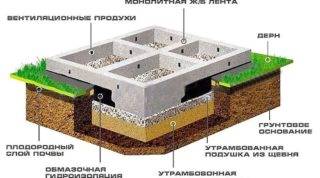
Precast foundation: design features
Diagram of the device of a concrete foundation.
When arranging a prefabricated foundation, reinforced concrete blocks are used, previously created in the factory, which makes it possible to significantly speed up the erection of the base of the building. They are used not only in civil, but also in private low-rise construction. With their help, the walls of the basements and the basement of the building are erected. To determine the overall dimensions of the block, its volume and mass, the value of which must be taken into account when choosing lifting equipment, is determined from its marking. It should be borne in mind that the marking for each type of block has its own standards. For example, FbS24-3-6T means the following: the foundation block has a length of 2.28 m, a width of 0.3 m and a height of 0.58 m.In order to make the supporting structure of a building, blocks are used, the width of which varies from 0.3 to 0.6 m with a graduation of 10 cm. This thickness of the blocks allows the foundation to withstand any loads.
Before using a prefabricated foundation, it is necessary to determine the type of soil on the site. Arrangement of such a base on wet and damp soil will lead to water seepage through the joints in the blocks. When installed on clay and loam, there is a high probability that the blocks will sag due to the swelling of the soil, and this will threaten the integrity of the entire structure. Therefore, the soil must be dry and hard, then the precast foundation will fully justify itself.
Arrangement of a strip foundation will cost more than a monolithic one. This is due to the fact that in this case, the use of special construction equipment is mandatory. The calculation of a prefabricated foundation depends on its design, depth and foot area. This must be done correctly, since mistakes made in the calculation can lead to the destruction of the entire structure. In order to correctly calculate the number of blocks of each size, it is necessary to use a strip foundation plan, which must be present in the project.
Pros and cons of prefabricated strip foundation
Diagram of the strip brick foundation device.
Prefabricated strip foundations have both pluses and minuses, the study of which will allow you to make the right decision on the choice of the type of foundation for each specific case.
Advantages of a prefabricated foundation:
- speed of assembly of the structure. Literally a couple of hours after the completion of the installation work, it will be possible to start building the walls. There is no need to wait a month or more, as in the case of using a monolithic base;
- significant reduction in construction materials costs. If the blocks are not installed in a continuous row, but at a small distance from each other, you can reduce up to 25% of the materials. But at the same time, it must be remembered that the level of strength will be slightly lower, although with low-rise construction this is not so noticeable.
Cons of a prefabricated foundation:
- such a base cannot be strengthened by installing an additional reinforcing cage, the release of blocks is standardized;
- the rigidity of the prefabricated structure is lower than the monolithic analogue.
The base, which is erected by assembling prefabricated slabs, is ideal for low-rise buildings. It is unsafe to use it when building a house with 2 or more floors.
Types of prefabricated foundations
Sandy strip foundation scheme.
The strip foundation is a continuous load-bearing structure, the laying of which is carried out in pre-prepared trenches along the entire perimeter of the building being erected, as well as in places where internal load-bearing walls are being built.
Depending on how deep in relation to the level of freezing of the soil the prefabricated strip foundation will be installed, it can be divided into 2 types:
- finely chopped;
- recessed.
A shallow foundation is used in the construction of small buildings when the load transferred to the foundation is not too high. As for the level of soil freezing, the structure in this case does not reach it. The blocks are installed on a previously prepared and carefully compacted sand cushion.
The deepened foundation is indispensable for the construction of massive buildings. The depth of its inception necessarily exceeds the level of soil freezing. In this case, the blocks are laid on special reinforced concrete cushions, the width of which significantly exceeds their height. Due to this, a more stable base is obtained, which is not afraid of high loads.
Advantages and disadvantages of the design
Pile-belt structures are popular due to the following advantages:
- the ability to conduct construction on problem soils, including swampy areas and permafrost;
- profitability, since a small amount of materials is required to create the base;
- simplicity of technology, the ability to do it yourself without involving equipment;
- stability and reliability of the structure;
- applicability for the installation of surface structures when fastened to the bottom of the reservoir;
- bored piles are made from scrap materials, which eliminates the cost of purchasing factory products and their transportation.
The main disadvantage is the waste of time and money on conducting a geological survey of the construction site. It is advisable to start it only if you have all the data regarding the type, moisture and composition of the soil. There is no possibility of arranging a basement, the owner of a finished property needs to carefully consider the issues of insulation and waterproofing of the lower level of load-bearing structures. Without proper protection from moisture, the supports will quickly become unusable, and this is an expensive and time-consuming overhaul.
Types of piles used for the foundation
Today, there are several types of piles that can be used for the construction of a pile foundation. Among them:
- Driven piles.
- Screw piles.
- Bored piles.
Let's consider each of these types in more detail.
Driven piles
This type of pile gives the foundation the greatest stability. The thing is that during the design of the future structure, the designers calculate the future weight of the building and divide it between all the piles. During their installation, such a force acts on each pile, which then it will have to withstand. When the pile stops sinking into the ground, this may mean that it has reached the ground on which the structure can already withstand.
The compacted soil around it gives additional stability to the pile. It is possible to hammer such piles only with the use of a special pneumatic hammer, which is very expensive to use in private housing construction. That is why this type of pile is not recommended for self-erection of such a foundation.
Screw piles
This type of pile is an ordinary steel pipe, at the end of which elements that resemble threads are welded. In fact, this type of pile can be compared with a self-tapping screw, that is, they are screwed into the ground according to the same principle as a self-tapping screw. Thanks to its blades at the ends, the support area is increased, which in turn increases the strength and reliability of the structure. If the soil at the construction site is not dense enough and even unstable, then piles can be used, on which blades are welded along their entire length.
This type of pile can be used for both private construction and industrial construction. Piles can be screwed in either manually or using a special technique.In the case of screwing in the pile yourself, this will require several strong people
As a rule, at the other end of the pile, there are two holes that allow you to connect them with the twisting technique, while it is very important that when the pile is twisted, it is located strictly vertically. When the pile is completely screwed in to the desired level, concrete is poured into the pile pipe and the head is welded, on which the grillage is subsequently installed
Some disadvantages of such piles should also be noted:
- A screw foundation requires an accurate calculation of the depth of solid soil, otherwise the pile will not be stable, especially during heaving of the soil.
- The piles must have high-quality welded seams, otherwise, during the screwing of the pile, the blades may come off or be damaged. This can lead to a loss of bearing capacity.
- The piles must be covered with a high-quality layer of factory paint, otherwise a poor-quality coating can lead to corrosion.
Bored piles
This type of pile is often used in private housing construction. In order to carry them out, it is required to make pile wells with a hand drill, after which formwork is performed in the case of loose soil that crumbles.
Such piles are waterproofed with roofing material or any other insulating material (asbestos-cement pipes can be used), reinforced, after which concrete is poured directly into the well. Piles are installed along the entire perimeter of the future foundation, that is, in the corners, along the outer and inner walls. The number of piles depends on the total weight of the future structure.
Among the disadvantages of these piles, it can be noted that it is impossible to accurately determine whether the pile has reached solid ground or not.
Positive and negative aspects of technology
Advantages of a monolithic slab
Most specialists give preference for a monolithic foundation for the following reasons:
- The preparatory stage before pouring the foundation will be minimized. You do not have to spend a lot of time and hire highly qualified construction crews to prepare the site for the installation of this foundation due to the simplicity of the technology. Therefore, a monolithic foundation is considered one of the most budgetary, and since special equipment or tools for its construction are not required, you can easily cope with this type of work yourself.
- The state of the monolithic foundation is not affected by seasonal changes in the physicochemical characteristics of the soil, which makes it possible to avoid major repairs associated with freezing and thawing of the soil. During severe frosts, the entire structure, together with the base, will rise, and with warming in spring, it will fall without any significant deformations.
- The base, made of solid slab, is amazingly durable due to the absence of joints and seams. It is practically not subject to mechanical damage and is very durable.
- You can additionally save on the arrangement of the floor covering, since the slab of the monolithic foundation itself is the subfloor.
Minuses
Freshly poured monolithic foundation.
But, solid base has certain disadvantages, among which it is worth noting:
- It is almost impossible to combine a monolithic foundation with a cellar or basement, so it will have to be done separately.
- The construction of a foundation from a solid slab will cost a little more than, for example, a columnar foundation.
- When building in an area with rather harsh climatic conditions, a heat-insulating layer (for example, foam) will have to be placed under the monolithic base.
- It is strictly not recommended to erect a monolithic foundation on a site with a significant slope.
Sequence of work
 Construction tools
Construction tools
The main condition for successful construction is competent and well thought out planning. First you need to get data on the characteristics of the soil at the site. You can get them from your local government or ask your neighbors. However, it should be borne in mind that these indicators can differ significantly even within one hectare. Therefore, it makes sense to spend money and order a professional research. In addition to a clear picture of the composition of the soil, information about the levels of occurrence of groundwater can be obtained. This will help save money when drilling a well.
Based on the data obtained, conclusions are drawn about the bearing capacity of the soil. Then it remains to calculate the mass of the house, its contents, the base and then calculate the width of the foundation. The result of planning is a detailed drawing, which indicates all the dimensions of the support system and its depth. Then you should calculate the requirements for materials and prepare the tools.
For work you will need:
- concrete mixer;
- grinder, welding;
- hacksaw, shovel, ax, hammer
- rammer;
- roulette, level, rule;
- spatula, paint brush;
- components for concrete (crushed stone, sand, cement, plasticizers);
- reinforcement 10-12 mm;
- boards or panels for formwork;
- insulation, waterproofing, cellophane;
- cord.
 Step-by-step instruction:
Step-by-step instruction:
- Carry out the markup. Determine the exact location of the structure on the site, orient the projection to the cardinal points. The house should stand exactly where it is envisaged by the project, otherwise there will be problems with its commissioning. Using a cord and stakes, outline the outline of the future building.
- Carry out earthworks. First, the fertile layer is removed, then a ditch is dug. If a buried pile foundation with a belt is being made, it is advisable to rent a light wheeled excavator.
-
Dig in the trench to the desired level and shape the corners. This is done by hand using a shovel, tape measure, and a level.
- Make a backfill. The pillow is wetted, leveled and rammed. It is recommended to pre-lay geotextiles at the bottom of the pit, which will prevent the washing out of the sand filling.
- Assemble the formwork. It is allowed to combine with several materials (plates, sheets, panels, boards), provided that the same width of the opening is maintained throughout the entire length of the tape. All cracks must be hermetically sealed, and it is better to overlay the formwork from the inside with polyethylene. If it is planned to make a non-removable option, laying of expanded polystyrene plates with tongue-and-groove joints is carried out. Then all the cracks are glued with tape.
- Carry out reinforcement. Tying is best done with soft wire to avoid post-weld rust. Docking is not carried out at the corners. In such places, the reinforcement is bent, and even fragments are screwed to its ends. Immediately you need to put plastic pipes of a certain section between the walls of the formwork for airflows and laying communications. They are inserted back to back, acting as a spacer.
- Knead and pour concrete. To avoid the formation of voids, air bubbles are expelled from the solution with an electric vibrator or a steel bar. Align the top of the base with a rule.
- One day after pouring the end of the pouring, cover the foundation with cellophane, and after another three days start wetting it daily.
It is allowed to remove the formwork in 7-10 days, and continue construction in 4 weeks, when the concrete gains strength.
Requirements for the dimensions of the strip foundation
If the project of the house involves the construction of a foundation of this type, then a lot of accurate calculations regarding its depth and width will be required, which not only must correspond to the type of soil, but also withstand the mass of the building.
The heel of the strip foundation should be at least 30x80 cm, it is also very important to observe the dimensions of the bandaging of the reinforcing belt, since otherwise it may turn out to be too weak, and the foundation mass will disintegrate under load into several large fragments. When erecting a foundation on solid ground, it can be the same width as the walls, so the trench needs to be expanded only by the thickness of the formwork boards
When erecting a foundation on solid ground, it can be the same width as the walls, so the trench needs to be expanded only by the thickness of the formwork boards.
Such a pillow compensates for the movement of the ground during seasonal changes and sudden cold snaps, preventing changes in pressure on the foundation mass itself.
Monolithic slab foundation
 The thickness of the reinforcement and its number depends on the planned loads on the slab.
The thickness of the reinforcement and its number depends on the planned loads on the slab.
A slab foundation is a monolithic structure that completely fills the inner perimeter of the building base, creating a single horizontal surface.
Reinforcement of a monolithic structure is carried out depending on the loads. In some cases, a monolithic slab can be made without reinforcement. Such a device is permissible only on dense soils for lightly loaded bases.
This foundation can be made both below ground level and above. When building below ground level, the distance for the basement or basement is laid. When installing a slab base shallowly buried in the ground, the construction of a basement floor is not provided.
 A sand and crushed stone pillow is required under the slab
A sand and crushed stone pillow is required under the slab
The slab foundation is arranged on a sand and crushed stone pillow. In this design, the pillow performs not only a supporting function, but is also used as a drainage, preventing water from accumulating at the base of the building.
In some cases, the slab foundation design includes stiffening ribs, which are located under the load-bearing walls of the building. These ribs can be either from the bottom side of the slab, or from the top, forming the lower part of the walls. Due to such edges, it is possible to reduce the thickness of the slab in lightly loaded areas.
 If it is necessary to insulate the slab foundation, this process is carried out after the installation of a sand-crushed stone pillow. A layer of hard insulation is laid on the pillow, on top of which reinforcement is arranged and concrete is poured.
If it is necessary to insulate the slab foundation, this process is carried out after the installation of a sand-crushed stone pillow. A layer of hard insulation is laid on the pillow, on top of which reinforcement is arranged and concrete is poured.
The underfloor heating system can be partially built into a monolithic slab foundation. It is set up in areas where load-bearing and partition walls will not be installed, and the presence of heavy pieces of furniture is not planned.
Base
Tape fill is a concrete structure, which is partly underground, partly forms a grillage, slightly thicker in width than the walls of the future house.
The deepened foundation is carried out with immersion into the soil slightly below the level of groundwater flow from 1.5 to 2.5 m.
Inside the poured concrete there is connected reinforcement, which will take most of the load, distribute it, while maintaining the integrity of the structure. At the corners, the reinforcement is reinforced, which helps to significantly increase the period of operation of the structure.
Application
The structure is used in the construction of low-rise buildings of the frame type, made of wood. This can be a house made of shields, a gazebo, an outdoor toilet, a fence. Groundwater should be below the foundation level.
Shallow deepening provides for the possible content of clay, loess-like loam, peat, and silty sand in the soil. The decisive criterion is the bearing capacity of the support for the house.
 MZLF on terrain with height differences
MZLF on terrain with height differences
If you plan to build a basement, basement space, the monolith will not work, the solution is tape.The structure is suitable for simplified structures, for example, for household purposes.
Support types
Types of construction depending on physical parameters:
- prefabricated strip-shaped monolith to a depth of 40 cm, series 20;
- just a prefabricated monolithic version with a depth of 80 cm, series 60;
- tape monolith 40, 80 cm;
- reinforced monolith (used on difficult soils).
The choice depends on the climate, the type of soil, the degree of freezing of the earth, the material of the house, the final weight, the size of the construction budget.
Advantages and disadvantages
Plus structures - independent erection, earthwork becomes 2-3 times less.
Savings are noted, fewer materials are used, you can make a cellar, a basement deepening for storing things, vegetables, pickles.
The foundation endures ground movements associated with the change of seasons and seismic activity.
If the landscape is uneven, with drops, it will be possible to make a stepped, leveling base without a strong increase in costs.
 Shallow construction is suitable even for complex building shapes
Shallow construction is suitable even for complex building shapes
The downside is the impossibility of building a house from heavy material, even brickwork weighs a lot for MZLF.
When the height differences are too large, or the soil contains a lot of clay, peat bogs, a shallow digging is not enough, deepening is required.
If you are pouring concrete, you will need to wait almost a month until it is completely dry. You can use different types of blocks for the construction of MZLF, but not always appropriate.
When deciding to form a basement, a shallow foundation will not work, you can make not very deep niches.
The main types of foundations: pros and cons
Strip foundation
Depending on the design features, it can be monolithic and prefabricated. The choice depends on the degree of heaving of the soil: if it is small, then the prefabricated view is also suitable, if on the contrary, then the choice of a monolithic strip foundation will be the most correct. However, do not forget that the strip foundation is not the cheapest option and it is intended for a house with heavy walls, that is, for a heavy load. Therefore, before building, you need to thoroughly analyze all the facts so that the conclusion of such an expensive foundation is truly justified. The strip foundation can be divided into three types: rubble, brick and rubble concrete. Each type has its own service life. If it is a rubble species, then it is 150 years old. If brick - then from 30 to 50 years. If rubble concrete - 50-75 years. The advantages of the foundation are that the load is evenly distributed; then it will be possible, if necessary, to attach, remake as you want; and, of course, in reliability. The disadvantages are its massiveness and the high cost of building materials.
Column foundation
This is a more economical option, but it is only suitable for the construction of lightweight houses. There is one important feature in a columnar foundation: it withstands precipitation much better than a strip foundation and tolerates soil deformation more easily. It can be made of brick, stone, concrete, rubble concrete, monolithic reinforced concrete.
Pile foundation
The most suitable option for large-sized heavy buildings and for unstable ground. In private construction, this design is practically not used. A pile is a pillar with a pointed end. They are driven or screwed into the ground, bypassing possible floaters, mobility, and abut against solid ground. In the finished foundation, each pile can withstand a load of 2 to 5 tons. It is quite difficult for you to lay such a foundation. Now many organizations provide such services, and at the same time, they are also responsible for the work done. So, in this case, it is better to consult a specialist. But this will require a lot of money.If finances do not allow hiring workers, then drilling can be done with a hand-held construction drill. The reliability of such a foundation leaves no doubt. But there are a couple of disadvantages: the pile foundation is not suitable for horizontally moving soils - in this case, a rigid reinforced concrete grillage is needed. Also, this type of foundation does not provide for a basement room (this requires a lot of additional forces and funds).
Slab (floating) foundation
It is usually used in the construction of timber frame-panel and log houses. A feature of such a foundation is that, unlike a belt and pile foundation, it is located under the entire building area. The foundation itself is a metal frame filled with concrete. Moreover, the frame joints must be rigidly connected. The advantage of such a foundation is its relative simplicity. That is, it is not difficult to make it yourself and without the use of heavy earth-moving machinery. Also, a slab foundation can be laid on a plot of land in a high level of groundwater, on heterogeneous soil. The floating foundation tends to move along with the movements of the ground and, thus, the load on the walls is weakened. If we are talking about a shed or garage, then you can not add additional flooring, but use the surface of the foundation as a floor. The disadvantage of such a foundation is financial disadvantage, because a lot of money will be spent on concrete and metal reinforcement.
In fact, the point is not even about the economic profitability or disadvantage of a certain foundation. The whole point is what type of foundation is needed for your building. Therefore, you need to proceed from a set of specific parameters and features of a real site. As mentioned above, the foundation is the main part of the structure and therefore, how strong and durable the building will be depends on how the type of foundation is chosen correctly, how accurately the soil analysis is carried out, and, of course, the quality of the foundation itself. So, if there is no way to analyze it yourself, take the trouble to invite a specialist so that the building does not turn out to be useless and unreliable, and the money is "thrown away" to the wind.
Recommendations from the pros!
Bath accessories
DIY gazebo
Concrete fence
Diy potbelly stove
Do-it-yourself veranda
Screw foundation
Country toilet do it yourself
Decorative brick
Stone fence
Pouring the foundation
How to make a fence
Wicket from corrugated board
DIY fireplace
Brick fence
DIY flower beds
Forged gates
Do-it-yourself porch
Bath tub
DIY chicken coop
DIY ladder
Metal gates
Installation of lining
Installation of polycarbonate
Pump for giving
Garage arrangement
Fences for flower beds
Do-it-yourself blind area
Steam room in the bath
Railing for stairs
DIY cellar
Painting the walls
DIY press
Lattices on windows
Rolling gates
Do-it-yourself shed
Alarm for summer cottages
Benches for giving
Fence posts
Floor screed
Solid fuel boilers
DIY greenhouse
Fence installation
House insulation
Attic insulation
Insulation of the foundation
What materials will be required?
If you decide to build a strip foundation with your own hands, first you need to prepare all the necessary materials.
|
Image |
Name |
Description |
|
|
Edged board |
It is better to choose boards with a thickness of at least 15 millimeters. They are necessary for the installation of the formwork into which the concrete will be poured. |
|
|
Roofing material |
Used for waterproofing. If necessary, you can replace the roofing material with a thick plastic wrap. |
|
|
Steel wire |
With its help, the reinforcement is strapped and the formwork elements are tightened. |
|
|
Armature |
It is used for the installation of a reinforcing belt. It is recommended to choose a rod with a diameter of 10 to 15 mm. |
|
|
Nails and screws |
It will be needed for fastening the boards during the installation of the formwork. |
|
|
Crushed stone and sand |
Needed to create a cushion under the foundation. |
As the main material for pouring the formwork, you can use concrete, consisting of 1 part of cement grade M 400, 4 parts medium fraction crushed stone or gravel and 2 parts of sand.
If a prefabricated strip foundation is selected, then reinforced concrete blocks will be needed. They are installed close to each other, and the seams between them are filled with concrete. But since it will not be possible to install such blocks without the involvement of equipment, they are not suitable for performing work on their own.







