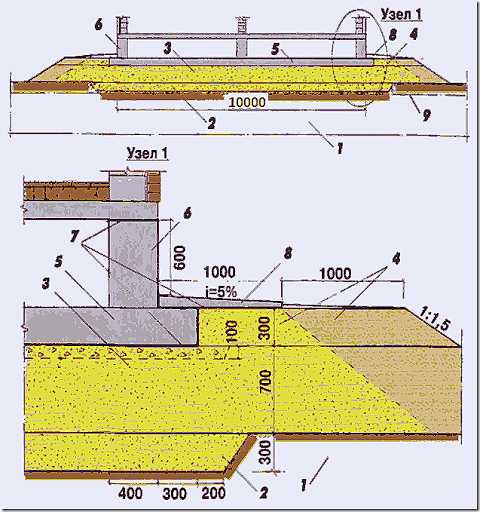
 Slab foundation for a one-storey house with aerated concrete walls and brick cladding. 1 - thickness of weak swampy soil - 10 m; 2 - sand pillow; 3 - embankment; 4 - planning dumping; 5 - foundation slab; 6 - base; 7 - waterproofing; 8 - blind area; 9 - groundwater level - 0.4 m from the surface.
Slab foundation for a one-storey house with aerated concrete walls and brick cladding. 1 - thickness of weak swampy soil - 10 m; 2 - sand pillow; 3 - embankment; 4 - planning dumping; 5 - foundation slab; 6 - base; 7 - waterproofing; 8 - blind area; 9 - groundwater level - 0.4 m from the surface.
Consider the measures taken by the designers of the foundation, allowing you to build a house on a weak swampy ground.
To improve the building properties of the soil at the base of the foundation:
- Partial excavation was carried out - the vegetative layer of the soil was cut off in an area 300 mm thick. (just above the water table). A sand and gravel cushion is arranged in the formed recess, item 2 in the figure.
- An embankment, pos. 3, was made from non-porous soil. The soil in the embankment is laid with layer-by-layer compaction. Under the weight of the fill soil, the underlying layers of the soft soil are compacted and settled. It is recommended to start building a house 6-12 months after backfilling to allow time for subsidence to stabilize.
After the installation of the slab foundation, the planning filling of the soil is additionally performed, pos. 4. Planning filling is performed with any soil.
Building a house on an embankment contributes to the general rise in the level of the surface of the site, ensures the drainage of melt and rainwater from the house and from the site.
The height of the embankment, pos. 3, can be reduced by increasing the thickness of the sand cushion, pos. 2, so that the total thickness of the filled soil of the cushion and the embankment remains unchanged. It should be borne in mind that it is quite problematic to fill and compact the soil of the pillow in the water below the groundwater level.
Constructive solutions for the construction of the foundation for a house in a swamp:
- To reduce the pressure of the house on the ground, a slab foundation was used - a monolithic reinforced concrete slab under the entire area of the house, pos. 5 in the figure. Moreover, the dimensions of the foundation slab are increased and go beyond the walls by 300 mm. from each side.
- The spatial stiffness of the foundation was increased by installing a monolithic reinforced concrete base, pos. 6, connected by outlets of reinforcement with the foundation slab.
- A monolithic reinforced concrete slab in the upper level of the plinth can further increase the rigidity of the foundation. The unified structure of the basement space box made of monolithic reinforced concrete is a fairly rigid base for a stone house.
- Near the house with the walls of their aerated concrete, they reinforce the masonry of the walls and arrange a monolithic reinforced concrete belt at the level of the floor overlap.
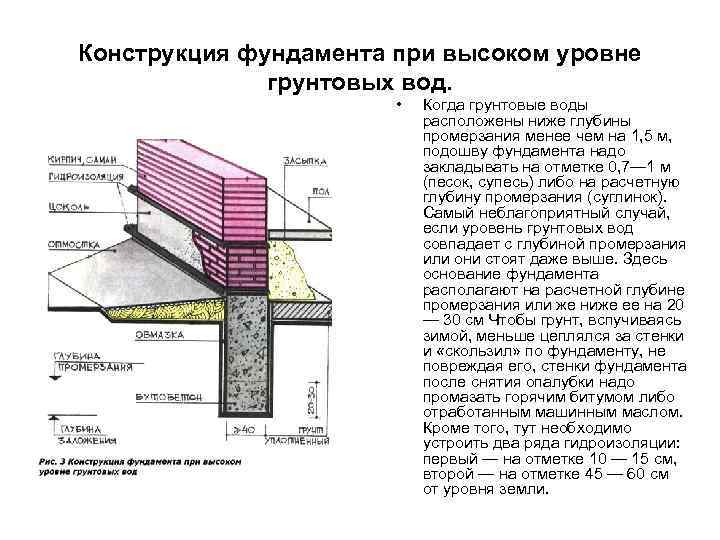
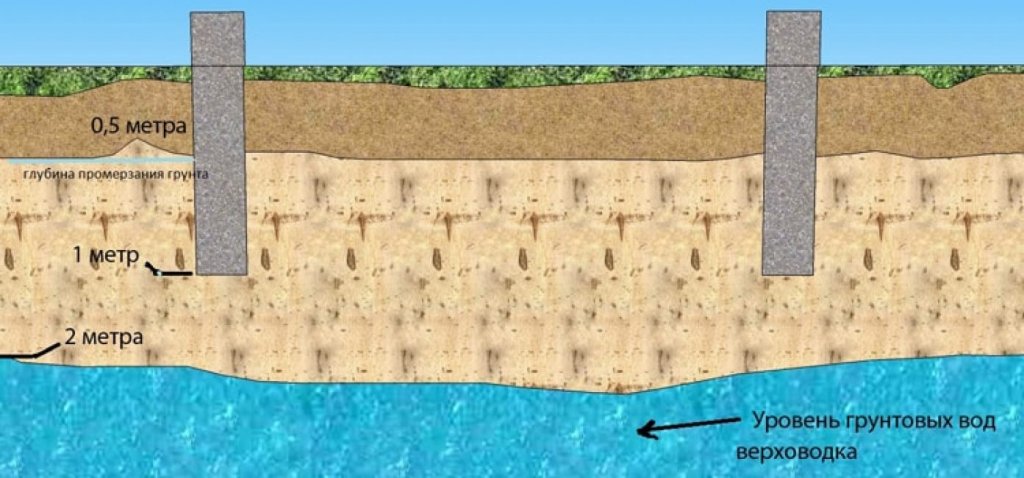
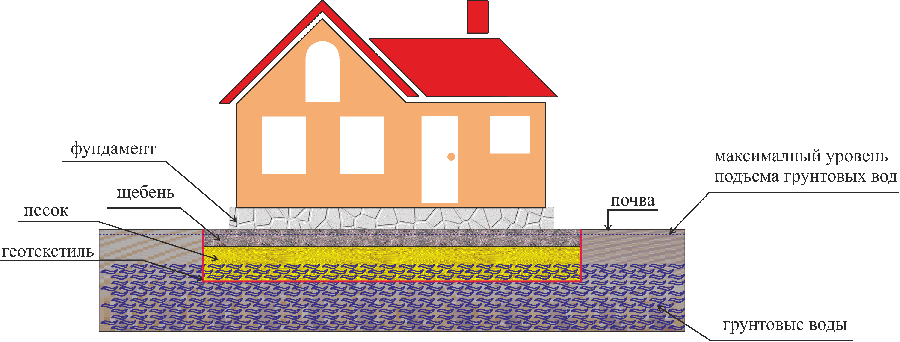
The construction of the foundation shown in the figure was developed for rather difficult ground conditions: the ground is water-saturated silt 10 m thick, a high level of groundwater is 40 cm from the surface.
For more favorable soil conditions, the volume of cushions and embankments, as well as monolithic reinforced concrete at the base of the house, can be significantly reduced.
Increasing popularity among private developers is gaining option of slab foundation - insulated Swedish plate. In this version, a heater is placed under the monolithic foundation slab, and the stiffeners are directed downward into the ground. The foundation slab serves as the base for the walls and the base for the ground floor. Some disadvantage of this foundation design is the low base. In conditions of a significant thickness of snow cover in most climatic zones of Russia, a low plinth increases the risk of wetting the bottom of the house wall.
The reinforcement cage for reinforcing the foundation slab of a private house usually consists of upper and lower reinforcing meshes and vertical ties between them. The number of rebars and their diameters are determined by calculation.
In the case of the construction of heavy two- or three-story brick houses in difficult soil conditions, it may be more profitable to build a foundation on driven piles.
On soft soils with a layer thickness of less than 3-5 m, the advisability of building a house on bored or screw piles with support on the underlying low-compressive soil layer should be considered.
Why is water in the soil dangerous?
One of the main enemies of any building structure is liquid. In most cases, problems arise with moisture in the vapor state and can be easily solved by installing a vapor barrier. But when erecting foundations, you can encounter not just the liquid phase of the substance, but also pressure water, which can cause much more trouble.
There are three most common problems if the groundwater level on the site is located close to the surface of the earth:
- the emergence of forces of frost heaving;
- wetting the material and reducing its characteristics;
- destruction of foundations when exposed to aggressive groundwater.
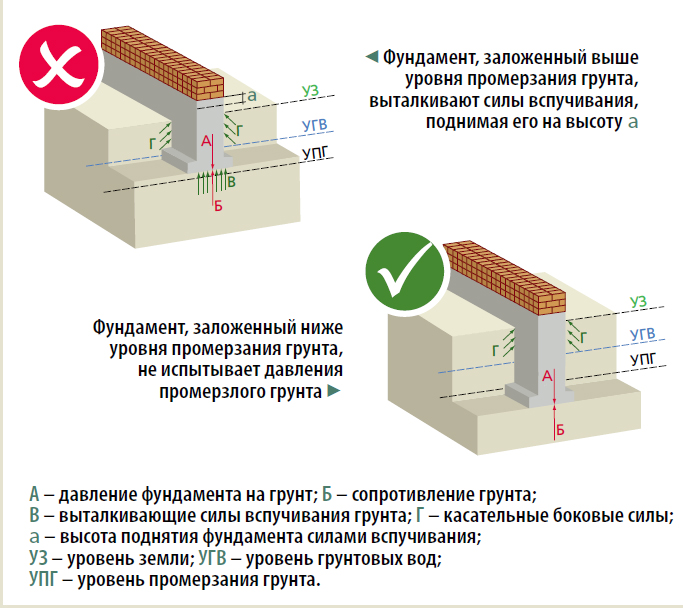
Frosty heaving
The phenomenon itself occurs imperceptibly, only consequences float to the surface: vertical or oblique cracks. Depending on the material of the walls, destruction can affect not only the foundations, but also the overlying structures of the house.
The cause of frost heaving lies in the unique property of water. All substances on the planet decrease in volume with decreasing temperature, but this rule does not apply to H2O. This liquid expands noticeably when turning into ice, leading to the appearance of excessive pressure under the building.
The pressure is unevenly distributed. In the center of the building, the soil is warmed up, and at the edges the temperature is slightly lower. Therefore, the outer parts of the foundation will rise more strongly with frost heaving, uneven deformation will lead to cracks.
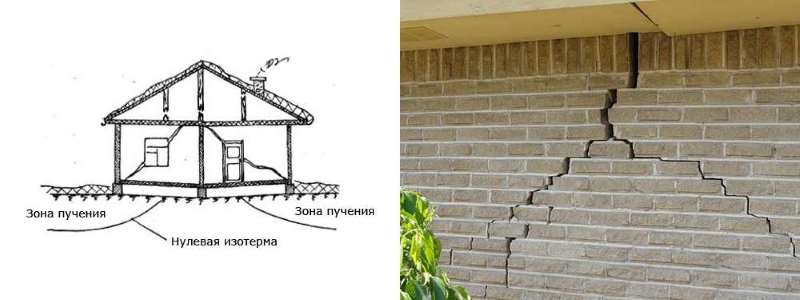
Scheme of exposure and consequences of frost heaving.
For such a situation to arise, the simultaneous presence of two components is required:
- moisture in the soil (for example, high GWL at the site);
- temperature below zero (in winter).
To prevent the likelihood of damage, it is enough to get rid of at least one factor.
Excessive hydration
Most often, the foundation is made of concrete. This material has a certain frost resistance, which shows the maximum number of freeze and thaw cycles. The limited cycles are also associated with the expansion of water during freezing.
If the groundwater level is located close to the ground, the concrete of the foundation is excessively wetted, while its internal structure is subject to strong "loosening". Excess moisture penetrates the pores of the material. In winter, it freezes, there is an increased pressure in the concrete. Thawing occurs in spring, the pressure decreases. Such constant fluctuations, in the end, lead to a decrease in strength and destruction.
Also, excessive moisture is dangerous because it destroys the surface of the foundation, gradually washing away material particles.
Aggressive environment
Such soils and moisture in them have a negative chemical and physical effect on building materials. We are talking about the corrosion of concrete and metal. For cement stone, there are three types of phenomenon:
- leaching of minerals from cement (most often occurs under the influence of carbon dioxide groundwater);
- damage caused by acids or alkalis;
- chemical reactions that cause crystallization processes in the pores of concrete in which the internal pressure increases.
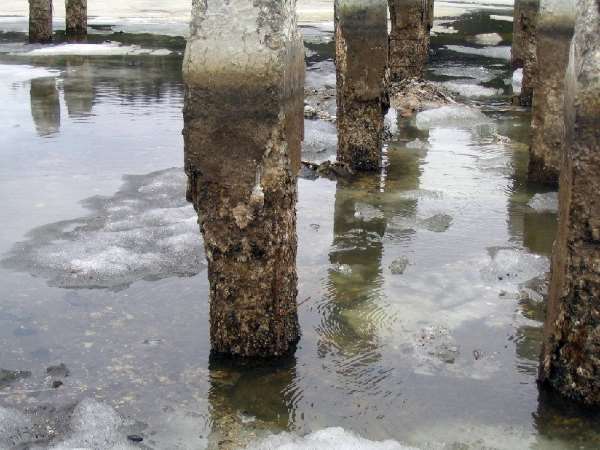

Consequences of concrete corrosion.
The aggressiveness of groundwater to metal is considered separately. It is not so dangerous, since when pouring monolithic structures, a protective concrete layer is provided.Requirements for materials, the need for protection and its choice are regulated by SNiP 2.03.11-85.
Advice
 For the manufacture of concrete, only clean crushed stone and sand are used.
For the manufacture of concrete, only clean crushed stone and sand are used.
- In conditions of high GWL, the main danger lies in the high content of sulfates in the groundwater, which loosens concrete. Therefore, it is better to use sulfate-resistant Portland cement of the 500 grade for the solution.
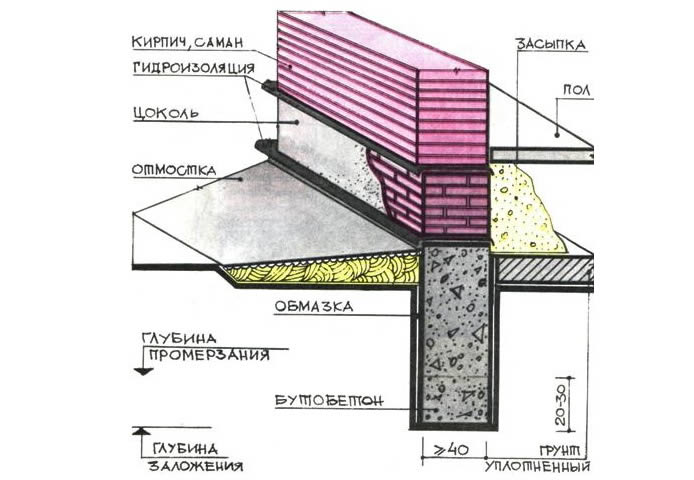
- The depth of the foundation in conditions when the groundwater level is less than 1.5 m below the freezing point should be within 0.7-1 m. This applies only to sandy loams and sands. For loams, the depth of laying should be 200-300 mm below the design point or at the same mark with it.
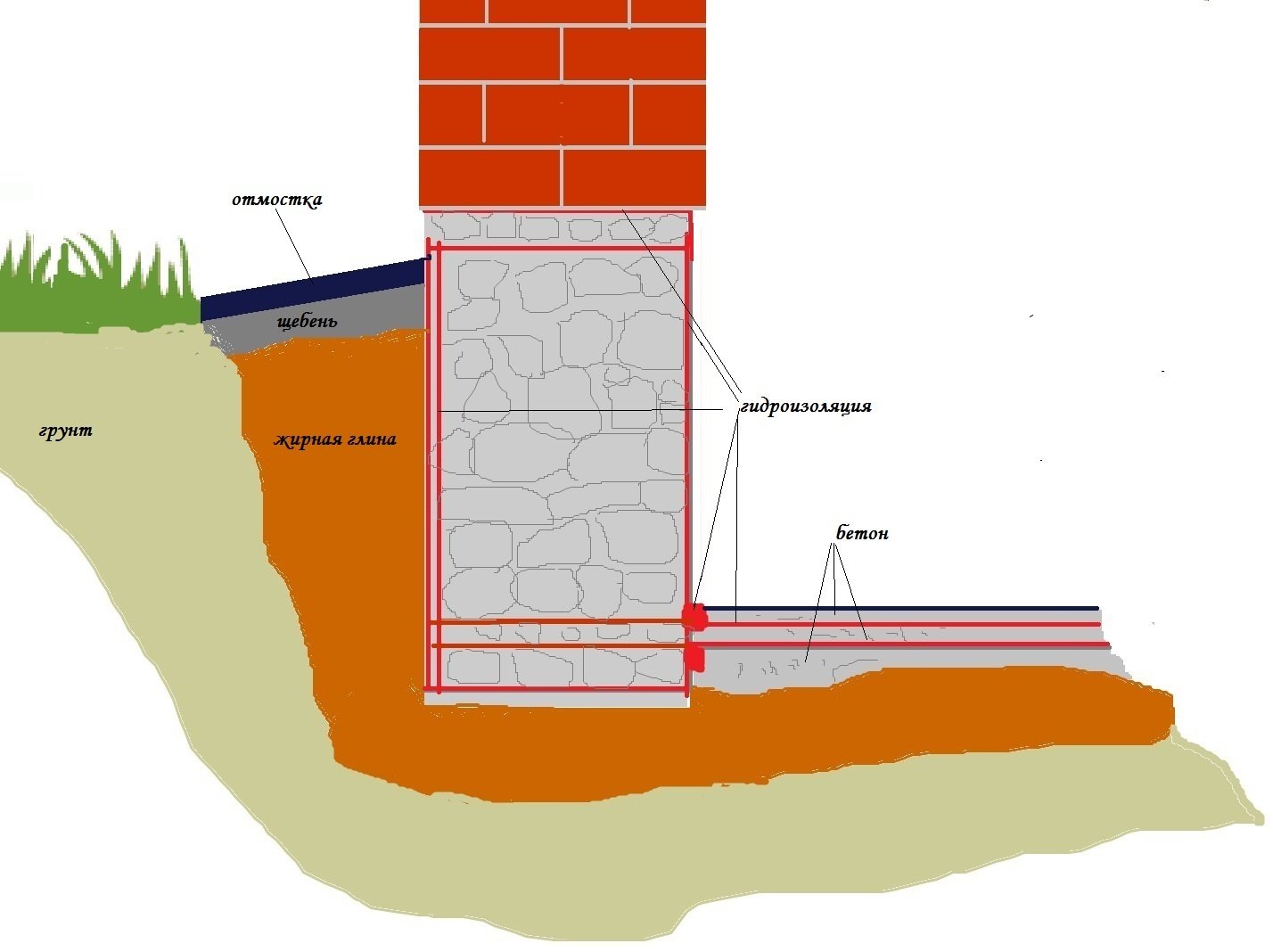
- When building on wet clay, the sole is made thicker than the foundation itself, and the walls of the structure are arranged with a slight slope. This will allow the base to better resist lateral heaving forces.
- For the manufacture of concrete, only clean crushed stone and sand are used. The solution should not be fluid, but viscous. To increase plasticity, you can use plasticizers that are added to the water.
- In order for the concrete solution to have water-repellent properties, it is possible to enter "Penetron Admix" into its composition. This dry mix can increase the strength of concrete by 15 percent.
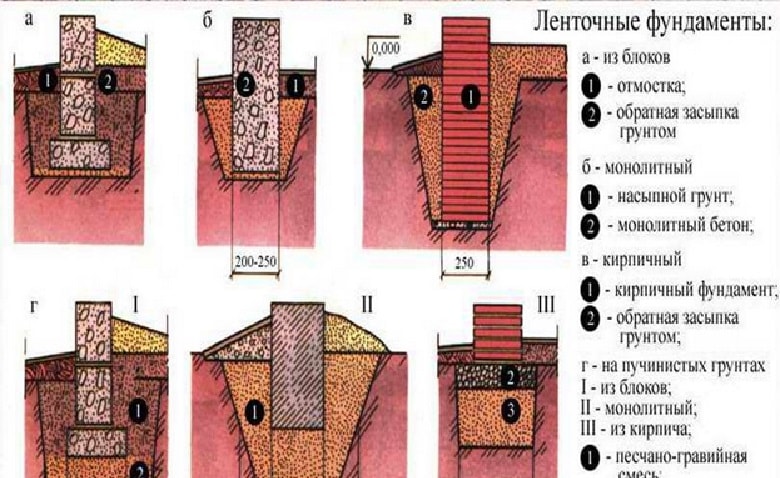
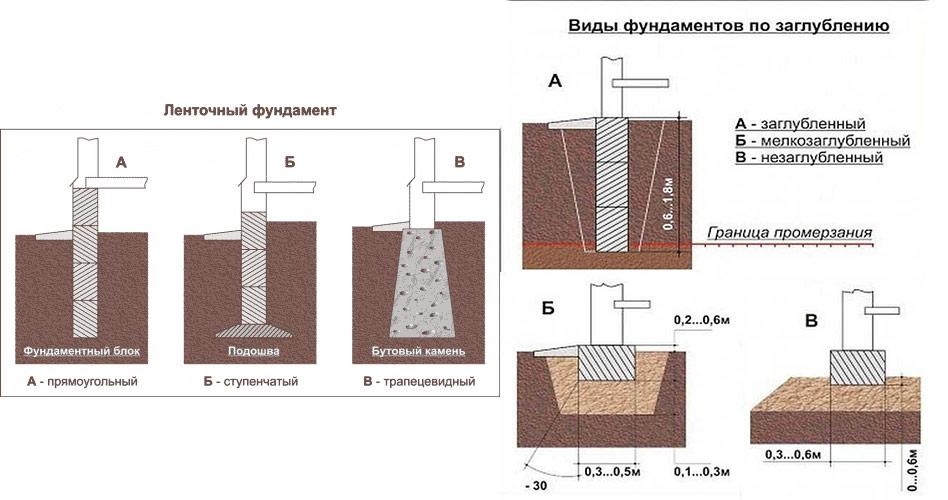
Types of strip foundations by device method
Depending on the design features, strip foundations are monolithic and prefabricated. They, in turn, can be subdivided into monolithic foundations with vertical supports and prefabricated strips made of bricks or foam blocks.
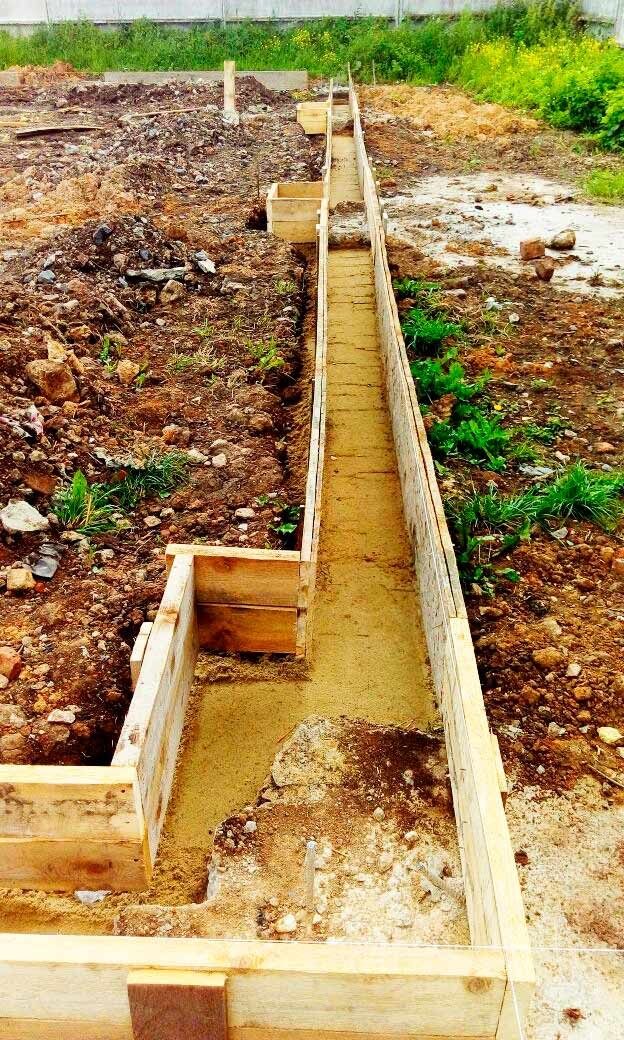
Monolithic strip foundation
When installing a monolithic strip base, the reinforcement and pouring of the foundation are carried out directly at the construction site. The result is the overall integrity and continuity of the carrier tape.
Monolithic strip foundation is an unbreakable reinforced concrete strip along the entire perimeter of the structure
Monolithic types of foundations, regardless of technology, are used to build objects for various purposes on heaving and mobile types of soil. The solidity of the structure ensures high strength and reliability of the supporting base.
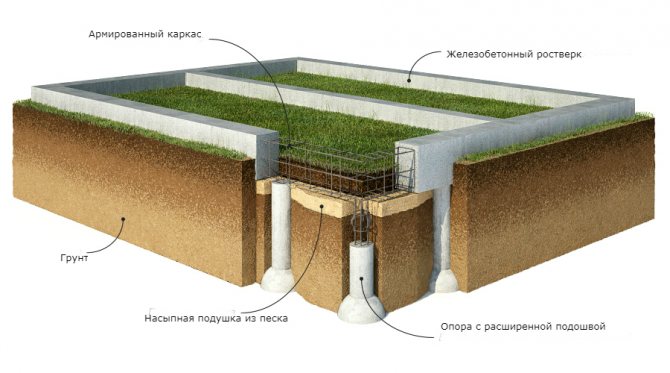
Pile and columnar-strip foundation
Pile-tape and columnar-tape types of foundations are a monolithic tape made of reinforced concrete, located on supports buried in the ground. In fact, these types of foundations are nothing more than a modernized version of pile or columnar foundations with a grillage.
Pillars or piles are located along the perimeter of the foundation with a step of 2 m
In the first case, steel products in the form of piles of various lengths are used as supports, which are screwed into the ground manually or automatically. In the second, the supports are made from the same concrete mixture that is used to pour the carrier tape.
Arrangement of pile and columnar foundations of the strip type is justified only during the construction of facilities in areas with a large depth of soil freezing. Steel piles or reinforced concrete pillars buried below the freezing level of the soil will distribute the load that is transmitted from the reinforced concrete belt.
Precast strip foundation
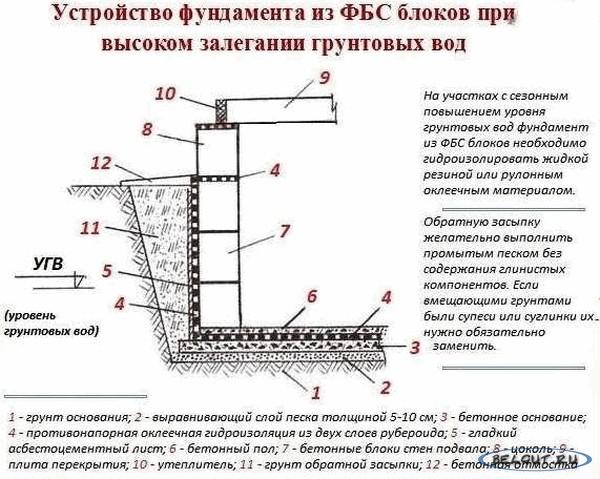
The main material for the construction of a prefabricated strip foundation is reinforced concrete foundation blocks (FBS) made of heavy grades of concrete. A carrier tape of the foundation is formed from the blocks, which is located along the perimeter and area of the future structure. To connect the blocks to each other, concrete of the M350 brand and steel reinforcement Ø15 mm are used.
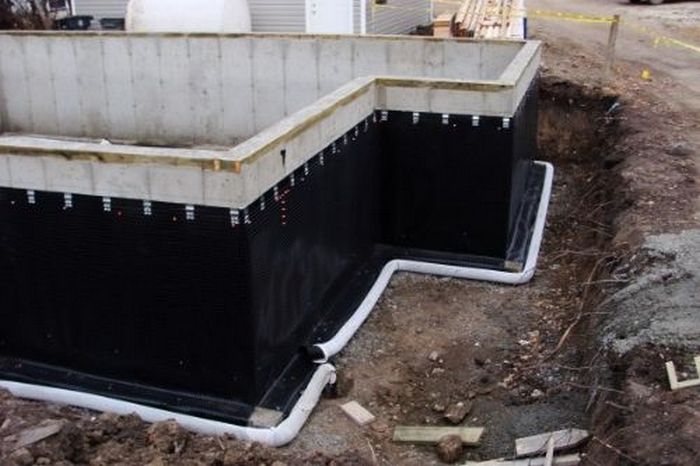
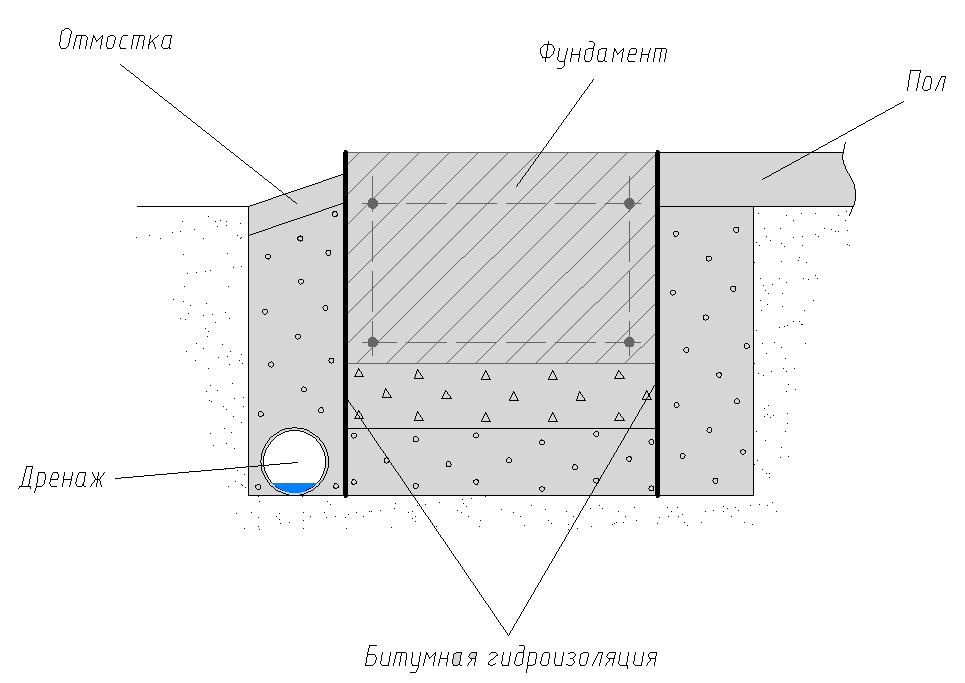
After assembling the foundation, the outer surface of the supporting base is treated with waterproofing materials. The most commonly used bitumen mastic and special bitumen membranes, which have a self-adhesive base.
The precast strip foundation consists of reinforced concrete foundation blocks connected by concrete
The main advantage of the prefabricated strip foundation is the short construction time. Unlike a monolithic base, you do not have to wait for the minimum strength of the concrete mixture. You can start building a house in a few days after assembling the tape.
Despite this advantage, prefabricated strip foundations are used for the construction of private houses a little less often than a monolithic concrete base. This is largely due to the fact that the prefabricated structure is not suitable for use on moving types of soil. With the same thickness, the strength indicators of the prefabricated structure are 20–30% lower than the monolithic structure.
Brick strip foundation
Brick strip foundations are a prefabricated structure and are often used for the construction of one-story houses using frame technology. Fired solid brick is used to make the tape. Laying depth - 40-50 cm.
Brick strip foundation is highly maintainable, but requires the arrangement of high-quality waterproofing
After assembly, as in the case of blocks, it is necessary to arrange a full-fledged waterproofing layer. The advantages of this foundation include:
- rigidity of the structure;
- high maintainability;
- ease of arrangement.
If we make a more detailed comparison of bricks with reinforced concrete blocks, then the foundations of the blocks are less hygroscopic and have higher strength. Brick is more fragile, which affects not only the frequency of repairs carried out, but also the service life of the structure as a whole. Taking this into account, it is recommended to erect a strip foundation made of bricks in areas with dry and hard soil, as well as with a low occurrence of groundwater.
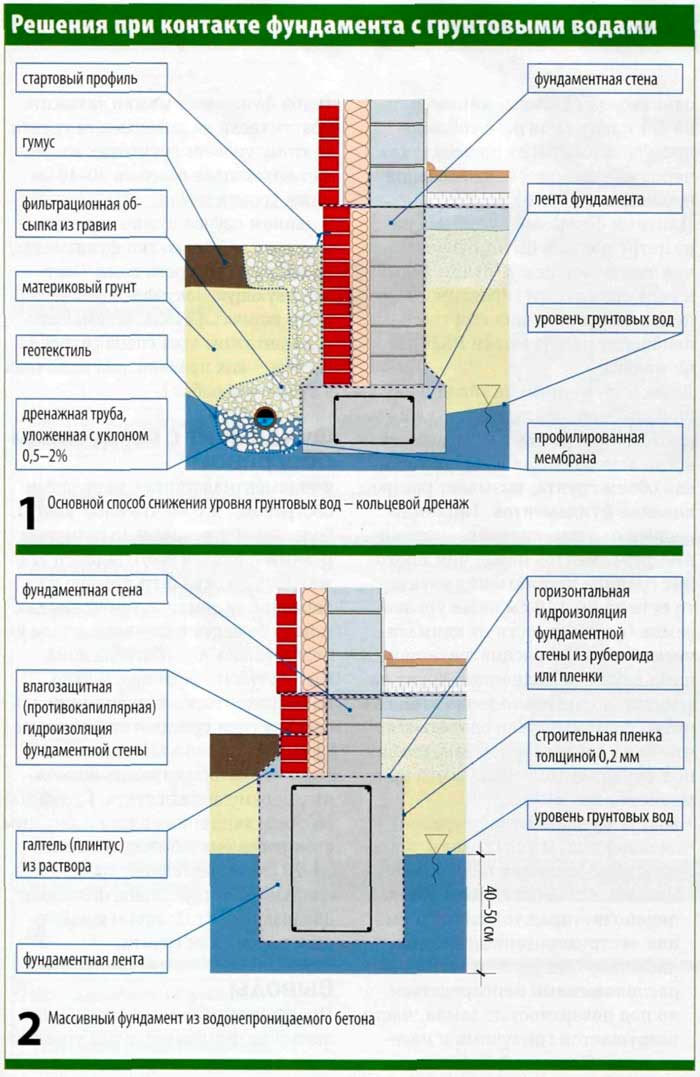
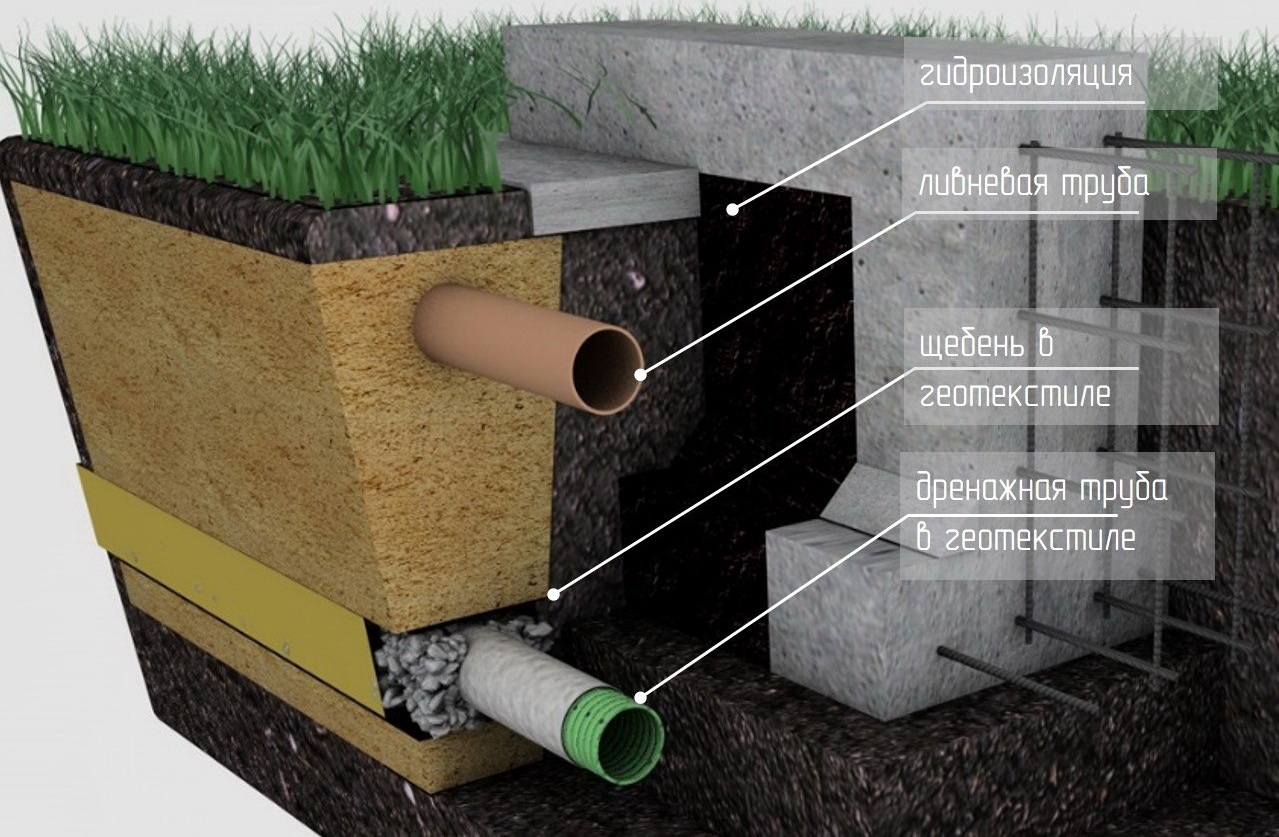
Installation of a drainage system in areas with high groundwater levels
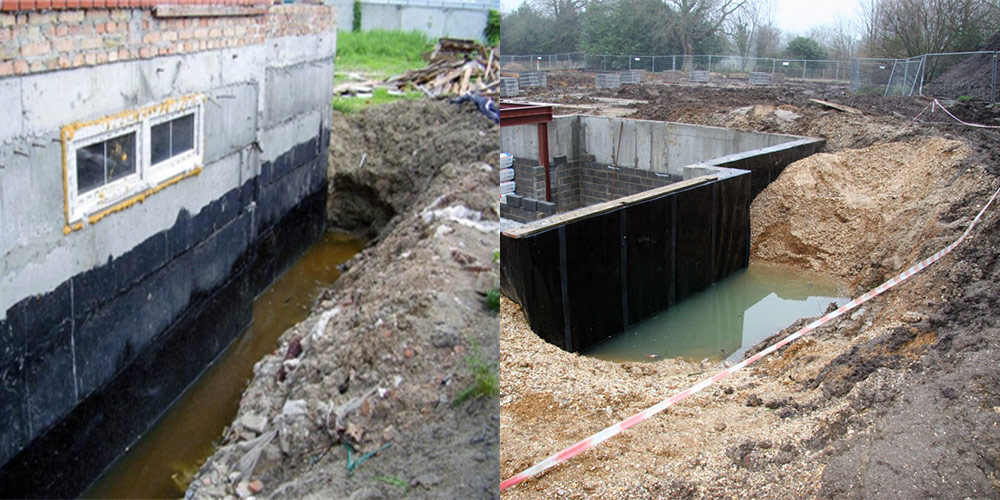
The construction of foundations, the soles of which are supposed to be built below the groundwater level, inevitably leads to the use of various methods of dewatering. In other words, options are selected for draining water from a pit or trenches and keeping it at a certain distance.

Drainage system installation
Drainage involves the removal of melt and groundwater. For the arrangement of the system, drainage pipes, wells, channels, pumps and much more are used.
There are 2 ways to install a drainage system.
Open water drawdown
You can pump out water with a drain pump, but in this case, certain conditions must be met:
- There is a reservoir nearby where the pumped-out water will flow.
- Lack of visible signs of suffusion. With this phenomenon, the smallest particles of soil are carried out along with the water, which leads to subsidence of the soil layers located above. The bearing capacity of such soils is very low due to constant subsidence.
Also, the open water lowering system assumes a simplified version of the removal of melt, groundwater and storm water. To organize such a process around the perimeter of the site, it is necessary to place drainage ditches. In them, water of various origins flows down for one reason: the absence of soil resistance and capillary rise of liquid. Such systems are most effective when the site is located on a slope.
Closed drainage system

Closed drain
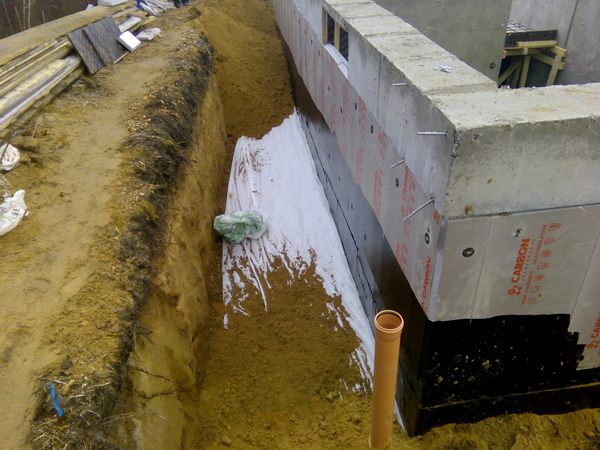
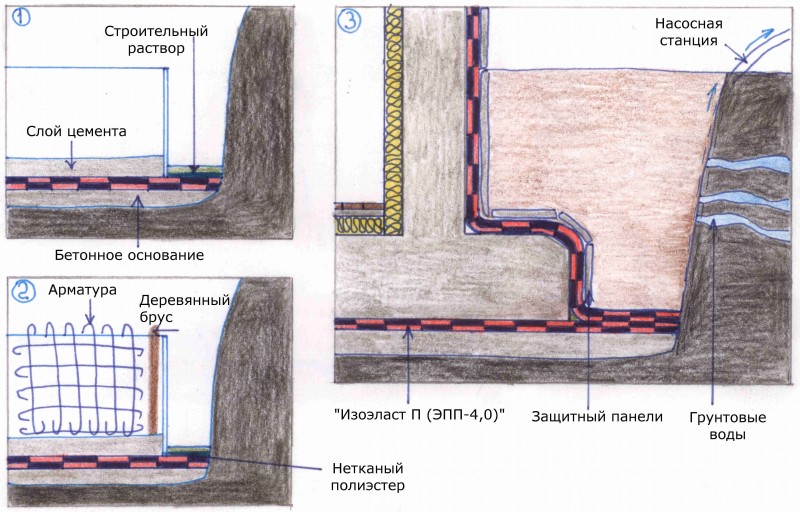
A closed drainage system helps to drain the groundwater, thereby preventing it from rising. The system is based on underground pipes. A closed drain is a carefully planned structure of pipes and wells. The system is located in a trench, the bottom of which is covered with sand and gravel, and also covered with geological fabric. Pipes of a closed drainage system are laid under groundwater. The top is covered with an additional layer of sand and gravel, which helps to drain water. The entire system is covered with soil and a layer of sod.
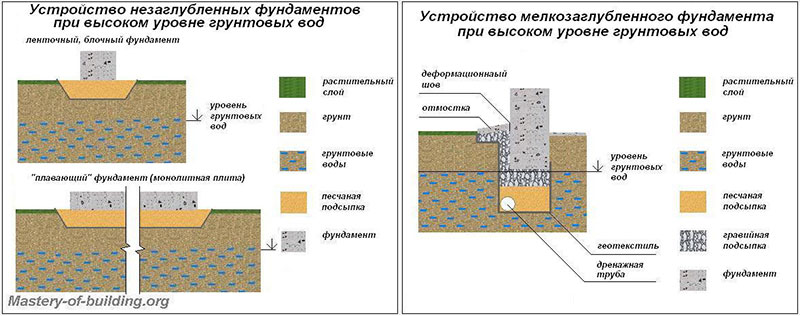
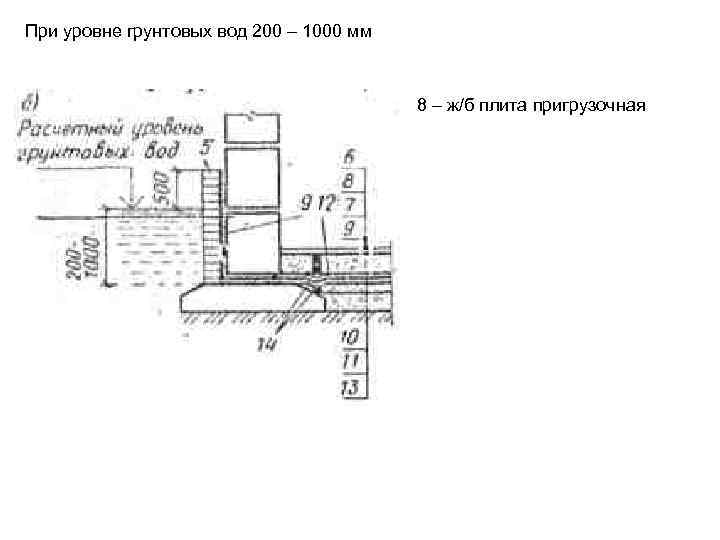
Foundation options with a close location of groundwater
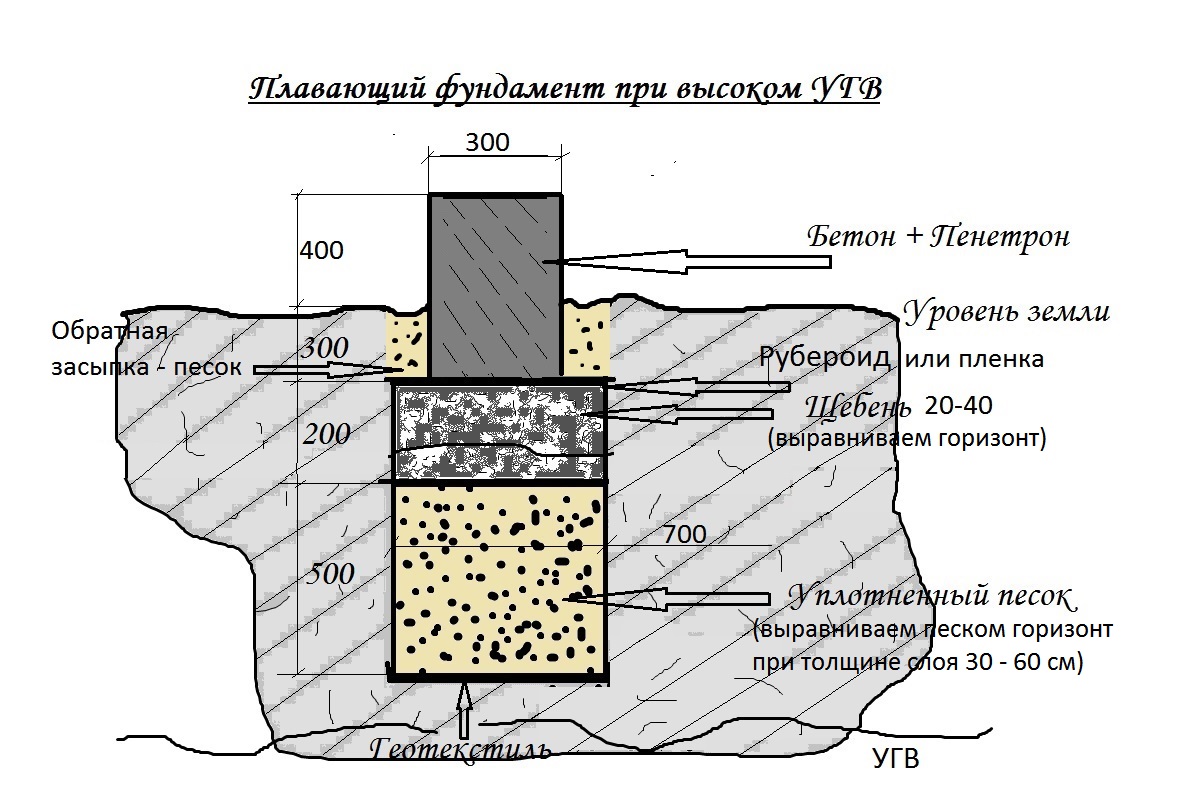
What kind of foundation is needed on the site if the groundwater is close to the surface? There is only one answer - this is a special floating type of foundation. Such a foundation is intended for laying on low-bearing soils, on bulk soil, on heavy heaving soil and under conditions if the groundwater does not lie high, that is, there is a possibility of flooding the structure of the foundation, basement, basement, and this has a negative effect on the entire structure.
A trench is dug under the slab, at the bottom of which a cushion of sand and rubble is poured.
The device of such a foundation for a frame house and any other structure is quite simple, it consists in pouring a monolithic concrete slab, which is reinforced with steel rods. The technology for arranging such a foundation for a frame house of a small area, when groundwater lies close to the surface, is simple: it is necessary to dig a trench with a depth of 60 cm, at the bottom of which a layer of rubble is poured by 10 cm and a layer of sand by 50 cm. After that, the resulting pillow is impregnated water, sits down and poured to the required level. Next, at ground level, pillars of bricks should be laid out, which are one and a half to two bricks wide (concrete blocks can also be used), covered with roofing material on top, a simple wooden board protected from decay (such a layer should be 40 mm).
In this case, it is not recommended to install a strip foundation, since moisture under the base of the house should be distributed evenly, and not squeezed out from under some areas and flow into others. A strip foundation, in spite of all its advantages, when installed on this type of soil, creates excessive hydrostatic pressure, that is, there is a danger of its distortions, deformations, cracks will begin to go along the walls of the structure. It is possible to use a strip foundation when the groundwater level is high enough, in other cases it is not recommended to use it. Sometimes such a structure can also be installed on loam, but it is necessary to ensure the correct waterproofing. If you decide to use the strip basement option, conduct preliminary geological studies that will show how realistic it is.
Can a pile foundation be used?
Variants of using screw piles for the foundation.
The pile foundation is recommended for difficult soils, heaving soils, it can be used for closely located groundwater, quicksand. For example, cities such as St. Petersburg and Venice have buildings on pile foundations, which perfectly protect houses from moisture, giving them strength and reliability.
Most often, the pile foundation is made using special screw piles, which are characterized by the highest bearing capacity. This is due to the fact that when it is in the ground, it does not loosen it, as when using conventional driven piles, but compaction, that is, the earth is compacted between the steel screws, makes the support reliable and stable. The question of which pipes are better for such a foundation is easily resolved. These are steel, which have a zinc coating for corrosion protection (if necessary, other types of protection are additionally performed). At the end of the pipe, which goes deep into the soil, there are helical blades that allow the pile to be screwed in securely.
Determining a place for construction is quite simple, since such a base option can be installed in almost any conditions. The construction of the foundation using screw piles is economically profitable; heavy construction equipment is completely unnecessary. This type cannot be used only for rocky soils.
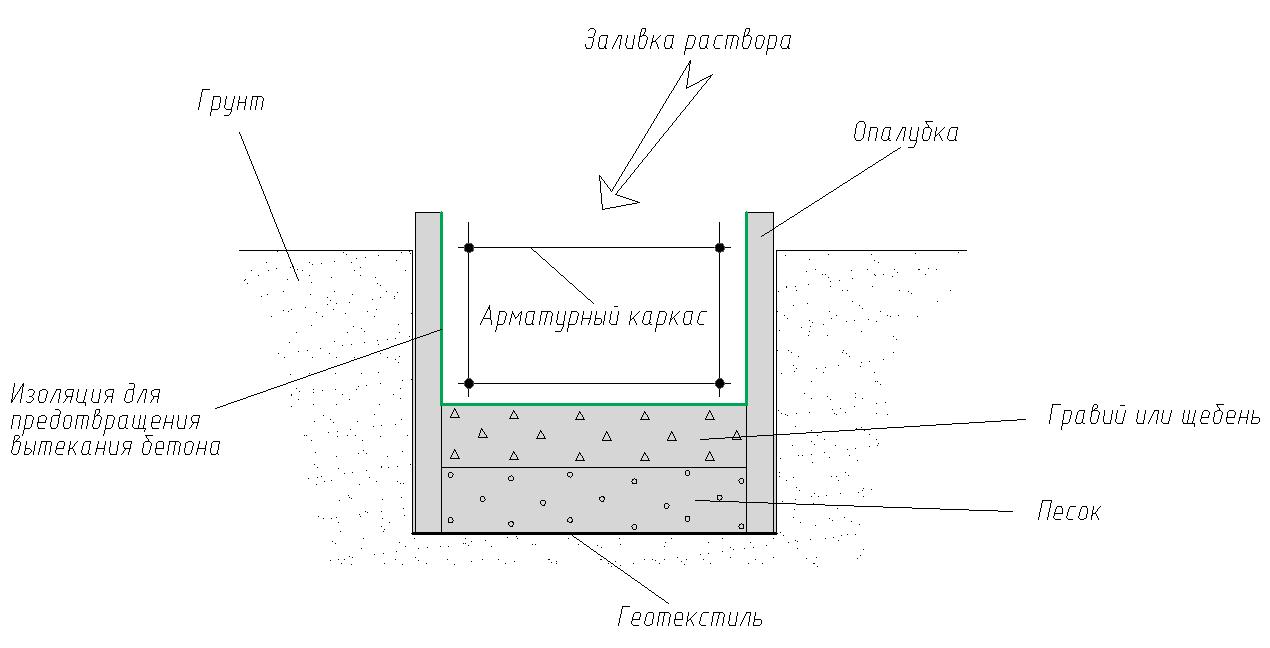
Foundation concreting and waterproofing process
When self-pouring, it is not recommended to rush and lay out large volumes of cement mixture into the formwork. The best option is to pour the composition in layers, since it requires careful compaction.It is performed using a piece of reinforcement that pierces the liquid concrete. This allows you to expel air from it. It is advisable to pour the next layer when the previous one grasps sufficiently and forms a fairly strong surface.
After the completion of the formation of the tape or slab, they must be protected from drying out and being washed out by rain. Therefore, in the early days, concrete is poured with water from a hose, and at night it is covered with a water-repellent material.
When it is finally ripe, the formwork is dismantled. Further, all the sides of the foundation are coated with bitumen or other waterproofing compound. Sheets of roofing material are laid on the surface of the slab or tape, which will serve as a shut-off waterproofing for the lower piping of the building.
What to do if the groundwater level is located close to the surface
Before starting construction on the site, it is necessary to carry out geological studies and determine the location of moisture. You can do this on your own using pits or hand drilling. To correctly determine the level of groundwater, you will need to dig the ground 50 cm below the estimated elevation of the base of the foundation.
Depending on which of the above problems protection is needed, the method of work is chosen. In most cases, you will need to consider not one but several consequences. For example, frost heaving and surface destruction from excessive moisture.
Methods of dealing with frost heaving
The construction of the foundation with a high groundwater level will be successful if you take care of the following protective measures:
- partial or complete replacement of soil;
- bedding made of non-porous materials;
- insulation of the structure;
- removal of moisture from the boundaries of the house.
Advice! Replacing the soil layer is a laborious and costly undertaking. It is recommended to consider it if there are other reasons. For example, soil strength is a significant reason for replacement. It is better to take out very fine sands, unreliable bases from the site, and instead fill in coarse or medium sand, which does not retain moisture at the surface and belongs to conditionally non-porous soils.
Adding coarse sand or crushed stone not only reduces the likelihood of heaving, it strengthens and levels the soil before making foundations. In some cases, it is enough to make a bedding with a thickness of 30-50 cm, but sometimes you will have to use more material. In practice, there have been cases when crushed stone literally sank into the ground. In this case, it must be poured until the base is solid.
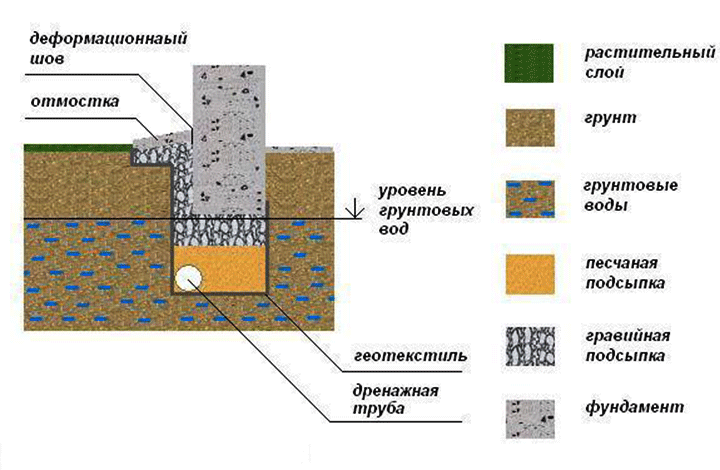
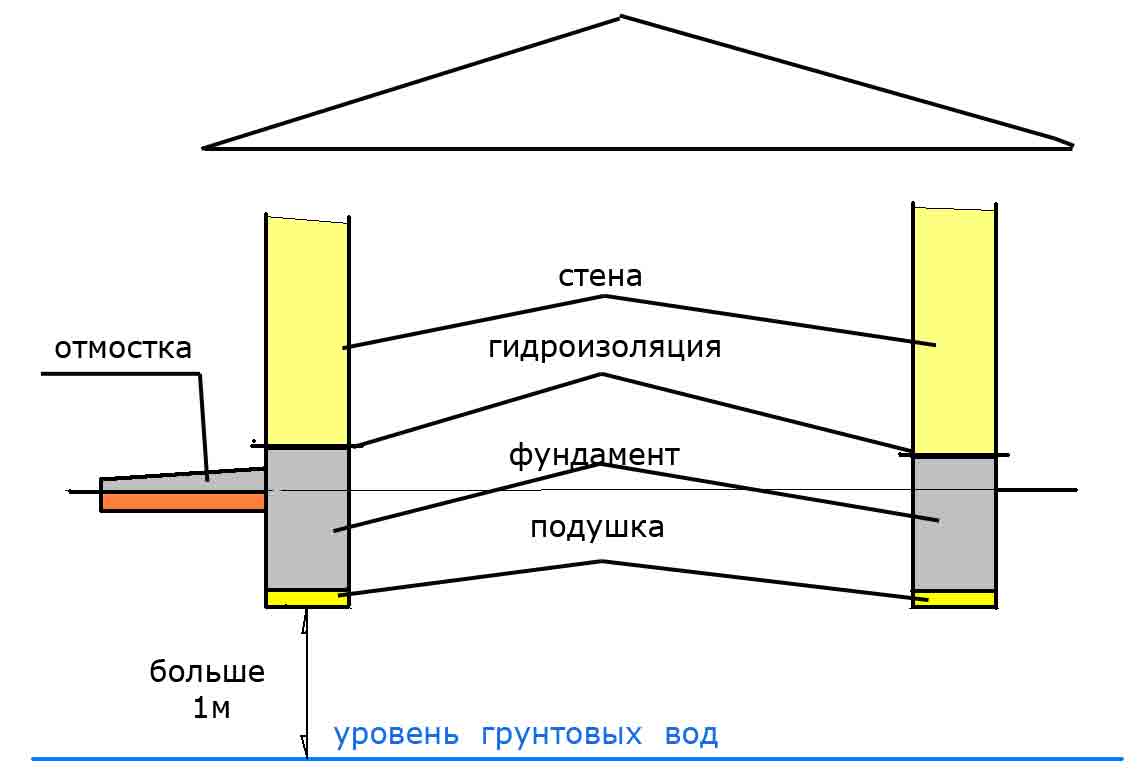
The standard deepening of the foundation is assigned below the freezing mark (determined by SP 22.13330.2011). But, if the water is located close to the surface, it will not work to do it according to the norms without dewatering. In general, it is necessary to mark the bottom of the foundation so that it is about 50 cm higher than the GWL.Depending on the location of the water horizon, we are talking about shallow (with GWL below 1.5 m) or shallow (with GWL below 0.5 m) foundations. When located above 0.5 m, pile foundations are used.
Important! For the building supports located above the freezing depth, thermal insulation will be required. It will be correct to carry out a set of measures, including thermal insulation, drainage (water disposal) and a competent designation of the sole mark
Waterlogging protection
Even if it is correct to protect the foundation from frost heaving in winter, there is a possibility that moisture will rise in spring. To prevent problems in this case, it is worth taking additional protective measures:
- waterproofing device;
- the correct choice of concrete grade.
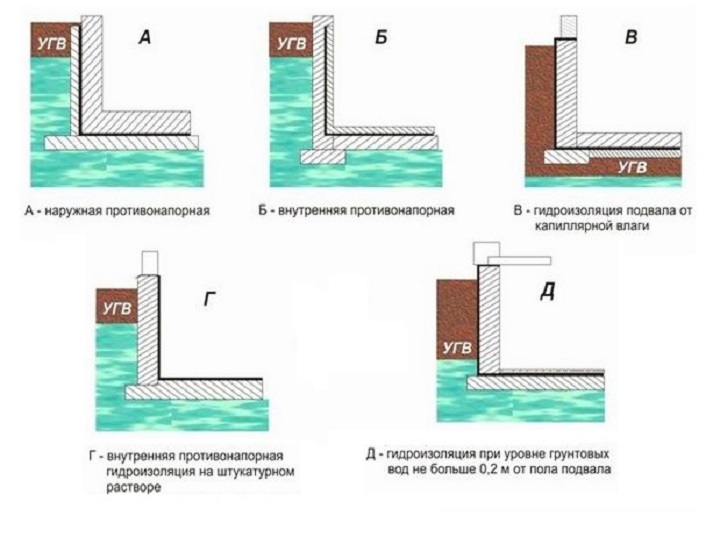
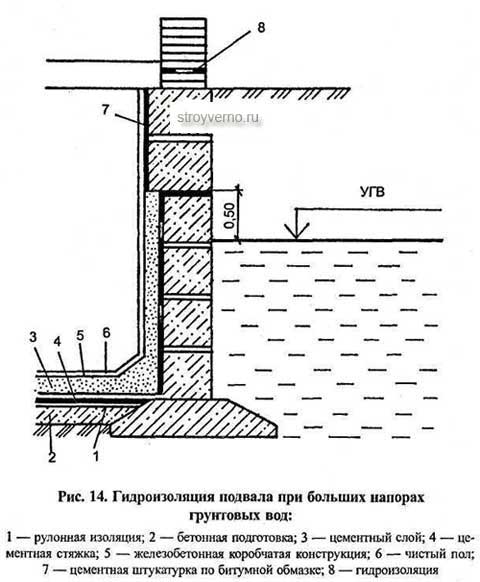
The foundation waterproofing device when groundwater is located close to the surface includes vertical and horizontal protection. Vertical can be done using bitumen mastic or pasting materials.In the presence of pressurized water, they consider the option of installing a caisson with metal waterproofing or the construction of brick walls.
Horizontal insulation is made of two layers of rolled material (roofing material, linokrom, waterproofing, etc.). Provided for prefabricated monolithic foundations at a level just below the basement floor.
If the moisture in the soil is close, the grade of concrete for frost resistance and moisture resistance is of great importance. For a foundation with a high ground level, a material with a water resistance of at least W8 - W10 is needed. It is recommended to assign a frost resistance grade not less than F100 - F150.
To protect against aggressive environments, paint and varnish, gluing and facing materials, impregnations and water repellents are used. The choice is made taking into account the composition of the groundwater and the degree of its mineralization.
In conclusion, it should be said that the construction of the foundation with a high level of groundwater requires careful preparation. All protection measures must be considered in a complex: bedding, waterproofing, insulation, drainage. On the choice of a constructive solution, in the general case, the following recommendations can be given:
- Groundwater level below 1.5 m - shallow tape or slab;
- below 0.5 m - unburied slab;
- above 0.5 m - piles (the easiest and cheapest are screw).
Installation of a foundation on a floating cushion
What is a floating cushion? This is a thick layer of a substrate made of several materials, which are separated from each other by insulating films. For high groundwater, it is done very often. Here's the sequence:
- Coarse-grained sand is poured onto the bottom of a pit or trench, which is well compacted.
- Backfilling is done in layers with tamping of each layer. In this case, the final result is a layer 50 cm thick.
- A waterproofing film is laid, roofing material is better.
- Crushed stone is poured, rammed to a thickness of 30 cm.
- Another layer of roll waterproofing.
- Pouring a screed with a thickness of 10 cm.
After that, you can fill in the monolithic reinforced concrete structure of the foundation itself. The pillow creates conditions under which the foundation can move relative to it. Such a foundation is often called a floating monolithic foundation.
The strip foundation on soils with high GWL is poured in exactly the same way as described in the previous sections.
It is important to understand here that a strong base in the form of a tape is a large material cost. They mainly relate to the consumption of concrete and reinforcement
At the same time, they try to construct the tape itself with an extended sole.
If you try to save on something, then the end result can lead to a weakening of the foundation structure, and, therefore, problems with the house itself will begin to arise. Therefore, one cannot deviate from the construction technology and from the exact sequence of the construction operations carried out.