Natural drying oil
According to GOST, the product in question must consist of at least 97% of natural vegetable oil (drying or semi-drying, as well as their mixtures, mainly flax oil, occasionally sunflower, soybean, hemp oil).
 During production, oils are exposed to prolonged exposure to high temperatures (at least 300 ° C) for 12 hours, the next stage is the use of an air purge.
During production, oils are exposed to prolonged exposure to high temperatures (at least 300 ° C) for 12 hours, the next stage is the use of an air purge.
As a result, we get an oily opaque thick liquid consistency of a saturated brown, and sometimes greenish color with a slight smell of the base oil.
Its main purpose is to perform the following tasks:
- priming of various surfaces: wood, metal or previously plastered;
- production and obtaining of the required consistency of light-colored thick-grated paint, putty, paste for greasing;
- as a paint composition of light color used indoors and outdoors for painting metal structures, window and door openings, flooring.
It will take no more than a day to dry completely at room temperature.
The drying oil from sunflower oil dries much worse and for complete drying it will take much longer than a day. In addition, although the film turns out to be quite elastic, it loses to the drying oils discussed above. by such indicators as:
- hardness;
- strength;
- water resistance.
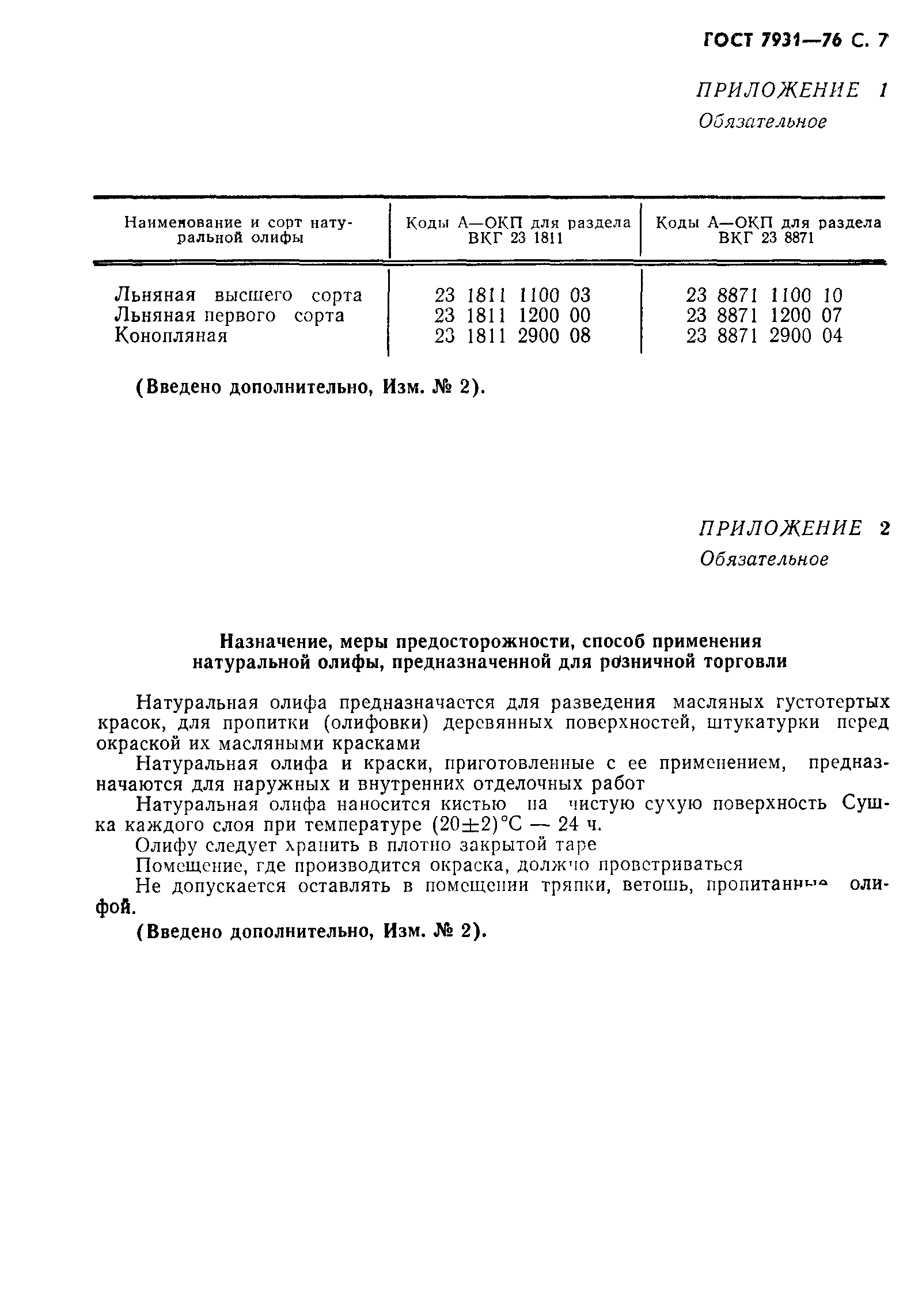
Table 1. Indicators of oil varnishes.
| Indicator name | Value for drying oil | Test Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| natural | oxol | combined | |||
| linen | hemp | ||||
| 1 Color according to iodometric scale, mg I2 / 100 cm3, not darker | 400 | 1600 | 800 | 800 | According to GOST 19266 and 9.3 of this standard |
| 2 Sludge,% (by volume), no more | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | According to GOST 5481 |
| 3 Nominal viscosity according to a VZ-246 viscometer with a nozzle diameter of 4 mm at a temperature of (20 ± 0.5) ° С, s | 26-32 | 26-32 | 18-25 | 20-60 | According to GOST 8420 |
| 4 Acid number, mg KOH, no more | 6 | 7 | 8 | 10 | According to GOST 5476 |
| 5 Transparency after settling for 24 hours at a temperature of (20 ± 2) ° С | Full | Full | Full | Full | According to GOST 5472 |
| 6 Drying time to degree 3 at a temperature of (20 ± 2) ° С, h, no more | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | According to GOST 19007 |
| 7 Mass fraction of non-volatile substances,% | — | — | 54,5-55,5 | 70 ±2 | According to GOST 17537 and 9.9 of this standard |
| 8 Flash point in a closed crucible, ° С, not less | — | — | 32 | 32 | GOST 9287 |
| 9 Density at a temperature of (20 ± 2) ° С, g / cm3 | 0,936-0,950 | 0,930-0,940 | — | — | According to GOST 18995.1 |
| 10 Iodine number, mg of iodine per 100 g, not less | 155 | 150 | — | — | According to GOST 5475, section 2 |
| 11 Mass fraction of phosphorus-containing substances in terms of P2 O5,%, no more | 0,026 | 0,026 | — | — | According to GOST 7824, section 2 and 9.13 of this standard |
| 12 Mass fraction of unsaponifiable substances,%, no more | 1 | 1 | — | According to GOST 5479 | |
| 13 Mass fraction of ash,%, no more | 0,3 | 0,3 | — | — | According to GOST 5474 and 9.15 of this standard |
| 14 Resin acids | Absence | — | — | By 9.16 | |
| Note - It is allowed to use drying oil of the oxol type with other indicators of the mass fraction of non-volatile substances and conditional viscosity, provided that this brand of drying oil meets all the requirements of the standard for this group of drying oils. |
Types of drying oil
This material is of 3 types: natural, composite and oxol. Natural linseed oil contains natural vegetable oils, moreover, usually - linseed and much less often - sunflower. In its structure, oil occupies 97%, and the remaining 3% are driers, which contribute to rapid drying. Natural drying oil is used for diluting thick paints, for impregnating wooden structures inside a building. Experts recommend not using drying oil for outdoor work, because it is impractical and quite expensive.
The cheapest and most fragrant type is composition drying oil. It is not approved by any state standards that would strictly regulate its composition. The composition of the composition drying oil contains components that serve as a substitute for natural, petroleum resins and other by-products of the oil industry. External and internal walls should not be treated with this material, as it is toxic, harmful to human health and even after drying it gives off an unpleasant odor.
Oxol contains linseed or sunflower oil (55%), white spirit (40%) and desiccant (5%).After it dries, a durable film appears that is hard, water-resistant and elastic. Usually, wood and plastered surfaces inside the building are treated with oxol. When applied to plaster, it will increase its adhesion to oil, dispersion, alkyd paints and putties. Oksol is good for both outdoor and indoor work, but do not forget that it preserves the surface only for a while, so after it it is necessary to use enamel, paint or varnish.
The cheapest oxol is made from sunflower oil; it is used to treat plastered surfaces inside the building. Outside, it is only suitable for surfaces that are under some kind of canopy and protected from moisture. From above, such drying oil is also covered with oil paint against decay.
Tips and tricks for use
When applying natural drying oil, you should adhere to certain stages. This will allow you to maintain a beautiful appearance for a longer time and perform its functions. Experts recommend following these rules.
- Before buying, you need to carefully read the instructions for use and the composition of the solution.
- Calculate the amount of impregnation required for the job.
- Thoroughly clean the surface to be treated from old materials, remove roughness and unevenness, dirt, dust.
- Degrease the coating with a special solution and dry.
- Apply natural drying oil using auxiliary tools - spray gun, roller, soft brush. Small items can be placed entirely in the solution.
Impregnation based on vegetable oils is an excellent tool for creating a special decorative style of the room. Therefore, the use of natural drying oil has not lost its relevance to this day.
General information about drying oil
Many vegetable oils, under the influence of oxygen, light and heat, thicken in air, and in a thin layer "dry up", turning into a semi-solid mass. This characteristic property is inherent in those vegetable oils, which include a fatty acid called linolenic (flaxseed). The more it is contained in the oil, the more it has a drying ability. Oils that do not contain linolenic acid do not dry out. The highest content of linoleic acid glycerides is distinguished by oils: linseed - with a content of up to 80% and hemp - with a content of up to 70%. Other oils, such as sunflower, poppy, nut, containing from 30 to 50% linoleic acid glycerides, dry out weaker and slower. Vegetable oils: rape, olive, etc., containing only traces of linolenic acid, deprived of the ability to dry.
Vegetable oil in its natural form, even with a high content of linolenic acid, oxidizes very slowly. To speed up drying, the oil is subjected to heat treatment with the addition of metal compounds (desiccants) to its composition. When heated, the oil decomposes substances that slow down the hardening, and metal salts provide faster oxidation. Thus, drying oils are obtained - compositions that, within 6-36 hours (depending on the composition, preparation technology and additives used), after being applied to the surface, turn into a hard, elastic film. Most modern drying oils have a drying time of the order of a day.
Historically, linseed oil was used to cover and impregnate wood, as the main means of protecting wood products from moisture, decay and wood pests. In the XX century, when other means of wood protection appeared, including more effective ones, the use of drying oil was limited to coating the internal wood finishing of rooms and preliminary coating of porous surfaces for subsequent painting (preliminary coating with drying oil improves paint adhesion and reduces its consumption by reducing absorption into surface).Also linseed oil is used as a base for oil paints, putties.
Test of linseed oil for admixture of rosin
Mix in a small bottle, at an ordinary temperature (not lower than 15 ° C), equal volumes of the test flaxseed oil and nitric acid (1.4 beats), shake the mixture well for about 1/2 minute and allow to settle. Upon separation of the oil from the acid layer, the following coloration is observed.
Pure linseed oil will give: the top layer is light brownish brown; the bottom layer is colorless.
Linseed oil with 5% rosin will give: the top layer is light brown-brown and the bottom layer is straw-yellow.
Linseed oil with 12% rosin will give: the top layer is dark olive and the bottom layer is dark straw yellow.
Linseed oil with 50% rosin will give: the top layer is blackish and the bottom layer is light orange.
List of sources
- .
- .
- .
- .
- .
- .
- .
Diy linseed oil varnish
It is not difficult to make a drying oil using linseed oil with your own hands. To do this, you must have on hand:
- any metal container - basin, ladle, saucepan, etc.;
- a heating device - for example, a gas or electric stove, a kerosene stove;
- rosin;
- potassium peroxide;
- respirator;
- gloves.
The sequence of actions is as follows:
- Initially, the oil is poured into a bowl and heated.
- As soon as it warms up to 110 degrees, there will be a release of water.
- It is necessary to monitor the evaporation process. The temperature should not exceed 160 degrees.
- Boil the liquid for 4 hours.
Upon completion of the evaporation of water and the formation of foam, a desiccant should be added in the proportion: 40 grams per 1 liter. oils
During this process, foam forms - do not be afraid of this, it is enough to observe elementary precautions
After that, the temperature rises to 200 degrees, and cook for the next 3 hours.
It is not difficult to check the readiness of the resulting product: a drop of the solution needs to be placed on the glass and if it is transparent, then the experiment has been completed successfully. If all is well, the composition should be refrigerated at room temperature.
It is quite simple to make a desiccant - you need to mix rosin with potassium permanganate peroxide in a ratio of 20: 1. First, the rosin must be brought to a boil so that a melting state is obtained - the temperature must be 150 degrees, and then add the manganese peroxide solution.
How to dry drying oil
Maximum drying speed for drying oil with polymetallic desiccants. If we take, for example, natural raw materials from flax, which contains a desiccant of manganese or lead, then it will dry for 12 and 20 hours. If you combine these components, you can achieve a much faster period, in some cases 6-7 hours.

The most important factors that directly affect the drying process are air humidity and temperature.
For comparison, an example can be given in the form of drying oil with a cobalt desiccant. If the temperature in the room is from 25 degrees, then it will dry out about twice as fast as at 10 degrees.
Again, to achieve this result, the air humidity should be within the recommended range and not higher than 70%.
If wood products are placed in a room where it is dry, warm and there are no drafts, then it will dry out quickly enough.
Any container with drying oil should be stored separately from any heating devices, out of the reach of children.
Such impregnation as drying oil is practically a panacea for the treatment of any wooden surfaces. And most importantly, it is an excellent alternative to expensive modern counterparts. Nevertheless, you should not use drying oil without making sure that it is suitable for use in a particular room.
Linseed oil treatment
The principle of operation of such a solution is as follows:
- when exposed to oxygen, heat and light in the open air, vegetable oils polymerize - the content of acids in linseed oil, which contribute to this, is about 80%;
- some of the substances penetrate directly into the porous thickness of the material, and the rest creates a thin layer on the surface, as a result of which the effectiveness of protection is achieved.
The rules for using drying oil are as follows:
- Before grouting any surface, clean all debris and dust. Woody materials are best sanded.
- Make sure the material to be treated is dry.
- Application is carried out in several layers - depending on the requirements for attractiveness and level of protection.
- Paint with a brush or roller - the estimated consumption will be from 50 to 100 grams per 1 m2.
- Upon completion of all work, take it out of the room and discard all rags soaked in linseed oil.
- Ventilate the room well, and if weather permits, leave the windows open throughout the painting process.
- Start operating the premises after 1 day, when the solution is completely polymerized.
Types of drying oils and their features
There are several varieties of drying oils for wood. Natural 97% consists of plant oils (sunflower or flax), the rest is a drier. Their main purpose is to dilute paints and treat wooden surfaces indoors. Such drying oils are divided into oxidized and polymerized. The latter have a darker color, and products processed with it age faster.
The characteristics of the Oksol varnish (GOST 190–78) practically do not differ from the natural one. It is used for indoor and outdoor work. But the composition also includes a solvent, which gives a pungent smell. Also, this type is cheaper than the previous one. Oksol linseed oil is produced in two grades - "V" and "PV". The first ones are created on the basis of flax or hemp oils. To create the latter, petroleum resins and other technical oils are used. Therefore, when working with drying oil, especially the "PV" brand, you should be extremely careful, wear respirators and protective gloves.

Often Oksol is marked "combined", "compositional" or "semi-natural", which once again proves its origin. But sometimes it makes a fundamental difference for those who care about the composition. Combined Oksol received rapeseed oil as a natural component, while sunflower oil was mainly used for production. But the situation was complicated by the fact that the new component belongs to the non-drying class. Then it was pre-oxidized, and as a result, the combined Oksol received the same characteristics as the original version of the composition.
In the broadest sense of the word, combined drying oil is obtained by mixing oils from several plants or those that have undergone different processing, the addition of synthetic substances and a solvent is also allowed. The use of this option is more common in the preparation of paints. Several brands of drying oil are produced. In the designation, the first is the letter "K", followed by a number. If an even number is indicated in the marking, then the mixture is used for interior work, and an odd number for painting exterior objects.

The last type is synthetic compounds. The basis for paints is alkyd drying oil, its cost is much lower than oil, which is an undoubted advantage. Another type is compositional compositions. Their quality is not high enough, and due to increased toxicity, the use is limited only to outdoor work. When choosing synthetic drying oils, you should be extremely careful, since if there is even a small sediment of natural oils in them, then the layer after painting may not dry out for a very long time. The presence of such inclusions can be determined visually. This mixture has a reddish tint and black sediment.
Not natural - linseed oil varnish!
The closest to natural drying oil is combined - these compositions contain about a third of the solvent, often white spirit.This allows you to reduce the cost of production and offer the buyer a product that dries at a higher speed. The use of drying oil on solvents fits perfectly into the repair from the outside - both quickly and reliably, and the smell will quickly disappear.
If you dilute vegetable oils even more, you get the so-called oxol, the production of which is regulated by GOST 190-78. Oksol varnish is the required 55% of natural oil, the remaining 45% are divided between solvents and driers. Oxol dries much faster due to the active evaporation of the solvent, and therefore it is convenient to use it in outdoor work with your own hands. In its internal use, as in the case of the combined one, it is not recommended - due to the solvent, the composition has a sharp, unpleasant odor, which can persist even after the layer has hardened.
The low cost of oxol makes it popular among the general public. Oksol is used to dilute oil paints and enamels, since by itself it will not be able to adequately protect wooden structures. If you choose oxol, we recommend giving preference to more expensive formulations based on linseed oil - they create a strong and elastic film on the surface of the tree, and such drying oil dries faster.
Alkyd linseed oil is a film-forming compound, the main component of which is alkyd resin (glyphthalic, xyphthalic or pentaphthalic), as well as modified oils and solvents. Objectively, this is the most acceptable combination of price and quality - alkyd compositions perfectly withstand temperature extremes, withstand the effects of atmospheric phenomena and are not very susceptible to ultraviolet radiation. Is post-processing necessary? Necessarily! Such drying oil dries for about a day, after which at least two layers of varnish or paint should be applied.
The last place in terms of the quality of the created coating and its characteristics is occupied by composite drying oil. However, it is difficult to call it drying oil - it is an oil refining product, which has a similar purpose, for example, to dilute paint. There is not even a corresponding GOST for the manufacture of such compositions. In appearance, such compositions are easy to distinguish by their high degree of transparency. Composite drying oil dries longer and is poorly absorbed into the wood surface. This material should be used only for coatings of temporary structures or to thin out inexpensive paint.
Varieties of drying oil for wooden surfaces
Manufacturers produce various options for woodworking mixes. They differ not only in quality characteristics and properties, but also in price. Some drying oils are suitable only for indoor work, others are universal means for basic repairs. Drying oils are represented by the following types:
- natural;
- oxols;
- combined;
- synthetic.
Natural formulations
The natural mixture is obtained by exposure to high temperatures for 12 hours, followed by oxidation. As a result, a viscous liquid with a characteristic smell of plant materials is formed at the outlet. Depending on the type of oil, the color may be dark brown or lighter in color. Drying oil of the highest grade is made from flax. However, it is the most expensive.
Natural compounds are a good impregnation of wood, creating a film on the surface, and serve to lighten. They are non-toxic, therefore they are recommended for use inside residential buildings. The only drawback is the long hardening period, especially at high humidity. On average, drying time for wood varnish is 24 hours.

Semi-natural formulations - oxols
The semi-natural composition contains a mixture of oils, which make up about 60 percent. The remaining components are driers in combination with petroleum polymer resins, turpentine or white spirit. The advantage of oxol is its fast setting time. When the drying oil is applied, a durable elastic layer is formed.This solution option is an affordable tool for treating wood, given the low price. Oxol has an unpleasant odor that persists for a long period of time.
Combined formulations
Many are interested in what a mixture of a combined composition is needed for. It can be applied to wood surfaces both indoors and outdoors. The solution contains 7 parts of natural oil and 3 parts of solvent, which allows the product to dry quickly. Two types of mixture are produced.
- K-2 - is used for processing wooden surfaces. It practically does not smell, therefore it can be used for decorative finishing indoors. It has a beautiful fawn tint.
- K-3 - covers facades, pillars and frame structures on the streets. The product is resistant to atmospheric factors.
Synthetic compounds
The scope of synthetic drying oil is exclusively for outdoor use. The mixture is rarely used for wood, more often it is used to cover metal or wooden structures in non-residential premises. The solution has a pungent unpleasant odor, which is felt for a long time and may not be completely
erode. Given the toxic effect of refined products inside houses, it is not used. The slurry contains only 20% natural oil, the rest is made up of components from diesel shale oil, shale gasoline and solvent. The main advantage is the cheap cost.
How to do it yourself?
If there is no store drying oil at home, you can make it yourself.
We offer a recipe for homemade drying oil. The preparation process of the product is as follows:
- you need to take a metal pan and pour oil into it;
- for 4 hours, the oil is cooked over low heat;
- after evaporation of water, add a desiccant at the rate of 40 g per 1 liter of oil;
- the temperature is increased to 200 degrees and cooked for another 3 hours.

To prepare the desiccant, the rosin is mixed with potassium permanganate. It is necessary to take 20 parts of rosin and melt it at a low temperature, then dilute one part of manganese peroxide and add it to the liquid.


To prepare linseed oil in a cold way, you should:
- heat the oil, constantly stirring the base, bring it to a temperature of 150 degrees;
- then add a desiccant at the rate of 5-8%;
- during the addition, all components should be thoroughly mixed;
- remove the dishes from the heat and cool in the room.

To cook linseed oil in a hot way, you should:
- bring the oil to a temperature of 170 degrees, then add a desiccant, expecting that it should be added from 1.5 to 2.5% of the total volume;
- before adding, the desiccant is pre-diluted with oil and then added to the hot mixture;
- after the foaming has weakened, the temperature should be gradually increased to 280 degrees;
- cook the mixture, stirring constantly, for four hours.

For information on how to cook drying oil, see the next video.
The use of natural drying oil
Historically, "boiled linseed oil" was used to impregnate and coat all wood products and objects to prevent rotting, deformation when wet, and to increase resistance to parasites.
Today, the area of application of natural linseed oil has expanded significantly - these are the following areas:
- interior and exterior finishing works - painting of windows, floors, walls, doors;
- priming of metal and wood surfaces;
- inclusion in the component composition of thick-grated oil paints, primers, fillers;
- processing of any items made of wood to extend the service life;
- restoration of furniture;
- pre-treatment of surfaces and objects before painting to increase adhesion properties;
- protection against water permeability during the construction of small ships - all metal and wooden surfaces are processed;
- dilution of solutions of paint, putty, primer, to obtain the desired consistency;
- as an antiseptic in the construction of wooden log cabins;
-
as a decorative finish for floors, such as parquet, and for further maintenance of such coatings.
Views
There are many types of decorative wood impregnations. Some of them are used indoors, and some are better for outdoor use.
Natural drying oil is divided into two types:
- Polymerized. This composition is heat treated without the use of purging.
- Oxidized or oxidized. In its manufacture, the oil languishes for a long time at a very high temperature, and then it is purged.


Natural drying oil is used:
- when carrying out finishing work inside and outside the house;
- when painting flooring, window frames, doorways, walls;
- for priming products;
- as part of soil mixtures, putties and paints;
- during restoration work;


- for pre-treatment of products and surfaces before applying paint to increase adhesion;
- when diluting paints, putties and primers until the required consistency is obtained;
- often natural oil is used when carrying out finishing work.


Natural linseed oil without fragrances has long been used in icon painting, in the restoration of paintings, since it is considered an excellent plasticizer. In ancient times, when other materials had not yet been invented, oil varnish was used to cover icons. But since over time the drying oil begins to turn black, the icons after a while needed restoration. Natural linseed oil drying oil is suitable for auxiliary materials for painting.
During production, vegetable oil is mixed with desiccants after heat treatment. They speed up the film polymerization process. When choosing a mixture, you need to look at which drier was used in the process of its production. If you take into account the standards, then more than 5% of the drier should not be added to the drying oil.

Among other alternative means for treating wooden surfaces, it is still worth choosing natural drying oil. This product is environmentally friendly, which has a beneficial effect on the human body. In addition, no harmful substances will be released from them either during work or after impregnation of products.
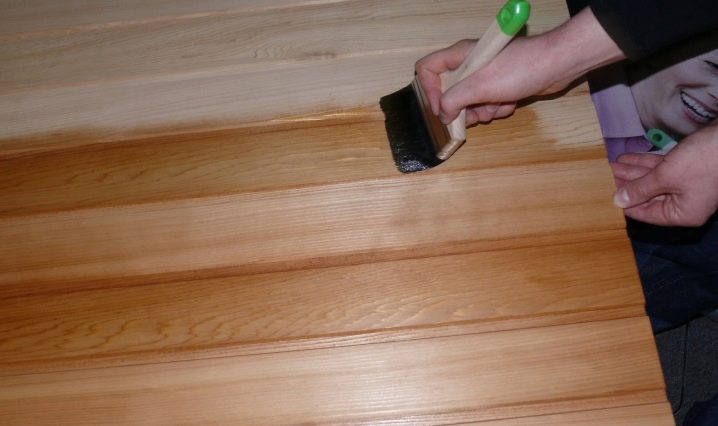

Natural materials - in search of safe ones!
If you have chosen a tree for decorating your house, guided, first of all, by its environmental friendliness, then it will probably be important for you to comply with this condition to the end. After all, an environmentally friendly tree can be covered with your own hands with so much chemistry that all sense of using this material is lost.

And here a slightly forgotten drying oil enters the arena. Of all the film-forming materials that are on the market today, it is, objectively, the most natural one. This statement can be easily confirmed by the fact that most drying oils consist of natural oil (hemp, linseed, sunflower, etc.) - the percentage of the natural component is from 45 to 95%.

Drying oil, or, as it was called in the old days, "boiled butter" was known to master painters several centuries ago. Already in the 17th century, every artist used this material. Today, the technology for making natural linseed oil practically does not differ from the methods known in antiquity. There are different types of this film former, the properties of which differ quite strongly.
Specifications
Drying oil "Oksol" is produced according to GOST 190-78, which specifies the norms of various indicators for grades "B" and "PV". There are eight basic standards by which the drying oil is determined to be of one type or another.
They vary depending on the type of oil used and the brand of the drying oil itself:
The first in the table is the color index. For both brands, this value is identical, the color should not be darker than 800 mg J / cm³ (iodometric scale).But there are exceptions for drying oil, where camelina oil ("PV" brand) acts as the basis, this indicator has a different numerical expression. The color of such drying oil should not be darker than 1800, and for drying oil made on the basis of soybean oil, this figure is 1100 J / cm³.







According to GOST 190-78, there are strict requirements prescribing in which container the drying oil can be poured, at what temperature the liquid can be safely stored and what precautions to take when opening the jar with the composition. All safety requirements are detailed in this document.

Application features for various surfaces
In most cases, natural suspension is used for a certain type of work, taking into account its features and pricing policy. The mixture forms aesthetic qualities after application and carries a functional load. Therefore, there are features of application to various surfaces.
- Wooden floors are treated with a wide soft brush or roller several times. Each layer is allowed to dry well before applying the next.
- For large wood and metal products, you can apply the solution using a spray bottle. For metallic coatings, one coat is usually sufficient.
- Small items can be dipped into a container with natural drying oil and wait a while for the mixture to be well absorbed.
- When applied to furniture frames and window frames, spread the compound evenly using a small brush.
Composition and specifications
Natural linseed oil includes oil that can be heat-treated at a maximum temperature of 300 ° C.
The finished linseed oil product is a transparent liquid of light yellow color with an oily character.
The composition of linseed drying oil in accordance with GOST includes:
- flax oil - not less than 97%;
- driers - metal particles or carbonic salt, used to speed up the drying period, no more than 3.
Depending on the production technology used, drying oil can be of several types:
- standard - production is carried out by heat treatment, without purging;
- oxidized - blowing is used during the simmering of the oil.
According to the requirement of GOST 7931-76, the technical characteristics must fully comply with the following parameters:
- oil and silicates should be in a 97/3 ratio;
- aroma - natural;
- drying period - no more than a day at 22 ° C;
- shade according to the iodometric school - 200;
- density indicators - 0.93-0.95 g / m3;
- acid value - 5;
- transparency during settling can be traced within 24 hours;
- phosphorus-containing components - no more than 0.015%.
How to choose the drying oil correctly
When choosing drying oil, you should be guided by the simplest rules:
First of all, you should familiarize yourself with the composition of the impregnation, which is always on the container, whether there is a GOST, is indicated only on products with a semi-natural or completely natural composition. If it is a synthetic mixture, you should read the certificate.
Any impregnating agent, natural or combined, must have a completely homogeneous structure.
If you can visually see impurities or a particle, it is not recommended to buy this impregnation.
You should also pay attention to how transparent it is. Natural compounds have only brown shades, synthetic ones can be expressed from colorless to rusty tones.
Technical characteristics of PF-115 paint
-
Resistance to atmospheric and weather factors (precipitation, ultraviolet light, temperature extremes, wind loads).
-
Resistance to chemical influences: paint PF-115 is able to withstand the effects of fuels and lubricants for 24 hours, for at least 2 hours - for water, for up to 15 minutes - for aggressive detergents.
-
Adhesion - about 1 point. There are also oil versions of enamel paint on sale that have less adhesion.
-
Covering rate - 80 ± 40 g / m2.
-
The percentage of non-volatile components in enamel paint is in the range of 49–70% (depending on the manufacturer of paintwork materials).
-
Specific hardness - 0.15-0.25 conventional units.
-
Viscosity - 90 ± 30 conventional units.
-
Drying time - up to 24 hours under normal conditions (humidity up to 65% and temperature about 20 ° C). For cherry and red paint, the drying time is up to 48 hours.
-
Flexural elasticity - about 1 mm.
-
Operating temperature range - from -50 to +60 ° С.