Despite the name, cable ladders only look like stairs.
About what they are, what they are and what alternatives can be found on sale - this article.
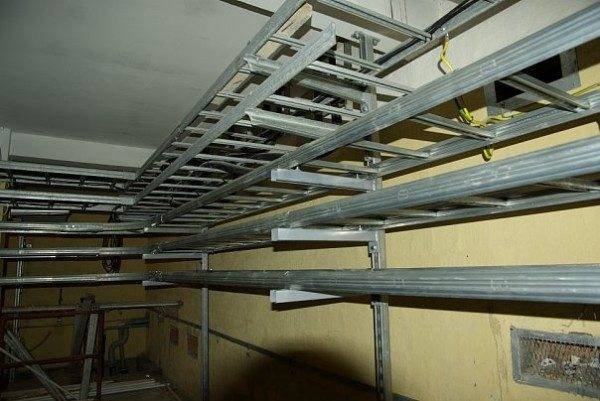

What it is
Ladder cable tray (kabelrost) is an open cable channel for laying in one direction (vertical or horizontal) a large number or, more precisely, a large mass of wires.
A typical (but not the only) material is galvanized steel. The zinc coating is designed to protect the steel profile from corrosion. An alternative solution is polymer coated steel. According to the production method, the profile is usually cold-rolled; spot welding is used to connect longitudinal and transverse elements.
Useful: in most cases, both longitudinal and transverse elements are perforated.
The holes make the structure lighter and cheaper with minimal loss of strength; in addition, they serve to secure the cables with cable clamps.
How is the cable laid? It's very simple: it fits on the crossbeams or is attached to them in a vertical (or inclined) position; while the longitudinal guides ensure the rigidity of the structure.

Specifications
What specifications affect the choice of tray?
- Length of a single structural element... Usually it is equal to 3 meters: with a longer length, both installation and transportation of the tray in the room are difficult.
- Width, height of the guide profile and thickness of its metal... These parameters are interrelated: the wider the tray, the more space on it for the cable, and therefore the greater the load on it. Consequently, the requirements for strength are also increasing.
As an example of the lineup, consider the products of the Italian brand DKC. The buyer is offered products with a width of 200 to 600 millimeters with a guide profile height of 50, 80 and 100 mm. The thickness of the guide (spar) is 1.2 millimeters for the younger models and 1.5 for the older ones.
The price of products is proportional to the consumption of materials for their production - approximately from 500 to 1000 rubles.

It is worth clarifying: the dimensions shown are not a standard.
On sale you can find trays up to a meter wide and up to 6 meters long.
- The load on the tray, evenly distributed over the area, can reach 300 kilograms per linear meter. With sufficient strength of the product, it is worth remembering an additional limiting factor - the bearing capacity of the structure on which the tray is fixed.
- All ladders are IP 00 by definition - simply because they are open structures.
- The operating temperature range for all metal staircases is from -60 to +90 degrees. The lower limit is due to the brittleness of the metal at extremely low temperatures (primarily in relation to shock loading). Upper - the possibilities of plastic clamps used for fastening the cable and the insulation itself.
Application
Installation Basics
A completely intelligible instruction for installing a cable tray with your own hands is contained in GOST 20783 - 81, which, however, is no longer used in the Russian Federation.
What information can be found in the text of the standard?
- The connection of the individual elements of the tray must be collapsible. Its attachment to any type of support is the same. The exception is trays without zinc, polymer or paint coating (primer is acceptable). The goal pursued by this requirement is to exclude corrosion of welded joints, which is clearly indicated by the next paragraph.
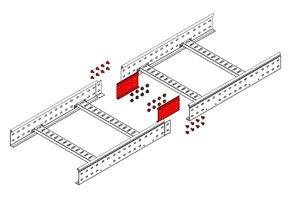
- Elements coated only with primer must be protected with a paint-and-lacquer coating during installation.
In addition, the standard sets requirements that are not very interesting to us for testing, acceptance of batches and transportation of finished products. Let's add on our own a certain amount of additional information contained in the documents, links to which are contained in GOST.
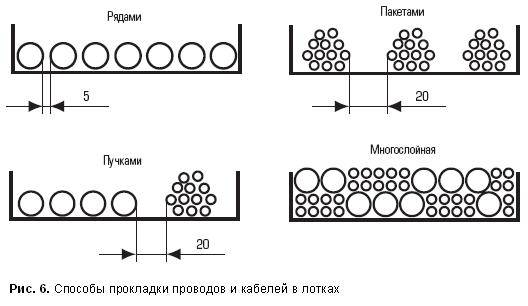
- A cable channel of any type, including a staircase, is filled only by 30-60 percent of the cross-section. The exact percentage of filling depends on whether you plan to re-install, the bending radius of the cables, how the connections are installed, and a number of other factors.
Helpful: Typically, the tray is selected based on 50 percent coverage.
- Cables are laid out in a tray with the most even distribution over the area. The goal is not only to create a uniform mechanical load, but also to optimize heat dissipation: at high currents, a certain amount of heat can be generated on the wiring. However, if the wiring is calculated based on a peak current of 8-10 amperes per square millimeter of cross-section, it does not threaten overheating.
Connecting elements
How, with the help of what, the trays can be connected to the supports and to each other?
As a sample, we will take all the same DKS ladders and consider the branded connecting elements offered by their manufacturer.
- Horizontal angle - a rather complex design that allows the tray to rotate in the horizontal plane by 45 or 90 degrees. The manufacturer's assortment includes corners for all the main standard sizes of trays.
- Vertical hinge corners - multifunctional elements that make it possible to implement a transition between different levels of the tray (of course, when the level difference does not exceed its own length) or to connect the horizontal and vertical sections with a relatively smooth bend. Hinges allow you to make the connection angle arbitrary.
- Vertical and horizontal mounting plates serve for joining, respectively, vertical and horizontal elements. The difference between them is that in the first case, the design of the connector prevents mutual displacement of the elements under the influence of their own gravity and the weight of the cable.
Curious: the manufacturer offers in separate positions reinforced, adjustable and rather expensive hot-dip galvanized horizontal mounting plates.
At the same time, for all elements without exception, a zinc layer with a thickness of 55-120 microns, applied by hot-dip galvanizing in accordance with GOST 9.307, is indicated as an anti-corrosion coating.
- Wall mountings, as you might guess, are designed to fix the tray on vertical surfaces.
- T- and X-couplers allow you to combine trays in a T-shaped or cross structure with the transition of cables between directions.
- Simplified reductions - structurally simple elements that allow to connect the trays with a slight displacement in a plane parallel to the surface of the tray.
- Finally, the plastic end caps all basic sizes are only needed to protect installers, maintenance personnel and cable insulation from cuts and damage.

Alternatives
Kabelrosta are quite versatile and can be used indoors, including for laying hidden communications, and (with the appropriate quality of insulation of the cables themselves) outdoors. However, in general, both the appearance of the cable tray and the degree of protection provided by it leave much to be desired. What alternatives can you find on sale?
Mesh tray
It looks like an open channel made of anti-corrosive wire mesh. The thickness of the wire ranges from 3 to 5 millimeters, depending on the requirements for the mechanical strength of the structure. Clamps and clamps are used as a fastening element.
Such a channel differs from kabelrostov in its relative cheapness and lower bearing capacity.
Rolling trays and boxes
Material for the production of rolling boxes and trays - cold-formed steel sheet; often, to increase the bearing capacity, the bottom and side walls are equipped with additional stiffeners. The sheet can be solid or perforated; it is supplied with an anti-corrosion coating in the form of a layer of zinc, polymer or powder paint.
Captain Evidence suggests: the difference between a tray and a box is in the presence of a lid.
The box provides a much greater degree of protection against any adverse environmental influences.
Plastic box
Closed PVC ducts are usually laid indoors. The reader has probably seen this design more than once in office buildings: the plastic tray is covered with a lid with a longitudinal latch.
The duct tray can be U-shaped or have internal partitions to separate the cable groups. Most often produced without perforation; fastened with clamps, self-tapping screws, glue, etc.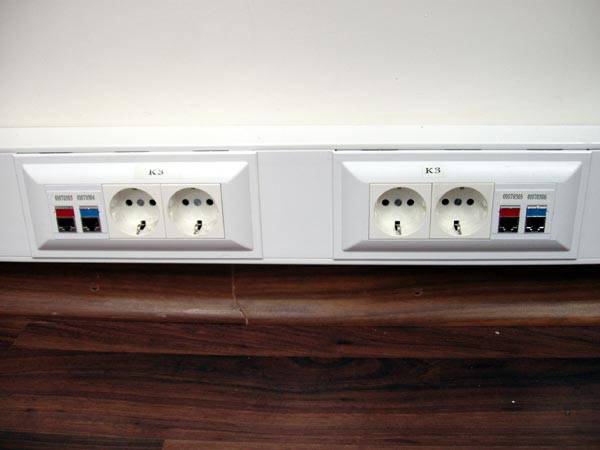 
Sockets and switches can be mounted directly in the box.
Corrugated pipe
It combines flexibility with a sufficiently high mechanical strength and water resistance. Steel wire is often placed inside to prevent the pipe from stretching and bursting. Material - PVC or low pressure polyethylene; field of application - hidden wiring under decorative wall coverings or in a screed.
Output
As you can easily see, there are many ways to hang and protect the cable. In the video presented in this article, you will find additional information on this topic. Good luck!






