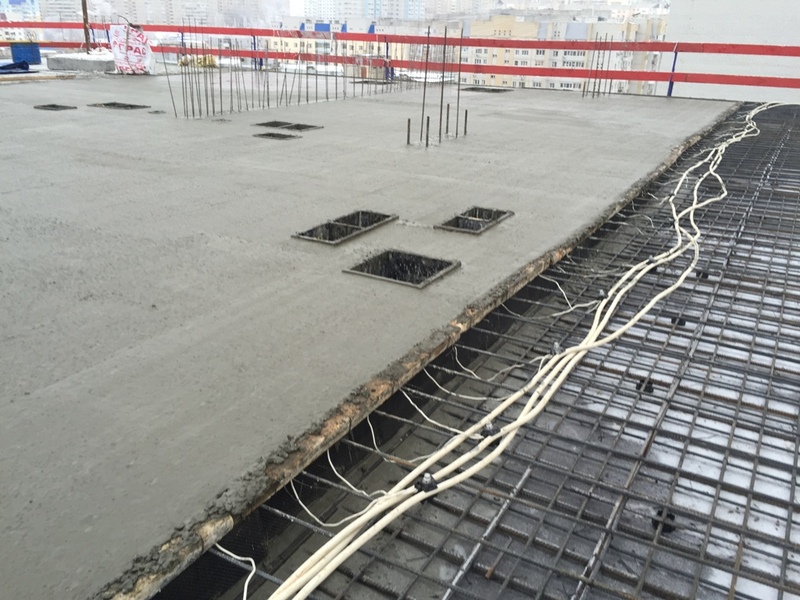
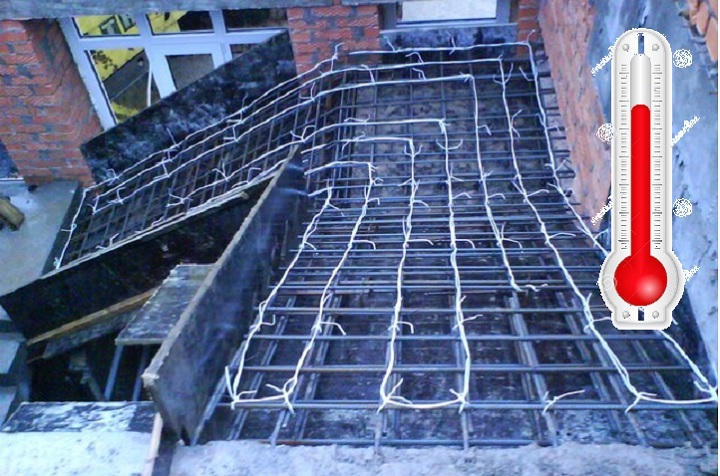
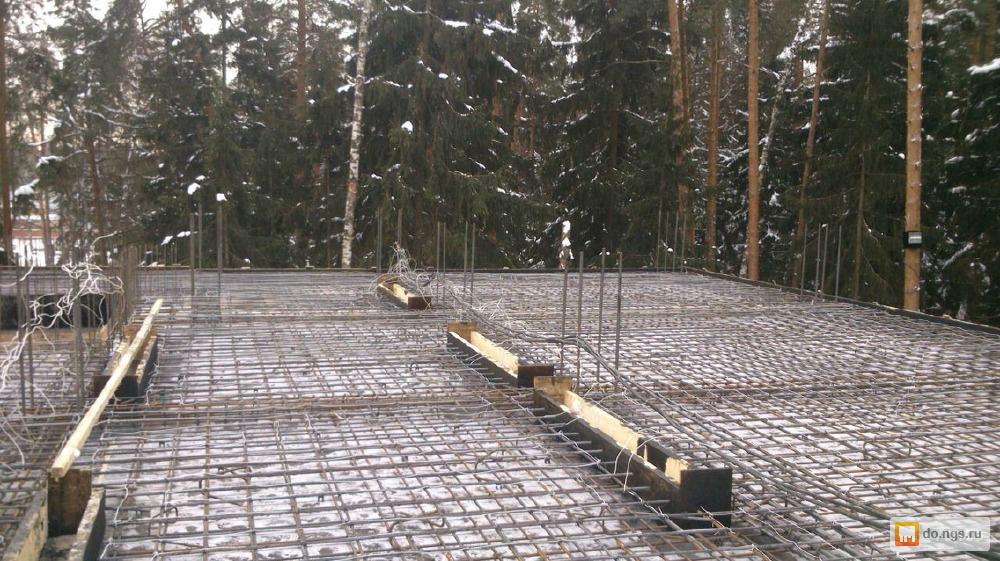
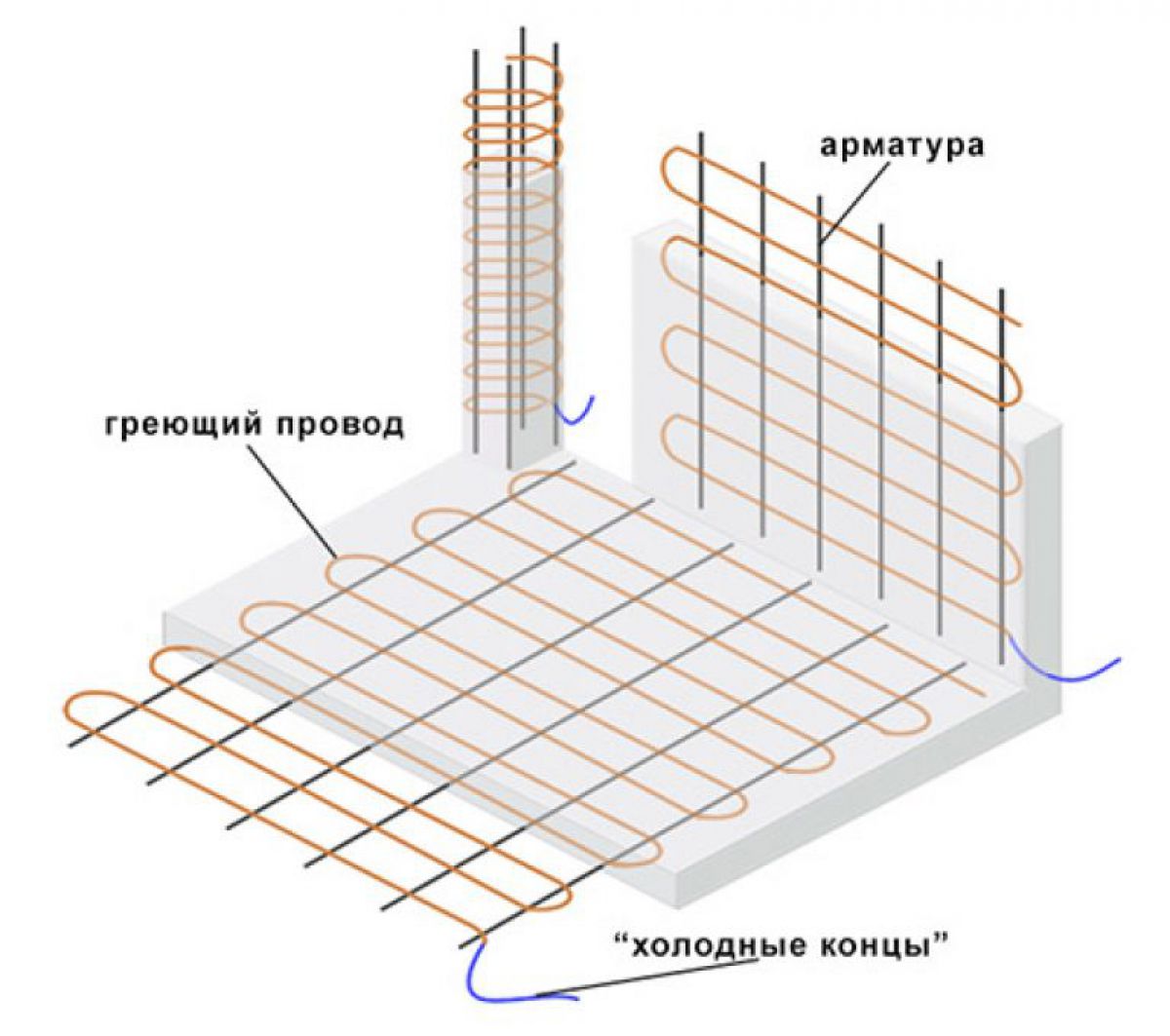
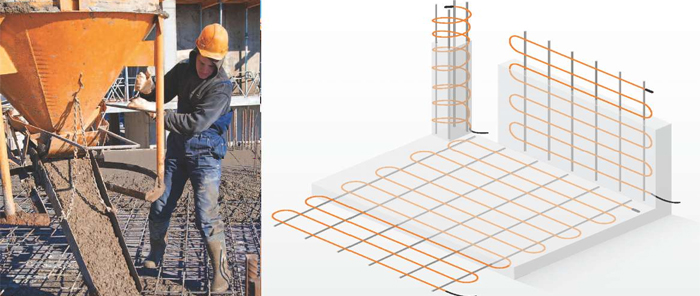
Heating of concrete with electrodes: connection diagram
It should be understood that the method of connecting electrical heating will differ depending on the type of electrode selected. When working with plate electrodes, one phase is fed to the first electrode, and the second to the one located on the opposite side. As a result, we have two electrodes that are parallel to each other, each has a phase. In the case of bar reinforcement, the first and last electrodes in the row are connected to one phase. The rest work from the 2nd and 3rd phases.
I would like to note that you should not neglect the installation of transformers. In some cases they are not needed, but in most situations it makes sense to install them. So, the temperature of concrete heating will be optimal, that is, not too high, otherwise such an undesirable effect as overdrying may appear. For this simple reason, it makes sense to bring all electrodes through a step-down transformer.

Comparative characteristics of the new and previous model of thermomat
|
PREVIOUS MODEL |
NEW MODEL |
|
|---|---|---|
|
THE CONSTRUCTION OF THE THERMOMAT |
The heating element was freely positioned between the awning and the heat insulator. With careless use, this led to its breakage and failure of the thermomat. |
The wear resistance and strength of the thermomat is increased. Monolithic segments exclude warpage of the heating layer. Resistive inside does not break. Heaters have become vandal resistant to damage. |
|
THERMAL INSULATION |
Insulation material was used with worse thermal properties than that of modern heat insulators. |
Reduced heat loss by 25%. Insulation material with improved thermal insulation properties is used. |
|
CONVENIENCE OF USE |
If folded incorrectly, the thermomats could wrinkle, wrinkle. Which led to the breakdown of the heater contact. |
The segments of the thermomat do not break. The new design allows the thermomats to be folded in any convenient way, and not just "accordion", as was previously required. |
|
WATER RESISTANCE |
Due to the presence of air gaps, with a slight damage to the shell, water got inside the heater. |
The water resistance of the thermomats has been increased. Due to the solidity and tightness of the new structure, there are no voids between the awning and the heating layer. Water does not penetrate inside the heater. |
|
THERMAL RESISTANCE |
A film with an unstable linear dependence was used. When overheated, the heating element warped. This led to the failure of the thermomats. |
Increased heat resistance. The film for the production of the resistive element is pre-stabilized. The resistive element does not shrink up to 1800C. |
|
SELF-REGULATING EFFECT |
Unstable thermal performance with little negative self-regulating effect. With an increase in temperature, the heater increased its power and overheating occurred. |
A positive self-regulating effect has been achieved. When there is a danger of overheating, the heater reduces power. Overheating does not occur. The service life of the thermoelectric device is increased. |
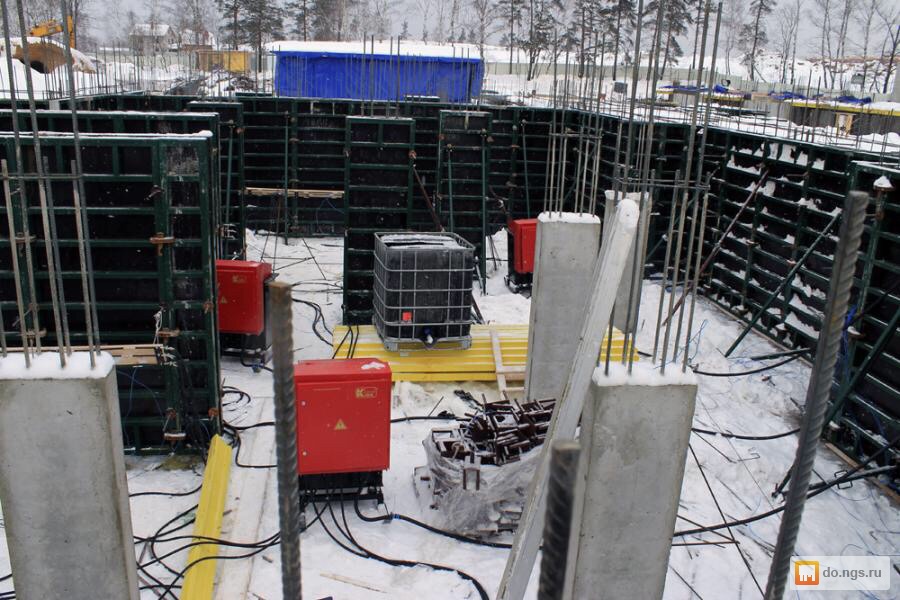
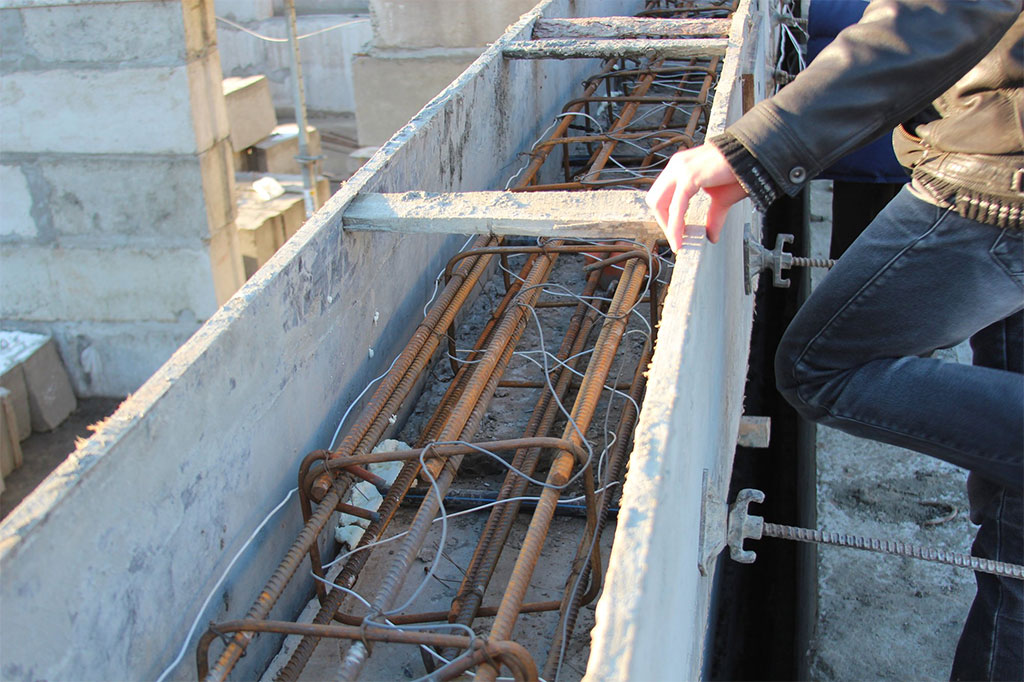
Warming up with a special formwork
Special formworks are thermoactive structures, in the body of which heating elements are mounted. For safety reasons, the heating elements are reliably isolated from the formwork body. The formwork is assembled from individual panels, each of which is individually marked. Shields differ in electrical parameters (power, current and voltage). The technical characteristics of the switchboard are indicated on its rating plate.
To preserve heat, the formwork is pre-covered with slag or glass wool insulation.
To prevent insulation from moisture and mechanical damage, the board is completed with a plywood cover.
The formwork at the concreting facility is assembled into a single block from separate panels. Small shields are assembled by hand. For heating large areas, enlarged panels are used, which are assembled into blocks by lifting mechanisms.
To connect the assembled formwork to the electrical network, special control units are used. They consist of step-down transformers, a power supply system and a control panel. In addition, the facility provides premises for the duty electrician or operator.
If the outside air temperature is less than + 5 ° C, then the reinforcement and previously poured concrete should be preheated before placing the concrete. For this, the concreting surface is first covered with a scrappy concrete material in winter (tarpaulin, film or greenhouses) and the formwork is switched on for a short time.
Advantages of special formwork:
- simplicity of design and the ability to quickly eliminate malfunctions and replace damaged heating elements;
- versatility, which allows you to use the formwork on various objects as much as you like, without restrictions;
- ease of use;
- allows you to work with concrete at temperatures up to -25 ° С;
due to continuous concreting, the construction period is reduced; - the ability to maintain the time of a given technological process, which ensures the optimal pour point of concrete. This is achieved through deep temperature control.
The disadvantages include the high cost of the structure and the difficulty in heating areas with a complex configuration.
Varieties of electrolytes for heating concrete
Depending on the type and geometry of the structure, different electrodes are used to heat the concrete. For each of them, its own connection diagram is developed:
- Strings.
- Rod.
- Lamellar.
- Striped.

Electrode connection diagram
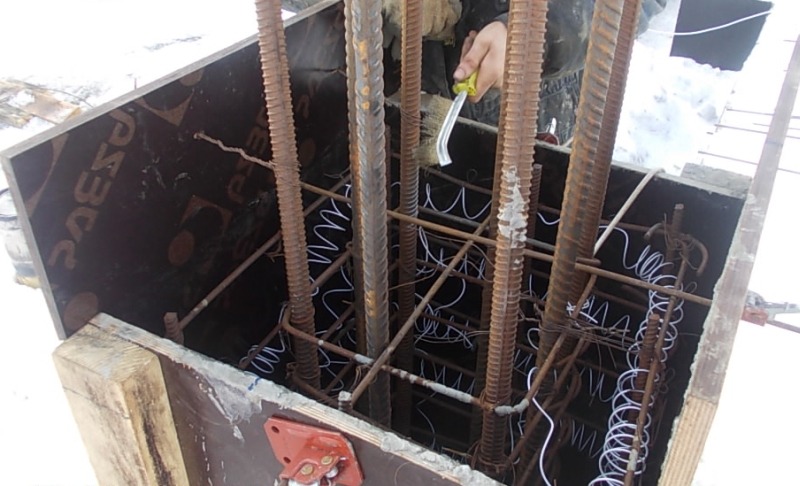
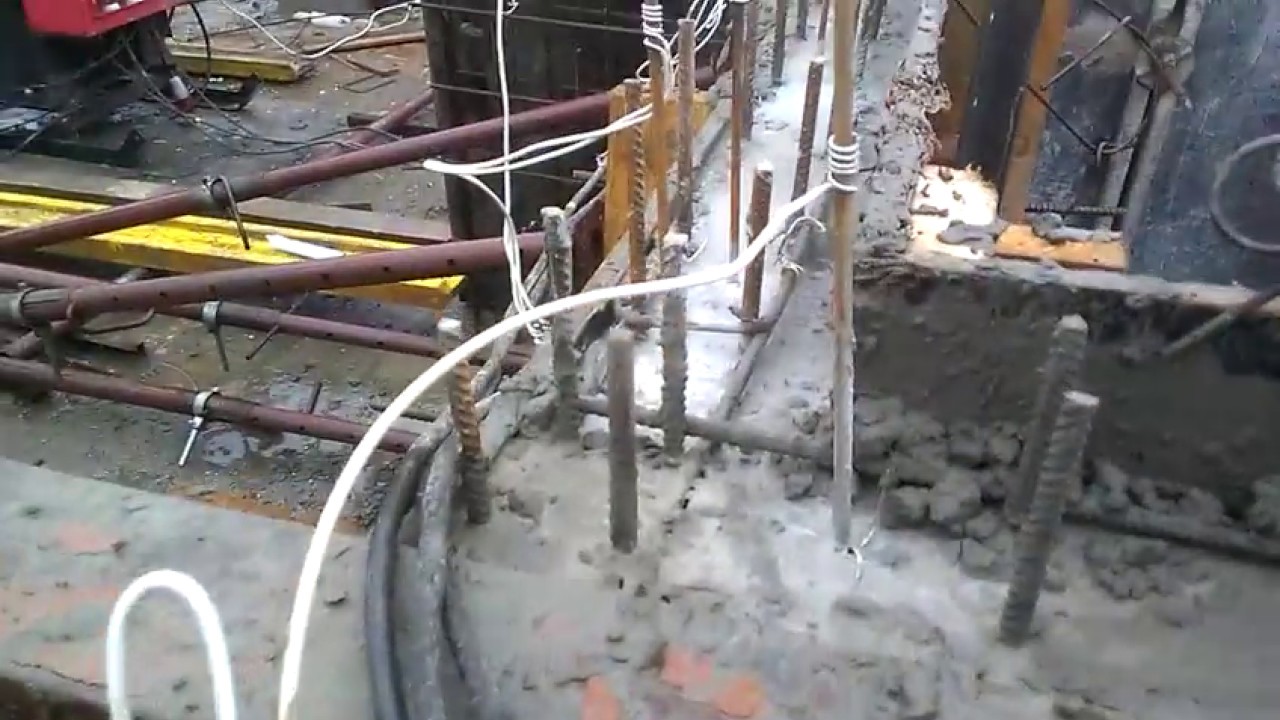
Strings. They are made of reinforcement with a length of 2–3 m and a diameter of 10–15 mm. Used for columns and other similar vertical structures. Connect to different phases. A reinforcing element can be used as one of the electrodes.

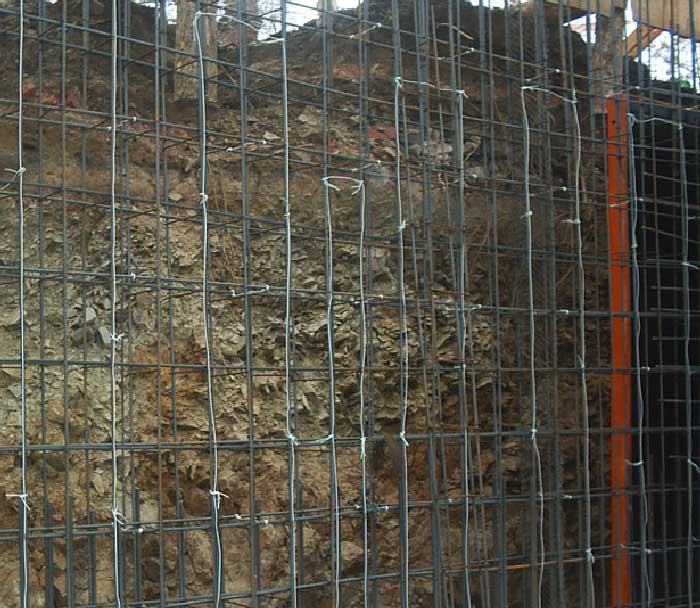
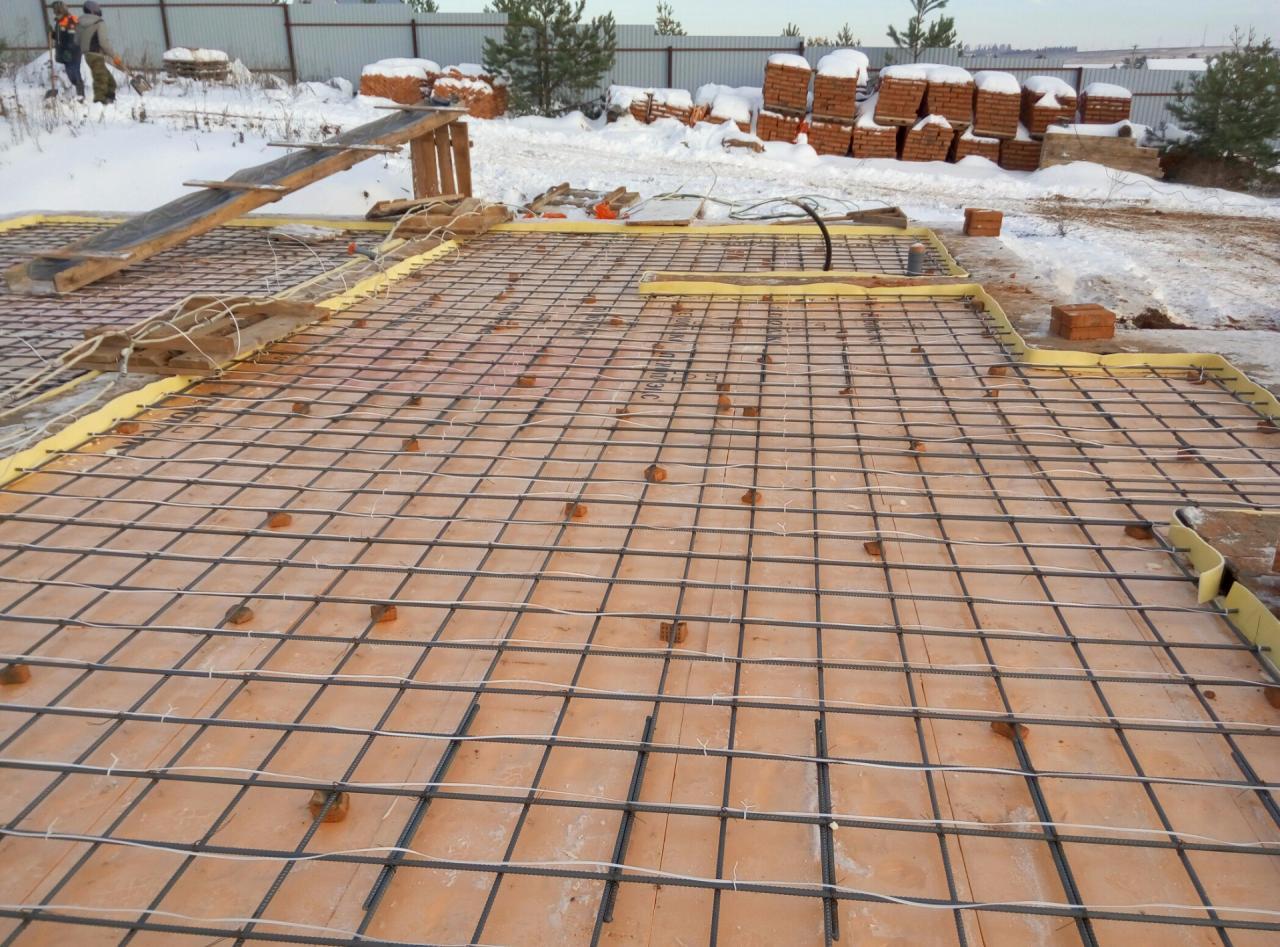
Rod. They are pieces of reinforcement with a thickness of 6–12 mm. They are located in the solution in rows with a calculated step. The first and last electrode in a row is connected to one phase, the others to the 2nd and 3rd. They are used for a plot of any complex geometry.
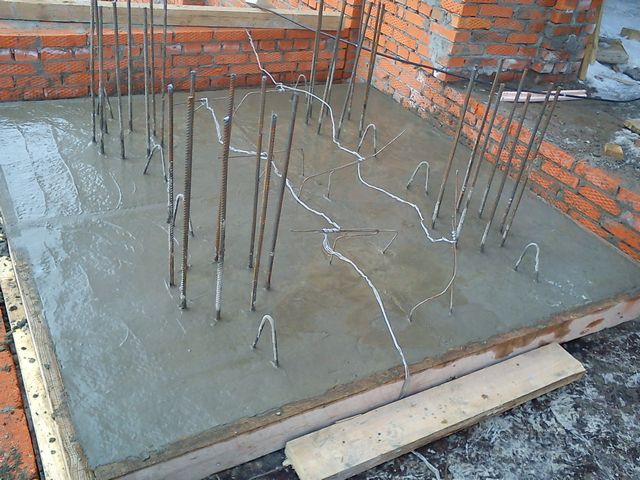

Rod electrodes for concrete
Lamellar. They are suspended on the opposite edges of the formwork without being buried in the mortar and connected to different phases. The electrodes create an electric field that heats up the concrete.

Arrangement of plate electrodes
Striped. They are made in the form of metal strips 20-50 mm wide. They are placed on the surface of the solution on one side of the structure and connected to different phases. Used for floor slabs and other elements in the horizontal plane.
Heated formwork
Electric heating of concrete in winter can be carried out immediately in the formwork. This is one of the new ways that is very effective. Heating elements are installed in the formwork panels. In case of failure of one or more of them, the faulty equipment is dismantled. It is replaced with a new one.

Equipping with infrared heaters directly the form in which the concrete solidifies has become one of the successful decisions taken by the managers of construction companies. This system is able to provide the required conditions for a concrete product in the formwork, even at a temperature of -25 ºС.
In addition to high efficiency, the presented systems have a high efficiency rate. It takes very little time to prepare for heating
This is extremely important in severe frost conditions.The profitability of the heating formwork is higher than that of conventional wired systems
They can be used multiple times.
However, the cost of the presented type of electrical heating is quite high. It is considered unprofitable if you need to heat a building of non-standard dimensions.
Concrete pouring conditions in winter
- The transport in which the solution is transported must be insulated to prevent heat loss. That is, it must be closed.
- The concrete to be laid and the formwork must be heated, the mortar is laid and immediately compacted.
- Snow must not fall on the reinforcement and formwork to be laid. In order to warm up the formwork and mortar, do not use hot water.
- Do not pour on frozen soil or structure.
- The first days the temperature of the solution should be at least +10 degrees, all rooms that are adjacent to the building must be heated.
At a low temperature, the solidification of the solution stops, as a result, the basic structure of the structure is disturbed, which subsequently cannot be restored. After the concreting is completed, the structure is covered with insulation, otherwise there is no point in heating the solution. Usually, with the help of electrodes, the layers of the appearance are heated so that there is no heat loss. Before starting the main work, it is necessary to make accurate calculations and purchase the necessary materials. Thanks to this method, it is possible to heat structures of various thicknesses and configurations, but this method is not effective for the construction of slabs. The type of electrodes is chosen depending on the weather conditions and the quality of the material used. Strip electrodes can be used to heat floor slabs and other horizontal elements, as well as concrete that touches frozen ground. Rod electrodes are used to heat columns, beams and other complex structures. String electrodes are used to heat the columns, if the structure contains metal components, then the consumption of electrical energy will be higher. When concrete is heated by the electrode method, the structure must be covered, otherwise there will be a significant loss of heat, and a large consumption of electrical energy, the desired result cannot be achieved. Correct connection and voltage supply also depend on the type of electrodes used. If the work is done correctly, the solution quickly hardens, gives minimal shrinkage, does not collapse due to frozen water that is part of the mixture. If it is difficult to do the work on your own, then you need to resort to the help of specialists.
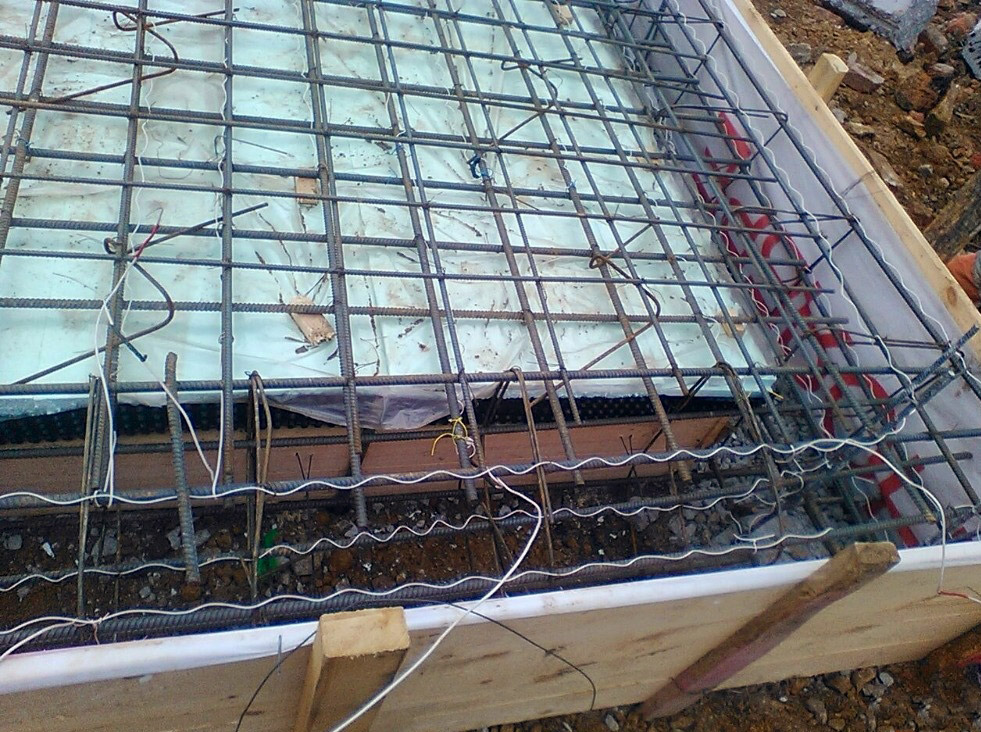
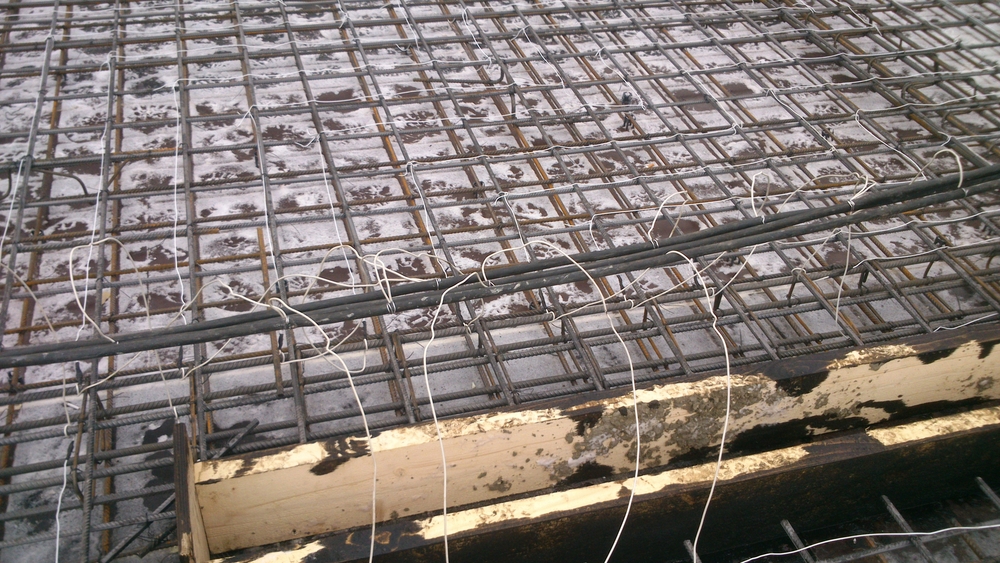
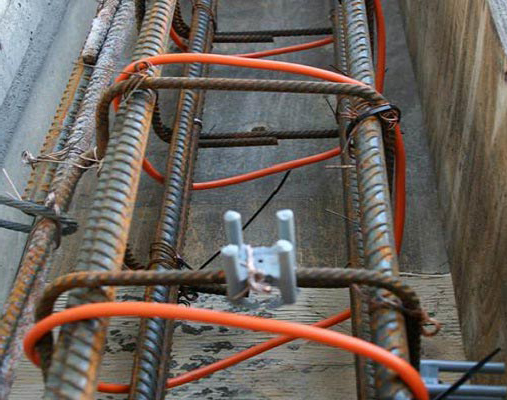
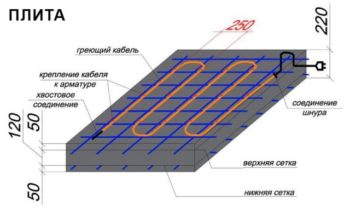
Installation of sectional heating cable
Since such heaters for concrete are not supplied in coils, but in ready-made sections, the issue of pruning is removed. All that is needed to assemble the installation for winter concreting is to calculate the capacity of the segment based on how many cubes of concrete are in the structure, and then select the cable of the appropriate length.
Let's start with a quick calculation guide and small installation guidelines:
The instructions for the TMT concrete technology indicate that heating a cubic meter of the mixture requires from 500 to 1500 W (depending on the air temperature). Energy consumption can be significantly reduced by applying a few simple techniques:
- Use special additives for the mixture to lower the freezing point of the solution.
- Insulate the formwork.
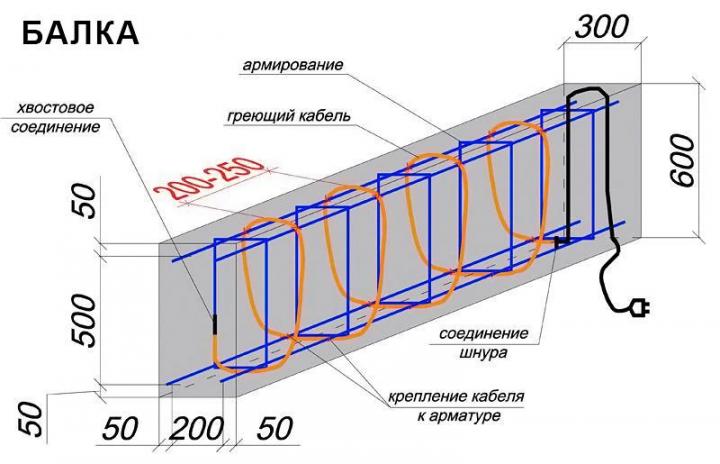
- If a beam or floor is being poured, the heating cable is calculated from 4 running meters per 1 m2 of surface area. When erecting volumetric elements, such as concrete I-beams, electric heating is laid in tiers, with a distance between them not more than 40.0 cm.
- The protection of the cable allows it to be tied to the armature.
- The distance from the surface of the structure to the electric heater installed inside must be at least 20.0 cm.
- In order for the concrete mixture to warm up evenly, the heaters must be placed at the same distance.
- There must be at least 40.0 mm between different contours.
- Crossing of heating conductors is prohibited.
Features of the technique
General scheme of work
The very technique of heating the concrete mass using electrodes is quite simple.
It is implemented according to the following algorithm:
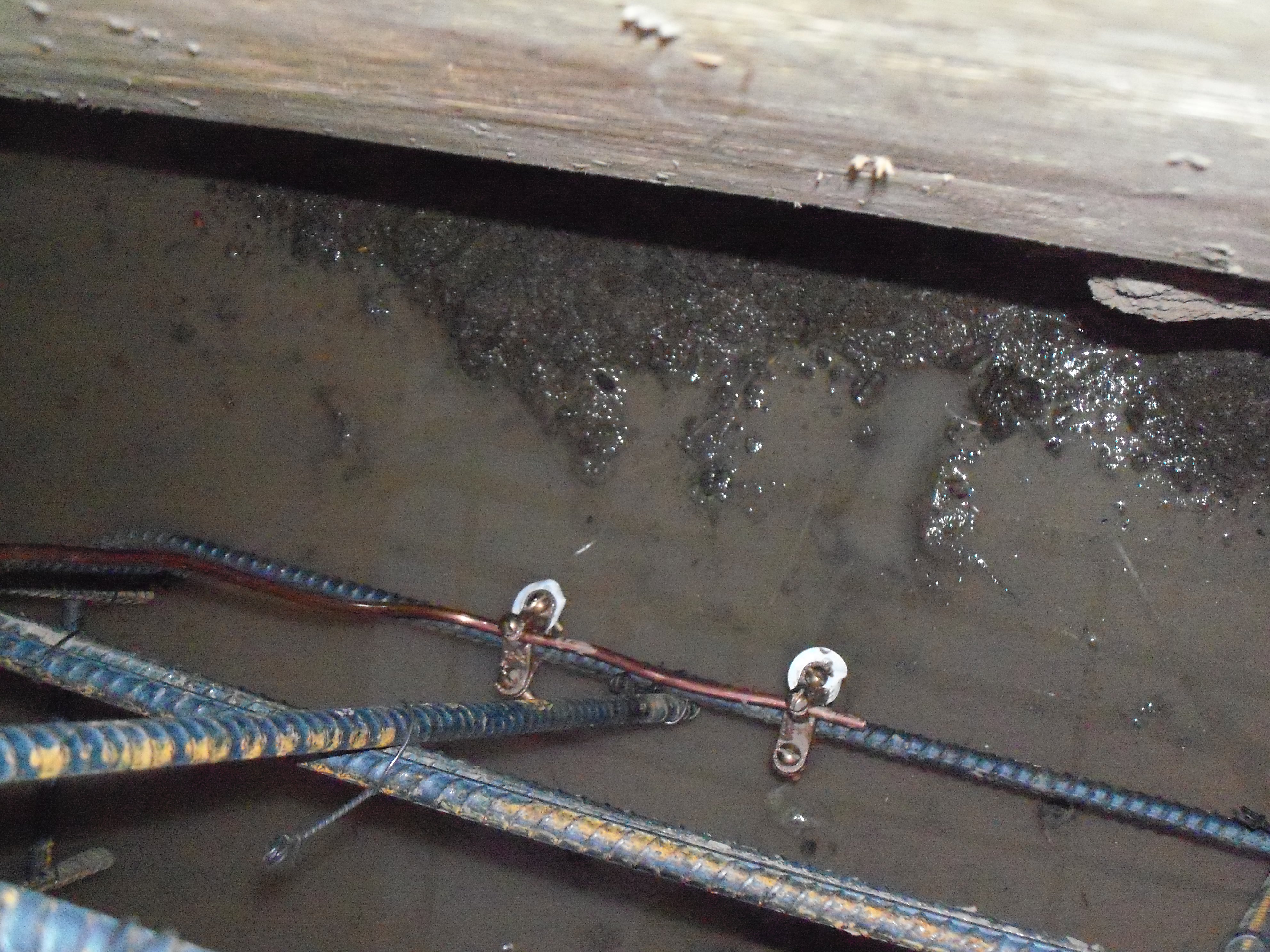
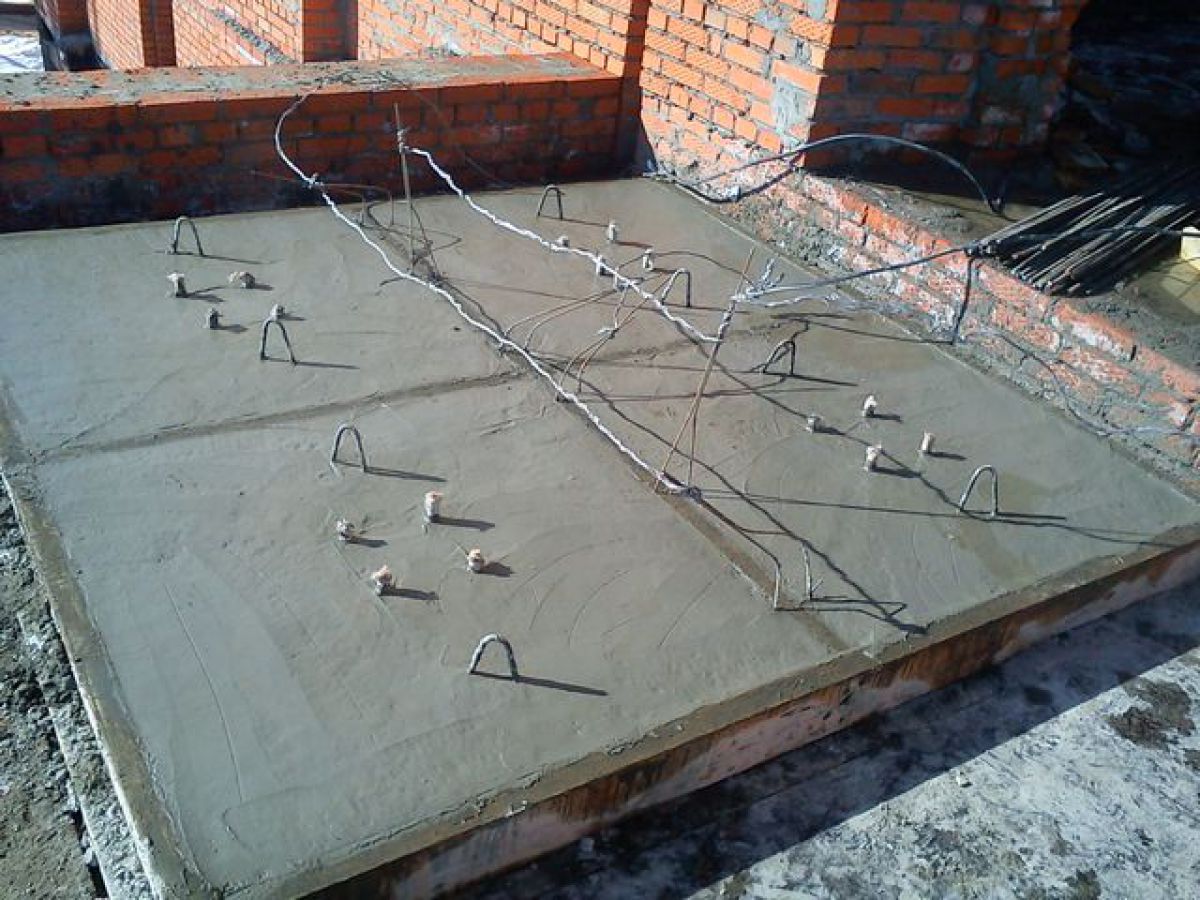
- Conductive elements connected to the power supply are mounted inside the formwork. The placement configuration and type of electrodes are selected separately, depending on the design features.
- After the electrodes are placed, mortar is poured into the formwork. Being in a liquid state, it turns into one of the elements of the electrical circuit, which conducts current quite well.
- A voltage is applied to the electrodes, due to which an electric field is created in the concrete body. It gradually gives up its energy to the surrounding substance, heating it.
- By changing the parameters of the current (strength, voltage), you can adjust the degree of heating with your own hands.

Photo of connected electrodes
As a result, the optimum temperature is maintained in the cement while the cement is gaining strength. Such processing is sufficient to ensure a homogeneous structure of the solidified material. Cutting reinforced concrete with diamond wheels confirms this - on the test samples, voids and loose areas are practically not found.
The warm-up time depends on many factors, among which the most important are the volume of the structure to be concreted and the outside temperature. In some cases, it takes up to 4-5 weeks to heat the solution, i.e. until a full set of strength. However, more often than not, additional heat is required only at the initial stages.
Types of electrodes
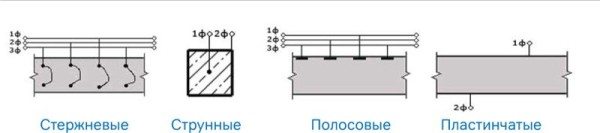
Types of electrodes
To implement this method, current-carrying elements of various configurations are used. You can study their design features by analyzing the table given here:
| Electrode type | Characteristic |
| Lamellar | It has the shape of an elongated plate, most often made of the same metal as the reinforcement itself. It is mounted on the formwork from the inside without deepening into the thickness of the mortar. |
| Stripe | It is a strip of metal with a width of 40 to 50 cm. Pairs of strip electrodes are placed along the edges of the site so that the current passes between them. |
| String | It is used in the manufacture of structures elongated in length (columns, pillars, capital piles, etc.). The string is laid in the center of the formwork, and a conductive strip is installed along the periphery. |
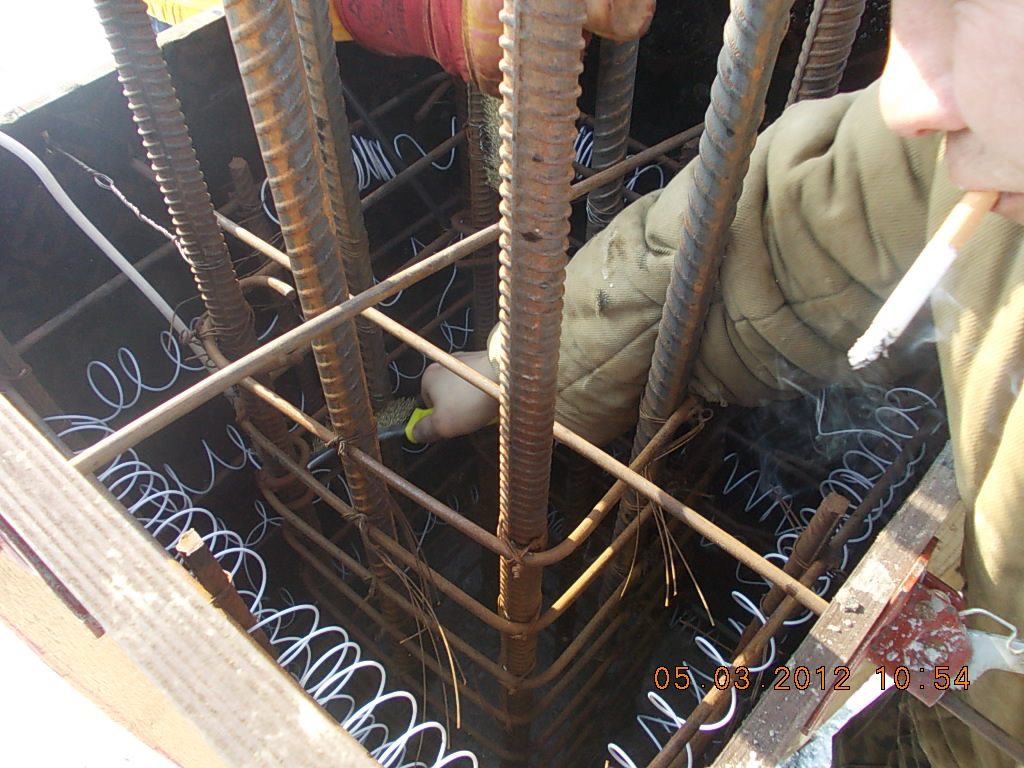
| Rod | It is a scrap of reinforcement with a thickness of 5 to 12 mm. It is installed singly or in groups with a step of up to 50 cm, while it sinks into the solution almost to its entire length. The extreme elements are mounted in such a way as to exclude contact with the formwork. Rod-type electrodes are used for heating structures of complex shapes. |
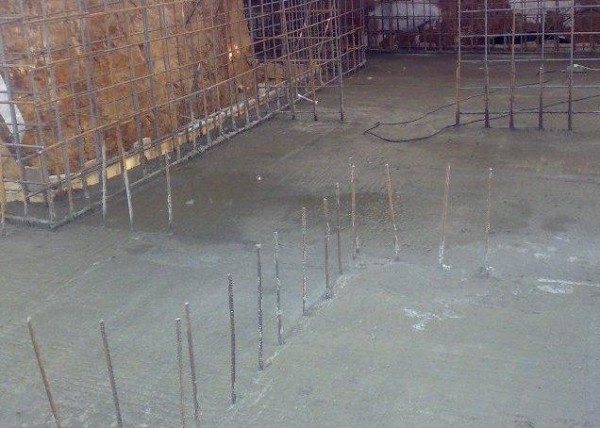

Bars from reinforcement in the thickness of the fill
Depending on the type of parts involved, the following methods of increasing the temperature are distinguished:
- Surface (peripheral) treatment - electrodes are applied to the surface of the solution without immersion, often using special conductive substrates. After completion of work, they can be dismantled and reused at another facility.
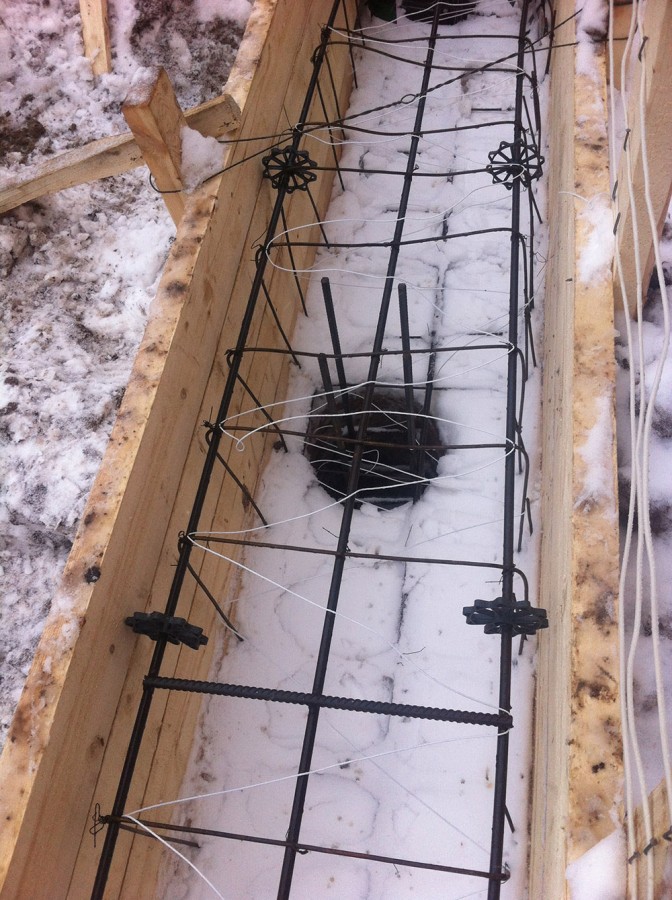
- Submersible (through) electric heating of concrete - the electrodes are inside the material, and after it has hardened, they are not removed. So that the strength of the structure does not decrease, we place the conductive elements no closer than 30 mm from the surface.
Immersion scheme
Using welding machines
Craftsmen who try to implement this technique on their own are often interested in how to heat concrete with electrodes using a welding machine (see also the article "How concrete is heated with a welding machine").
Indeed, it is quite possible:
- A conventional welding machine includes two blocks - the engine and the actual welding generator. At the same time, the power of the latter is sufficient to provide heating of about 50 m3 of concrete mortar.
- Before starting work, we lower the electrodes into the cement. For most tasks, a step of 20-30 cm is sufficient.
- We connect the electrodes in series, forming several parallel circuits.
- To monitor the voltage between circuits, experts recommend installing an incandescent lamp.
- We connect the circuits to the device and apply voltage. Heating control is carried out in special wells.

Such a device may well be used
Timing
Concrete heating begins with the choice of the optimal scheme, taking into account the requirements of the construction site, the region (Moscow requires some measures, Sochi or Norilsk - completely different), opportunities, etc.
The main factors that are taken into account in calculating time and temperature:
- The average annual weather forecast for the winter in the region, taken for the previous couple of years, as well as the forecasted mark of the average air temperature during this winter period.
- Calculation of the module of the heated working surface, determination of the thermos holding of the solution.
- Calculation of the average temperature of the structure during the period of its cooling.
- Accounting for information about the temperature of the finished concrete mixture, its isothermal properties (provided by the manufacturer of the solution).
- Determination of heat losses in the process of transporting the mixture, unloading.
- Determination of the temperature of the mixture from the beginning of laying (taking into account the heat transfer for heating the reinforcement, formwork).
- Calculation of the solution cooling time (in accordance with the standard strength requirements).
All these data are used in forecasting, to take into account heat losses in the process of pouring, heat radiation from the surface. But all this is rather approximate, therefore, during the heating process, you need to carefully control the temperature every half hour or hour when heating and once every 12 hours when cooling. If the mode is violated, you need to increase or turn off the current by adjusting the parameters.
In the technological map, a heating schedule should be marked with an indication of the optimal values and all important calculations performed in accordance with SNiPs and rules.
Warming up concrete is an extremely important event when performing repair and construction work in the winter. Without the implementation of these methods, concrete simply will not gain standard strength, casting doubt on the strength, reliability and durability of the entire structure.
Heating types
Through (internal, submersible)
It is used for structures with a large thickness or complex shape. From the name it is clear that the electrodes are placed inside the poured mass of solution. The general rule is that the electrodes are installed at a distance of at least 3 cm from the formwork element.
Peripheral (surface, sewn on)
A lining is installed under the stripes. In practice, for this, pieces of roofing material are most often taken, which allows such electrodes to be easily removed and reused.
General rule
If a metal frame is installed in the formwork, then it is FORBIDDEN to use a voltage of more than 127 V. For unreinforced structures, it can be no more than 380 V.
What to consider when heating concrete
- As the poured mass hardens, its electrical resistance changes, as moisture evaporates. Therefore, it is necessary to systematically adjust the strength of the supplied current, therefore, an adjustment element must be included in the circuit (for example, a rheostat, a transformer with several outputs).
- The surface of the structure to be heated must be covered with materials that reduce heat loss. It can be sawdust, mats, polyethylene film, roofing felt and the like. Otherwise, the heating process itself loses its meaning.
- With the rod method, it is necessary to maintain the same distance between the electrodes both in one row and in adjacent ones. This will ensure uniform loading of the "lines" and eliminate phase imbalance.
- Reducing energy consumption can be achieved by introducing special plasticizer additives into the solution, which accelerate the process of concrete hardening.
- Experts do not recommend using electrode heating for small structures. There are other techniques for this.
- A direct current source cannot be used as a "power supply", since in this case electrolysis of the liquid cannot be avoided.
- For small fill volumes, welding transformers can be used as a voltage source.
- There is no unified recommendation for placing electrodes on (c) filling the solution. The scheme is determined individually and depends on external conditions, formwork parameters, cement grade and a number of other factors.
- At certain time intervals (depending on the specifics of the work), the temperature is measured. For this, special "pits" are made.
- PROHIBITED. When using the rods of the reinforcing cage as electrodes, work with a voltage of more than 60 V. In exceptional cases (more than this rating) - only if additional measures are taken and locally (on individual segments of the structure).
To receive from a solution of high-quality artificial stone complex heating of the mass is recommended, combining several methods, including the "passive" ("thermos").
 Heating of concrete with the help of electrodes is done in winter or in an area with subzero air temperatures.
Heating of concrete with the help of electrodes is done in winter or in an area with subzero air temperatures.
This process is carried out so that the aqueous solution that is part of the concrete does not freeze in the cold and does not turn into ice. Only in a liquid state can water enter into a chemical reaction with cement mortar.
Plus, during the freezing of water in concrete, all connections are broken, and they simply begin to crack, respectively, it makes no sense to talk about the strength of the structure.
Construction temperature
This parameter has a great influence on the final strength of the concrete. It should also be taken into account that fresh mortar can freeze in the case when its temperature was at + 10 ° C for 3 days. Therefore, electrode heating of concrete is necessary in winter. Know that when placing concrete at 5 ° C, you will have to wait 2 times longer for them to reach strength, which can be compared with a temperature of 20 ° C.
When the thermometer drops below freezing point, hydration may simply stop. We must also not forget the following - the unbound water in the concrete solution will begin to increase in volume during freezing.
If the processes of freezing and thawing are repeated many times, this will cause:
- loosening of the structure;
- reducing moisture;
- weathered concrete;
- the price of the work will increase.
But, when the mixture has gained strength in excess of 5 N / mm2, it becomes resistant to single freezing. In this case, the period of demoulding must be increased for the period when the concrete was below 0 ° C.
General scheme of concrete heating in winter with electrodes
In this case, it is necessary to ensure that it quickly gains strength so that freezing does not disrupt the process.
For example:
- during the month, concrete should be protected from precipitation in the form of snow and rain;
- it should not come into contact with loose anti-icing salt for the first winter.
Fresh composition temperature relative to DIN 1045 shouldn't be below are the parameters that are taken depending on the ambient temperature and the type and amount of cement.
In the first case, this will lead to rapid hardening and a decrease in the plasticity of the material, which will make it difficult to work with it.
It will also cause:
- large shrinkage;
- premature strength gain;
- low final strength of concrete material.
To prevent this from happening, in each specific case, for example, a technological map of concrete heating with electrodes is developed.
How to protect
To do this, you should take the following steps:
- heat mixing water and aggregate, never use frozen last component;
- use high strength cements. They harden faster and generate more heat during the process than cements of lower strength classes;

Use for hole drilling equipment with diamond core bits
- increase the cement content in order to accelerate the set of strength;
- lower the ratio between cement and water, this will allow the mortar to harden and gain strength faster, while generating a high level of heat;
- add with your own hands in special cases and after conformity tests with a hardening accelerator. Do not use chlorine hardening accelerators in prestressed concrete.
What needs to be done when transporting the mortar and laying it down:
- protect vehicles from heat loss. Do not use open trays and conveyor belts;
- place as much preheated concrete as possible into the preheated formwork and compact immediately;
- keep the reinforcement and formwork planes free of snow, you can use heated air or flame burners to warm up. Never use a jet of hot water;
- do not place concrete on frozen structures or on frozen ground;
- keep the concrete temperature, if possible, during the first 3 days at least + 10 ° С, and also heat the adjoining rooms.
Using welding machines
Concrete heating with a welding transformer is a widely used method that provides good heating performance of the structure with the additional use of various types of heating elements.
The use of modern transformer welding machines is a completely safe process that does not pose a danger if the safety standards are observed.
Most modern welding machines are equipped with additional modules:
- frozen soil heating unit;
- block for drying electrodes;
- undervoltage module;
- generator of electric current.
Before you heat the concrete with a welding device, you should check for additional options that greatly simplify the process of heating the concrete structure in winter.
Heating scheme for concrete structures.
Heating the cement-sand mixture using a transformer-type welding device consists of the following steps:
- Uniform arrangement of reinforcement sections along the poured area.
- Connection of electrodes in two parallel circuits.
- Installation of a warning light bulb.
- Lead-in of wires of direct and feedback.
If the water evaporates too quickly from the surface of the cement-sand structure, it makes sense to cover the site with a small amount of sawdust.
The connection of the heating system to the cement-sand structure is carried out in several stages:
- connection of current-carrying aluminum cables with a welding device;
- checking each loop with a current clamp;
- increasing the power of the device up to 50% after an hour of operation and up to 100% after two hours after turning on the heating;
- control of the current strength within 25 amperes.
Typical mistakes
Electrode heating of concrete
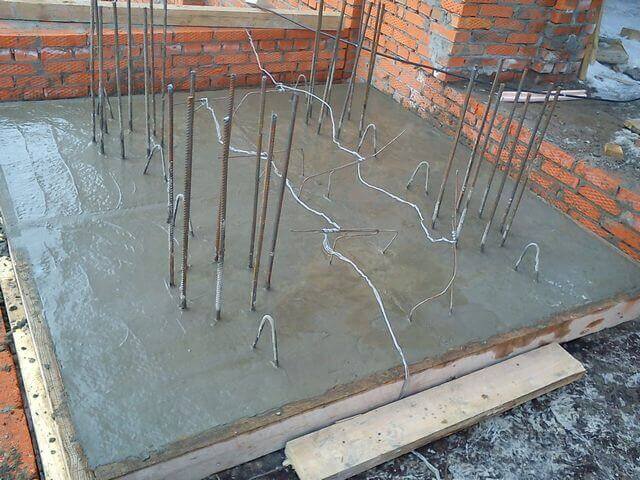

Electrode heating of the mixture is often accompanied by the following errors:
Mistake # 1. The electrodes have a low contact area with concrete, which is due to their design features. As a result, the heating becomes of poor quality. Air bubbles can also appear between the electrodes and the mixture.They cause the water to boil, blocking the spread of heat energy through the concrete. It concentrates in one place, forming cavities.
Mistake # 2. There is a reinforcing metal "skeleton" inside the concrete. If the electrode touches it during immersion, it instantly leads to a short circuit. Thus, expensive equipment fails, which may not be repairable. If there is nothing else to heat, then the mixture hardening technology is disrupted.
Mistake number 3. Increasing the current density in the immediate place of contact between concrete and electrodes. This is fraught with a slowdown in the rate of hydration, local overheating and the formation of a porous structure. It is noteworthy, but outwardly it is impossible to detect the mistake made. You can learn about it in the future, when the structure begins to collapse ahead of time.
Heating of concrete with a heating cable

Errors also occur when heating concrete with a heating cable:
Mistake # 1
Few builders pay attention to the connection diagram of heating elements. Especially if none of them have an education in electrical engineering
As for checking the integrity of the wires, this almost never happens at all. They are simply laid out on the surface. If the integrity is violated, then the heating cable cannot fulfill the role assigned to it. Or heating occurs only in certain places. Uneven heating leads to cracks and to rapid destruction of the internal structure of concrete.
Mistake # 2
When laying wires, pay attention to their insulation and correct positioning. Many people forget about it.
The cable must have optimal length - no more and no less than the prescribed amount. Otherwise, its overrun is carried out, which leads to an increase in the duration of construction work.
The disadvantages of using a heating cable are as follows:
- Large capacities are required to heat up a significant volume of concrete. Often they are not present at the work site.
- It will take a lot of electrical calculations. This takes extra time and effort.
- An extremely limited number of specialists are able to properly lay the cable. Not all companies can afford to keep one on their staff.
These errors are the most common during concreting and heating by the listed methods. Knowing about them in detail, it is best to try to avoid them. After all, it is better to do everything right at once, rather than spend money on dismantling the old and installing a new structure in the future. Sometimes this requires the complete destruction of a building or object.
Heating with electrodes
The most popular concrete heating method is the use of electrodes. This method is relatively inexpensive, because there is no need to purchase expensive equipment and devices (for example, wire type PNSV 1,2; 2; 3, etc.). The technology for its implementation also does not present great difficulties.
Physical properties and features of electric current are taken as the fundamental principle of the presented technology. When passing through concrete, it releases a certain amount of thermal energy.

When using this technology, do not apply a voltage higher than 127 V to the electrode system if there is a metal structure (frame) inside the product. The instruction for electric heating of concrete in monolithic structures allows the use of a current of 220 V or 380 V. However, it is not recommended to use a higher voltage.
The heating process is carried out using alternating current. If a direct current is involved in this process, it passes through the water in the solution and forms electrolysis. This process of chemical decomposition of water will interfere with the performance of its functions, which the substance has during the hardening process.