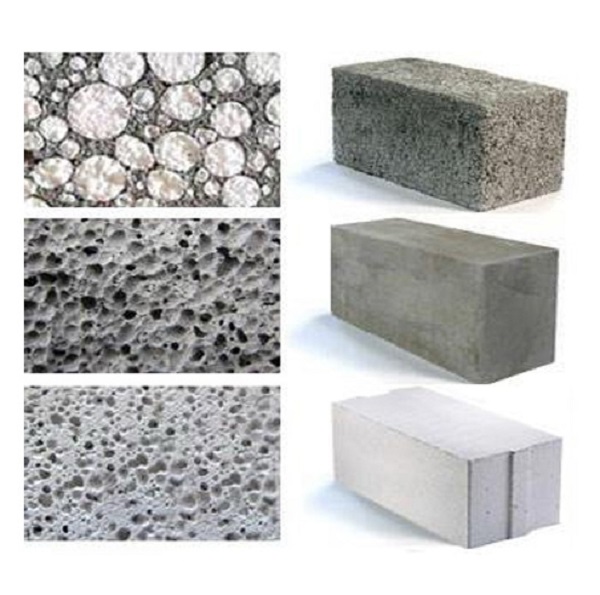
What is the difference between a foam block and a gas block - we compare the characteristics
Comparison of the characteristics of materials will help answer the question of which foam block or gas block is better. Reviews of private developers and professional builders allow you to analyze the main properties and main characteristics of building materials:
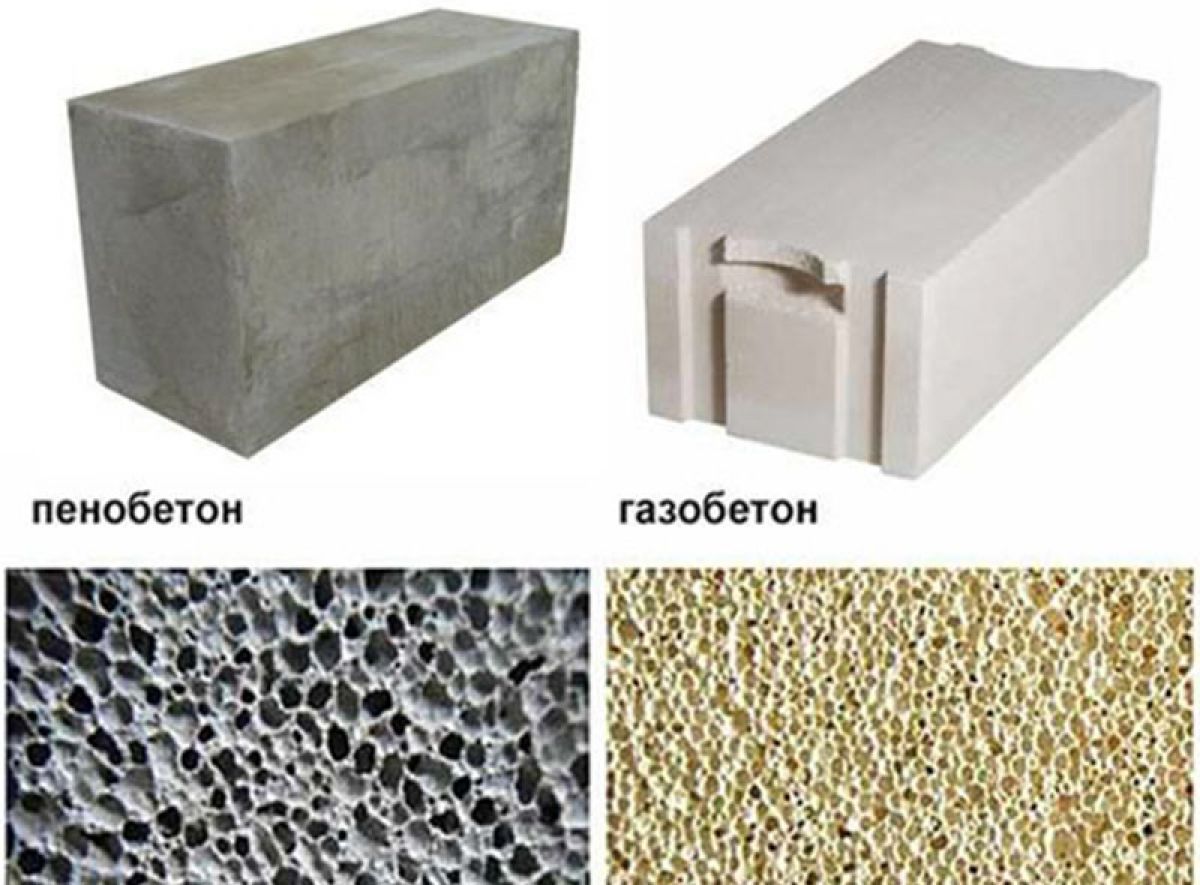
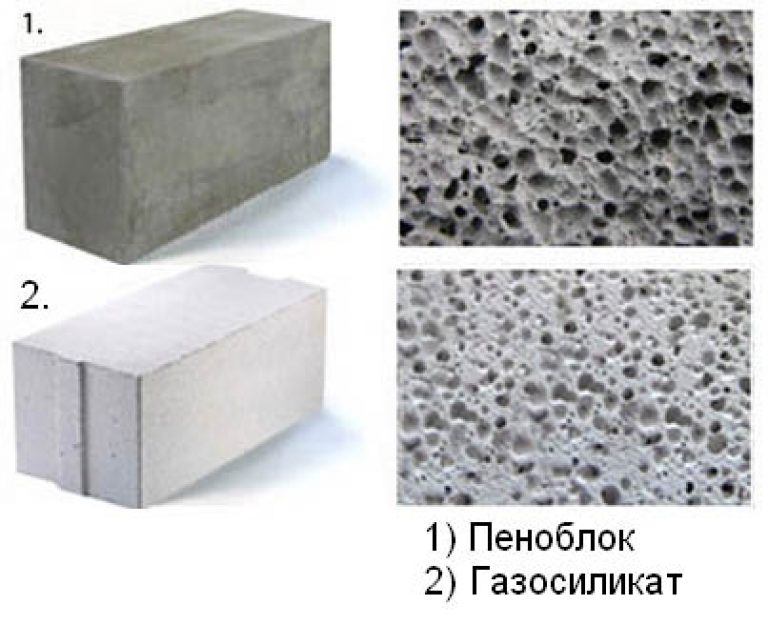
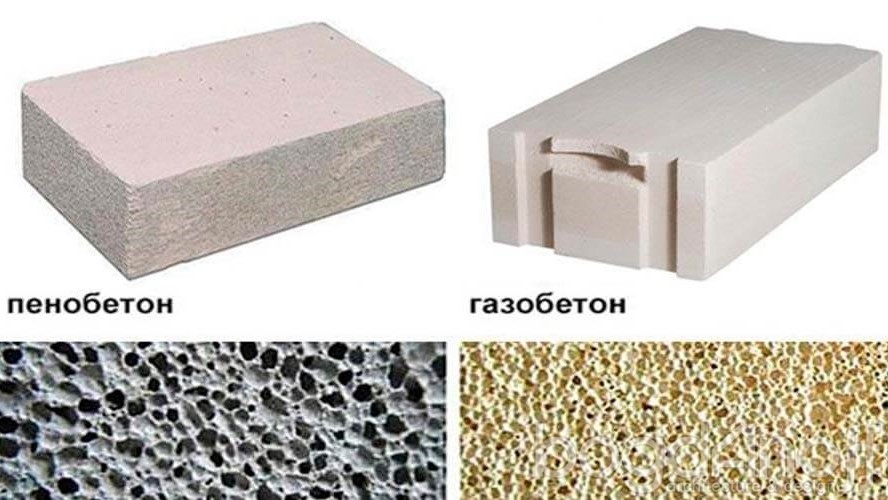
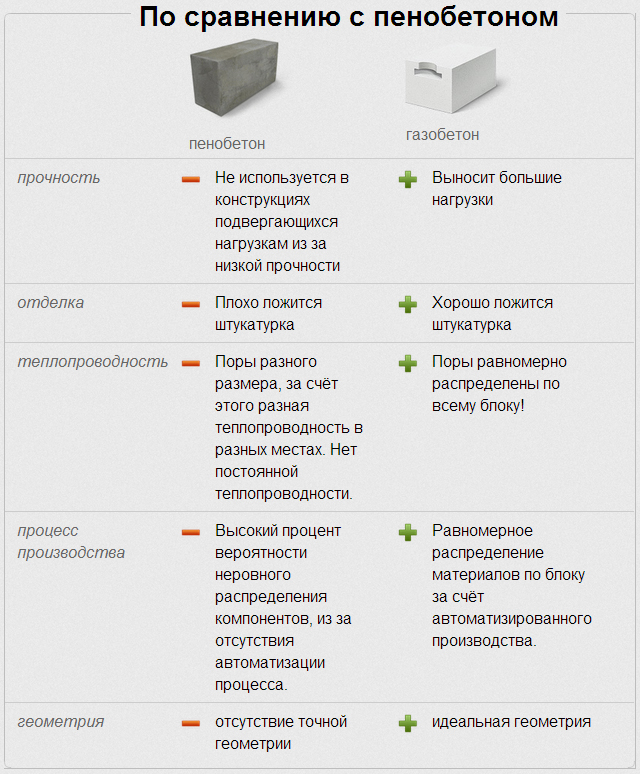
size and location of air cavities. For foam concrete products, an irregular shape is characteristic, as well as an uneven distribution of cells with significant size deviations in the range from 1 to 5 mm. The aerated concrete mass is characterized by the correct shape of air inclusions, the diameter of which is about 1 mm;
Foam blocks are not perfect
- density. Answering the question what is lighter aerated concrete or foam concrete, it should be noted that the density and, accordingly, the mass of each material are the same. The weight of one cubic meter of foamed concrete corresponds to the weight of one cube of aerated concrete composite and is 350-1250 kg. Weight is determined by the grade of the material;
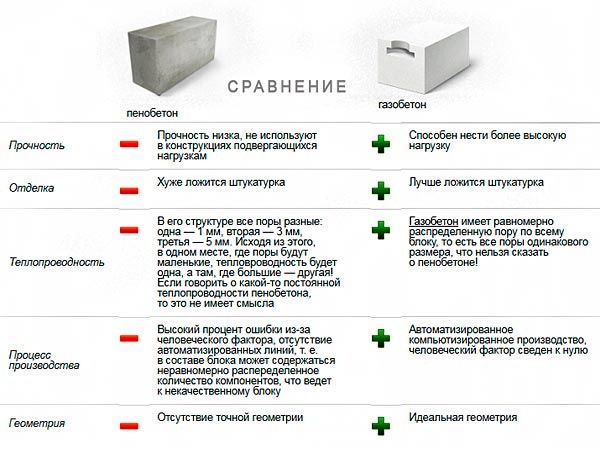
- strength. Reviews of gas blocks and foam blocks confirm that both materials have insufficient strength when exposed to bending moments, although they normally perceive compressive loads. The strength characteristics of composites are determined by the quality of the ingredients used and the characteristics of the production technology;
- duration of curing. Aerated concrete blocks immediately after manufacturing have a maximum safety margin, which slightly decreases during long-term storage. In foam block products, the increase in strength properties occurs gradually, reaching a maximum value by the end of the fourth week after production;
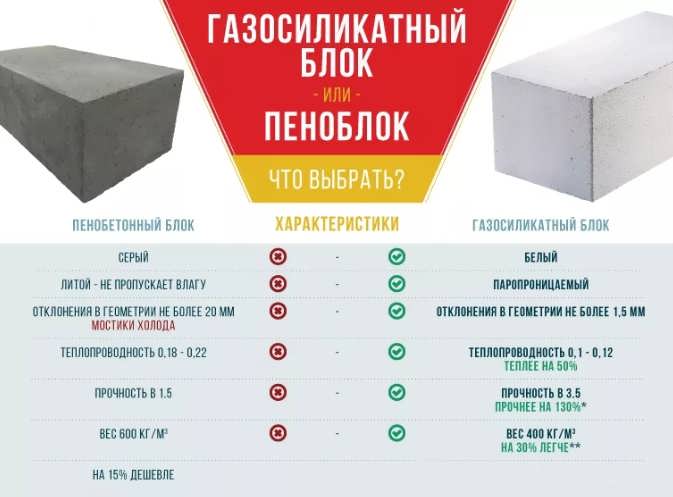
- dimensional accuracy. Aerated blocks, obtained by cutting a solid mass, are characterized by precise geometry and minimal tolerances. This allows the binder to be applied in a thin layer, while reducing heat losses through the cold bridges. The deviation of the dimensions of foam concrete products reaches 3-4 mm, which is reflected in the thickness of the seam;
- ability to conduct heat. The thermal insulation performance of composites is related to density. With equal specific gravity, materials differ in different thermal conductivity coefficients. Gas-filled composites retain heat better in the room compared to foam concrete building materials.
It is also necessary to note the fire safety of materials, as well as the absence of a negative impact on human health.
Foam block concept
|
ROOM PARAMETERS: |
|
| Wall height (m): | |
| External walls: | |
| Density class: | |
| Wall length (perimeter) (m): | |
| Wall (block) thickness *: | 100 mm. 150 mm. 200 mm. 250 mm. 300 mm. 375 mm. 400 mm. 500 mm. |
| Area of door and window openings (m2): | |
|
PARTITIONS: |
|
| Density class: | |
| Partition wall length (perimeter): | |
| Partition wall thickness: | 50 mm. 75 mm. 100 mm. 150 mm. 200 mm. |
| Area of door and window openings (m2): | |
| Total for the premises: | |
| APPROXIMATE VOLUME OF BLOCKS: m3 | |
| VOLUME OF PARTITIONS: m3 |
|
| QTY BAGS OF GLUE **: PCS. |
|
| * - wall thickness according to the project ** - glue consumption: 25kg per 1m3 of aerated concrete blocks with an adhesive layer thickness of no more than 3mm and a block size of 600x375x250. |
| Choice of block size, LxHxD | 600x250x500600x250x375600x250x300600x250x250600x200x500600x200x375600x200x300600x200x250600x200x150600x250x100600x250x75600x250x150600x200x100600x200x75625x250x500625x250x375625x250x300625x250x250625x200x500625x200x375625x200x300625x200x250625x200x150625x250x100625x250x75625x250x150625x200x100625x200x75625x200x400625x250x400 |
| The total length of the walls, meters | |
| Average wall height, meters | |
| Total area of window and door openings, m2 | |
| Number of blocks: |
m3 |
PCS. |
| The number of blocks is a multiple of a pallet: |
m3 |
PCS. |
| Number of blocks on a pallet: | ||
| Number of pallets: |
To understand for yourself the difference between foam blocks and gas blocks, you need to read their characteristics. What is the difference between foam concrete and aerated concrete? Aerated concrete is a simple material, but high-tech equipment is required to create it. During processing, it can pass through an autoclave, in which the material is sintered at high temperatures.It can also be performed by the non-autoclave method. The first one will be much stronger. The components for the manufacture are the same:
- Portland cement;
- water;
- lime;
- sand;
- aluminum powder.
By combining substances, you can change the characteristics of foam concrete and aerated concrete blocks. Products made of foam concrete or aerated concrete are made in about the same way. The foamed mass, which has acquired initial strength, is cut into blocks and dried in the open air or in a special device. Which is better: a gas block or a foam block?
What is the difference between a foam block and a gas block? One is created using chemical reactions, the other is created using special foam. These materials can be made in a special installation or using a conventional concrete mixer. The solution is expanded into molds, from which ready-made blocks are taken out. The forms themselves can be:
- plywood;
- metal.
Plywood are cheap products, but they have drawbacks. They quickly get wet and fail after a month or two of work. Therefore, they are not suitable for the manufacture of blocks on an industrial scale. For metal molds, 4 mm thick metal is used, which is cut with a laser. And such products have disadvantages.
The poured mass in the form of a large slab is cut with saws into pieces of the desired size. The equipment is expensive, dust and crumbs remain during operation. It can be 0.5% of the total mass of the used solution. The difference between the gas block and the foam block is almost imperceptible at first glance. Both materials are very similar in appearance.
But some benefits can be found in each of them. Aerated concrete blocks are light and easy to process. This material is very easy to process: cut, drilled even with hand tools. Blocks are used to build walls for a bathhouse and a house. It is easy to make grooves in the walls of a house made of aerated concrete for placing water and sewer pipes, laying electrical wiring.
Comparative characteristics
The fact is that to answer the question: how does aerated concrete differ from foam concrete - at first glance, it is quite simple - in composition. The building codes indicate the characteristics for the entire group of aerated concrete, which means that the gas block, that of the foam block, can be made the same in strength and other indicators.
However, with a detailed study of the question: what is the difference between aerated concrete and foam concrete, it turns out that foam blocks are universally produced only by an autoclave-free method. While most of the aerated concrete blocks on the market are autoclaved. With such a separation, as described earlier, products that harden without the use of an autoclave are lost.
When looking at the comparative characteristics of strength, it should be borne in mind that, by and large, it is the autoclaved gas block and the unreinforced foam block of autoclave production that are compared. In this case, the foam block will, of course, lose.
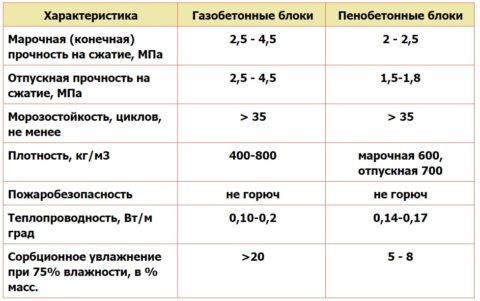 Comparative table of characteristics
Comparative table of characteristics
But, gas blocks can also be made by the non-autoclave method and using fiber reinforcement. In this case, the differences between aerated concrete blocks and foam blocks will be minimal.
Physical and mechanical characteristics of non-autoclaved gas blocks:
| Product brand | D600 | D500 |
| Compressive strength class | B2 - B2.5 | B1.5 - B2 |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient, W / m ºС | 0,13 -0,14 | 0,1 — 0,12 |
| Shrinkage, mm / m, no more | 3,0 | 4,0 |
| Frost resistance | F 50 | F 50 |
| Water vapor permeability, mg / m h Pa | 0,16 – 0,18 | 0,20 – 0,25 |
At the same time, if reinforcing fibers are added to the foam concrete, the strength characteristics will increase by at least one and a half times, and the block made in this way can even surpass autoclaved gas blocks during testing (see the video in this article).
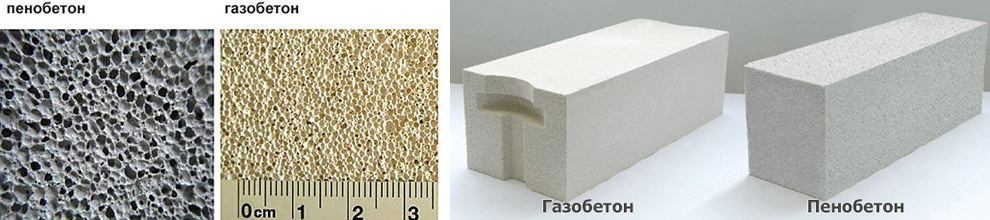
Another thing that differs aerated concrete from a foam block is a cellular structure:
- In the gas block, the pores have the same diameter, and by hardening in an autoclave installation, filling is obtained uniform over the block section.
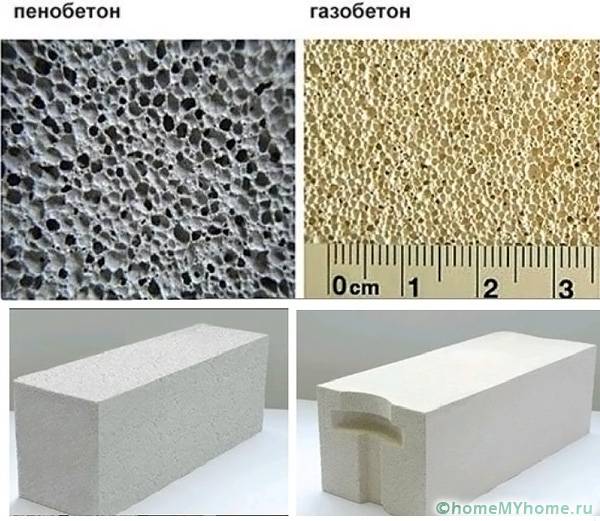
- And in foam concrete, hardening in natural conditions, firstly: there is a state when, under the action of gravity forces, light bubbles rise, and the porosity is accordingly distributed over the section from bottom to top. Secondly, the structure of the foam itself is heterogeneous, bubbles of different sizes may come across - this is clearly seen in the photo below.
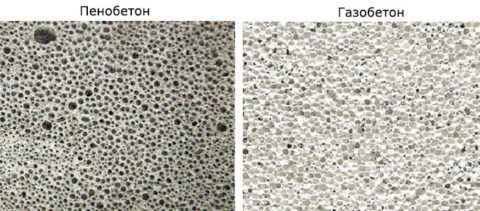 Differences in porous structure, appearance.
Differences in porous structure, appearance.
So, it turns out that the differences in the technical characteristics of building materials from foam and aerated concrete are minimal.
In general, they are both:
- fire resistant;
- environmentally friendly;
- vapor permeable (favorably affects the microclimate in the room);
- thermal insulation qualities during the operation of the building will reduce the cost of heating it.
How much do foam blocks and gas blocks cost?
The cost of building materials is an important argument in favor of one type or another. Especially when it comes to similar specifications. But you need to understand what to compare. There will be a strong price bias when comparing products of different quality. Handicraft foam blocks using outdated technology will be significantly cheaper than gas blocks from a plant with advanced equipment. But this approach will not be beneficial, since the savings mean the loss of quality.
We will analyze the price of certified products from large manufacturers with a good reputation. The price of blocks depends on the grade of strength and size.
In Moscow and the Moscow region, the cost of one wall foam block of the D600 brand and the size of 600x300x200 from different manufacturers ranges from 100-115 to 160 rubles. At the same time, 1 m3 costs 2900-3750 rubles.
The price of heat-insulating and structural aerated concrete wall blocks of the D500 brand and the size of 600x300x200 in Moscow and the region starts from 110-112 rubles. per piece, and the upper limit is at around 167-175 rubles. per piece 1 m3 contains 27.8 blocks, respectively, the average price of 1 m3 of gas blocks is 3058-3700 rubles.
The price of blocks in remote regions (Siberia, the Far East), like other building materials, will, on average, be 1.5 times higher than in the Central region. In addition, during construction, thicker walls must be laid to increase thermal insulation.
The budget also needs to include the costs of paying for masonry services. On average, 1 m2 of a wall made of cellular blocks costs 1500-1700 rubles. The price list of contractors indicates the cost per cubic meter, which varies from 2,400 to 4,000 rubles.
Advantages and disadvantages of the gas block
The advantages of aerated concrete include the following:
- due to its low weight, the product has sufficient strength;
- simple processing, the material can be processed using any available tool (saw, milling cutter);
The video shows an example of cutting a module
- good thermal insulation, due to low thermal conductivity, the material retains heat in winter, and in summer it does not allow heat to penetrate inside the house;
- fire safety, aerated concrete modules are classified as I and II degrees of fire resistance;
- high soundproofing qualities (depends on the thickness of the module);
- high environmental friendliness, the material does not emit harmful toxins;
- high biological resistance, the material is not susceptible to the formation of mold, rot and mildew.
The photo shows a finished house made of aerated concrete
 The advantages of aerated concrete include good thermal insulation.
The advantages of aerated concrete include good thermal insulation.
Of the shortcomings of the building material, it is worth noting:
- high water absorption, as a result of which the plaster on the front part simply disappears;
- difficult to work for bending, the base of the house must be strong and not shrink, otherwise the structure will begin to crack and collapse;
- in the case of fastening some additional elements, a problem may arise, which will help to solve special fasteners;
- metal elements installed in the wall will begin to oxidize over time;
Characteristics of gas blocks
The porosity of aerated concrete blocks arises from the reaction of a gas generator - aluminum powder with lime under the action of high temperature and pressure in an autoclave furnace.
p> In the course of the reaction, a gas arises, which, coming out to the outside, forms a network of microcracks and bubbles in the body of the block. The resulting cells are open and allow air to pass freely, which has a positive effect on the vapor permeability of the material.
Aerated concrete composition
- Portland cement grade not lower than M400;
- Fine sand;
- Lime;
- Water;
- Aluminum powder or paste;
- Chemical additives and plasticizers (if necessary).
Advantages of aerated concrete blocks
The advantages of aerated concrete include the following properties:
- Durability - the manufacture is autoclaved, which guarantees high strength and longevity;
- Lightness - the presence of voids in the structure of the block makes it noticeably lighter in comparison with ordinary concrete;
- Ease of processing - aerated concrete does not require special tools for additional processing - cutting, drilling, sawing, etc.;
- Low thermal conductivity - gas blocks keep heat well, the room heats up quickly and cools slowly;
- Fire resistance - the blocks can withstand up to 8 hours of exposure to fire, while maintaining their technical characteristics;
- Sound insulation - voids in the body of the block absorb noise;
- Biostability - aerated concrete is not susceptible to damage from fungus, mold, insects and rodents;
Cons of aerated concrete
Among the negative properties, poor moisture resistance stands out. Gas, during the manufacture of blocks, formed a network of microcracks in the block structure, which absorb and conduct water. Therefore, during construction, it is necessary to think carefully about the waterproofing of the structure.
Also, developers note low flexural strength and difficulty in securing additional elements. To hang a shelf or cabinet on a gas block wall, you need to use special fasteners.
Building a house
When the plan of the future house is ready, the question arises: which gas blocks or foam blocks is better? Before you start doing something, you need to understand that the strength of the structure will depend on the quality of the selected materials and the type of foundation pouring. Experts recommend pouring the foundation using reinforced concrete. This type of foundation will allow you to build a house from any material (foam block, gas block) that will meet all operational characteristics. If you do not know what to build your cottage or country house from, we advise you to study the recommendations of specialists. Recommendations:
The strength of the material. Aerated concrete is considered the most durable product, if you want to increase the service life of the future structure, use gas silicate modules;
The video shows the comparative characteristics of the modules
- Application of modules. The foam block is used for the construction of partitions, fences and load-bearing wall structures located above the 3rd floor; The gas block is used for the construction of load-bearing walls, partitions, the construction of high-rise buildings and the filling of frame voids;
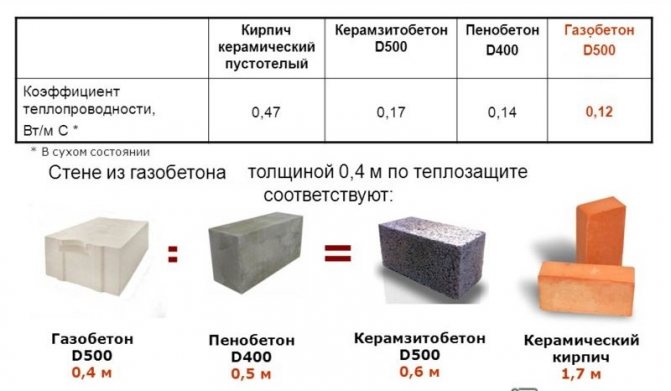
- Thermal conductivity coefficient. Aerated concrete is twice as warm as foam concrete, with the same wall thickness. And by completing the device of a ventilated facade, you can create a favorable climate inside the building;
- The cost of the modules. 1 cubic meter of foam concrete will cost $ 22, and aerated concrete $ 31;
Choosing a building material is not easy, because any mistake made is costly. If you still have doubts, we advise you to read the reviews of the owners of already built houses from these modules or watch a video of what to build a house
Remember, the main thing is to purchase certified products from a manufacturer with a good reputation.
Gas block and foam block: what is the difference
It may seem that these types of aerated concrete have a set of almost identical properties. However, there is a difference between them and it is significant. Let's compare the most significant characteristics.
Module geometry
The better it is, the easier it is to style.So, flat structures can be mounted using special glue. The seam thickness is only 2-3 mm, which allows you to completely get rid of cold bridges. At the same time, the speed of work with geometrically correct elements is much higher. Finishing costs are also reduced as no alignment is required. Foam blocks are noticeably different in this indicator. The error of their sides is 3 mm and more, for gas blocks it is no more than 1 mm.
Insulating properties
Both varieties are filled with air bubbles, but their number is not the same. Aerated concrete is more porous, therefore, it retains heat better and drowns out noise. However, the differences are small. In both cases, structural and insulating models are available. The latter are intended for insulating buildings made of "colder" materials, for example, cinder blocks.
How the gas block differs from the foam block in composition
Aerated concrete block includes the following ingredients:
- Portland cement marked M400, the concentration of which reaches 50% of the total volume of the mixture;
- sand fraction based on quartz, which is an aggregate and is introduced in the amount of 30–40%;
- lime in the amount of 10–25%, participating in the chemical reaction of gas formation;
- aluminum powder, which promotes vaporization and is introduced in an amount of not more than a tenth of a percent;
- calcium chloride and calcium silicate introduced into the working mixture as special additives.
The amount of ingredients introduced into the foam concrete products is determined depending on the required specific weight of the blocks. The simplified technology makes it possible to obtain products with a density of 0.35–1.25 t / m³.
Cement brand M500
The mixture contains the following components:
- cement grade M500. Added as a binder;
- medium coarse sand. Replacement of sand with expanded clay is possible;
- foaming additives. Their number determines the porosity of the product.
The amount of sand is three times the volume of cement for expanded composites with increased bulk density.
What is the difference between a gas block and a foam block according to manufacturing technology
To decide which material to use for construction - aerated concrete or foam block, consider the manufacturing methods:
- aerated concrete composites are made only in production conditions using special equipment. The manufacturing technology of products provides for high-temperature treatment of the concrete composition in closed tanks, in which the performance properties are achieved under the influence of increased pressure. After hardening, the formed aerated concrete mass is cut into products of various sizes and shapes, which makes it possible to expand the range of products;
- the manufacture of foamed composites does not require the use of special equipment and can be carried out in the conditions of small enterprises, as well as by private owners. The working mixture is poured into special forms that determine the size of the products. When mixing the foaming agent with the working mixture, a cellular structure of the array with closed pores is formed. The process of hardening of the foam concrete composition takes place in molds at a temperature corresponding to the ambient temperature.
The laboratory quality control system operating at industrial enterprises guarantees compliance with the characteristics of the produced aerated concrete products. Privately produced aerated concrete composites can differ significantly from the requirements of the standards
When purchasing aerated concrete, foam concrete and other types of block materials, pay attention to the availability of certificates of conformity
 Aerated concrete composites are made only in production conditions
Aerated concrete composites are made only in production conditions
The main differences between the material
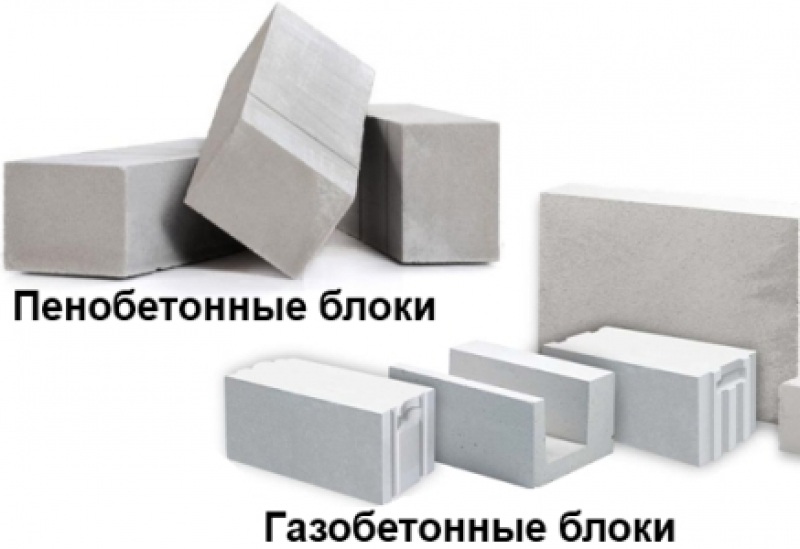
Foam block and gas block, let's understand the difference.
Foam concrete is a product made on the basis of sand-cement raw materials, with the addition of a foaming agent. During the production process, the entire mixture is thoroughly mixed, poured into molds and the block is left to harden naturally.This technology involves the production of blocks both indoors and on the construction site. The photo shows the foam block
 Foam concrete - a product made on the basis of sand-cement raw materials, with the addition of a foaming agent
Foam concrete - a product made on the basis of sand-cement raw materials, with the addition of a foaming agent
A gas block is a product that requires high temperature and humidity in a room. The composition includes: lime, sand, cement mixture and water. Aluminum powder is used for gassing. The technological process takes place by an autoclave method of hardening, with mandatory heat treatment under high pressure. As a result, the material is reliable, durable and resistant to the processes of decay and combustion (see the example of the product in the photo)
 Gas block - a product that requires high temperature and humidity in the room
Gas block - a product that requires high temperature and humidity in the room
It is worth noting that both products are similar to each other, but despite this, they have quite a lot of differences:
- different production mechanism;
- strength level;
- the degree of drying shrinkage;
- water absorption level;
- thermal insulation qualities;
- environmental friendliness;
But what is better to choose a foam block or a gas block, let's take a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages of a building material.
All about foam blocks
Foam concrete blocks are made of foam concrete, which is formed by mechanical mixing of the concrete mixture with foam. Thus, the weight of the material is greatly lightened. The pores of the foam blocks are closed, which contributes to the hanging moisture resistance.
Components of foam blocks:
- sand;
- cement;
- water;
- foam.
Specifications:
- the sizes of foam blocks and gas blocks are chosen the same - 200x300x600 mm;
- the weight of one block of the corresponding size is 22 kg;
- material density - (300 - 1200) kg / m3;
- water absorption - 14%;
- thermal conductivity - (0.1 - 0.4) W / m * K;
- frost resistance - 35 cycles;
- compressive strength - (0.25 - 12.5) MPa;
- material consumption - (21 - 27) pcs / m3.
Advantages of foam blocks:
- Low level of thermal conductivity. This allows you to keep out the cold and keep the room warm for a long time. The thermal conductivity of foam blocks is lower than that of most building materials.
- Low weight. The mass of a foam concrete block is much less than that of other building materials of the corresponding volume, although the gas block is lighter. This property allows you to reduce the cost of the foundation, because it is possible to reduce its strength and volume. Also, light piece material is easier to transport and install.
- High strength. When using blocks of the D900 brand, it is possible to erect load-bearing walls from a foam block for a three-story house. For a high-rise building, load-bearing structures made of other materials are used.
- Microclimate. Due to its low thermal conductivity and moisture resistance, foam concrete forms a comfortable microclimate in the house. This is facilitated by the ability to give and take away moisture and thereby control the level of humidity in the room.
- They can withstand low temperatures well, even severe frosts are not afraid of him.
- Fire resistance. The foam concrete load-bearing structure is able to withstand high temperatures and is exposed to open fire for more than 4 hours. At the same time, it does not lose its carrying capacity.
- Environmental friendliness. The material is made from environmentally friendly components, and the foam is formed using protein or synthetic foaming agents that do not emit harmful substances. In addition, the structure of foam concrete is similar to the structure of foam and all pores are isolated.
- Biostability. The material does not rot.
- Moisture resistance. Due to the insulated cells, aerated concrete has good moisture resistance.
- Ease of processing. The foam block is easy to saw and drill without the use of special equipment and large physical costs.
Their disadvantages:
- The shrinkage of a structure made of foam blocks can be up to 3 mm per meter of wall height. This property is especially manifested if the technology for the manufacture of piece material has been violated.
- The ability to absorb moisture by foam blocks and the need for their additional protection.There is a small chance of such a nuisance, you may need to perform additional finishing.
- If damaged, chips form in the corners of the blocks. That is why it must be transported on pallets in packaging and carefully transported to the place of work.
- If you need to drive a nail or a dowel into the wall from the foam block, it will not hold. For these purposes, it is necessary to use special dowels made of ABC-plastic.
- Due to the simplicity of manufacture, handicraft production of foam blocks is widely developed. In the case of purchasing such piece material, its technical characteristics may not correspond to the factory parameters. At first glance, it is difficult to determine which batch of foam blocks is a factory one.
Table of technical parameters of foam concrete and aerated concrete
The final comparative table shows the main technical parameters that determine the operational properties of aerated concrete and foam concrete. Such a comparison will determine which of the materials should be chosen for the construction of residential buildings and other objects.

| Technical specifications | Foam blocks | Gas blocks |
|---|---|---|
| Filler for creating a porous structure | Saponified tree resin | Fine dispersion aluminum |
| Technological process | By cutting blocks or cassette casting | Single block casting method |
| Component components |
|
|
| Equipment for the production of | Factory equipment or homemade installations | Industrial equipment - autoclaves and electric ovens |
| Pore type (cells) | Closed-cell heterogeneous structure | Homogeneous porous structure with external open and internal closed pores |
| Pore sizes | Different sizes | One size |
| Standard sizes of blocks, cm | ||
| Height | 20, 30, 40 | 20 |
| By lenght | 60 | 50, 60 |
| By width | 10-30 | 7,5-50 |
| Density, kg / cu. m | 300-1600 | 200-600 |
| Weight, kg / cu. m | 300-1600 | 300-600 |
| Compressive strength index of material | 1,2 | 2,5 |
| Time to gain strength | Gradually with a subsequent increase in strength over 2-3 weeks | Instantly when concrete sets within a few hours |
| Shape Geometry Accuracy | When cutting a solid base - minor errors. In the case of cassette production, there are significant discrepancies. This is the main disadvantage of the material. Up to 25 mm | Minor discrepancies are allowed. This is the main plus of the material. Up to 2 mm |
| Moisture absorption level,% (in direct contact with water) | 10 | 45 |
| Frost resistance (number of freeze and thaw cycles) | Average frost resistance - up to 35 cycles | High frost resistance depending on the density of the material - from 35 to 75 cycles. A decrease in the level of humidity leads to a significant increase in frost resistance |
| Soundproofing | High | Low |
| Environmental friendliness indicator | 4 | 2 |
| Thermal conductivity, W / M * k | For thermal insulation - 0.2 For the construction of structures - 0.35 | For thermal insulation - 0.1 For the construction of structures - 0.18 |
| External component | Smooth gray surface | Rough white surface |
| Vapor permeability index, mg / m × h × Pa | 0.8 to 0.12 | 0.15 to 0.23 |
| Life time | Not more than 35 years old | Over 60 years |
| Features of the installation work | Since porous concretes are lighter than solid materials, they are easier to cut, drill, grind and lay. | |
| Adhesive requirements | For masonry work, traditional concrete compositions or special adhesive mixtures can be used. Joint thickness - 22 mm | Special masonry compounds are intended for installation. Joint thickness - 3 mm |
| Additional protection of wall structures | Not required | |
| Shrinkage, mm / sq. m | 2-4 | 0,6 |
| Ability to hold fasteners | The same. The need to use special fasteners designed for porous materials | |
| Cladding material | All available materials | Breathable materials |
| Insulation material | If necessary, a reliable heat-insulating material is used - mineral or basalt wool | |
| Application of plaster | For plastering porous substrates, special plasters with a high level of air permeability are suitable. To increase the adhesion of the composition to the treated surface, a reinforced mesh is additionally used | |
| Price, USD / cu. m | 35-50 | 55-60 |
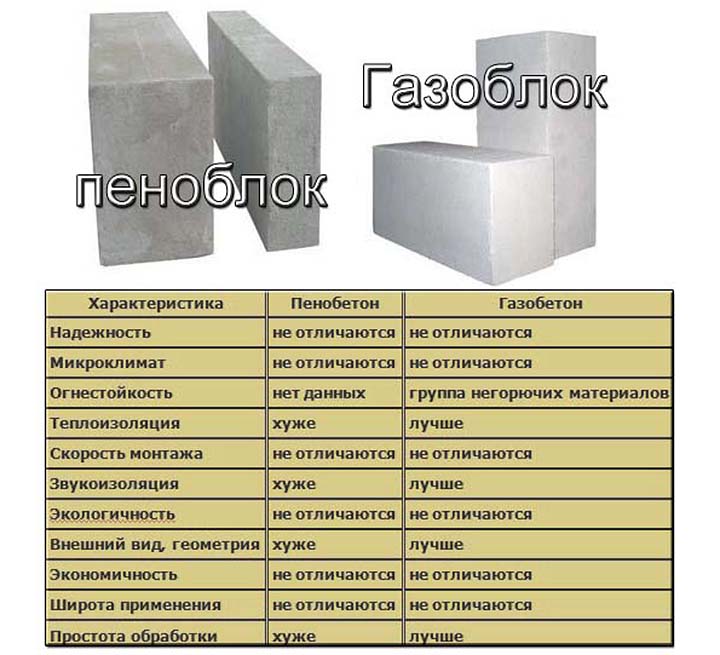
p> It is difficult to give an unambiguous answer to the question of which material is the best - foam concrete or aerated concrete. Each of the materials has its own distinctive advantages and disadvantages. Based on the presented table, a short conclusion can be drawn: gas blocks have higher indicators of frost resistance and strength, and foam blocks - thermal conductivity and environmental friendliness. Which technical parameter is more important depends on the scope and characteristics of the use of the building material.
Calculation of the number of foam blocks
| Choice of block size, LxHxD | 600x250x500600x250x375600x250x300600x250x250600x200x500600x200x375600x200x300600x200x250600x200x150600x250x100600x250x75600x250x150600x200x100600x200x75625x250x500625x250x375625x250x300625x250x250625x200x500625x200x375625x200x300625x200x250625x200x150625x250x100625x250x75625x250x150625x200x100625x200x75625x200x400625x250x400 |
| The total length of the walls, meters | |
| Average wall height, meters | |
| Total area of window and door openings, m2 | |
| Calculate |
| Number of blocks: | m3 | PCS. |
| The number of blocks is a multiple of a pallet: | m3 | PCS. |
| Number of blocks on a pallet: | ||
| Number of pallets: |
We recommend reading:
Alternative energy and heating systems for a private house
All about country life and real estate
Where is Moscow expanding? And what does this threaten summer residents? 294265
Will the Central Ring Road be able to relieve the highways near Moscow? 163312
What metro stations will be built in the Moscow region? 155012
What areas of the Moscow region are the cleanest and dirtiest in terms of ecology? 140065
The best cottage settlements of the Moscow region 106846
Where is the best place to live in the suburbs? Neighborhood ranking 82935
How much does it cost to connect a house and a plot to communications? 79441
How many acres of land do you need to build a house? 72106
Districts of New Moscow. What are their advantages and disadvantages? 68760
How to calculate hundreds of square meters of land? 65390
Construction norms and rules for the development of land plots 64414
What are the exhibitions of ready-made houses in Moscow and the Moscow region? 62492
What houses are currently on sale in the Moscow region? 60956
What are land plots without a contract? 58012
What are the restrictions on construction near rivers and water bodies? 55623
Are the basement and basement considered floors? 51221
What taxes do I need to pay for a house, garage, sauna and other buildings? 51086
Which house heating is more profitable: gas or electric? 48237
Is it profitable to build a house for sale? 44774
The best places for fishing in the Moscow region 43577
Arrangement of the site from scratch. Where to begin? 43110
Pitfalls when buying a house
What should you pay attention to? 42219
What is the right way to bargain for a house? 42096
Can I get out of SNT? 42017
Where will the gas be available soon? Gasification plan for settlements in the Moscow region 37860
Life in a cottage community. Pros and cons 37039
Do I need to get a permit to build a house on my site? 34080
The largest and most expensive cottages in Russia 33652
How much does it cost to build your house? 32879
Is it worth buying a house in SNT for permanent residence? 32261
What is the best way to build a house for permanent residence? 31142
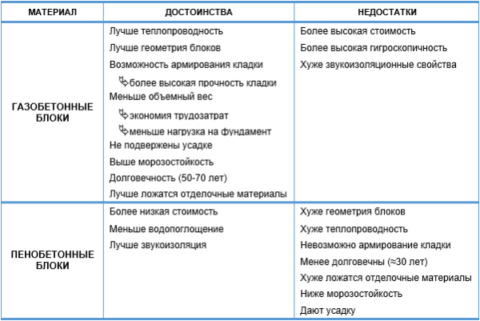
Comparison of properties and qualities of materials
Since we have already considered all the main properties and qualities of materials, it's time to analyze them and find out which is better: aerated concrete blocks or foam concrete blocks?
 What's better? Comparison of materials
What's better? Comparison of materials
- Thermal conductivity in comparison "aerated concrete-foam block". There is no clear winner in this indicator. Both one and the other material have similar numerical values. The gas block wins quite a bit in the strength-thermal conductivity ratio.
- Frost resistance. In this case, aerated concrete wins the palm. It significantly outperforms its competitor in its ability to withstand a large number of freeze and thaw cycles. This is especially true for autoclave products.
- Environmental friendliness and fire resistance of materials are the same.
- The indicators of vapor permeability and construction speed are also similar.Both products are easy to process and have impressive dimensions. Allowing you to quickly build a structure.
- But the geometry of the block is better for autoclaved aerated concrete.
- Foam concrete is significantly ahead of the latter in moisture absorption, which is directly related to the closed pore structure. It absorbs less moisture.
- Soundproofing characteristics are slightly better for aerated concrete.
- If we talk about the appearance, then, according to the developers, aerated concrete looks more attractive.
- What is cheaper foam block or aerated concrete? Definitely - a foam block. The price difference is not big. But still she is.
- The most significant differences between these materials lie in their composition and the method of pore formation. The porous structure of foam concrete can be achieved by introducing a blowing agent into the solution. Cells in aerated concrete are obtained as a result of a chemical reaction of lime and aluminum powder, which acts as a blowing agent.
Foam concrete composition: water, cement, sand, foaming agent. Aerated concrete: lime, sand, cement and aluminum powder (or its substitutes).
As for the variability of finishes, then, as already mentioned, there can be a lot of options for both materials. The main thing is to strictly adhere to the rules of application and installation technology. Interior and exterior finishes must be technically compatible.
- Shrinkage is more typical for foam concrete. Aerated concrete also sits down, but the numerical indicator is still lower.
- If we compare the recommended wall thickness, then for aerated concrete it may be less. For foam concrete, this is 63 cm, and for aerated concrete - at least 40 cm.
- It is also worth noting that fragility is inherent in both products - this is their common drawback. The same goes for fixing the fasteners.
- The standard sizes of the products are also similar. In their assortment they have both wall and partition blocks.
- Foam concrete is distinguished by the presence of cladding products that do not require further finishing. Aerated concrete cannot boast of their presence.
- Separately, I would like to note the fact that when finishing both materials, additional costs will be required for processing and surface reinforcement. The fact is that both aerated concrete blocks and aerated concrete are characterized by low adhesion to finishing materials. This necessitates priming and surface reinforcement.
 Foam concrete blocks comparison
Foam concrete blocks comparison
Aerated concrete, as follows from the table, still wins in more characteristics. However, if low cost and moisture absorption, for example, are most important to you, then aerated concrete is just what you need. Therefore, when choosing, it is worth being guided, first of all, by individual wishes and requirements for future construction.