Application of LDPE film
The material has been used as a packaging container for five to six decades. Today LDPE is used as:
food packaging, for the manufacture of food and non-food bags. The film allows you to preserve the integrity of the product and prolong its storage, creates protection from dust, unpleasant odors and water. Bags made of this material are resistant to crushing.
LDPE packages
- wrap food, using in most cases bags and stretch film.
-
Shrink film material is excellent for packaging all kinds of goods.
- Large-sized items are packed in high-pressure polyethylene, which facilitates the process of loading and transportation.
packing large-sized items in LDPE film
- In a thickened version, brick and block material is packed, furniture and equipment are wrapped in it during repair work.
- During the cleaning of construction waste, large bags that are resistant to damage have proven themselves excellent.
The film is in great demand in the rural industry. It is appreciated for two qualities - it does not allow moisture and vapor to pass through. The material is used for greenhouses, as it is much cheaper than glass. Foil is used to cover the bottom and top of the silo storage pits to speed up the process and protect the ground.
The manufacturing process is straightforward, the film is relatively cheap. With careful handling of technical polyethylene, it becomes possible to use the material multiple times.
Differences in application
Technical film is limited in use, while its cost is significantly lower compared to the cost of the primary one. It is not used, for example, for packaging medicines and food. The rapid destruction of the so-called "secondary" under ultraviolet exposure does not allow its use in greenhouses. The presence of its own odor and less attractive external characteristics should be taken into account when packaging industrial products.
Scope of use
The "secondary housing" found active use as an agricultural film for mulching the soil, for steaming the soil and for arranging feed storage facilities, as well as as a secondary packaging film for doors, windows and other construction mechanisms and components.
Recycled LDPE film is used for finishing construction work, as well as for steam and waterproofing, in addition, it is used for the manufacture of garbage bags. This film is ideal for protecting building materials and equipment from moisture and rain.
In general, construction film can be used everywhere, provided that there is no prolonged exposure to sunlight and the appearance is not important, and also if there are no products, cosmetics or medicines in the place of its application - that is, where it can be dispensed with.
How to choose
Purchase plastic wrap based on net weight (excluding packaging and spool) and film thickness. You can find out the real thickness and price of 1kg of film only by knowing its net weight. Indeed, many film manufacturers significantly underestimate its thickness, taking advantage of the plasticity of the film itself, which cannot be characterized by the same thickness at all points, and the lack of micrometers for buyers.
Weighing the film is the surest way to control film density. That is why specialists in the field of plastic wrap always focus on the price not per running meter, but per kilogram.
If, in the process of choosing a supplier, you went to a site that provides information only about the thickness of the film, but there is not a single word about the weight of the roll, leave from there, despite the attractiveness of its price. The actual thickness will not correspond to the declared one with almost 100% probability. For example, in the markets of the capital, the thickness is usually underestimated by 45-55%.
According to the standards, the final weight of a roll of 1 or 2 grade film with a width of 3 m, a thickness of 100 microns, with a 100-meter winding length should be equal to 27.6 kg. Unfortunately, due to the high cost of this quality film, it sells very poorly. Even in our country, the premium 100 micron film has a real thickness of 90 microns, since it weighs 25 kg. However, with the help of our equipment, a film of 10% thickness difference is produced (i.e., the thickness varies within 81-99 microns), therefore such a film has full compliance with GOST, which determines a thickness deviation of ± 20% (i.e. 80- 120μm) for premium grade.
MegaPlast produces secondary and primary films. Data on the price of the product per kilogram and its net weight can be clarified by calling (495) 970-43-59.
Features of production and technical characteristics
LDPE shrinkable polyethylene film is produced by extrusion. The property of heat shrinkage is imparted to the film by pneumatic stretching of the finished product at a high temperature with further cooling in the stretched state. Subsequently, under the influence of a given temperature, the film will tend to return to its original dimensions before stretching, thereby decreasing in volume.
The production of shrink films is carried out according to world standards in an industrial way. In Russia, this is the state standard GOST 25951-83.
| Index | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Thickness, mm | 0,024-0,24 |
| Longitudinal shrinkage,% | 30-60 |
| Transverse shrinkage,% | 20-40 |
| Colour | transparent, colored |
| Weight 1 m2, g | 27,6-184,0 |
| Use temperature, С | -50 — +30 |
| Shrinkage temperature, С | 120 — 300 |

The required film thickness is chosen depending on the tasks. Softer and lighter goods can be packed in thinner films. If the item is very heavy or has sharp edges and details,
then a thicker shrink film is used for its packaging. However, as the film thickness increases, the temperature and shrinkage time increase. The problem is solved by using a multilayer heat-shrinkable LDPE film. This film is produced by coextrusion, and allows you to achieve the required strength of the package without increasing its thickness. Each of the layers of the multilayer film provides additional protection for the packaged product from tearing, cutting or puncturing.
Usually, the color of LDPE shrink film is left typical for polyethylene - white, translucent. It is possible to paint the film in any color, as well as to apply advertising slogans and logos to the surface.
Application of technical polyethylene films
The main application of the recycled film is in the packaging of goods, construction, agriculture.
Food manufacturers use secondary PVC sleeves for mulching the soil, warming up the earth after winter cold weather, and sheltering plants in the early stages of growth, when a large light transmission capacity is not yet required.
Drip irrigation tubes are also made from "secondary".
The low price attracts builders. Technical film sleeves:
- arrange waterproofing of floors and foundations;
- harbor tools and equipment;
- protect surfaces during finishing work from dust, dirt, paint ...;
- perforated membranes equip a vapor barrier.
Garbage bags and packaging for household chemicals are also made from recycled LDPE.
When choosing a secondary (technical) film, it is necessary to focus mainly on the conditions of use and purpose. Taking into account the dimensions, thickness, technical characteristics and qualities of the material will help you make the right choice.
Getting to know the processing technologies
It is possible to use secondary LDPE in Russia thanks to two technologies:
- By processing polyethylene into granules, allowing the return of polymers in the form of raw materials to production.
- The pyrolysis process, the result of which is the production of energetically valuable liquids and gases used as heating oil or raw material for the production of organic substances.
During processing, the decomposition of polyethylene is accompanied by changes in polymer chains. At high temperature and stirring, loss of mechanical properties occurs due to their shortening.
Recycled polyethylene is oxidized using atmospheric oxygen.
Thermomechanical technology for the production of granules
Thermomechanical recycling is a technology by which granules are obtained using LDPE waste. With this production, it is impossible to convert LDPE to HDPE or vice versa, since it is impossible to change the molecular weight and structure of the polymer. But the addition of one type of polymer to another allows you to give the material more rigidity, make it more fluid or plastic.
Processing of secondary HDPE or LDPE granules consists of the following stages:
- Collection and sorting of raw materials, which are produced manually or using mechanisms. When sorting waste, their composition, size, degree of pollution and safety are taken into account.
- Grinding with crushers and shredders, separation of solids and heavy particles using a flotation bath or jet ski.
- Flushing, if necessary.
- Removal of excess moisture during drying in a centrifuge and a chamber with thermal drying.
- Agglomeration at pressure with elevated temperature, when HDPE and LDPE waste partially melts and flows down.
- Granulation in special equipment. Inside the granulator, the substance is heated to a melting state, cleaned of impurities, and degassed. Under pressure, the mixed material enters the holes, which are called molding dies, after which it is cooled with water and compressed air, and cut into granules.
Thermochemical processing: pyrolysis
The pyrolysis technology is used when HDPE is processed, from which it is difficult to produce secondary granules. In this process, secondary HDPE is obtained from multilayer films and waste of cross-linked polyethylene with large contamination. It contains no compounds of nitrogen, sulfur and phosphorus, which makes the material better and safer for others. According to the pyrolysis technology, processed raw materials are obtained through three stages:
- splitting off branches
- cracking the carbon chain
- decomposition of residues
In the first two stages, there is a release from resins, gases and heavy waxes.
The third stage promotes the decomposition of heavy fractions into light ones.
Polyethylene products
PE types
Polyethylene is made by enlarging ethylene hydrocarbon molecules. The polymerization process can take place under completely different conditions: temperature, pressure, and accompanying reactions of the substance give different polymer modifications with a wide range of characteristics:
- Polyethylene "high pressure" (LDPE) has a low density, belongs to the softest plastics and is used to make more flexible and elastic products. Products from it are obtained with the smoothest and most shiny surfaces, having a high transparency coefficient.
- "Low pressure" polyethylene (HDPE) is much denser and harder. It is used for the manufacture of the most durable products that can withstand heavy loads.
- Linear PE combines the strength of HDPE and the elasticity of LDPE, which is necessary in the manufacture of a number of products and is especially used in the manufacture of films.
- Supermolecular polyethylene has unique properties of strength and resistance to various physical and chemical influences.
IMPORTANT! Contrary to beliefs about the impossibility of operating polyethylene at high temperatures due to its thermoplasticity, some of its types are freely used for the manufacture of heating pipes and hot water supply. These are heat-resistant and so-called "cross-linked" (supermolecular) types of polyethylene, which have a structure close to the crystal lattice of especially solid substances.
Types of products
The range of polyethylene products is striking in its breadth and "comprehensiveness":
- Films for packaging, waterproofing, building greenhouses (glass replacement), making waterproof clothing (raincoats, gloves), etc .:
- Smooth,
- Bubbly,
- Stretch,
- Heat shrinkable,
- Scotch.
- Containers for various purposes - from a plastic bottle and food container to canisters and tanks with a volume of up to 200 liters.
- Pressure or non-pressure pipes with a diameter of 10 to 1600 mm with different wall thicknesses:
- Plumbing,
- Gas,
- Sewer,
- Drainage,
- Heating.
- Tableware, both disposable and for longer use, as well as flower pots, etc.
- Toys for children and Christmas trees, souvenir products.
- Electrical insulating shells and plates.
- Anti-corrosion coatings for metal pipes, tanks and other products.
- Shock absorbers for mechanical protection of objects during transportation, protection of pipelines buried in the ground from seasonal and seismic rock displacements, etc.
- Foam materials for heat-insulating shells, substrates, gaskets in building construction, instrument and automotive industry.
- Housings for various devices, apparatus, boats, etc.
- Engineering structures, landscaping items for adjoining and playgrounds.
- Storage tanks for environmentally hazardous substances and waste disposal sites.
- Medical devices and prosthetic elements.
- Dry hot glue in the form of polyethylene powder.
The main stages of production
- Polyethylene granules (or powder) are poured into the hopper. At this stage, it is possible to use special additives to adjust the physical characteristics of the film and its color.
- From the hopper, the polymer flows onto the screw surface of the auger.
- As the screw rotates, the starting material, under the influence of pressure and friction force, self-heats up and begins to melt.
- Having achieved homogeneity, the melt is directly extruded. By forcing the resulting plastic mass through the head, a product of the required shape is obtained:
- Sleeve. The billet obtained after passing the molten polyethylene through a ring-shaped slot is inflated to the required size. The diameter and thickness of the tubular film is regulated by the intensity of the air supply.
- Canvas. The melt is forced through a gap formed between the two plates. Accordingly, the slit width affects the film thickness.
- After forming, the polyethylene sleeve or web is cooled, pulled through the receiving device and wound into a roll.
At all stages, careful control of production parameters (temperature, pressure, etc.) is required to ensure high quality of the resulting film: uniform thickness, without creases and folds.
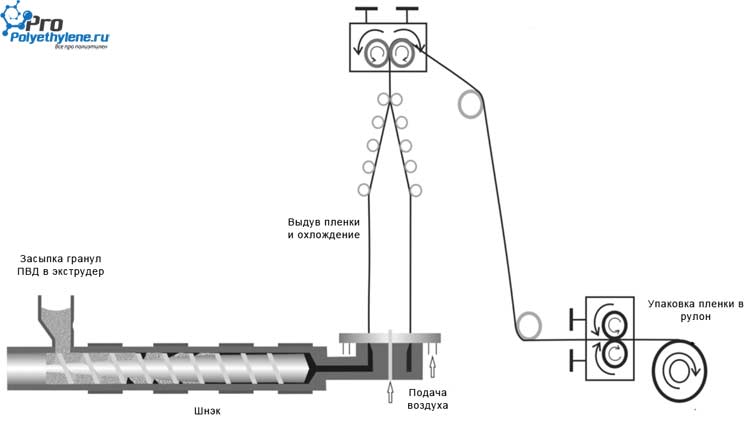
If a drawing or text is planned to be applied to the LDPE film, then its surface, after broaching, is additionally subjected to a corona discharge of an electric current.
LDPE pipes: production, characteristics and purpose
LDPE pipe is made of high pressure polyethylene - a plastic and very durable polymer. It is produced in various diameters in the range of sizes from 10 to 1200 mm and is used in the construction of various communication systems - water pipelines, drainage networks and insulation of electric mains, as well as for the formation of technological openings in monolithic building elements.In particular, HDPE pipes have proven themselves well as casing pipes for wells, as they perfectly withstand both water pressure and small rock displacements.
Basic properties of LDPE pipe
The possibility of widespread use of LDPE pipes is explained by the characteristics of high-pressure polyethylene from which they are made. LDPE is a soft plastic material with very low chemical activity and low brittleness temperature. That is why the products made from it are flexible and resilient, withstanding significant loads.
LDPE pipe characteristics
LDPE polyethylene pipe has the following technical capabilities:
- Resistant to mechanical deformation of impact, tension and compression,
- The possibility of increasing the working pressure of the liquid in the pipe up to 25 atmospheres,
- Resistance to tearing when the content is frozen,
- Imperviousness to corrosion and other destruction of chemical origin,
- The maximum operating temperature is + 40 ° C during normal operation and +80 ° C in an emergency.
Difference from HDPE pipes
LDPE pipes, for which the same monomer is used in the production of raw materials, but a different technology, differ in many respects from LDPE products. They have:
- harder and harder walls and greater strength,
- especially high resistance to chemically active substances,
- lower production cost.
But at the same time, they are more fragile and more susceptible to rupture during deformation, and can also contain many impurities, which is explained by the use of a large number of catalysts for polymerization at low pressure.
Classification
Pipes are made of high-pressure polyethylene, which differ both in diameter and wall thickness, as well as in external and internal structures:
- Smooth one-layer,
- Corrugated,
- Double-walled,
- three-layer reinforced with synthetic thread.
LDPE pipe production
What brands of LDPE are used
According to GOST, domestic high-pressure polyethylene is produced in two basic grades, depending on the manufacturing method (No. 108 - in autoclaves, No. 158 - in tubular reactors) and three grades for each brand. PVD-108 is one of the best materials for the manufacture of plastic pipes, it does not rot, deteriorate or corrode, and PVD-158 can produce the thinnest materials. For the production of LDPE pipes, polyethylene of both grades can be used with the difference that LDPE 108 will be slightly tougher and more resistant to aggressive media, and LDPE 158 will be smoother and with fewer volumetric inclusions.
Production technology
LDPE pipes are manufactured by extrusion from high-pressure polyethylene by heating it to the melting point of the initial raw material - LDPE granules. There are several stages before the final product is obtained:
- Melting of granular polyethylene until a homogeneous mass is obtained in an extruder and forming a pipe of the required diameter from it.
- Vacuum calibration or calibration in hollow cylinders under pressure with partial cooling of the obtained workpiece, which is carried out to maximize the specification of the diameter of the future pipe.
- Complete cooling of the pipe to normalize its temperature by passing through a series of cooling tanks.
- Cutting into individual, ready-to-use products of a specific length.
- Marking and warehousing in finished goods departments. \
Double-layer pipes LDPE - HDPE
In the manufacture of plastic pipes, the technology of combining two layers of different types of polyethylene - LDPE and HDPE can also be used. Double-wall LDPE-HDPE pipe has an outer corrugated layer of high pressure polyethylene and a smooth inner layer of low pressure polymer. This combination can provide a synthesis of product strength and flexibility, which is explained by the properties of both polymer.Corrugated double-walled pipe is used to protect the electrical (telephone) cable during installation work in the ground, concrete, etc. It provides the following benefits:
- Relatively low weight of the structure,
- Resistance to external power loads,
- Excellent chemical protection against various reagents,
- The ability to easily pull the cable along the smooth interior of the pipe.
.
Classification of linear low density polyethylene
There are several classifications of linear polyethylene:
- LDL are copolymers of ethylene with higher alpha-olefins - hexene, butene, octene. It would be appropriate to clarify here that copolymers are one of the types of polymers, the chain of molecules of which consists of 2 or more different structural units. So, in accordance with the above, there are three groups of linear polyethylene - hexene, butene and octene. They vary in strength. Octene LDL is the most durable, hexene is the least durable and butene LLDP is the least strong of the three. In terms of cost, they are also different. The most expensive is, accordingly, the most durable - octene LDL, hexene costs slightly less and butene polyethylene is the least expensive.
- Classification according to the processing method. There are three types of LDL: injection, stretch films and a linear polyethylene tank.
LDL injection molding. Injection molded linear polyethylene is characterized by high elongation at break and excellent tensile strength. Its high melting point of 118 ° C made it suitable for filling hot food. Injection-molded LPVD has good melt elasticity.
LDL film. In almost all areas of film production, linear polyethylene is used - in its pure form, as well as in mixtures with high-density polyethylene. The use of LDL makes it possible to reduce the film thickness by approximately 20-40% in comparison with traditional polyethylene, which naturally leads to savings in raw materials.
LDL rotary. Rotational molding is a fairly new polymer processing method that has developed rapidly over the past decade.
This method produces a wide range of products (tanks, road blocks, containers for liquids and products, plastic pallets, overall design, and so on).
Currently, LDL is used in many areas of human activity and, due to its excellent characteristics, promises to replace the usual LDPE in the next 10-20 years.
High pressure polyethylene (LDPE)
High pressure polyethylene (decoding LDPE or LDPE - abbreviations) is a thermoplastic polymer obtained by polymerization of the hydrocarbon compound "ethylene" (ethene) under the action of high temperatures (up to 1800), pressure up to 3000 atmospheres and with the participation of oxygen.
LDPE is a lightweight, durable, elastic material used in many areas of modern human activity. It can also be referred to as low density polyethylene (LDPE or LDPE), as it has relatively weak intramolecular bonds and, therefore, a lower density than other types of polymers.
Also, the abbreviation LDPE is used for its designation - the English equivalent of LDPE.
High pressure polyethylene (LDPE) is produced in the form of LDPE granules. It has a density of 900-930 kg / m3, a melting point of 100-115 ° C and a brittleness temperature of up to -120 ° C, as well as low water absorption (about 0.02% per month) and high plasticity. These physicochemical characteristics of LDPE as a substance explain the following properties of objects and materials made from it:
- Softness and flexibility of low density polyethylene products,
- The ability to create especially smooth and shiny surfaces from LDPE granules,
- Resistance of LDPE objects to mechanical damage by rupture and impact, as well as to tensile and compressive deformations,
- High strength of LDPE (LDPE) when exposed to low temperatures,
- Moisture and air tightness of LDPE products,
- Resistance of LDPE to light, in particular to solar radiation.
IMPORTANT! The use of high-pressure polyethylene (LDPE) is absolutely safe for both humans and the environment, since it does not emit any toxic substances. That is why LDPE can be used even for contact with food and in the manufacture of baby products.
The difference between LDPE and other polymers
Polyethylenes (LDPE, HDPE, etc.) are materials that are made from one monomer, but can be of different density depending on the manufacturing characteristics.
This indicator strongly affects the properties of polyethylene: an increase in density leads to an increase in rigidity, hardness, strength of products and their chemical resistance.
But at the same time, other indicators fall: impact resistance, the possibility of stretching at break, permeability to liquids and gases. So, LDPE has significant differences from other similar polymers:
- LDPE and HDPE High pressure polyethylene is also called low density polyethylene (LDPE or LDPE) for a reason. Compared to it, hard polymers such as HDPE (low pressure polyethylene) are more susceptible to rupture under the impact of impact, more likely to break in the cold and crack with increasing load, although they are more resistant to radiation, alkalis and acids. LDPE granules and products made from them tolerate ultraviolet radiation much better, and also have a more beautiful glossy surface.
- LDPE and LDL. Another polymer - LDL (linear polyethylene), like HDPE, has a rigid structure, but its technical characteristics are between LDPE and HDPE. It is more resistant to chemically aggressive environments than LDPE and has better puncture and cracking resistance than HDPE.
Types of polyethylene LDPE
Additional processing of high-pressure polyethylene gives qualitatively new materials that differ in chemical and physical properties. In particular, there are modifications of LDPE with improved adhesion to paints and other materials (for example, to metal) and with reduced flammability. At the moment, polyethylene is distinguished:
- foamed LDPE,
- sewn LDPE,
- copolymers of low density polyethylene (LDPE) with other monomers or with other types of polyethylene.
Scope of LDPE
High-density polyethylene (LDPE) currently occupies a leading position in world production volumes among many other polymers. Due to a successful set of chemical and physical properties, LDPE granules are used in the manufacture of:
- LDPE films, open and in the form of a LDPE sleeve for sacks and bags,
- LDPE plastics by injection molding (polymer pipes, technical parts, etc.),
- blown products (bottles, cans, etc.),
- foam insulation materials,
- electrical insulating materials (cable sheaths, etc.),
- LDPE hot melt glue in the form of a powder prepared by crushing LDPE granules.
INTERESTING! LDPE was the first polymer to be used as an insulating material in the electrical industry for insulating submarine cables and later for radars.
Types of BOPP films
Often on sale you can find 5 types of these products. Films are produced with different parameters of thickness (20-40 microns) and width (10-1500 mm). Its sale is usually carried out within a predetermined length.
- BOPP transparent film consists of 3 layers: 2 of them are heat-sealable, and the central one, polypropylene, carries the main load. It is often found in bulk food packaging, as it has excellent transparency and is also complemented by anti-reflective components. The material does not accumulate static charge and glides perfectly. In addition, it is officially approved for food packaging - from ice cream to hot products.
- The mother-of-pearl BOPP film differs from the previous type by the presence of an OOP layer with a microporous structure, which gives the film a “pearl” tint. It is used where protection from direct sunlight is needed, and also, due to its resistance to low temperatures, in the packaging of frozen foods. Like the previous one, it is protected from static charge, glare, glides well and is excellent for printing.
- Metallized BOPP film - the main difference of this material is the increased barrier properties, which are provided by sputtering from aluminum. This coating will be in close contact with the crowned layer, due to the initially high adhesion, and will perfectly tolerate not only printing, but also heat sealing, without losing its reflective properties. Excellent protection against odors, suitable for packaging fish and meat.
- Shrink biaxially oriented has a high ability to heat shrink at relatively low temperatures. Due to this feature, it is often used for packaging cigarettes, therefore it is sometimes called "tobacco". The properties are closest to the first type.
- General purpose BOPP film is the basis for making adhesive tape, as well as packaging products, labels, tapes, etc. Unlike previous types, it cannot be used for heat sealing, since it is made without appropriate layers.
There are other types, for example, BOPP film with polyethylene lamination (packaging of large weight or packaging of products with high fat content), or perforated.
