Basic installation errors
When performing the reinforcement of the slab foundation, the reinforcement scheme is drawn up in strict accordance with the technologies.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with How to make a foundation from tires for a bath with your own hands: a diagram, video instructions
If the need arises, this scheme can assume an uneven distribution of the rods. The places where the installation of load-bearing interior partitions and columns (punching zones) is planned are subject to additional reinforcement.
The reinforcement is laid in one layer if the thickness of the slab does not exceed fifteen centimeters. In other cases, it is recommended to arrange a reinforcing cage.
Calculations for a slab-pile foundation are performed separately, taking into account the location of the pile supports and the material from which they are made. In each of the cases of slab reinforcement, the drawing is drawn up according to preliminary design data.
Slab parameters
Most often, the reinforcement is laid in two rows, the joint actions of which are provided by vertical rods. The distance between the rods should be equal to the step of the main metal structure. Reinforcement at the ends of the slab is performed with U-shaped clamps, their minimum length is equal to two parameters of the base thickness.
All rows should be covered with a rod strapping in order to ensure the reliability of the perception of torque at the edges of the foundation, and to be able to anchor the ends of the longitudinal rods.
Punching zones
At the support points of vertical structures, bars are laid out with a reduced reinforcement pitch. If the rods are laid out with a step of twenty centimeters across the entire width of the foundation slab, then it is recommended to reduce this distance to ten in the places where the partitions are located. This will prevent the appearance of cracks and punching.
When reinforcing a monolithic foundation, joint strapping of frame elements of slabs and walls should be performed. When concreting the base, it is necessary to leave parts of the vertically placed rods, which later act as connecting links. Such ends are launched into the base, the edges are folded at the level of two dimensions of the slab height, then snapped to the main frame.
To provide the foundation with the necessary properties, to protect it from destruction, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the reinforcement technology. As a rule, inexperienced builders make typical mistakes:
no polyethylene material is pulled over the poured concrete solution. Cement milk flows out, cracks appear on the surface;
- having covered a pillow of sand and gravel, many neglect its compaction. The foundation shrinks, cracks form;
- on the installed formwork, the gaps are not sealed through which the mortar mixture flows, which entails the appearance of irregularities;
- poor insulation of the slab from the soil surface will lead to premature destruction of the foundation base, and restoration work will be quite expensive;
- it is a mistake to use stones as spacers;
- reinforcing bars during installation work are fixed in the soil layer, the metal corrodes and quickly collapses;
- in front of the foundation, a cushion of sand and crushed stone is not poured, from which the strength indicator of the slab decreases. Another characteristic mistake is that only crushed stone is used for the device of the pillow, and after all, the minimum percentage of sand in the pillow under the foundation slab before reinforcing it should be within forty;
- the spacing of the grid rods exceeds the permissible maximum limit of forty centimeters, or does not at all correspond to the calculated data on loading effects;
- from the side of the reinforcing ends there is no protective layer of concrete mortar, and the metal corrodes ahead of time;
- there are no vertical reinforcing bars under the walls and columns, and the load forces are unevenly distributed.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the Foundation for a frame bath with your own hands
These are the most serious mistakes that can clearly have a negative impact on the performance of the foundation. There are also more non-obvious features that only experienced specialists can tell about.
Materials (edit)
Reinforcement is the reinforcement of a concrete block from the inside using various materials. Bars or fibers can be used that prevent the block from cracking when the block is stretched.
In practice, reinforcement materials can be divided into 3 groups:
- metal rods,
- composite reinforcement,
- fiber.
Steel bars
The standard length of a steel bar for reinforcing concrete structures is 11.75 m. The reinforcement can have different diameters and brands. Depending on the marking, the rods in the reinforcing frame are connected by welding or knitted with wire.
In the mass of concrete, the connection of steel rods with mortar is quite strong due to the corrugation on the rod. The steel frame inside the monolith redistributes the loads and keeps the concrete from cracking, since the metal has a higher tensile strength. In this case, concrete, in turn, protects the metal from corrosion.
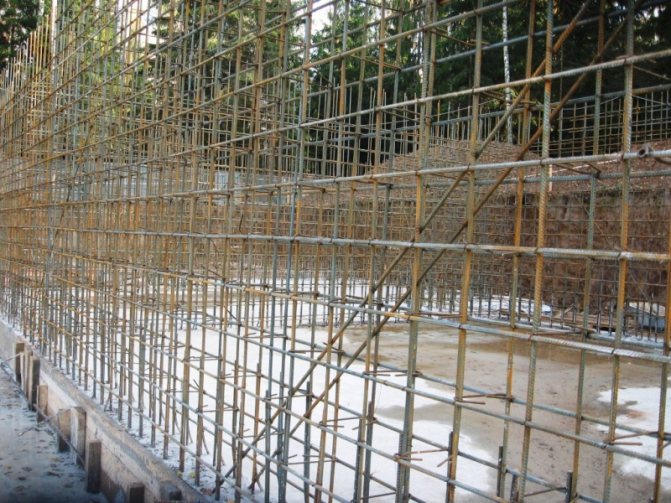

Steel reinforcing frame
Composite material
Such fittings have a fairly wide range of raw materials, which is increasing almost every year. At the moment, fiberglass and basalt-plastic rods with a spiral wrap, imitating the periodicity of the profile of steel reinforcement, are more or less used.
In addition, polyethylene terephthalate and hydrocarbon fittings, which have not yet gained wide popularity, are presented on the construction market. The indisputable advantage of the composite is its low weight. But when constructing foundations or retaining walls, this advantage is of little importance, but the strength characteristics are very important.
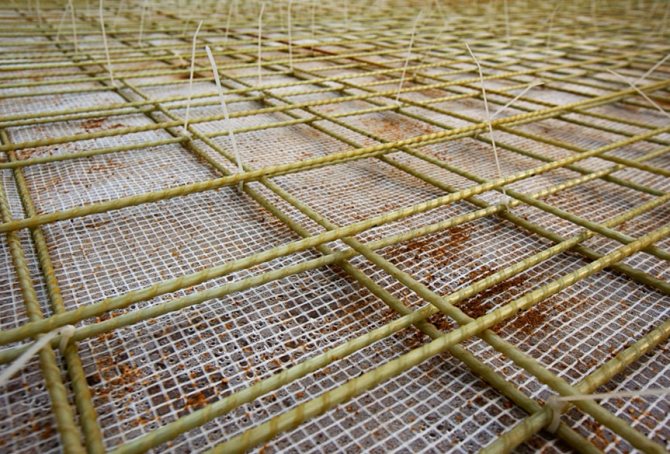

Composite reinforcement is usually used in horizontal structural elements supported on the ground
Fiberglass
Finely dispersed material (fiber) is added to the solution at the kneading stage. In this case, the fiber itself can have a different diameter and length.
Fiber is made from fiber based on:
- become,
- glass,
- polypropylene compounds,
- basalt.
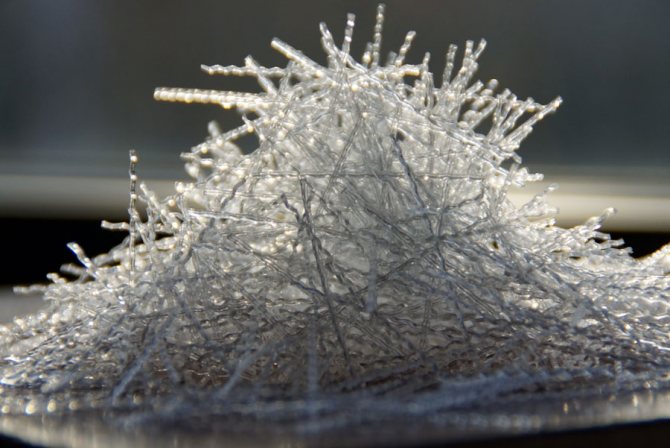

Fiber reinforcement for tensile strength of concrete
How to avoid mistakes when creating a reinforcing frame
Mistakes can be made at any stage of construction; foundation reinforcement is no exception in this case. Even the slightest flaws can contribute to the destruction of the slab base or complicate the concreting process. Therefore, it is necessary to know in more detail what mistakes are made at the reinforcement stage in order to completely avoid them or minimize them.
- The most important mistake when reinforcing a foundation slab can be called incorrect calculations of the expected load on the foundation or their absence. Indeed, on the basis of these data, the dimensions of the reinforcing rods are selected, the layout of the reinforcement is determined.
- The reinforcement rods are joined end-to-end. This method cannot guarantee the strength of the structure, therefore it is recommended to overlap the elements, the length should be at least 15 diameters.
- In the process of laying the reinforcing frame, the rods are located in close proximity to the soil or are stuck into it. As a result of heaving or movement of the soil, the reinforcement cuts into the soil, which leads to the formation of corrosion on the rods. This phenomenon reduces the strength of the frame and the entire base.
- Failure to comply with the rules for the location of the rods can also cause the destruction of the plate. The recommended distance between the rods should be no more than 40 cm, and in some situations this parameter is reduced to 20 cm.
- If the ends of the reinforcement do not have a protective coating, then under the influence of moisture from the concrete solution, corrosion of the elements can form.
- Correct reinforcement under the load-bearing walls and in the corners of the structure is of great importance.
- The installation of the frame is carried out not on clamps, but on wooden blocks or other non-standard elements. They not only violate the integrity of the concrete, but also contribute to the penetration of moisture to the metal elements.

Reinforcement of the foundation slab
Reinforcement of the foundation slab is a very important and difficult stage. But subject to the rules and accurate calculations, you can independently carry out this process.
Advantages and disadvantages of monolithic frame technology
Monolithic reinforced walls have the following advantages:
- one-piece construction without seams is durable and reliable, it does not blow through, temperature bridges are not formed;
- smooth flat surface allows you to start finishing work without preliminary preparation;
- construction of the building in a short time;
- monolithic houses have a free layout;
- increased service life of reinforced concrete structures;
- complex architectural curvilinear elements and arches are easy enough.

Disadvantages of monolithic walls:
- low sound insulation;
- compulsory wall insulation;
- the ability of concrete to conduct vibrations.
Reinforcement rules for slab foundation
The basic requirements for a monolithic slab are given in 52-101-2003. They have recommendations for the location and knitting of reinforcing meshes, which supports to use to provide the bottom protective layer. The use of rods with flaking rust is not allowed.
Bars of periodic section provide high adhesion, knitting wire is more reliable than plastic clamps. However, reinforcement should be started in stages: the choice of a rational scheme, the calculation of the cross-section of the bars, the fixation of the frames in space with the help of special elements.
Reinforcement schemes
In the recommendations of SP 63.13330 for reinforced concrete structures, there is a special section for the manufacture of the main supporting structures (10.4). In particular, for a slab foundation, the following requirements are indicated:
- reinforcement is laid in two directions (mesh with a cell of 30 x 30 cm maximum), connected by wire knitting or welding;
- the nets are placed as close as possible to the upper and lower edges, taking into account the protective layer of 3 cm;
- With U-shaped clamps, the mesh rods are tied together at the ends;
- in places where monolithic walls and columns are installed, vertical rods are released or anchored with hooks to strengthen the slab;
- under load-bearing walls, the cell pitch decreases in comparison with the rest of the slab;
- it is allowed to discharge the mesh cell in the central part to the minimum allowable percentage of reinforcement (0.3%).
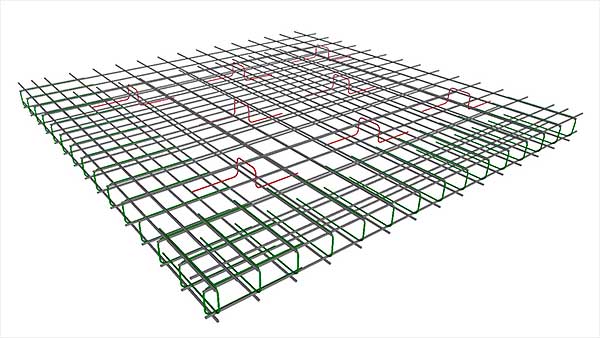
It is possible to correctly position the grids taking into account the side protective layers (at least 4 cm between the bar and the formwork), the location of the communication entry points (relevant for non-buried slabs).
In practice, for low-rise cottages, the following scheme is used:
- mesh of 8 mm reinforcement in the top layer;
- a similar mesh in the lower layer;
- reinforcement of the ribs of the USP or a smooth slab (thickness 30 cm and more) with frames along the perimeter of 10 - 14 mm rods of periodic cross-section.
This is due to the lack of heaving forces when using a warm blind area, ring drainage around the foundation, replacing the soil with non-metallic materials to a depth of 40 cm.The recommended cell size in the discharged part is not more than 1.5 of the slab thickness, under the walls 10 x 10 - 20 x 20 cm In the absence of a foundation, the lower protective layer increases to 5 - 7 cm.
Openings
In non-recessed slabs, it is impossible to do without openings in a monolithic structure for entering engineering systems.This issue is very poorly described in the special literature. An individual developer should be guided by the design guidelines for reinforced concrete buildings:
- cutting holes in welded meshes with upward bending of the rods;
- bordering of openings more than 30 cm diagonally located to the mesh cells with rods of 10 - 14 mm;
- reinforcement of the perimeter of holes less than 15 cm is not required.
In deep slabs, communication input nodes are absent by default. To increase the maintainability of engineering systems, the sewerage and water supply systems are run through the walls of the basement.
Plate / tape interface
It is possible to correctly mount the reinforcement rods in the formwork of a recessed slab foundation with a basement, taking into account the conditions:
- it is forbidden to place walls on a recessed slab close to its edges, the minimum indent along the perimeter is equal to the thickness of the foundation tape (from 10 to 40 cm);
- the anchorage scheme for the tape mating unit and the monolithic basement wall has several options.

Reinforcement outlets in the slab under the walls.
For example, a U-shaped clamp can be released up from the plate, the distance between the rods of which corresponds to the size of the tape frame, in order to subsequently tie the two structures. In addition, you can tie rods bent at right angles to the lower and upper grid of the slab, and release them 40-60 cm outward similarly to the previous version.
If the project does not have a rigid connection between the tape and the wall with a deep slab, in these places the meshes are reinforced with U-shaped clamps to avoid punching.
Basic installation errors
To provide the foundation with the necessary properties, to protect it from destruction, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the reinforcement technology. As a rule, inexperienced builders make typical mistakes:
no polyethylene material is pulled over the poured concrete solution. Cement milk flows out, cracks appear on the surface;
- having covered a pillow of sand and gravel, many neglect its compaction. The foundation shrinks, cracks form;
- on the installed formwork, the gaps are not sealed through which the mortar mixture flows, which entails the appearance of irregularities;
- poor insulation of the slab from the soil surface will lead to premature destruction of the foundation base, and restoration work will be quite expensive;
- it is a mistake to use stones as spacers;
- reinforcing bars during installation work are fixed in the soil layer, the metal corrodes and quickly collapses;
- in front of the foundation, a cushion of sand and crushed stone is not poured, from which the strength indicator of the slab decreases. Another characteristic mistake is that only crushed stone is used for the device of the pillow, and after all, the minimum percentage of sand in the pillow under the foundation slab before reinforcing it should be within forty;
- the spacing of the grid rods exceeds the permissible maximum limit of forty centimeters, or does not at all correspond to the calculated data on loading effects;
- from the side of the reinforcing ends there is no protective layer of concrete mortar, and the metal corrodes ahead of time;
- there are no vertical reinforcing bars under the walls and columns, and the load forces are unevenly distributed.
These are the most serious mistakes that can clearly have a negative impact on the performance of the foundation. There are also more non-obvious features that only experienced specialists can tell about.
Choice of fittings
Three types of fittings are used for construction work:
- Reinforcement with a smooth surface (A240), used for reinforcement in the vertical plane. Not recommended for reinforcing monolithic slabs;
- Grade A300 (diameter within 10-12 mm). The surface of the bars is covered with annular notches;
- Brand A400. The rods have a sickle-shaped profile.Due to its larger working diameter, it is best suited for slab reinforcement.
Before reinforcing a monolithic foundation, it is necessary to calculate the optimal size of the cross-section of the bars. The reinforcement mesh consists of two layers, the elements of which are located at right angles to each other. The lower and upper row are connected by means of vertical clamps. Knowing the cross-section of the concrete slab, you can calculate the size of the cross-section of the reinforcing mesh bars passing in one direction: it should be about 0.3% of the total area of the monolithic slab.
If the width of one side of the foundation is less than 3 meters, the minimum diameter of one bar is 10 mm. For more massive slabs, it is often sufficient to use reinforcement with a diameter of 12 mm. The maximum bar diameter for the slab is 40 mm.
Common mistakes in reinforcement
There are frequent cases of errors leading to a violation of technology and a reduction in operating time. These include:
- there is no polyethylene protective film on the surface of the erected monolithic slab (due to the outflow of water when the concrete hardens, the base surface dries out unnecessarily, due to which cracks are formed);
- prepared sand and gravel substrate is not compacted (distortions and cracks);
- during the formation of the formwork system, cracks are not closed, which leads to the outflow of the concrete mixture and a reduction in the optimal level of water in the solution;
- there is no waterproofing on top of the equipped substrate (lowering the water level in the poured solution);
- reinforcement rods are placed directly into the ground (corrosion of the material occurs as soon as possible, violating the integrity of the structure and the meaning of performing the reinforcement of the base);
- non-observance of recommendations on the dimensions of fractions of reinforced frames (voids are formed);
- when arranging column elements, the reinforced frames are not fastened to the rods of the columns, which leads to an uneven distribution of loads on the erected foundation;
- lack of a protective layer (premature corrosion of metal elements).
Watch a video on how to avoid mistakes when laying reinforcement and further pouring the base.
Excavation
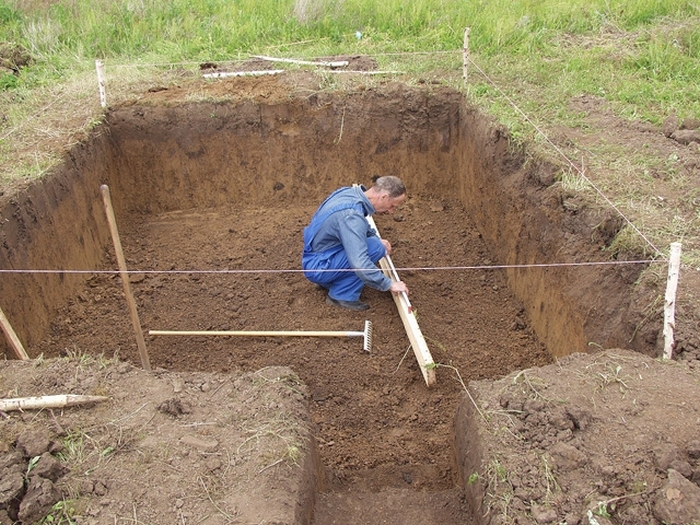 The soil is marked according to the design standards, increasing its perimeter by 50 cm on each side for the device of the drainage system
The soil is marked according to the design standards, increasing its perimeter by 50 cm on each side for the device of the drainage system
- The soil is laid out according to the design standards, increasing its perimeter by 50 cm on each side for the device of the drainage system. It should be remembered that the slab itself should protrude from the walls of the future house by 10 cm on each side.
- Stakes are driven into the ground and a marking cord is pulled. The axis of the future slab should also be drawn.
- The soil is taken out of the pit to a depth of 60 cm. At the same time, it is worth carefully monitoring the quality of the soil taken out. If an early digging of soil is observed on a building site, then the loosened earth must be removed layer by layer until you reach the layers untouched by the shovel. Here, according to the instructions, you will have to remove the layers of soil around the entire perimeter of the pit in order to completely level it. After that, the bottom of the pit is rammed and covered with sand to the design level of the pit. If this is not done and the foundation is mounted on soft soil, then the force of the house's pressure on the slab will simply break it over time in the place of the loose soil.
- Around the design area of the base, a drainage system is laid in the form of special perforated pipes with their slope towards a storage well or a central storm drain.
- Then a layer of crushed stone with a thickness of 20 cm should be laid and carefully tamped according to the principle of laying a sand cushion.
- Now we are assembling the formwork from high-quality wooden panels. Their height should be at least 40 cm. It is advisable to clean the inner walls of the formwork. The formwork is fastened with bolts, screws or self-tapping screws. On the outside, the timber frame can be propped up with wedges for greater stability.
What is the need for reinforcement?
In order to increase the strength of concrete and reduce its amount, reinforcement is used. In theory, any material can act as reinforcement. But in practice, steel and composite are most often used.
A composite is a complex of materials. The base can be basalt or carbon fibers, which are filled with polymer. These fittings are lightweight and non-corrosive.
Steel, in comparison with composite, has a much greater strength and relatively low cost. In the process of reinforcing monolithic walls, channels, corners, I-beams, corrugated and smooth rods are used. In the case of creating complex building structures, metal meshes are used for reinforcement.
The fittings come in different shapes. But most often on sale you can find a pivot. In the construction of low-rise buildings, corrugated rods are usually used. They have a low price and excellent adhesion to concrete, which makes them very popular with buyers. Steel rods that are used in the construction of monolithic structures usually have a diameter in the range of 12-16 mm.
What reinforcement is needed for a slab foundation
Any bar used in the foundation frame must comply with the requirements of GOST 5781 of 1982. However, reinforcement, like most structural materials, has a classification:
- AIII - corresponds to the A400 and A500 markings, has a variable cross-section, popularly referred to as "corrugated";
- AII - corresponds to the current class A300, the cross-section is periodic, discharged;
- AI - new marking A240, smooth profile.

For the foundation, reinforcement A400 (AIII) is used, it has a crescent-shaped profile.
On sale, you most often find rods of the A500C class (for welded meshes, frames) or A500. Armature with a C index at the end is suitable for welding and knitting, without an index - only for knitting.
We recommend reading in more detail: What reinforcement is needed for the foundation.
Due to the complexity of the calculations and the small dimensions of buildings in low-rise construction, a simplified scheme is recommended. Two nets at a distance of 10 cm vertically with at least the same cells. If the developer wants to save on pouring the slab, the calculation should be ordered by specialists who will calculate the minimum required reinforcement, use thin reinforcement in the center of the foundation, strengthen the perimeter, the places where the internal walls pass.
If the dimensions of the foundation are more than 3 m on either side of the slab, it is recommended to use rods of at least 12 mm. To determine the minimum possible cross-section, the following method is used:
- calculation of the section of the slab - the length multiplied by the thickness (for example, 6 mx 0.3 m);
- calculation of the minimum allowable bar area in the section - the previous figure is divided by the minimum reinforcement percentage (0.3% for B20 concrete, 0.15% for B22.5 grade, 0.1% for B15 grade), for this example 1.8 m2 / 0 , 15 = 27 cm²;
- calculation of the area of reinforcement in each row - the result is divided in half (in the example 27/2 = 13.5 cm²);
- determination of the minimum allowable bar section depending on the grid spacing (13.5 cm² / 31 bars every 20 cm for a 6 m long slab = 0.42 cm²;
GOST 5781 contains a table of assortments with cross-sections of reinforcement of different diameters. For example, for bar diameters of 14 mm, 12 mm, 10 mm, this value will be 1.54 cm², 1.13 cm², 0.785 cm², respectively. Thus, even 10 mm reinforcement provides twice the reinforcement percentage compared to the minimum. Knitting is done in the building spot after the layout is in order.

Rebar laying template.
Then it is necessary to correctly calculate the total amount of the assortment of rolled metal of each diameter. The rods are sold 11.7 m in length, the overlap for longitudinal anchoring is 40 rebar diameters. The length of the workpiece for each U-shaped clamp is equal to 5 dimensions of the plate thickness, their number coincides with the total number of longitudinal, transverse bars in one mesh.It is possible to recalculate the length in kilograms using tables from the same GOST, however, there are similar translation tables in every construction market.
The upper mesh is laid on supports, the most popular in private construction are:
- spider - U-shaped clamp with legs bent in opposite directions;
- supporting frame - a lattice curved at a right angle.
The length of each of them is calculated individually, taking into account 2 pcs / m².

A spider made of reinforcement with a diameter of 8 mm, such elements must be made in advance for laying the upper mesh.
Reinforcement and pouring order
Formwork device
Reinforcement of floors begins with the installation of the formwork. The following requirements are imposed on the formwork: it must withstand the weight of the green mixture, while not visually deforming. This is a rather large load, with a concrete layer of 200 mm it will amount to 500 kg per square meter. Therefore, the formwork structure must be quite impressive. For panels, you can use plywood with a thickness of 18 ... 20 mm, for beams, racks, crossbars, use a beam with a section of 100x100 mm.
You can use professional formwork. Its advantages are that it is designed for high loads, it includes telescopic racks that can withstand significant weight and allow you to adjust the level. This is a rather expensive piece of equipment, but now you can find a company that rents out both formwork and racks.
The formwork assembly scheme is easy to find in the literature, and if you take a professional formwork, then instructions are attached to it. The main thing is to check the horizontal position after assembly using a level or other available means.
Installation of fittings
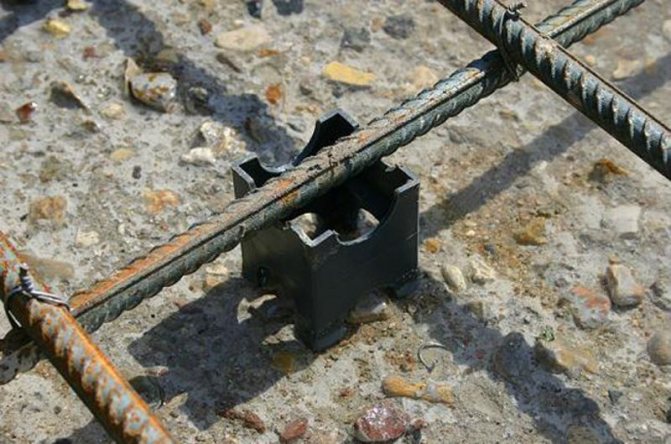

Plastic clips are required to create a cover for the reinforcement at the bottom of the slab.
The reinforcement is done in this way: the bottom row is laid on the clips - special plastic supports 25-30 mm high to create a protective layer. We put the rods with the same pitch, parallel to each other. We put the next row on them at an angle of 90? and tie with knitting wire at each intersection. Then we set the grid dividers, bend them, tie them with the same pitch. The drawing given here will tell you which one. The reinforcement of the slab along the edges is supplemented with reinforcements. Longitudinal and then transverse reinforcement bars are laid on dividers and U-shaped reinforcements. The upper level of the finished reinforcement should be 25-30 mm below the upper plane of the formwork. The assembled reinforcement should be a fairly rigid frame that can withstand the weight of a person without any special deformations.
Fill
After the reinforcement is completed, you can start pouring. This work is best done with a concrete pump, be sure to compact the mixture with a special deep vibrator. It is advisable to fill it in one go. When hardened, the concrete shrinks. The faster it dries, the more shrinkage, which can lead to the appearance of microcracks. To prevent this from happening, you need to wet the surface of the hardening slab with water for 2-3 days. This is best done by spraying. But even on a rainy day, pouring is not worth it, it is recommended to protect the fresh mixture from precipitation. The slab must dry for 30 days, only after that the formwork can be removed.
General recommendations for reinforcement
In order to carry out high-quality reinforcement of a concrete structure, general rules should be followed, taking into account the construction technology and the properties of the materials involved. In private construction, they are often neglected, dispensing with accurate calculations and drawing up a working project, since one- and two-story houses do not put serious stress on the foundation. The reinforcement is laid according to the schemes already used earlier, which saves time.In such cases, it is enough to comply with the minimum requirements specified in SNiP.
A monolithic reinforced foundation has a sufficient level of strength for the construction of multi-storey structures. True, to create the basis for a high-rise building, a more complex technology is used, which involves the use of several types of reinforcement, accurate calculations of the dimensions of the slab and the characteristics of the soil.
Laying reinforcement in the pit
Many owners prefer to carry out all reinforcement work directly in the prepared pit. This is certainly advisable if you look at it from the point of view of saving time. So you do not have to transfer the prepared structure from the reinforcement from the place of work and lay it in the foundation.
But such operations often damage the rammed pad and waterproofing of the base itself, allowing moisture from the soil to gradually destroy the entire foundation of the structure.

It is better to lay the prepared lower belt with the connected props into the pit, and there, already in place, make a one-piece frame, tying the upper ends of the props and the outer reinforcement belt.
In this case, before laying the lower belt, it is worth completing the sides of the pit with formwork so that the reinforcement is immediately performed firmly. And the metal frame of such a foundation will not require additional modifications in the form of alignment or displacement.
Rules for laying frames
Having finished with the formation of reinforcing cages, you should clean the place of laying of third-party debris and install a metal structure along the marked lines.
The presented procedure is performed without the help of special equipment, since the total weight of finished reinforced products rarely exceeds 100-150 kg.
 The size of the squares of the lattice varies according to the weight of the building.
The size of the squares of the lattice varies according to the weight of the building.
During implementation, it is important to keep track of the following features:
- In no case should the reinforcing bars touch the erected formwork.
- The optimal sizes of fractions (cells) are 25-30 cm.With a significant weight of the structure and arrangement on soft soils, it is advisable to reduce the dimensions of the cells to values of 10-15 cm.However, in this case, you should not be too zealous and reduce the size of fractions to 5 cm, since the penetrating power of concrete can be compromised, leading to the formation of air pockets and voids.
- The need to place reinforcing cages at a distance of 5-7 cm from the boundaries of the pour.
