The principles of calculating the sheathing for corrugated board
Like most roof coverings, the profiled sheet is attached to the battens. The step of the lathing for the corrugated board is stipulated in the building codes.The SNiP specifies the requirements for this parameter, based on slope angle roofs :
- with a minimum slope of the roof, for the installation of corrugated board, a solid lathing is required, or a lathing with a step not exceeding 400 mm (the choice depends on the thickness of the metal and the grade of the material used);
- with an average slope, the wooden base can be mounted with a step of 300 - 650 mm;
- if the roof has a large slope angle, the step can be up to 1000 mm;
- individual grades of corrugated board with high rigidity can be mounted with a lathing step up to 3000 or 4000 mm, if the slope angle is more than 8 degrees.
When designing a roofing system, you should decide in advance on the material of the topcoat. Manufacturers of corrugated board in the accompanying documentation indicate the requirements for laying a specific material. It is recommended to calculate the sheathing for corrugated board, in accordance with the parameters specified by the manufacturer (they do not go beyond the requirements of SNiP).
In private construction, corrugated board with a profile of 35 mm in height from a steel sheet with a thickness of 0.6-0.7 mm is often chosen. Such material can be mounted on the batten in steps of up to 1.5 meters, while the roof is designed for a load of up to 600 kg per square meter.
You can safely move along such a roof when cleaning or repairing, but it should be noted that this structure of increased strength is somewhat more expensive than a roof made of corrugated board of lower rigidity.

If it is supposed to use corrugated board with a profile height of 21 mm or less, the step of the lathing for the corrugated board should be minimal, or a continuous lathing is mounted. This roofing material is not designed for high loads, it requires a solid base to avoid deformation of the sheets.
Profiled sheet with a profile height of 44 mm or more is practically not used in private construction, since this material is intended for arranging the roof of industrial structures .
Preparation of material for lathing
To calculate the amount of lumber required, you need to know the length and width of the ramp, as well as calculate the step. In addition, it should be borne in mind that two boards should be mounted at the ridge and the cornice in order to ensure the necessary strength of the roofing.
Reinforcements also require places of abutment to chimneys, skylights, ventilation ducts, etc. Another 10% should be added to the calculation result. since during the installation process, the lumber will have to be cut to the required size and some will go to waste.
The cross-section of the bar must be at least 50 × 50 mm. Also, the lathing can be made of edged or unedged boards with a thickness of 50 mm. It is required to use well-dried lumber. It is recommended to use beams and boards made of spruce, pine, beech, alder
The material may not be planed, but you should pay attention to the straightness of its surfaces.
Boards and beams should not be warped; if necessary, the surface of the elements should be corrected.

The lathing for corrugated board is operated in conditions of high humidity, therefore there is a high risk of damage to wooden elements by fungus and microorganisms. To prevent wood rotting, lumber needs to be treated with antiseptics. Fire protection of roof elements is also required. Today, special compositions for fire-retardant protection are produced, which allow both types of treatment to be carried out at one time.
It is allowed to process an already finished crate, but the roof structure will be much more efficiently protected if it is assembled from elements that have been qualitatively impregnated with a fire retardant compound in advance.
Determination of the cross-section of the rafters
The rafter legs of roofs of various steepness do an ambiguous job. The bending moment acts mainly on the rafters of shallow structures; on the analogs of steep systems, a compressive force is added to it. Therefore, in the calculations of the cross-section of the rafters, the slope of the slopes must be taken into account.
Only bending stress acts on the rafter legs of the roofs of the indicated steepness. They are calculated for the maximum bending moment with the application of all types of load. Moreover, temporary, i.e. climatic loads are used in calculations based on maximum values.
For rafters that have only supports under both their own edges, the point of maximum bend will be in the very center of the rafter leg. If the rafter is laid on three supports and is made up of two simple beams, then the moments of maximum bending will fall in the middle of both spans.

For a solid rafter on three supports, the maximum bend will be in the area of the central support, but since there is a support under the bending section, then it will be directed upward, and not, as in the previous cases, downward.
For normal operation of the rafter legs in the system, two rules must be followed:
- The internal stress formed in the rafter during bending as a result of the load applied to it must be less than the calculated value of the bending resistance of the sawn timber.
- The deflection of the rafter leg must be less than the normalized deflection value, which is determined by the ratio L / 200, i.e. the element is allowed to bend only by one two hundredth of its real length.
Further calculations consist in the sequential selection of the dimensions of the rafter leg, which, as a result, will satisfy the specified conditions. There are two formulas for calculating the cross section. One of them is used to determine the height of a board or timber by an arbitrary specified thickness. The second formula is used to calculate the thickness at an arbitrary height.

In calculations, it is not necessary to use both formulas, it is enough to apply only one. The result obtained as a result of the calculations is checked according to the first and second limiting states. If the calculated value turned out with an impressive margin of safety, an arbitrary indicator entered into the formula can be reduced so as not to overpay for the material.
If the calculated value of the bending moment is greater than L / 200, then the arbitrary value is increased. The selection is carried out in accordance with the standard dimensions of the commercially available sawn timber. This is how the section is selected until the moment when the optimal version is calculated and obtained.
Let's consider a simple example of calculations using the formula b = 6Wh². Suppose h = 15 cm and W is the M / R ratioexile... We calculate the M value using the formula g × L2 / 8, where g is the total load vertically directed to the rafter leg, and L is the span length equal to 4 m.
Rexile for sawn softwood we accept 130 kg / cm2 in accordance with technical standards. Suppose we calculated the total load in advance, and we got it equal to 345 kg / m. Then:
M = 345 kg / m × 16m2 / 8 = 690 kg / m
To convert to kg / cm, divide the result by 100, we get 0.690 kg / cm.
W = 0.690 kg / cm / 130 kg / cm2 = 0.00531 cm
B = 6 x 0.00531 cm x 152 cm = 7.16 cm
We round the result as it should be in the big direction and we find that for the device of rafters, taking into account the load given in the example, a beam of 150 × 75 mm is required.
We check the result for both states and make sure that the material with the cross section calculated now is suitable for us. σ = 0.0036; f = 1.39
The rafters of roofs with a steepness of more than 30º are forced to resist not only bending, but also the force compressing them along their own axis. In this case, in addition to checking the bending resistance described above and by the amount of bending, it is necessary to calculate the rafters by internal stress.

Those. actions are performed in a similar order, but there are slightly more verification calculations.In the same way, an arbitrary height or arbitrary thickness of the lumber is set, with its help the second parameter of the section is calculated, and then a check is carried out for compliance with the above three technical conditions, including the compression resistance.
If it is necessary to increase the bearing capacity of the rafters, the arbitrary values entered into the formulas are increased. If the safety margin is large enough and the standard deflection significantly exceeds the calculated value, then it makes sense to perform the calculations again by reducing the height or thickness of the material.
To select the initial data for the production of calculations, a table will help, which summarizes the generally accepted sizes of lumber we produce. It will help you choose the section and length of the rafter legs for initial calculations.

General scheme for calculating the rafter step
The rafter system is the supporting structure of the entire roof. It consists of rafter legs, uprights and inclined struts.
Each rafter is located at a certain distance from the next - this distance is called "rafter step".
The strength of the roofing structure, the maximum permissible load per square meter and materials that can be used for roofing work depend on it.

According to GOSTs, the minimum permissible value of the rafter pitch is 60 cm, the average is more than 1 m.
To determine the approximate pitch, you can use the following formula: D / (D / m + 1), where D is the length of the roof from the ridge to the ridge, m is the approximate rafter pitch.
All results obtained must be rounded to the nearest larger integer. Obviously, this formula is only for approximate calculations.
To determine the exact step size, the following factors need to be taken into account:
- own weight of the rafter system, that is, the materials from which it is made;
- the weight of the material with which you plan to cover the roof;
- weight of additional heaters, seals, hydro and vapor barrier systems;
- crate weight;
- weight of attic finishing materials;
- climatic loads (wind, snow accumulation).
In addition to the above loads, the roof must be able to support the weight of at least one adult so that, in the event of repair or installation of an antenna, the installer can safely climb onto the roof.
If you plan to install a chimney, then its location must be initially included in the calculations so that in the future it will not be necessary to remove part of the roof and install additional support points.
Installation of lathing
How to make a crate for corrugated board? First of all, you should pay attention to the structure of the roofing pie of the pitched roof, if corrugated board is used as the topcoat. On top of the rafters, it is required to lay waterproofing from roofing material or a special waterproof membrane
A roof made of profiled sheet requires high-quality ventilation, therefore, along the rafters, on top of the waterproofing, it is necessary to fill bars with a cross section of 50 × 50 mm - the counter lattice makes it possible to create the required ventilation gap.
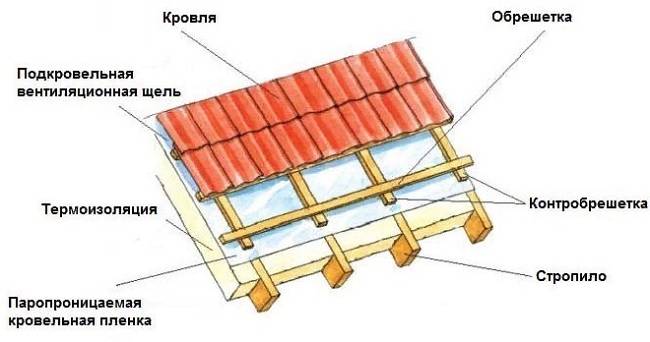
The battens are attached to the counter battens. For this, boards or bars are stuffed parallel to the cornice strictly horizontally. To simplify installation, it is recommended to tighten the rope by fixing it along the edges of the ramp and making sure it is horizontal, it is better to use a wooden template.
The lathing is attached to the wooden bars of the counter-lattice with staples or nails, if metal elements are used, self-tapping screws should be used. It is attached to the concrete base of the roof using dowels.
In the lower part of the ramp, parallel to the cornice, the main board of the sheathing is attached, its thickness should be greater than that of the other elements.The thickness of the board is selected based on the height of the profile of the profiled sheet, as well as the length of the fasteners used, with which the outer side of the roofing sheet is fixed.
It is necessary to install wind boards at the ends of the roof slope. Their surface should be higher than the rest of the lathing elements, to the height of the corrugated board profile.

The installation of the lathing under the corrugated board is then carried out in the direction from the bottom up. Each bar is attached to each rafter with one nail. To fasten the board to each rafter, two nails should be used along the top and bottom edges to avoid turning the board over and damaging the roofing under high loads.
The elements of the lathing should be docked along the length on the rafter, securing each of the ends with nails or staples. On one rafter leg, the sheathing of adjacent tiers should not be joined.
How to calculate the length of the gable roof rafters
The rigidity of the structure of the truss system is a mandatory requirement, and its provision excludes deflection when exposed to loads. The rafters bend in the event of errors in the design calculations and the step size with which the rafter is installed. In the case when this defect is detected after the end of the work, it is necessary to strengthen the structure with the help of struts, thereby increasing its rigidity. With a rafter length of more than 4.5 m, the use of struts is mandatory, since the deflection will be formed in any case under the influence of the beam's own weight
This factor must be taken into account when performing calculations.
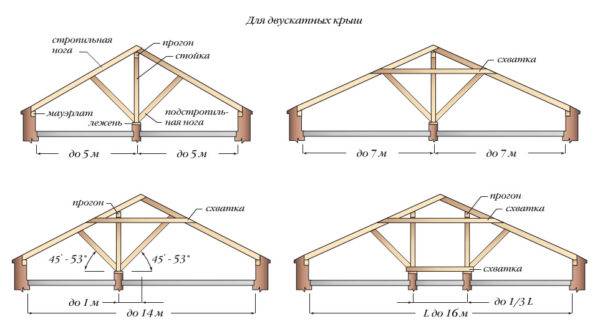 The length of the rafters depends on their location in the system
The length of the rafters depends on their location in the system
Determining the distance between rafters
The standard step with which the installation of rafters in a residential building is carried out is about 600-1000 millimeters. Its value is influenced by:
- calculated load;
- section of the bar;
- roof characteristic;
- angle of inclination of the roof;
- the width of the insulation material.
 It is not recommended to artificially decrease or increase the step of the rafters.
It is not recommended to artificially decrease or increase the step of the rafters.
The determination of the required number of rafters is taking into account the step with which they will be installed. For this:
- The optimal installation step is selected.
- The length of the wall is divided by the selected step and one is added to the resulting value.
- The resulting number is rounded to the nearest whole.
- The length of the wall is divided again by the resulting number, thereby determining the desired step of mounting the rafters.
Truss system area
When calculating the area of a gable roof, you need to take into account the following factors:
- The total area, which consists of the area of two slopes. Based on this, the area of one slope is determined and the resulting value is multiplied by the number 2.
- In the case when the sizes of the slopes differ among themselves, the area of each slope is determined individually. The total area is calculated by adding the values obtained for each slope.
- In the case when one of the slope angles is greater or less than 90 °, in order to determine the area of the slope, it is "divided" into simple figures and their area is calculated separately, and then the results are added.
- When calculating the area, the area of chimneys, windows and ventilation ducts is not taken into account.
- The area of gable and cornice overhangs, parapets and firewall walls is taken into account.
 The calculation of the rafter system depends on the type of roof
The calculation of the rafter system depends on the type of roof
For example, a house is 9 m long and 7 m wide, the rafter is 4 m long, the eaves overhang is 0.4 m, and the pediment overhang is 0.6 m.
The value of the area of the slope is found by the formula S = (Ldd+ 2 × Lfs) × (Lc+ Lcop), where:
- Ldd - wall length;
- Lfs - the length of the gable overhang;
- Lc - the length of the rafter bar;
- Lcop - the length of the eaves overhang.
It turns out that the area of the slope is S = (9 + 2 × 0.6) × (4 + 0.4) = 10.2 × 4.4 = 44.9 m2.
The total roof area is S = 2 × 44.9 = 89.8 m2.
The size of the gable roof is calculated in order to determine the required amount of roofing material. With an increase in the angle of inclination of the roof, the consumption of material also increases. The stock should be about 10-15%. It is caused by overlapping stacking.To determine the exact amount of material, taking into account the slope of the slopes, it is best to use reference books.
What is the step depending on the roofing material
Ondulin
If ondulin is used as a roofing material, then the rafter system is constructed of pine boards with a cross section of 50 x 200 mm, and the rafters should be located at a distance of at least 60 cm and no more than 90 cm from each other.
A crate of timber with a section of 40 x 50 mm is laid on top.
Metal tile
Metal roofing is most often used in the construction of country houses.
Because this material is much lighter than ceramic or cement tiles.
Although in appearance it is very similar to her.
The low weight of the metal tile makes it possible to use boards of a smaller section when creating a rafter system, and use thinner bars for the lathing.
Reducing the size of the elements of the rafter leg system, in turn, reduces the load on the walls of the building and its foundation.
During the construction of the rafter system under the metal tile, the rafters are mounted in increments of 60 - 95 cm.
The cross section of the material is 50 x 150 mm.
According to experts, if a heater with a thickness of 150 mm is placed in the gap between the rafters, then the most comfortable living conditions will be created in the attic.

The manufacturing technology of the truss system for metal tiles does not differ significantly from the technology for manufacturing the frame for other roofing materials.
Its only difference is the mounting at the top.
The mounting of the upper support is carried out not on the ridge beam from the side, but on the ridge girder.
The presence of a free zone between the rafters allows air to fully circulate under the deck, which helps to prevent condensation from forming.
Ceramic roof tiles
The design of the system for ceramic tiles has its own characteristics.
After all, clay is used for the manufacture of such a roofing material.
And this is a very difficult material.
If we compare metal and ceramic tiles, the latter weighs 10 times more.
Accordingly, the rafter system is significantly different.
For 1 square meter of the roof surface, there is a load of 40 - 60 kg, depending on the manufacturer and brand of the product.
Rafters for such a frame system are made from wood that has undergone a long drying.
Such wood should have a moisture content of no more than 15%.
A bar is used with a cross section of 50 x 150 or 60 x 180 mm.
It's safer this way.
And the distance between the rafter legs can be 80 - 130 cm.
The exact value can be called if the angle of inclination of the slopes is known.
If the angle of inclination is 15 degrees, then the step of the rafters will be 80 cm.
And if the angle of inclination, for example, is 75 degrees, then the step can be more - 130 cm.
More than 130 cm the interval between the rafters is not made.
Also, when calculating the step of the rafters, their length is taken into account.
The larger the dyne, the smaller the distance between them.
The shorter the rafter legs, the more distance you can make.
If the angle of inclination is 45 degrees, then the roofer can move safely along the roof if the pitch of the rafters is 80 cm.
Corrugated board
When creating a rafter system for corrugated boarding, the minimum distance between the rafter legs is 60 cm.
The maximum size is 90 cm.
If, for some reason, the pitch of the rafters is more than 90 cm, then it becomes necessary to install cross-section boards of a large section.
The rafter legs themselves can have a cross section of 50 x 100 or 50 x 150 mm.
Slate
Despite the emergence of a large number of new roofing materials, asbestos-cement slate remains one of the most popular.
If it is planned to lay slate on the roof, then the rafters should have a cross section of 50 x 100 either 50 x 150 mm.
The distance between them is made not less than 60 and not more than 80 cm.
The lathing is made from a bar with a cross section of 50 x 50 mm or a board with a cross section of 25 x 100 mm.
When constructing any building structure, it should be remembered that there are still unforeseen situations.
And, therefore, when calculating the cross-sections of the rafters and the distance between them, it is necessary to provide a margin of safety.
Video about the installation of the truss system.
What else to read on the topic?
How to strengthen the rafter system
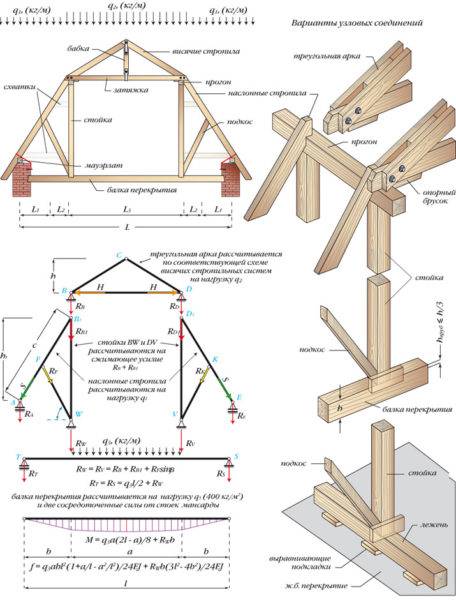
The first and most important element of fastening the rafter system is the tightening of the rafters. It is used in cases where hanging rafters are used during construction. As elements for tightening, a bar or logs are used, which are attached to the bases of the legs. This technology reduces the forces that spread the legs in the horizontal plane.
At a certain height from the base of the legs, a second puff should be made. It is made more massive, since it is designed to prevent the legs from bending at the base. This significantly increases the strength and durability of the roof. Another way to strengthen the rafter system is to mount the filly. In fact, these are boards that are nailed to the legs (at the base) of the rafters to continue it. The section of the boards should be 2 times smaller than the section of the legs, however, 2 boards should be stuffed on each leg. The length of one filly should be about 1.1 meters. In this case, 50% of the length is attached to the leg, and the remaining half hangs from it.
To strengthen the roof structure, roofing experts recommend using special corners. They allow you to carefully fix all structural elements, while increasing the reliability of fastening. This ensures the high bearing capacity of the rafters. Long self-tapping screws should be used as fastening elements.
Installation features
When installing the attic roof truss system, fastening and installation of rafters in the form of simple geometric shapes are used. The linkage in a triangle has the greatest rigidity (strength), which is used in the construction of a mansard roof. So, the most common gable roof includes a series of triangles made of rafters, connected by longitudinal logs (girders). Tying the rafters into a triangle is provided by the lower transverse beam (Mauerlat). To facilitate the fastening of the outer roof covering and the redistribution of its weight on the rafters, a lattice is made in the form of transverse bars or boards.
The sloping roof combines two types of rafter connections. The lower rafters with the help of the Mauerlat and the posts are connected into right-angled triangles, which, in turn, are fastened with a longitudinal run to each other at the top. At the bottom, the attic rafters rest on the wall of the house. The upper ones are connected in a triangle by analogy with a gable structure.

Figure 1. Table for the selection of the cross-section of the timber for the rafters.
The lower end of the rafter is fixed on the transverse log, and the upper ends are connected together through the longitudinal upper girder. The lower corners of the bonded triangle are connected to each other using a longitudinal bottom girder. The hanging rafter system is fixed to the lower rafter system. Additional vertical racks are used to strengthen the upper triangles. Thus, the mansard roof is a surface with a break on each side. A slope with a greater steepness begins from the wall, and then it acquires a more gentle appearance.
The connection of the attic rafters with the longitudinal beams (including with the floor beam) is made by cutting the rafters into the beam at a third of its height. It is advisable to fasten it to the cross beams with a screw connection. With such fastenings, the functions of two different rafter systems are separated and they are calculated as separate systems.
Types of gable roof truss systems
The gable rafter system comes with hanging and layered rafters. Both one and the other schemes can be used for arranging metal roofing.To know how they differ from each other, and what elements they consist of, it is worth considering each of them. It should be noted here that in the diagrams presented below, only the main elements of the rafter systems are indicated, but if necessary, they can be reinforced with additional details, which were discussed above.
Rafter roof system
The gable rafter system of the layered type rests on the inner wall of the building
The roof rafter system consists of the following main elements:
1 - Bearing walls.
2 - Mauerlat.
3 - A stand installed on a bed.
4 - rafter.
5 - Lathing.
The elevated system differs from the hanging system in that it is installed on a structure that has internal capital partitions. The main internal walls are used to secure a plank on them, on which stands are installed, supporting the ridge girder, to which the upper ends of the rafter legs are fastened. Then the sheathing boards are fixed on the rafters.
This design is more popular than hanging, as it is reliable and easy to install.
rafters
Hanging rafter system
Hanging rafters rest only on the side walls of the building and are connected on a ridge
The hanging rafter system diagram looks as shown in the illustration, and includes the following main elements:
1 - Bearing walls.
2 - Mauerlat.
3 - Rafters.
4 - Lathing.
5 - Tightening (crossbar).
The hanging rafter system is mounted on two external load-bearing walls, on which the Mauerlat is pre-fixed. This roof option can only be used if the distance between the load-bearing walls is no more than 7000 mm, since there is no additional support for the roof truss structure besides them. Such a system is usually equipped with puffs supported by slopes - these elements will remove some of the load from the walls of the building.
In addition to overhead and hanging systems, there are combined options that include individual elements of both designs.
When the rafter system is selected, it is recommended, before purchasing materials, to draw up a detailed drawing of the roof with the indicated dimensions - this will make it easier to calculate the amount of everything needed and the amount for their purchase. In addition, such a scheme will greatly help to carry out installation work. But in order to draw up a drawing, you will have to carry out some calculations.
