Advantages and disadvantages
Oksol varnish can be used not only for wood material, it is perfect for other objects as well. This is due to its technical characteristics. There are a number of other advantages over other types of drying oil:
- provides the material with a shiny and hard protective layer;
- increased degree of water resistance;
- behaves well in adverse weather conditions;
- perfectly absorbed into any wood surface with varying degrees of porosity;
- increases the performance characteristics of wooden structures;
- does not collapse with sharp fluctuations in ambient temperature;
- fungus and mold do not act on it;
- when applied, the product evens out the surface;
- dissolves well in oil paint, which allows you to increase the volume of paint and varnish material;
- can be used as an impregnation.
In addition to the advantages, drying oil also has disadvantages:
- afraid of constant mechanical stress;
- has a pungent unpleasant odor that eats into the material and does not fade for a long time;
- highly flammable.
2 Oxol - a composition with special characteristics
Drying oil Oksol belongs to the group of semi-natural compounds used for wood protection, production and dilution of paints (oil-based, thick-grated). Let's see what this composition is made of. It contains 55% natural oil, 40% solvent (in most cases - white spirit, less often - nephras or turpentine), 5% desiccant. The composition is produced in accordance with GOST 190–78. About its provisions further.
Oksol is subdivided into two brands. The first, B, is made from hemp and flaxseed oil. This drying oil is allowed to be used for wood processing both inside and outside the premises. The second - PV, is made from soybean, camelina, sunflower, grape or corn oil. The composition is used exclusively for internal painting work. Nuance. Both brands are not suitable for use on floor surfaces.

Gosstandart 190–78 describes all the technical characteristics of Oksoli. Let's highlight the most important of them:
- acid index - up to 6 mg KOH / g (grade B); up to 8 (PV);
- drying period - 20-24 hours
- viscosity (conditional) - 19-25 s (PV), 18-22 (V).
Oksol is characterized by complete transparency, flammability and a pungent odor. The latter, after using drying oil, does not erode from the room for a long time. At Oksol factories it is packed in containers made of metal (cans of different capacities) or plastic
Important! When opening metal containers, you should use a tool that does not allow a spark to appear (do not forget about the flammability of the composition). It is not allowed to use Oksoli near working heating equipment and sources of open fire.
In case of fire of the composition, it can be extinguished by any means (asbestos cloth, steam and chemical foam, gas, fine water).
True, the cost of linen compositions is slightly higher. At the same time, Oksol of any brand guarantees obtaining a durable waterproof film on the treated surfaces that does not turn black for a long time.
Semi-natural drying oils
Representatives of this species also received their second name "oxol", technologically they are also made from oils, but subjected to oxidation, with the addition of solvents and driers. At the same time, the percentage of oil is 55%, the solvent (white spirit is most often used) is at least 40%. Due to this composition, the liquid has a rather unpleasant and pungent odor, which can last for some time even after drying.
In terms of cost, oxol is much more economically profitable than natural, but at the same time it practically does not differ in basic properties and is almost identical in appearance.
For even greater cost reduction, it is also produced from sunflower oil, but its film is much lower in characteristics than from flax oil.
Natural drying oil
According to GOST, the product in question must consist of at least 97% of natural vegetable oil (drying or semi-drying, as well as their mixtures, mainly flax oil, occasionally sunflower, soybean, hemp oil).
 During production, oils are exposed to prolonged exposure to high temperatures (at least 300 ° C) for 12 hours, the next stage is the use of an air purge.
During production, oils are exposed to prolonged exposure to high temperatures (at least 300 ° C) for 12 hours, the next stage is the use of an air purge.
As a result, we get an oily opaque thick liquid consistency of a saturated brown, and sometimes greenish color with a slight smell of the base oil.
Its main purpose is to perform the following tasks:
- priming of various surfaces: wood, metal or previously plastered;
- production and obtaining of the required consistency of light-colored thick-grated paint, putty, paste for greasing;
- as a paint composition of light color used indoors and outdoors for painting metal structures, window and door openings, flooring.
It will take no more than a day to dry completely at room temperature.
The drying oil from sunflower oil dries much worse and for complete drying it will take much longer than a day. In addition, although the film turns out to be quite elastic, it loses to the drying oils discussed above. by such indicators as:
- hardness;
- strength;
- water resistance.
Table 1. Indicators of oil varnishes.
| Indicator name | Value for drying oil | Test Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| natural | oxol | combined | |||
| linen | hemp | ||||
| 1 Color according to iodometric scale, mg I2 / 100 cm3, not darker | 400 | 1600 | 800 | 800 | According to GOST 19266 and 9.3 of this standard |
| 2 Sludge,% (by volume), no more | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | According to GOST 5481 |
| 3 Nominal viscosity according to a VZ-246 viscometer with a nozzle diameter of 4 mm at a temperature of (20 ± 0.5) ° С, s | 26-32 | 26-32 | 18-25 | 20-60 | According to GOST 8420 |
| 4 Acid number, mg KOH, no more | 6 | 7 | 8 | 10 | According to GOST 5476 |
| 5 Transparency after settling for 24 hours at a temperature of (20 ± 2) ° С | Full | Full | Full | Full | According to GOST 5472 |
| 6 Drying time to degree 3 at a temperature of (20 ± 2) ° С, h, no more | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | According to GOST 19007 |
| 7 Mass fraction of non-volatile substances,% | — | — | 54,5-55,5 | 70 ±2 | According to GOST 17537 and 9.9 of this standard |
| 8 Flash point in a closed crucible, ° С, not less | — | — | 32 | 32 | GOST 9287 |
| 9 Density at a temperature of (20 ± 2) ° С, g / cm3 | 0,936-0,950 | 0,930-0,940 | — | — | According to GOST 18995.1 |
| 10 Iodine number, mg of iodine per 100 g, not less | 155 | 150 | — | — | According to GOST 5475, section 2 |
| 11 Mass fraction of phosphorus-containing substances in terms of P2 O5,%, no more | 0,026 | 0,026 | — | — | According to GOST 7824, section 2 and 9.13 of this standard |
| 12 Mass fraction of unsaponifiable substances,%, no more | 1 | 1 | — | According to GOST 5479 | |
| 13 Mass fraction of ash,%, no more | 0,3 | 0,3 | — | — | According to GOST 5474 and 9.15 of this standard |
| 14 Resin acids | Absence | — | — | By 9.16 | |
| Note - It is allowed to use drying oil of the oxol type with other indicators of the mass fraction of non-volatile substances and conditional viscosity, provided that this brand of drying oil meets all the requirements of the standard for this group of drying oils. |
Application of drying oil
As noted earlier, the main purpose of these products is the processing of various surfaces, they are also indispensable in the production of paints. If you stop at surface treatment, then drying oil is perfect for wood. It is used both for impregnation of products and walls in general. But for external work, it is recommended to apply drying oil only for preparation before further painting. And it would be more optimal to use oxol or alkyd drying oil. Natural is better suited for interior work (due to its environmental friendliness and lack of smell) and to obtain the required consistency of paints.
Almost all types are involved in the manufacture of paints.So, natural becomes the basis for thick grated, and alkyd is an excellent basis for oil. Only composite is not used due to poor quality.
Synthetic drying oils
This type is currently considered the cheapest and this is what made it quite widely used. After all, the main component is not natural oil or resin, but their substitutes, most often - a variety of products obtained during oil refining. The composition of such drying oils can be different, since they are produced not on the basis of GOST, but according to technical conditions. They also differ significantly in appearance - the color is often light, the transparency is much higher than that of compositions based on oil. Also, the disadvantages include a very pungent odor and a longer drying process. The most common representatives are oil shale oil and, of course, ethinol.
Oil shale oil looks like a darkish liquid, as it was noted, there is a pungent odor and is a derivative of the oxidation process of shale oil with further dissolution in xylene. Dries a little over a day. Differs in good resistance to weathering. The main direction of use is dark tinting, dilution of paints to the required consistency, which are used mainly for outdoor work and sometimes indoors for painting the surfaces of their metal, wood and covered with plaster. It is forbidden to use this drying oil for application to flooring materials and household items.
Linseed oil ethinol, on the contrary, looks like a transparent liquid of lightish tone, with the same specific smell and is produced from waste obtained in the manufacture of chloroprene rubber.
Often this type is used as an additive to other drying oils, but not more than 15%. The main direction was the production of paints and primers for metal on its basis.
Table 3. Indicators of synthetic drying oils.
| Indicator name | Meaning | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| 1 Color according to iodometric scale, mg I2 / 100 cm3, not darker | 700 | According to GOST 19266 and 9.3 of this standard |
| 2 Sludge,% (by volume), no more | 1 | According to GOST 5481, section 2 |
| 3 Nominal viscosity according to a VZ-246 viscometer with a nozzle diameter of 4 mm at a temperature of (20 ± 0.5) ° С, s | 18-25 | According to GOST 8420 |
| 4 Acid number, mg KOH, no more | 12 | According to GOST 5476 |
| 5 Transparency after settling for 24 hours at a temperature of (20 ± 2) ° С | Full | According to GOST 5472 |
| 6 Drying time to degree 3 at a temperature of (20 ± 2) ° С, h, no more | 24 | According to GOST 19007 |
| 7 Mass fraction of non-volatile substances,%, not less | 50 | According to GOST 17537 |
| 8 Flash point in a closed crucible, ° С, not less | 32 | According to GOST 9287 |
Application of drying oil
The order of work
- Before starting work, it is required to clean and degrease the surface to be treated.
- If a composition based on semi-natural drying oil is used in the work, then application is recommended only on a dry surface.
- Using drying oil and paint and varnish products based on it, it is recommended to apply with a brush, roller or paint spray.
The average working consumption when using semi-natural drying oil is from 150 to 200 g. per cubic meter. As already noted, the drying time with natural drying will take no more than a day.
How to reduce paint consumption?
The use of a primer mixture significantly reduces material costs when painting any surface: smooth, textured or embossed. The primer also, on the one hand, ensures - strong adhesion of the oil paint to the base, and on the other hand, facilitates the removal of the coating if necessary in the future.
This is especially true for walls or ceilings made of concrete (cleaning them from oil-based coatings is a big problem) and for wooden surfaces. If you paint an untreated wood, the composition will penetrate into the porous structure so deeply that it will be almost impossible to remove it (before restoration, for example) without damaging the natural material.
You should not buy very cheap oil paints.Often they have too low covering power, which leads not only to additional costs, but also to an unsatisfactory finish, as well as an increase in the time spent on work.
Odorless oil paint for walls, is such an option possible?
How to dilute oil paints?
Enamel consumption pf-115
The most popular is PF-115 pentaphthalic enamel. The film formed by this enamel has a homogeneous structure, does not delaminate. The average consumption is 110-130 g / m2. on a single layer coating. Depending on the color used, 1 kg of enamel is enough to paint a surface with an area of: White - 7-10 m2, black - 17-20 m2, blue / light blue - 12-17 m2, green - 11-14 m2, brown - 13-16 m2 , yellow / red - 5-10 m2. The enamel can be diluted with a solvent or white spirit or their mixture 1: 1. The paint is applied with a brush or roller in several layers, the drying time of each layer is about a day.
Consumption of acrylic-based water-dispersion paint
Acrylic-based water-based paints are used both indoors and when working with facades. They have a matte appearance, tinted with color pastes. They give a large palette of colors that do not fade in the sun. The manufacturer indicates the consumption of up to 8 m2 per 1 liter, but in practice the spreading rate is usually 115 g / m2 (i.e. 1 liter per 6-7 m2). The fact is that the manufacturer indicates the given consumption rates in a thin layer, on a smooth surface, under ideal conditions. In practice, a lot depends on the absorbency and roughness of the surface. The method of application also matters. For example, when using a spray gun, less paint will go away than when using a roller. Again, a roller is more economical than a brush. Assume that your paint will take 5-15% more than indicated on the package. Apply 2-3 coats of acrylic paint on a clean, dry surface. Moreover, a high-quality composition will overlap the color of the base in 2 layers, in a cheaper version you will need 3 layers. Thus, cheap paint can be more expensive in practice.
SAFETY REQUIREMENTS
3.1. Oksol varnish is a toxic and flammable liquid, dangerous at elevated temperatures, due to the properties of its constituent solvents and oils.
The characteristics of the toxicity and fire hazard of the solvents that make up the oxol drying oil are given in table. 2.
table 2
|
Name solvent |
Maximum permissible concentration in the air of the working area |
Temperature, ° С |
Concentration limits of ignition,%, by volume |
Class dangers |
||
|
industrial premises, mg / m3 |
FLASH |
self-ignition changes |
LOWER |
upper |
||
|
White spirit (nephras C4-155/200) (GOST 3134) |
300 |
33 |
270 |
1,4 |
6,0 |
4 |
|
Nefras S4-150/200 |
100 |
31 |
270 |
1,4 |
6,0 |
4 |
|
Turpentine (GOST 1571) |
300 |
34 |
300 |
0,8 |
_ |
4 |
Indicators of fire and explosion hazard of drying oil oxol are given in table. 3.
Table 3
|
Product name |
Temperature self-ignition |
Flash point in a closed crucible, ° С |
Open crucible temperature, ° С |
Temperature the limits ignition, ° С |
||
|
changes, ° С |
FLASH |
ignited changes |
LOWER |
upper |
||
|
Drying oil oxol (solvent - white spirit (nefras C4-155/200)) |
254 |
32 |
48 |
55 |
36 |
70 |
|
Drying oil oxol (solvent - nefras C4-150/200) |
244 |
35 |
46 |
52 |
34 |
73 |
TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
2.1. Oksol varnish must be manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard for recipes and technological regulations.
(Modified edition, Amendment No. 1).
2.2. For the production of drying oil oxol, the following types of raw materials are used: for drying oil oxol grade B:
industrial linseed oil in accordance with GOST 5791;
hemp oil in accordance with GOST 8989 for technical purposes;
Official edition
★
Reprinting prohibited
Standards Publishing House, 1978 IPC Standards Publishing House, 2001
for drying oil oxol grade PV: camelina oil (technical) in accordance with GOST 10113; technical grape oil;
vegetable oils unsuitable for direct consumption or for industrial processing into food products according to sanitary indicators or acid number;
sunflower oil in accordance with GOST 1129 and other normative and technical documentation (NTD) with an acid number of not more than 15 mg KOH / g;
soybean oil in accordance with GOST 7825 and other NTD; safflower oil;
unrefined corn oil in accordance with GOST 8808.
Oils used in the production of oxol varnish must contain phosphorus-containing substances determined according to GOST 7824, no more than 0.026% in terms of P205 or not more than 0.3% in terms of stearooleolecithin.
The use of edible vegetable oils suitable for food purposes for the manufacture of drying oil oxol grade PV is not allowed.
Desiccants:
naphthenate in accordance with GOST 1003, fused oil, fatty acid, resinates (lead, manganese, cobalt, lead-manganese, lead-manganese-cobalt). Solvents:
white spirit (nephras C4-155/200) in accordance with GOST 3134; gum turpentine in accordance with GOST 1571; nefras C4-150/200 according to NTD; synthetic substitutes for vegetable oils:
light oil-polymer resins such as pyroplast, pyrene according to the current normative and technical documentation.
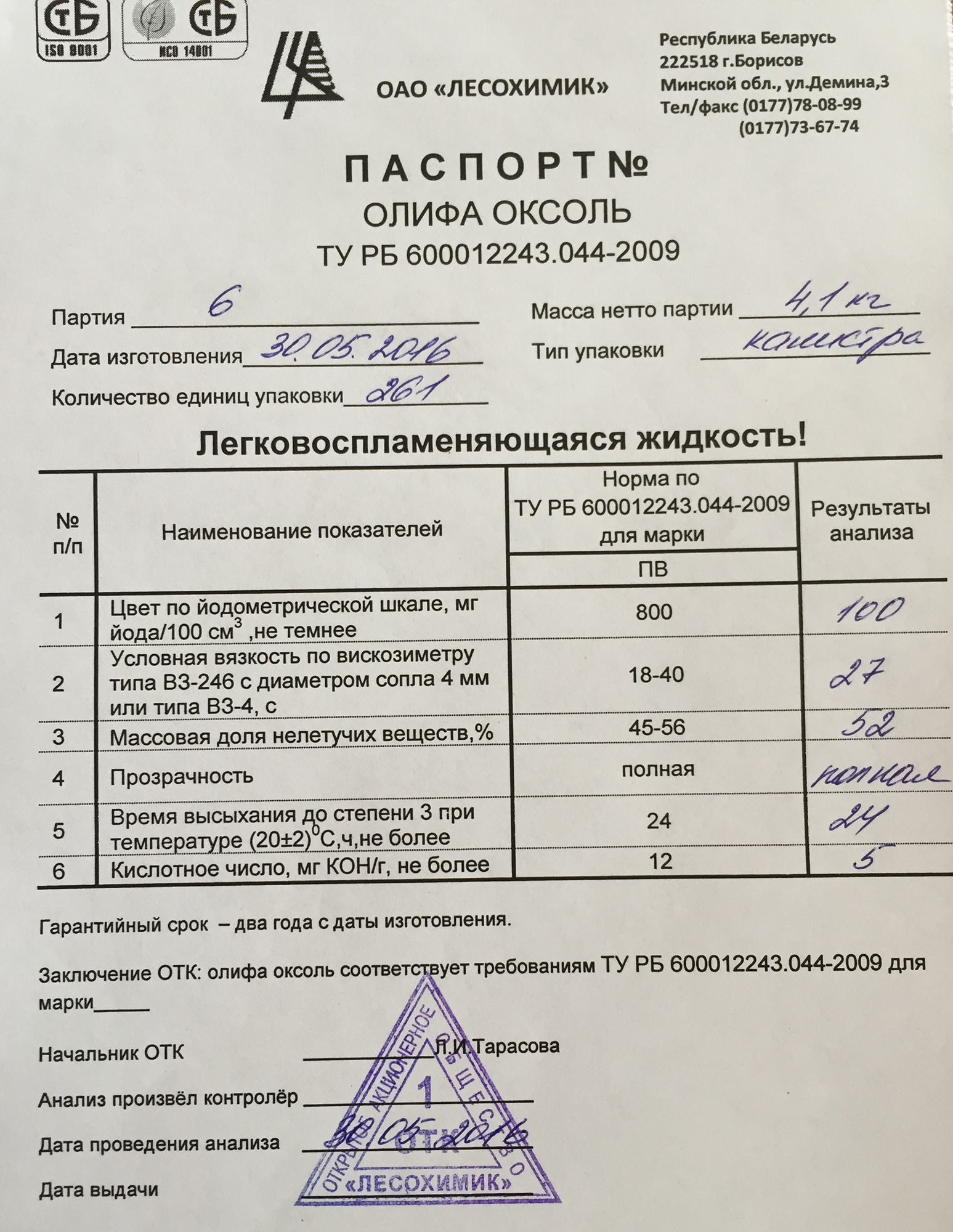
2.3. Oksol varnish must comply with the standards specified in table. 1.
Table 1
|
Indicator name |
Norm for brands |
|
|
V |
PV |
|
|
1. Color by iodometric scale, mg |
||
|
C / YO cm3, not darker |
800 |
800 |
|
2. Nominal viscosity according to the viscometer |
||
|
type VZ-246 (or VZ-4) with a nozzle diameter |
||
|
4 mm at a temperature of (20.0 ± 0.5) ° С, s |
18-22 |
19-25 |
|
3. Acid number, mg KOH / g, no more |
6 |
8 |
|
4. Mass fraction of non-volatile substances,% |
54,5-55,5 |
54,5-55,5 |
|
5. Sludge by volume,%, not more |
1 |
1 |
|
6. Transparency |
Under |
shaya |
|
7. Flash point in closed |
||
|
crucible, ° С, not lower |
32 |
32 |
|
8. Drying time to degree 3, h, at |
||
|
temperature (20 ± 2) ° С, no more |
20 |
24 |
Notes:
1. For drying oil oxol grade PV from camelina oil, a color of no more than 1800 is allowed, from soybean oil - no more than 1100.
2. For drying oil oxol grade B from hemp oil, a color of no more than 1100 is allowed.
3. When using sunflower oil with an acid number 8 to 15 mg KOH / g is allowed for drying oil oxol grade PV acid number not more than 10 mg KOH / g.
4. For varnish of PV brand from vegetable oil mixed with petroleum resin, the mass fraction of a film-forming substance (57 ± 2)% is allowed with mandatory compliance with the requirements for the "viscosity" indicator.
Consumption of composition on wood
- Preparatory work. The surface must be cleaned of dust and degreased, then completely remove traces of moisture;
- Application. For DIY processing, a brush with soft bristles is best suited; for large volumes of work, you may need a roller or spray gun. It is necessary to apply drying oil generously enough, otherwise the wood fibers will not be able to be completely saturated. For deeper impregnation, hot drying oil is used. Usually, 130 ml of drying oil is enough to treat one m2 of surface. The number of layers may vary, most often a 2 - 3 layer coating is sufficient;
- Drying. The optimal conditions for quick drying of drying oil are considered to be an air temperature of 20 degrees Celsius and the absence of drafts. On average, wood impregnated with linseed oil dries completely after 24 hours.
Good to know: residues of drying oil and used brushes must be disposed of, as these materials have a high degree of fire hazard. Keep drying oil residues away from electrical appliances and open flames.
Oil-based enamels and paints often have too thick consistency, it is difficult to paint anything with such a composition. In this case, the paint must be diluted by adding the required amount of drying oil until the composition acquires the desired consistency. Among other things, this technique can significantly reduce paint consumption and save money.
3 Application of semi-natural drying oil - how to apply the composition?
Since Oxol has a pungent odor and belongs to the group of toxic oil compounds, we adhere to some mandatory rules when working with it. Firstly, we carry out the planned painting activities in a respirator, hand-protecting rubber gloves and thick overalls. In this case, the danger of poisoning with vapors of drying oil and the ingress of its drops on the skin is significantly reduced. If, nevertheless, Oksol got on human skin, you must immediately wipe it off with a clean cloth.After that, thoroughly wash the damaged area with soapy water.

Secondly, it is allowed to work with linseed oil indoors only on condition that they have efficiently functioning ventilation. Directly the scheme of processing wooden structures by Oksolya looks like this:
- 1. We clean the product from the old coating (varnish, paint, and so on). We remove grease stains, dust, and other dirt from the surface.
- 2. Dry the cleaned structure. If there are significant roughness on its surface, we additionally grind the wood.
- 3. We open the jar with Oksolya. Mix the composition well. If you use a container from which the composition was taken earlier, add a little white spirit to the jar. Then we can easily stir the thickened mass.
- 4. Using a brush or a roller, apply drying oil to the product. We make the layer not very thick.
- 5. We are waiting for 24 hours. Then we re-paint the product with Oksolya. If it is necessary to apply the third layer, we again wait a day. And only after that we once again process the surface with the described composition.
It is recommended to work with the use of oil compositions at an air temperature above 15 ° C, optimally at 22 °. That's all the wisdom of using Oksoli. Good luck!
The choice of drying oil
Before you buy drying oil, you need to take a good look at what is in the container. First, it should be determined by the color, whether it corresponds to the declared type of product. In addition, you should carefully read the description of the components and check whether it complies with GOST if you buy a semi-natural or natural drying oil. They will have a certificate of conformity, and for a composite one - only hygienic
And in general, with the use of the latter, you should be careful, since it is toxic and it is important to note that it should not contain residues of oil (the so-called fuse) and osprey (oil refining residues), otherwise the drying process will become endless. And finally, it should be noted - carefully examine the liquid for homogeneity, sediment or mechanical particles should not be present
PACKAGING, LABELING, TRANSPORTATION AND STORAGE
6.1. Packing - in accordance with GOST 9980.3, group 16.
6.2. Packaging marking - in accordance with GOST 9980.4 without color indication, indicating the classification code "Oksol oil, 3313" and a hazard sign (class 3) in accordance with GOST 19433.
6.3. Marking of consumer packaging intended for retail trade - according to GOST 9980.4 without color indication, with the inscription "Keep away from fire"
Purpose, method of application, precautions when handling oxol drying oil for retail are indicated in the appendix
6.1-6.3. (Modified edition, Amendments No. 1, 2).
6.4. Transport markings - in accordance with GOST 14192 with indication of the manipulation sign "Protect from heating".
(Modified edition, Amendment No. 1).
6.5. Transportation of drying oil oxol - according to GOST 9980.5.
6.6. Storage of drying oil oxol - according to GOST 9980.5.
It is allowed to store the drying oil oxol in steel tanks in accordance with GOST 1510, subgroup 6, located in open areas, in conditions excluding the ingress of atmospheric precipitation and dust into them.
1 Drying oils - different in properties and composition
Drying oil is a special film-forming composition made in the form of a thick transparent liquid. It is used to protect wooden products and surfaces from parasitic insects, decay, and the negative effects of natural factors. Thus, drying oil increases the service life of wood structures. Also, its use allows you to reduce the consumption of varnish for the treatment of wooden surfaces.

The compositions of interest to us are made from various oils, to which solvents and desiccants are added - compounds that include strontium, lead, iron, lithium, cobalt, and other chemicals. elements. All drying oils are divided into:
- natural;
- alkyd;
- combined;
- synthetic;
- semi-natural.
Natural composition 97% consists of sunflower or linseed oils, which are heat-treated. The cost of such drying oils is high. Now they are rarely used.Usually they are used to dilute paints and varnishes. Any wooden surfaces can be treated with a natural composition, provided that they are indoors. Linen compounds are also used for the production of special lubricating pastes, putties, dilution of thickly grated paints and putties.
Semi-natural and combined drying oils are more affordable. They differ from natural compositions in that volatile solvents (for example, white spirit) are necessarily added to them. The most famous semi-natural composition is Oksol. We'll look at it in the next section. Alkyd drying oils are made from solvent-diluted and oil-modified resins. And synthetic compounds, which are often called composite, are made from rubber processing products, materials from the oil and coal industries. They do not contain natural oils. Such drying oils are not used indoors due to their increased toxicity. The only plus of synthetic solutions is the low price.
REFERENCE REGULATORY AND TECHNICAL DOCUMENTS
|
Designation of NTD referenced |
Item number |
Designation of NTD referenced |
Item number |
|
GOST 12.1.004-91 |
3.2 |
GOST 7825-96 |
2.2 |
|
GOST 12.1.044-89 |
5.8 |
GOST 8420-74 |
5.3 |
|
GOST 12.3.005-75 |
3.2 |
GOST 8808-91 |
2.2 |
|
GOST 12.4.009-83 |
3.2 |
GOST 8989-73 |
2.2 |
|
GOST 12.4.011-89 |
3.4 |
GOST 9980.1-86 |
4.1 |
|
GOST 1003-73 |
2.2 |
GOST 9980.2-86 |
5.1 |
|
GOST 1129-93 |
2.2 |
GOST 9980.3-86 |
6.1 |
|
GOST 1510-84 |
6.6 |
GOST 9980.4-86 |
6.2; 6.3 |
|
GOST 1571-82 |
2.2; 3.1 |
GOST 9980.5-86 |
6.5; 6.6 |
|
GOST 3134-78 |
2.2; 3.1 |
GOST 10113-62 |
2.2 |
|
GOST 5472-50 |
5.7 |
GOST 14192-96 |
6.4 |
|
GOST 5476-80 |
5.4 |
GOST 17537-72 |
5.5 |
|
GOST 5481-89 |
5.6 |
GOST 19007-73 |
5.9 |
|
GOST 5789-78 |
5.4 |
GOST 19266-79 |
5.2 |
|
GOST 5791-81 |
2.2 |
GOST 19433-88 |
6.2 |
|
GOST 5955-75 |
5.4 |
GOST 25336-82 |
5.7 |
|
GOST 7824-80 |
2.2 |