Types of foundations
The basis for the construction of buildings is formed taking into account the load, types of soil, structure. Depending on the type of foundation and its volume, the calculation of the need for materials is performed.
- The strip base is a closed loop made of reinforced concrete, arranged under the load-bearing and internal walls of the building. How to make a tape-type foundation mortar? To calculate the requirements for materials, you must determine the volume of each section and add them. The mixture must be poured continuously, with layer-by-layer compaction and observing the protective layer of the reinforcement.
- The columnar type of base is used for lightweight structures located on dense soils. In practice, a combination of both types of foundation is often used.
- The slab type of foundation is practiced on weak, heaving soils. Made of reinforced concrete. Pouring should be done in one go to prevent delamination of the finished structure. The concrete mixture is distributed evenly with the obligatory compaction with vibrators or bayonet.
- Pile-rammed foundations. The volume of concrete is calculated according to the geometric formula: the cross-sectional area of the well must be multiplied by the depth of the pile and by the number of rods.
After pouring into any type of base, the concrete mixture requires moistening, otherwise the structure may crack due to the rapid drying of the top layer. The first week should be regularly watered and covered with a film or tarp.
DIY foundation concrete
You can use the materials separately or ready-made sand and gravel mixture (proportions in buckets: 1 volume of cement for 5 volumes of the mixture).
Components per 1m3 of concrete must be mixed in the ratio:
- cement - 300-350 kg;
- crushed stone - 1200 kg;
- sand - 600-700 kg;
- water - 150-180 liters.
Calculation of the amount of cement and sand, crushed stone and water should take into account the properties of materials, their qualitative composition, the value of strength, the presence of impurities (clay particles may be in the sand).
To correctly make a cement mortar for pouring the base, dry components are poured into a concrete mixer, mixed for 2-3 minutes. Then, without stopping to interfere, water is poured in portions. It is better to dissolve the necessary additives in water first. The mixing process should not be long, 5 minutes is enough.
Methods for calculating materials
The concrete recipe for the foundation includes the following components: cement, sand, gravel or crushed stone as aggregates, water. Each component is responsible for quality. In order for the final result to meet regulatory requirements, you need to correctly perform the calculation and determine the required number of components, observing the proportions.
Calculation of components and preparation of concrete for the foundation in buckets is relevant for small volumes of construction work, where 1-4 m3 of mortar is required. The basis for this calculation is usually the volumetric value of the cement.
What should be the ratio of sand and cement for pouring the foundation
Each component of the concrete mix differs in volumetric weight, therefore, in practice, the following proportions are used: 5 buckets of sand are taken for 2 buckets of cement and 9 are crushed stone or gravel.
The preliminary calculation of ingredients can be done using the online calculator in liters or kilograms. The calculation of emergency situations is carried out taking into account the requirements for concrete and the characteristics of the main materials.
For example, to obtain 1 m³ of concrete grade M200 in the presence of a concrete mixer for 180 liters, cement M400, sand and crushed stone, you will need:
- water - 215 l;
- cement - 233 l;
- rubble - 818 l;
- sand - 389 liters.
Under the given conditions, the calculator will calculate the need for materials for 1 batch and the number of downloads.
When it is necessary to adjust the consumption of raw materials, taking into account the operating conditions of the structure being erected, the type of mixture, the use of a plasticizer, the value of the coefficient of expansion of concrete particles, it is necessary to use the correction table.
Giving concrete special properties
If additional requirements and special properties are imposed on the structure to be erected, for example, water resistance or frost resistance, then additives and special concrete of exposure class XD, XF, XM or XA should be used.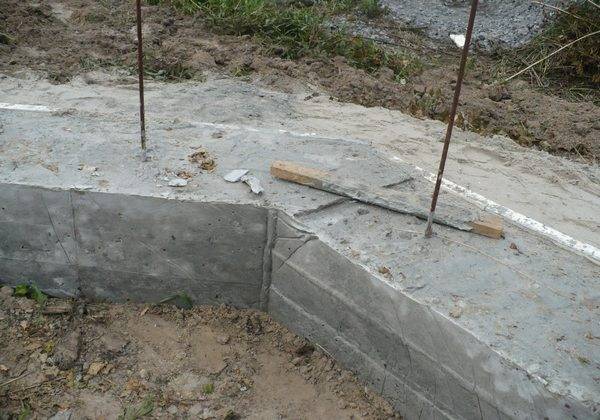
To give the concrete solution special properties, various additives are added to it, which can increase and improve certain qualities of the material.
Concrete with high frost resistance requires the addition of an appropriate additive, which increases the level of frost resistance of the concrete base.
The addition of this type of additive ensures that the foundation can withstand a large number of freeze-thaw cycles.
If, in addition to frost, the structure is exposed to salts, additives with high frost resistance and resistance to thawing salts acting on the base are used.
Also, additives are used that can increase the plasticity of the solution. Typically, they are used in formwork mortars with frequently repetitive metal mesh reinforcement. This additive contributes to a better distribution of the mixture along the entire perimeter of the formwork.
They also use additives that increase the degree of stability of the foundation of the structure to erosion by groundwater (waterproof concrete). It is almost impossible to do without them in places where the soil is too saturated with moisture. A solution of a denser consistency is used for buildings with a thickness of 10 to 40 cm so that the depth of water penetration does not exceed 0.6, and for structures with a greater thickness - 0.7.
Components for concrete
Before making a cement mortar for the foundation, you will need to prepare the following materials:
- basic substance;
- river sand;
- crushed stone;
- water;
- additional components (plasticizers, stabilizers).
The filling liquid must be purified, free of clay and chemical components (gasoline, engine oil, fuel oil, etc.). Optimal use of running water.
The sand is selected without impurities, silt and clay inclusions (the permissible percentage of suspended matter is 5%). Fatty components can form a film that will reduce the bond quality. The size of the sand particles should be 1.2-3.5 mm. The grains are sieved, washed and dried.
The cement is selected of high quality (grades M200-500). The technical parameters of the building material must correspond to the operational conditions of the building, dimensions of the foundation, climatic conditions, etc. Fracture strength and retention of compressive loads are important.
For the construction mixture, crushed stone is selected. Limestone material and gravel are not suitable as fillers. Crushed crushed stone enhances the strength of the composition. Its optimal size is 1-8 cm. Less durable additives from expanded clay, gravel. A mixture without crushed stone for the manufacture of a foundation is prepared during block construction of a structure or for operational pouring of pile supports.

Additional components are required to create a solution for different conditions (frosty weather, heat, high humidity, high loads, exposure to aggressive chemical compounds). When adding components, you need to respect the proportions.
The following additional substances are in demand:
- antifreeze;
- fiber increasing strength;
- plasticizers;
- coarse filler.
Concrete composition and special additives
 Concrete composition
Concrete composition
During production, sand, crushed stone, cement and water are mixed, the concentration of ingredients is determined by the brand of the binder cement, the size of the aggregate, and the quality of the sand. The concrete mass includes a number of water repellents, plasticizers. During the concreting process, water and cement remain the main binding components of the mixture.
According to the purpose, there are ordinary mixtures for civil and industrial construction, special solutions for laying roads, erecting hydraulic structures, and thermal insulation devices. There are compounds for special purposes that resist high temperatures, chemical aggression, and protect against radiation.
Concrete is subdivided in accordance with GOST 74.73 - 2010, GOST 25.192 - 2012, depending on various indicators:
- type of binder - slag, super-cement, alkaline, alabaster, silicate compositions;
- structure - porous, dense mixtures, aggregates of special consistency;
- curing conditions - hardening in the natural environment, with heat and moisture treatment, various pressures.
Types of regulatory additives in accordance with GOST 24.211 - 2008:
- plasticizers to reduce the volume of water, stabilizers to prevent delamination;
- mobility adjusters for long distance transportation;
- additives to increase frost resistance, corrosion resistance, water resistance;
- retarders to delay the onset of setting;
- accelerators for fast hardening.
Components are introduced to increase the density, impact resistance, abrasion of the artificial stone. Photocatalytic components allow the solid material to self-clean from dirt and dust. The concrete formula involves the introduction of mineral ingredients to increase the viscosity and pozzolanic activity.
Giving concrete special properties
If additional requirements and special properties are imposed on the structure to be erected, for example, water resistance or frost resistance, then additives and special concrete of exposure class XD, XF, XM or XA should be used.
To give the concrete solution special properties, various additives are added to it, which can increase and improve certain qualities of the material.
Concrete with high frost resistance requires the addition of an appropriate additive, which increases the level of frost resistance of the concrete base.
The addition of this type of additive ensures that the foundation can withstand a large number of freeze-thaw cycles.
If, in addition to frost, the structure is exposed to salts, additives with high frost resistance and resistance to thawing salts acting on the base are used.
Also, additives are used that can increase the plasticity of the solution. Typically, they are used in formwork mortars with frequently repetitive metal mesh reinforcement. This additive contributes to a better distribution of the mixture along the entire perimeter of the formwork.
They also use additives that increase the degree of stability of the foundation of the structure to erosion by groundwater (waterproof concrete). It is almost impossible to do without them in places where the soil is too saturated with moisture. A solution of a denser consistency is used for buildings with a thickness of 10 to 40 cm so that the depth of water penetration does not exceed 0.6, and for structures with a greater thickness - 0.7.
Views
There are three types of concrete foundations:
- Tape.
- Plate.
- Columnar.
It should be noted that each is selected depending on the specific conditions of use. To make it clear when to use each type, you need to point out the functions they provide.
Tape
 Strip foundation ”width =” 300 ″ height = ”216 ″ />
Strip foundation ”width =” 300 ″ height = ”216 ″ />
This type of foundation is used for heavy-walled buildings. Typically, the walls of such buildings are made of brick, concrete, stone, wood, etc. Such a foundation is installed along the entire perimeter of the building. The depth of placement will depend on the calculated mass that the structure has. You also need to take into account that the foundation is laid to a depth that is greater than the depth of soil freezing.
Platen

Typical use when the soil is unstable. And also in cases where the soil has water sills. Typically, such a foundation has a monolithic structure, which is installed around the entire perimeter of the building in the form of a solid slab. This type of foundation significantly increases the cost of concrete. Therefore, in this case, your construction costs will be significantly exceeded.
Column foundation

It is used in cases where the overall structure has a small load on the base. A characteristic feature of such a foundation is that all the posts are installed in places that create a load. This type of foundation is best used if there is unstable soil movement in the region. Also, such a foundation can be used for regions in which there is a high depth of soil freezing.
Now that we have specified the types, let's talk about the amount of concrete that is needed to build a foundation.
How to mix concrete correctly?
For the preparation of a small volume of solution, a bucket is used as a measure of the weight of the components. The proportions are calculated in accordance with the fact that the components have different bulk density. Based on this fact, when preparing a 1-m3 solution, a ratio of 9: 5: 2 (gravel or crushed stone, sand and cement) will be needed.
The production of concrete M 200 is carried out according to the rules in order to achieve a high quality mixture as a result.
Rules for mixing concrete for a foundation:
- Initially, sand and crushed stone should be well mixed together so that there are no lumps afterwards when adding water. Furrows are made on the surface, into which cement is poured. The mixture should be mixed until a completely uniform color is obtained.
- Give the mixture the shape of a cone and add water in small portions, mix everything thoroughly.
When deciding what is the best way to mix the solution, needs and financial capabilities should be correlated. The best option would be to use a concrete mixer, but buying it for a small building is unprofitable, so it is better to use manual production.
Preparation of concrete mix for strip foundations
For this type of foundation, you first need to calculate the amount of material required. The parameters of one tape (length, width and depth) should be multiplied by their number.
Example. Length 20 m, width 0.5 m, depth 1 m. We multiply these values and get, on one side of the foundation it is necessary to prepare 10 cubic meters of concrete solution.
Having prepared the required amount of the mixture, it is poured into the formwork. It is performed in layers, for example, if the depth of the base is one meter, then there should be four layers, each 0.25 cm. After laying each of them, it is necessary to tamp. Then, to release excess air, reinforcement should be slowly pushed into the solution every meter or two.
Preparation of concrete for a columnar foundation
Calculations in this type of foundation correspond to the strip version. The difference is that the concrete solution is not poured in stages, but immediately, after which it is rammed.
Required properties of foundation concrete
The concrete base of the house has different properties and characteristics. They directly depend on what quality materials and their original components are used. Also, the properties of concrete depend on the proportions of its components, which are used for the construction of various types of structures.
Required strength of foundation concrete
The strength of a concrete foundation is a key indicator that determines whether the foundation will withstand the planned load on it. It is measured in terms of kilogram per square centimeter.
You can calculate this indicator by calculating the exact degree of load that the structure will exert on the base. To do this, you will need to summarize the total weight of all structures and communications, as well as indicators of the useful and possible load that is created by climatic conditions. Then the result obtained should be divided by the area of the entire foundation.
The final concrete strength indicator should be several positions higher than the planned load on it.
The strength of concrete is indicated in its grade, which means the ultimate load on the foundation in kg / cm2.
According to the calculations obtained, a concrete solution with the appropriate characteristics should be prepared.
The required proportions of the material can be found in the tables:
Concrete from cement grade M 500, sand and crushed stone
| Concrete grade |
Mass
composition, C: P: U, kg |
Volume
composition for 10 l cement, P: U, l |
Quantity
concrete from 10 l cement, l |
| 100 | 1:5,8:8,1 | 53:71 | 90 |
| 150 | 1:4,5:6,6 | 40:58 | 73 |
| 200 | 1:3,5:5,6 | 32:49 | 62 |
| 250 | 1:2,6:4,5 | 24:39 | 50 |
| 300 | 1:2,4:4,3 | 22:37 | 47 |
| 400 | 1:1,6:3,2 | 14:28 | 36 |
| 450 | 1:1,4:2,9 | 12:25 | 32 |
Concrete from cement grade M 400, sand and crushed stone
| Concrete grade |
Mass
composition, C: P: U, kg |
Volume
composition for 10 l cement, P: U, l |
Quantity
concrete from 10 l cement, l |
| 100 | 1:4,6:7,0 | 41:61 | 78 |
| 150 | 1:3,5:5,7 | 32:50 | 64 |
| 200 | 1:2,8:4,8 | 25:42 | 54 |
| 250 | 1:2,1:3,9 | 19:34 | 43 |
| 300 | 1:1,9:3,7 | 17:32 | 41 |
| 400 | 1:1,2:2,7 | 11:24 | 31 |
| 450 | 1:1,1:2,5 | 10:22 | 29 |
Solution components
 Cement is a powdered binder that hardens in water and outdoors. Together with large and small aggregates, it ensures the strength and reliability of the structure being erected.
Cement is a powdered binder that hardens in water and outdoors. Together with large and small aggregates, it ensures the strength and reliability of the structure being erected.
Cement is obtained as a result of grinding a mixture of clinker, gypsum and special additives in specified proportions. In turn, clinker is a product from firing limestone with clay and other components, on which the properties and name of cement depend. Depending on the feedstock, the following types of hydraulic binder are distinguished:
- Portland cement:
- slag portland cement;
- pozzolanic;
- lime;
- backfill;
- sulfate resistant and others.
When forming a cement-sand mixture (CPM) in order to obtain concrete of a given strength, it is necessary to take into account the strength grade of Portland cement. The following table shows the strength characteristics of the material for the old and new system:
| Class | Brand | Strength | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MPa | kg / cm3 | ||
| H 22.5 | M300 | 22,5 | 300 |
| H 32.5 | M400 | 32,5 | 400 |
| H 42.5 | M500 | 42,5 | 500 |
| H 52.5 | M600 | 52,5 | 600 |
In addition, when choosing a material for preparing concrete with the desired characteristics, other properties of cement are also taken into account:
- The fineness of grinding directly affects the strength properties of the concrete mix, especially at the beginning of hardening.
- The density is reflected in the value of the water-cement ratio, and therefore on the water consumption. To reduce it, while obtaining good workability of the mixture, plasticizing additives are used.
- Frost resistance is especially important during construction in winter or in areas with year-round low outdoor temperatures.
- Crack resistance. This indicator is influenced by such a concept as the uniformity of volume expansion during hardening.
Depending on what components the cement is made of, the above qualities vary over a fairly wide range.
The concrete mixture, which, in addition to cement, includes sand, as well as crushed stone or gravel, is formed depending on the purpose of the composition. What proportions of cement, sand and crushed stone should be contained in it is determined in accordance with the recommendations of GOST 27006 - 86 (1989) “Concrete. Rules for the selection of compositions "and GOST 7473 - 94" Concrete mixtures. Technical conditions ".
For concrete mix, sand with a grain size of 1.2-3.5 mm is used.
When choosing this component, pay attention to the purity of the material. In order for the prepared cement-sand mixture to be of high quality, the presence of silt and clay particles in the sand should not exceed 5%
You can check the suitability of the sand for use with water.To do this, you need to pour a small amount of the investigated component into the container, add water and shake the composition. If the liquid is cloudy and contains suspended particles of clay, then the sand is not suitable for preparing concrete.
The composition of the concrete mixture used when pouring the foundation includes crushed stone or gravel of an average fraction. The use of coarse grains will lead to a loss in the strength of the foundation for the construction of the building.
Production of high quality concrete is possible using warm and clean water, without minor impurities (oils, paints).
When preparing a cement-sand mixture, it must be borne in mind that there are no absolutely pure components. In practice, it can be difficult to accurately calculate the proportion of sand, cement for the foundation, especially when pouring the base for individual construction.
Additionally, you need to take into account the factor that over time, the cement for the foundation loses some of its properties. For six months of storage, the material lowers the binding qualities by a third. Accordingly, the grade that characterizes the compressive strength is reduced.
Types of concrete foundations
The most basic types of concrete foundations are columnar and tape, but there are other subtypes and varieties of them:
-
Tape. It is installed in the form of a continuous tape, which consists of reinforced concrete, placed under all the load-bearing walls of the structure. The depth of the base of the building is formed depending on the level of soil freezing plus an additional 20 cm. Two subtypes can be used from the indicators of the quality of soils and the climatic zone:
- intermittent;
- continuous.
The material for this type of base is used:
- Booth, which has excellent durability. The material is not affected by low temperatures and flowing groundwater. A buta stone of the same fraction is used. The construction process requires a lot of labor and money, therefore it is used very rarely. The depth of the bookmark does not exceed 70 cm, and its durability is about 150 years.
- Rubble concrete, which includes a combination of cement mortar and filler (crushed stone, small quarry stone, brick fragments). In terms of strength, it has qualities no worse than rubble, but it is much easier to build and more affordable. It is used to build structures made of weighty materials or consisting of several floors.
- Concrete. This type of house base is better known as jellied, because the material is mixed in a concrete mixer, after which the formwork is filled with it. The service life of the material is over 50 years, and its cost is much higher due to the large volumes of cement used. Most often, this option is used in construction for the construction of walls from heavy materials, as well as the construction of country cottages and houses.
- Columnar, which is used for the construction of lightweight structures (for example, baths, garden houses, sheds). This version of the base includes a set of support posts located at the corners of the structure and in places experiencing increased stress. The pillars are formed from pipes, concrete, rubble and reinforced concrete. This foundation is used on solid soils.
- Tape and columnar. It is somewhat cheaper than the strip type of foundation and combines only the best qualities from both types of foundation.
The correct selection of the material and type of foundation allows you to make the structure more solid and durable. There is an opportunity to buy material for the foundation in a ready-made version, in the form of mixtures at industrial enterprises. But it is much better to make the concrete solution yourself, which can significantly save money.
Concrete preparation
For small construction work, it is convenient to measure the number of components in buckets. It is easier and faster to mix good quality concrete. How many buckets of materials are required in order to prepare the working staff depends on the amount of work
It is important to take into account the fact that all the components of the concrete test have different bulk density: a bucket of cement weighs about 15 kg, a bucket of sand - about 19 kg, and the mass of crushed stone is about 17.5 kg.

The optimal proportions of the components in one cube of concrete test using buckets are approximately as follows: 2: 5: 9, where, respectively, cement / sand / crushed stone. Having measured the components, they begin to prepare concrete mortar m200, which can be used both for pouring the foundation and for screed floors, erecting porches, etc. Water is usually added to the concrete composition in an amount equal to half the volume of cement. The working solution is prepared immediately before the start of concreting in the amount that is planned to be produced in 2 hours.
Preparation of concrete using buckets is relevant in the following cases:
- to perform small-scale work;
- when the foundation is poured in stages;
- inaccessibility of the construction site for special equipment (concrete mixers);
- remoteness from factories supplying the finished composition.
Component proportions
Even an experienced concrete worker cannot give an answer to the question: "How many components in weight equivalent should be taken to mix the ideal mortar?" Everything is too approximate, since in each case the constituent parts have different moisture content and fraction sizes. One thing remains - to adhere to the recommended proportions. It is more convenient to measure the ratio of components by volume in buckets.
Table of proportions of M-400 cement, sand and gravel:
| Concrete marking | Component weight in kg (C: P: G) | The volume of ready-mixed concrete, obtained from 10 liters of cement, in liters | Component ratio by volume (C: P: G) |
| M 100 | 1,0 : 4,6 : 7,0 | 78 | 10 : 41 : 61 |
| M 150 | 1,0 : 3,6 : 5,6 | 64 | 10 : 32 : 50 |
| M 200 | 1,0 : 2,7 : 4,9 | 54 | 10 : 25 : 42 |
| M 250 | 1,0 : 2,3 : 3,8 | 43 | 10 : 19 : 34 |
| M 300 | 1,0 : 2,0 : 3,5 | 41 | 10 : 17 : 32 |
| M 400 | 1,0 : 1,3 : 2,5 | 31 | 10 : 11 : 24 |
Table of proportions of M-500 cement, sand and gravel:
| Concrete marking | Component weight in kg (C: P: G) | The volume of ready-mixed concrete, obtained from 10 liters of cement, in liters | Component ratio by volume (C: P: G) |
| M 100 | 1,0 : 5,8 : 8,1 | 90 | 10 : 53: 71 |
| M 150 | 1,0 : 4,5 : 6,7 | 73 | 10: 40 : 58 |
| M 200 | 1,0 : 3,5 : 5,5 | 62 | 10 : 32 : 49 |
| M 250 | 1,0 : 2,6 : 4,4 | 50 | 10 : 24 : 39 |
| M 300 | 1,0 : 2,4 : 4,4 | 47 | 10 : 22 : 37 |
| M 400 | 1,0 : 1,7 : 3,3 | 36 | 10 : 14 : 28 |
Conversion to kilograms
It is convenient to measure components with buckets directly on the construction site. However, when purchasing materials, we are used to operating with kilograms. How to calculate how many and what components should be in one cube of concrete? Initially, you should decide on the proportions attributable to the ingredients.
If we proceed from the proportion of 1: 3: 5, necessary for the construction of the foundation, then the shares are 9 (1 + 3 + 5). One cube contains 1,000,000 cubic meters. cm, we divide this number by 9 shares, we get 111111 cubic meters. see in 1 cubic meter. cm, the cement content is 3.33 g, then in 1 cubic meter. its 333 kg.
Specificity of concrete mixes
Cement and water are the most important components in the composition of concrete, they are responsible for the integrity of the structure, and then form the concrete slab. However, during hardening, the board can deform and shrink up to 2mm / m 2. In order to avoid cracking and deformation of the cement stone, sand and crushed stone must be included in the composition (expanded clay and gravel can also be used). These fillers create a structured reinforcement that absorbs the shrinkage stress on itself. As a result, concrete becomes more durable and shrinkage errors are reduced.
You should not buy cement in advance, as it quickly absorbs moisture contained in the air, and this reduces its quality properties. Thus, the cement purchased six months ago may no longer correspond to its brand and you will not be able to correctly calculate the proportions.
Features of concrete mixes
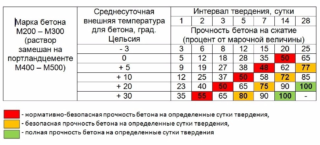 Concrete strength
Concrete strength
The concrete class is determined by the compressive strength.The cube is tested by compression and in 95 cases collapses from a single load, which is taken as the limit. The class is indicated by the letter B and numbers that indicate the value of the boundary pressure in MPA (megapascals), for example, B25.
When designing, the age of the mixture is assigned, which corresponds to its tensile and compressive strength along the central axis at a certain solidification time. Concrete grade with letter M and numbers from 50 to 1000 means ultimate strength in kgf / m³.
The workability of the mixture means the settling time of the cone of the selected concrete sample and is an important indicator when concreting with a concrete pump:
- super-hard - more than 50 seconds;
- hard - 5 - 50 sec .;
- movable - less than 4 sec.
Other indicators are bending strength, frost resistance, water resistance. Frost resistance is shown by the letter F and numbers 50 - 1000, which indicate the number of series of freezing and thawing until destruction. Water resistance is shown by the letter W and numbers 2 - 20, which indicate the amount of pressure that a cylindrical sample can withstand.
Cooking methods
When choosing what proportions of cement, crushed stone and sand for the foundation are needed, the method of making the composition is taken into account:
- mechanical (using a concrete mixer powered by electricity);
- manual.

Mechanical method
Before mixing a cement and sand bonding composition for large-scale construction mechanically, it is required to ensure the availability of the following equipment:
- concrete mixer;
- buckets;
- water tank;
- hoses;
- shovels;
- extension.
Measure the ratio of building materials optimally using buckets. The concrete mixer is selected depending on the area of the base of the building and other structures. When deciding how to dilute cement for the foundation, the dimensions of the named device are taken into account, the standard dimensions are 50-300 liters.
For the construction of a private cottage, a 220 V concrete mixer will be required; large-scale projects require high power (3-phase 380 V apparatus). Electricity is connected using an extension cord.
The components are mixed in the selected device according to the standard proportions of sand, concrete, stabilizers, water. The mass should be homogeneous, the consistency of sour cream.
Manual way
For the manual method of making the composition, the following tools and equipment are used:
- mixing container;
- metal buckets;
- barrel for water, hose;
- shovels (bayonet and shovel);
- the cloth.

Water with additional components (stabilizers, plasticizers) is poured into the container, sand and cement powder are poured. Using a bayonet shovel and a paddle, the solution is stirred to a homogeneous creamy consistency. Then the crushed stone is included in the composition and the mixture is brought to a state of readiness.
