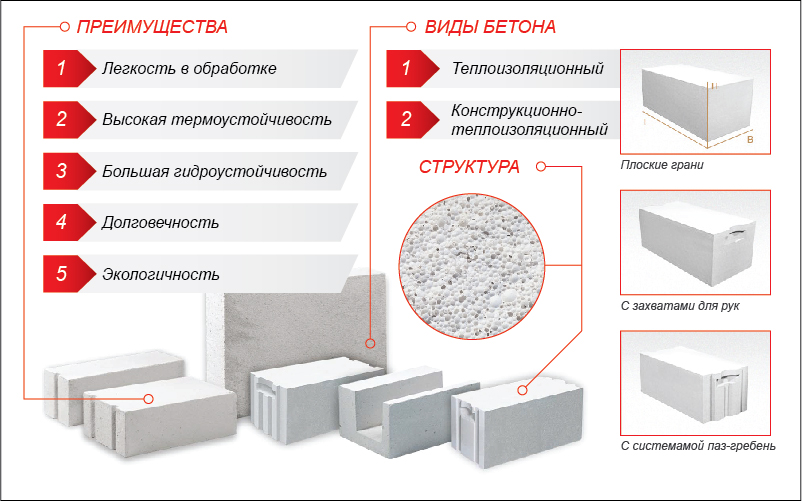
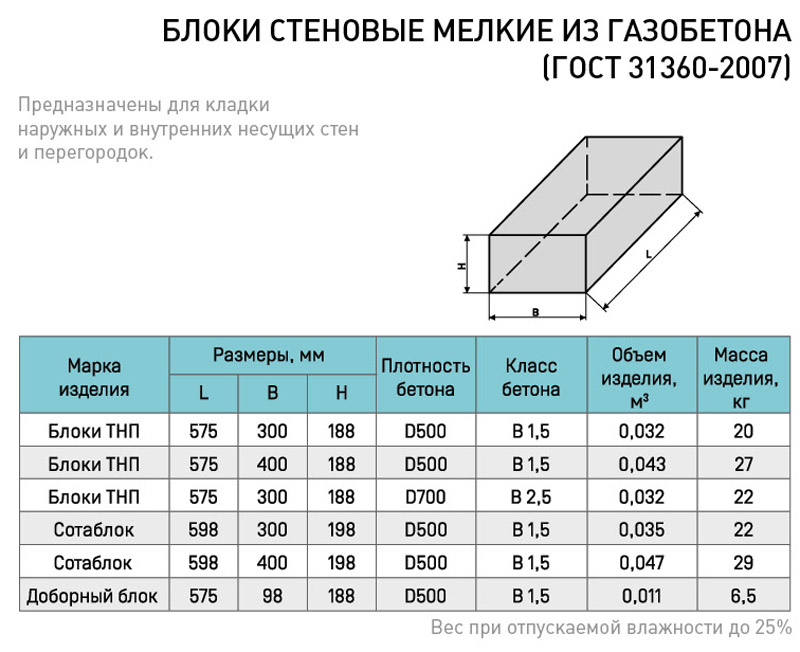
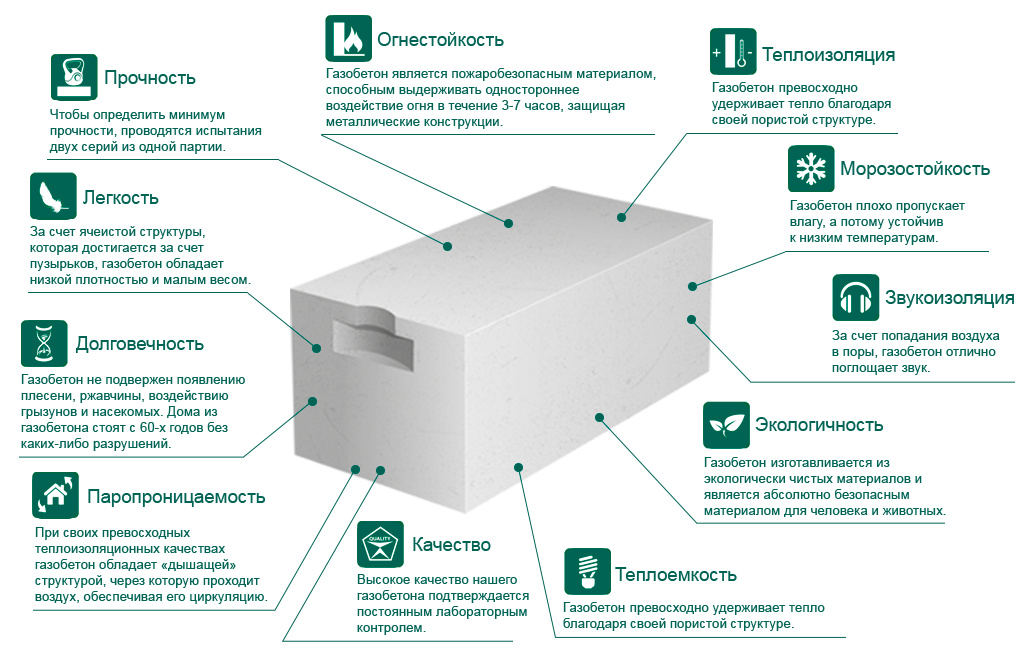
Characteristics of aerated concrete
Now it's time to analyze the characteristics of aerated concrete and products from it. Let's start by identifying the main qualities and properties of the material that determine its competitiveness in the building materials market.
Physicomechanical and technical characteristics
Let's use the table.
Properties and qualities:
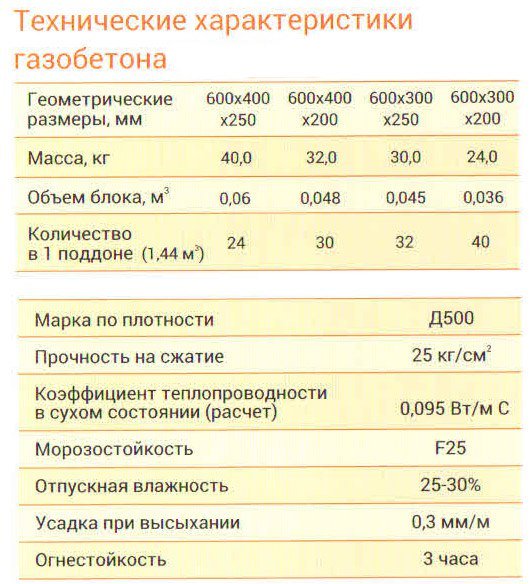
| Indicator name | Meaning and comments |
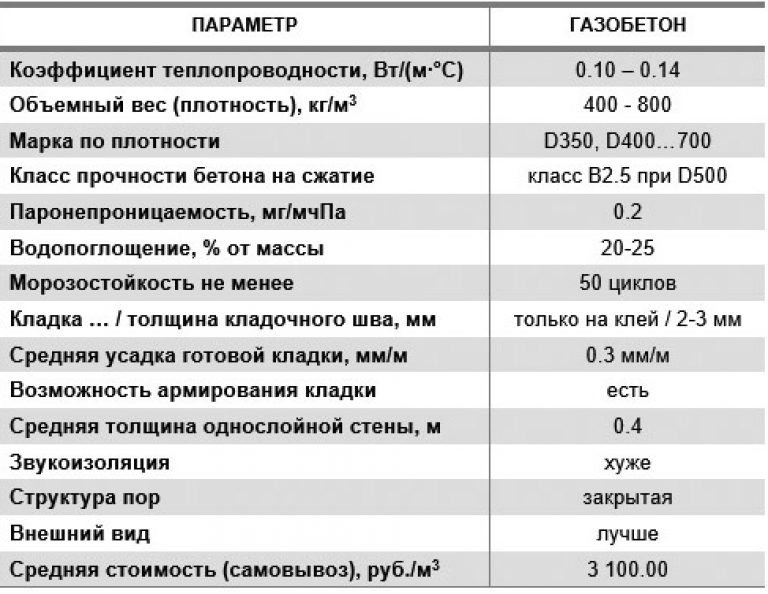
| Dry heat conductivity | From 0.09 for heat-insulating aerated concrete |
| Frost resistance | 35 to 150 cycles |
| Strength grade | From B 1.5 in accordance with GOST for non-autoclaved aerated concrete, average at D500 - B3.5 |
| Density | 300-1200 |
| Shrinkage | 0.3 mm / m2 |
| Water absorption | About 25% |
| Recommended wall thickness | From 0.4 |
| Environmental friendliness | 2 |
| Fire resistance | Does not burn, withstands up to 120 minutes of exposure to high temperatures |
Types of aerated concrete
Since aerated concrete and aerated concrete blocks are varieties of aerated concrete products, the classification, in accordance with GOST, applies to them the same. Therefore, it makes no sense to disassemble it in detail again.
Let's just look at the differences in the performance of autoclaved and non-autoclaved aerated concrete with the help of a table, since some of them differ significantly.
Aerated concrete blocks characteristic: comparison of autoclaved and non-autoclaved products:
| Characteristic | Its value for synthetic hardening aerated concrete | Its value for hydration hardening aerated concrete |
| Vapor permeability | 0,2 | 0,18 |
| Frost resistance | 35-150 cycles | 15-35 cycles |
| Shrinkage | 0.3 mm / m2 | From 0.4 mm / m2 |
| Strength grade | B2.5-B5 | B1.5-B2.5 |
| Thermal conductivity | From 0.09 | From 1.7 |
| External wall thickness | From 400 mm | From 650 mm |
| Durability promised by manufacturers | Up to 200 years | Up to 50 - 60 years old |
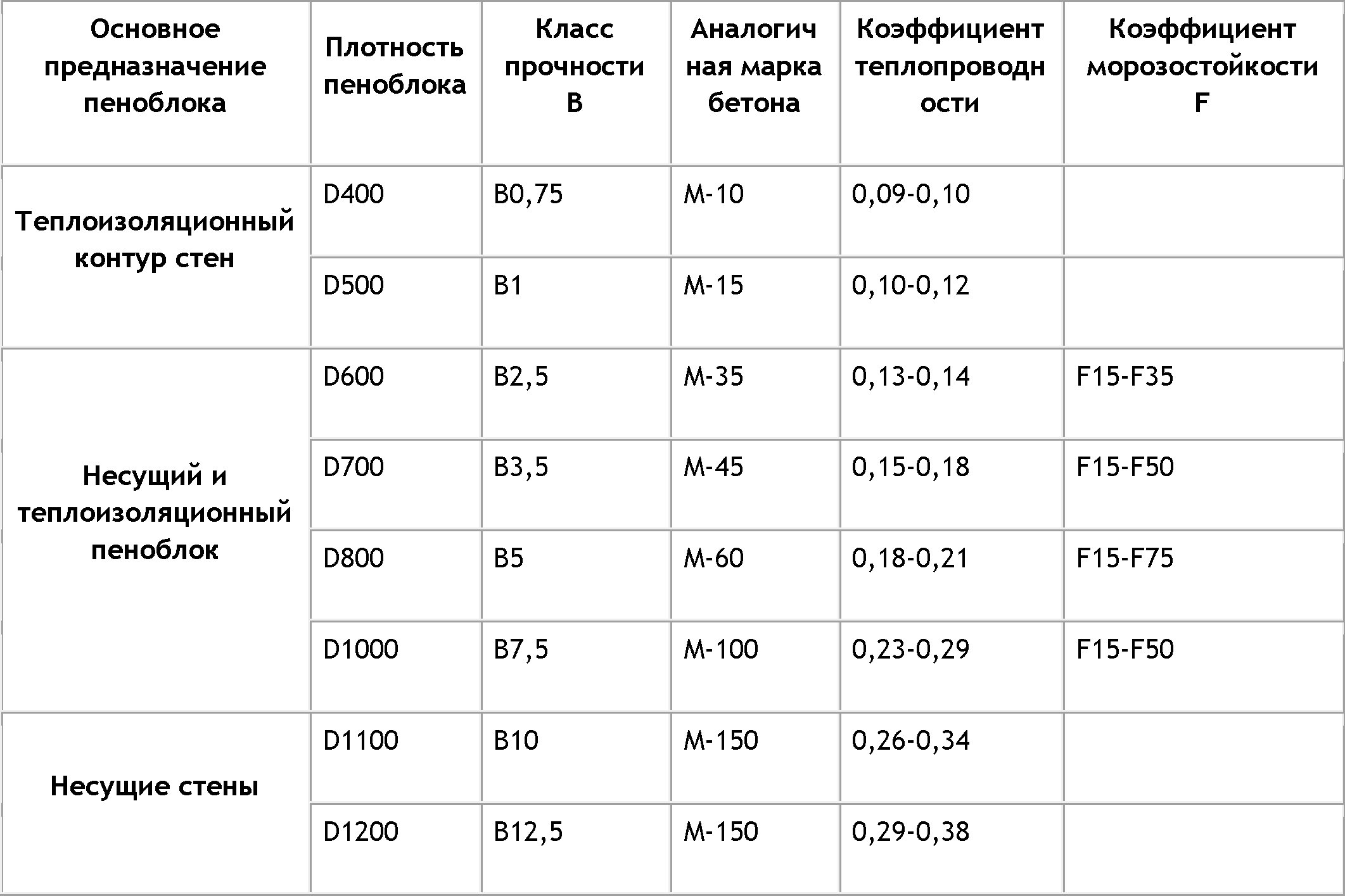
Since aerated concrete is also divided into types depending on density, let's analyze: how does the thermal conductivity of products change in this case.
Thermal conductivity, density: ratios and bonding:
| Type of aerated concrete | Density | Thermal conductivity of products in a dry state. |
| Structural | D400 | 0,09-0,1 |
| D500 | 0,1-0,12 | |
| Structural and heat-insulating | D500 | 0,13-0,14 |
| D600 | 0,15-0,18 | |
| D700 | 0,18-0,21 | |
| D800 | 0,21-0,22 | |
| D900 | 0,22-0,23 | |
| Structural | D1000 | 0,23-0,29 |
| D1100 | 0,26-0,34 | |
| D1200 | 0,29-0,38 |
Advantages and disadvantages of products and structures erected from them
Some of the advantages of aerated concrete are very similar to the advantages of foam concrete products. These include:
- Low weight of the material, which allows you to save a little on the construction of the foundation due to the absence of serious loads;
- Ease of processing. Aerated concrete is also easy to saw, cut and grind. At the same time, unlike, for example, a ceramic block, the presence of highly specialized equipment is not required. You can use a regular hacksaw or any other tool suitable for such purposes.
- Due to the presence of the above characteristics, a high construction speed.
- Environmental friendliness, fire resistance are also characteristic of aerated concrete.
- High production efficiency, low product cost.
- Possibility of almost any interior and exterior decoration, subject to technology and technical compatibility.
- An enviable indicator of frost resistance for other wall materials. Some manufacturers promise up to 150 freeze and thaw cycles, and the service life is set - up to 200 years.
- High strength characteristics, sufficient for the construction of a building in several floors and, at the same time, a low coefficient of thermal conductivity.
- Resistance to atmospheric and partly biological effects.
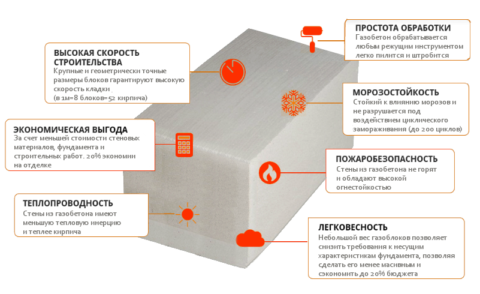 The advantages of aerated concrete
The advantages of aerated concrete
The cons boil down to the following:
- Material hygroscopicity. Aerated concrete absorbs moisture better than other products. It has an open pore structure, which only enhances this ability.
This is especially fraught with products during the period of prevalence of negative temperatures. When moisture can crystallize and begin to break down the block from the inside.
- With hardware, the situation is the same as in the case of foam concrete. The structure of the material is similar, therefore, when fixing the elements, developers are faced with the same problem.
- Fragility is also characteristic of aerated concrete. He requires careful handling.
- Shrinkage. The appearance of cracks on the finished walls is not uncommon.
This is where the main disadvantages end. As you can see, there are still more advantages, and most of the weaknesses can be leveled with the help of proper finishing and adherence to the technique of wall construction.
Disadvantages of foam concrete blocks
Like any building material, the foam block also has disadvantages that the builder should know about. Foam concrete blocks are fragile.
It is recommended to make a rigid foundation (pile or strip). Reinforce the wall every 3 rows. Foam concrete absorbs moisture well. Which reduces its heat-saving characteristics.
In order to avoid dampness of the walls, a moisture-resistant protection and waterproofing should be created between the walls and the foundation. Vapor permeability of blocks. Here it is necessary to use a vapor barrier outside to protect it from rain.
Inaccurate geometry of the foam block, resulting from the use of low-quality forms (production of material by small manufacturers).
Do not be surprised at a 2 - 3 cm discrepancy in size, which will naturally affect the thickness of the seam. The thermal conductivity and the facade of the building also depend on this.

Nevertheless, foam concrete blocks are a high-quality building material.
Watch the video: The whole truth about FOAM CONCRETE, foam block, not autoclaved gas block. Manufacturing.
Where is it used?
Foam blocks are materials used in construction that are in great demand. Their demand is due not only to good characteristics, but also to the multitasking of such products (even floors in houses are made of foam concrete).
Let us consider in more detail in what cases a foam block can be used.
- First of all, foam concrete blocks are very often used in the construction of private houses of various modifications, summer cottages and cottages. In these buildings, load-bearing wall ceilings, additional insulating and sound-insulating structures, and internal interior partitions are made of foam blocks.
- They also turn to foam blocks when arranging office / residential buildings. In this case, insulating and sound-insulating structures, combined load-bearing walls, and internal partitions are also constructed from these materials.
- Foam blocks are ideal options for renovating and rebuilding buildings. With their help, you can insulate old structures, as well as increase the number of floors without strengthening the foundation.
- From foam concrete blocks it is possible to build industrial structures, the height of which does not exceed 3 floors.
- These materials are also suitable for the construction of commercial / administrative buildings.
- Various outbuildings / outbuildings are built from foam blocks.
- Reliable fences and fences are made from these materials.


What brands are foam blocks divided into?
Foam blocks can be of several types, which in turn are subdivided into brands depending on technical characteristics.
There are four types of foam concrete in total:
- Heat insulating. Its peculiarity is the emphasis on heat-insulating properties, due to which strength suffers somewhat. This type includes foam concrete grades from D150 to D400. Grades below D400 are not standardized according to the strength class, and for the latter it is 9 kilograms per cubic centimeter;
- Constructional and heat-insulating. This includes grades D500 to D900. Minimum strength (for D500) - 13 kg per cm3. For D600 - 16 kg per cc, D700 - 24 kg per cc, D800 - 27 kg per cc, D900 - 35 kg per cc.This type is considered the most balanced;
- Structural. The brands that refer to it are from D1000 to D1200. The D1000 has the lowest strength and is 50 kg per cm3. The D1100 and D1200 have 64 and 90 kg per cc, respectively. Foam concrete of this type is used in cases where strength characteristics are given priority;
- Structurally porous. It includes brands up to D1600. A rarely used type that is produced in small batches. In this regard, its characteristics are not indicated in the GOSTs.
Rules for laying products
The rules for laying all products from aerated concrete are very similar to each other.
Let's look at them, and also pay attention to the features inherent in the process of erecting walls from foam concrete blocks
Basic requirements and tips
- The surface of the base must be flat, it can be corrected with a cement mortar.
- The blocks can be slightly moistened so that they do not absorb moisture from the solution.
- It is worth mixing the solution (glue) in a small amount in order to work out before it sets.
- The proportions should be observed when preparing the solution, it should not be too liquid.
- When using glue, choose specialized mixtures, they will not only emphasize, but also improve the characteristics of the finished wall.
- It is necessary to apply the glue in a thin layer to avoid excessive consumption and increase of cold bridges.
- Use a rubber mallet to correct the location of the block and the evenness of the masonry. It is quite heavy, but it will not cause mechanical damage if used correctly.
- Strictly observe the technology and order of laying, since it is not possible to disassemble the finished wall.
Required tools, solution preparation
To carry out the work, you will need the following tool:
- Rubber mallet (hammer);
- Roulette;
- Building level;
- Container for solution (glue);
- Specialized scraper bucket with teeth;
- Construction thread;
- Drill and mixer or concrete mixer;
- Grater;
- Corner;
- Wall chaser;
- Hacksaw.
 Tools for laying foam concrete, photo
Tools for laying foam concrete, photo
For self-preparation of the solution, you will need materials:
- Cement grade not lower than 400;
- Sand;
- Water
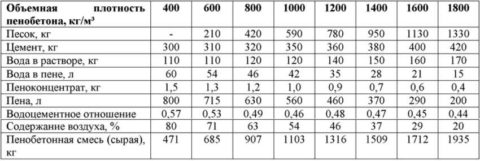 Proportions and composition of raw materials for solution preparation
Proportions and composition of raw materials for solution preparation
Masonry work
It should be noted right away that the production of foam concrete can take place in several ways:
- Bar technology, in which the foam generator is not used. The process of beating the foam takes place under the influence of high pressure. Subsequently, cement and sand are added to it.
- Dry mineralization method. It is characterized by mixing the components in a dry form with a foam mass. This method allows you to get foam concrete directly at the construction site.
- The classic method. With it, foam is introduced into the cement composition mixed with water.
The work process contains the following stages:
- The first blocks are laid in the corners and a cord is pulled between them. The blocks and thread will serve as a guide when laying.
- Lay out the entire row completely.
- If there is a gap, the block must be cut to size.
- The second and subsequent rows are laid with a seam offset of about 30%.
- Reinforcement is performed on the first and every fourth row. In the process, reinforcement with a diameter of at least 8 mm is laid in the grooves.
- Evenness checks and adjustments should be made as often as possible, since the solution sets quickly, after about 10-15 minutes.
- After the completion of the construction of the wall, an armopoyas device should be made.
On this, the masonry work on the construction of the outer walls can be considered completed.
Advantages of foam block houses
The high popularity of building houses from foam blocks is due to the significant advantages of this building material.
In general, houses built from foam blocks are characterized by the following positive aspects:
Low thermal conductivity and favorable microclimate.
Previously, lower quality foam concrete was used as wall insulation. The porous structure of the material creates an effective heat-insulating layer, which significantly reduces the heat loss of the building, retains heat well. Compared to concrete and brick, the thickness of the wall made of foam blocks is two or more times thinner. While maintaining the same properties of thermal insulation. This allows you to save more usable space inside the house.
Minimal water absorption.
The closed structure of the pores of the walls made of foam blocks creates a closure of the void inside the block, which ensures low hygroscopicity of the house. This is a significant difference between the foam block and the gas block, which absorbs water well. Therefore, the foam block floats in the water, and the gas block picks up water and sinks. More details about the properties of the gas block.
Fire resistance
The foam block is a building stone that does not burn and does not support combustion. In the event of fires, as in the case of brick houses, the basic structure of the building will remain intact. Basically, only wooden, plastic and other combustible components of the house will be damaged.
Quiet house
The cellular structure of foam concrete walls creates good sound insulation inside and does not release unnecessary sounds outside, which additionally creates comfort for both you and your neighbors.
Light weight at home
Compared to other building stones, a foam concrete house has a significantly lower load on the foundation. The weight of the heaviest and densest brand of foam concrete is 1200 kg cubic meter. The average running weight ranges from 300 to 900 kg. This is an opportunity to save on the arrangement of the foundation and this is several times less than a brick house and a cinder block house of the same area.
an expensive foundation is not needed for a foam concrete house
Facade finishing
The facade of the house can remain without finishing for a long time. Unlike hygroscopic materials such as cinder block, shell rock, panel houses, frame houses and others. The front sides of the walls of the house made of foam concrete do not need to be immediately finished with facing, protective materials. Most private developers face this problem due to lack of funds. When building from other materials, instead of completing all the internal repairs necessary for settling, limited funds have to be invested in protective facades. In the case of building a house from foam concrete blocks, facing work can be done last.
Eco-friendly home.
Due to the use in the production of foam blocks, only natural environmentally friendly materials, such as sand, water, cement and foam, the house is absolutely environmentally friendly. Does not cause or provoke allergic reactions. The house does not accumulate radiation and other harmful backgrounds for humans. What a brick house cannot boast of, a cinder block house or houses in the construction of which were used crumbs of some types of natural stone, such as granite.
Speed and ease of construction
The laying of foam blocks is carried out faster than the installation of any building stone. This is due to the lightness of the material, large dimensions, ease of cutting processing.
The cost of a foam block house
A foam concrete house is the most economical option in comparison with other types of building stones. The price of a cubic meter of a block and its installation is much cheaper than a brick. In addition, the foam block makes it possible to save on additional wall insulation, on the foundation. A massive and expensive foundation is not required for a heavy concrete and brick house. Facade finishing is needed only for aesthetics and does not require serious investments to protect against moisture.
the foam block is easy to use
Ease of installation of communications
Foam concrete walls are flexible for laying strobes, cutting openings of any shape and volume.This makes it easy to make changes to the layout, as well as to lay water supply, sewerage and electrical communications, even after the construction of the box at home. Unlike concrete houses, where openings for plumbing communications must be laid in advance.
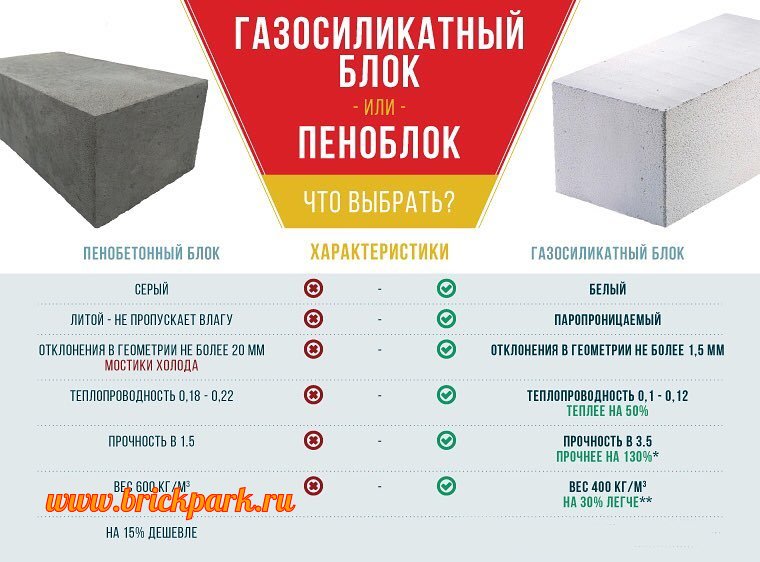
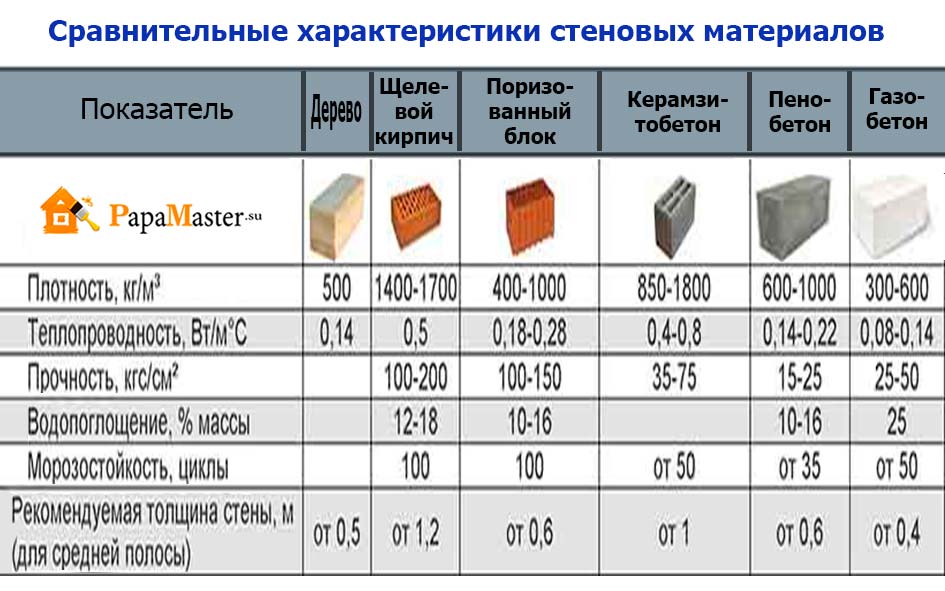
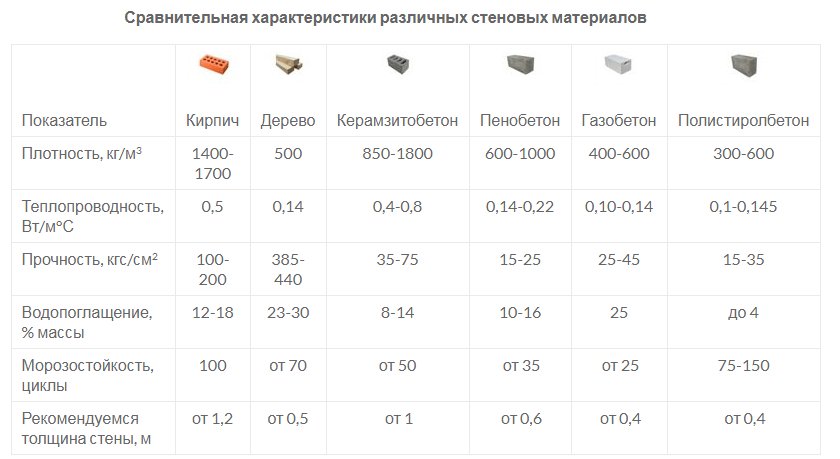
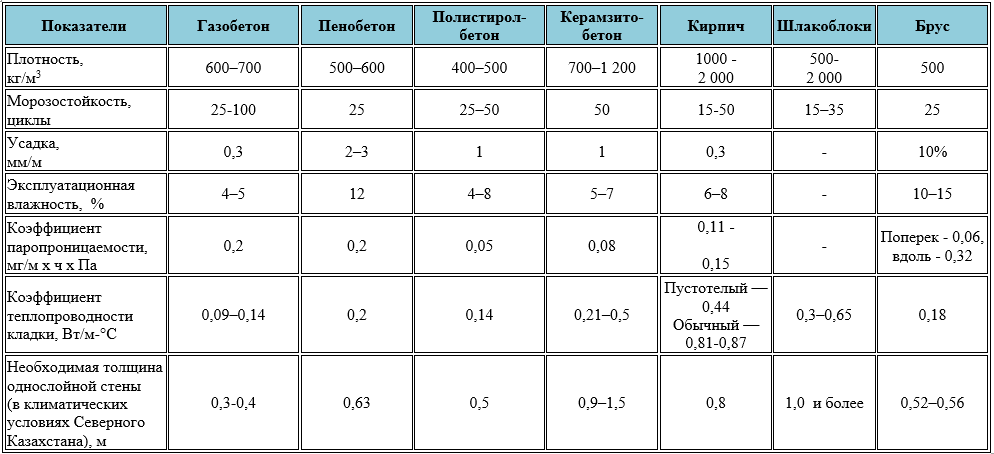
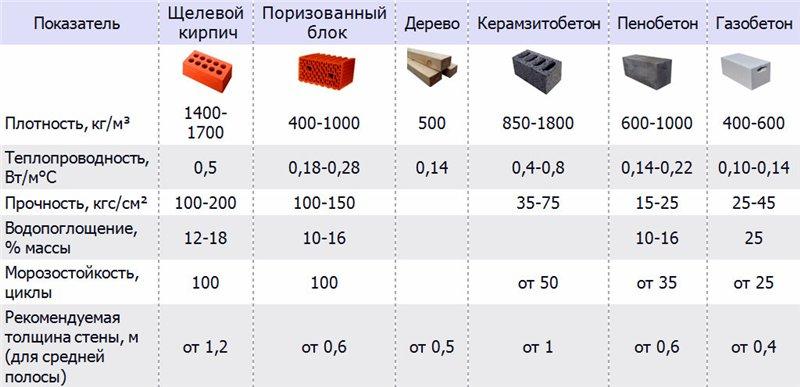
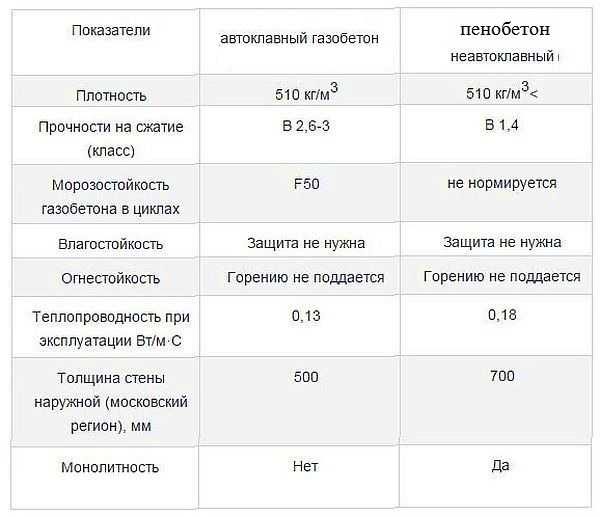
Table of technical parameters of foam concrete and aerated concrete
The final comparative table shows the main technical parameters that determine the operational properties of aerated concrete and foam concrete. Such a comparison will determine which of the materials should be chosen for the construction of residential buildings and other objects.
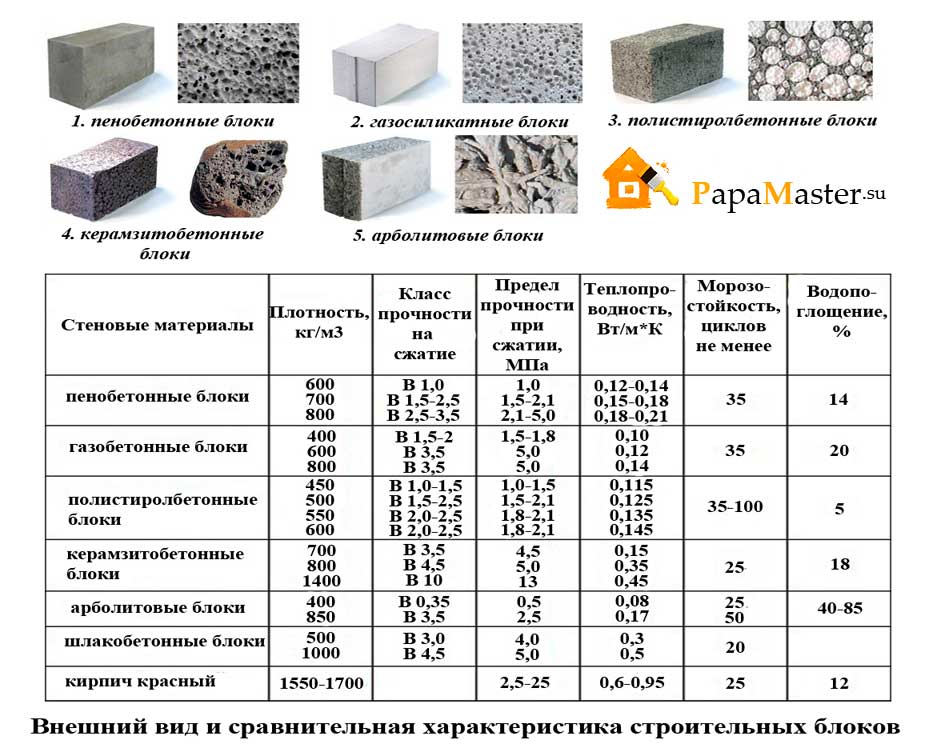
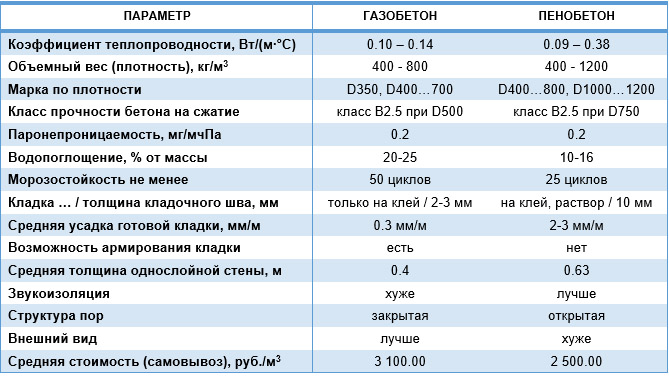
| Technical specifications | Foam blocks | Gas blocks |
|---|---|---|
| Filler for creating a porous structure | Saponified tree resin | Fine dispersion aluminum |
| Technological process | By block cutting or cassette casting | Single block casting method |
| Component components |
|
|
| Equipment for the production of | Factory equipment or homemade installations | Industrial equipment - autoclaves and electric ovens |
| Pore type (cells) | Closed-cell heterogeneous structure | Homogeneous porous structure with external open and internal closed pores |
| Pore sizes | Different sizes | One size |
| Standard sizes of blocks, cm | ||
| Height | 20, 30, 40 | 20 |
| By lenght | 60 | 50, 60 |
| By width | 10-30 | 7,5-50 |
| Density, kg / cu. m | 300-1600 | 200-600 |
| Weight, kg / cu. m | 300-1600 | 300-600 |
| Compressive strength index of material | 1,2 | 2,5 |
| Time to gain strength | Gradually with a subsequent increase in strength over 2-3 weeks | Instantly when concrete sets within a few hours |
| Shape Geometry Accuracy | When cutting a solid base - minor errors. In the case of cassette production, there are significant discrepancies. This is the main disadvantage of the material. Up to 25 mm | Minor discrepancies are allowed. This is the main plus of the material. Up to 2 mm |
| Moisture absorption level,% (in direct contact with water) | 10 | 45 |
| Frost resistance (number of freeze and thaw cycles) | Average frost resistance - up to 35 cycles | High frost resistance depending on the density of the material - from 35 to 75 cycles. A decrease in the level of humidity leads to a significant increase in frost resistance |
| Soundproofing | High | Low |
| Environmental friendliness indicator | 4 | 2 |
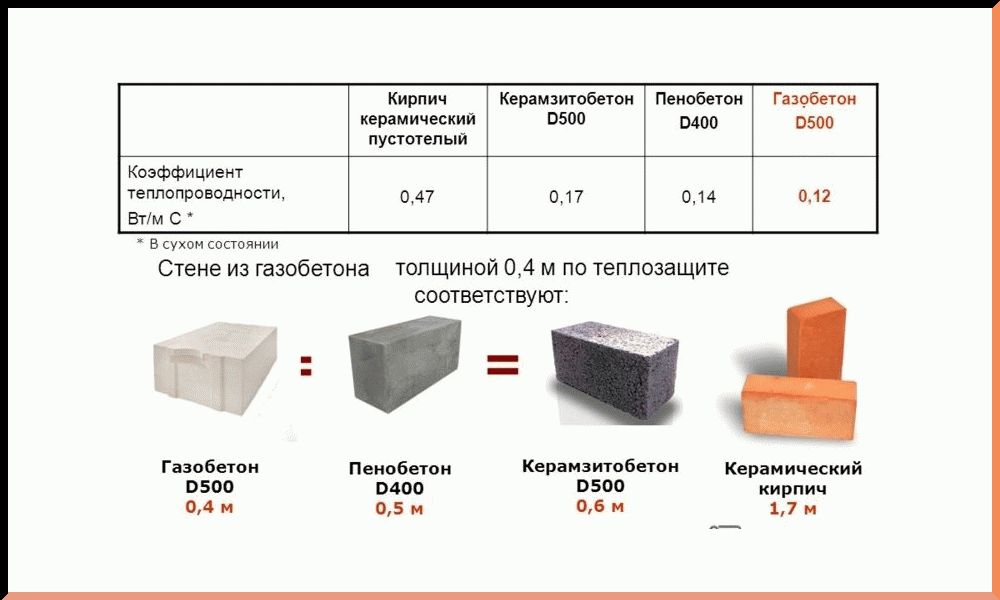
| Thermal conductivity, W / M * k | For thermal insulation - 0.2 For the construction of structures - 0.35 | For thermal insulation - 0.1 For the construction of structures - 0.18 |
| External component | Smooth gray surface | Rough white surface |
| Vapor permeability index, mg / m × h × Pa | 0.8 to 0.12 | 0.15 to 0.23 |
| Life time | Not more than 35 years old | Over 60 years |
| Features of the installation work | Since porous concretes are lighter than solid materials, they are easier to cut, drill, groove and lay. | |
| Adhesive requirements | For masonry work, traditional concrete compositions or special adhesive mixtures can be used. Joint thickness - 22 mm | Special masonry compounds are intended for installation. Joint thickness - 3 mm |
| Additional protection of wall structures | Not required | |
| Shrinkage, mm / sq. m | 2-4 | 0,6 |
| Ability to hold fasteners | The same. The need to use special fasteners designed for porous materials | |
| Cladding material | All available materials | Breathable materials |
| Insulation material | If necessary, a reliable heat-insulating material is used - mineral or basalt wool | |
| Application of plaster | For plastering porous substrates, special plasters with a high level of air permeability are suitable. To increase the adhesion of the composition to the treated surface, a reinforced mesh is additionally used | |
| Price, USD / cu. m | 35-50 | 55-60 |
p> It is difficult to give an unambiguous answer to the question of which material is the best - foam concrete or aerated concrete. Each of the materials has its own distinctive advantages and disadvantages. Based on the presented table, a short conclusion can be drawn: gas blocks have higher indicators of frost resistance and strength, and foam blocks - thermal conductivity and environmental friendliness. Which technical parameter is more important depends on the scope and characteristics of the use of the building material.
Choosing foam concrete correctly - selection criteria
1. First of all, look at exactly who makes these foam blocks. Ask for a certificate, check the terms of delivery and compliance of the products with GOSTs. If a manufacturer openly provides as much information as possible, then he has nothing to hide, and the material is of proper quality. By the way, this is what large firms, reliable and well-proven, do. A good foam block manufacturer usually has a production area of at least 180 square meters with a block cutter. Moreover, the production area must be heated and have a roof.
2. Price matters too. On average, for the D800 brand, it is about $ 80 per cubic meter. If the material is much cheaper, you should think about it - this can affect the quality.
3. Inspect the blocks carefully - they should not be pure and bright white. Technology will not allow this. Normally, foam concrete should be grayish, slightly lighter or darker, and non-uniformity of the surface color is not allowed.
4. Check how tight the aerated concrete cells are. If they join together, moisture will easily penetrate into the material. Split one block and see if its structure is the same on the outside and inside. The cells must be round, the presence of chips or cracks is unacceptable.
5. To lay the walls without problems, the blocks must be strictly rectangular - check this. Putting two foam blocks one on top of the other, try to shake them, see if there are any gaps
Moreover, examine all four sides of the blocks - this is important, since there can be a flaw on only one side. And in the future it can take a lot of your time, and spoil your nerves.
6. Having bought fresh material, do not immediately use it for the construction of walls. After all, foam concrete blocks will acquire the necessary strength and other technical characteristics only 28 days after production. Therefore, the most correct solution would be to withstand the purchased foam concrete for two or three weeks. At the same time, it must either be well sheltered from moisture, or be indoors. This will help you get out of trouble if underexposed material has been sold to you.
An example of improperly organized storage of foam blocks, from above they are not covered with anything and it is already clear that they have saturated moisture from the damp earth.
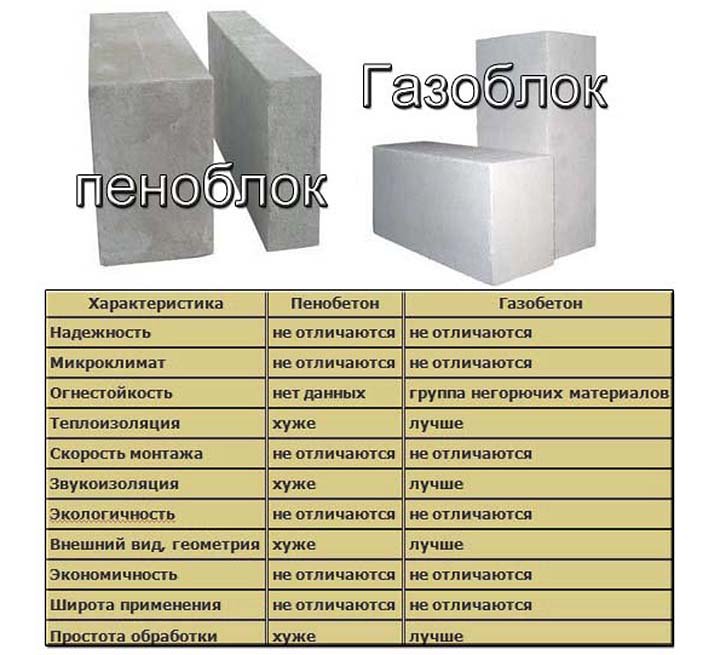
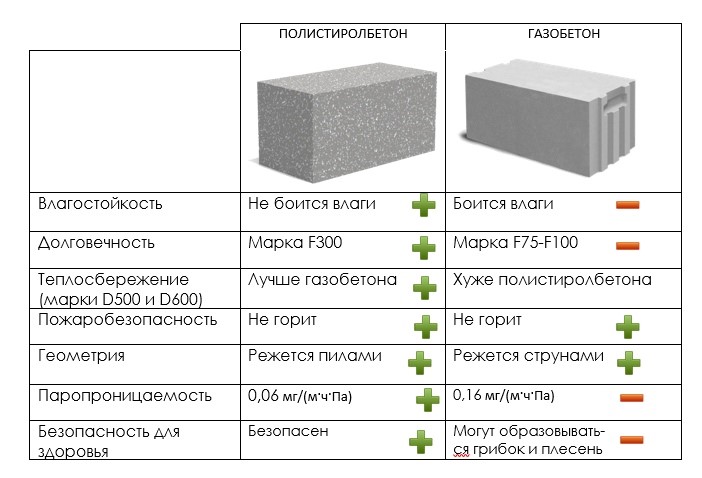
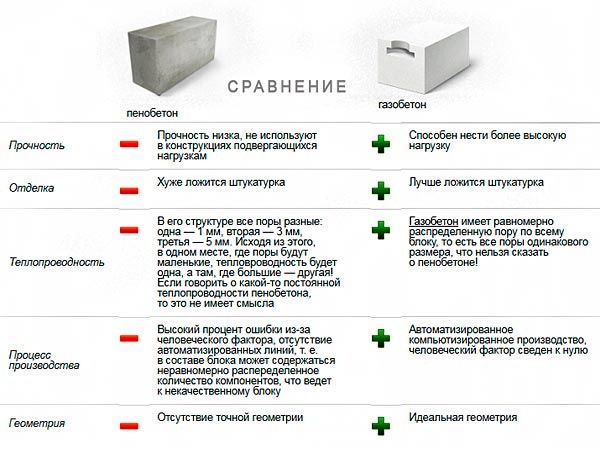
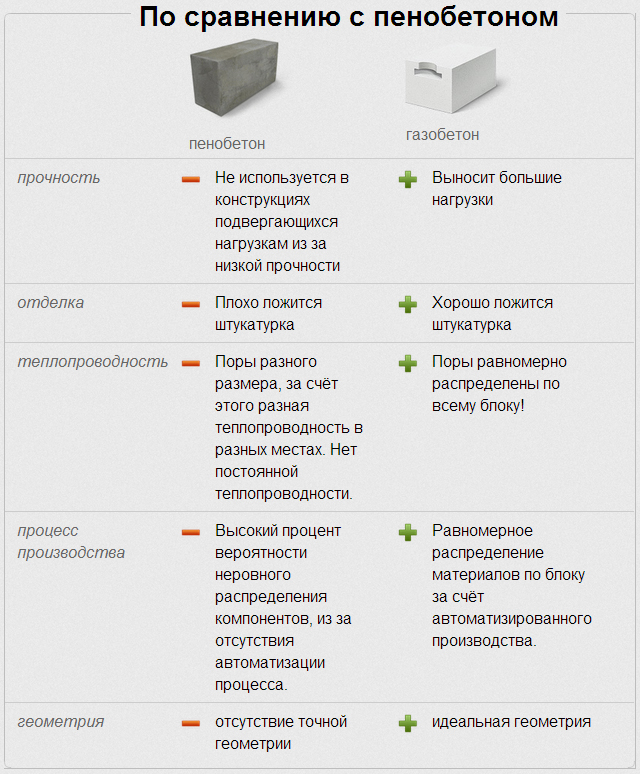
Comparison of properties and qualities of materials
Since we have already considered all the main properties and qualities of materials, it's time to analyze them and find out which is better: aerated concrete blocks or foam concrete blocks?
What's better? Comparison of materials
- Thermal conductivity in comparison "aerated concrete-foam block". There is no clear winner in this indicator. Both materials have similar numerical values. The gas block wins quite a bit in the strength-thermal conductivity ratio.
- Frost resistance. In this case, aerated concrete wins the palm. It significantly outperforms its competitor in its ability to withstand a large number of freeze and thaw cycles. This is especially true for autoclave products.
- The environmental friendliness and fire resistance of the materials is the same.
- The indicators of vapor permeability and construction speed are also similar. Both products are easy to process and have impressive dimensions. Allowing you to quickly build a structure.
- But the geometry of the block is better for autoclaved aerated concrete.
- Foam concrete is significantly ahead of the latter in moisture absorption, which is directly related to the closed pore structure. It absorbs less moisture.
- Soundproofing characteristics are slightly better for aerated concrete.
- If we talk about the appearance, then, according to the developers, aerated concrete looks more attractive.
- What is cheaper foam block or aerated concrete? Definitely - a foam block. The price difference is not big. But still she is.
- The most significant differences between these materials lie in their composition and the method of pore formation. The porous structure of foam concrete can be achieved by introducing a blowing agent into the solution. Cells in aerated concrete are obtained as a result of a chemical reaction of lime and aluminum powder, which acts as a blowing agent.
Foam concrete composition: water, cement, sand, foaming agent. Aerated concrete: lime, sand, cement and aluminum powder (or its substitutes).
As for the variability of finishes, then, as already mentioned, there can be a lot of options for both materials. The main thing is to strictly adhere to the rules of application and installation technology. Interior and exterior finishes must be technically compatible.
- Shrinkage is more typical for foam concrete. Aerated concrete also sits down, but the numerical indicator is still lower.
- If we compare the recommended wall thickness, then for aerated concrete it may be less. For foam concrete, this is 63 cm, and for aerated concrete - at least 40 cm.
- It is also worth noting that fragility is inherent in both products - this is their common drawback. The same goes for fixing the fasteners.
- The standard sizes of the products are also similar. In their assortment they have both wall and partition blocks.
- Foam concrete is distinguished by the presence of cladding products that do not require further finishing. Aerated concrete cannot boast of their presence.
- Separately, I would like to note the fact that when finishing both materials, additional costs will be required for processing and surface reinforcement. The fact is that both aerated concrete blocks and aerated concrete are characterized by low adhesion to finishing materials. This necessitates priming and surface reinforcement.
Foam concrete blocks comparison
Aerated concrete, as follows from the table, still wins in more characteristics. However, if low cost and moisture absorption, for example, are most important to you, then aerated concrete is just what you need. Therefore, when choosing, it is worth being guided, first of all, by individual wishes and requirements for future construction.
Construction of a building from foam concrete blocks
 The foam block should be gray
The foam block should be gray
After purchasing the material necessary for the project, you can start building the building with your own hands.
Walling
Tools that will be needed to build a house from foam blocks:
A layer of roll waterproofing should be laid on the foundation. The first blocks are placed in the corners of the building, placing them on a cement-sand mortar. Between them (as shown in the photo), a cord is pulled along which the remaining blocks are laid out, if necessary, sawing them with a hacksaw.
 Installation start
Installation start
The second row of blocks is installed two hours after the first. The blocks are mounted on an adhesive mixture (it should be diluted as prescribed by the instructions on the package), which is applied with a notched trowel.
Further styling is carried out using bandaging:
 Bandaging with half a block
Bandaging with half a block
- The quality of the installation must be checked using a level.
- To strengthen the structure, reinforcement is carried out. The reinforcement rods are placed in the pre-made grooves in the blocks.
- For the equipment of window and door openings, ready-made supports are used.
- If it is necessary to erect a second floor to distribute the load on the walls, a monolithic armored belt should be poured over the foam block wall, be sure to insulate it. Floor slabs are laid on the armopoyas after it has hardened.
- For attic floors, it is best to use wooden beams. Roof installation is carried out depending on the project.
The walls from the inside are best finished with plasterboard sheets or gypsum plasterboard installed on the frame.
Outside finishes
Walls erected from foam blocks, for protection from atmospheric agents, need cladding.
It can be:
plaster laid on a reinforcing mesh;
 Decorating a house from foam blocks using plaster
Decorating a house from foam blocks using plaster
facing brick or tile (in this case, it is imperative to provide an air gap between the brick and the foam block);
 Insulation can be installed between the block and the brick
Insulation can be installed between the block and the brick
ventilated facade.
 Ventilated facade layout
Ventilated facade layout
Siding, panels, corrugated board, block house, etc. can be used as a facing material.
Types of fasteners for working with foam concrete
A very important detail in the construction and decoration of a foam concrete structure (due to its fragility) is the selection of fasteners.
For fastening to foam concrete, the following types of hardware are used:
| Fasteners | Features, use |
|
|
The dowel has a wide surface thread, due to this it is securely fixed. Suitable for placing furniture, appliances, household items. |
|
|
It is used for the installation of slats, door frames, window frames. The collar prevents the dowel from falling into the hole. |
|
|
It can be plastic or metal. Holds hinged structures well. |
|
|
It is used for the installation of heavy structures. |
|
|
Gives good adhesion to foam concrete. However, a special tool is needed to mount it. |
|
|
Due to the spacer, it is securely fixed in the foam concrete. Has 4 fixing elements. |
The house, which was built according to your own design with your own hands, is the best. The structure, erected from high-quality foam concrete, will serve its owner for many years. Well, if the walls are finished correctly, the shortcomings of foam concrete will not matter.



























 Plastic dowel
Plastic dowel Metal dowel with half ring
Metal dowel with half ring Foam concrete anchor
Foam concrete anchor Anchor bolt for foundations
Anchor bolt for foundations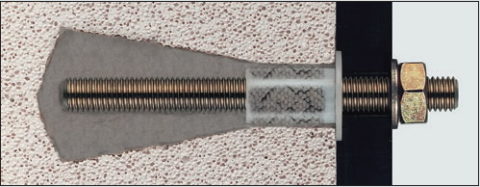 Chemical anchor
Chemical anchor Screw M4
Screw M4