Peculiarities
A feature of swampy soils is a tendency to deformations, instability due to a large number of fine-grained particles, and high moisture saturation indicators. During the off-season, such soils are subject to strong heaving, and in winter - to freezing. The high moisture content in the soil causes the formation of dangerous quicksands. All this becomes the reason that the soils are weakly resistant to compression, and it is necessary to look for non-standard solutions to the construction of the foundation.
In each case, the decision in favor of a particular system is made on the basis of an analysis of soils, soil layers directly under the construction site, and the water table. The method of drilling wells is used as a way to obtain the necessary data. It is recommended to do them in winter, when the moisture saturation of the soil is at its maximum.


All types of highly compressible soils are classified as swampy:
- clay soils with a porosity of about 52% and loams with a similar indicator of more than 50%;
- loose sandy soils and sandy loam, characterized by high water saturation and porosity over 41%;
- peat (containing less than 50% organic soils) clay and sandy soils;
- silt - highly porous (up to 60% porosity) soil containing a large amount of moisture and formed under the influence of microbiological processes in water bodies;
- sapropel is a type of sludge containing a high percentage of moisture, having porosity values of more than 75%, containing less than 10% of organic components.


Under a highly compressible boggy soil, there is always a slightly compressible soil suitable for construction.
Several systems of foundations are most widespread in wetlands.
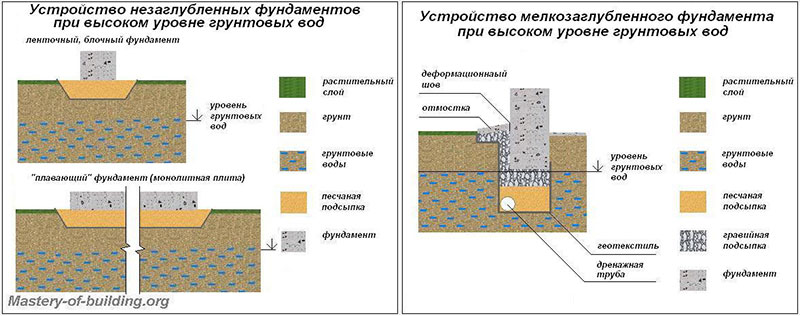
Strip foundation with powerful drainage from the basement and drainage
In some cases, this type of foundation can be used on swampy soils with a high content of coarse sand, provided that there are no aquifers under the foundation, as well as springs and other sources nearby.

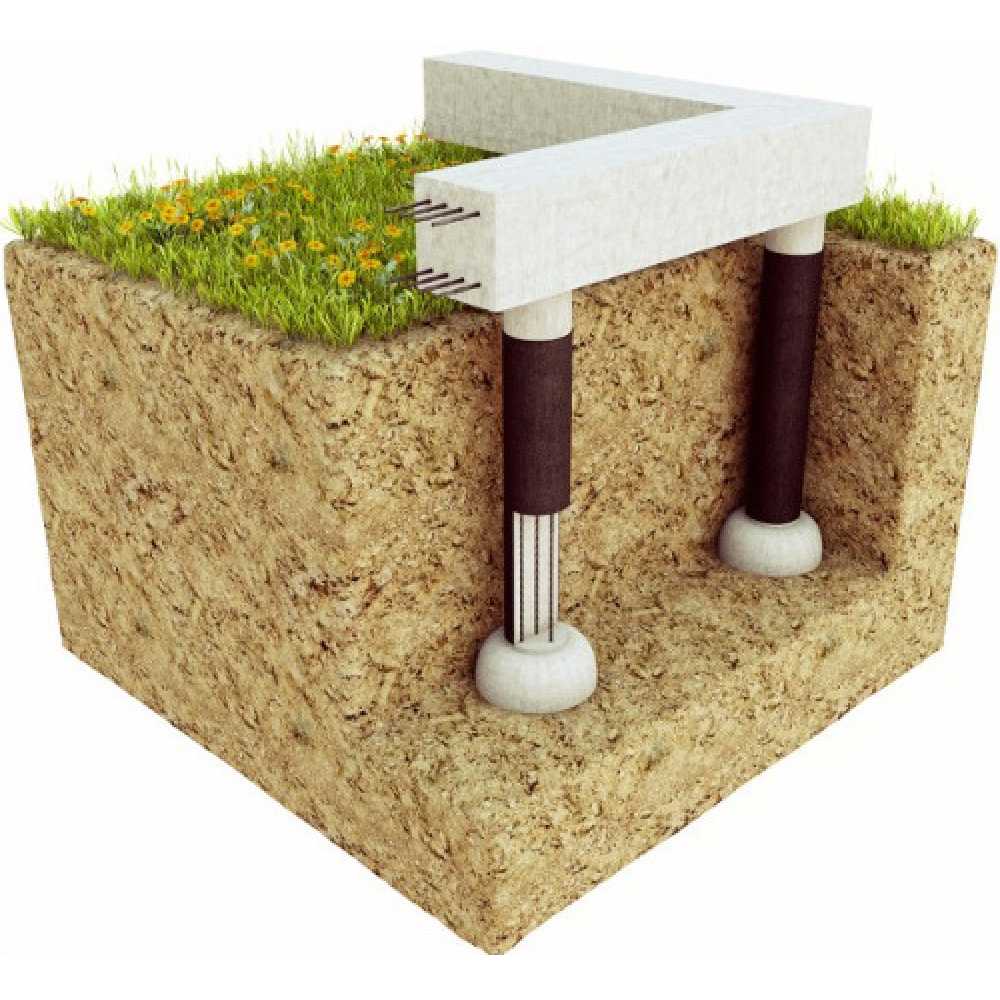
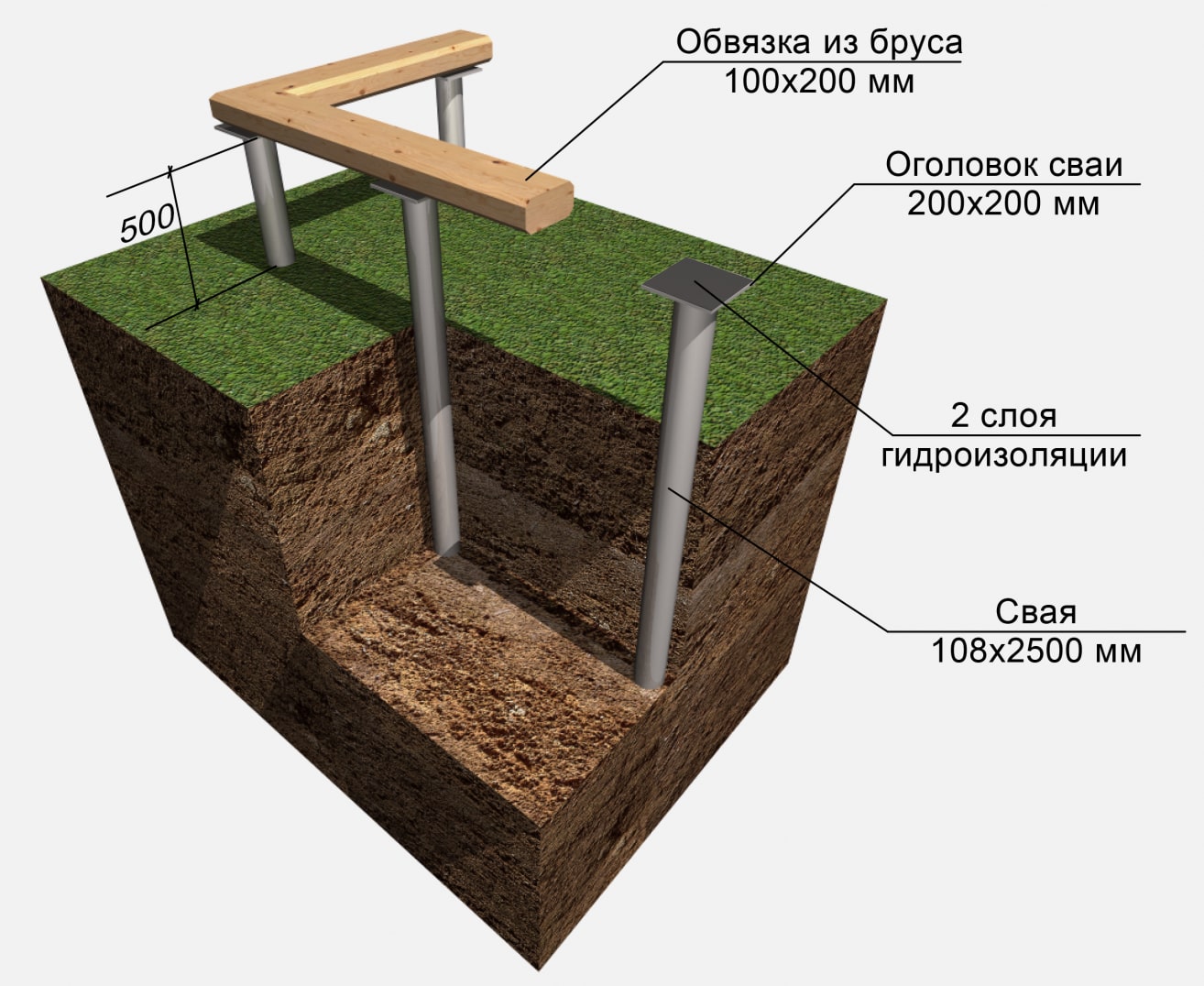
Pile foundation
Most often, this type of foundation is the only possible option for swampy areas. It is suitable even for soils that are eroded to a moist slurry state. In such cases, the piles rest on solid layers of soil at the bottom of the swamp.


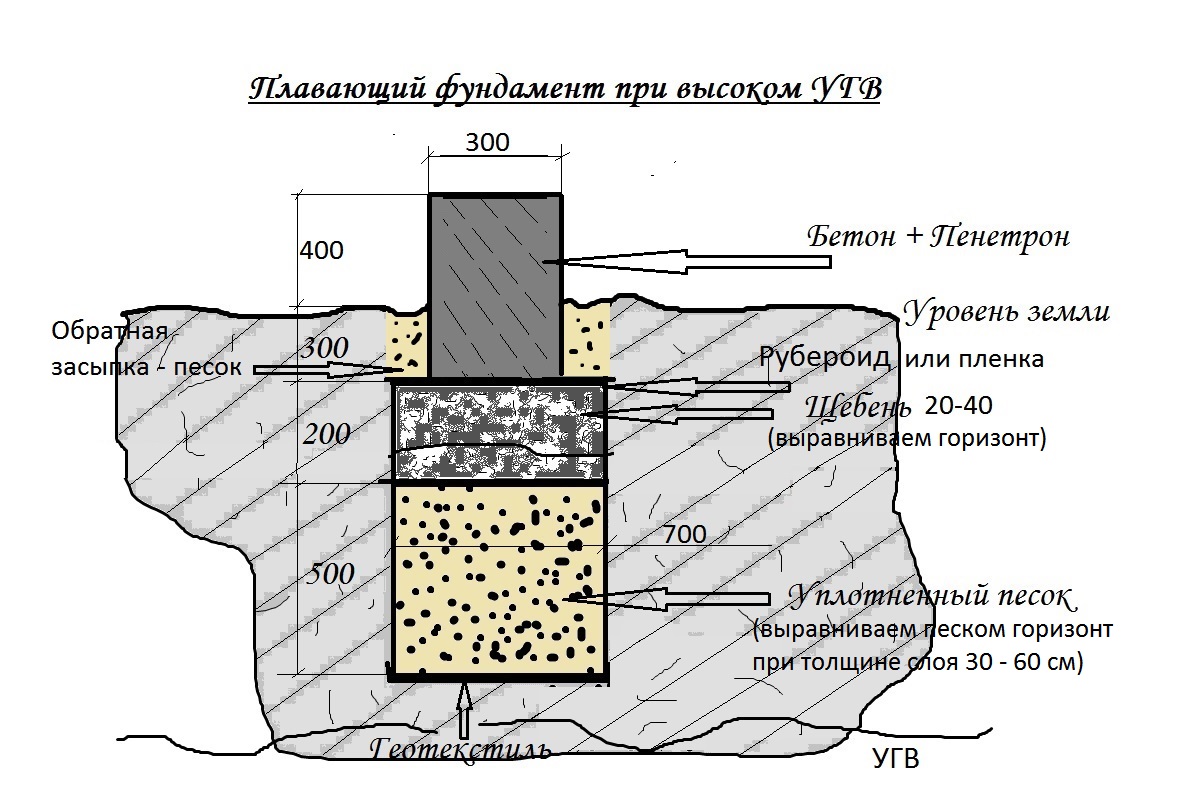
Floating foundation
It is a monolithic slab that is able to change position along with the soil, but not deform. Due to the design features, such a system has another name - slab base.

Preparatory work
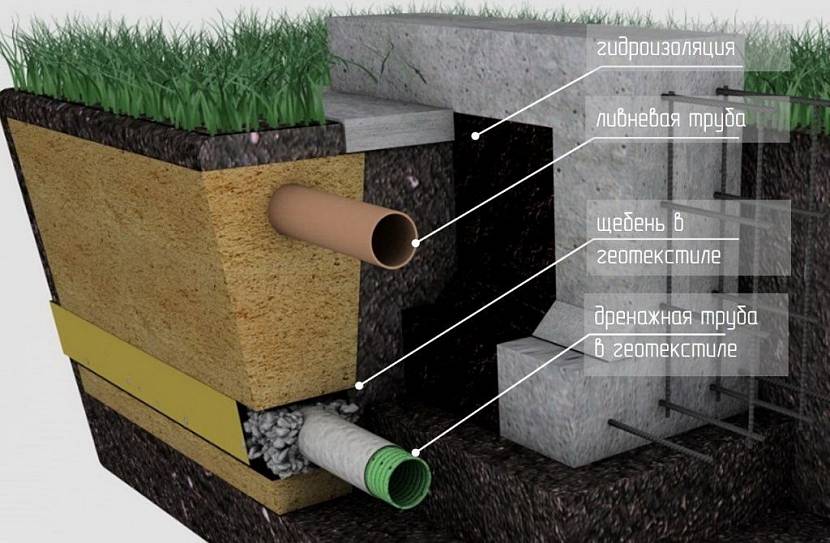
After the removal of excess vegetation, the most important operation at high groundwater levels is to drain the site.
Erection of a foundation in a swampy area is fraught with certain difficulties. The supporting structure must be constructed from elements capable of withstanding increased loads. Such a structure will have a maximum bearing capacity. You can achieve this goal by using the required number of piles.
A properly erected pile foundation under a house in a swamp with a high GWL is able to withstand the load of a brick building. The depth of pile penetration depends on the geological features of the swamp. Preparatory work on the swampy area begins with the cleaning of the site.
For this purpose, trenches are dug with a depth of at least 50 cm, into which special pipes are laid, which ensure the removal of excess moisture, preventing its accumulation. However, before proceeding with the installation of the drainage structure, the topsoil is removed with a thickness of 70-80 cm.
When determining the depth of introduction of screw piles, it is necessary to take into account the following indicators:
- groundwater level;
- freezing depth;
- mobility characteristic of swampy soil.
The features of the soil characteristics make you think about how many piles will be required to create a durable structure. One of these characteristics is the presence of fine-grained elements and the upper peaty layer.
The last thing to do is to calculate the total mass of the building. If you plan to build a building with several floors, then you will have to abandon screw piles and choose bored elements.
Installation procedure
An important point is the decision to use construction equipment. Heavy vehicles will not be able to traverse wetlands and get close to the construction site. Therefore, most (or even all of the work) will have to be done manually. After drainage, it is necessary, in accordance with the construction plan, to mark the site, having well calculated the number of piles to be introduced into the ground.
To build a house, the base of which is a pile-screw foundation, you will need a certain set of tools:
- manual pile driver;
- screw piles;
- shovels;
- level equipped with a spirit level;
- boards for assembling the formwork structure;
- bars for the wooden frame of the sheathing;
- ribbed and smooth reinforcing rods;
- rebar tying tools.
Materials will require sand, gravel (medium fraction crushed stone), cement. After marking and determining the installation locations of the piles, each of them is treated with an anti-corrosion compound. Since swampy soils are oversaturated with moisture and are highly mobile, the depth of penetration of screw piles is determined in strict accordance with the data of geodetic surveys. You need to know at what depth a layer is located that can become a high-quality and reliable support for piles.
 The foundation on stilts for a house in a swampy area is one of the most reliable structures.
The foundation on stilts for a house in a swampy area is one of the most reliable structures.
A mesh is created over the entire area of the site, at the intersection of the lines of which the screw elements will be introduced. Having noted the installation locations of the base components, first dig out a small depression, then begin to screw in the piles. This must be done by constantly monitoring the verticality of each element. The penetration continues until the pile blades reach the supporting solid formation.
The easiest way is to screw in the piles using a special lever, but each builder chooses the most convenient method. The screwing is carried out by two or three people, and one of the workers constantly monitors the verticality of the element. Having reached the required depth, the implementation is stopped and the next support is started. After completing the screwing of the latter, using a level and a tape measure, mark the height of each support. Now you can start creating the grillage.
In more detail, the process on the video:
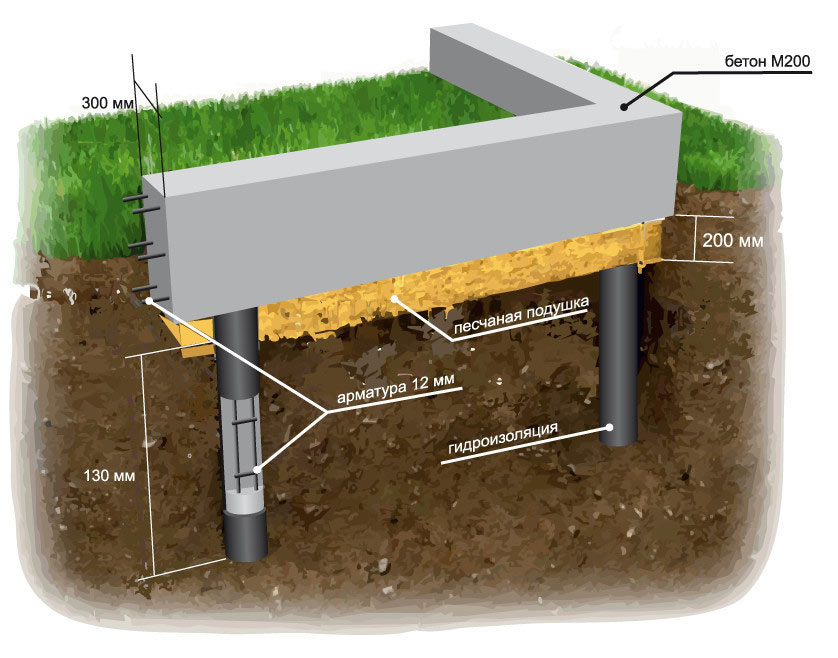
The grillage, which is a concrete cushion, which is poured after the crate is assembled under the bottom of the formwork and the reinforcement cage is assembled, will help to fasten the heads of the supports. After a few weeks, when the concrete has reached its final strength, the formwork can be removed. If it is planned to erect a heavy brick building in a swampy area, then the construction of a pile foundation would be the best solution.
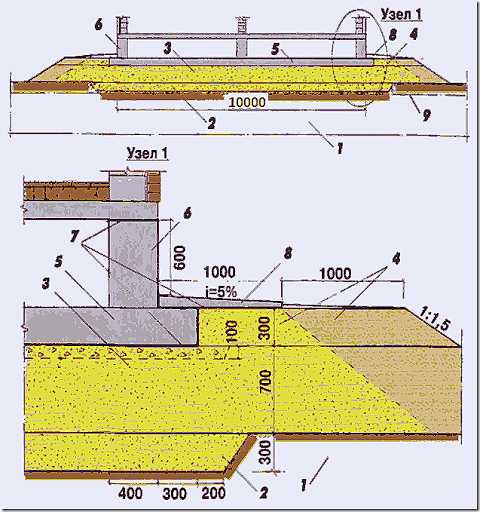
Monolithic tape device
Installation of the strip part of the foundation completely repeats the technology described in SNiP 3.02.01-87. The algorithm for creating a monolithic tape is as follows:
- Plank formwork. The formwork must be carried out for the tape along the entire height, incl. for the shallow part.
- Backfilling of the trench with a gravel-sand mixture with a layer of 10 cm, followed by tamping.
- Laying a waterproofing layer: waterproofing, roofing material.
- Knitting of a reinforcing frame for 4 or 6 rods of corrugated reinforcement A3 with a section of 10-12 mm.
- Connection of the reinforcement cage of the tape with the outlet fittings of the bored supports.
-
Pouring a monolithic tape with a concrete mixture of class B15 ... 17.5 with compaction of each layer in 20-30 cm.
- During the period of concrete hardening, standard care of reinforced concrete products is carried out.
What foundation is right
It is a number of soil shortcomings that make many seriously think - what kind of foundation in a swampy area will best solve all problems? After all, if the foundation was chosen incorrectly, after changing the ground level, the building may simply be destroyed.

An example of a monolithic foundation in a swampy area
In addition, after a few years, the building may simply begin to sink into the ground from its own gravity. Therefore, the solution to this problem should be approached as seriously and responsibly as possible.
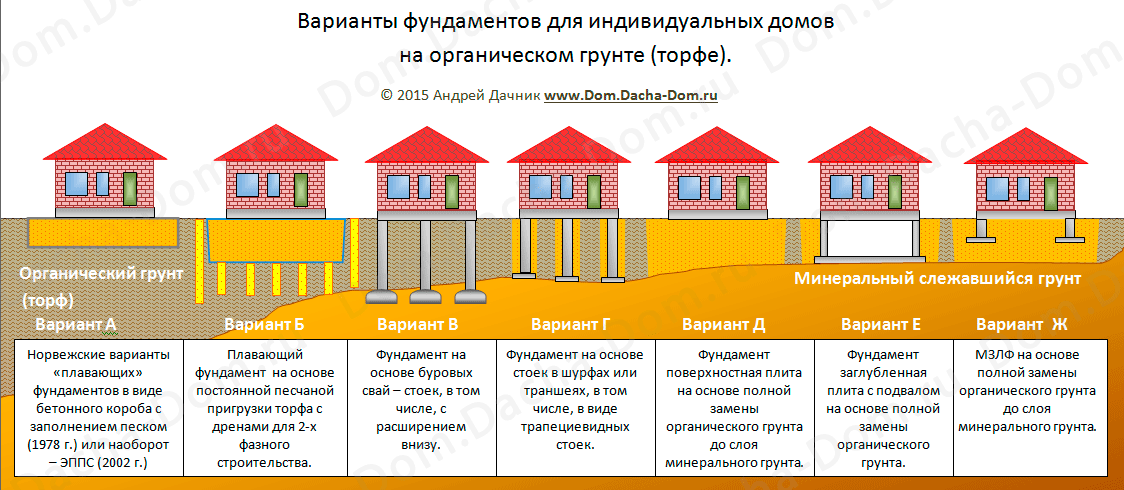
Fortunately, today there are several options for solving this problem. Yes, you can decide for yourself which foundation in the swamp best suits your requirements and financial capabilities.
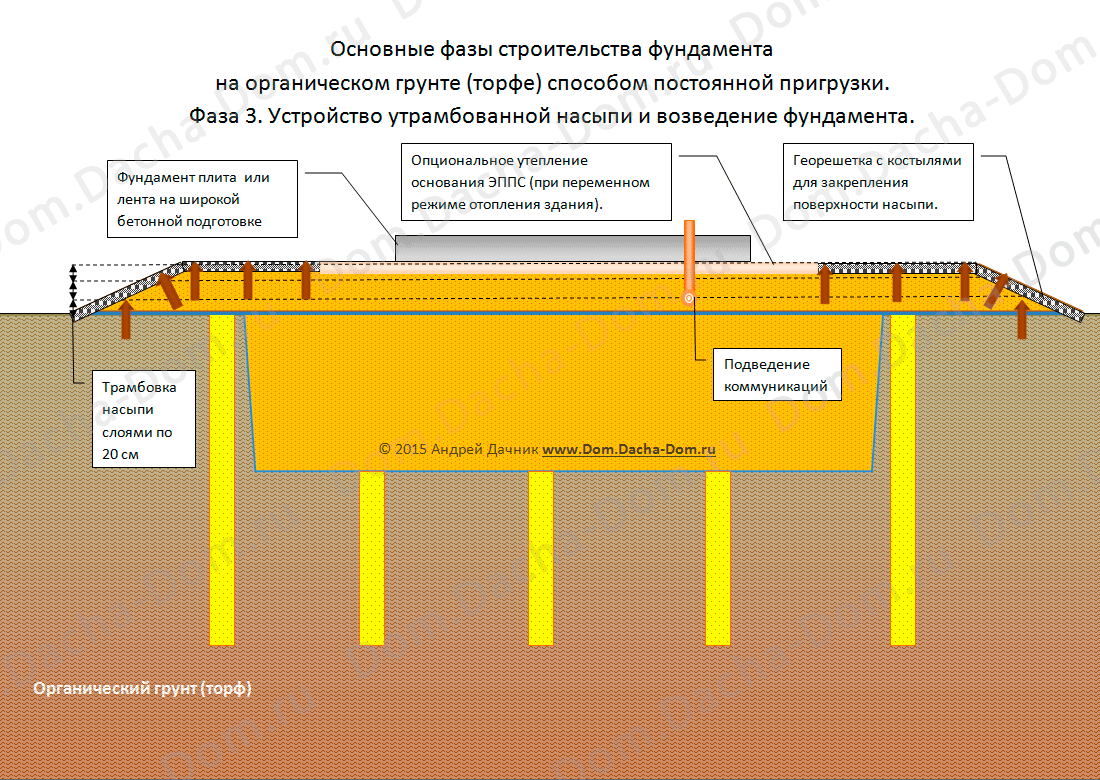
Pile foundation. This is a great solution if you need to complete the foundation in the shortest possible time. The main elements are piles - reinforced concrete or bored. With the help of special equipment, they are laid to a great depth - most often about 10-12 meters, but in areas with especially difficult types of soil, this depth can reach 20 and even 25 meters! Having passed to such a depth, the pile simply pierces the swampy soil layer, resting on a solid foundation.
This makes the foundation and the entire structure of the house completely immune to seasonal fluctuations in soil level - the foundation acts as a support for the piles, the level of which does not change depending on the season or precipitation
It is important that all the work can be done in two to three days. Installation cost is relatively low
Such a foundation can be installed both in summer and winter. Pile foundations in swamps have proven themselves to be reliable, durable and unpretentious, they have collected thousands of positive reviews from different parts of our country.
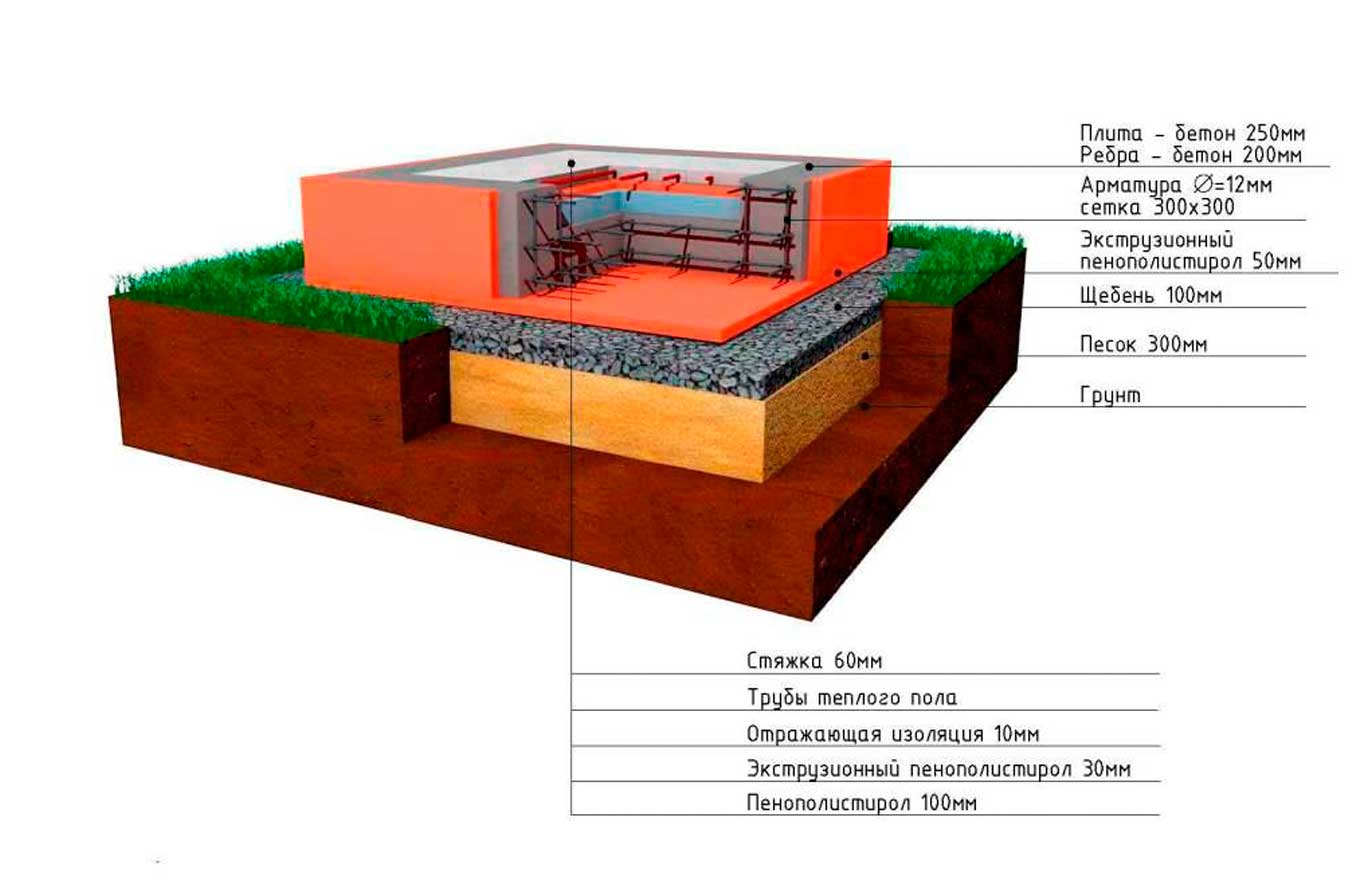
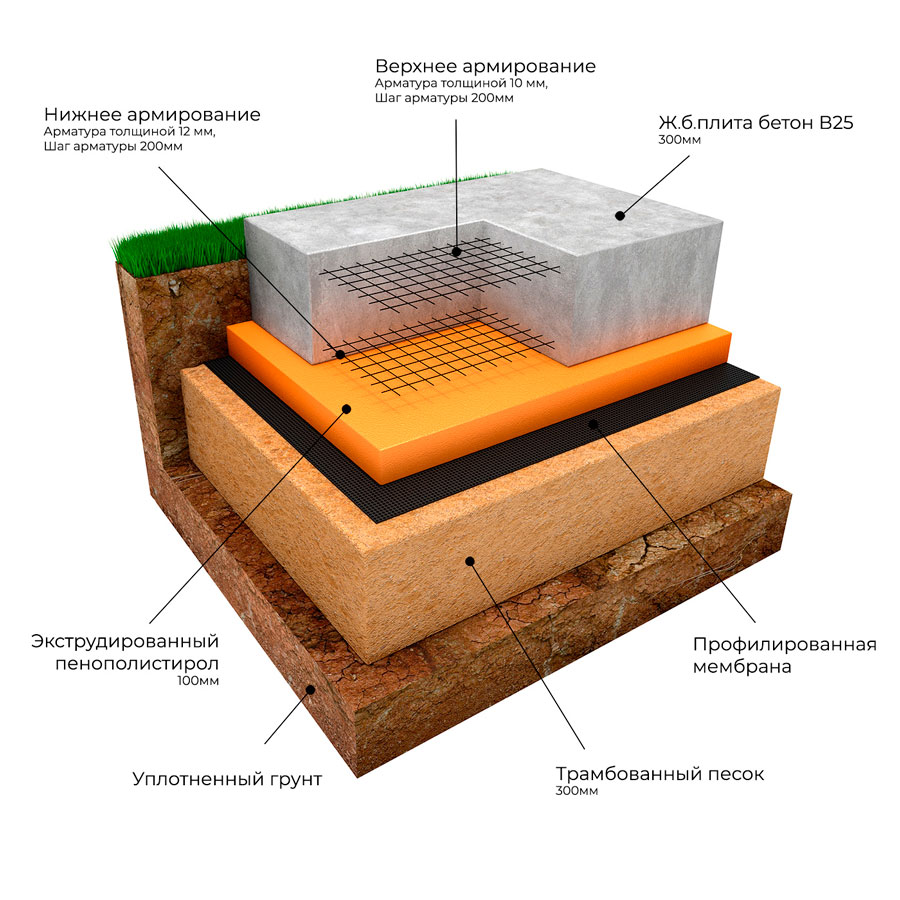
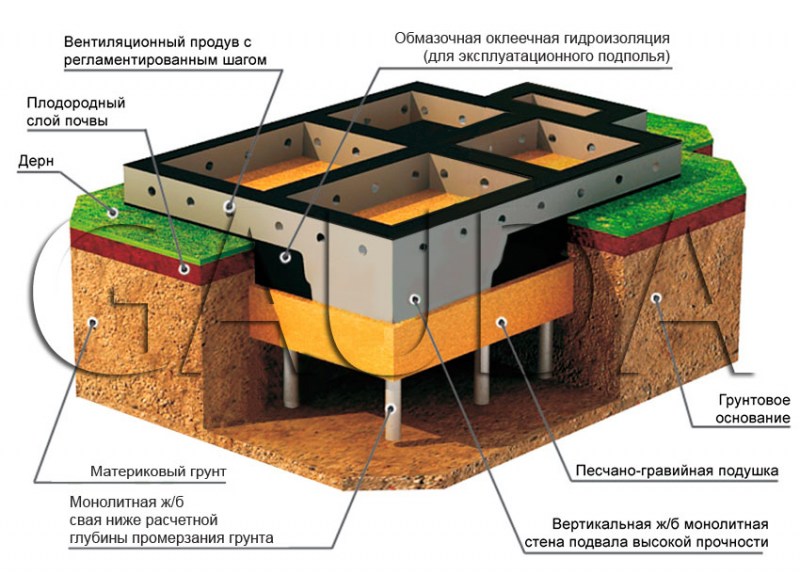
Monolithic foundation. The most expensive and difficult to manufacture. And yet, in the northern, swampy regions of our country, it is a monolithic or slab foundation that is most often used in the construction of private and multi-storey buildings. It is one huge, monolithic slab, buried to the level of freezing of the ground.
Even if the soil around heaves a lot, this in no way affects the reliability and safety of your foundation. The large weight of the slab (tens of tons!) Excludes the possibility of raising the foundation, which could lead to the destruction of the house. High strength allows the monolithic foundation to withstand enormous compressive, bending and tensile loads without harm. Therefore, it is it that is most often used in construction in the swampy regions of our country, despite its high cost.
Shallowly buried foundation. It occupies an average niche between the pile and monolithic foundations, both in terms of cost and construction time. Such a foundation in the swamp has also worked well.
However, it should be borne in mind that a shallow foundation is only suitable for the construction of relatively small houses - one-story wooden or frame houses. The fact is that the relatively small thickness of the foundation does not allow it to withstand significant compressive loads. At the same time, it perfectly resists loads from heaving of the soil. Since it is also monolithic, under heavy loads from the soil, it simply rises or falls slightly, like the whole house built on it. This, together with the low cost and speed of manufacture, makes this type of foundation quite popular in swamps.
As you can see, people who decide to build a house even on problematic, swampy soil have a fairly large selection.However, some of them do not want to spend extra money, preferring to build a foundation in the swamp with their own hands. Is it possible?
What methods are used to prevent the influence of heaving of the soil?
The effect of heaving of the soil is completely surmountable; for this, some construction techniques are used, which will now be listed:
- The base of the concrete foundation is extended, in the form of a trapezoid. In addition to increased stability, the influence of tangential heaving forces on such a foundation is reduced.
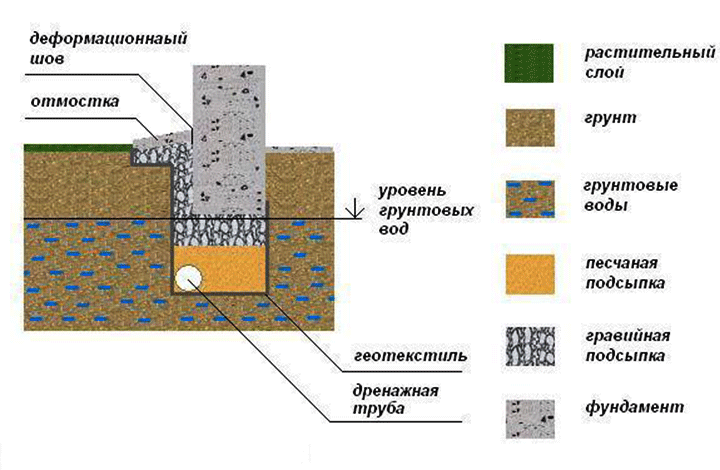
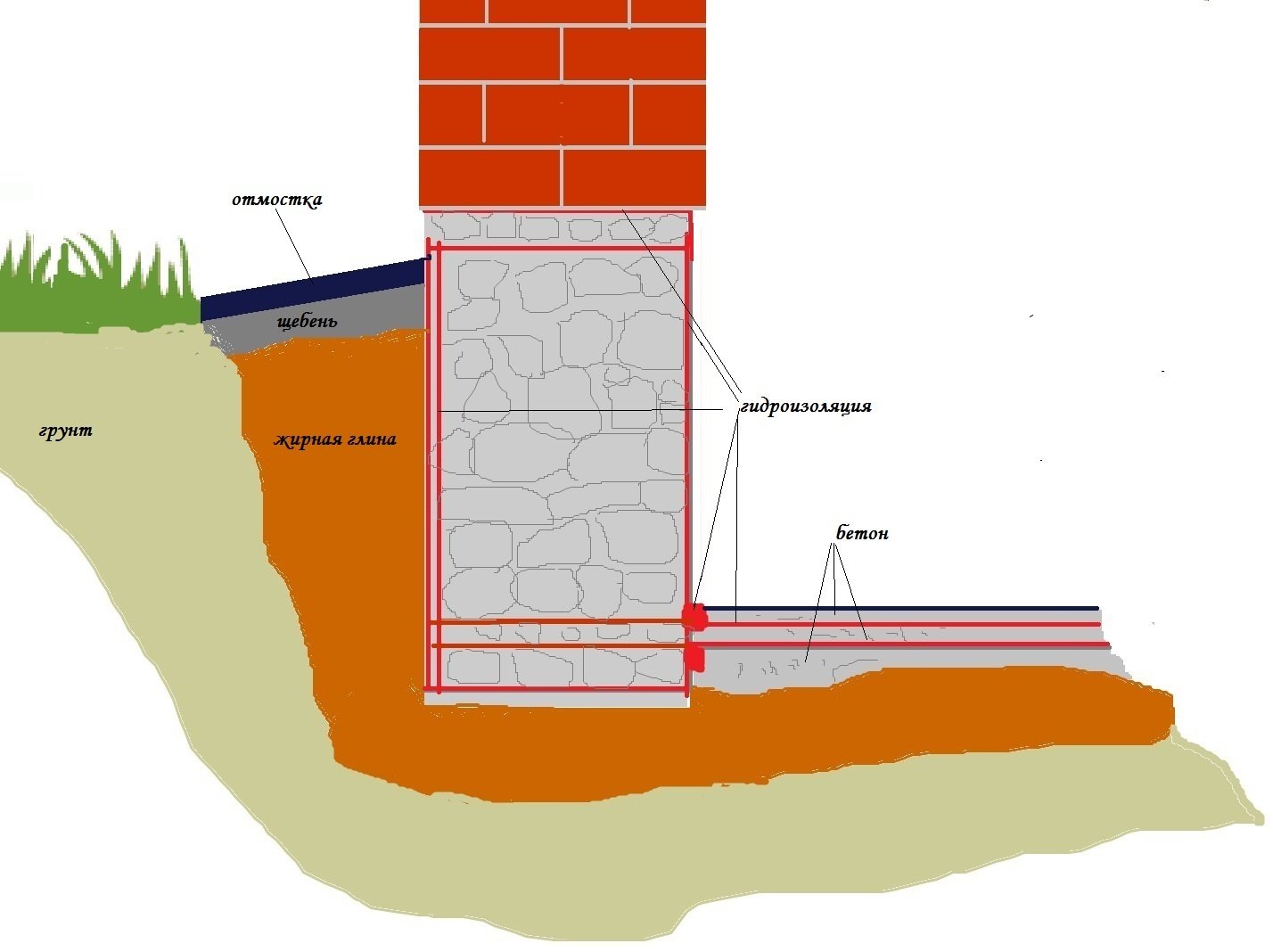
- The walls of the trench, in the case of using a buried and shallow foundation, are lined with waterproofing material. This isolates the foundation walls from the adjacent soil.
- The width of the foundation is increased. Due to this, the heaving of the soil is leveled.
- From the bottom and side of the foundation, the heaving soil is replaced. Sand or gravel backfill is performed.
- Installation of thermal insulation around the outer perimeter of the building. Under the heat-insulating layer, the soil does not freeze in winter, so the heaving of the soil does not appear.
- The foundation is deepened so that it is not affected by the frozen ground. However, this entails an overspending of building materials.
Columnar foundation on heaving soils
The base of the columnar type involves laying the pillars to a depth located below the level of soil freezing.  For this, predominantly reinforced concrete pillars are used. Also, in the form of supports, metal and asbestos-cement pipes filled with concrete mortar can be used. In the lower part of the supports, an anchor element is usually attached in the form of a platform. This guarantees additional stability and fixation of the supports in the soil.
For this, predominantly reinforced concrete pillars are used. Also, in the form of supports, metal and asbestos-cement pipes filled with concrete mortar can be used. In the lower part of the supports, an anchor element is usually attached in the form of a platform. This guarantees additional stability and fixation of the supports in the soil.
The pillars are buried in the ground, after which the formwork is installed and the concrete foundation is poured, connecting all the supports with a concrete tape. Be sure to use metal reinforcement, which is tied with steel wire. The height of the columnar foundation can be different. The concrete tape can run over the soil level, or be buried in it.
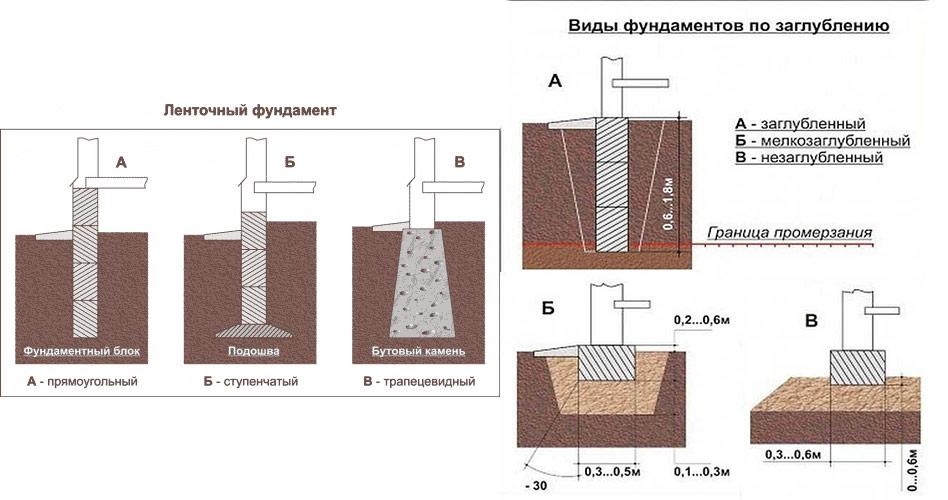
Arrangement of strip foundation
The strip foundation is one of the most popular bases that you can make yourself. The strip foundation on heaving soil has its own characteristics.  It can be shallow (we will talk about it below) or buried. Let's consider the second option. A prerequisite is the location of the concrete fill at a depth exceeding the level of soil freezing for a given area. For different climatic zones, the depth of the base may vary.
It can be shallow (we will talk about it below) or buried. Let's consider the second option. A prerequisite is the location of the concrete fill at a depth exceeding the level of soil freezing for a given area. For different climatic zones, the depth of the base may vary.
A pit is dug, at the bottom of which a layer of rubble is poured, and then a layer of sand about 20 cm thick. This encloses the foundation from below. To neutralize lateral influences from the side of the soil, the walls of the pit are fenced with a layer of waterproofing. In the pit, there are reinforcement segments connected to each other, after which the concrete solution is poured. Above the soil level, pouring is carried out into the prepared formwork.
Pile foundation for heaving soil
For problem soils, a pile foundation is an excellent option. Moreover, regardless of the size and weight of the structure being built. The foundation on heaving pile-type soils consists in screwing metal screw piles into the ground, below the level of soil freezing. Such a foundation is used on sandy, loose, heaving, peat and swampy soils. The piles can be rolled deep enough until they reach solid ground.
A house on a pile foundation can be built almost anywhere, even on a mountainside, without digging.
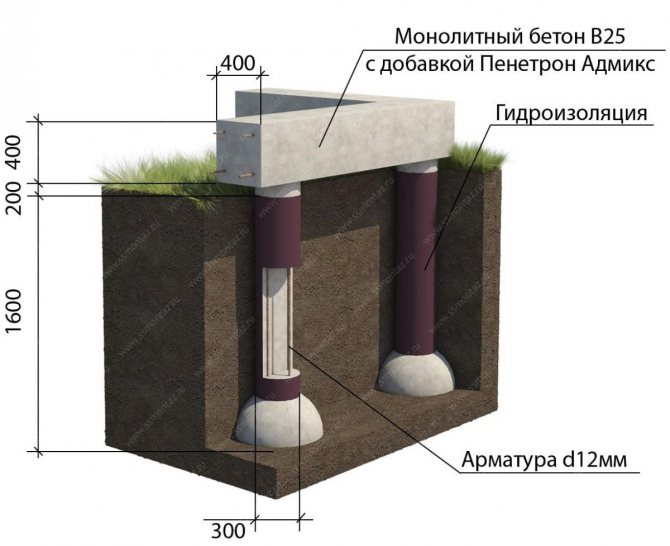
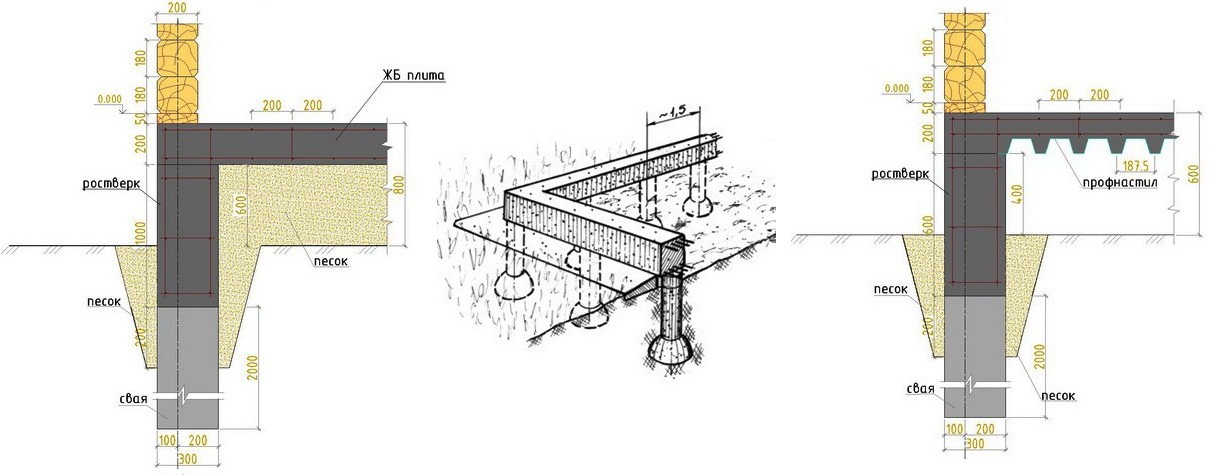
One of the varieties of the pile foundation is the so-called bored foundation. Concrete is used instead of metal piles. In certain places in the soil, holes are drilled into which concrete mortar is poured.All wells are pre-reinforced. The depth of filling depends on the depth of soil freezing. The concrete piles must be at least 30 cm below this level. A reinforced concrete grillage is erected on top of the concrete piles, connecting all the piles into a single structure.
Bookmark technology
 Eskih device of a columnar foundation according to TISE
Eskih device of a columnar foundation according to TISE
For heaving soils, it is preferable to choose pillars with an extension at the bottom, in other cases, structures in the form of a parallelepiped or a cylinder are suitable. There are several ways to lay a columnar foundation.
The first way. Pits are dug under the pillars, which in size exceed the parameters of the pillars by 30-40 cm, then formwork and a frame made of reinforcement are installed in them. Next, concrete is poured. After it has solidified, the formwork is removed, and the pillar is filled up. The technology makes it possible to create monolithic iron pillars of high strength and stability, but it requires a large amount of work.
Second way. A special foundation drill is used - TISE-f, with its help it is possible to make wells with a diameter of up to 20 cm, with an extension at the bottom of up to 60 cm. This is a simpler method that allows you to lay the foundation yourself.
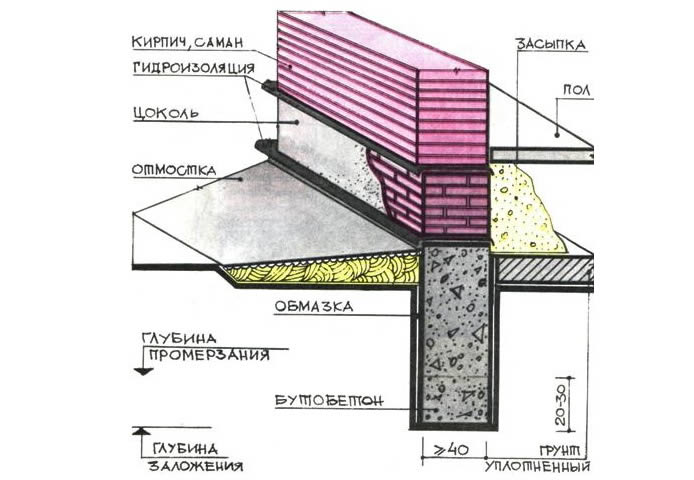
What to look for? At the intersection of the walls (points of greatest loads), under the frame post, pillars are erected at a distance that is a multiple of the step to the beams of the lower strapping (1.5 - 2.5 m). The section of concrete blocks or brick pillars must be at least 50x50 cm
The thickness of the walls with the ball of thermal insulation is up to 25 cm, the floors (except for the basement) are made of wood.
The pillars are mounted vertically, concrete blocks are placed on them. A fence is installed between the posts - a light wall that insulates the subfloor and protects it from moisture. It should be the same along the entire perimeter of the building (usually brick or concrete). The wall thickness is 12 cm, the level of deepening into the soil is 25 cm.If the soil is on clay and very heaving, the pick-up is installed on a sand cushion 20 cm high and 30 cm wide.