Heated greenhouses: we grow vegetables all year round
Heated greenhouses are an excellent solution for countries with harsh climates for growing agricultural products all year round. They allow not only to have fresh vegetables on the table in any season, but also to provide the owner with a year-round income.
However, before building a greenhouse, it is worthwhile to carefully study all its features, since it is quite difficult to provide stable heating in the harsh Russian winter. It is necessary to calculate the costs in advance and select a suitable heating system.
Content:
- Benefits of a heated greenhouse
- Which greenhouse project to choose?
- Greenhouse selection: which material is better?
- Optimal location for a greenhouse
- Heating systems for greenhouses: types and description
Benefits of a heated greenhouse
Before choosing a greenhouse, you need to estimate the estimated costs of electricity or other types of heating. If the greenhouse will be used to generate year-round income, you need to weigh in advance all the pros and cons of such a building. When studying the design of greenhouses, it becomes clear that today there are many different types of greenhouses. From this multitude of projects, you can choose a suitable one that is reasonably economical and provides plants with optimal conditions throughout the year, regardless of the weather outside the greenhouse.
The main advantages of heated greenhouses:
- The ability to harvest all year round. In most Russian regions, the short summer does not allow experimenting with varieties and growing thermophilic crops. A heated greenhouse removes all restrictions.
- In a heated greenhouse, you can grow not only vegetables or greens, but also many other cultures: mushrooms (for example, champignons), flowers and even exotic fruits. All this will not only decorate your table, but also bring tangible material income.
- A greenhouse crop can generate tangible income. Selling fresh vegetables, flowers, or other beneficial crops can be the foundation for a thriving business. And the opportunity to get a harvest all year round will make it possible to successfully compete with other agricultural producers.
Which greenhouse project to choose?
Project selection greenhouses - a responsible decision. It will depend on this choice whether the greenhouse will bring benefits, or will its maintenance require more costs and go to a loss? To design a greenhouse that generates income, answer a series of questions:
- How harsh is the climate in your area? How many days will it take to heat the greenhouse?
- What is the purpose of your greenhouse? If you plan to grow vegetables only for your table, the greenhouse area may be small, but for a commercially successful business, it is better to build a greenhouse with an area of at least 60 m2.
- How will you heat the greenhouse? Different heating systems require different greenhouse canopy designs.
- How much money can you allocate? If the budget allows, you can make a more capital structure, and if you need savings, choose cheaper options.
All the existing variety of greenhouse projects can be divided into several groups.First of all, a greenhouse project can be typical and individual. Often there is no point in reinventing the wheel and you can stop at proven solutions. Typical projects are cheaper and often you can immediately purchase everything you need for construction in one place.
But sometimes the terrain conditions do not allow choosing the optimal solution among typical projects, so you have to create a fundamentally new solution.
Such a project, of course, will be more expensive and may require expert advice. However, with subsequent operation, it will turn out to be more profitable. But for building a greenhouse with your own hands, it is still better to choose one of the standard options.
Several groups can be selected among typical greenhouse projects:
- By their location in the ground, greenhouses are distinguished, buried in the ground, located on the surface of the earth, as well as greenhouses located on the upper floors of buildings (for example, garages, garden houses, etc.).
- According to the solutions used in architecture, greenhouses can be very diverse. The most common are single-slope, gable and arched options, but they do not exhaust the whole variety of architectural forms developed for greenhouses. The specific shape can be chosen based on the available budget, the shape of the site and considerations of aesthetics of the appearance of the greenhouse.
- According to the building materials used, brick, wooden, frame greenhouses, as well as combined options, are distinguished.
- According to the method of placing plants, there are projects designed to place plants on the ground or in boxes installed on racks.
Greenhouse selection: which material is better?
First of all, decide what material the greenhouse frame will be made of. The most common are wooden frames, as well as metal frames. Wooden frames are relatively economical, but they have less durability and strength than metal ones.
The service life of a wooden frame can be extended with the help of special impregnations, as well as painting with special resistant paints. But even in this case, the metal frame will be more durable, albeit more expensive.
When choosing a coating, the decisive indicators are the ability of the material to transmit sunlight and heat, as well as strength.
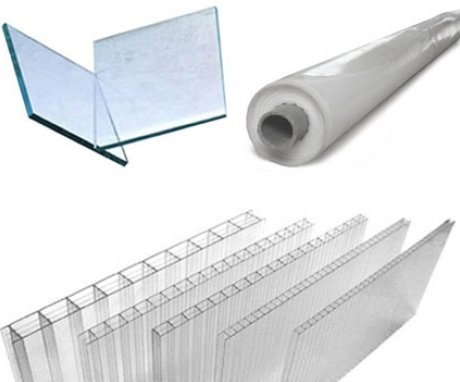
Glass and cellular polycarbonate are most often used in typical greenhouse projects. Let's analyze the main advantages of these materials:
- Glass is a traditional material for greenhouses. It transmits the light and heat of the Sun best of all and remains transparent for a long time. But this material is fragile, so it is not very suitable for winter greenhouses. The glass can crack under the weight of snow accumulated on the slopes of the greenhouse; therefore, when making glass greenhouses, it is worth making steeper slopes so that snow does not accumulate on them. In addition, glass is a rather heavy and inconvenient material to process.
- Cellular polycarbonate is a new solution in the field of greenhouse design. It is lighter than glass, easily cut and mounted on the greenhouse frame. Polycarbonate insulates the greenhouse well from cold outside air and allows enough light and heat to pass through. The disadvantage of this material is the loss of transparency over time. But, despite this, for 6 - 7 years, the transparency of polycarbonate will remain sufficient for the greenhouse.
In addition, it is not necessary to dwell on one material. A number of typical greenhouse projects are based on combining the useful properties of each material. For example, you can make the walls of the greenhouse stack them, and the roof slopes from polycarbonate. Such a solution will provide good illumination of the plants and not be afraid that the roof will collapse under the weight of the snow.
Optimal location for a greenhouse
Choosing the right place for placing the greenhouse will save on heating. It is better to place the greenhouse in an area protected from the wind. It is better if the building stands on a hill, this will give more solar heat.Therefore, if there is no elevation on the site, you can place the greenhouse on a special embankment.
If strong winds blow on the area where you plan to build a greenhouse, it is worth building a windshield.
Such protection can be hedge or embankment. Please note that the windscreen should not be positioned too close to the greenhouse so as not to create turbulent air turbulence. The optimal distance from the structure to the windscreen is 10-15 meters.
The greenhouse should be oriented along the East-West line. In this case, you can hope for sunlight throughout the day. This placement of the greenhouse will significantly reduce heating costs. And of course, you should make sure that there is a wide and convenient entrance to the greenhouse entrance. This will be important both during the construction of the greenhouse and during further work in it.
Heating systems for greenhouses: types and description
The type of heating most strongly influences the greenhouse design and its future economic efficiency. The most common are 4 types of heating:
- Stove heating consists of a stove for burning fuel and a system of pipes through which the air heated from the stove is diluted through the greenhouse. The advantage of such a system is the low cost of fuel. You can burn anything in the stove - firewood, dung, straw, peat; this makes the stove heating system quite economical. However, the efficiency of this scheme is the lowest, therefore, it is worth arranging such heating only in small greenhouses, the area of which does not exceed 20 m2.
- Water heating is based on the use of water as a heat carrier. If the greenhouse adjoins the house with one wall, then water heating can be done simply by bringing pipes from the central heating system into the greenhouse. But in this case, it is worth taking care of ways to regulate the water supply to the heating system of the greenhouse in order to be able to reduce the temperature if the greenhouse starts to overheat on a sunny day. If the greenhouse is not adjacent to the house, you will have to make an autonomous water heating system. In this case, a separate boiler, gas or electric, is installed to heat the water. Pipes for water heating can be used both metal and plastic. However, plastic pipes are preferable because they can be laid under the floor of the greenhouse and then they will warm not only the air, but also the soil. Metal pipes can quickly rust on contact with soil.
- Electric heating uses several schemes. One of the simplest solutions is to use air heaters. But with such a scheme, it is not possible to ensure uniform heating of the entire greenhouse room. Therefore, heaters are best used only in addition to other sources of heat. Convectors heat the air in the greenhouse with heating coils and circulate the heated air throughout the greenhouse. The disadvantage of this scheme is that convectors do not warm up the soil. Infrared lamps are gaining in popularity lately. The radiation from such llamas does not heat the air in the greenhouse, but the plants themselves and the soil. And the heated soil already gives off heat to the air. These heaters have temperature controls and only operate periodically. When the temperature in the greenhouse rises, the emitter turns off and saves energy. Such lamps are considered harmless and do not harm either plants or humans, therefore it is completely safe to be in the greenhouse while the infrared lamp is operating.
- Heating with biofuels involves the use of heat generated by the decomposition of manure, sawdust or straw. This is perhaps one of the most economical types of heating.
Whatever heating scheme is used, it is worthwhile to understand that there are no absolutely reliable technical solutions. Therefore, it is worth taking care of backup heat sources.
It is quite possible to build a heated greenhouse according to a standard design.Today there are many companies that assemble such greenhouses on a turnkey basis, and if you have the skill, then it is quite possible to build such a structure with your own hands. A winter greenhouse will be useful both for the household and for obtaining economic benefits.
More information can be found in the video: