Types of lining for room decoration
The lining, according to the material used for its manufacture, is divided into 2 types:
- plastic;
- wood.
PVC panels are made by extruding a mixture of additives and PVC resin. It should be noted that all materials used are environmentally friendly and non-flammable. Plastic panels are intended for decorative interior decoration of ceilings and walls, as well as for external cladding:
- building facades;
- roof overhang;
- veranda ceiling, etc.
Such facing material has the following positive qualities:
- good heat, sound and moisture insulating properties;
- resistant to ultraviolet radiation, which allows it to be used outdoors;
- an operational period of at least 10 years at an air temperature of -50 to + 50 ° С;
- to maintain cleanliness, it is enough to wipe the material with plain water and any detergent.
The main advantage of wooden lining is its naturalness. A room in which boards were used for wall and ceiling cladding will have a favorable microclimate. This is due to the fact that the tree tends to absorb moisture in case of its excess and to give in case of its lack.
Wooden lining is made of coniferous and deciduous species of wood: ash, aspen, beech, spruce, alder, pine, etc. The board, like any other natural product, is distinguished by its design and environmental properties. But do not forget that the price for it is significantly higher than for plastic panels.
Wood requirements and grade
The type of board or its grade is a classification in which the permissible flaws in the wood and their quantity are indicated. The board and bars can be of five grades - perfect, 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th. The bar is not perfect, so it has only four varieties, indicated by numbers.
Selected lumber, first, second and third grades are made:
- from dry wood with a moisture content of not more than 22%;
- from raw;
-
raw, treated with antiseptics.
Wood for the fourth grade is not regulated. The grade is determined by the worst face or edge. That is, find the worst part, and determine the grade by the presence and number of defects and flaws. All of them are given in the tables, and the possible defects themselves are in the form of pictures.
How to determine the grade of the board
Do you know how the grade of the board is determined in production? Approximately. No one counts knots, cracks and other defects. And the difference between, say, the first and second grade is very small. And not all manufacturers try to sort it out correctly. So it's better to control everything yourself. But the tables are so large, and there are a lot of defects - it's impossible to remember everything. But there are certain criteria that can help you determine how much the quality meets the declared one.

Selected and first-class edged planks may not have such damage.
If there is at least one knot that has fallen out, this is definitely not a perfect and not the first grade. At least the second, or even lower.
Planks and beams of the first grade should be free of rot, fungi and core. These are all places that are destroyed in the first place
So they shouldn't be.
When choosing a bar, pay attention to the number of annual rings. The more there are, the higher the quality of the wood.
It's also worth looking at storage conditions. In general, high grade planks should be stored at least under a canopy. It should be stacked in ventilated piles and not in bulk. Ventilated stacks are with spacers that separate one row from another and allow the wood to dry evenly.
What is edged board, timber and bar
It is not so easy for an ignorant person to understand construction terminology. If you started a construction project, you will have to do it. First, let's figure out what a board is, how it differs from a bar and a bar. All definitions of lumber are given in GOST 18288-87. They are based on size. According to this doc:

What is the difference between a bar and a bar? The cross-section of the bar has the shape of a square with a side of more than 100 mm. The bar can be square, but the side should be less than 100 mm, but most often the bar looks like a rectangle
- A board is lumber that has a thickness of no more than 100 mm and a width of more than two times the thickness.
- Beam - more than 100 mm wide and thick. The maximum cant size is not standardized. Only minimal.
- Bar - up to 100 mm thick and no more than double the width.
So, if you look at the timber from the end, all its sides should be equal. The cross section of the bar will give us a square. The board and the bar are rectangles. It's just that the width of the board is more than twice the thickness, and the bar is less. For example, 25 * 75 mm is a board, and 25 * 45 mm is a bar. And by the way, 50 * 50 mm and 75 * 75 mm are also a bar, not a bar, because according to the standard, a bar is a product with a side of 100 mm. With these names, it seems, sorted out.

What is a croaker and a boardwalk, it is clear from the photo
For rough work, a croaker is sometimes used. What it is? By the same standard, this is the side of the log, one side of which is propylene, the other is not. There is also a plank slab - this is when the outer part of the slab is partially propylene.
Edged and unedged board
It is also worth deciding what a face and an edge are. It is either of the two wider surfaces in the board or bar, and either of the surfaces in the bar. The edge, respectively, is the narrower part of the lumber.
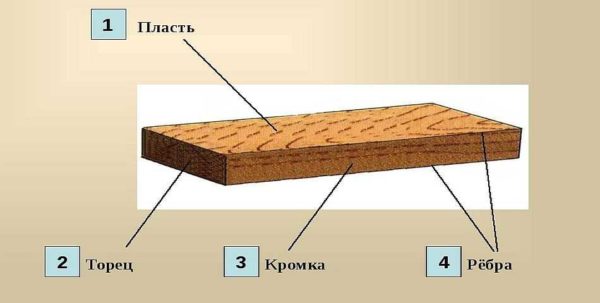
The seam of a board or bar is a wide surface
Now you can find out what an edged board is and how it differs from an unedged board. The edged board has edges that are sawn off perpendicular to the faces. On the edge there may be wane (remnants of bark), but no more than permissible in terms of grade. Unedged board, respectively, has uncut or partially cut edges. Edged lumber, in which wane exceeds permissible limits, falls into the same category.
There is also a semi-edged board. This is when only one edge is flat, and the second can be wane. The timber, by the way, can also be wane. The two-edged one has two opposite sides, the three-edged one has three, and the four-edged one has all four.

Edged and unedged board. The difference is in the form of edges. In edged ones, they are smooth; in low varieties, a small amount of wane is allowed. For unedged boards, the edges are not cut at all or only partially
You may also need such a concept as calibrated lumber. There is a calibrated board, a bar and a bar. This is lumber dried and processed (on a thicknesser or planer) to the required size. It must be understood that an uncalibrated one may have deviations in size (the limits of deviations are normalized), a calibrated one should not differ in size. Rather, the permissible deviations are very small.
There is also a planed board. It differs from edged with smoother sides, as it undergoes additional processing. The edged board is dried, and then sent for additional processing on a planer. There, its roughness, which was left by the saw, is removed. Calibration can occur at the same time, but this is not necessary. The planed board may not be calibrated.
Business and construction board: what is the difference
Also in the price lists there is a board with the same dimensions, of the same type, but one is construction and the other is business. The difference is that the business one is made from non-dead trunks. It is dried, has no fungal or bacteriological lesions, wormholes, even if they are allowed by the standards. Therefore, it is significantly more expensive.
The business board is used for roofing. Goes to the logs, rafters. It is also used in frame housing construction. The business board can be processed directly at the enterprise with the necessary compositions, but this is discussed specifically before delivery.
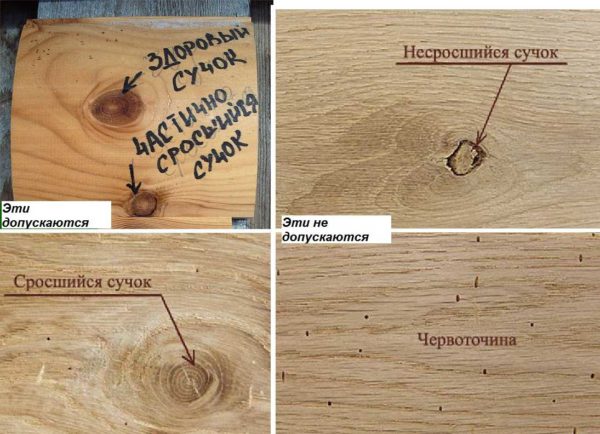

To understand the lumber or business lumber in front of you, look at the knots. A business board or bar can only contain healthy (light) intergrown knots
Parquet - about general standards
Natural wooden parquet is always practical, reliable and respectable. Parquet-based flooring can consist of parquet boards and piece rivets. Small boards with strict geometry, rubbed to a shine and laid in a certain order, allow you to create a special atmosphere of warmth and comfort in the room.
When choosing a material, it is worth remembering that everything plays a role, starting from the type of material and ending with geometry, dimensions (parquet thickness, width and length), drying method. The most demanded coverings are from beech, oak and maple. Oak parquet is beyond competition, which has established itself as the most reliable and durable. The beech covering is more whimsical, not too resistant to moisture, and requires laborious installation.

An important point is the degree of moisture content of the material. It is not only about the degree of drying, but also about the method. The best is parquet, dried by the vacuum method, but the material obtained as a result of the air-steam method is not the most correct solution, just like the components dried in natural conditions.
Only vacuum-dried parquet flooring at temperatures ranging from 52 to 70 degrees will have an ideal surface without cracks and is not affected by moisture.
