Other options for choosing polycarbonate
The material is chosen not only for color. In order for the canopy to be not only beautiful, but also durable, the following parameters must be taken into account when choosing:
Thickness. The polycarbonate sheet for the canopy or canopy must be at least 6 mm thick, you can choose thicker options.
Type of. Colored polycarbonate can be not only cellular, but also monolithic. This material is most similar to glass, but it will be much stronger. It can be bent to certain limits, which allows you to create various curvilinear structures.
Quality. There are more and more polymer manufacturers, but not all of them can offer really good and reliable products.
When choosing, you need to pay attention to the homogeneity of the material, in addition, when bent, it should not crunch or crack.
Manufacturer country. Chinese products are often not durable, but they are quite cheap.
The most expensive, but also the most reliable, is European and Korean plastic.
Correctly selected polycarbonate sheet can last up to 10 years, while the canopy will retain all its qualities. It is a lightweight and practical material that is easy to care for and will do its job perfectly. Cellular polycarbonate has excellent thermal and sound insulation qualities, so it will be an excellent choice for verandas, gazebos and closed terraces.
Polycarbonate is able to visually change and expand the space: the canopy will be light and elegant, it is a real decoration of the local area. If it matches the color and decoration of the home, it can be transformed into a beautiful and useful space that enlarges the home and allows you to enjoy clean air.
Total score: 8 Voted: 1
You can find out detailed and expanded information on the topic of the article from the book "Wooden Houses", which reflects all the stages of building a house, from laying the foundation and ending with the installation of the roof. Book price = 77 rubles.
You may also be interested in other BOOKS on the construction of wooden houses with your own hands.
Home> Additional sections of the site > Articles> What color of polycarbonate to choose for a greenhouse canopy or gazebo
Modern summer cottages and the territory of country houses cannot be imagined today without the use of such a convenient and durable material as polycarbonate. Due to its quality characteristics, it can be used in a wide variety of designs. Garden owners use this polymer when installing greenhouses, building sheds and gazebos. But not everyone knows what color polycarbonate should be for each type of structure.
Combination of polycarbonate and wood
Wood frames are made of timber - an affordable, environmentally friendly and natural material. The tree has a natural beautiful structure, and the structure turns out to be warm and cozy. The wooden frame serves as a good support for weaving plants.

One of the simplest solutions is an open gazebo on wooden posts with a flat polycarbonate roof

A more practical and convenient solution - a closed design with a domed roof and sliding doors
Among the tangible disadvantages: instability to changes in temperature, moisture. If not treated with special impregnations, there may be a problem with insects. In addition, such gazebos are difficult to maintain.
Advantages of polycarbonate gazebos
Thanks to several advantages of polycarbonate gazebos, there are more and more people who want to install them on their sites. Compared to other designs for summer vacations, they:
- have an affordable price;
- have low weight, therefore, does not require special preparation of the site;
- easy to install;
- have a variety of shapes, types and designs.

Types of gazebos
Depending on the type of gazebo, there may be:
- Open.
- Closed.
Open ones are great for hot summer days, but closed ones can be used not only on cold summer evenings, but also at other times of the year, especially if a fireplace or barbecue is installed inside. Closed gazebos have more advantages, as they can hide from the wind and rain.
Also, a gazebo made of closed polycarbonate, like an open type, can have different shapes:
- rectangular;
- round;
- multifaceted;
- square;
- oval.

For the manufacture of the frame, metal square pipes are most often used. But it can also be made from wood, stone, or brick. Depending on the material of the frame, it may be necessary to pour the foundation.
Closed gazebos can have aluminum glazing (installation of metal-plastic opening windows), frameless (part of the wall is glazed) or combined.
Self-installation of a polycarbonate gazebo
Today in the store you can buy a ready-made gazebo, but many make it with their own hands, since there is nothing difficult about it. You do not need special equipment and professional help. But most importantly, you can make a gazebo that will have a special style and match the design of your site.
Making dreams come true
If you want a closed summer gazebo with polycarbonate to appear on your site, then first think over its future dimensions, shape, frame material, fasteners, location and other important points.
When the project is completed, get to work.
Site preparation
This stage of work consists of several actions:
- Decide on a location.
- Cut down trees and remove bushes and hemp if they get in your way.
- Clear the gazebo area.
- Level the ground.

Foundation
A strip foundation is sometimes poured under a closed gazebo, but more often the main posts of the frame are simply concreted, which can be made of metal pipes or wooden beams. You need to dig a small hole. Its depth depends on the height and scale of the structure. Pillars are inserted into the dug holes. Fix and fill them with cement mortar.
Frame
The installation of the frame is started after the pillars have solidified well in the concrete. Metal pipes can be connected in two ways:
- using bolts or other fasteners;
- welding seams.

Sometimes both methods are used to make the frame more durable and stable.
If wood is used as a material for the frame, then the beams are connected with bolts, self-tapping screws or nails.
Polycarbonate sheathing
When the frame is completed, you are faced with the task of how to close the gazebo with polycarbonate. First you need to cover the roof and then sheathe the walls.
- Cut the polycarbonate to suit the roof size.
- Secure the material to the frame using self-tapping screws and other fastening devices.
- Watch carefully so that there are no gaps and crevices.
- Then cut out the polycarbonate for the walls and fasten it to the frame, remembering to install the windows, if any are provided for in your design.

Decoration and arrangement of internal space
The last stage of work is the installation of a table, benches or chairs inside, as well as decoration. The gazebos covered with polycarbonate have an attractive appearance, but the main thing is that they are comfortable for relaxation both in the scorching sun and in cool weather.
Rubric: Gazebos.
General characteristics
On the construction market, you can come across two types of polycarbonate: from recycled or from primary raw materials. The latter are the most reliable and durable solution, they are resistant to deformation and burnout, they are not afraid of temperature changes and chemical influences.Panels made from recycled materials are worse in quality, inferior to those mentioned above in all parameters, except for one - prices, their cost is significantly lower, which makes them an economically viable option.
Also, polycarbonate can be monolithic or cellular. In the first case, we are talking about a homogeneous cast plate that looks like glass, in the second - about hollow sheets equipped with stiffening ribs. Honeycomb panels are cheaper, in terms of the ratio of functionality and practicality, they can be called an extremely successful solution, however, not suitable for all situations.
Types of polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is quite diverse in structure. It is difficult to answer the question of which polycarbonate is better. It all depends on the operating conditions, goals and objectives set by the consumer.
Cellular polycarbonate - features
Represents two or more sheets, interconnected by means of vertical partitions, which resembles a honeycomb in section. It has flexibility, lightness and great strength. Often, colored cellular polycarbonate is used in the construction of fences, since it has high aesthetic characteristics in addition to high strength, low weight and other useful characteristics.
In addition, this type of polycarbonate, according to the assurances of experts, is extremely durable and, with a thickness of 120 mm, can withstand a pistol shot at point-blank range. So there is absolutely no need to worry about gravel from under the wheels of a passing car or about hail. This type of polycarbonate is often used in the construction of fences, greenhouse glazing, roofs, awnings, etc. And in general, it is used more often than other types.
Advantages of cellular polycarbonate:
- low specific gravity - 16 times lighter than glass of the same dimensions;
- low thermal conductivity (this is achieved due to voids filled with air, due to these voids, a significant level of sound insulation is achieved;
- plasticity and flexibility;
- low cost.
Characteristics of monolithic polycarbonate
Outwardly, it is very similar to glass, which is why it is most often used for the construction of windows in greenhouses or gazebos. Colored monolithic polycarbonate is used with great success in the manufacture of stained-glass windows. Available in various thicknesses (from 0.75 mm to 40 mm). It has many more advantages compared to honeycomb.
Advantages of monolithic polycarbonate:
- resistance to physical impact (this polycarbonate is 200 times stronger than glass and about 8 times stronger than acrylic);
- good sound insulation;
- abrasive resistance (not scratched);
- ease of use (if you buy monolithic polycarbonate, the sheet size may be larger than what you need; you can cut to the required dimensions in many ways, but cutting with a jigsaw is best).
When monolithic polycarbonate is destroyed, the formation of sharp fragments is excluded. Also, this type of material can withstand a lot of pressure from the snow cover. This makes polycarbonate awnings very practical and popular.
Corrugated polycarbonate
This type of polycarbonate is used less often than the first two. It is used primarily for roofing. The wave pitch is the same as that of modern slate. Thus, these two materials can be combined with each other. However, corrugated polycarbonate is not very popular.
What to look for when buying
Having calculated the estimated consumption of material, it should be taken into account that:
It is necessary to select sheets with a weight corresponding to the load, otherwise the bearing characteristics will be minimal, which will provoke the appearance of cracks. So, a 4 mm honeycomb sheet weighs 0.8 kg, 6 mm - 1.3 kg, 8 mm - 1.5 kg.
For closed gazebos, it is not recommended to purchase lightweight sheets. Their service life is much shorter than that of standard ones. Yes, they are cheaper, but you will have to create a powerful crate for them, and this will result in additional costs.
You need to immediately decide what should be the thickness of the material
At the same time, do not forget about the snow load, wind, the shape of the bends, the step of the sheathing.
Special attention should be paid to the choice of colors. For summer buildings, light colors are the best option, but do not use transparent sheets, otherwise it will be very hot inside.
It is necessary to immediately buy components - thermo washers, profiles, end tape, sealant.
No need to experiment with purchasing products from little-known manufacturers
Such savings can result in wasted time and money.

With the choice of high-quality polycarbonate and the correct installation, the summer building will last for many years, and the original shape or color will make it a bright decoration of the summer cottage.
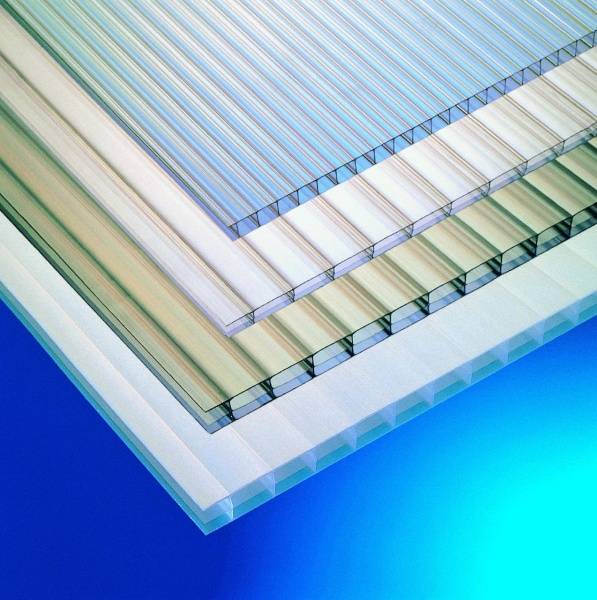
Variety of types of polycarbonate
Before you choose which polycarbonate is right for your task, it is worth considering its main characteristics. These include the structure of the material, the shade of the sheets and the thickness.
Color palette
Whatever construction is planned, when choosing polycarbonate for the roof, you should pay attention to the degree of light transmission. Polymers with different thicknesses differ significantly in this indicator.
You should also find out how well polycarbonate allows heat to pass through. For gazebos, they often choose a material that does not allow most of the sun's rays to pass through. This allows you to hide from them on hot summer days.

For example, to cover a greenhouse, you need white and beige panels. This choice is due to the ability of light sheets to perfectly heat the greenhouse from the inside. Due to this, the temperature in the greenhouse increases significantly. Colored panels have an ability to transmit light in the range from 30 to 60%. Sheets with a dark shade allow less light to pass through.
Polymer device
Polycarbonate sheets of different types have a different structure from each other. They can be one of 2 types, each of which has some advantages. To understand the features of such panels, you should learn more about them.

Monolithic polycarbonate has an integral shape. It is easy to install and not subject to contamination. The sheet of panels does not contain any voids. This allows it to be used for a wide range of tasks.

The honeycomb panels are designed in such a way that they have 2 layers connected by a plurality of ribs. The finished sheet can be compared to a honeycomb. Due to these structural features, cellular polycarbonate is characterized by high thermal conductivity and lightness. It is also quite flexible.

Thickness
Before choosing the thickness of polycarbonate sheets for the gazebo, it is worth deciding on the installation site of the building. For example, 4mm thick panels can be used to create awnings and canopies. Also, such products can be used for small greenhouses. To cover large buildings, you should choose thicker polycarbonate.
Sheets 8 mm thick are suitable for greenhouses, conservatories, large gazebos. They are often used in greenhouses. Such products perfectly cope with heavy loads and temperature changes.
For open verandas and balconies
For example, colored polycarbonate is better suited for balconies and open verandas. To create partial shade inside the space of the gazebo or canopy, opaque polycarbonate of a white-milky or smoky-bronze shade that can hold up to 80% of sunlight will be a more suitable option.

But bronze of a red hue should not be used for the manufacture of hinged structures. this plastic scatters light very badly.
A good option for roofs of terraces and gazebos would be muted bronze or amber polycarbonate. The color palette of cellular polycarbonate for the production of gazebos and awnings can be different, but it is necessary that the shades are calmer and more discreet.

The brightness of the polycarbonate sheets will irritate people in the gazebo and make the rest in it uncomfortable.
You should not use transparent cellular polycarbonate for curtain structures that are planned for resting people, since bright sunlight will penetrate through it and heat the interior space, creating a greenhouse effect there.
Applications
Polycarbonate sheets have many positive properties. For this reason, they are used for different purposes. The thickness of the panels is only 0.4-2.5 cm. Polycarbonate is in demand when carrying out both large-scale and small construction works. It is used for roofing, when creating sound screens, gazebos and protective visors.

Polycarbonate sheets are especially in demand for creating partitions in offices. Panels are also used in the field of agriculture. Greenhouses, hotbeds and winter gardens are erected from it. Polymer is also in demand in advertising. Various shields and plates are made from it.

Self-installation
Depending on the material of the gazebo, polycarbonate will be laid in approximately the same ways - using a profile. I propose to consider two of the most popular roof options when the structure is made of metal or wood. The general concept of fastening is shown in the photo below.
 Fastening polycarbonate through the profile to the roofing screws
Fastening polycarbonate through the profile to the roofing screws
Fastening to metal
The roof must be in the same plane, which is why laying polycarbonate is a fairly simple process. Conventionally, the whole process is divided into several stages, which must be performed strictly in turn.
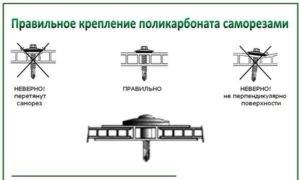 The correct position of the screw
The correct position of the screw
- Preparation of material and tools. Calculate in advance the number of polycarbonate honeycomb boards, self-tapping screws with washers, end and connecting profiles, and self-adhesive dust strips. Before the sheets begin to rise up, you should have all the material in abundance. The battery of the screwdriver must be charged and the bits must be in place.
- Fasten the base profile from the edge of the roof onto the self-tapping screws.
- Remove the bottom layer of the protective film.
- Cover the honeycomb holes with dust tape. This is done to prevent moisture ingress.
- Insert a sheet of polycarbonate into the profile.
- Fasten the polycarbonate sheet to the roof structure using self-tapping screws with a thermal washer or ordinary roofing. Keep in mind that the hole for the self-tapping screw should be slightly larger than the size of the self-tapping screw itself. A similar trick is needed to smooth out the thermal expansion of the polycarbonate so that it does not burst.
- Close the base profile with the roof clamping profile. Make sure the cover is firmly seated in the base before proceeding.
- Repeat this procedure for each sheet. Make sure that the carbonate slabs do not burst from excessive tightening of the self-tapping screws.
This instruction is clearly shown in the video of the Polygal company, which tells about the installation of polycarbonate on a metal structure. Everything is told in a very accessible and understandable language, I recommend it for viewing.
Fastening to a tree
The concept of fastening to wood is not very different from metal. For fastening, a profile is used that allows individual sheets to be fastened together and to achieve a certain tightness between them so that rain or melting snow does not fall into the gaps.
I would like to give a video, which shows directly the laying of polycarbonate sheets on a hexagonal wooden roof.
The laying process is accompanied by its sharp
Pay attention to how many people are involved in this process. When erecting such a roof with your own hands, difficulties may arise.
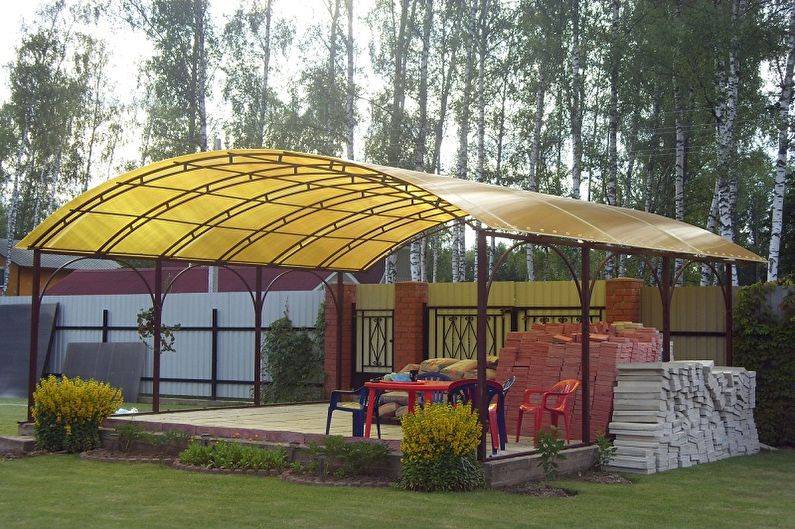
Consider the main stages of building a gazebo

Seat selection
Due to its low weight, the gazebo with a polycarbonate roof can be installed on almost any type of ground. In general, a flat and dry area is perfect, a little on a hill (so that rainwater does not accumulate), in the shade of trees, protected from drafts.It is good to install a gazebo near the reservoir - even on a hot day, this will provide an influx of fresh cool air. The models of polycarbonate gazebos themselves can be different in shape (round, square, rectangular, etc.), both open and closed - it all depends on the wishes and capabilities of the site owner.

Almost any soil is suitable for installing a polycarbonate gazebo

Wonderful gazebo in Mediterranean style
Foundation preparation
A small gazebo can be installed directly on the ground without laying a special foundation, but for a capital structure (especially on fragile soils), a foundation will be required. However, due to the low weight of polycarbonate, for a metal gazebo, you can limit yourself to concreting only supporting pipes, at the same time, you can pour the site. For solid wooden arbors, a columnar foundation is suitable.

Stylish gazebo attached to the house

Cozy gazebo with monolithic stone supports
Assembling the frame
As a material for assembling the frame, you can use both metal profiles and wooden posts. The advantages of wood are that it is an inexpensive material that is easy to process and does not require special tools, but during operation the tree will require constant maintenance. A metal gazebo made of polycarbonate will cost more, but it is easier to operate and less susceptible to moisture. In a wooden structure, the elements are connected using self-tapping screws, staples and nails, in a metal structure - nuts and screws.

Metal profiles as an option for the frame

The metal frame, although more expensive than a wooden one, is more durable and more practical
Roof installation
The installation of the roof begins when the frame is firmly fixed. Polycarbonate is convenient because it is very well cut with a hacksaw, hand saw or jigsaw, for speed, you can even use a circular (we use a disc for aluminum). Therefore, the roof can have a rather complex shape.

Installation of a polycarbonate roof

Corrugated polycarbonate canopy
To install the roof, 8 (less often - 6) millimeter cellular polycarbonate is used. If the material was previously stored in a damp room, condensation may accumulate inside the sheet. It must be removed by blowing the sheet with compressed air. After cutting and cutting the sheets, the end edges must be closed using aluminum adhesive tape, sealant or end profile.
When attaching sheets to the roof, you must not step on the polycarbonate - it can crack, so all installation work has to be carried out only from the stairs. When mounted on a metal base, holes are pre-drilled in polycarbonate. Fastening of polycarbonate sheets can be carried out using self-tapping screws, and the use of rubber washers with screws and silicone sealants will prevent water leaks and destruction of the base of the sheet.

Stylish, bright minimalistic polycarbonate gazebo

The roof of the gazebo made of polycarbonate with an optical illusion of openwork
How to make a gazebo made of polycarbonate - see the video for interesting ideas:
Cellular and monolithic polycarbonate
Today on the construction market you can find two types of material - monolithic and honeycomb. The first type allows you to get a very attractive transparent structure. Outwardly, such polycarbonate is similar to glass, while it is not so heavy and fragile. You can choose a ribbed or smooth material texture, depending on your preference.
Such gazebos are beautiful, but quite expensive, so they are rarely worth it.
Please also note that if you want to make a roof from such a material, then be sure to buy options with a thickness of at least 0.5 cm
Cellular modifications are distinguished by a good ratio of cost and quality characteristics. They are not as beautiful as monolithic surfaces, but more practical, cheaper and lightweight.
For a gazebo, select three- or two-layer materials - depending on the quality characteristics, they can last from 20 to 50 years. Suitable thickness of honeycomb coverings is 0.8 cm or more.



Guideline for technical characteristics
When choosing polycarbonate for a future gazebo, it is worth starting not only from the cost, but also from the technical characteristics. As practice shows, more expensive is not always better. One of these indicators is the thickness of the material.
The thickness of the polycarbonate sheets will depend on the installation site of the future gazebo and the project of the future structure. Panels with a thickness of 8 mm are ideal for creating a powerful (overall) gazebo. A 4–6 mm sheet can be used to make a canopy.
At the same time, you need to pay attention not only to the thickness of the sheets, but also to the manufacturers, since high-quality 6 mm sheets have greater strength than cheap 8 mm sheets. Some experts agree that it is advisable to minimize the use of 4 mm sheets, since their service life often does not exceed two years.
If we compare monolithic and honeycomb polycarbonate in terms of such an indicator as fragility, then here the honeycomb polymer has an advantage. This is due to the peculiarities of its design, due to which such a material is distinguished not only by high thermal conductivity, but also by plasticity.
It is impossible not to mention the weight of the sheets, since with the same thickness, the weight may be different. To do this, you need to know the specific gravity of one square meter of finished products. Many manufacturers and suppliers rely on the following indicators:
| Sheet thickness | 4 mm | 6 mm | 8 mm | 10 mm | 16 mm |
| Cellular polycarbonate kg / sq. m | 0,8 | 1,3 | 1,5 | 1,7 | 2,7 |
| Monolithic polycarbonate kg / sq. m | 4,8 | 7,2 | 9,6 | 12 | 19,1 |
It should be noted that monolithic polycarbonate is preferable to use in windy, heavily blown areas. If the territory is protected from environmental factors, then you can give preference to honeycomb sheets.
Monolithic polycarbonate
Monolithic polycarbonate differs from its polymer relatives in high impact resistance and transparency (transmits up to 90% of light and blocks UV rays), which allows it to be used in structures where high protective properties are required. These are, for example, roofs of public transport stops, various fences, protective screens. The material tolerates temperature extremes, squally wind and hail well, so summer residents often use it as a cover for carports, playgrounds and canopies. As for greenhouses, monolithic polycarbonate does not have cells, therefore it is moisture resistant, however, its thermal insulation properties are lower than that of cellular polycarbonate.
Monolithic polycarbonate in its ability to transmit light is not inferior to ordinary glass, but the weight of polymer sheets is half that of glass of the same thickness. Consequently, polymer structures are lighter and less costly to install.
If you use "bronze" colored polycarbonate sheets, the light transmission is reduced by about 50%, and the penetration of heat rays by 60%, which allows you to save on air conditioning in the summer. And due to its low thermal conductivity, the material can also be used for glazing housing.
There is still no consensus on the effect of the agents used to combat harmful insects on the strength of polycarbonate, therefore, these substances must be used with caution in greenhouses lined with this material. If you want to use monolithic polycarbonate as a material for a fence, then remember - you will not hide anything behind such a fence.
However, this polymer material lends itself well to processing - it can be cut, sawed, drilled, bent, molded, glued.For high-quality installation of polycarbonate cladding, it is necessary to use special accessories, such as thermo washers, sealants, hardware and seals. Polycarbonate goes well with most structures made of wood, PVC, aluminum, steel
If you want to use monolithic polycarbonate as a material for a fence, then remember that you will not hide anything behind such a fence. However, this polymer material lends itself well to processing - it can be cut, sawed, drilled, bent, molded, glued. For high-quality installation of polycarbonate cladding, it is necessary to use special accessories, such as thermo washers, sealants, hardware and seals. Polycarbonate goes well with most structures made of wood, PVC, aluminum, steel.
Monolithic polycarbonate also has disadvantages - it is not cheap, vulnerable to solvents and acids, and on hot days the surface temperature of the polymer sheet can reach 50 degrees, so touching it can cause a burn.
How to choose a good polycarbonate for a greenhouse, gazebo, canopy, fence
Useful tips and advice on the choice of material for summer cottages.
Optimum thickness of polycarbonate for the canopy
This aspect is also one of the most important. Each type of structure has its own thickness standards laid down in the corresponding documentation, in particular, in SNiPs
To determine this parameter, it is necessary to take into account the functional purpose of the canopy and calculate the load falling on it. For cellular polycarbonate, it is advisable to adhere to the following recommendations:
- panels with a thickness of 4 millimeters should be used for small structures with a small radius of curvature;
- 6 and 8 mm options are best suited for objects subject to snow and wind loads;
- panels from 10 millimeters and more are optimal for those structures that are exposed to severe climatic and mechanical stress.
When deciding on the thickness of the canopy, it is also necessary to take into account such an aspect as the internal stiffening ribs of the panels and their structure. In this regard, the following regularity is observed: the larger the dimensions of the lathing cell, the thicker the polycarbonate panel. For panels with a thickness of 16 millimeters, the factor of the internal structure of the sheet is of decisive importance, in this case we are talking about sheets with three- and five-layer cells.
Which is best for the veranda: glass or polycarbonate
Polycarbonate surpasses glass structures in aesthetics and decorativeness. The optics for Mercedes are made of polycarbonate. The roofs of international stadiums are constructed from carbonate. Why not build a glazed veranda out of this polymer?
Glass is heavier and more expensive. Polycarbonate is lighter and cheaper. The polymer has another advantage: glazing work can be done independently.
The veranda belongs to the category of lightweight structures; this structure is partially or completely adjacent to the house. During its construction, rationality comes first - low costs, a given result. Polycarbonate is a great alternative to glass: the polymer is transparent like glass, hard and impact-resistant like a wall. The room should turn out to be cozy, light, able to withstand winds, snows, and rains.
With the help of polycarbonate, you can make a veranda with curved walls. Plastic provides another interesting opportunity: to make roller shutters from transparent polymer strips and aluminum H-shaped profile. Then the veranda can be easily turned into an open terrace and vice versa.
For an expensive veranda, it is better to order polished display glass. There are companies that can build sliding or rotary doors. Such frameless designs look impressive and aristocratic. The cost of such a veranda is quite comparable to the cost of a modest residence.But here, too, polycarbonate will almost certainly be present: most showcase glasses are made in the form of triplex - with a polycarbonate film soldered between two silicate plates.
Comparative characteristics of glass and polycarbonate:
- Glass is 16 times heavier: there is no need for heavy, powerful supports.
- Polymer sheets are flexible and flexible: work can be done without the use of expensive machinery.
- Plastic can withstand significant shock loads: the walls of the veranda will reliably protect the room from wind and precipitation.
- Polycarbonate retains its properties at low and high temperatures: the veranda can be used at any time of the year.
- The thermal conductivity of organic glass is almost two times lower, the room turns out to be warmer and more comfortable.
Brief description, pros and cons of each type
There are 3 types of material on the construction market. They differ in properties, scope, cost.
Cellular polycarbonate
A practical option for covering and upholstering a gazebo. Light in weight. In appearance, these are 2 or 3 colorless plates, which are connected by jumpers, so on a cut it is very similar to a honeycomb, which is why it got its name.
It happens two-, three-, five-layer. If in the first and second cases the service life of the product is about 30 years, then the five-layer one will last 50 or more.
It has low thermal conductivity, good impact resistance, is used in the manufacture of greenhouses, sheds, roofs, summer kitchens, fences. Does not burn, begins to melt at a temperature of +120 0 С.
It is recommended to take such polycarbonate for a gazebo with a thickness of at least 8 mm. Then the building will be reliable and will last longer.

Photo: 8mm polycarbonate honeycomb panel
Given the structural features of the sheet, the following types are on sale:
- 2H - two-layer with rectangular partitions (stiffeners) inside.
- 3H - three-layer type. The inside is held together by rectangular lines. Thickness from 6 to 10 mm.
- 3X - three-layer with straight, inclined bridges.
- 5W - reinforced material. Consists of 5 layers with straight honeycomb inside. Produced with a thickness of 16 to 20 mm.
- 5X - five-layer sheets with inclined and straight edges. Thickness - 25 mm.
A significant drawback of this polycarbonate is vulnerability to the effects of low temperatures, it becomes brittle, and begins to crack under low load. But if it is covered with a protective film, the strength of the material will remain at the same level.
Monolithic
A modern substitute for silicate glass. Its advantages:
- Durable. It tolerates blows well, it is difficult to break it with a hammer, therefore it is safe to use.
- 2 times cheaper than ordinary glass.
- Flexible. Suitable for glazing arbors and other buildings of any shape. Does not need preliminary heat treatment.
- Comfortable . Light in weight, which greatly simplifies installation.

Photo: monolithic polycarbonate
The disadvantages of monolithic polycarbonate cannot be ignored. Among them:
- It begins to deform at a temperature of +40 0 C. This complicates the glazing of the structure. The correct solution is to increase the distance between the material and the frame of the structure.
- Constant exposure to ultraviolet rays on the product leads to its yellowing. The color fades over time. You can avoid this by covering the sheets with film.
- Easy to scratch.
Despite such disadvantages, arbors from this material are beautiful and bright.
For summer gazebos, it is recommended to take monolithic polycarbonate with a thickness of 4 mm or more. Such a structure will be reliable and durable.
Corrugated material. It looks similar to corrugated board or slate. It is often used as a roof covering. It can be colored, matte or transparent.
Produced in a thickness of 0.65–2.5 mm.

Photo: corrugated polycarbonate
