Where is applied
At the moment, you can find stoves of various models, but the principle of their operation is always the same. Their main difference lies in the type of fuel. They can run on oil, coal, gas and electricity - more modern electric ovens. Furnaces are used for:
- Firing bricks.
- Firing ceramics.
- Bread and pastry production.
- The goals of the metallurgical industry.
Typically, furnaces operate without interruption (around the clock), this allows you to reduce the cost of heating it. Electric ovens are costly, but when working in several shifts (most often three), they quickly pay off. Firing modes can differ depending on two main factors:
- fired product (type, shape, size);
- type of coolant.
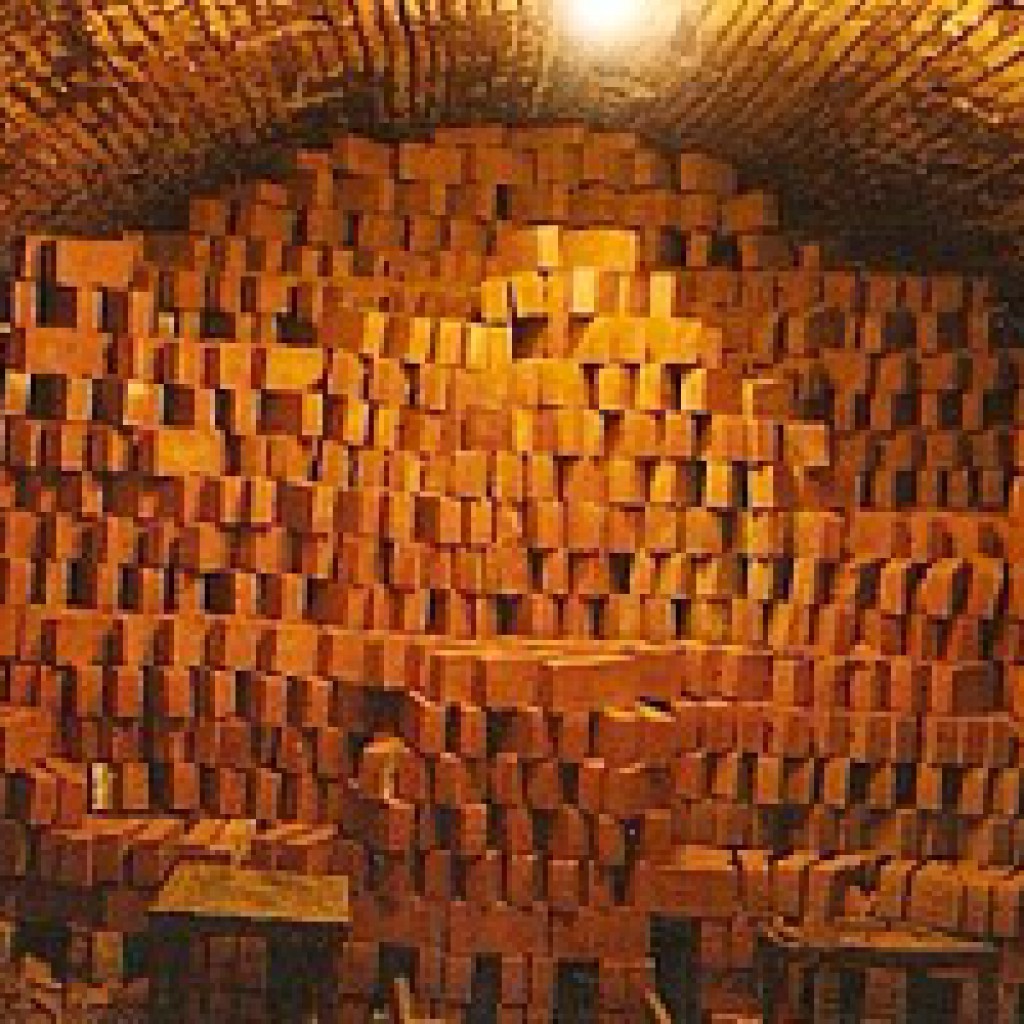
The intensity of firing and its quality is directly related to the type of loading of raw bricks on the trolleys. The trolleys move along the entire length of the tunnel, and are subject to wear due to temperature changes, this is probably the only minus of the furnace. The firing mode is selected from the type of product, the mechanization of the process, the size of the channel and, of course, the fuel. It is unprofitable to install a tunnel kiln at home, it takes up a lot of space, with rare use it is not economical, and without the mechanization of individual stages, the quality of firing will be far from ideal.
Firing in electric tunnel kilns takes place at temperatures up to 1400 degrees. The loading process is carried out on tiles, fireclay or ferrite. To eliminate the adhesion of clay, the tiles are treated with powdered alumina. In some cases, ferrite tiles are fired, this is necessary when laying high rows. Each row is covered with powdered alumina so that the products do not stick together or deform.
Choosing a kiln brick manufacturer
The market for this type of building materials is extremely saturated with products of domestic and foreign companies. In this segment, products manufactured by enterprises from Russia, Belarus and the Baltic republics are widely represented.
Vitebsk brick factory shop №1.
Ceramic bricks from this manufacturer meet the requirements for the material for furnaces in terms of density grade. Frost resistance of products is extremely low. Density grade 180 - 200. The brick can be used for facing the stove and chimney ducts, it is unsuitable for other elements. We can say that this is one of the most common, today, materials for the construction of a furnace. It cannot be used for laying the firebox and the first chimney of the stove. It is required to lining the furnace and the first chimney with refractory fireclay bricks.
With constant direct contact with fire, this brick collapses quickly enough. Since the products have low frost resistance, the use of this brick for laying the outer walls of a chimney street pipe is also excluded. The advantages of this material include the fact that this is one of the most budgetary options and, given all the nuances, it is quite possible to use it for laying the stove. Has 2 working surfaces. In general, the quality of this brick can be described as satisfactory.
LODE.
LODE bricks are produced in the Baltics. Ceramic brick has a high density grade - 500 and frost resistance. The product is used for cladding the outer surfaces of the stove and chimney. The brick of this brand has various shapes and is often used to create all kinds of decorative elements of the stove. According to its main purpose, it is a facing brick.
Borovichi brick factory.
Products of the Borovichi brick factory located in the Novgorod region. The mass production of products began in 2011, experts assess its quality as good.Density grade of ceramic brick M-250, frost resistance indicators at the level of F25. Significant deviations of products from the established standards are noted, up to 10 - 12 mm in one batch. This must be taken into account when laying the stove and it is best to take a little more bricks than necessary. Further, it all depends on the professionalism of the stove-maker and his ability to select the necessary products. The brick has rounded top and bottom edges and 3 work surfaces.
Refractory or fireclay bricks of Russian production.
The quality of products varies greatly, ranging from outright marriage to quite decent products. Fireclay brick has an even cream color and high density, the shape is correct with right angles. As we have already found out earlier, this brick is necessary for the lining of the combustion chamber of classic furnaces, hearths and fireplaces. But it is rather difficult to single out certain manufacturers here.
The answer to the question of which brick is best for the furnace is usually decided by the customer in agreement with the master. It takes into account several factors, among which the main ones are compliance with the requirements of standards and cost. The operational properties of the structure depend on the correct choice of refractory bricks, saving at the expense of quality is expensive.
Features of firing bricks
- What does the brick making process look like?
- Practical advice
- Fired brick production technology
- How to determine the unsuitability of a brick?
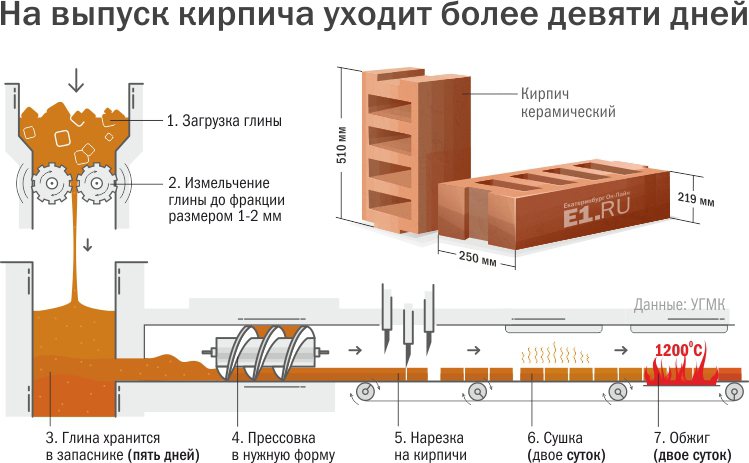
Why brick firing? Construction is one of the most ancient crafts. Since ancient times, people have built their own homes. Initially, branches and leaves were used for this, then clay was used. With the development of mankind, building materials have changed. Brick is very popular today.
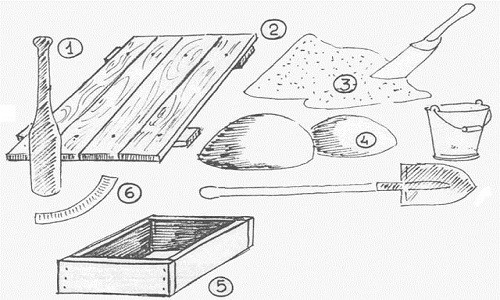
Materials and tools for making bricks: 1 - pestle (tolkun); 2 - flooring; 3 - sand with a scoop; 4 - clay with a shovel; 5 - created; 6 - bracket or scraper.
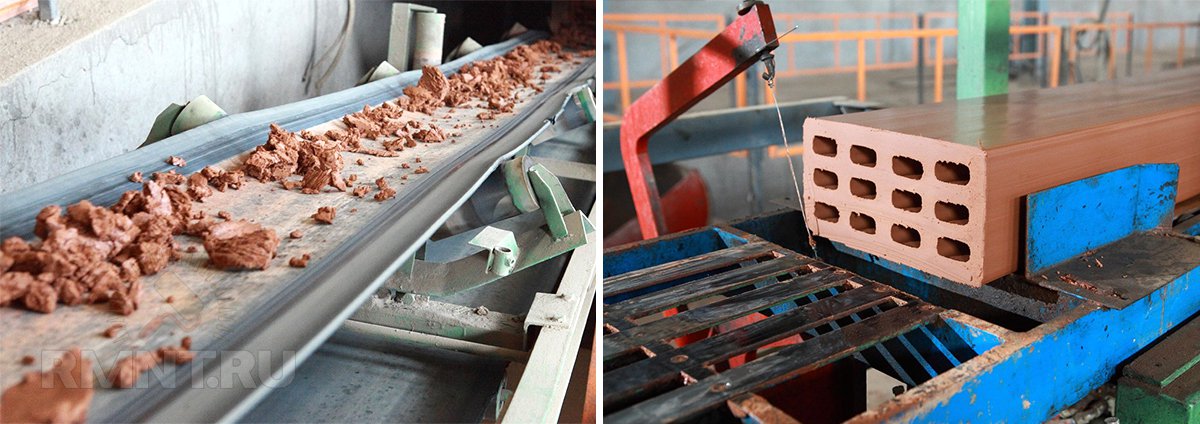
Such material is relevant for residents of rural areas, and they are engaged in its production on their own. The simplest technology for its production requires clay and additional components. The resulting forms dry out, and then the brick firing process follows. It should be said right away that this work requires temperature control during the final firing. Otherwise, the clay will not create a quality material.
Batch furnace device
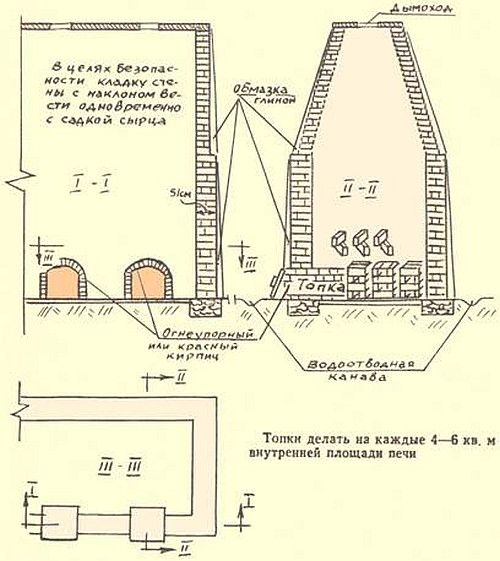
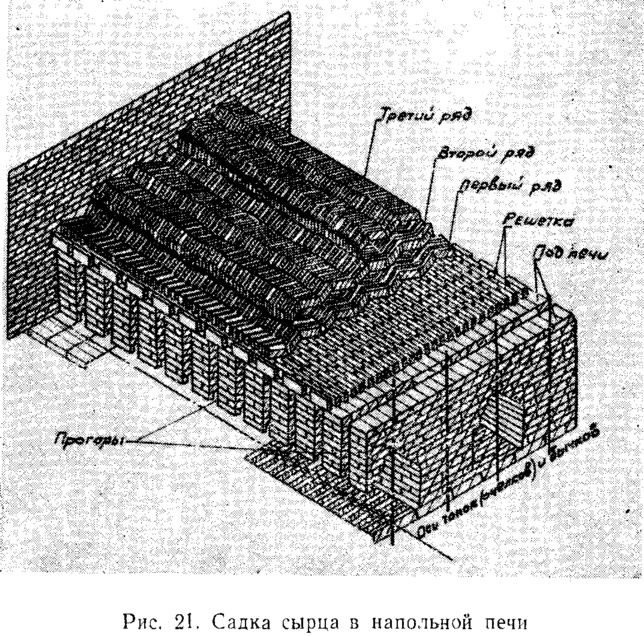
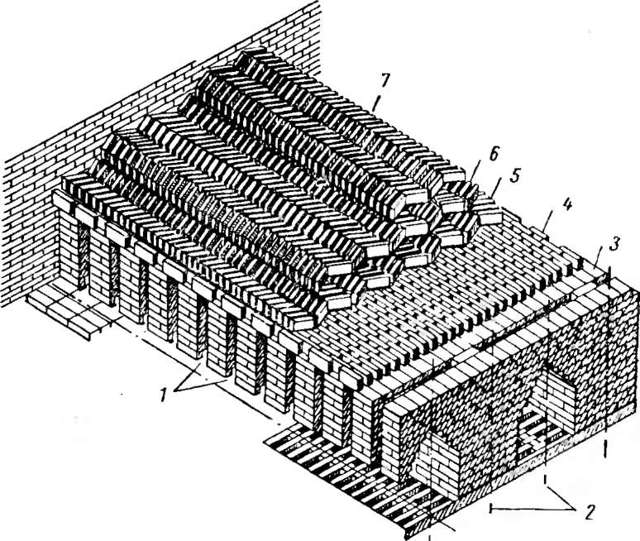
The site for the furnace is selected, if possible, on an elevated place, inaccessible to sedimentary and ground waters. It is cleaned of the vegetation layer, after which they are engaged in horizontal planning and tamping. The smallest furnace has a capacity of 1500 pcs. finished products. Its width - 1.6 m, length - 2 m, stacking height - from 160 to 185 cm. The walls of the furnace are erected from raw bricks one brick thick.
The overlap is built on a metal frame, if each row of bricks of the vault lies on two strips of steel or rods, which are mounted by welding, forming a frame. Above the laying of bricks, the arch in the middle should have a height of at least 35 cm. The firebox or hearth is a through corridor 50 cm wide and 40 cm high. Along its entire length, steps are made at a height of 25 cm on both walls. Then the grains are placed there with coal fuel.
When using firewood as fuel, the grates do not need to be installed. Also, a small square door 40 × 40 cm is provided in the firebox.The vault is equipped with smoke channels with a cross section of 25 × 28 cm.With low-calorie fuel (peat, brown coal), holes 25 × 15 cm are provided with lids serving for fuel supply. The brick chimney is erected up to 5 m in height with an internal section of 40 × 40 cm.
It is installed near the stove, behind it, connected to the smoke channel. It is located in the back wall. In the middle of the wall, holes are left for viewing, they are subsequently laid with bricks, covered with clay.For laying the side and rear walls, vault, pipes, corners of the front wall, use traditional clay-sand mortar. Without mortar, a part of the front wall is laid, which will be disassembled for cutting the cage.
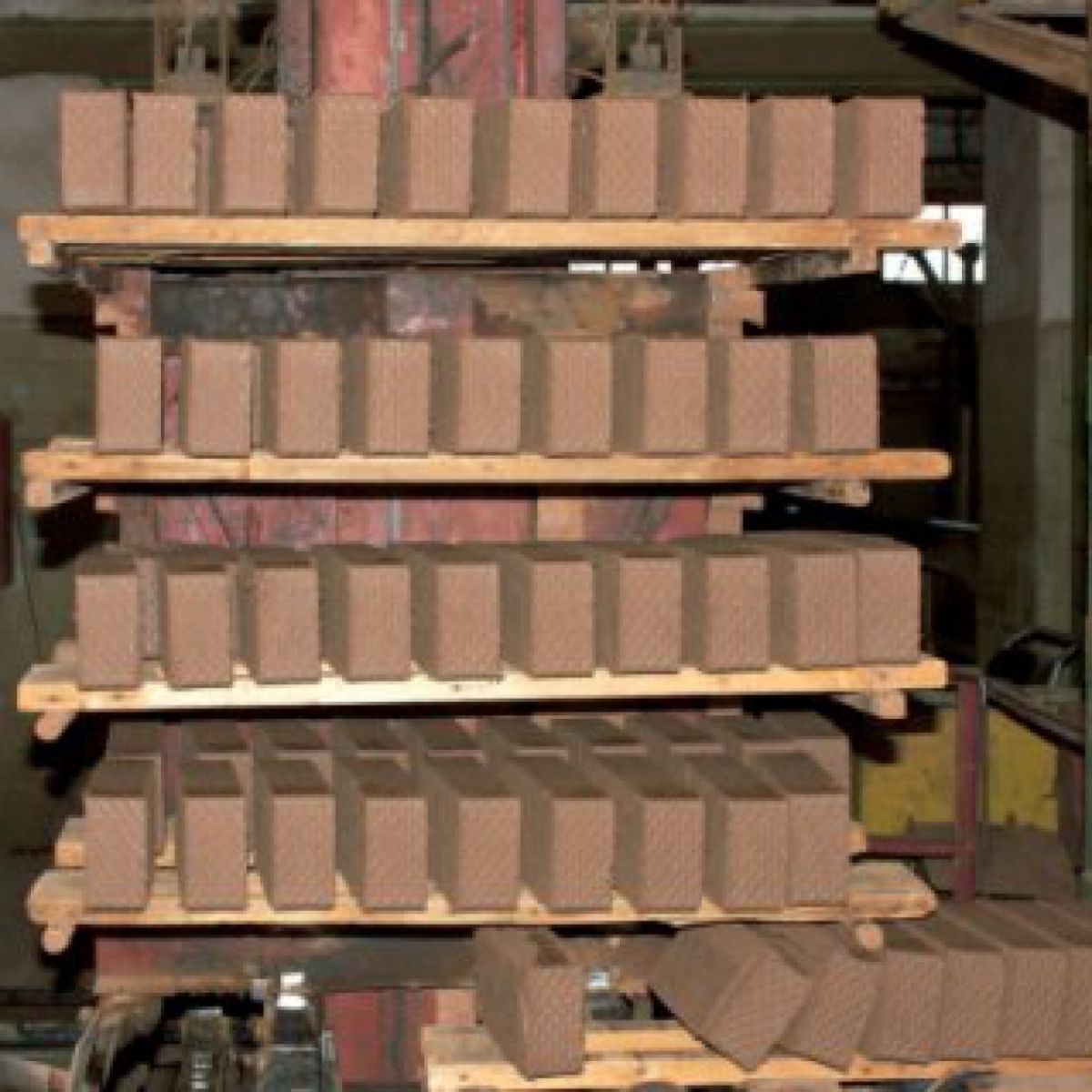
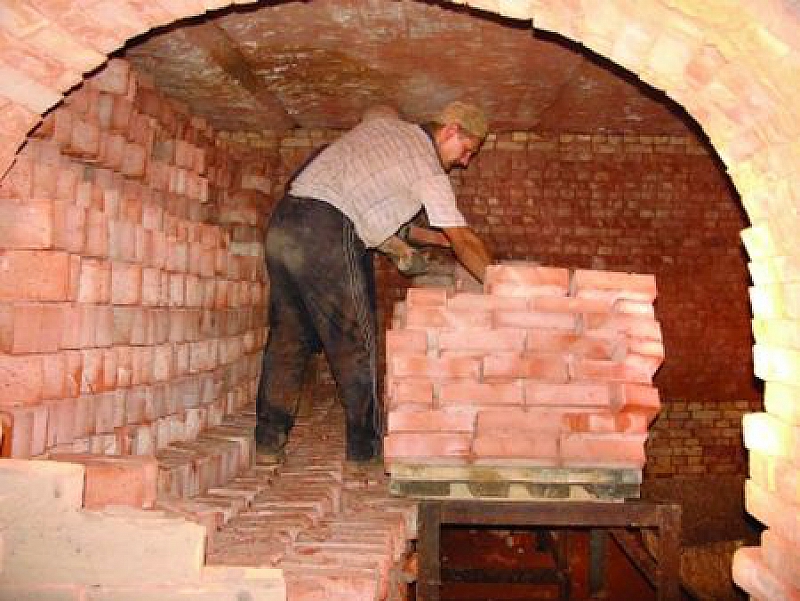
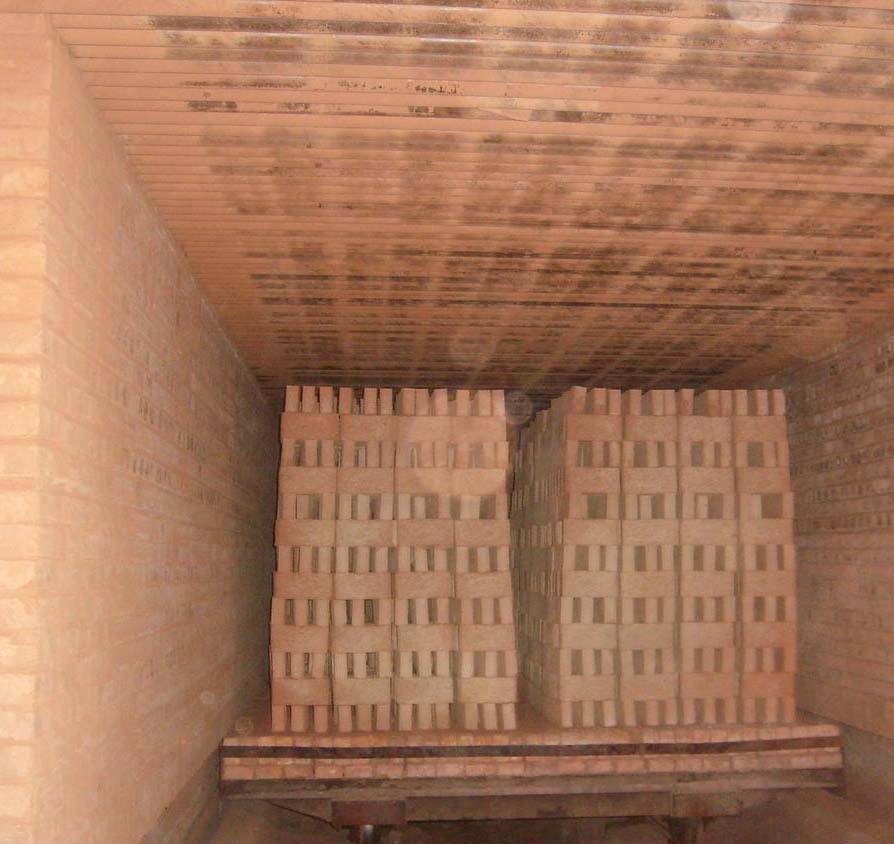
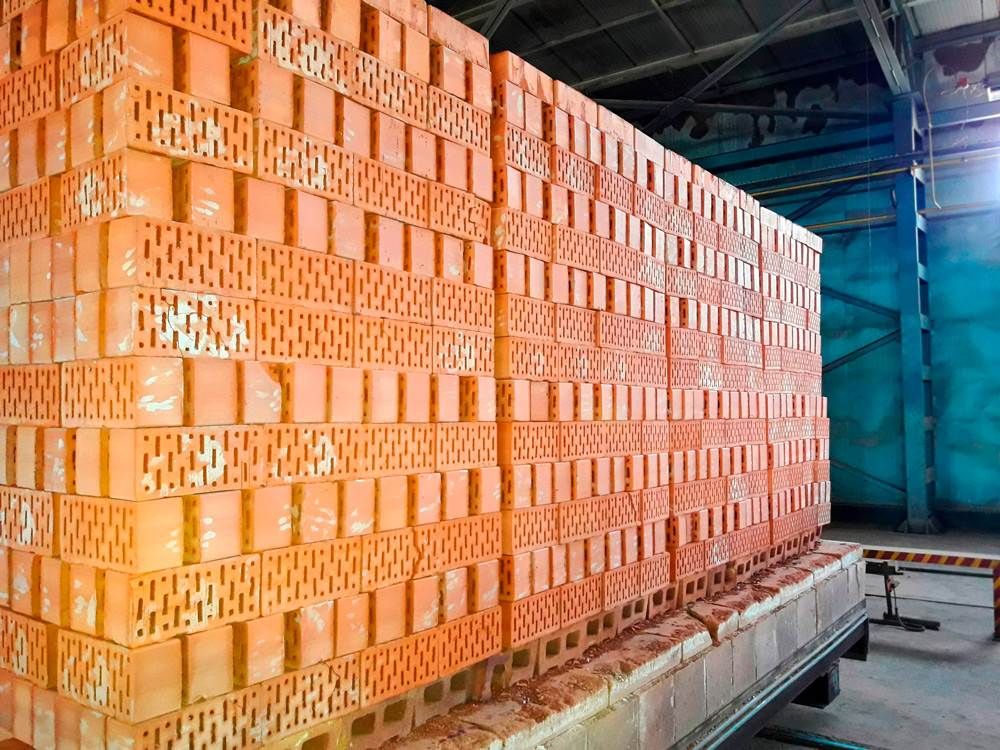
Loading principle in tunnel kilns

loading bricks into tunnel kilns
To create gas ovens for baking bricks, you need
calculate a certain number of products in the required time. Basically in such furnaces there is a large chamber where the raw materials are placed. These chambers are like a tunnel, and in the middle there is an element for heating them. Thanks to these devices, the entire system begins to work. Each of them is divided into sections, which, during the manufacture of bricks, have a certain temperature.
The scheme of brick kilns varies from the structure itself, which has special pushers in each section. They, in turn, cannot work without carts, and for their movement, rails must be laid. To speed up the work process, it is necessary to automate everything, this will significantly save financial investments, and this is a cherished desire for every entrepreneur who decided to start this production.
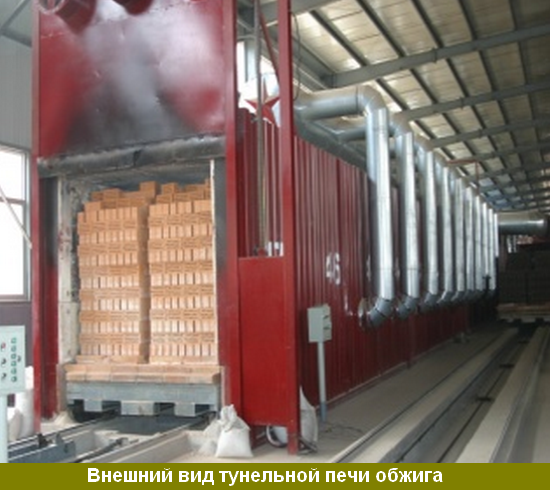
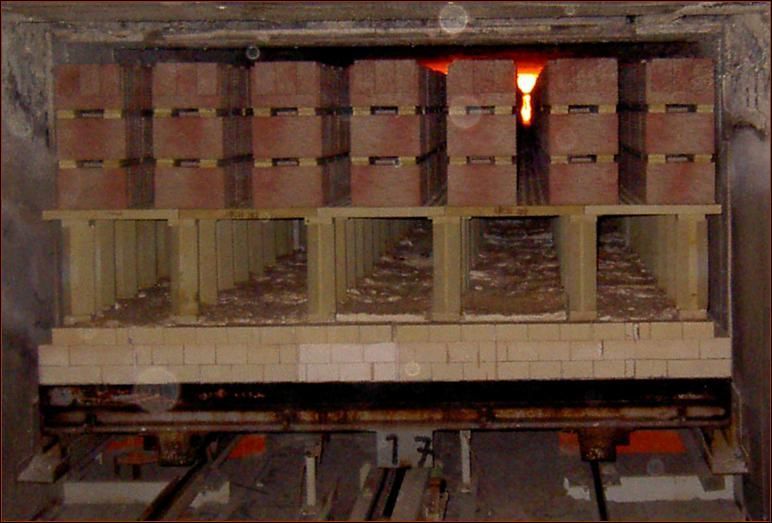
tunnel kiln diagram
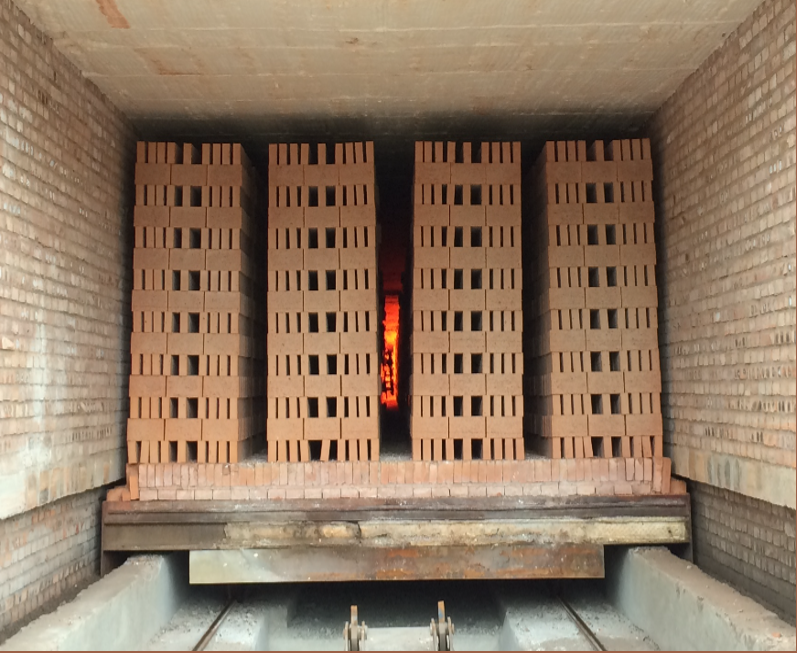
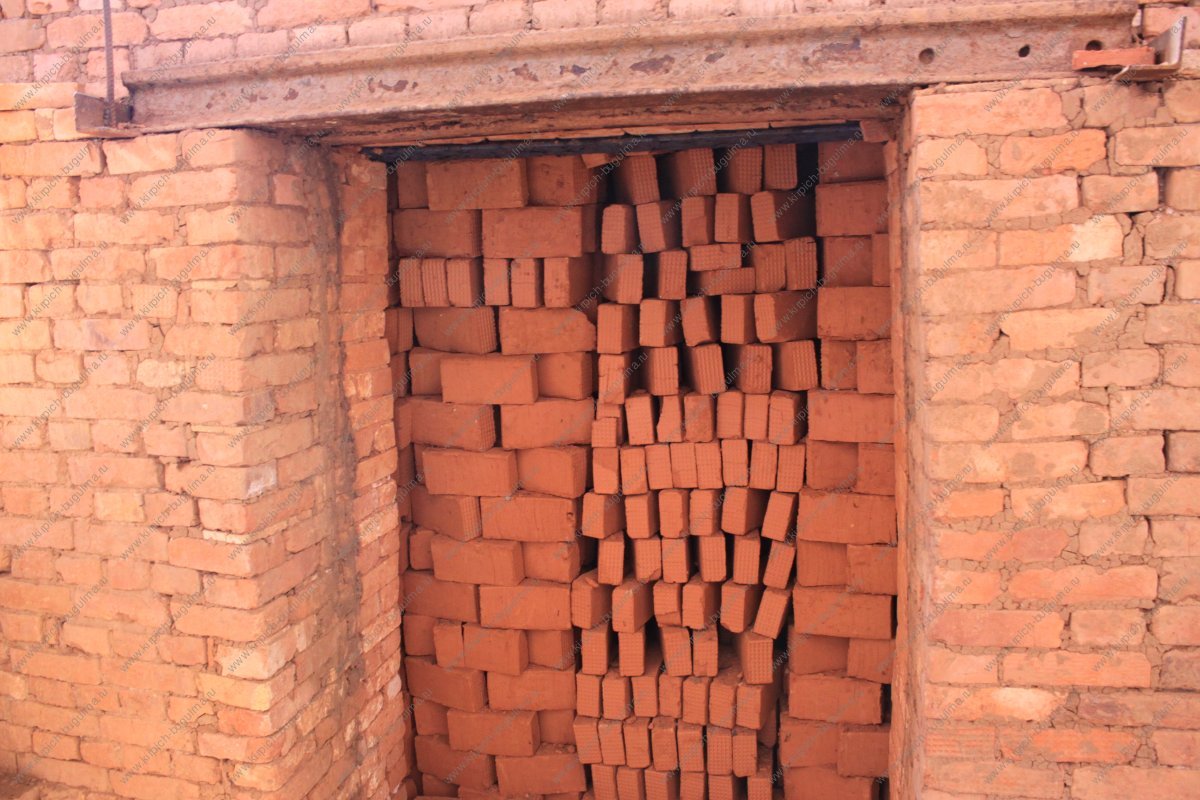
To design a tunnel kiln for firing bricks, you need to contact a specialist for a drawing, since it can have different shapes. At the time when the brick is loaded, it is gray, and when it leaves, it turns orange, which can be seen in building markets and markets. In the process of manufacturing a product, the furnace works according to a certain principle:
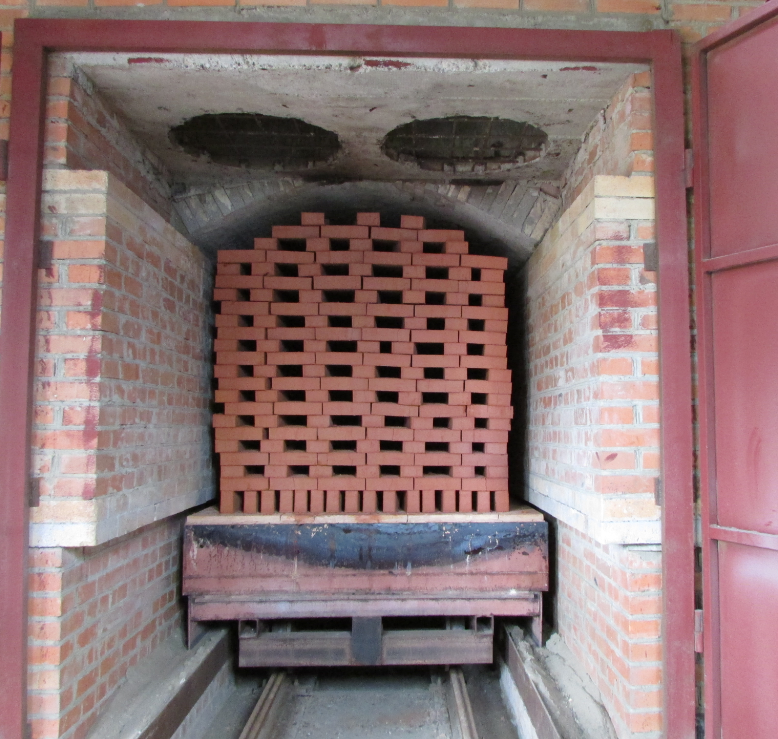
- The 1st cart, which has a pallet, is loaded with raw brick in a couple of rows. When loading it, you must observe the height. It should be no more than 1 m, if this threshold is exceeded, then the brick will become defective:
- In order for the tunnel kiln for firing bricks to work, it is necessary to turn on the automatic devices and pushers. The cart is activated loaded with material. As soon as she drives into the stove, raw bricks fall into the 1st chamber. An uninformed person may ask the question: "How do you put the bricks on the trolley so that after the procedure they acquire a certain shape?":
- The next step in conventional technology is the intermediate drying of the raw product. The layout of a brick kiln at home is completely different than a production facility.
tunnel kiln design
With the gradual heating of the furnace, all the moisture comes out of the brick, and if this building material is loaded into a hot furnace, it will simply burst or be deformed. Therefore, it is necessary to be more attentive to the working volumes.
- In order to gradually move the raw product, chamber kilns are used for firing bricks. When the brick approaches the chamber, the temperature there already reaches about 900 degrees Celsius, and maybe even higher. Each material is in this department for a certain time. After the expiration of the allotted period, another batch arrives, and this one goes on to the next stage of processing. If such a tunnel structure is implemented at an enterprise, then a very good result can be obtained in a short period of time.
- The next step in designing brick kilns involves connecting all the particles of the product. When the moisture that is between the crystals completely evaporates, then the raw material is somewhat similar to ceramics. The most interesting thing is that ceramics are made in exactly the same way.
- on this, in general, the firing ends and the future building material goes into the next chamber for cooling. This process should also be gradual, not abrupt. Meanwhile, the automatic conveyor continues its work and the almost finished building material ends up in the last section. Before being sold, the product is stored in a mobile tunnel kiln for firing bricks in the last section, where the lowest temperature is maintained.
- At the final stage, the pushers push the trolley out, as it were, and the brick finally cools down without physical or mechanical intervention, as well as without a sharp temperature difference. After it cools down, it is transported to the warehouse.
Mini brick kiln is the most mobile and automated structure for the production of this product. It cannot be compared with the results of the tunneling one, because all the work is built on the pipeline method. Of course, in such an enterprise you need to invest significant funds, but with such equipment that can produce a huge volume of products, all costs will quickly pay off.
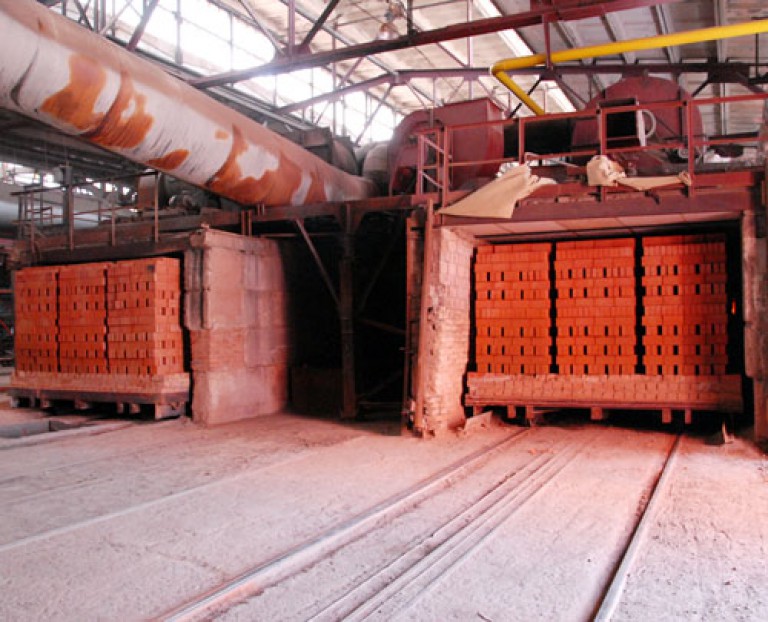
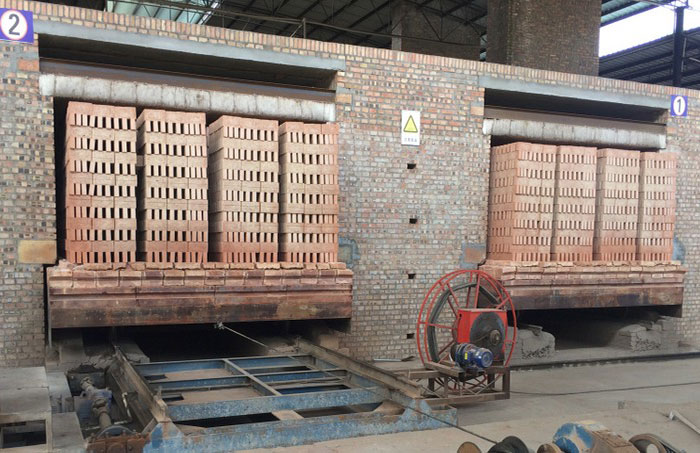
Tunnel oven
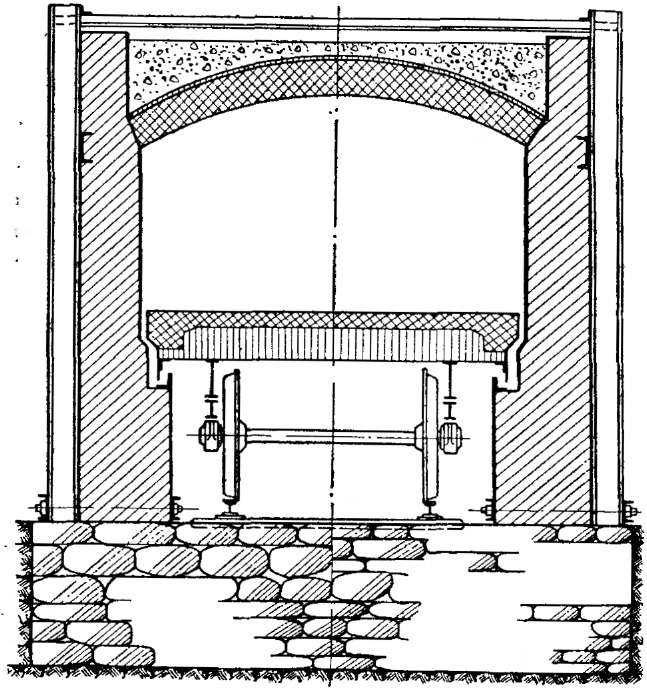
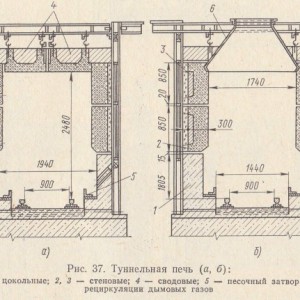
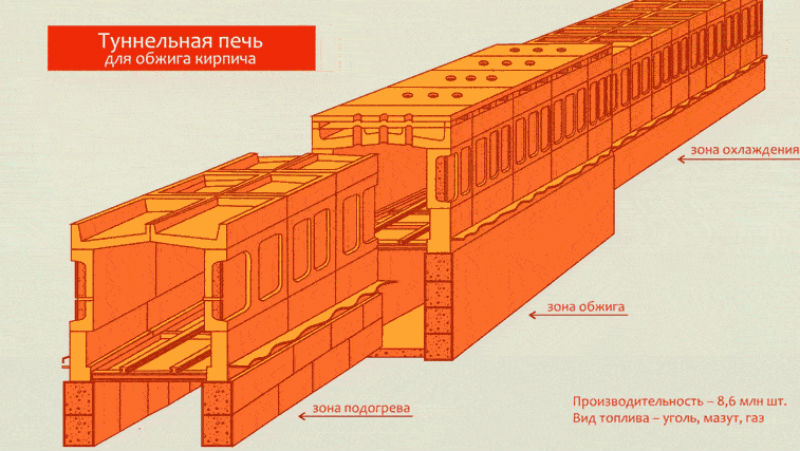
Most brick factories producing single solid bricks and ceramic stones are equipped with furnaces of this type. They represent a tunnel through which trolleys or a conveyor belt with raw materials move. Their working space can have one or two channels located in a straight line or having a closed, annular shape.
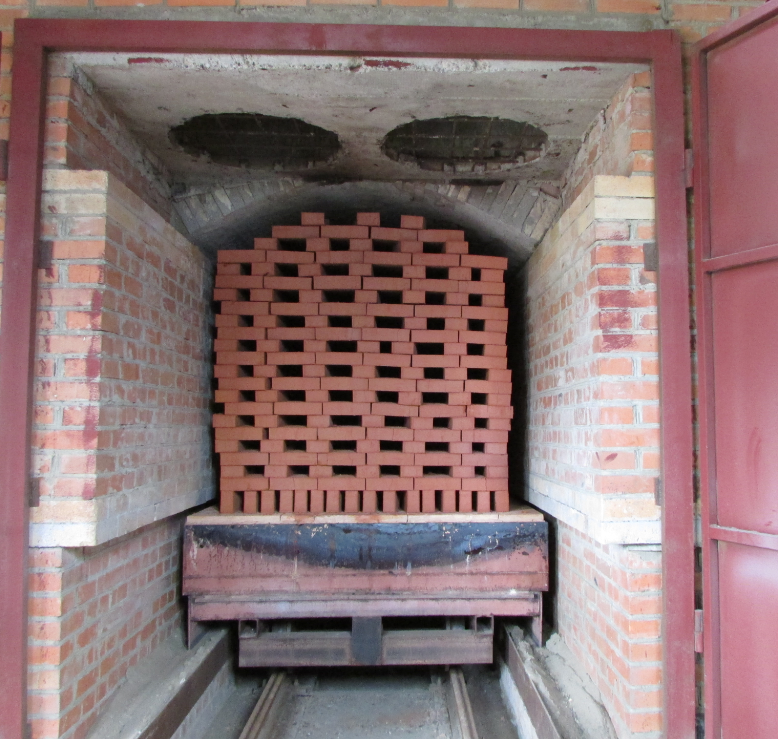

Principle of operation
In contrast to ring plants, here everything happens the other way around: the material moves through the remaining stationary, clearly demarcated zones of heating, annealing and cooling. The material moves sequentially from zone to zone. In such a furnace, there is only one entrance and one discharge area. They are located at opposite ends of the tunnel and are equipped with mechanisms that hermetically seal the inner space of the furnace during loading and unloading of material. Sealing occurs automatically, which avoids excessive consumption of the coolant. The space above the floor, under the conveyor or the bottom of the trolleys also does not warm up, as it is fenced off with a sand gate.
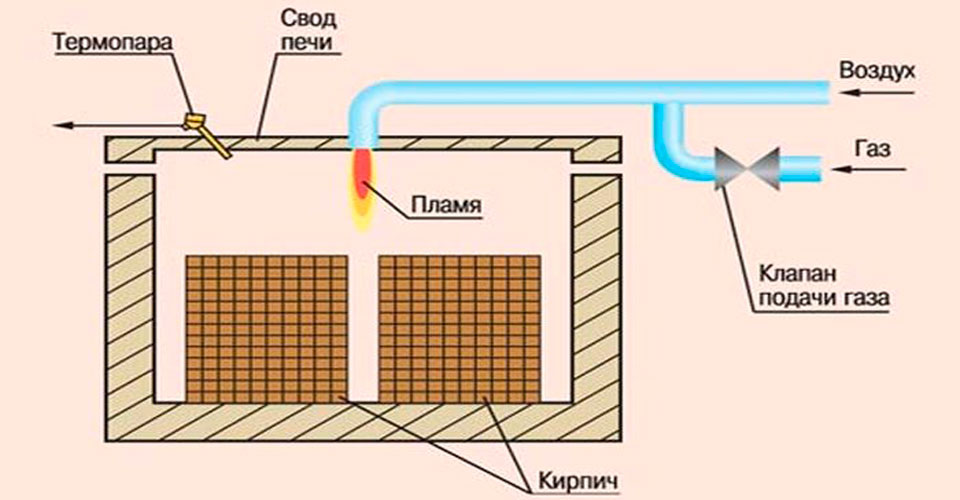
Natural gas is used as a heat carrier. Sometimes they are modified to run on fuel oil, diesel fuel, heating oil, and electrical energy. Combination of options is possible.
The oven works around the clock. Gas burners direct flares of burning gas onto the brick mass directly (in open furnaces) or through protective screens (in muffle furnaces). Fans and smoke catchers are installed along the entire channel, directing the required amount of heated air and flue gases to the required zones of the furnace through special circulation channels. These devices work independently of each other and are remotely controlled by the operator. The furnace is loaded manually by workers, and the unloading is mechanized.
The firing technology is automated as much as possible. Special computer programs with the help of numerous sensors monitor the technological process and give control commands:
- temperature regime in all zones.
- air pressure.
- the speed of the trolleys.
The choice of the operating mode of the furnace is carried out automatically and depends on the initial parameters of the raw brick (type, shape, size, moisture level, type of cage). The controller stores all possible modes in memory and selects the most optimal one. Quality control of finished products is also automated. The duration of the technological cycle for solid products is from 36 to 40 hours, hollow stones are ready in a day.
Advantages and disadvantages
The most important advantage of tunnel installations is the ability to minimize manual labor and automate the control process. All workers loading the kiln and unloading the product are kept away from the hottest firing zone. They work in good sanitary and hygienic conditions (acceptable air temperature, good lighting). The automated control system allows you to adjust the unit for the production of the highest quality products.
Disadvantages of tunnel ovens:
- work mainly on expensive heat carriers.
- large temperature differences in neighboring zones, threatening the appearance of material defects.
- contamination of products with ash when using coal in open-type furnaces.
- high cost of some production equipment (protective sleeves, radiant panels) and automation system.
- quick breakdown of their rolling stock.
Good bricks can be obtained in any of these types of kilns. In ring plants, high product quality is ensured by the hard work and skill of the burners, manually feeding fuel and adjusting the process as they please. In more modern tunnel structures, even perfect automation often cannot protect the goods from deformations, cracks, and non-compliance with the specified parameters. When choosing a brick, you should not pay much attention to the method of firing it. Just take a closer look at the material.
Technical parameters of bricks
Brick size and shape
One of the unchanging rules for the construction of furnaces is the accuracy of the design. Most of the projects are designed for specific brick sizes. Therefore, from which brick is it better to lay the stove, the question is very important.
Brickwork plans usually indicate not only the number of brick units, but also its dimensions. It is believed that the standard dimensions of a brick correspond to the dimensions of a single type - length 250 mm, width - 120 mm and height 65 mm... This is considered to be the "gold standard". True, it is worth noting that these are the dimensions established by the Soviet standard. Today, in addition to this traditional size, there are other sizes used for laying stoves:
- "Euro standard" - with the same length and height as the normal standard, its width is 85 mm (it is often denoted 0.7 NF);
- Thickened brick (KU) - differs from the usual format in height, it is 88 mm (designation 1.4 NF);
- Single modular brick (KM) - length is 288 mm, width is 138 mm, height is 65 mm (designation 1.3 NF);
- The thickened brick with horizontal voids (CUG) has the dimensions of the thickened brick 250x120x88 mm (designated 1.4 NF).
There is one more specific brick for laying stoves - the stove module, its dimensions are 230mm x125mm x65mm. Despite the fact that this standard is considered outdated, many successful furnace designs have schemes designed specifically for this size. The popularity of this kiln standard is such that many manufacturers of refractory bricks for individual kilns still produce bricks with dimensions for the kiln module - 230x114x40 or 230x114x65 mm.
There is also a specific type of brick - wedge-shaped or arched for the construction of the vaults of the furnaces and arches of the cladding. Its peculiarity lies in the fact that the dimensions indicate both the wide side and the narrowed one, for example, 230x114x65 / 45 mm.
Ceramic oven bricks used for decorative purposes can have different shapes. For example, have rounded corners, convex or concave sides, and have a glossy surface. The use of this type of material must necessarily be indicated in the ordinary scheme of the oven masonry.
Brick strength
The second point that you need to pay attention to when choosing a brick for laying ovens is the brand strength. This characteristic shows what kind of load a brick can withstand without showing signs of deformation. The marking is usually indicated by the letter designation "M" and a numerical corresponding to the ultimate load expressed in kilogram / square centimeter
So the M150 marking is allowed for the construction of most furnace designs. M 200 is suitable for the construction of a stove for heating two floors. But higher grades, for example M-300 or M-500, are usually not used for the construction of furnaces. The fact is that special chemical additives are used to form a material of this density, therefore, when heated, such a material partially loses its properties, which negatively affects the state of the structure.
Frost resistance, thermal conductivity and hygroscopicity
Frost resistance of bricks is especially important for the construction of stoves in houses where permanent residence in cold weather is not planned.Usually it is denoted by the letter F, next to which is indicated the minimum number of freeze-thaw cycles without loss of strength and the beginning of the process of mechanical destruction
This indicator is important for such structural elements as the base and head of the chimney.
When choosing a brick for masonry, it is worth paying attention to such an indicator as thermal conductivity - the ability of a material to retain heat
This is especially important for laying the walls of the firebox and chimney. For these purposes, material is taken with indicators of at least 0.61 W / m × ° С
For these purposes, material is taken with indicators of at least 0.61 W / m × ° C.
But as for hygroscopicity, then the material should be chosen with the lowest indicator. The lower the coefficient, the less the brick is able to absorb moisture. For the base and chimney, this is a very important indicator of the quality of the brick, since it is these parts of the structure that are most susceptible to moisture.
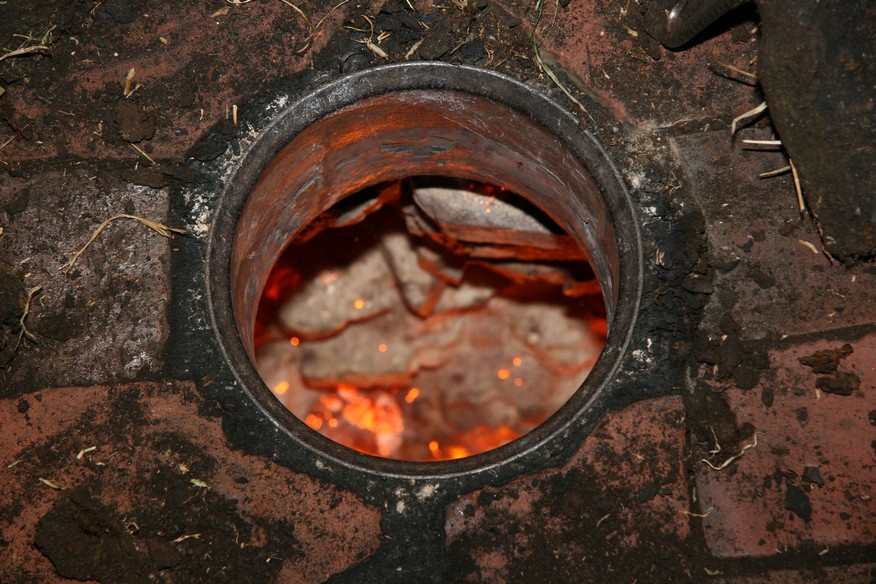
Burning
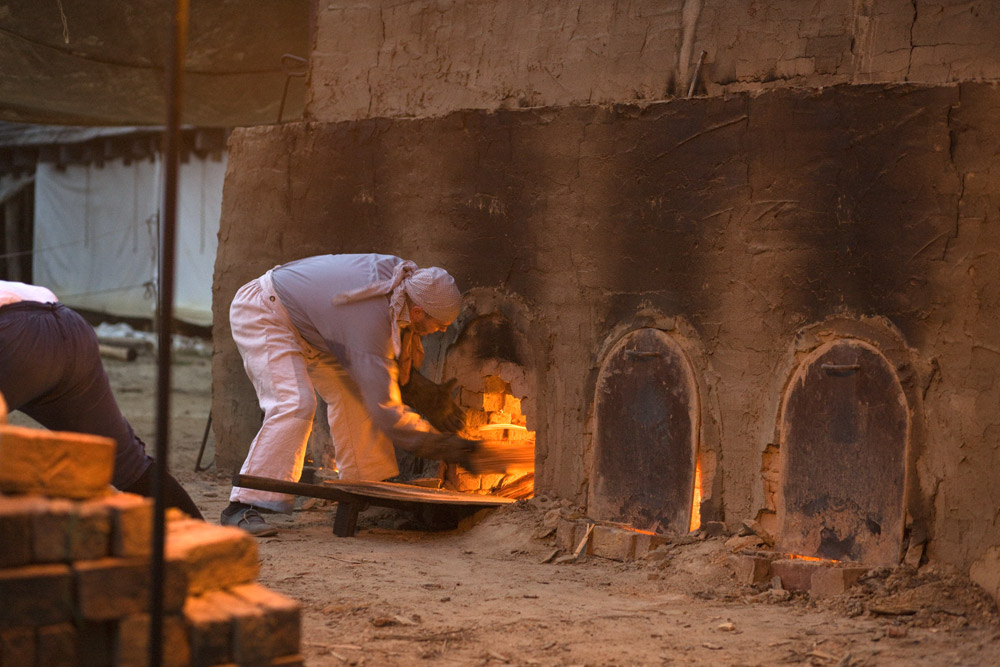
The stove is heated with straw, brushwood and then wood.
The first stage is drying. This is the most critical stage.
Heating should be done lightly, using low-calorie fuel (wood waste), until the brick gets rid of internal moisture. The presence of moisture in the brick is determined by the presence of condensation in the upper rows.
Drying can be considered complete if the iron pin lowered into the oven for a couple of minutes does not fog up. With some experience, the presence of moisture can be determined with the hand by placing the palm of the hand over the escaping gases.
The drying process usually takes up to 12 hours.
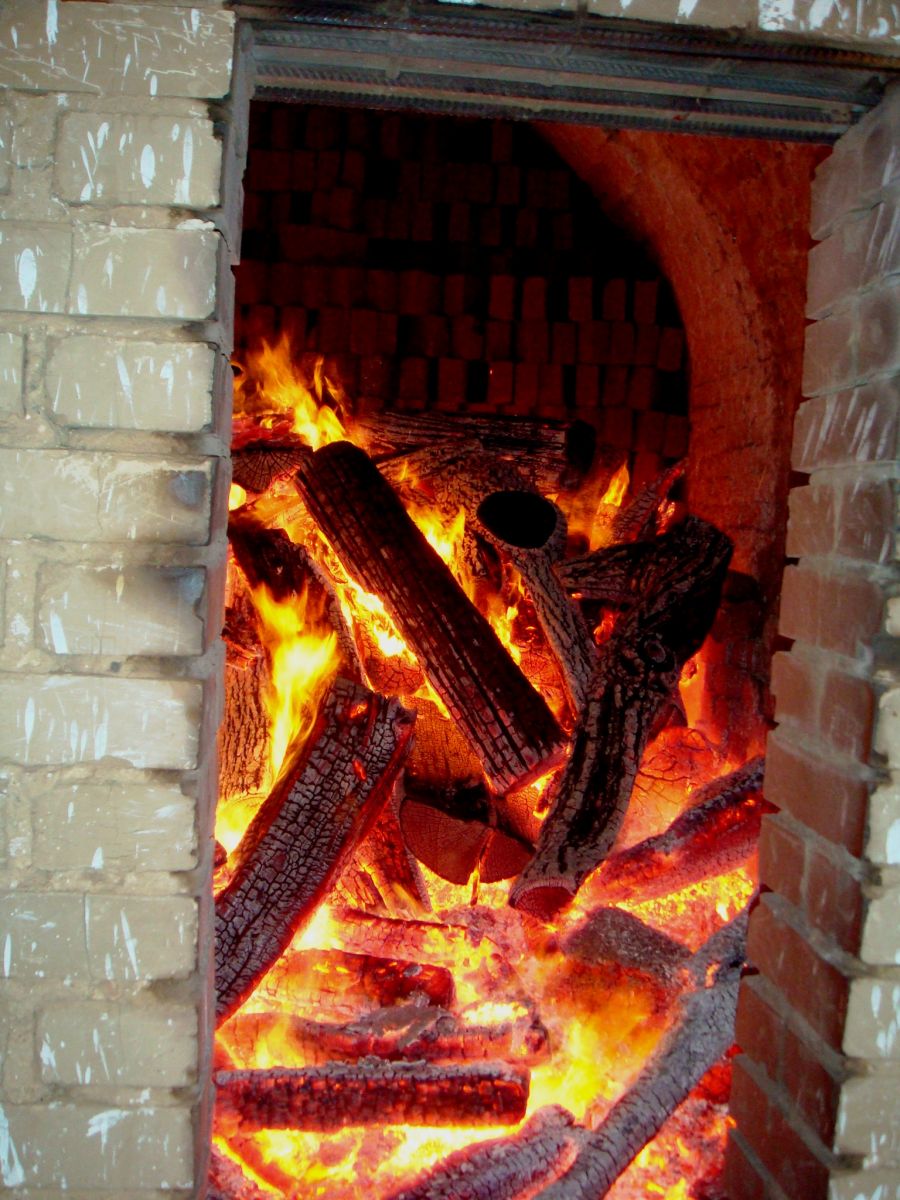
After it is established that the residual moisture has been removed, the fire is gradually intensified, bringing the brick to a dark red color (observing the vault). Heating lasts up to 9 hours, then switch to high heat until the fire comes out.
 The increase in heat is produced only by increasing the fuel supply. If, for any reason, the flame begins to knock out of any place, this place is immediately covered with earth.
The increase in heat is produced only by increasing the fuel supply. If, for any reason, the flame begins to knock out of any place, this place is immediately covered with earth.
When a fire appears in the upper part of the stove (900-950 ° C) - the upper rows are light red and the lower ones are yellow, the stove is “put to cool down”. To do this, the furnace hole is laid with a brick and coated with clay, and dry earth, brick dust or dry sand are poured onto the top of the furnace with a layer of 10-15 cm.
The firing temperature regime is characterized by four stages:
- Drying: temperature 20-90 ° С, time 10-13 hours.
- Heating: temperature 90-600 ° С; time 8-10 hours.
- Firing: temperature 600-1000 ° C; time 10-12 hours.
- Cooling down: temperature 1000-50 ° C; time 7-10 hours.
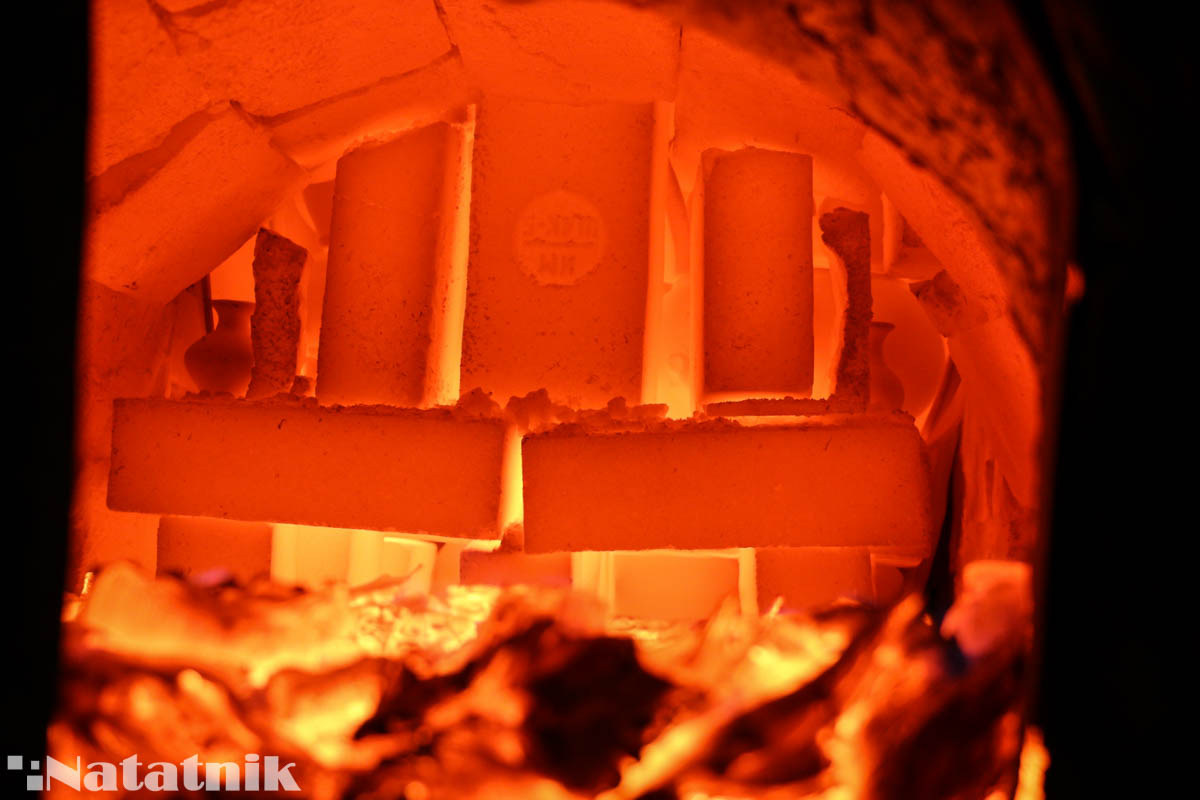
The control of the firing temperature in the furnace is carried out visually by the color of the vault:
- Dark red, visible in the dark - 450-500 ° C.
- Dark red - 600-650 ° C.
- Cherry red - 700 ° C.
- Light red - 850 ° C.
- Yellow - 950-1000 ° C.
- White - 1200 ° C - BURNING!
Previously, to obtain high-quality bricks, the furnace was kept closed for up to a week and only then began to cool. This gave excellent results as the thermal stress relief was very slow.
In practice, it is enough to withstand 7-10 hours.
The cooling of the furnace begins by punching a small hole in the firebox - the size of a chicken egg, after an hour the hole is doubled, after another hour - already four times. Thus, after 6 hours, you can open the furnace door and wait for the furnace to cool completely.
After cooling, the front wall of the furnace is disassembled and the charge is cut, starting from the upper rows. After disassembly, sorting and rejection, high-quality bricks are stacked tightly to each other.
Unfired are folded separately and in the future are used in non-critical structures for partitions or in the upper rows of masonry.
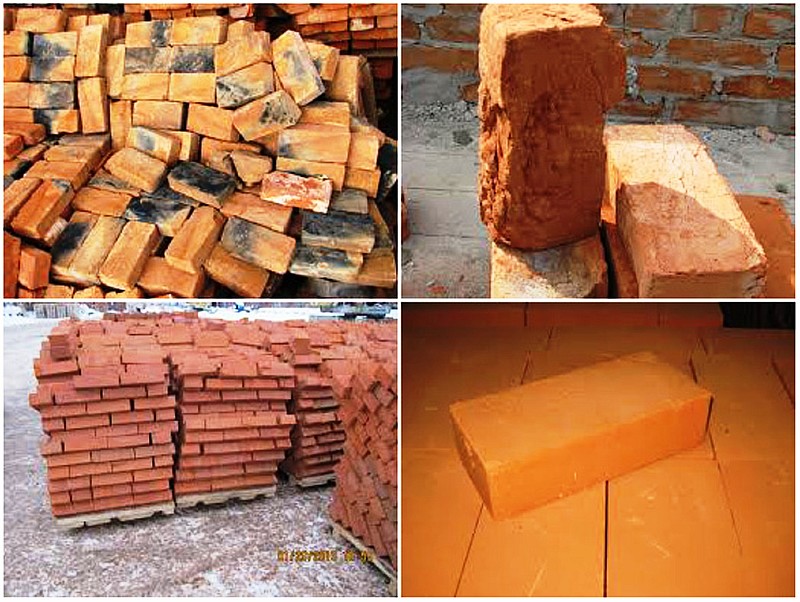
Visual determination of the quality of the brick. Reasons for marriage.
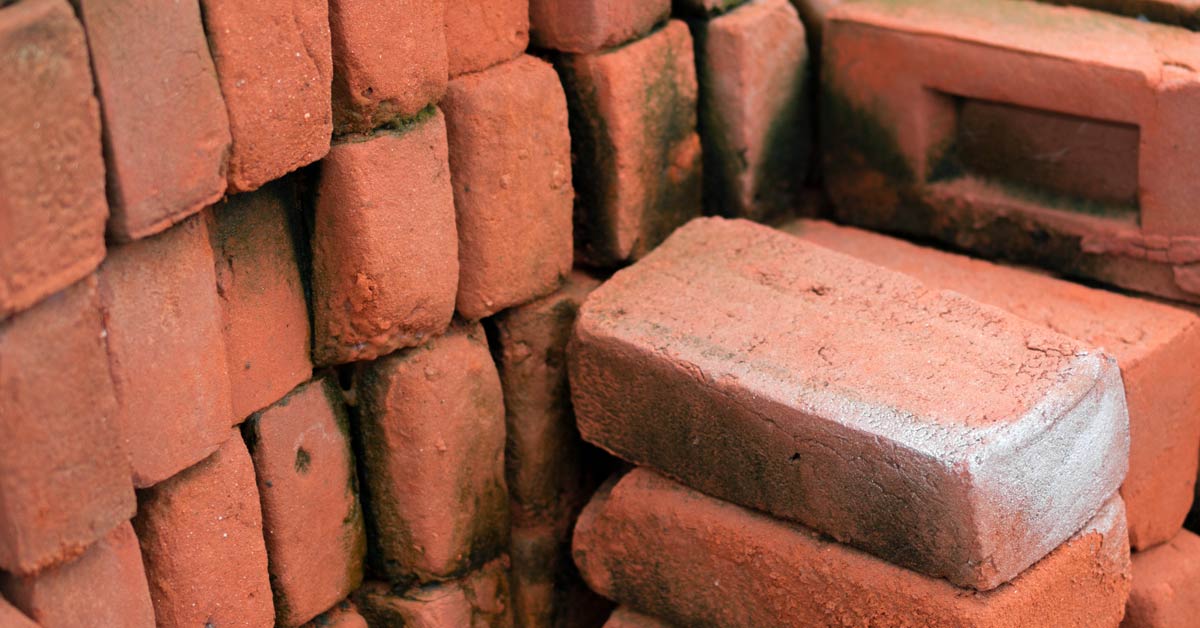
Correctly fired brick has a uniform orange-red color. It has a regular shape with straight edges and smooth surfaces. Produces a clear sound when struck with a metal hammer.
Unfired - has a lighter color, non-uniform at the fracture. On impact, it emits a dull sound (the reason is insufficient temperature or firing time).
Burnt - has a dark gray or blue-black color, often with traces of melting on the surface. Produces a high-pitched sound when struck. Formed at an excessively high firing temperature.
Damage to the corners and edges of the product is the result of careless handling, transportation or careless laying of products in the oven. Deformation of the product - underdriedness before placing in the oven
Deformation of the product - underdriedness before placing in the oven.
Small cracks form when the oven heats up or cools down too quickly.
Read about how to determine the quality of clay for making raw material here.
Large cracks and through cracking of the product are the result of an incorrect ratio of clay and sand, poor clay quality, violation of the drying and firing regime.
Black brick is obtained due to lack of air or due to poor circulation in the oven.
White spots on the finished product are the result of improper drying (overdrying).