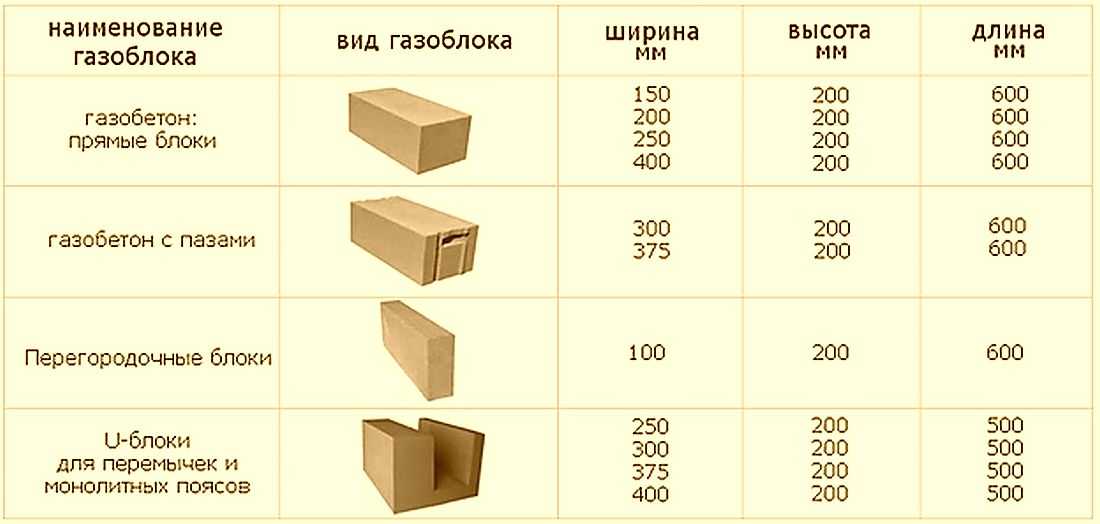
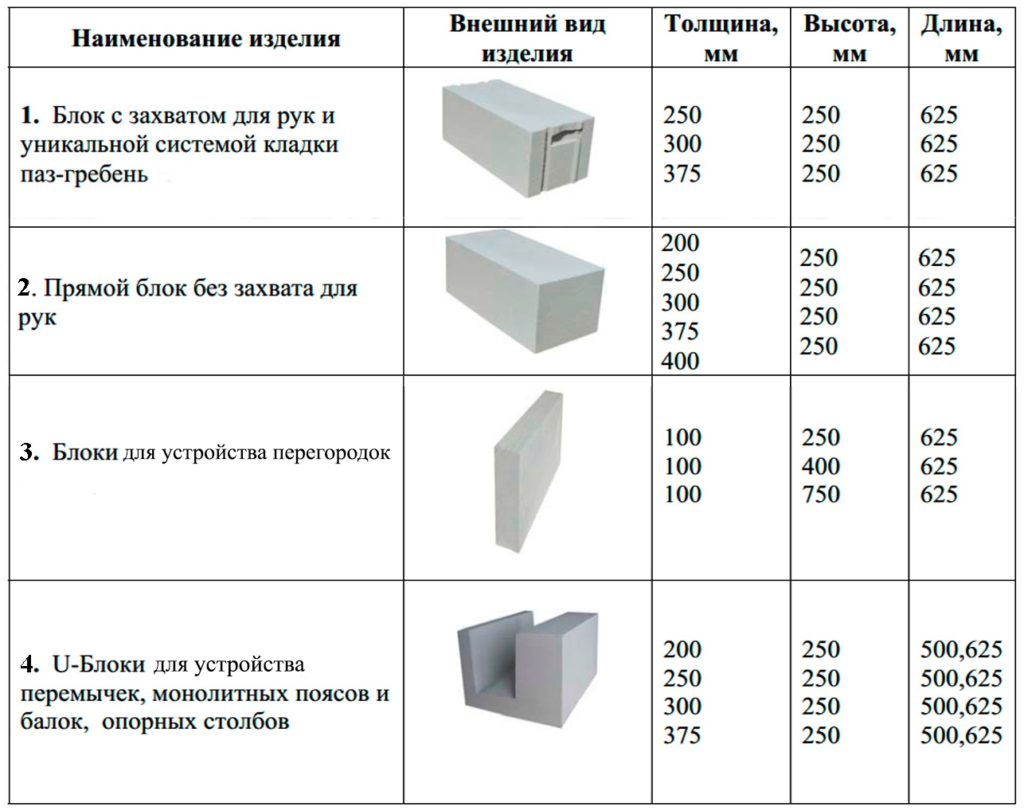
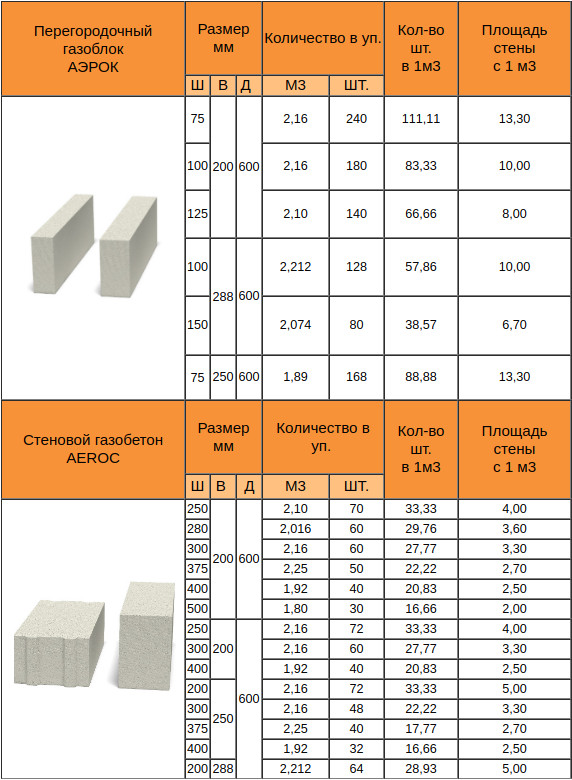
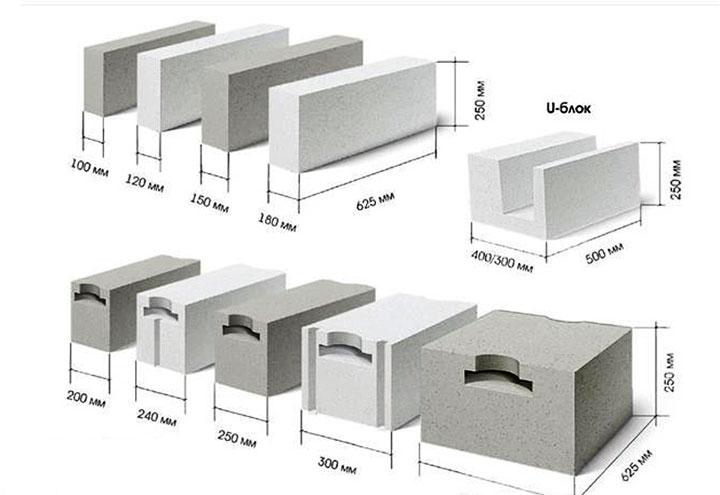
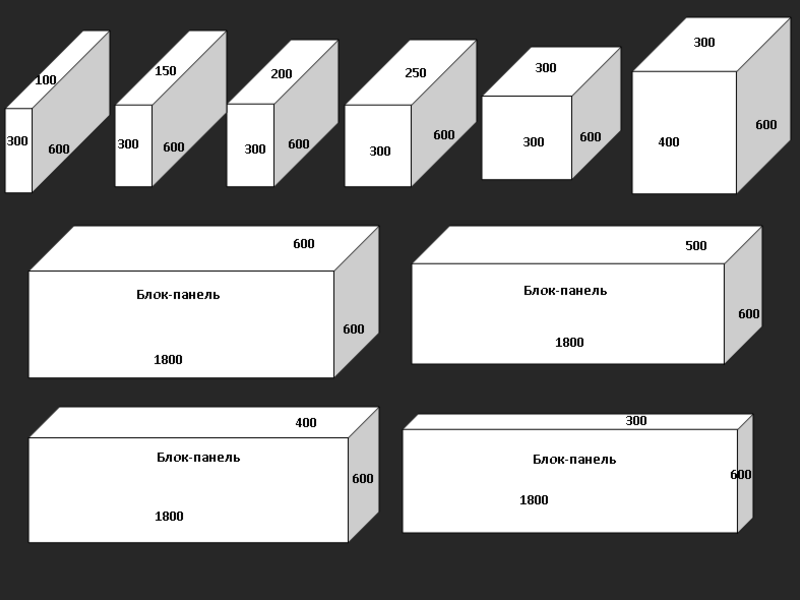
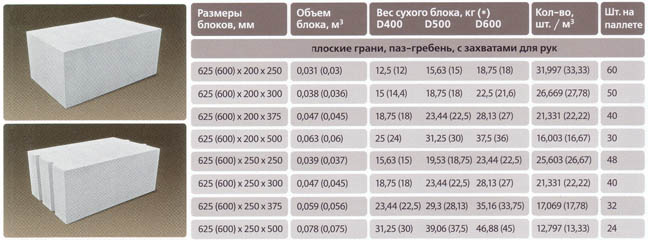
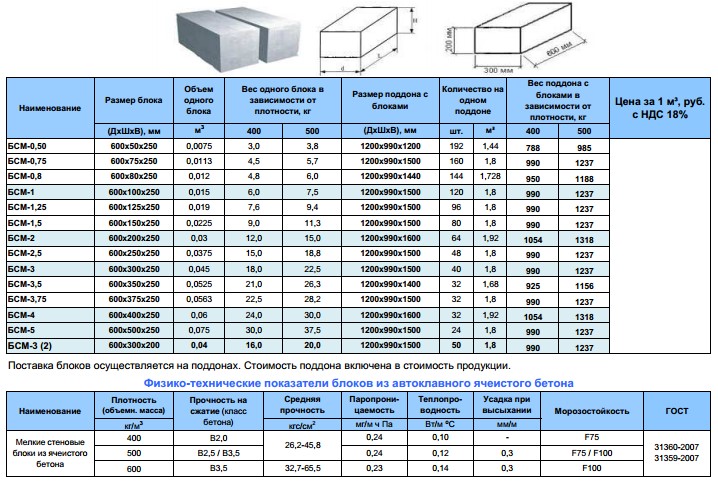
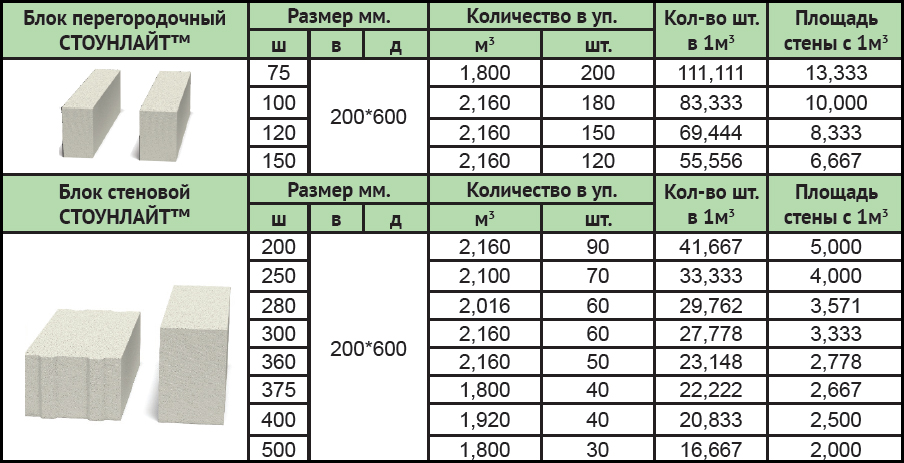
Gas block classification
The calculation of the design parameters of a building under construction depends on the size of the materials used:
- Strength degree;
- Thermal insulation of the structure;
- The choice of the type of masonry walls and partitions;
- And also for the costs of transportation, storage and installation.
The final price for bricks will also depend on their geometric dimensions.
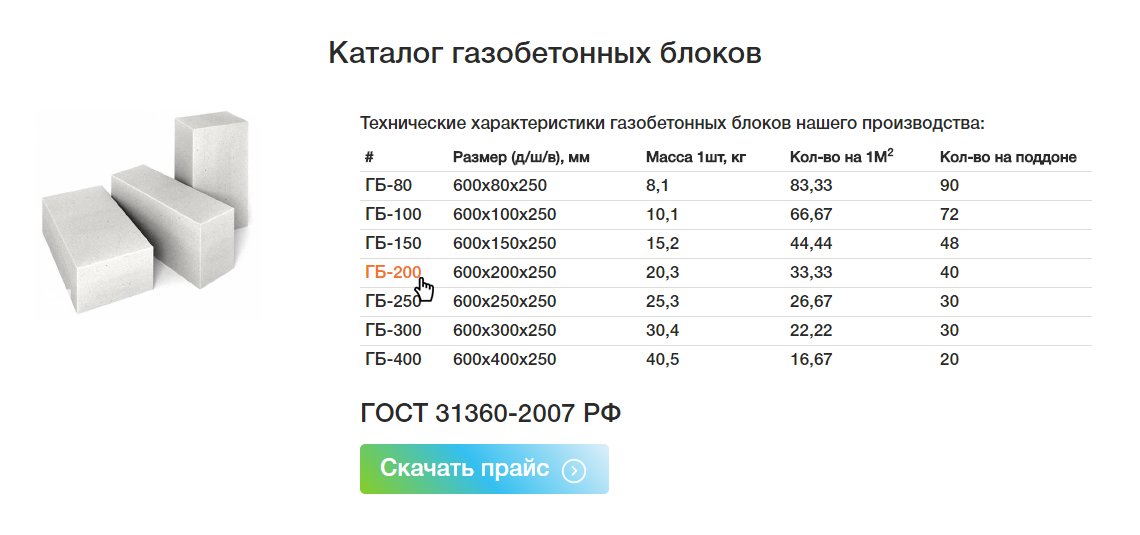
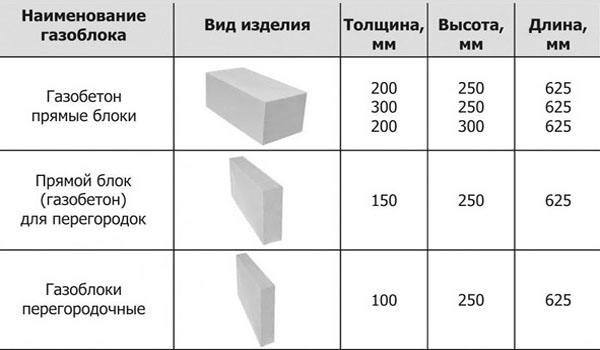
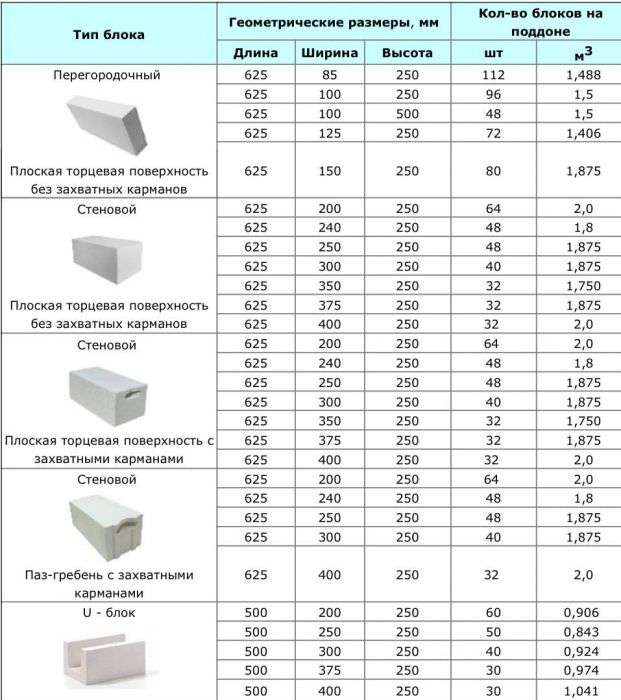
 Dimensions and weight
Dimensions and weight
The main geometric parameters are determined by:
- Their width;
- In height;
- Length.
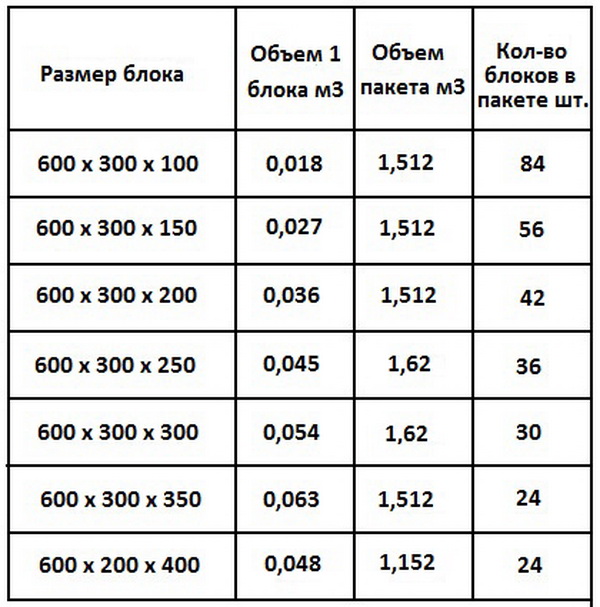
 Standard dimensions
Standard dimensions
In terms of height and length, the material is selected taking into account convenient installation, in proportion to the general parameters of the walls. Manufacturing is standardized by GOST 31360-2007.
They are produced:
- Standard parameters;
- Non-standard.
Ordinary gas blocks are produced by all manufacturers of these products. Non-standard dimensions can be produced according to individual orders, or be a feature of a particular brand.
 Product range
Product range
Geometric parameters depend on:
- Forms;
- Appointments and places of application;
- Material categories.
Material categories
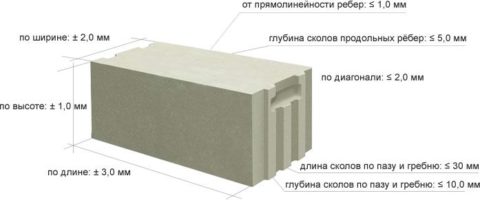
The category of aerated concrete bricks is assigned according to the maximum deviations:
- Category I;
- II category.
Limit deviations are set according to it:
- Customized size;
- Geometric shape;
- General appearance.
 Limit differences from the specified parameters
Limit differences from the specified parameters
Geometric parameters
Deviations in geometric dimensions are determined by:
- Brick length;
- Thickness;
- And also the height.
Shape deviations
Deviations from correctness in shape are considered in terms of such parameters as:
- The difference in the lengths of the diagonals;
- The straightness of all the edges of the brick.
 Deviations from the correct geometric shape - photo
Deviations from the correct geometric shape - photo
Deviations in appearance
By their appearance, gas blocks are assessed for cracks, chips, and the depth of bumps:
- Corners;
- Longitudinal and transverse ribs;
- Grooves and ridges - if any.
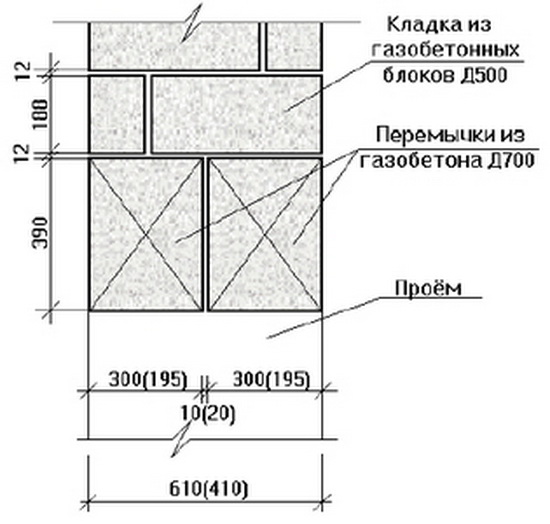
Table of maximum deviations of various parameters of aerated concrete products
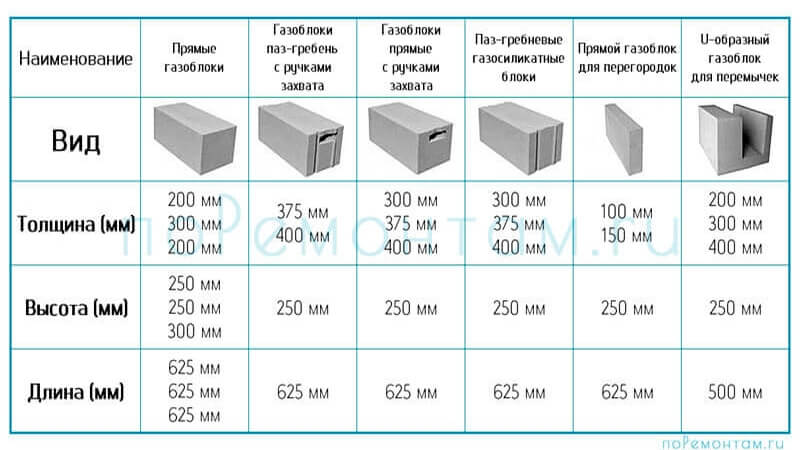
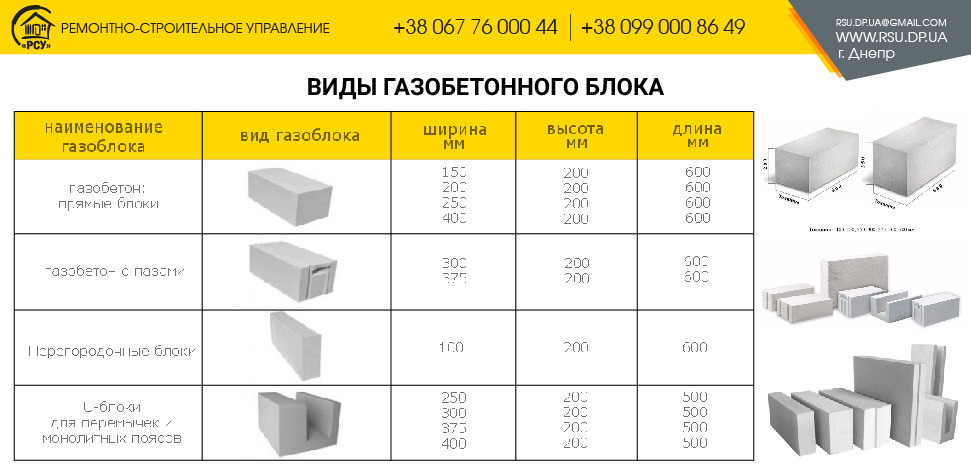
Aerated concrete block shapes
The bricks are made according to the shape:
- Smooth rectangular;
- Rectangular with grip pockets;
- With groove-comb system;
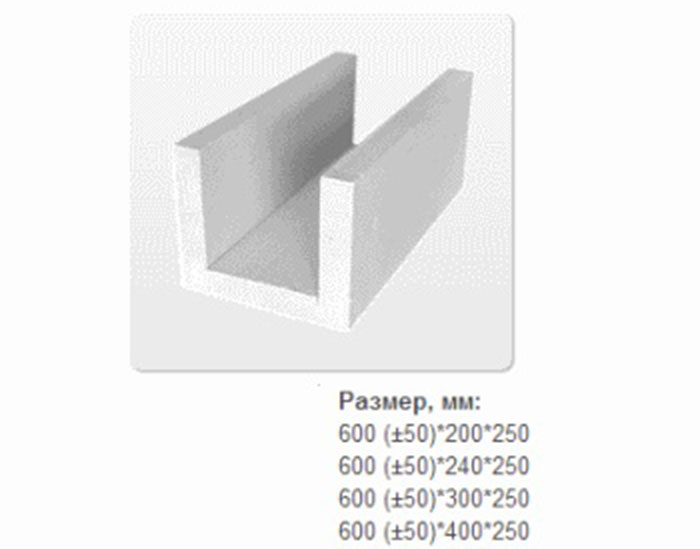
- U-shaped;
- Non-standard shapes.
 Standard sizes
Standard sizes
The gas block can also be produced with curly chamfers and depressions.
Scope of application
They differ in the scope of application:
- For the construction of walls;
- Jumper devices;
- Laying and fixing floor slabs;
- Erection of permanent formwork under the foundation.
When installing walls, the dimensions vary depending on:
- Single layer construction;
- Multi-layer construction.
The use of the material as a permanent formwork is possible only if the protective waterproofing of the brick is used.
Pros and cons of gas blocks
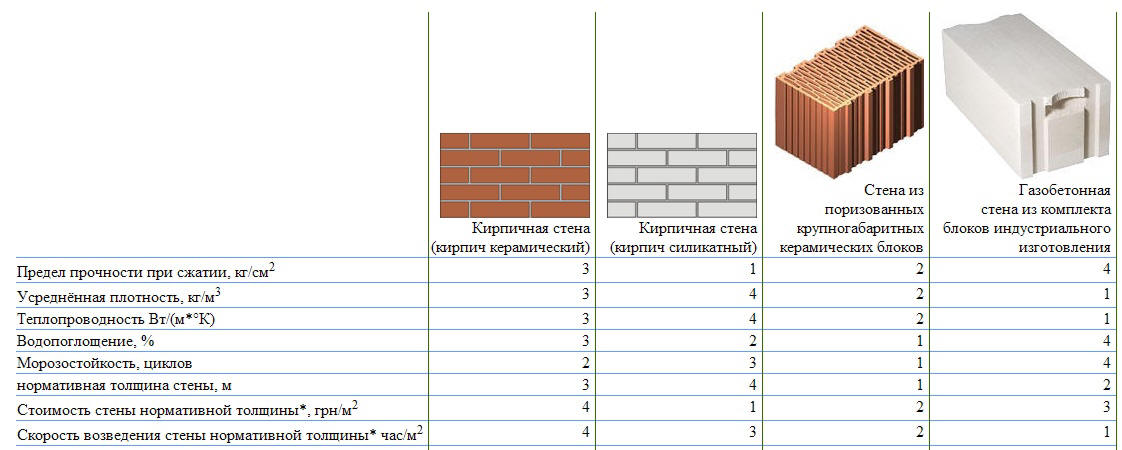
Gas blocks are an excellent building material. They are easy to handle. You can saw them with an ordinary hand hacksaw for metal, they are drilled without problems. When using blocks of sufficient density, the fasteners are normally twisted in them. The material does not burn and does not support combustion. Lightweight, warm, durable, breathable.
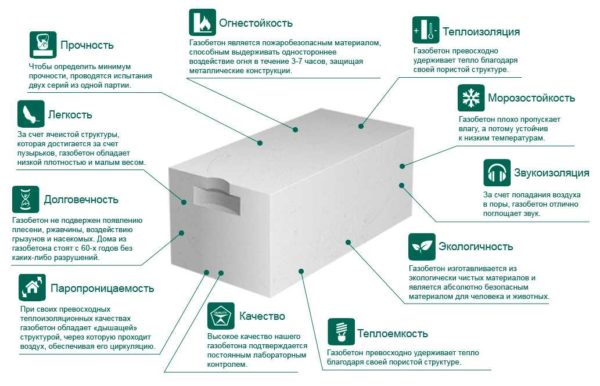
Aerated concrete blocks are a building material with good thermal insulation properties.
Advantages of gas blocks:
- High strength with low weight. Autoclaved aerated concrete has sufficient strength to be used to build a two-three-story mansion. At the same time, the weight is low. This means that there will be less load on the foundation, which reduces the cost of its arrangement.
-
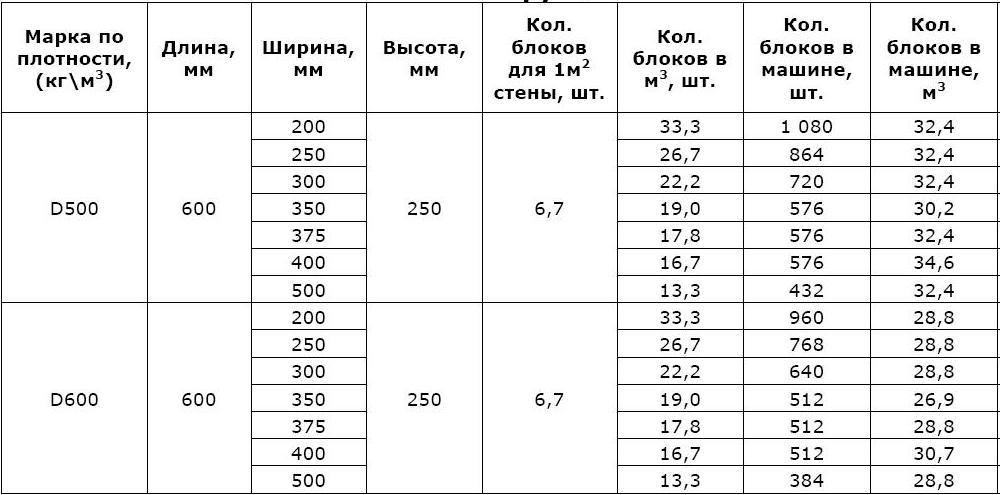
Low weight of aerated concrete block. For the construction of walls, blocks with a width of 200 mm are usually used, strength grade D500 or D600. Even gas blocks of this size - of considerable width - weigh from 12 to 16 kilograms.
- Excellent thermal insulation properties.According to thermal engineering calculations, a wall made of gas blocks 200 mm thick has the same thermal resistance as a brick wall 60-70 cm thick. Despite the fact that it has several times less weight, the cost of building a house is much lower. There are also such names for this material as a heat block, a heat gas block, etc.
- High geometry accuracy. If the blocks do not differ in size, laying is easy. But this parameter is very much dependent on the manufacturer.
- Moisture resistance and frost resistance. Autoclave gas blocks have good moisture resistance. These figures are much lower than those of bricks, but they are more than enough for building a house.
For all its advantages, the gas block is not ideal. Leaving the walls without finishing is not worth it. But the decoration of the aerated concrete house must also be correct. The material is breathable and hygroscopic. To prevent moisture from being trapped inside, it is necessary to correctly select the vapor permeability of the finishing materials.
Disadvantages of aerated concrete blocks
The disadvantages of aerated concrete are a consequence of its advantages. For example, ease of handling. When building is good. But it is also easy to cut a passage in the wall from aerated concrete with a chainsaw. Some cybercriminals take advantage of this. The way out is to make a "burglar-proof" finish, for example, brick the house. There are other disadvantages of the gas block:
Aerated concrete is fragile, does not hold bending loads poorly. The problem is solved by the device of reinforcing belts
But it is important that there is no foundation subsidence.
When laying gas blocks, special glue is used, which costs a lot. The plus is that with good geometry of the blocks, its consumption is very small - the seams are made by 3 mm.
If built from blocks containing lime, it quickly corrodes the reinforcement
The problem is solved by using polymer, not metal reinforcement.
When using gas blocks of low density, special fasteners are needed.
The material is not bad, but you need to really evaluate the pros and cons of gas blocks. A house of permanent residence of them can be built without any special fears. For the construction of a bath, aerated concrete blocks are not suitable, as they are too hygroscopic. It is better not to use them for the construction of a house in the country - the low frost resistance of the material will lead to the fact that it will begin to quickly collapse. Unless the temperature in the house will be kept above zero, and the walls will be well insulated.
How to choose?
Many people who do not know the intricacies of the construction business are faced with the problem of choosing an aerated concrete block. In order not to make the wrong choice, which can subsequently lead to instability of the building, when choosing the type of blocks, it is recommended to follow the following criteria.
When choosing an aerated concrete block, it is important to remember that this material is not universal. For carrying out various types of buildings, it is important to choose the material that suits the purpose of the construction
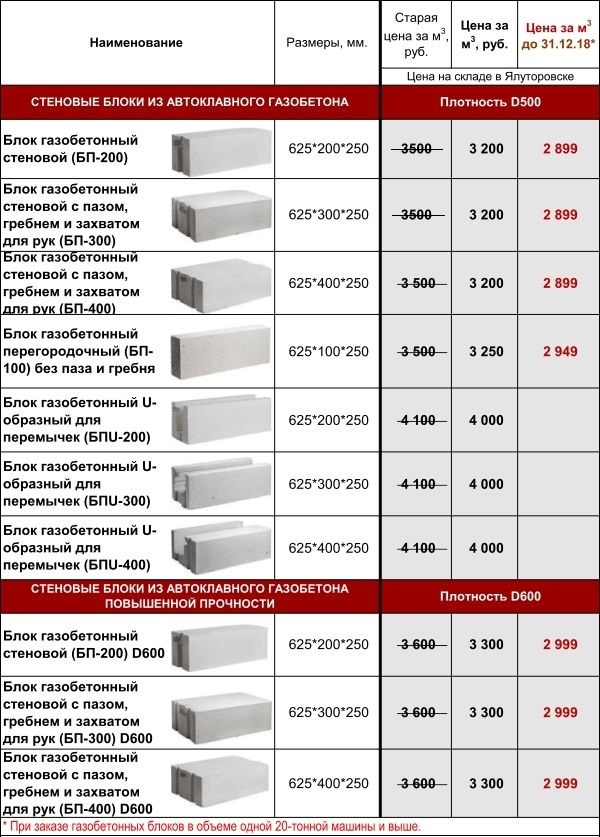
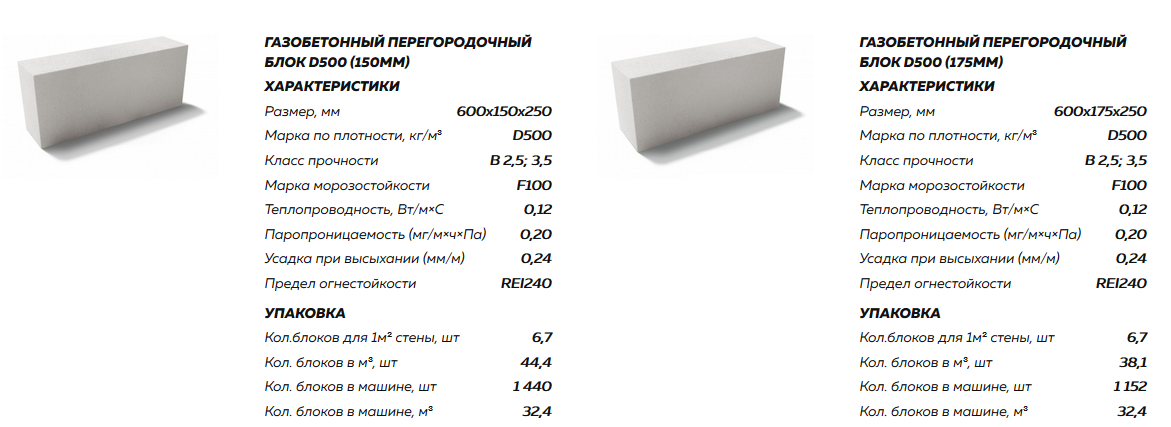
For the construction of load-bearing walls and the construction of capital partitions, wall blocks are suitable; when erecting an internal partition, a partition type of a gas block is used. It is not difficult to understand what is the difference between them. The difference between a partition block and a wall block is thickness. For partition walls, it does not exceed two hundred millimeters.
And also when choosing, it is recommended to clarify the density of the block. High density shows high strength of the material and high thermal conductivity. Consequently, the building material with the highest density mark needs to consider thermal insulation. The medium density brand D500 is very popular. It is suitable for all types of construction. But when erecting partitions, it will be more rational to use the D500 brand.
When choosing a dimensional block, the builder needs to find out the size of the block and carry out the calculation. This is necessary in order to understand how many blocks will be needed to build all the walls. In addition, it is advisable to check with the seller about the presence of a groove and a ridge in the blocks.This is an optional requirement, but thanks to the presence of these elements, laying it becomes easier, and the consumption of glue is much more economical. However, the price of this type of block is much higher than the cost of a regular one.
Another important criterion that you need to rely on when choosing aerated concrete blocks is its brand. Most often, produced aerated concrete blocks of all brands are made in the same way using the same equipment and a similar composition. If in a store the cost of one brand significantly exceeds the cost of another, then in it the buyer simply overpays for the brand and the fame of that same brand.
In addition, you should pay attention to the location of the plant, manufactured products. Often the high price is due to the remoteness of the plant, and the store overpays for logistics


In accordance with GOST standards, no more than five percent of chips and debris on block material are allowed. However, this indicator is suitable only for products of the first grade. The material of the second grade is inherent in an indicator of ten percent. Chipped aerated concrete is suitable for laying exterior walls with subsequent cladding. The choice of this type of block will save a quarter of the costs planned to be spent on material.
The final important criterion for choosing a block is the cohesion base. From the type of the adhesion base, the appearance of the gas block itself also changes. For a dry screed, it is required to select a building material with a deviation in all parameters. The block should be no more than one and a half millimeters thick. Glue laying also requires a deviation. It should not be more than two millimeters, and for masonry using mortars - no more than five.
What is a gas block, about its types and sizes, see the video below.
Areas of application of blocks
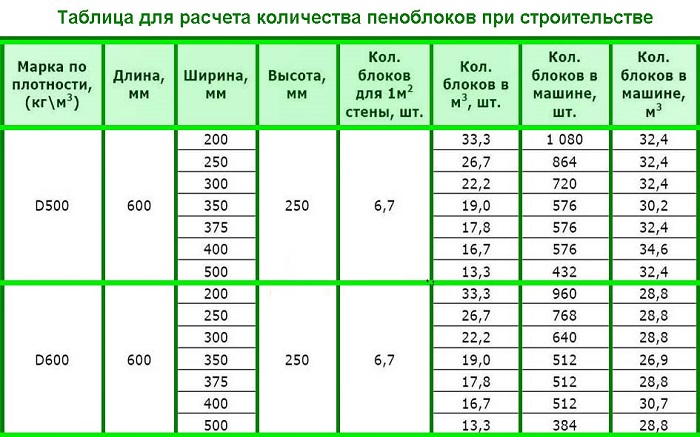
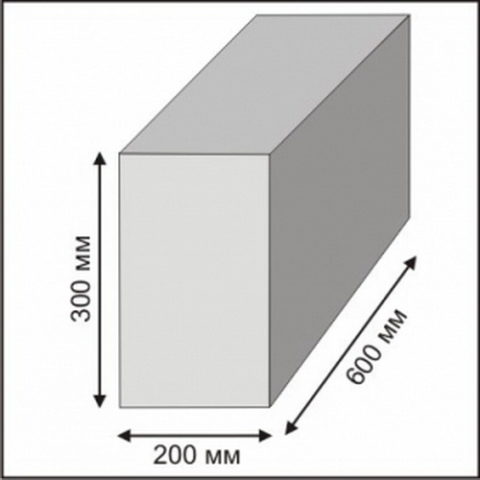
 Universal blocks for creating walls have a pronounced cellular structure and a standard shape. The dimensions of aerated concrete blocks for load-bearing walls are 200x300x600 mm. In this case, both autoclave and non-autoclave blocks can be used. The latter variety is used more often, since it is more affordable for most people.
Universal blocks for creating walls have a pronounced cellular structure and a standard shape. The dimensions of aerated concrete blocks for load-bearing walls are 200x300x600 mm. In this case, both autoclave and non-autoclave blocks can be used. The latter variety is used more often, since it is more affordable for most people.
The dimensions of aerated concrete blocks are of great importance in the construction of structures, the outer walls of which need additional thermal insulation. If it is not planned to insulate the building, then aerated concrete blocks with a thickness of about 300 mm are used. However, there are products with a thickness of up to 360 mm, and they are used in the construction of houses in extreme cold conditions.
There is a document that defines the rules for building from aerated concrete blocks. According to STO:
When calculating the dimensions of a structure made of aerated concrete blocks, it is necessary to take into account, first of all, the bearing capacity of the walls, as well as their interaction with each other.
It is impossible to construct buildings with a height of more than 20 m from gas blocks, that is, the maximum in such a structure can be 5 floors.
The thickness of the wall, according to the rules, should be determined taking into account the type of building and the climatic characteristics of the area in which it will be operated. In mild climates, light buildings, for example, a garage and a summer kitchen, are best built from gas blocks 200 mm thick
They can also be used as insulation material.
Construction of dividing walls
In our country, it is recommended to use blocks with a thickness of 300 mm to create load-bearing walls and partitions. If partitions are created between rooms in the same apartment, then gas blocks are often used for this, having a thickness of 100 to 150 mm and a low density. Of course, in this case, there is no need to protect the room from the loss of warm air, since the temperature in one apartment is usually evenly distributed.
But sound insulation, which, like thermal conductivity, depends directly on porosity, plays a very important role here.Indeed, for this, the partition between the rooms is created so that you can, for example, go to the bedroom and sleep peacefully while someone is talking or watching TV in the next room. But when creating partitions between apartments, thicker gas blocks are used, the thickness of which can be up to 300 mm.
Construction of private houses
 As for houses designed for permanent residence, the thickness of the size of the gas block for building a house must be determined based on the average winter temperature, as well as on the density of the aerated concrete itself. The lower the temperature and the higher the density, the thicker the block should be.
As for houses designed for permanent residence, the thickness of the size of the gas block for building a house must be determined based on the average winter temperature, as well as on the density of the aerated concrete itself. The lower the temperature and the higher the density, the thicker the block should be.
For example, with an average winter temperature of minus 20 degrees and, if desired, create a load-bearing wall of gas blocks with a density of only 500 kg per cubic meter. meter (denoted in the marking - "D500"), it is reasonable to make the thickness equal to 150 mm.
In more severe weather conditions, the thickness of the gas block should increase during the construction of a house, since thin walls will not be able to keep heat indoors for a long time. Therefore, if the average winter temperature is equal to minus 50 degrees, then even the gas block with the lowest density should have a thickness of at least 300 mm. And if the density is high and reaches 1 thousand kg per cubic meter. meter, then the block thickness must be more than 500 mm.
Since aerated concrete cannot always have good strength, professional builders advise to strengthen the structure created from it with reinforcing elements. True, it is advisable to do this only if the building has not one, but at least two floors. It is recommended to erect a reinforcing belt between the ceilings of each floor.
Material classification
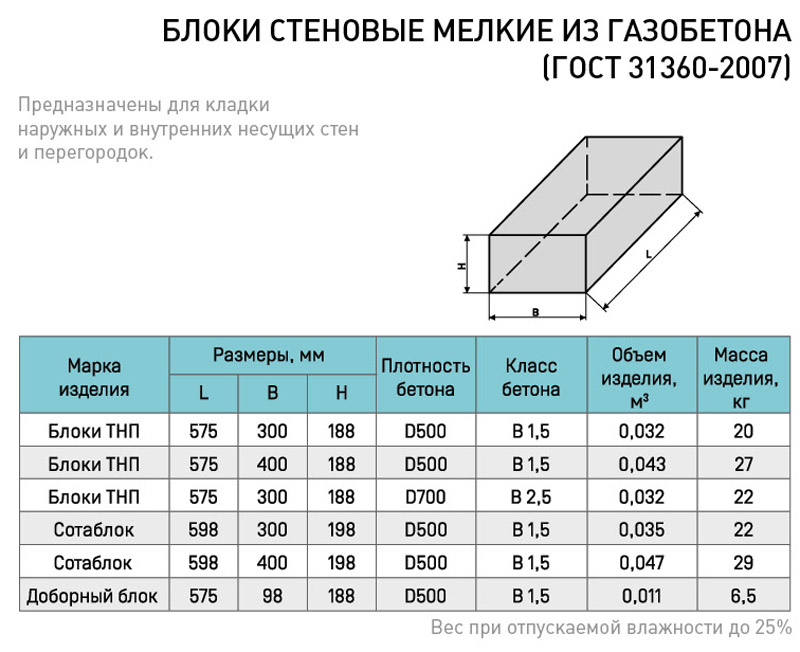
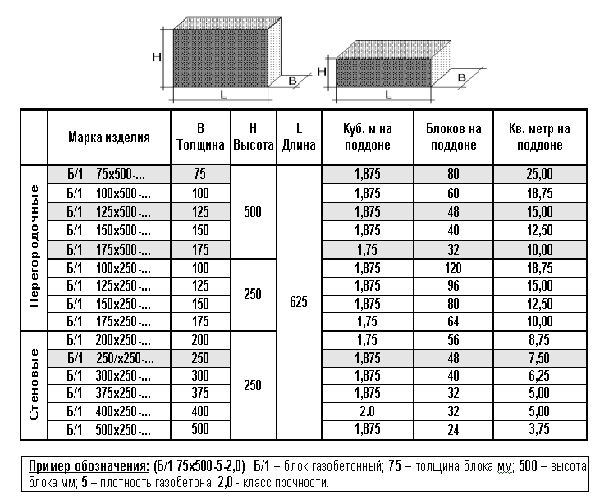
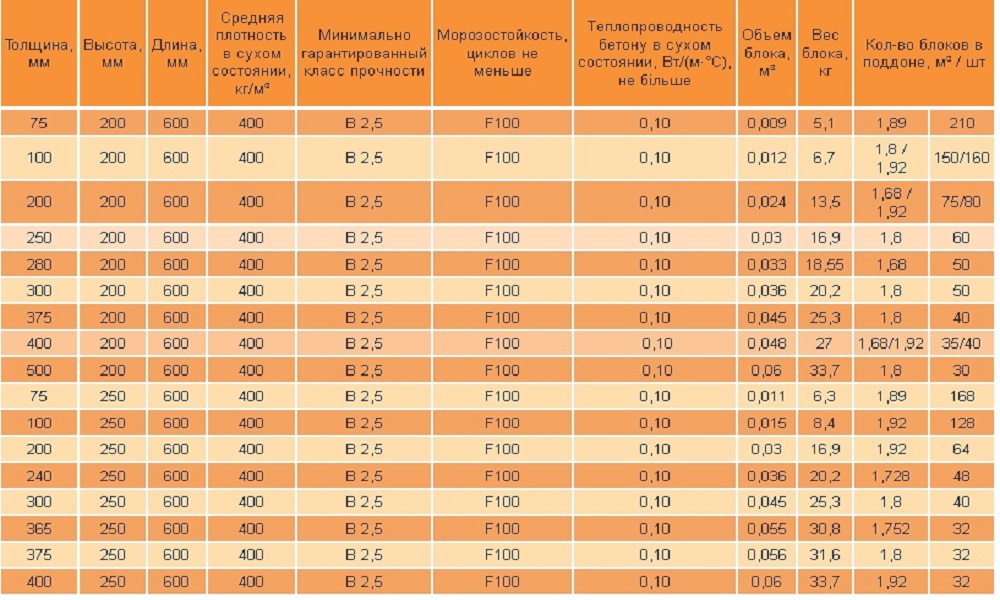
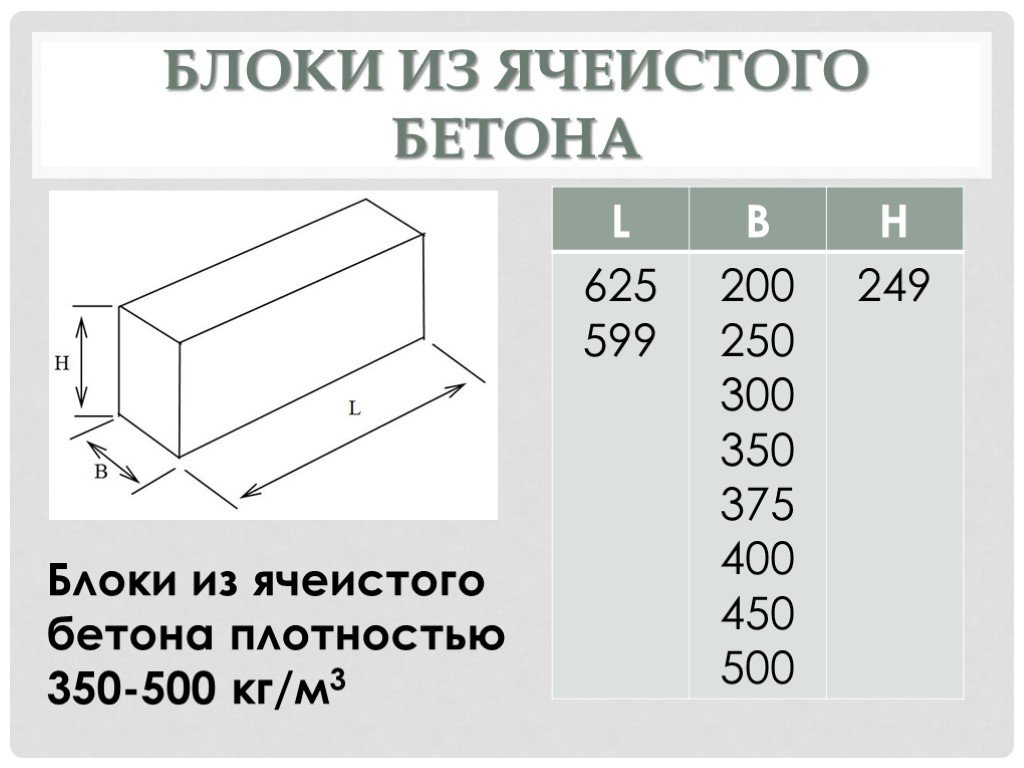
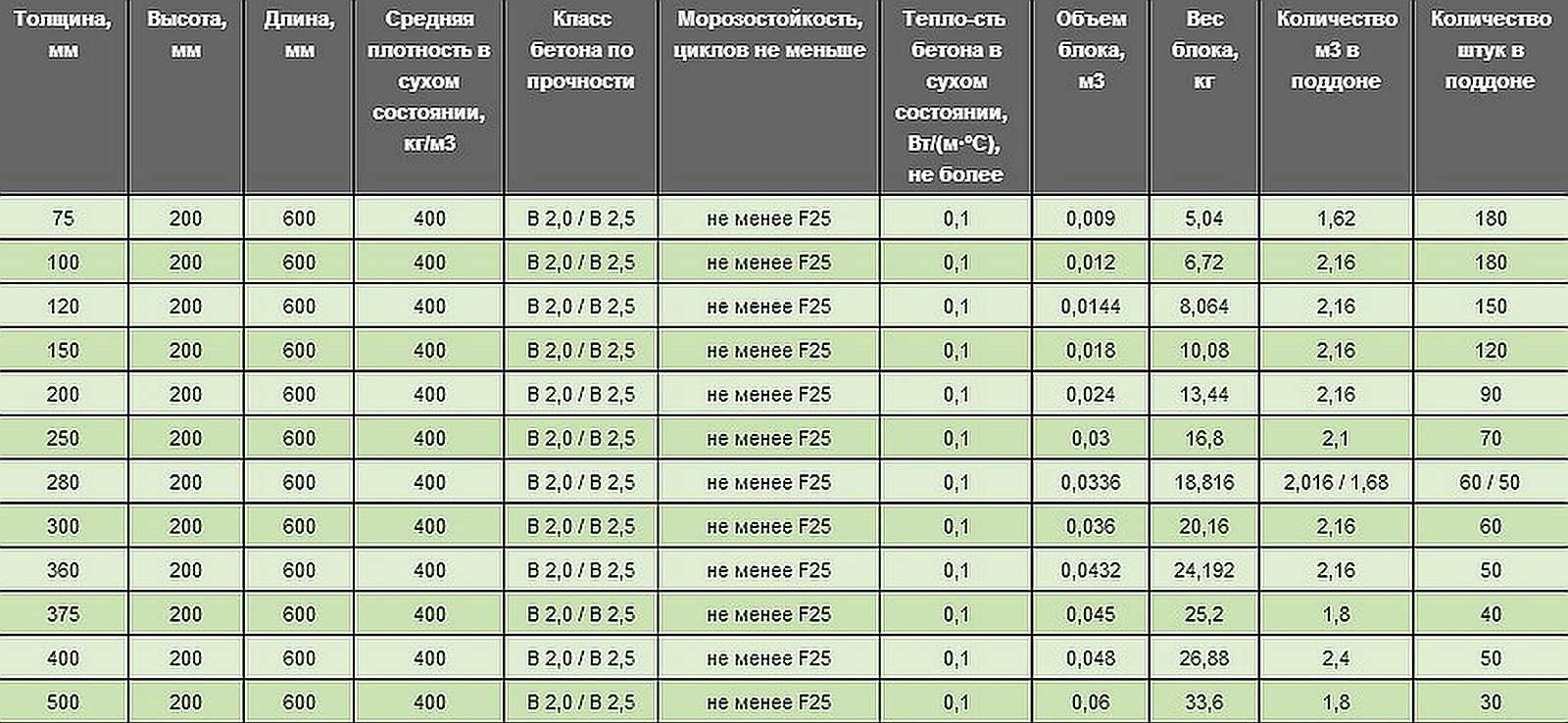
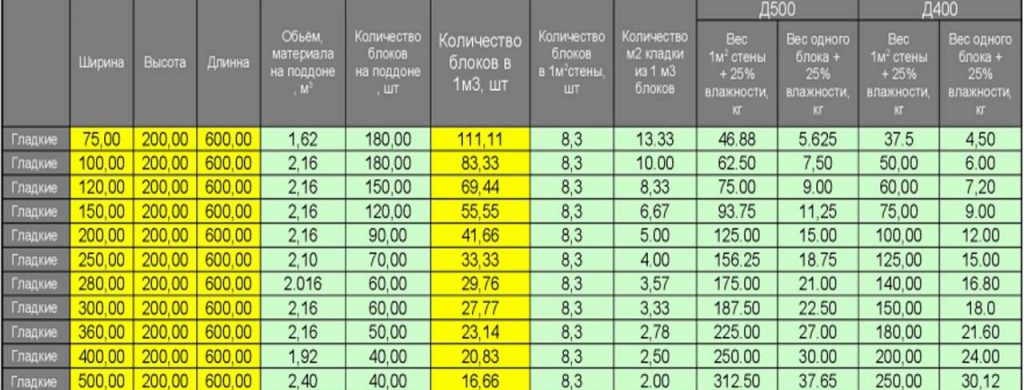
 The dimensions of the aerated concrete block for the walls of the house are, as a rule, the following:
The dimensions of the aerated concrete block for the walls of the house are, as a rule, the following:
- length - 600 mm;
- height - 250 mm;
- width - varies from 75 mm to 500 mm.
Not all blocks are the same in length and height. Only average figures were given above, but blocks of other sizes are often used in construction.
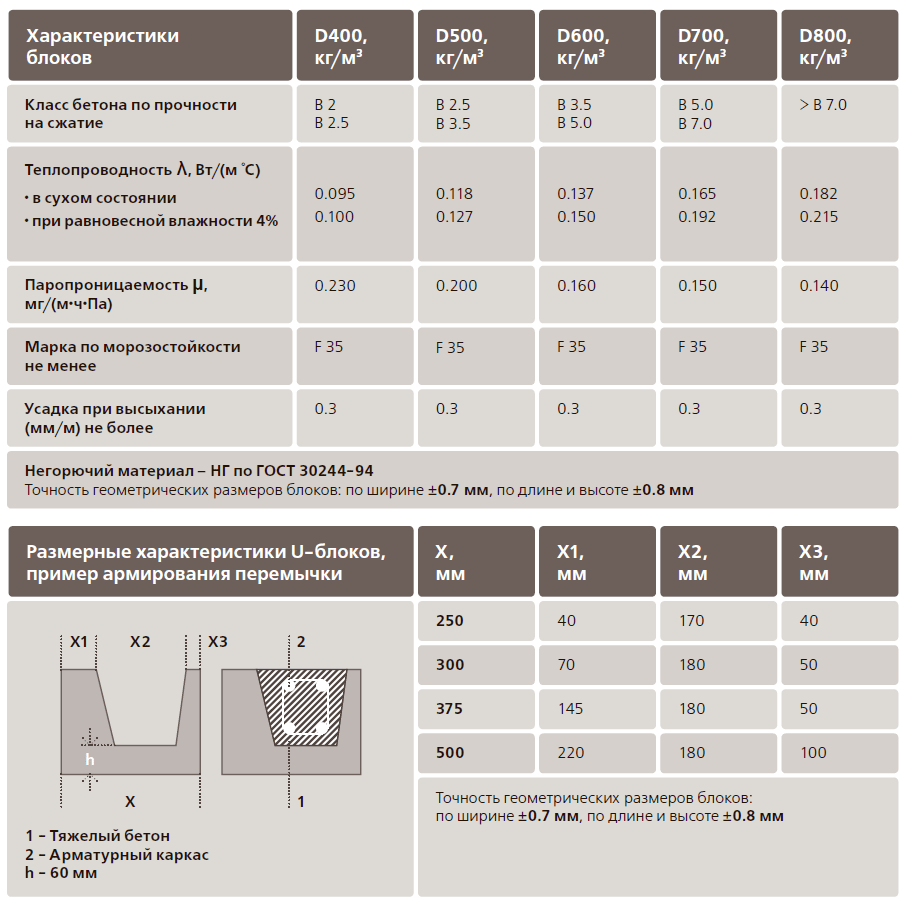
There are several classifications of gas blocks. One of them is based on density: the higher the density index, the stronger the product and the less porous its structure. However, this does not mean that denser gas blocks should always be chosen. With a decrease in porosity, the thermal conductivity of the material increases, which will inevitably cause a rapid cooling of the air in the room in winter and, conversely, its rapid heating in hot weather.
Density types
The density of gas blocks is indicated by the letter "D" and a number from 300 to 1200.
There are three types of this material:
- Structural. They have the highest density and, therefore, are the most durable. If in the marking the value of the number following the letter "D" exceeds 900, then these gas blocks are structural. The thermal insulation properties of such materials are not the best, therefore, when they are used in the construction of a residential building, it will be necessary to additionally insulate the walls with heat insulators.
- Heat insulating. They have the lowest density, and therefore are able to keep warm air indoors for a long time. This category includes all blocks that are marked with the letter "D" and numbers from 300 to 500.
- Structural and thermal insulation. They are a cross between the two categories described above. These blocks are labeled with the letter "D" and a number between 500 and 900.
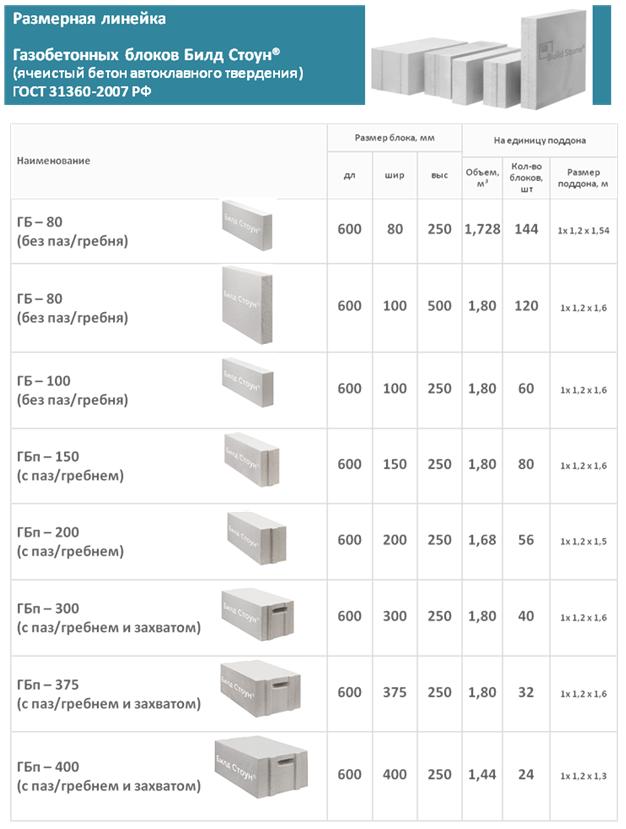
Various shapes
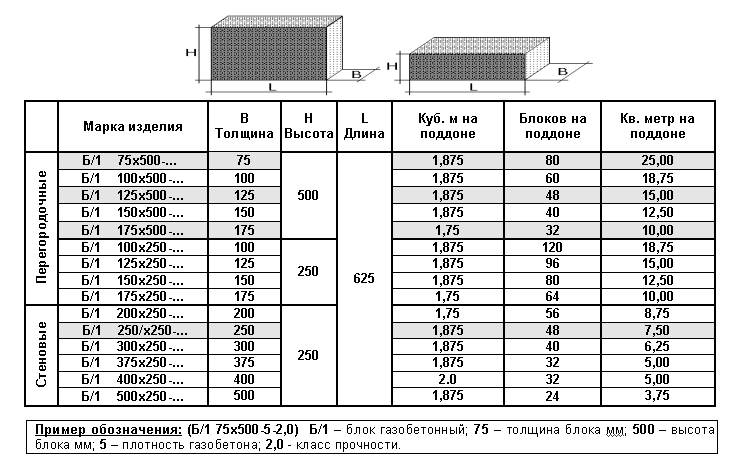
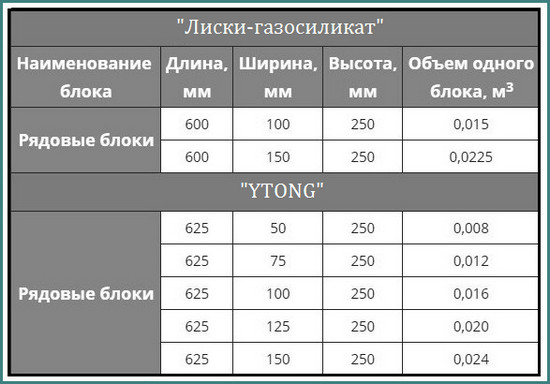
 Aerated concrete blocks can be straight, that is, they can be a regular parallelepiped. In this case, their thickness is usually 200 or 300 mm, height - 250 or 300 mm, and length - 625 mm.
Aerated concrete blocks can be straight, that is, they can be a regular parallelepiped. In this case, their thickness is usually 200 or 300 mm, height - 250 or 300 mm, and length - 625 mm.
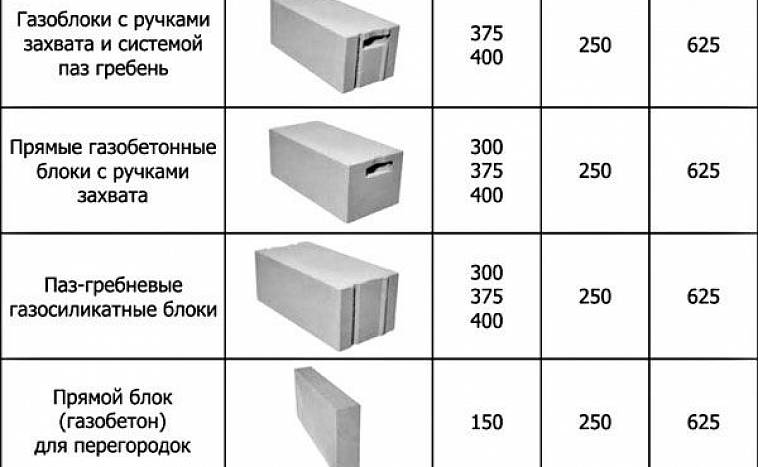
They can be equipped with special handles for easy handling and carrying. And also for a more convenient connection, grooves and ridges may be present at their ends.
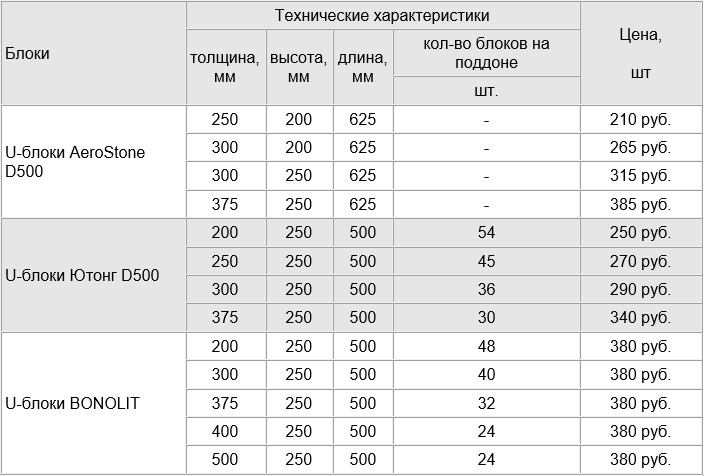
There are especially thin gas blocks specially designed for creating partitions. They can be as little as 150 or even 100 mm thick.And the most complex shape are U-shaped gas blocks, which are used to build openings in the wall. They are usually 500 mm long, 250 mm high and vary in thickness from 200 to 400 mm.
Site classification
Gas blocks are divided into three types, depending on the place where they are used:
- Partition blocks. They are very thin and are about 150 mm thick. The scope of their application is the creation of interior partitions. In addition, they simplify the arrangement of communication. Also, their distinctive feature is the ease of installation and finishing.
- Cellular blocks. They are suitable for the creation of load-bearing walls and correspond to service stations in all their characteristics.
- Autoclaved gas blocks. They are characterized by high strength and good resistance to low temperatures, and also have good thermal insulation properties. But they also have a serious drawback - the high price. The cost of such a material is too high, since the autoclave treatment that it undergoes during production is not a cheap process.
Reinforcement of aerated concrete masonry walls
Diagram of the device of a band of U elements
What is the reason for the device of reinforced belts in aerated concrete walls? First of all, the reinforcement of the masonry with metal reinforcement increases the bearing capacity of the walls. Consequently, it can be concluded that the reinforcement of the outer walls of the building allows the fences to be made thinner. This brings significant cost savings on the construction of the entire home.
According to established practice, a reinforced belt (band) is arranged in the upper row of the floor masonry. The bandage is of two types.
This is a belt of trough-shaped blocks (U elements) and laying of reinforcement in the grooves of aerated concrete masonry:
- The last row of the floor is laid out of U elements. A frame made of reinforcement is laid in the cavity. Then the cavity is poured with liquid concrete.
- The second type of reinforcement is that grooves are cut in the blocks of the last row of the floor. Usually, two parallel grooves are cut along the perimeter of the building, which are filled with adhesive. Reinforcement with a diameter of 8 to 10 mm is pressed into the grooves. Then the surface of the grooves is finally leveled with glue.
Reinforcement insertion into grooves
Thanks to the reinforcement of external fences with reinforced belts, the thickness of the masonry instead of 400 mm can be made 300 mm wide.
Facing of aerated concrete walls
Fences made of gas silicate products are often faced with decorative bricks. This is done in order to form the aesthetic appearance of the facade of the building. At the same time, the cladding is performed at a distance from the base of the aerated concrete walls. The gap between the walls is filled with a reinforcing cage with insulation laying.
Facing of aerated concrete walls with decorative bricks
Reinforcement outlets are laid in horizontal interblock seams on one side. On the other hand, the reinforcement is laid in the brickwork. As a result, the entire structure of the external fence is a single structure.
Due to this, high thermal insulation of the external fences of the house is achieved. For masonry walls, high-density aerated concrete is used, which makes it possible to increase the number of storeys of the building and arrange floors from reinforced concrete slabs.
More details on the video:
In any case, the thickness of the walls of the aerated concrete blocks must be calculated in such a way that the house is strong and warm.
Aerated concrete block - what is it
In the first version, voids arise due to the chemical processes taking place inside, and in the second, from the addition of pre-prepared foam.
Quite often, aerated concrete and gas silicate are considered the same material. But in fact, the second type is considered a subspecies of the first. The main components used in the manufacture are the same in each case. The differences lie in their proportional ratio and technological features of production.From this materials differ in characteristics in terms of density, strength and ability to conduct heat.
In the production of aerated concrete they use:
- cement and sand;
- lime;
- clean water;
- aluminum powder as a blowing agent.

During the combination of water, aluminum and lime, the release of hydrogen begins, from which a large number of pores are formed in the concrete mass, which in certain brands make up about eighty percent of the total volume. The more voids, the less strength the block has, but it weighs less. It should be added here that the thermal conductivity of the blocks leaves much to be desired.
Concrete is poured into molds and hardened, or it is preliminarily sent to an autoclave. There, under the influence of high temperature and pressure, the material gains the required strength. This manufacturing technology is used to obtain blocks for the construction of residential buildings.
Types of material
Often the buyer is confused or not particularly versed in the differences between aerated concrete and foam concrete. The latter is attracted by the lower cost.
However, it is important to remember about the disadvantages of foam blocks:
- shorter service life;
- during construction, they give a large shrinkage;
- low properties of heat and sound insulation due to the uneven size and arrangement of pores;
- cheaper materials are used in the manufacture.
Such blocks are bought to reduce the cost of the material, and if the object does not have special requirements. It all depends on what is planned to be built, with what dimensions and in what weather conditions.
Thermal conductivity of walls
When building houses for permanent residence, strength alone is no longer enough. Here you also need to take into account the thermal conductivity of the materials used. In accordance with the calculations, either the required thickness of the blocks is determined for your climatic zone, or the thickness remains as for summer buildings, but insulation is additionally used.
And in this case, you need to count on money, which will be cheaper - an increase in wall thickness due to aerated concrete or insulation.
Important! When calculating the cost of insulation, it is worth adding the price of fasteners and payment for the work of builders.
In accordance with GOST, which regulates the main technical parameters, as well as the composite characteristics and dimensions of absolutely all cellular blocks, the thermal conductivity of such a building material is 4 times lower than that of a solid brick, which makes it possible to erect structures with narrower walls.
Coefficient of thermal conductivity of material it is the ability to conduct heat. The calculated indicator of the amount of heat passing in 1 hour through 1 m3 of a material sample with a temperature difference on opposite surfaces of 1 ° C.
I will give a detailed comparison with a solid brick. The thermal conductivity of aerated concrete is approximately equal to 0.10-0.15 W / (m * ° C). For brick, this figure is higher - 0.35-0.5 W / (m * ° C).
Thus, to ensure the normal thermal efficiency of a residential building for the Moscow region (where the air temperature in winter rarely drops below -30 degrees), the brick wall must be at least 640 mm thick. And when used in construction of D400 aerated concrete blocks with a thermal conductivity of 0.10 W / (m * ° C), the walls can have a thickness of 375 mm and conduct the same amount of thermal energy. For D500 blocks with a thermal conductivity of 0.12 W / (m * ° C), this indicator will be in the range from 400 to 500 mm. A detailed calculation will be below.
Indicators of thermal conductivity depending on the thickness of the wall:
| Aerated concrete | Wall width (cm) and thermal conductivity values | |||||||||||
| 12 | 18 | 20 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 40 | 48 | 60 | 72 | 84 | 96 | |
| D-600 | 1.16 | 0.77 | 0.70 | 0.58 | 0.46 | 0.38 | 0.35 | 0.29 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.14 |
| D-500 | 1.0 | 0.66 | 0.60 | 0.50 | 0.40 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.12 |
| D-400 | 0.8 | 0.55 | 0.50 | 0.41 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.10 |
There is an inverse proportionality between the coefficient of thermal conductivity and thermal insulation of walls, which must be taken into account when performing independent calculations.
An article about the difference between gas silicate and wood concrete blocks may be useful to you.