Polyethylene products
PE types
Polyethylene is made by enlarging ethylene hydrocarbon molecules. The polymerization process can take place under completely different conditions: temperature, pressure, and accompanying reactions of the substance give different polymer modifications with a wide range of characteristics:
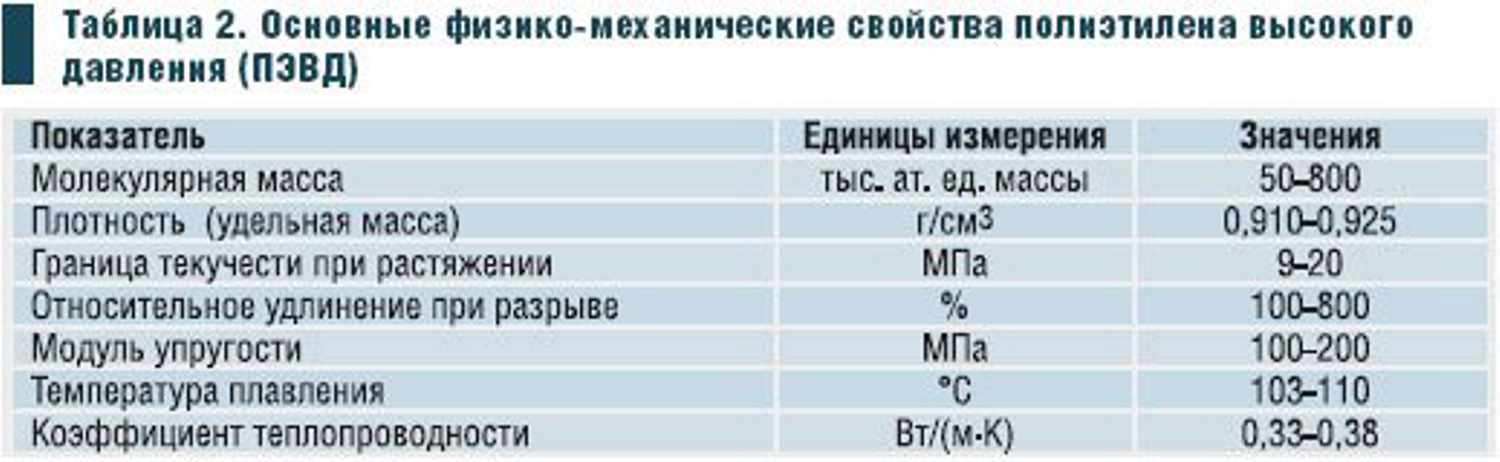
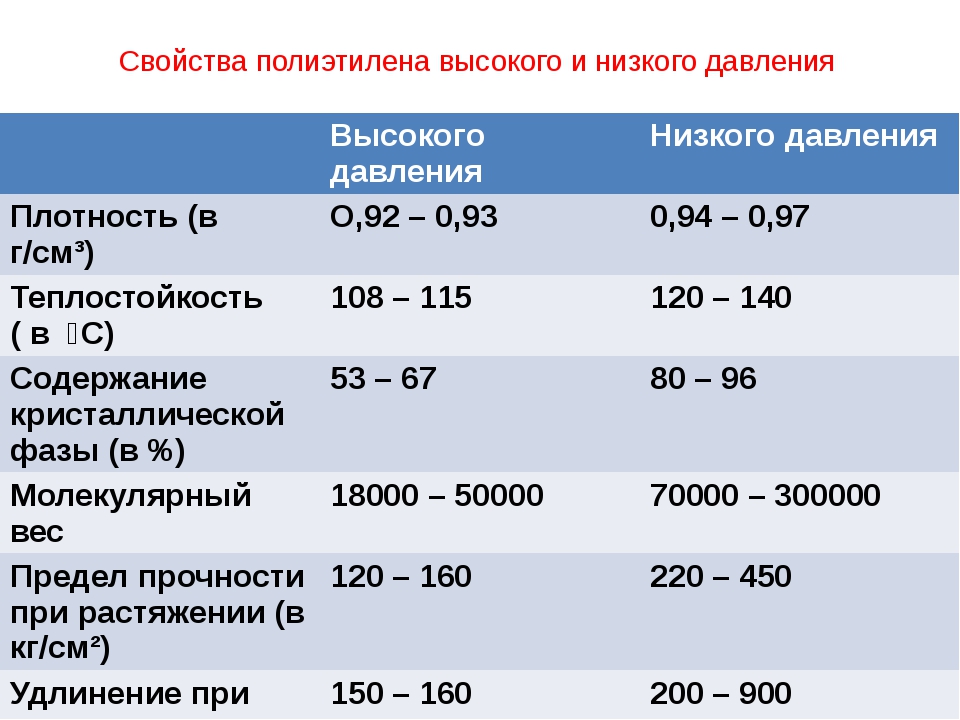
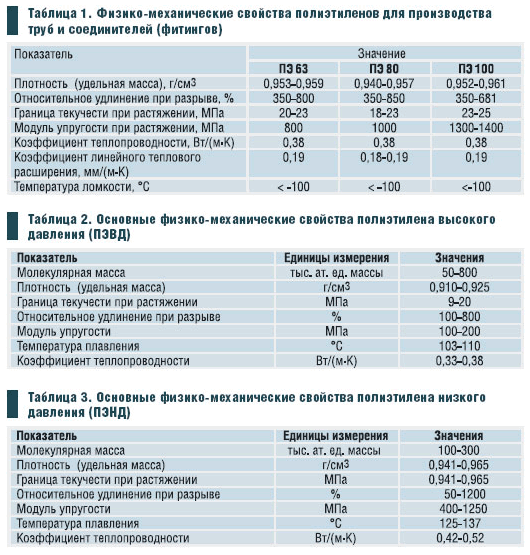
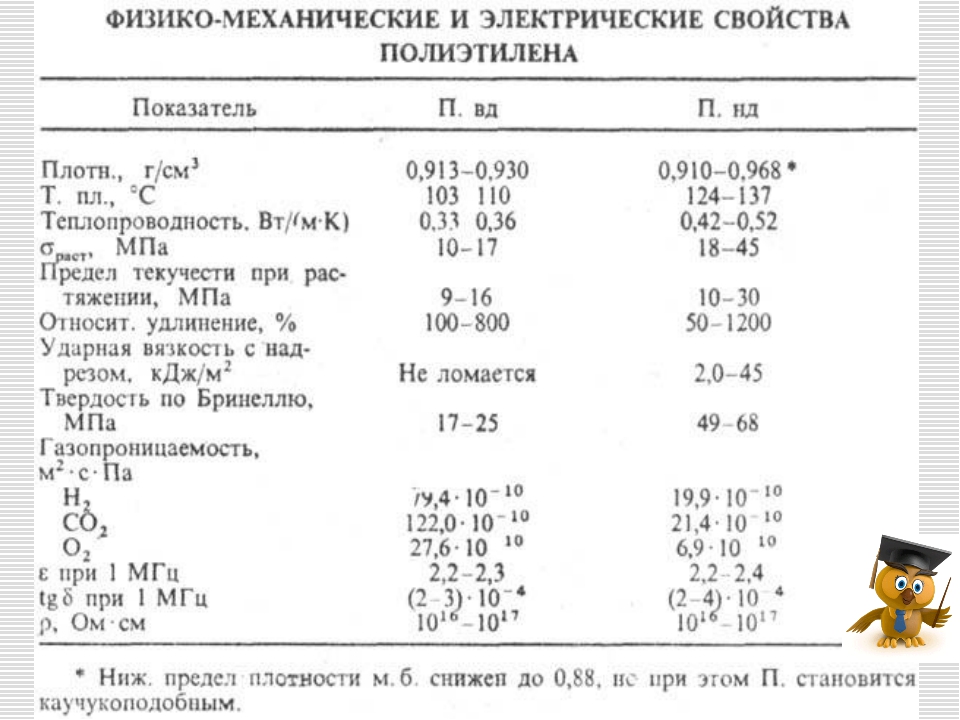
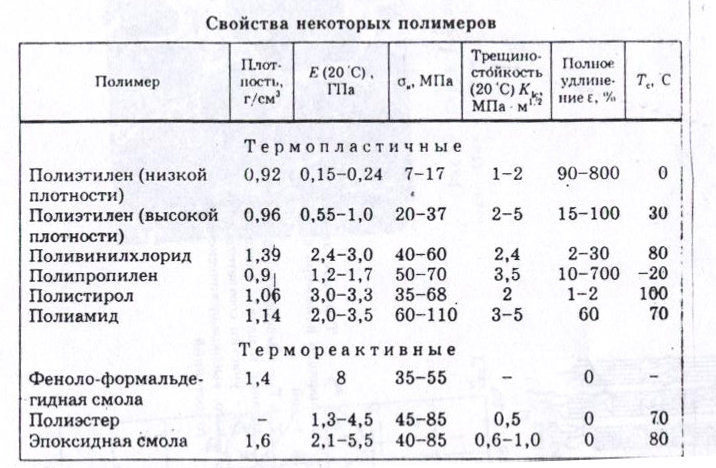
- Polyethylene "high pressure" (LDPE) has a low density, belongs to the softest plastics and is used to make more flexible and elastic products. Products from it are obtained with the smoothest and most shiny surfaces, having a high transparency coefficient.
- "Low pressure" polyethylene (HDPE) is much denser and harder. It is used for the manufacture of the most durable products that can withstand heavy loads.
- Linear PE combines the strength of HDPE and the elasticity of LDPE, which is necessary in the manufacture of a number of products and is especially used in the manufacture of films.
- Supermolecular polyethylene has unique properties of strength and resistance to various physical and chemical influences.
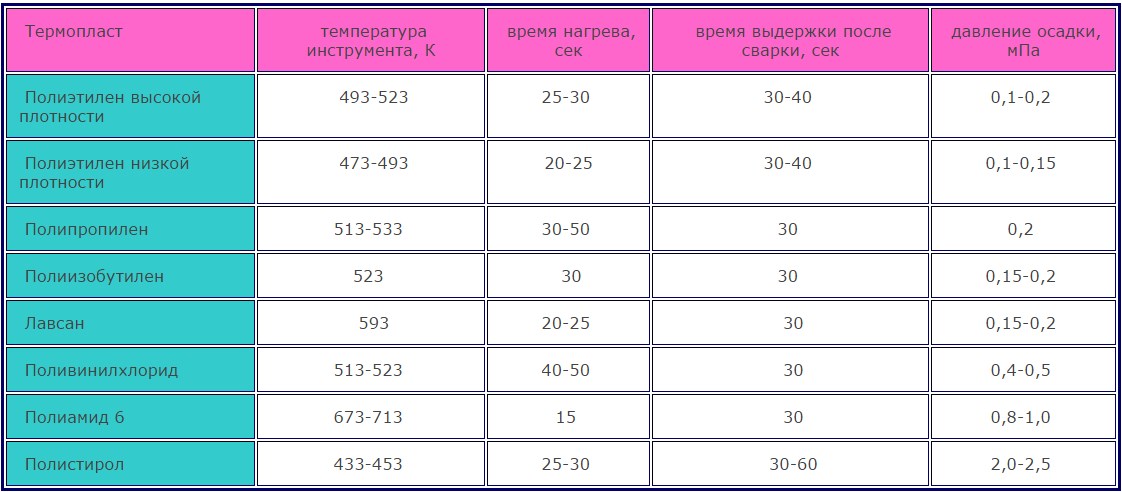
IMPORTANT! Contrary to beliefs about the impossibility of operating polyethylene at high temperatures due to its thermoplasticity, some of its types are freely used for the manufacture of heating pipes and hot water supply. These are heat-resistant and so-called "cross-linked" (supermolecular) types of polyethylene, which have a structure close to the crystal lattice of especially solid substances.
Types of products
The range of polyethylene products is striking in its breadth and "comprehensiveness":
- Films for packaging, waterproofing, building greenhouses (glass replacement), making waterproof clothing (raincoats, gloves), etc .:
- Smooth,
- Bubbly,
- Stretch,
- Heat shrinkable,
- Scotch.
- Containers for various purposes - from a plastic bottle and food container to canisters and tanks with a volume of up to 200 liters.
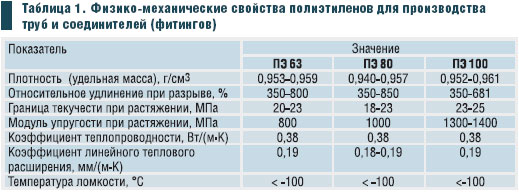
- Pressure or non-pressure pipes with a diameter of 10 to 1600 mm with different wall thicknesses:
- Plumbing,
- Gas,
- Sewer,
- Drainage,
- Heating.
- Tableware, both disposable and for longer use, as well as flower pots, etc.
- Toys for children and Christmas trees, souvenir products.
- Electrical insulating shells and plates.
- Anti-corrosion coatings for metal pipes, tanks and other products.
- Shock absorbers for mechanical protection of objects during transportation, protection of pipelines buried in the ground from seasonal and seismic rock displacements, etc.
- Foam materials for heat-insulating shells, substrates, gaskets in building construction, instrument and automotive industry.
- Housings for various devices, apparatus, boats, etc.
- Engineering structures, landscaping items for adjoining and playgrounds.
- Storage tanks for environmentally hazardous substances and waste disposal sites.
- Medical devices and prosthetic elements.
- Dry hot glue in the form of polyethylene powder.
Properties and advantages of polyolefin films
Due to its properties, POF film has the following advantages:
- Strength, resistance to tearing, stretching, impact and puncture;
- Equal thickness, neat welds throughout the bond. Reliability. Resistance to high and low temperatures: polyolefin shrink film withstands heat up to +30 and frost up to -50 degrees Celsius;
- Lightness and speed of shrinkage, which reaches 64%, at a temperature of 120 degrees provides a shrinkage rate within two minutes up to 60%.With a high degree of shrinkage (up to 80%), it is possible to achieve the "second skin" effect and to pack objects with complex shapes;
- Complete tightness of the resulting coating;
- Resistant to solvents and fats;
- Glossy shine and high transparency. Pof film fits round and angular shapes of packed items equally well.
- Resistance to extraneous "chemical" odors;
- Ease of use and, in comparison with similar products, a small price;
- Environmental friendliness and safety of production and use of polyolefin films. For example, chlorine contained in another film material - PVC, harms the health of workers, quickly spoils the machines involved in production and shrinking processes, and pollutes the air during disposal.
Areas of use
Due to its wide distribution, technical characteristics and low cost of obtaining, polyethylene is used in many industries and the national economy. The main areas of use are the following:
- construction. Today there are a lot of special installation films and membranes, which are widely used in the construction of objects as steam and waterproofing. For the laying of various utilities (mainly cold water supply lines), pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene are widely used. As insulation of wires, special protective boxes made of polyethylene are also used;
- package. The most common area of application for PE. We can no longer imagine an alternative to plastic bottles in which we regularly buy drinks, oil, household chemicals and many other goods. There are many polyethylene containers for technical use and the food industry. Packaging tape and stretch films are also made of polyethylene. Bags for food that are sold in any supermarket are also a product of ethylene polymerization;
- Agriculture. A large selection of various films and membranes made of polyethylene makes it possible to quickly and inexpensively manufacture greenhouses and greenhouses; irrigation and irrigation systems with polyethylene nozzles are also widely used;
- Common consumption goods. Starting from children's toys (only food grade PE is used) and ending with household appliances, polyethylene is widely used in our life.
In addition, some varieties of this polymer are used in the automotive industry and medicine.
Low cost, easy and fast production process, allowed polyethylene to become widespread in many industries and households, which rightfully puts this polymer in first place in popularity.

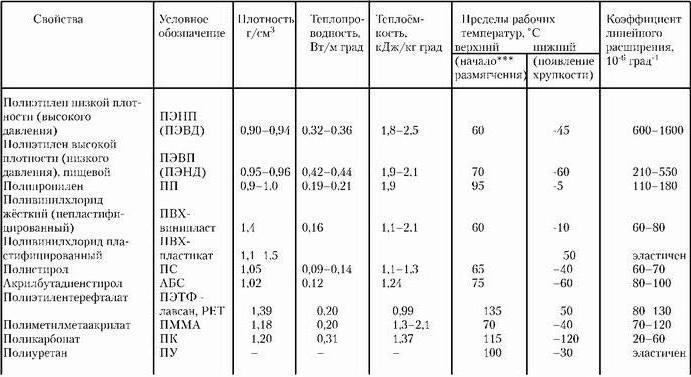
LDL properties
LDL has high physical and chemical characteristics. The properties of LDL can be called intermediate between the properties of PVP and PNP. But in comparison with LDPE, LDPE has a more uniform distribution of polymer groups by molecular weight. This material has the following properties:
Significant tensile strength, high resistance to cracking and elongation at break.
- High performance
- Quite high melting point. This allows the use of LPVD when filling hot products.
- A huge advantage of linear polyethylene is its chemical resistance in a large temperature range. LDL can withstand temperatures in the range of -45-100 ° C.
- Excellent melt elasticity. This property makes it possible to obtain a fairly thin film (from 6 to 25 microns).
- Linear polyethylene is chemically inert at room temperature, and with sufficient heating it is capable of nitriding, oxidation, and sulfonation reactions.
- LDL is perfect for storing food, because it does not affect their taste.
- LPVD is not exposed to ultraviolet rays, corrosion, does not deteriorate in extreme weather conditions. It is used at a peak temperature of 60 ° C.
- Due to its high crystallinity, linear low density polyethylene is less transparent than other types of polyethylene. To obtain a more transparent LDL, special optical additives are introduced into it.
- Externally, LPVD is a hard material with a barely noticeable pearlescent tint.
- Linear polyethylene in thin films is practically transparent, elastic, thermoplastic and flexible, easily cut with a knife. LDL in thick sheets is difficult to cut with a knife.
- LPVD lights up very slowly, burns without soot, with a weak blue flame, exuding the smell of hot paraffin.
- When melted, linear polyethylene is converted into a soft jelly-like mass with almost no fluidity.
- LDL is practically insoluble in organic liquids below 60 ° C. At higher temperatures, linear polyethylene dissolves rapidly in halogen derivatives, hydrocarbons, and some other products.
- LPVD absorbs water to an extremely small extent. Absorption and its rate increase slightly at high temperatures.
- The permeability of water vapor through the linear polyethylene film is extremely low. LDL is one of the best waterproof film-forming materials.
Distinctive properties of materials
And although both categories of materials can be painted in any color or used to place inscriptions and drawings, it is possible to distinguish cellophane from polyethylene without special means. To be known as an “expert” among friends and to show off your erudition without having a chemical education, it is enough just to remember the distinctive properties of materials. The well-known saying “there is no comrade for taste and color” is very suitable for transparent bags.
- Taste. The cellophane bag contains glycerin in its composition, which gives a slightly sweet taste to the material. You can always verify this by licking a clean bag.
- Colour. The structural feature of cellophane allows the applied paint to hold for a very long time. But drawings on polyethylene are erased much faster, which makes the bags look untidy.
- Tactile sensations. A plastic bag feels soft and a little greasy to the touch, while a cellophane bag feels hard, rustling heavily and easily bending (wringing).
Pros and cons of choosing cellophane
Cellophane bags are very convenient packaging material. However, when choosing cellophane or polyethylene for daily use, you should know all the advantages and disadvantages of this type of packaging. After all, these two, similar in appearance, but different in composition of the material, have completely different properties. And, despite the fact that cellophane bags are much less common due to the high cost and complexity of manufacturing, they should still be preferred in the choice of packaging.
- Many factory-made sausage and cheese packaging is made of cellophane. The structure of such a package will always allow the contents to “breathe” and food products will stay fresh longer. For example, fresh bread will stay soft for 5 days.
- Cellophane, which is afraid of moisture, will not collect water released from the products, as polyethylene, which is unable to pass it through, does. Therefore, a plastic bag will always protect the product placed in it from excess moisture.
- In case of accidental contact with heating devices or fire, polyethylene instantly melts, while cellophane does not weld, but only shrinks.
- Cellophane is a safe material for both humans and the environment. Rapidly decomposing in a natural way, such a package does not emit harmful artificial substances, because is entirely biological material.
For the sake of fairness, it should be noted that cellophane is insignificant in terms of material strength, but still inferior to plastic.If a polyethylene bag stretches under the weight of the weight, then the cellophane packaging, although very strong, will instantly “climb along the seams” of the rupture at the slightest tear. However, this small flaw is not able to overshadow the positive aspects of cellophane. And its ability to keep food fresh for a long time, preventing them from being saturated with excess moisture, and the natural disposal of the material without causing harm, rightfully make the cellophane bag the king of packaging.
Polyethylene film - what is it? Its properties and characteristics
The material has many advantages that determine its popularity:
- Resistant to chemical environment, inertness. Due to this quality, polyethylene is widely used in public catering;
- Stretch and elasticity. The polyethylene sheet stretches easily and wraps around the packaged item;
- Moisture and vapor tightness. The material is widely used in waterproofing during construction work, as a covering material, in product packaging;
- Tightness - provides a barrier to air intake;
- Transparency (for unpainted films) - provides good visibility of goods in film packaging;
- Good dielectric qualities;
- Long service life.
The disadvantages are:
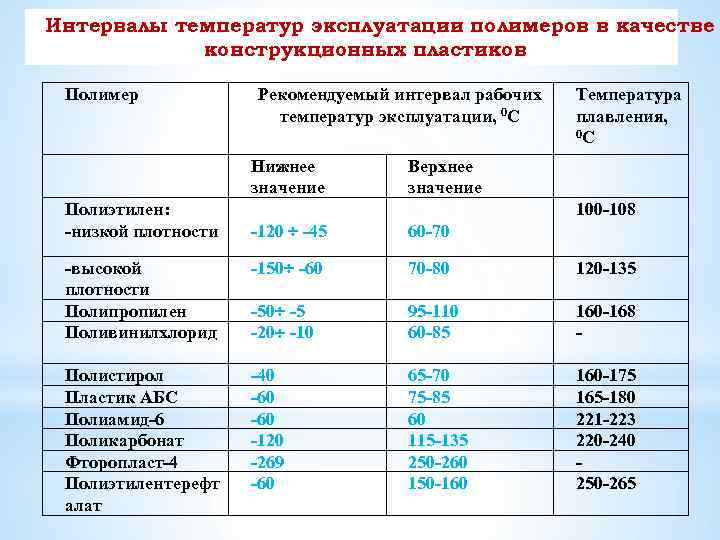
- Fear of high temperatures. Above 115 degrees, the film begins to melt;
- Sensitivity to UV rays. With a long stay under their influence, polyethylene ages and begins to disintegrate, strength characteristics deteriorate;
- Low temperature instability. With a long stay in the cold, polyethylene becomes brittle.
Application of LDPE film
The material has been used as a packaging container for five to six decades. Today LDPE is used as:
food packaging, for the manufacture of food and non-food bags. The film allows you to preserve the integrity of the product and prolong its storage, creates protection from dust, unpleasant odors and water. Bags made of this material are resistant to crushing.
 LDPE packages
LDPE packages
- wrap food, using in most cases bags and stretch film.
-
Shrink film material is excellent for packaging all kinds of goods.
- Large-sized items are packed in high-pressure polyethylene, which facilitates the process of loading and transportation.
packing large-sized items in LDPE film
- In a thickened version, brick and block material is packed, furniture and equipment are wrapped in it during repair work.
- During the cleaning of construction waste, large bags that are resistant to damage have proven themselves excellent.

The film is in great demand in the rural industry. It is appreciated for two qualities - it does not allow moisture and vapor to pass through. The material is used for greenhouses, as it is much cheaper than glass. Foil is used to cover the bottom and top of the silo storage pits to speed up the process and protect the ground.
The manufacturing process is straightforward, the film is relatively cheap. With careful handling of technical polyethylene, it becomes possible to use the material multiple times.
Classification options
LDPE film can be classified according to several criteria. The most important is the direction of further use:
- Packaging;
- Agricultural.
In turn, the packaging film is:
- Food grade;
- Industrial.
Shrink and stretch films can be distinguished into a separate category.
The shrink film has a thickness of 40-180 micrometers and a melting point of 120-200C. Under the influence of temperature, it changes shape, shrinking. At the junction, sufficiently strong welded seams are obtained.
 The stretch film is very thin and elastic. It stretches well, which reduces its consumption, but at the same time does not lose its properties.And thanks to the property of reverse stretching, it adheres tightly to the packed product, emphasizing its shape, and minimizes the volume of the package. The use of stretch film in several layers ensures almost 100% tightness of the package.
The stretch film is very thin and elastic. It stretches well, which reduces its consumption, but at the same time does not lose its properties.And thanks to the property of reverse stretching, it adheres tightly to the packed product, emphasizing its shape, and minimizes the volume of the package. The use of stretch film in several layers ensures almost 100% tightness of the package.
LDPE film can be purchased in various colors. The transparency of the film is very dependent on the thickness - the thinner, the more transparent. The thickened film used in construction has the white color typical of polyethylene. At the request of the end consumer, a film of any color can be obtained by adding the desired dye during production.
LDPE film comes in the following forms:
- Canvas;
- Sleeve;
- Half sleeve.
The half-sleeve and the sleeve have one or two side seams and are very convenient for use in bulk packaging of goods using packaging machines.
Scope of linear polyethylene
LDL is quite resistant to impacts, tears, punctures, and has high ductility. In these characteristics, it is similar to HDPE. A very thin film is produced from linear polyethylene, which makes it possible to save material and reduce the negative impact on the environment. LDL is great for a wide variety of applications, but due to its excellent transparency, strength and flexibility, LLDPE is most often used in the production of packaging films.
In the global polymer market, it is LDL that is the most dynamically used polymer - in comparison with HDPE and LDPE - because it allows the production of thin films with high strength characteristics. This material is intended, in particular, for the production of medical bags. Nevertheless, linear polyethylene has found the widest application in the production of so-called stretch films for packaging. LPVD packaging has the following advantages: no need for a heat chamber for shrinking films, reduced film consumption (as a result of its small thickness), as well as excellent performance properties.
In Russia, almost the entire volume of LDL consumed is used in the production of films (for example, stretch films obtained on cast lines and by blowing, as well as lamination films and multilayer shrink films). At the same time, interestingly, LPVD is almost never used for the manufacture of garbage bags in our country. In the near future, it is expected that linear polyethylene will increasingly displace the already familiar LDPE in the manufacture of single-layer and multilayer films.