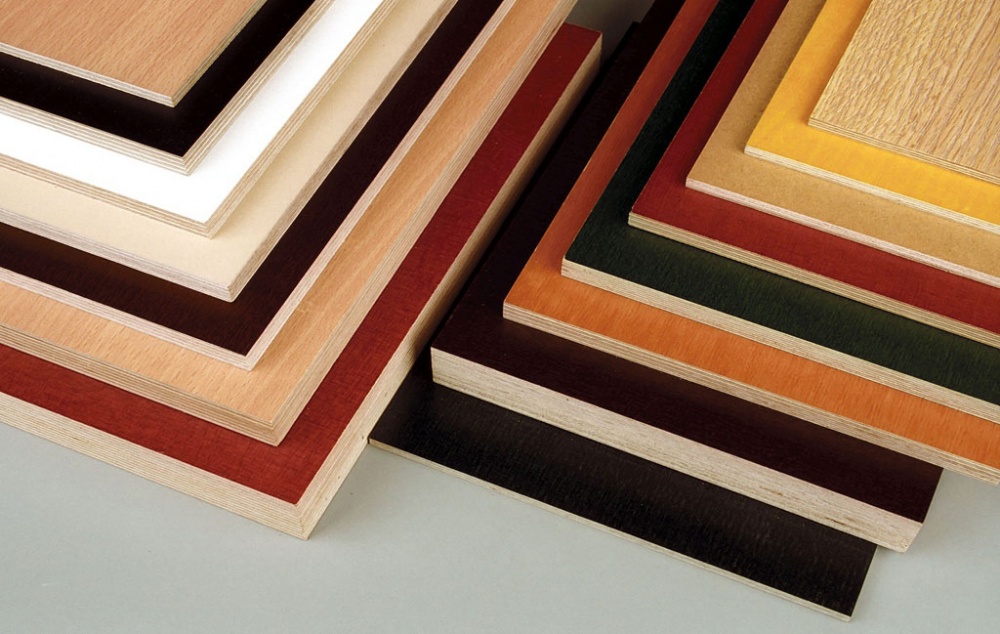
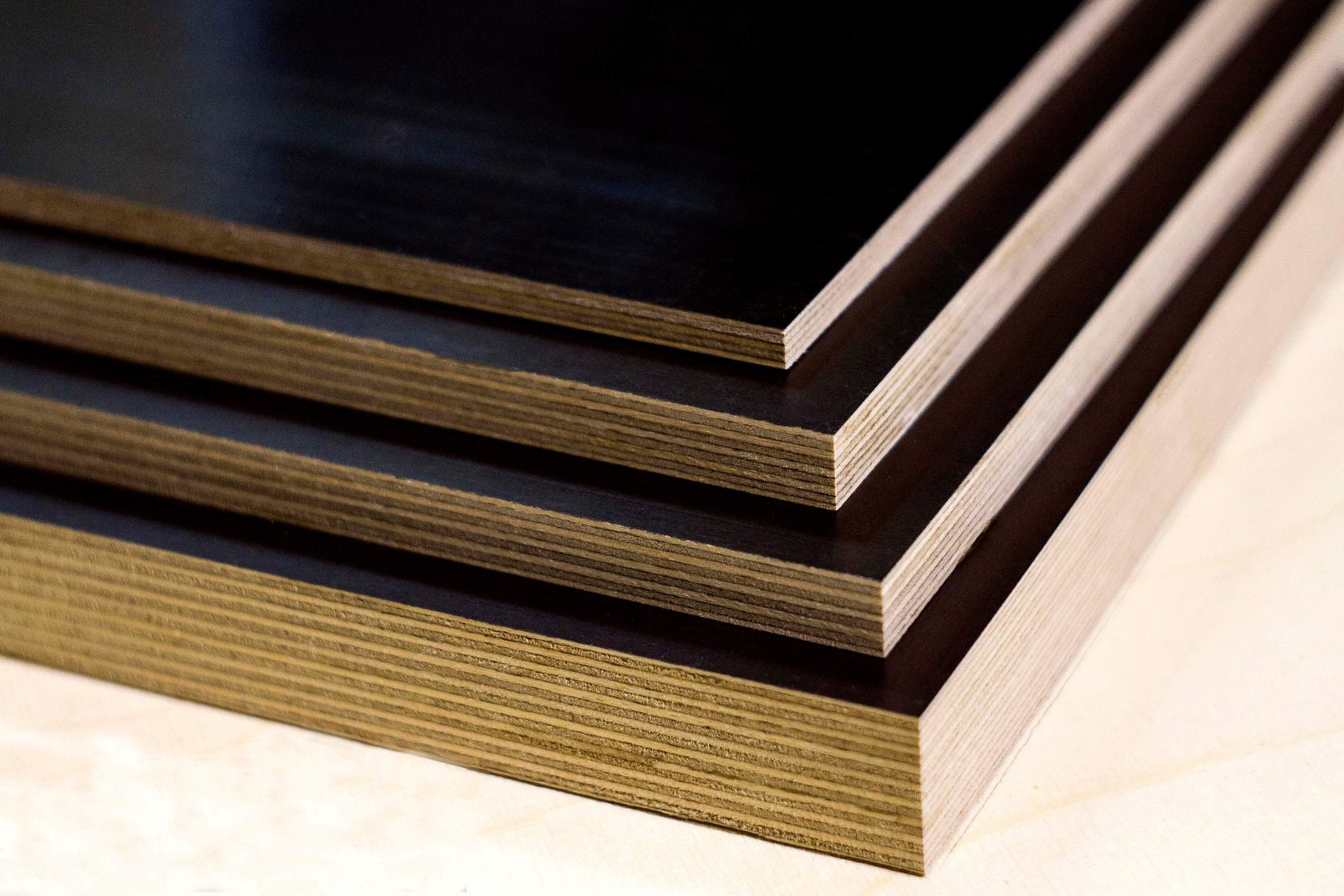
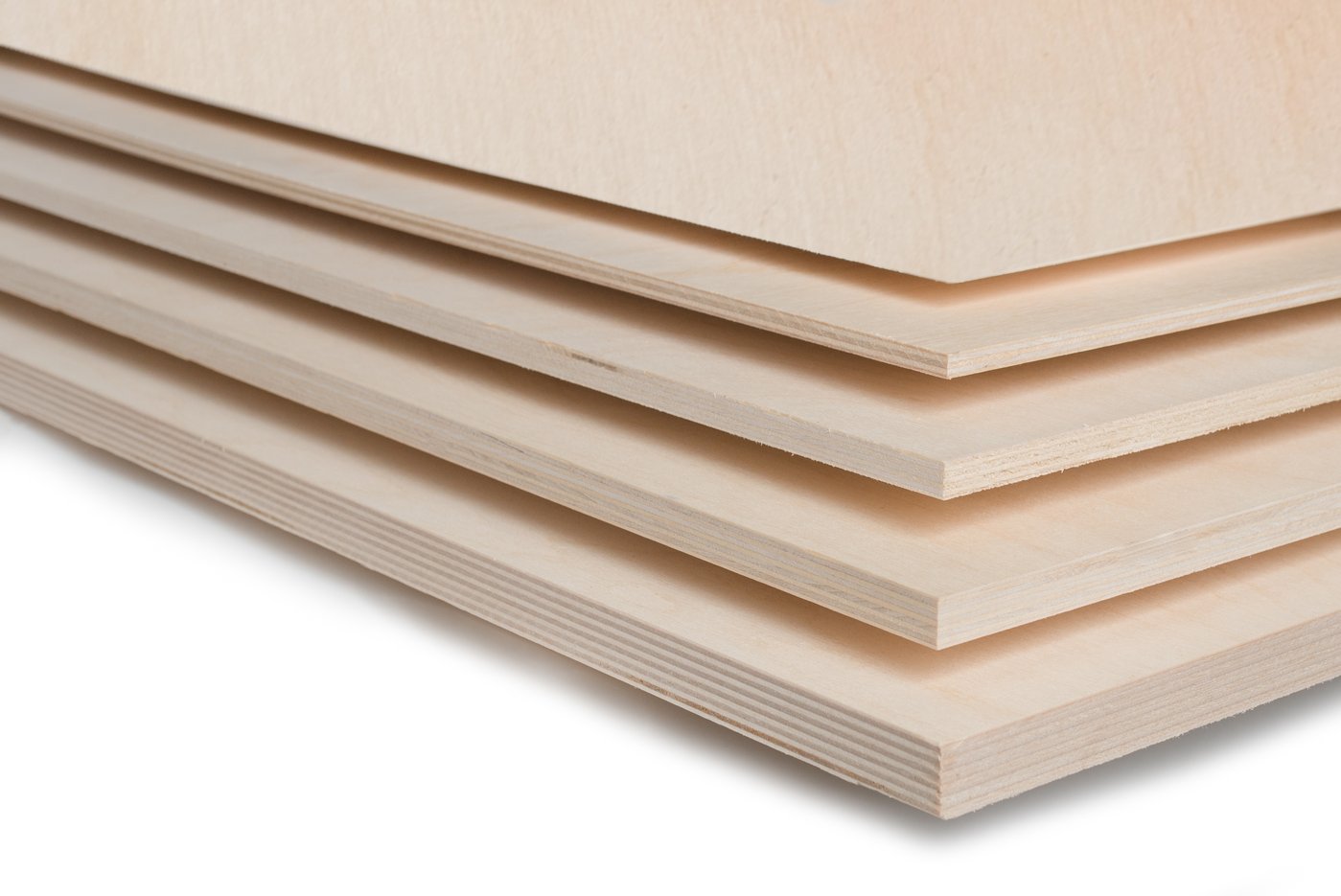
Application area
The easiest and cheapest way to fix plywood in the manufacture of a sub-floor with self-tapping screws on the logs. Laying this sheet material directly onto the screed is more time consuming. In addition, the budget for the renovation / finishing of the premises is increasing. It is impossible to mount insulation between the concrete base and the plywood. Therefore, the thermal insulation must already be laid in the screed at the preliminary stage. Under the flooring, you can only use a film warm floor.
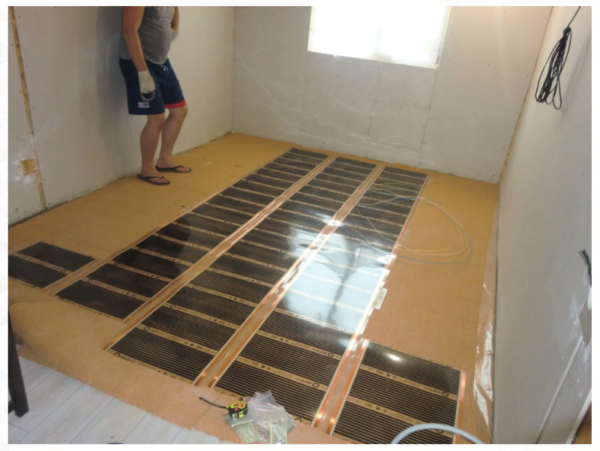

All these disadvantages of technology are compensated for in the following cases:
- logs cannot be used, since the level of the finishing cladding will rise in one room, an uncomfortable step will appear;
- the insulation is already laid inside the screed or thermal insulation of the subfloor is not required;
- the room will use floor coverings with a coefficient of thermal expansion that is significantly different from the illogical characteristics of a concrete screed.
Therefore, PVC linoleum, synthetic carpet, parquet board and natural parquet, laminate manufacturers of these finishing materials always recommend laying on plywood.
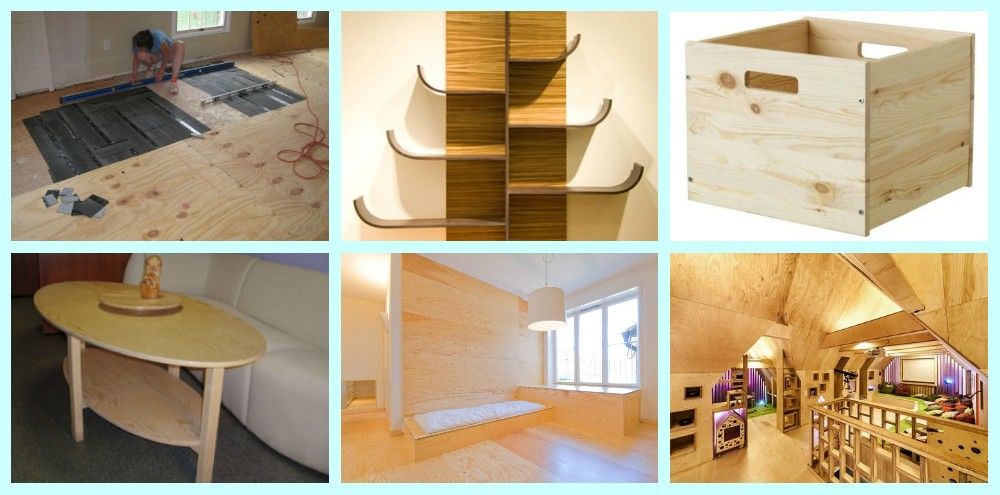
Features of furniture plywood
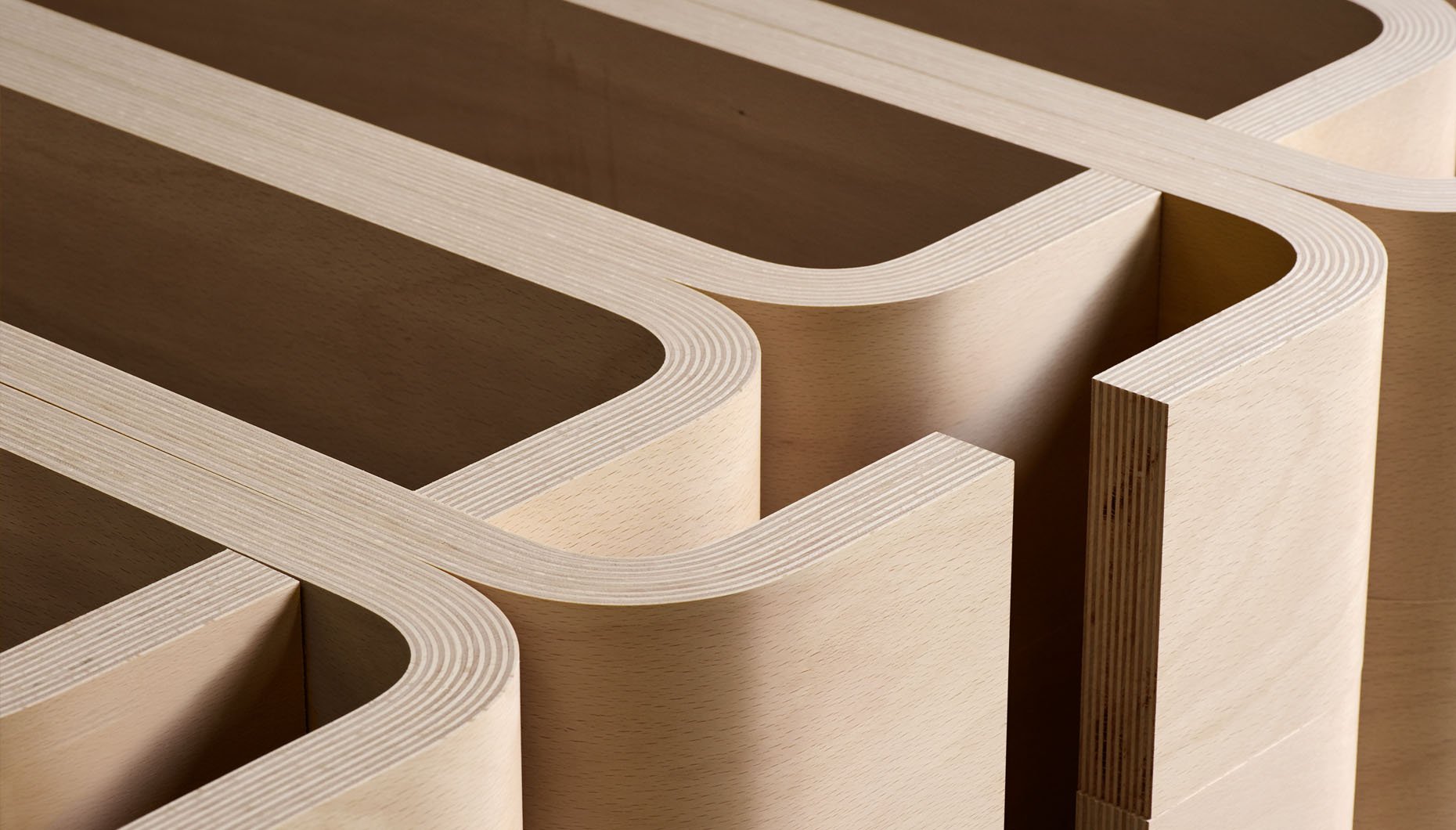
Film faced plywood for the manufacture of furniture.
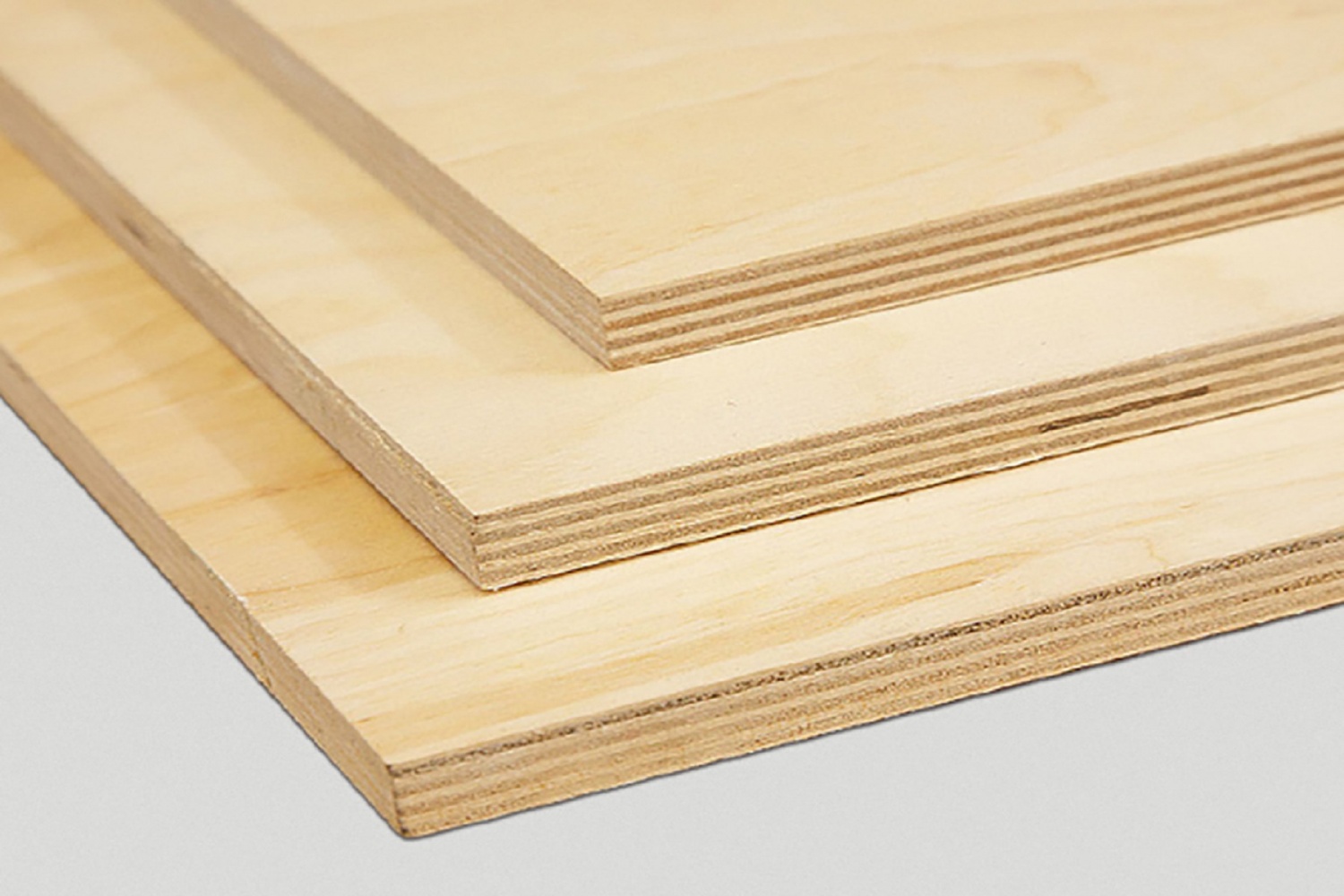
- For the manufacture of furniture, sheets are used with a thickness of 3 mm (three-layer plywood of low grades, which is most often used for the back walls of mirrors and the bottoms of drawers) to 30 mm (five-layer panels of a high grade, which are used for desktops).
- In the production of high quality furniture, expensive decorative veneer is used as the front layers.
- Since plywood furniture must not only be durable, but also have an attractive appearance, its production is carried out in special workshops, where adhesives and workpiece parts are carefully selected.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Plywood Sheets Compared to Wood
 The photo shows a TV stand made of plywood.
The photo shows a TV stand made of plywood.
Materials such as panel board or plywood are successfully used in furniture production, and today, much more often than natural wood. As mentioned above, the main reason for this is the low price of plywood sheets.
However, in practice, this material has a significant number of advantages.
Let's take a look at some of them:
- It consists of wood, only of its thin layers (about 1 mm), while its price is an order of magnitude cheaper.
- Even large plywood sheets are dimensionally stable. This is achieved due to a special production technology - crossing the veneer fibers.
- Real freedom of choice in terms of size.
- High lateral strength when compared to a wooden panel of the same thickness.
Unfortunately, this material besides the advantages.
It also has some disadvantages:
- The mass of the plywood sheet will be greater than the wood of the same thickness.
- The ends have stripes, which affects the aesthetic perception of the product, since many people negatively regard plywood as a material.
 Facing the ends of plywood.
Facing the ends of plywood.
This material gives you less freedom in surface treatment, since the face layers are about 1 mm thick, so they can be "removed" with a tool if careless. Some manufacturers save on adhesives by using adhesives that are harmful to human health.
Thus, buying plywood from an irresponsible manufacturer can backfire, which cannot be the case with purchasing even the lowest quality natural wood.
Stamps
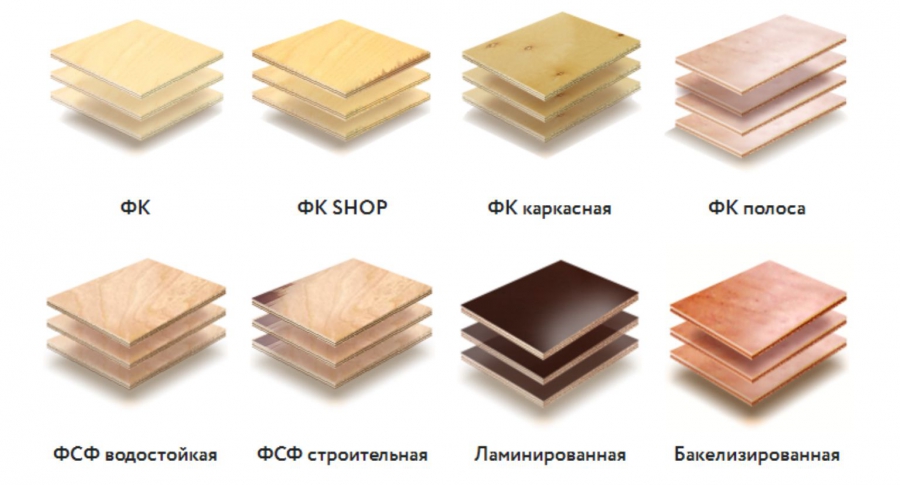
FBA
This type of plywood is produced by gluing the veneer with a special albuminocasein mixture. From an environmental point of view, FBA is an impeccable product, but it cannot be used everywhere. To maximize the use of such plywood is hampered by its insufficient moisture resistance.
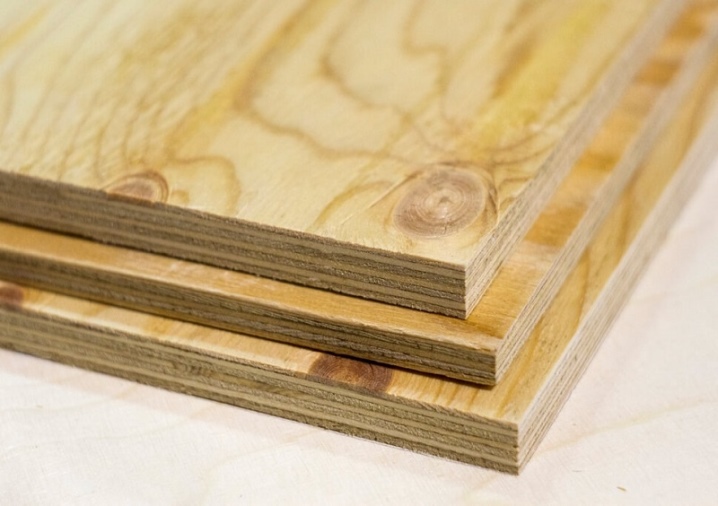

FSF
Such a brand means sizing with a resinous composition based on phenol-formaldehyde. Such processing guarantees excellent performance properties. The material will be mechanically strong and practically wear-free. The moisture resistance is quite high. FSF is used in the construction industry, industry, and is often purchased for roofing work.


FC
This option involves joining veneer using a carbamide composition. This technology is much better suited for various indoor environments. Plywood with urea glue is very durable. The level of safety is sufficient for use in furniture, so it is also suitable for the floor.


FB
In this case, the veneer is saturated with bakelite-based varnish. This solution dramatically increases the resistance to water ingress. The FB slab can be safely used even in tropical and subtropical regions. The thickness of the workpiece is usually small, since insulation is not provided. FB is also suitable for floors in laboratories, kitchens, workshops and other places where exposure to aggressive substances is likely.
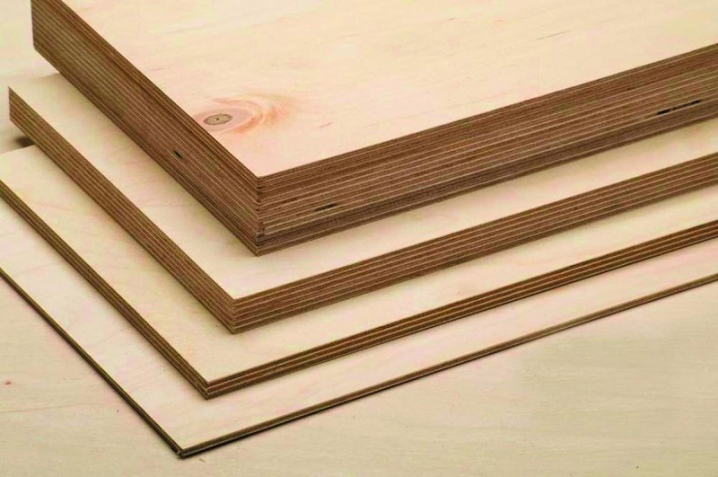

BS
In this case, treatment with a bakelite-based composition is also used, but not with varnish, but with glue. This veneer is sometimes called aviation veneer, since it was previously used in the production of aircraft and river, sea vessels. This material is very durable and perfectly tolerates contact with moisture. Harmful fungi do not grow in it.

BV
This type of plywood is glued with a water-soluble bakelite solution. Plates obtained in this way are not sufficiently resistant to water. But their strength is at a decent level. Bakelite plywood of any type must comply with GOST 11539-2014. There are no specific restrictions on the size, so it is necessary to cover this topic in more detail.

Selection of material
So that later the question does not arise why the laminate creaks, it is necessary to choose the right plywood for the base. Having decided on the general qualities of plywood, it is worth talking about its individual brands and determining which plywood to lay under the laminate.
There are a huge variety of plywood varieties, among which there are cheap very expensive options, for example, the BS brand has a very high price and is used only in the construction of ships and air transport.

Also, plywood differs in its strength, moisture resistance and toxicity, which does not allow the use of certain brands in enclosed spaces (read: "Which plywood is better for the floor - choose the brand and grade of material").
Types of plywood used for indoor flooring:
- FSF plywood has a high moisture resistance, but it is not recommended for use in residential premises due to the toxicity of the glue.
- FOF is a brand of plywood that is completely harmless, because adhesives without toxins are used for its manufacture, but here its minus is manifested - poor moisture resistance.
- The FC brand is able to withstand the effects of a small amount of water, but it is also not worth watering it. Plywood is harmless and can be used for mounting a base under a laminate.
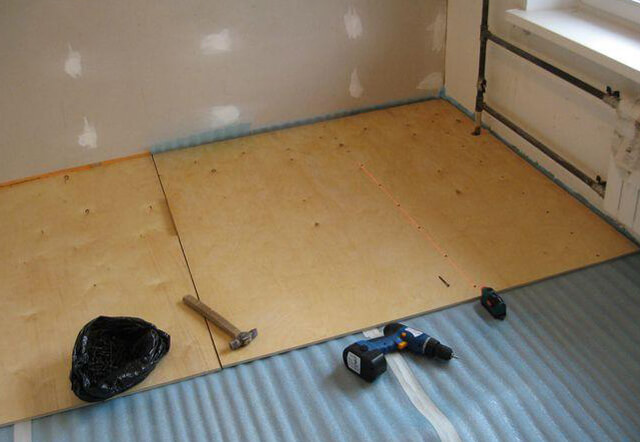

Talking about what kind of plywood is needed for floor under the laminate, you should also pay attention to the material from which the plywood is glued:
- Coniferous base it is resistant to various influences, for example, a fungus, however, when interacting with glue, the resin can release toxins, therefore it is practically not used in residential premises.
- Birch plywood - the best solution for laying the base under the laminate, because it does not emit toxins and is strong enough, however, it should be treated with special antiseptics against fungus and pests.
Having considered all the variations of plywood, it is worth noting that birch plywood of the FC brand is an ideal option for flooring under a laminate, and for outdoor work it is better to use the FSF brand of pine needles.
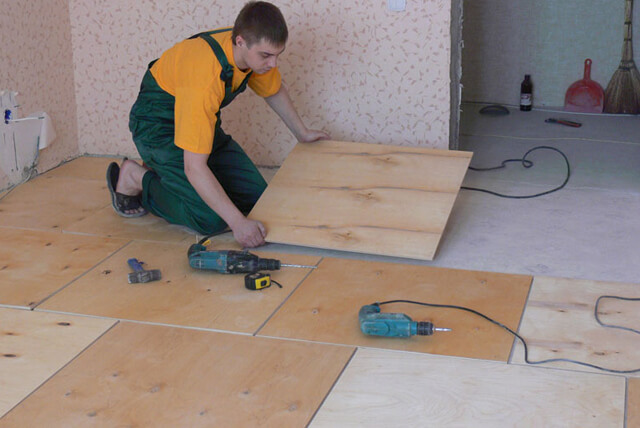

Having chosen the brand of plywood, it is worth choosing the appropriate grade and encoding. Varieties are divided according to the quality of the material:
- Premium plywood does not have any flaws and can be used to level the floor, but it has a very high price.
- Second-grade plywood has minor imperfections such as veneer inserts and knots. It is used for laying the base, but this is also not the cheapest option.
- Third-grade plywood is ideal for laminate flooring. There are many knots and cracks on the surface of the plywood, but they will not interfere with the work. Plywood has an excellent combination of price and quality. It is better to make a choice so that the thickness of the plywood under the laminate is slightly more than indicated below.
- The fourth grade of plywood is not suitable for installation work related to the floor, because it has strong irregularities, and its price is not much lower than the previous version.
The plywood price tag will also have an encoding written, for example, FK-3E1SH1, which we need. It contains various information about the plywood sheet, which is not necessary to understand.
Advantages
Plywood is considered one of the most convenient and practical materials for leveling the floor.
It is known that plywood is a product of wood processing, therefore it has the same basic properties as wood products, while plywood has a number of advantages over wood due to its structure. For example, sheets of this building material, thinner than boards, have the same resistance to mechanical stress with the latest indicators. It turns out that a lighter plywood structure can be no less rigid and resilient than a wooden one. In addition, veneer material can provide an absolutely flat surface, which makes it one of the most successful choices for arranging solid ceilings, walls and floors, and plywood can also be used to create a reliable base for different types of roofing. Nevertheless, the main task here is to determine which plywood is best for the flooring.
It should be said right away that plywood, yielding (and not always) to some related products in a number of indicators, has one main advantage - high environmental friendliness. And its properties are directly related to the brand, manufacturing technology and grade. It should be noted that the domestic industry produces fairly high-quality products, significantly superior to Chinese samples, whose manufacturers strive to use cheap binders and defective veneers in the manufacture. It is often very difficult to determine if the outer layers of products from China have passed the grinding stage.
Factors influencing the choice of plywood

Before making a plywood floor in a wooden house, you need to decide on the type of material. What to take into account when picking up sheets:
- Base type. For example, a concrete base has a high thermal conductivity; losses can be reduced with sheets of greater thickness (from 15 mm). But it is better to sheathe a subfloor made of plywood on logs with a material with a layer thickness of at least 12 mm.
- Room type (area of application). For residential areas, professionals recommend choosing the FC grade, it is produced without volatile chemicals.
- Thickness. Arrangement of plywood flooring on logs requires selection of parameters, since the service life of the subfloor depends on the thickness - the thicker the board, the less it will bend when walking. However, it is not necessary to bend in the direction of increasing the size - this increases the mass of the flooring, which also negatively affects the design of the log.
Considering all the factors, choosing plywood for a wooden floor is not difficult.
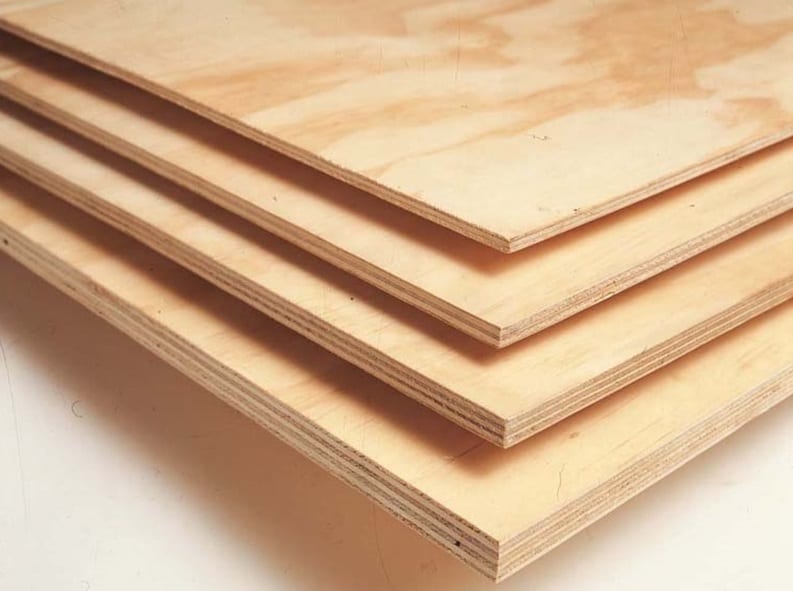
Thickness of sheets

The size range of plywood is varied: the length can reach 6 m, the width is 3 m, and the thickness starts from 3 mm.For roughing and finishing work on horizontal bases, the following are used:
- 1525 * 1525 mm with a thickness of 15 mm - this is the most popular product for mounting sheets on logs;
- 1210 * 2440 mm - used for leveling foundations in multi-storey typical buildings;
- 500 * 3000 mm - sheets for studio-type rooms.
As for what thickness of plywood to use for the floor along the logs, the type of prefabricated screed is taken into account, the load level:
- The degree of load. The greater the load on the floor, the thicker the sheets. Living quarters allow a parameter of 10 mm with a lag step of 0.4 m, but in commercial and other premises it is better to take plates of 22 mm thick.
- Finishing type. The materials of the final cladding also have their own weight, static load, which will press on the logs. If it is a laminate, then there is no big threat of an increase in mass, which cannot be said about an array of boards or tiles.
So, what thickness should be the plywood for the floor along the logs: at least 8-12 mm when installed in two layers, not less than 10-22 mm for a single-layer layout.
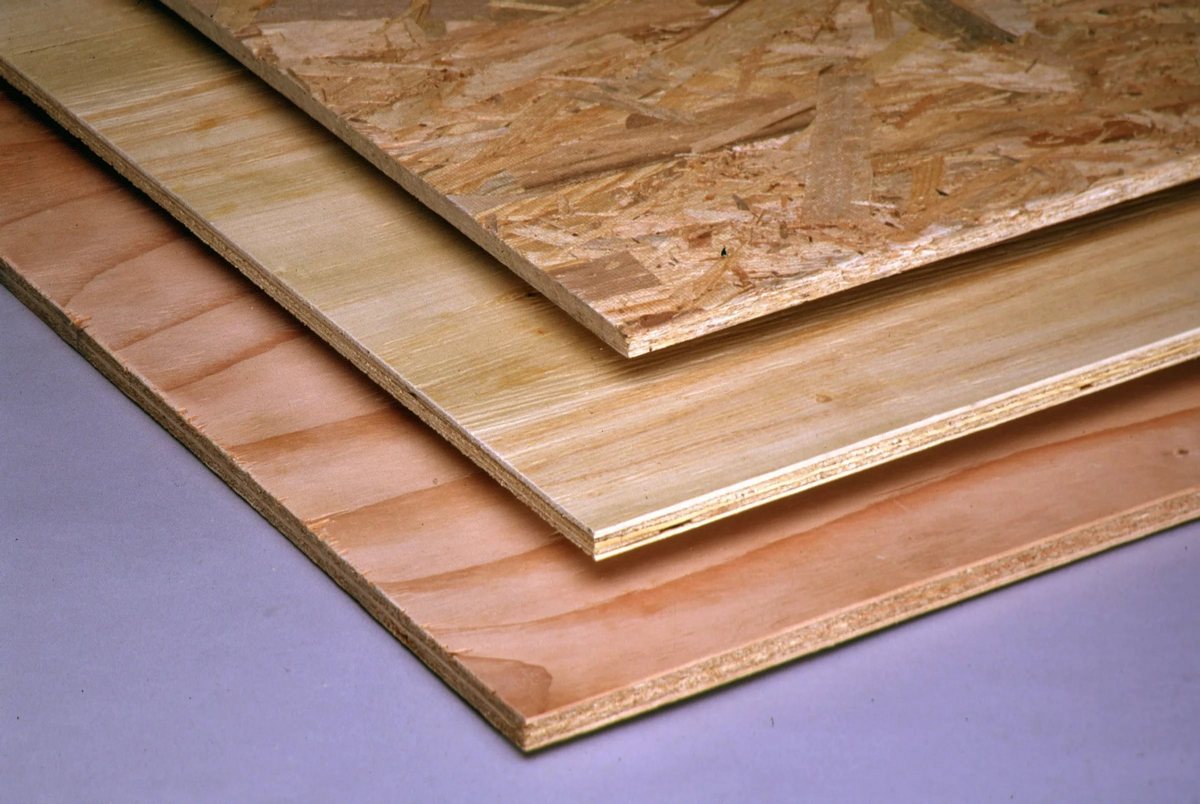
Types of plywood

Depending on the scope of application, the material differs:
- building;
- furniture;
- constructional;
- industrial;
- packing.
According to the classification, material is distinguished:
- Scope of application. For the arrangement of the prefabricated screed, structural and building types are shown.
- Brand. Determined by the type of adhesive used. It differs as follows:
- FSF - sheets with increased moisture resistance, can be used in rooms with normal and high humidity levels. Adhesive resin composition with the addition of phenol-formaldehyde components;
- FC - products of medium moisture resistance, it is better to use in dry rooms. The adhesive composition is urea-formaldehyde;
- FBA - sheets practically do not tolerate moisture. Glue with albumin-casein components.
- Grade. It differs in the permissible number of wood defects, processing defects:
- E - extra class, in the manufacture of which oak, walnut, birch are used. Perfectly flat sheets without knots, chips and other defects;
- I - there are knots of a light or dark shade, no more than 3-5 units / m2. There is no more marriage;
- II - knots (captive) with a diameter of not more than 6 mm in the amount of 6-8 units / m2 are visible, there may be cracks 0.2 cm long and up to 0.2 cm wide (fused or sealed);
- III - sheets with wormholes, knots up to 6 mm in the amount of 8-10 units / m2, cracks 0.3-0.6 cm long, 0.5 cm wide (sealed), dents, scallops;
- IV - grade with defects, chipping along the edge without restrictions.
- The nature of the processing differs in grinding: Ш1 - processing of one side, Ш2 - both sides are ground, NSh - no grinding. You can use any slabs for the floor on the logs, but it is better to take one-sided grinding in order to get a perfectly smooth base for the finishing.
Having figured out what thickness of plywood for the floor on the logs is better, you should determine other suitable dimensions:
- FC brand;
- emission class E1;
- grade: for rough floor 3-4, for finishing 1-2;
- humidity 12-15%;
- number of layers (thickness) 8-12 mm.
Factors influencing the choice of plywood
Before making a plywood floor in a wooden house, you need to decide on the type of material. What to take into account when picking up sheets:
- Base type. For example, a concrete base has a high thermal conductivity; losses can be reduced with sheets of greater thickness (from 15 mm). But it is better to sheathe a subfloor made of plywood on logs with a material with a layer thickness of at least 12 mm.
- Room type (area of application). For residential areas, professionals recommend choosing the FC grade, it is produced without volatile chemicals.
- Thickness. Arrangement of plywood flooring on logs requires selection of parameters, since the service life of the subfloor depends on the thickness - the thicker the board, the less it will bend when walking. However, it is not necessary to bend in the direction of increasing the size - this increases the mass of the flooring, which also negatively affects the design of the log.
Important! Professionals advise to be guided by the distance between the lags (step). If the cell size is 0.5-0.6 m, the sheet thickness must be at least 15 mm
Considering all the factors, choosing plywood for a wooden floor is not difficult.
Thickness of sheets
The size range of plywood is varied: the length can reach 6 m, the width is 3 m, and the thickness starts from 3 mm. For roughing and finishing work on horizontal bases, the following are used:
- 1525 * 1525 mm with a thickness of 15 mm - this is the most popular product for mounting sheets on logs;
- 1210 * 2440 mm - used for leveling foundations in multi-storey typical buildings;
- 500 * 3000 mm - sheets for studio-type rooms.
As for what thickness of plywood to use for the floor along the logs, the type of prefabricated screed is taken into account, the load level:
- The degree of load. The greater the load on the floor, the thicker the sheets. Living quarters allow a parameter of 10 mm with a lag step of 0.4 m, but in commercial and other premises it is better to take plates of 22 mm thick.
- Finishing type. The materials of the final cladding also have their own weight, static load, which will press on the logs. If it is a laminate, then there is no big threat of an increase in mass, which cannot be said about an array of boards or tiles.
Types of plywood
Depending on the scope of application, the material differs:
- building;
- furniture;
- constructional;
- industrial;
- packing.
According to the classification, material is distinguished:
- Scope of application. For the arrangement of the prefabricated screed, structural and building types are shown.
- Brand. Determined by the type of adhesive used. It differs as follows:
- FSF - sheets with increased moisture resistance, can be used in rooms with normal and high humidity levels. Adhesive resin composition with the addition of phenol-formaldehyde components;
- FC - products of medium moisture resistance, it is better to use in dry rooms. The adhesive composition is urea-formaldehyde;
- FBA - sheets practically do not tolerate moisture. Glue with albumin-casein components.
- Grade. It differs in the permissible number of wood defects, processing defects:
- E - extra class, in the manufacture of which oak, walnut, birch are used. Perfectly flat sheets without knots, chips and other defects;
- I - there are knots of a light or dark shade no more than 3-5 units / m2. There is no more marriage;
- II - knots (captive) with a diameter of no more than 6 mm in the amount of 6-8 units / m2 are visible, there may be cracks 0.2 cm long and up to 0.2 cm wide (fused or sealed);
- III - sheets with wormholes, knots up to 6 mm in the amount of 8-10 units / m2, cracks 0.3-0.6 cm long, 0.5 cm wide (sealed), dents, scallops;
- IV - grade with defects, chipping along the edge without restrictions.
Important! If you look at what plywood to use for the floor on logs of inexpensive cost, then grade 1-4 is suitable. But double marking of sheets is possible: 1/3, 2/2 - this means that one side corresponds to a high grade, and the other to a low grade
- The nature of the processing differs in grinding: Ш1 - processing of one side, Ш2 - both sides are ground, NSh - no grinding. You can use any slabs for the floor on the logs, but it is better to take one-sided grinding in order to get a perfectly smooth base for the finishing.
Having figured out what thickness of plywood for the floor on the logs is better, you should determine other suitable dimensions:
- FC brand;
- emission class E1;
- grade: for rough floor 3-4, for finishing 1-2;
- humidity 12-15%;
- number of layers (thickness) 8-12 mm.
Advice! Please note that with a two-layer flooring, the thickness of the overall structure is divided by 2. However, the choice of price here matters: 15 mm thick plywood sheets are not much more expensive than a 30 mm sheet, but laying and transporting lighter material is more convenient
What are the ways of laying parquet boards and block parquet on plywood?
- The floating method provides for the following laying technology: parquet blocks are simply laid on plywood.Since the joints and grooves of the segments coincide, the parquet will not "part" and bubble. Such parquet is easy to disassemble and reassemble if necessary, replace a couple of boards in case of breakdown. But! This method is quite suitable for a parquet board, and in the case of block parquet it is better not to use it: such dies are too small to hold evenly and firmly only due to mechanical adhesion. For block parquet you need glue.
- The glue method is as follows: first, the plywood sheets are laid with a small gap from each other, then they are attached to the base with dowels and screws. Then a special parquet glue is applied to the plywood. They let him dry. Parquet is laid on top of the glue. It is also necessary to glue the grooves and joints with glue.
The glue method is much more reliable than the floating one, it provides a stronger adhesion of the parquet to the plywood, respectively, the floor is smoother, it does not creak or bubble.
So, is it possible to lay parquet without plywood? It is possible, but only if you are dealing with a perfectly flat, noise-insulated base. Otherwise, this can affect the quality of the coating and lead to the fact that, in the worst case, you will be forced to re-finish the parquet. So if it is possible to lay plywood under the parquet, then it is better to do it. Yes, this will require additional costs for the plywood itself, and for glue, and for the work of craftsmen (or it will take more of your time if you do everything yourself). But it saves you the hassle of rework and allows you to enjoy a flat, warm parquet floor. We recommend that you read the article on how to lay your own parquet floor.
Varieties and labeling
There are five grades of plywood. The highest is E (Elite), and further, as it deteriorates, from I to IV. The grade is determined by the state of the upper - front layers. Moreover, the quality of both surfaces is assessed separately and written through a forward slash (slash). For example, I / II or III / IV.
In GOST, it is described in detail for which grade which surface errors are permissible, there are special tables by which this grade is determined. If at least one parameter is worse than the permissible value, the grade is reduced.
Varieties differ in the presence and size of certain defects
These are the features on the front surface of different grades of plywood.
-
Elite. For this brand of plywood, the veneer must be perfect. There can be only minor changes in the wood (no eyes). Everything. There shouldn't be any other drawbacks.
-
I grade. May be
- Knots:
- pin, no more than 3 pcs per square meter;
- healthy, intergrown, dark and light with a diameter of 15 mm, no more than 10 pcs / m², they can have cracks no more than 0.5 mm wide;
- partially accreted, not accreted, falling out with a diameter of no more than 6 mm in an amount of no more than 3 pcs / m²;
- Closed cracks no more than 200 mm long and no more than 1 mm of the sheet width.
-
Healthy discoloration - no more than 5% of the area.
- Knots:
-
II grade. Allowed:
- Knots:
- pin without restrictions;
- healthy, intergrown, dark and light with a diameter of 25 mm, no more than 5 pcs / m², they may have cracks no more than 0.5 mm wide;
- partially accreted, not accreted, falling out with a diameter of no more than 6 mm in an amount of no more than 6 pcs / m²;
- Closed cracks no more than 200 mm long and no more than 1 mm of the sheet width.
- Open cracks no more than 200 mm long, no more than 2 mm wide in an amount of no more than 2 pcs when covering with putty.
- Healthy discoloration is allowed.
- The overlap in the outer layers is not more than 100 mm in length, in the amount of not more than 1 piece per 1 m of the sheet.
- Leakage of glue no more than 2% of the sheet area.
- Torn fibers no more than 5% of the sheet area.
- Scratches, dents are allowed in depth (height) within the limits of the maximum deviations in thickness.
- The gap in joints with a width of not more than 1 mm is not more than 1 piece per sheet.
- Wood inserts no more than 8 pcs per 1 m².
-
Double insert - no more than 2 pcs per m².
- Knots:
-
III grade.
- Knots:
- pin without restrictions;
- healthy, fused, dark and light with cracks no more than 1.5 mm wide;
-
partially accreted, not accreted, falling out with a diameter of no more than 6 mm in an amount of no more than 10 pcs / m²;
- Closed cracks without limits.
- Open cracks
- length no more than 300 mm no more than 2 pieces,
- no more than 600 mm long, no more than 5 mm wide in an amount of no more than 2 pieces when covering with putty;
- Healthy discoloration is allowed.
- The overlap in the outer layers is no more than 200 mm in length, no more than 2 pcs per 1 m of the sheet.
- Leakage of glue no more than 2% of the sheet area.
-
Torn fibers no more than 15% of the sheet area.
- Scratches, dents are allowed in depth (height) within the limits of the maximum deviations in thickness.
- The gap in joints with a width of no more than 2 mm is no more than 1 piece per meter of sheet.
- Wood inserts and double insert - no limit.
- Non-ferrous metal brackets are allowed.
- Knots:
-
Class IV may have such defects.
- Knots:
- pin;
- healthy, fused, dark and light without limits;
- partially fused, not fused, falling out with a diameter of no more than 40 mm without restrictions;
- Closed cracks without limits.
- Open cracks
- no more than 300 mm in length without restrictions;
-
no more than 600 mm long and no more than 10 mm wide without restrictions;
- Healthy discoloration is allowed.
- Overlap in outer layers is allowed.
- Leakage of glue is allowed.
- Torn fibers are allowed.
- Joint clearance is allowed.
- Scratches, dents are allowed.
- Wood inserts and double insert - no limit.
- Non-ferrous metal brackets are allowed.
- Knots:
Compliance with the designations of plywood grades according to various standards: GOST 3916.1-96, TU 5512-002-00255214-2000, GOST 10.55-71
If there are defects that are not listed in the GOST, the product is considered off-grade. It is also considered off-grade when the maximum permissible size of defects is exceeded. Sometimes they try to sell such products as the fourth grade, but this is a re-grading and the price for it should be much lower.
By the way, if there are no obvious cracks and fallen out knots, the third grade can be used for interior decoration. In certain interiors, it looks even more interesting than E or the first, which are just a flat sheet without any peculiarities inherent in wood.
Other types of plywood products
Plywood for auto-railroad and container building (TU 13-832-85) is produced in the following brands:
Plywood can be of birch or coniferous veneer, on phenolic binders, with a density of no more than 900 kg / m3, format 2440x1525 mm.
Thermosetting plywood has a middle layer of electrically conductive material that can be heated up to 60 - 80 ° C. Plywood of the FTO-V brand is produced with a water-resistant coating of the outer layers based on SBS-1 resin, of the FTO-L brand - faced with a paper film impregnated with phenol-formaldehyde resin. Plywood of the FTO-B brand is produced using the bakelized plywood technology, and the FTO-P brand - using the technology of wood-laminated plastics. The thickness of the thermosetting plywood is 10 - 12 mm. Carbon fiber paper with a resistance of 45-90 ohms acts as an electrically conductive material. Supply voltage - 50-60 V, power density 400 - 500 W / m2.
Composite plywood is a composition of two or three different wood-based materials. A variant of plywood with a center of strips obtained by format cutting of finished products, intermediate and outer layers of business veneer is possible. The flexural strength of such products is not less than 30 MPa. A composition of rotary cut veneer with thin (3 - 10 mm) chipboards is possible. To obtain a strength of at least 50% of the strength of traditional plywood, the proportion of outer layers (veneer) must be at least 1/3 of the thickness of the finished product.
Fireproof waterproof plywood is produced for the construction of passenger railway cars, including subway cars, where the problem of fire safety is very acute.Plywood is produced with a thickness of 15 and 19 mm from hardwood and coniferous veneer impregnated with a fire retardant solution of ZhKU according to TU 6-47-02-88. The impregnated and dried veneer is glued with SFZh-3014 phenol-formaldehyde resin. As for the rest, this plywood is close to the PF-A plywood boards in terms of their performance. Plywood is a low-combustible material with a flame spread index of no more than 20 (GOST 12.1.044-89).
Veneer boards are a material of layers of peeled veneer, usually 3-4 mm thick, glued along the grain into products of almost any size. They are used as a building material for load-bearing and enclosing structures. Compared to conventional sawn timber, veneer boards have increased strength, resilience and dimensional stability.
Comparison of indicators of lumber and veneer boards (LVL beams)
| Index | Veneer boards | Laminated timber, grade L40 | Structural timber, grade T30 |
| Bending stress, N / mm2 | 16 | 14 | 11 |
| Allowable shear stress, N / mm2 | 1,7 | 1,2 | 1,2 |
| Flexural modulus, N / mm2 | 10 700 | 8 400 | 7 000 |
For plywood enterprises, the production of veneer boards is of interest as an opportunity for a more complete use of low-grade and lumpy veneer, for obtaining new products on the same raw material base.
In Finland, the first industrial line of the Raute company with a capacity of 20 thousand m3 was launched in 1975, and since 1984 the equipment has been sold in the USA. Boards are made of veneer with a thickness of 3 mm, the thickness of the finished product is from 19 to 90 mm, which allows it to be used as beams, panels, beams in the construction business. The width of the material is 200-600 mm, the length is 18-23 m and is limited by the capabilities of the vehicles. The new material is similar to thick plywood with the difference that the veneer fibers are located in only one (longitudinal) direction. Phenolic and melamine-formaldehyde adhesives are used, raw materials - spruce, pine, birch. The length of the blocks is 1.3-1.9 m, the consumption of raw materials is approximately 3 m3 / m3.
The production volume of veneered beams in Finland is about 30 thousand m3 per year. In Australia, the veneer-type material is called Hyspan. They produce boards with a thickness of 36, 45, 63 mm and a width of 150, 200, 240, 300, 360 and 400 mm. The length for transportation does not exceed 12 m.It is noted that Hyspan appeared on the market in 1986 and in residential construction (in overhead coverings, when installing floors, as racks, spacers, lintels, etc.) is more economical than lumber.
Material selection
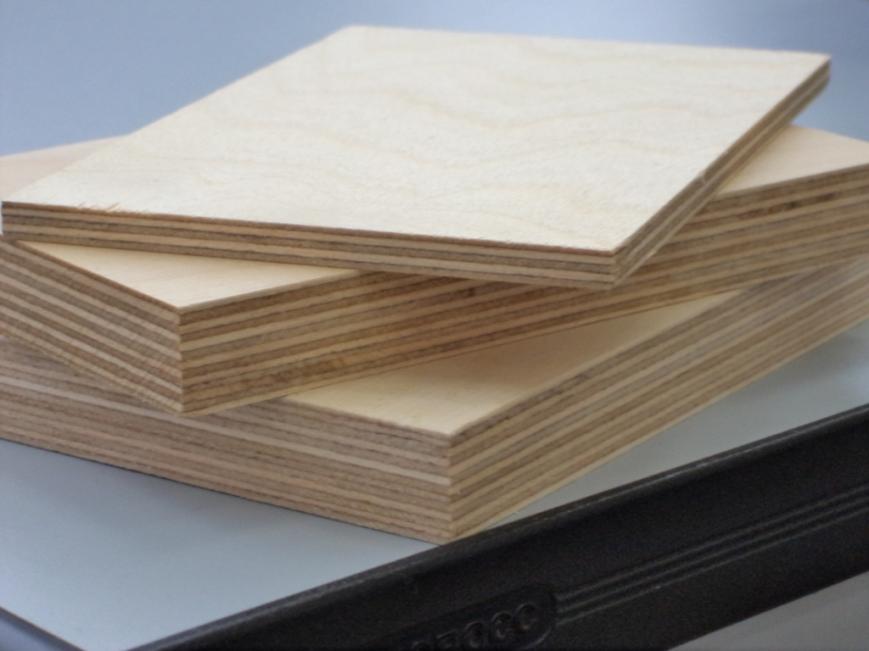
Some sizes of large-format plywood sheets.
When choosing plywood for the floor, you should follow the manufacturer's recommendations for its areas of application. When buying plywood, in order not to make a mistake and prevent unnecessary waste of money, ask the seller about its characteristics:
- brand, since the corresponding marking informs about the level of water resistance of the product;
- type of wood to know if this plywood can be used for floor installation;
- thickness and design of sheets;
- grade, since the quality of the material and the condition of the surface depend on it;
- the availability of lined materials on sale, which are best used when creating topcoats;
- plywood environmental safety class;
- sheet sizes to ensure the most economical use of building materials.
As a rule, the standard dimensions of plywood sheets in length and width are:
- 1.22-1.22 m;
- 1.27x1.27 m;
- 1,475x1,475 m;
- 1.525x1.22 m;
- 1.525x1.27 m;
- 1.525x1350 m;
- 1.525x1.475 m;
- 1.525x1.525 m.
There are also large sizes of plywood. These sheets are called large-format sheets, but they can only be obtained by prior order. In any case, plywood must be selected in accordance with the size and pitch of the lag. It is interrelated with the dimensions of the support beams and the distance between them and the thickness of the glued veneer sheets. Manufacturers produce plywood with a thickness of 3 to 30 mm. Material from 3 to 12 mm is classified as thin plywood, thicker building material is classified as thick plywood. For the installation of the floor, sheets from 10 to 15 mm thick are used. For example, parquet flooring up to 16 mm is laid on a 10 mm base, and from 16 to 20 - on a 12 mm base. For thicker parquet, 15 mm plywood is used.
Difference by brand
FK plywood is used for the manufacture of containers and packaging, as well as in construction and furniture production.
Now more about the brands of plywood sheets. They classify products according to the degree of their resistance to moisture.
- Bakelized (bakelite) plywood (grade FB) has high performance. It is often called Finnish. It is impregnated with bakelite varnish and can be used in any climatic conditions, aggressive environments and sea water. It is preferred by the builders of small vessels. The unique properties of FB are evidenced by its use in the construction of formwork for pouring with concrete. Floors made of this plywood have an almost unlimited life, but its price is significantly higher than the cost of products of other brands.
- BS - plywood, which is called aviation. The veneer is impregnated with alcohol-soluble bakelite glue. The qualities of this plywood are superior to those of BK, so it was widely used in ship and aircraft construction. It is distinguished by increased flexibility, strength, water resistance and resistance to fungi.
- BV plywood is also glued with bakelite compounds, but they are soluble in water. Sheets of this brand have high strength characteristics, but are not able to withstand dampness.
- FC - sheets glued with urea adhesives. This plywood is familiar to almost everyone. Its moisture resistance characteristics leave much to be desired, but the building material is one of the most environmentally friendly. It is possible to improve the resistance of FC to moisture by treating plywood with various impregnations.
- FBA - veneer is glued with albumen-casein adhesives. This brand is also afraid of moisture, but plywood is an environmentally friendly product that can be used to make products for food storage.
- FSF - waterproof plywood is made using phenol-formaldehyde resins. FSF is needed for the floor only on some external site, since this brand has a high level of formaldehyde emission into the atmosphere.
Advantages and disadvantages
Veneered plywood is an absolutely harmless and environmentally friendly material, as its covering is made of natural material. It does not have an unpleasant odor and does not cause allergies
In the production process of the material, you can achieve a variety of colors and surface patterns, which is very important for the manufacture of furniture for other purposes.
During its processing, you can achieve a variety of product configuration and structure, it is easy to cover and bends well. Veneered plywood products look like natural wood, but their cost is much lower than their counterparts, so they are in demand. In many products, a pattern with a beautiful texture is accurately and correctly selected, which gives them an excellent appearance. The material is practical, resistant to temperature fluctuations and high humidity, the surface does not crack or deform. It can be combined from several types of wood, it has a wide range of sizes and colors.
It is worth paying attention to the following disadvantages:
- in order for veneered plywood to serve as long as possible, you need to know that its surface is afraid of direct sunlight, under their influence it can change color;
- in order not to damage the surface of this material, cleaning agents with chemical additives must be excluded in caring for it;
- since a separate sheet has its own individual pattern, it is sometimes very difficult to pick up a pattern at the joints;
- products made from expensive types of veneer, it can be oak, ash, beech, still have a high cost;
- since the thickness of the sheet is not very thick, the material is not used in supporting structures; to improve the quality of veneered plywood, varnishes, natural oils and other compounds are used, with the help of which moisture resistance and wear resistance are improved.