Types of plywood
Plywood is divided into types based on the scope of its application: construction, furniture, construction, industrial, packaging.
The type of plywood is determined based on the glue used during production:
- FC is a water-repellent type of plywood. Its sheets are glued together with urea glue;
- FSF - plywood with enhanced water-repellent properties. In this case, the layers are glued with phenol-formaldehyde glue;
- FBA - ordinary plywood, sheets of which are glued with albuminocasein glue. Such plywood is afraid of moisture, but it is chosen because of its harmlessness to humans;
- FB is a plywood designed for use in extremely humid conditions, even in water. Such qualities are acquired by the material due to its impregnation with bakelite varnish.

Only the most famous types of plywood are listed above. There are additional classifications, depending on the thickness of the wood used, the quality of the surface.
Types, grades and marking of plywood
Plywood is a sheet material made of several layers of veneer glued together. The number of layers is always odd, the contacting layers are located perpendicular to each other, thereby ensuring the rigidity of the sheet and its high resistance to deformation.

Plywood varies in material of manufacture. The use of coniferous wood (usually pine, but spruce and larch wood can be used) increases resistance to decay, but such material has a looser structure.

Hardwoods (primarily birch) make it possible to produce plywood with increased strength characteristics. Plywood sheets intended for general construction work most often have the front layers of dense hardwood, and the inner layers of coniferous veneer.

The grade of plywood sheet indicates the degree of resistance of the material to moisture. This indicator depends on the substance with which the wood is impregnated. Before choosing plywood for the floor, it is recommended that you familiarize yourself with the characteristics of each type of material.
FB - bakelite (bakelized) plywood, the second name is "Finnish". The wood is impregnated with bakelite varnish, which makes it resistant to moisture, aggressive environments and high temperatures. It is the most durable, but also the most expensive plywood.

BS - aviation plywood, alcohol-soluble bakelite glue is used for impregnation. It is characterized by increased flexibility, resistance to moisture and fungal damage.
BV - veneer is glued with a water-soluble bakelite compound. Plywood is highly durable, but its moisture resistance is low.

FK - carbamide adhesives are used for gluing layers of wood veneer. The moisture resistance of this material is low, but it is environmentally friendly and suitable for interior work. To increase the moisture resistance of plywood, it can be additionally treated with an appropriate wood compound when installing the flooring.
FBA - albumocasein adhesives are used as an adhesive. It is also an environmentally friendly and safe material, but it is afraid of moisture.

FSF - plywood made with phenol-formaldehyde resins. The material is waterproof, but suitable only for roofing and outdoor work, as it emits substances harmful to humans.
Paste a VALID AdSense code in Ads Elite Plugin options before activating it.

There are 5 grades of plywood - from E (elite) to grade IV.
- The material of the lowest (IV) grade is characterized by low surface quality, the manufacturer guarantees only the reliability of the adhesive bond.
- Grade III plywood also has surface layer defects and is used for hidden work.
- Grade II is suitable for outdoor use, provided that a few permissible external defects are repaired.
- On the surface of grade I material, small dark streaks and single small knots are allowed.
- The E grade material is characterized by an ideal appearance.
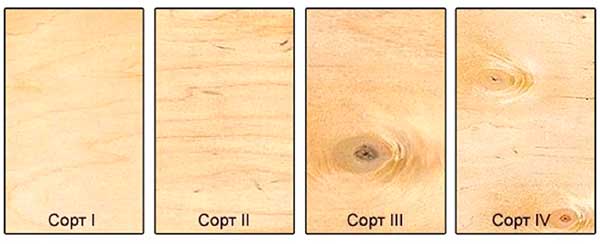
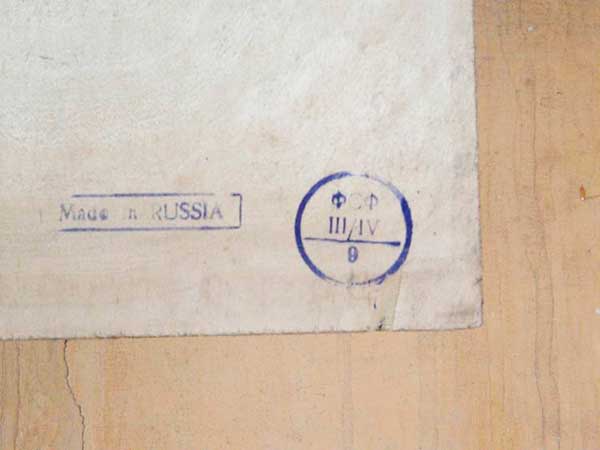
On the plywood label, the grade is indicated for the front and back, for example, III / IV or I / II. For laying the flooring under laminate or parquet, it is enough to use material of II - III grade. If plywood is supposed to be used as a topcoat with subsequent application of a decorative and protective layer, the material of the highest grades is chosen.

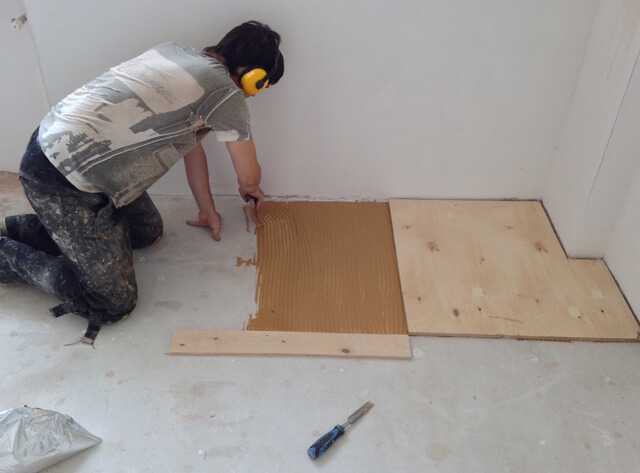
Concrete screed flooring
A concrete screed is the most reliable base, but its construction takes a lot of time and effort. Installation of such a screed begins with a markup: draw horizontal lines along the walls of your room along the building level. These lines are the upper edge of the future concrete screed.
The next stage is the selection and laying of the bars. The bars are used to organize the inner frame, so they must be thinner than the screed itself in order for the cement mortar to cover them. The bars are laid in a grid, the cells in which are equal to 1 square meter.

Concrete pouring is the final stage of concrete screed construction. For filling, a cement-sand mortar is used in proportions of 1: 3. Fill the cells with concrete and smooth it evenly, then let the concrete dry.
If the quality of the screed obtained is important to you, then make sure that it does not crack. To do this, maintain a high level of moisture, for example, by covering the concrete with polyethylene for 8-10 days. You should start laying the sub-floor only after the concrete floor is completely dry, otherwise the material used will become unusable.
It is worthwhile to start laying the subfloor only after the concrete floor is completely dry, otherwise the material used will become unusable.
There are two ways to check the moisture content of the floor:
- Use an expensive moisture meter that can be rented.
- Place polyethylene on the concrete area and press down along the perimeter, then leave overnight. If the concrete is not dry enough, then in the morning you will find condensation on the surface of the film, and if it is not, then you can safely proceed with the installation of the subfloor.
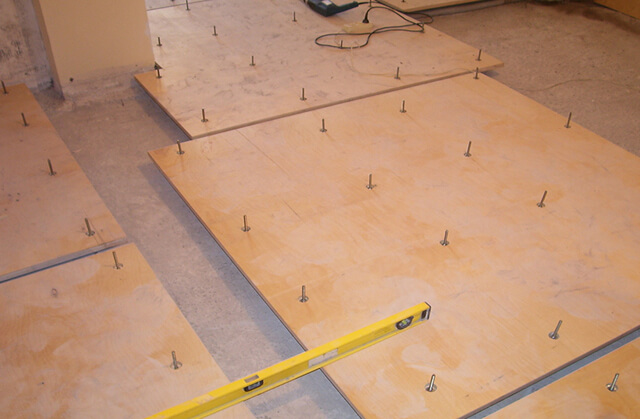

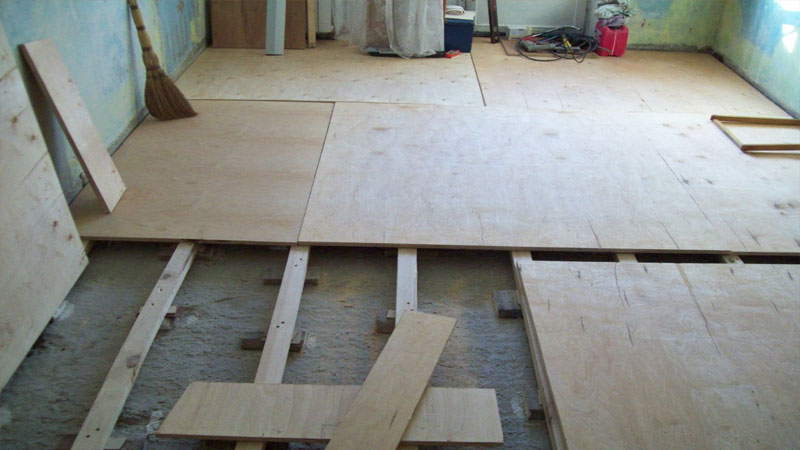
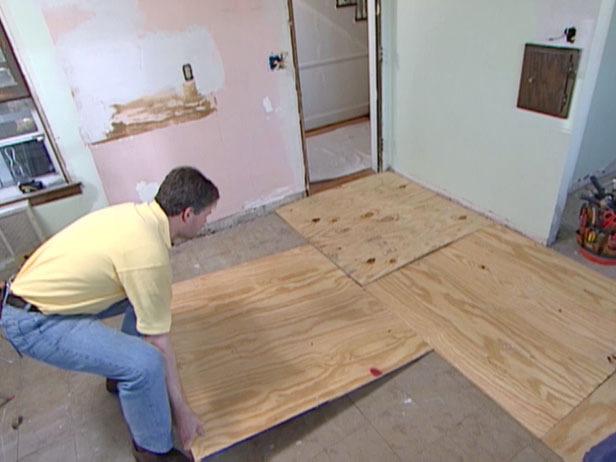
It is worth laying the slabs according to the brickwork rule in order to prevent premature wear of the material. After that, number them so you don't get confused later.
Apply glue to the concrete and lay the slabs, then, additionally fix them with dowels. You can see the finished result in the photo.
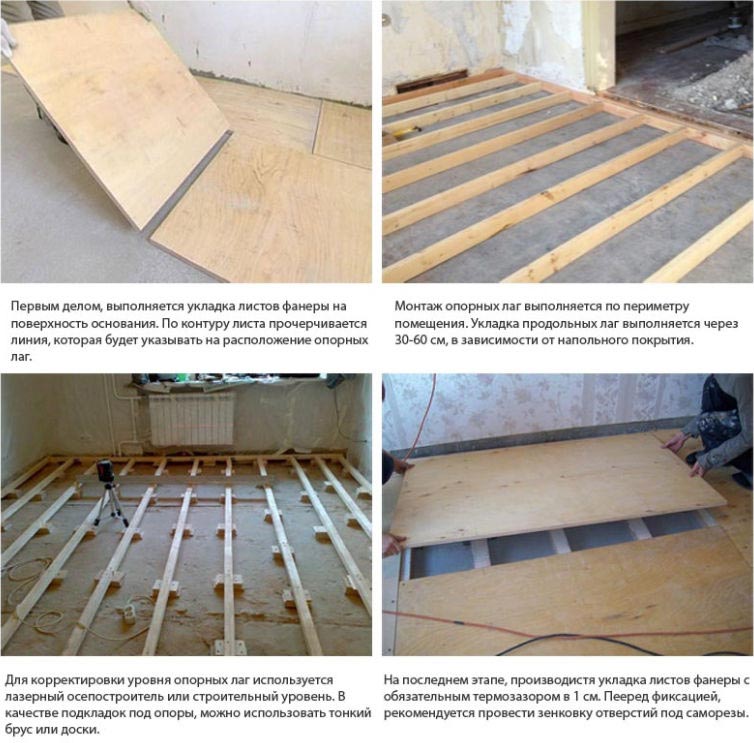
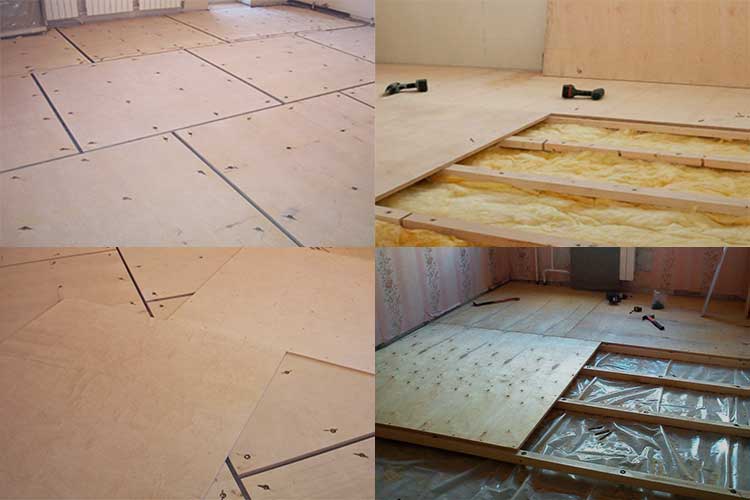
Method 1. Installation on an old wooden floor
At laying plywood on wooden floor there are many options for fixing sheets:
- on self-tapping screws;
- on glue;
- on liquid nails.
Among the adhesives, there are water-based glue, two-component composition, assembly glue and bustilate. However, it is preferable to mount on self-tapping screws.
Materials and tools
For the successful installation of plywood sheets, you will need the following tools and materials:
- plywood sheets;
- jigsaw;
- level;
- roulette;
- marker;
- self-tapping screws;
- screwdriver;
- substrate;
- construction vacuum cleaner or broom.
You may also need a sander, roller and primer, glue and sealant.
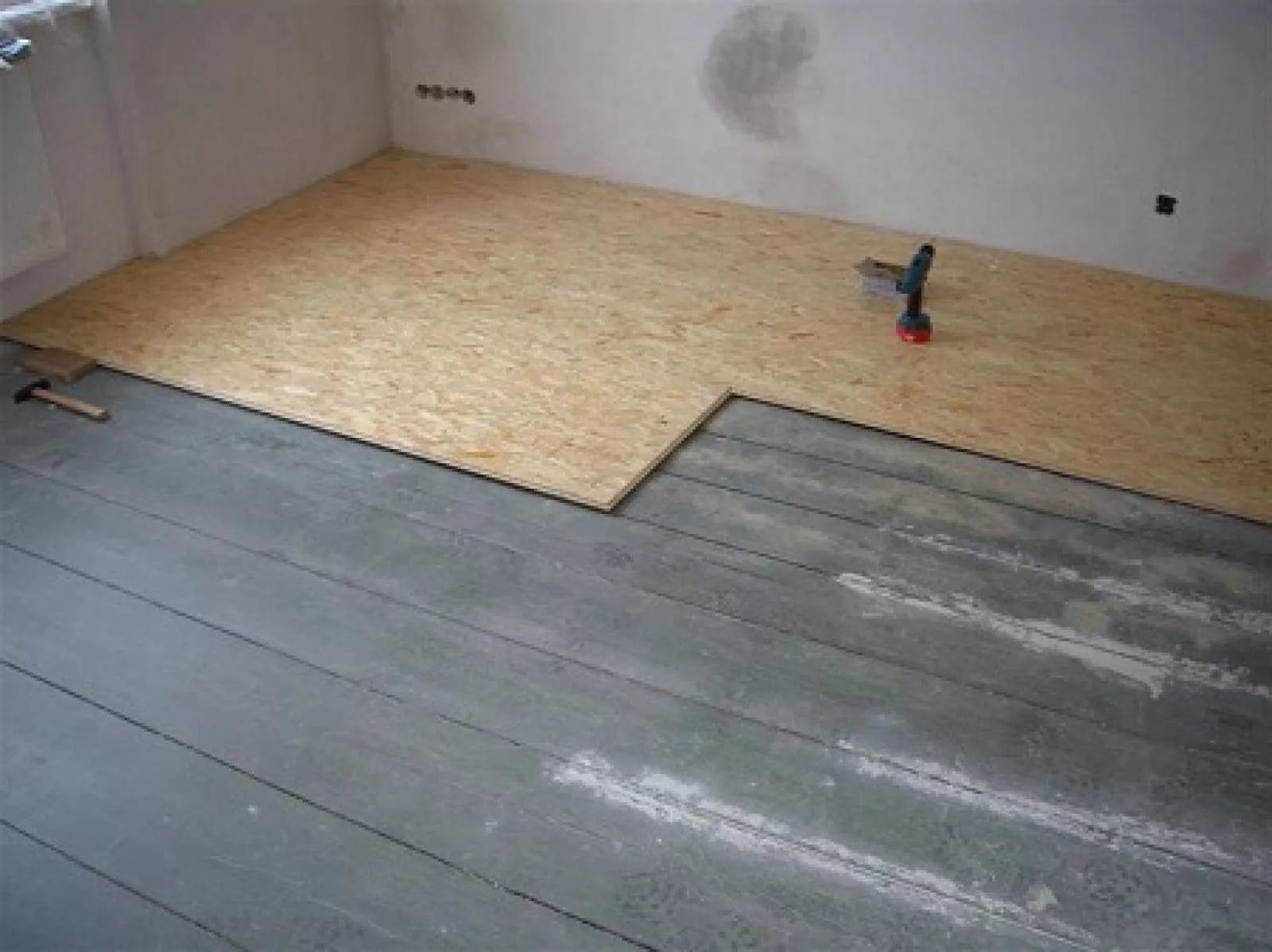
Preliminary preparation and priming of the floor
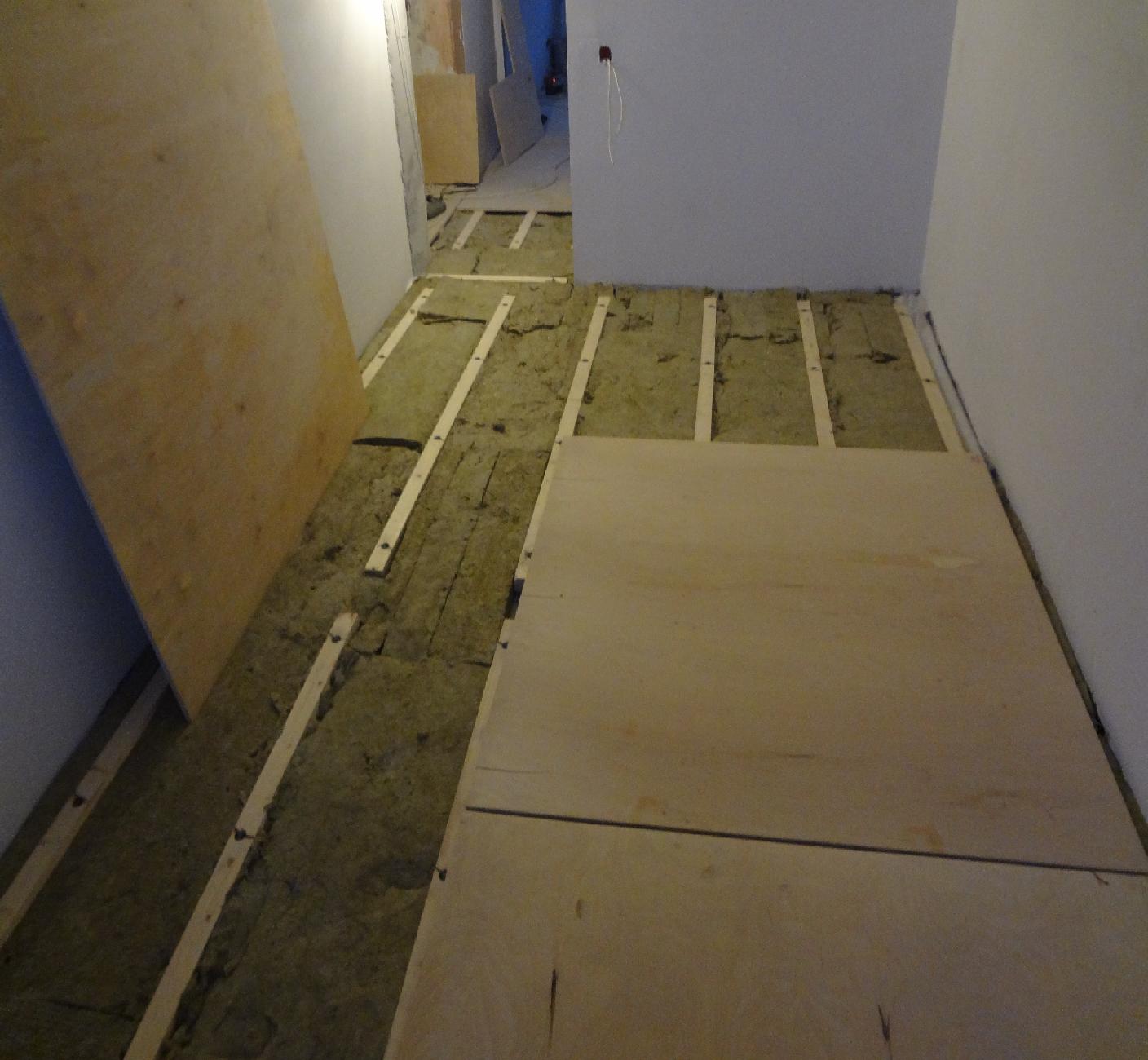
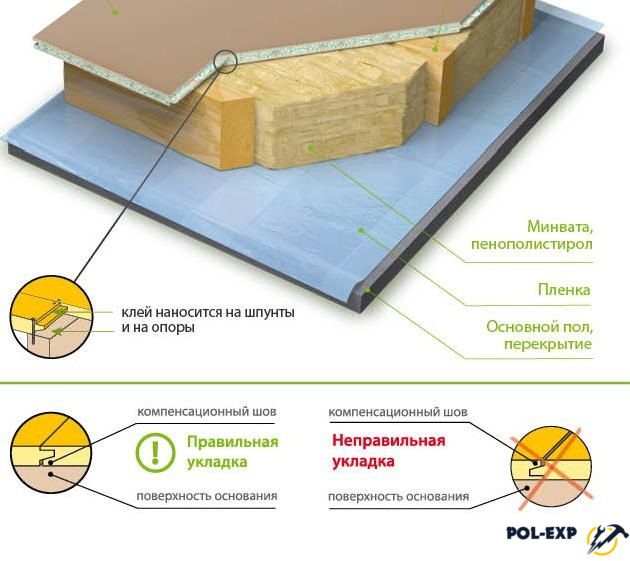
Installation of plywood on wooden floors is carried out only if the height difference when checking with a level is no more than 1 cm. In this case, you will also need a substrate compensating for unevenness and tape, which will need to glue the joints of the strips of material.
Inspect the condition of the floors. Strengthen creaking and loose floorboards, replace rotten and damp floorboards.Do not try to restore boards with traces of mold, damage, attacked by rodents. They must be removed, the room must be ventilated.

We remove the skirting boards, inspect the condition of the floor
Sweep dust and dirt off the floors with a broom. If desired, go through the wood primer twice for better material adhesion. And dry the base for at least 16 hours.
primer
Marking and cutting
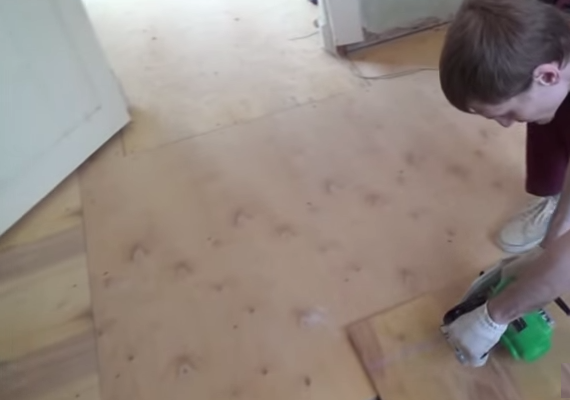

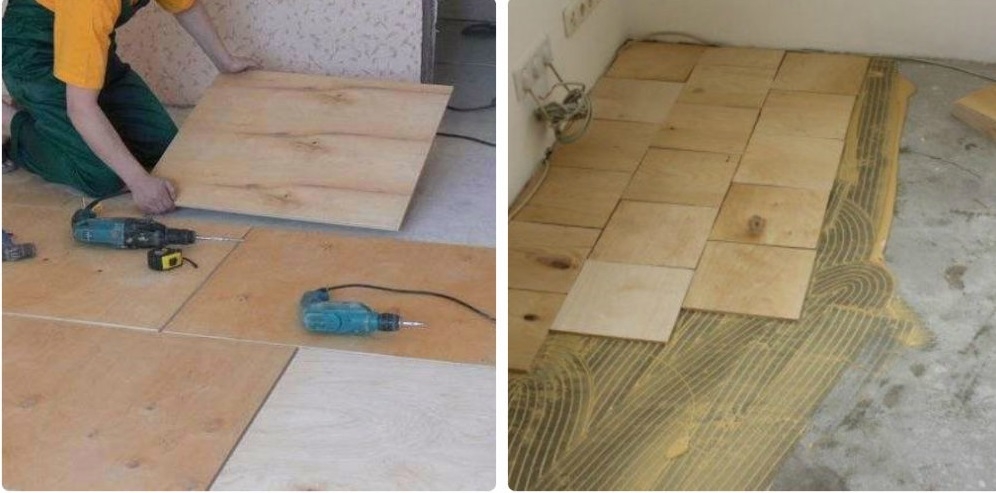
Sawing plywood
Saw plywood only on a hard surface
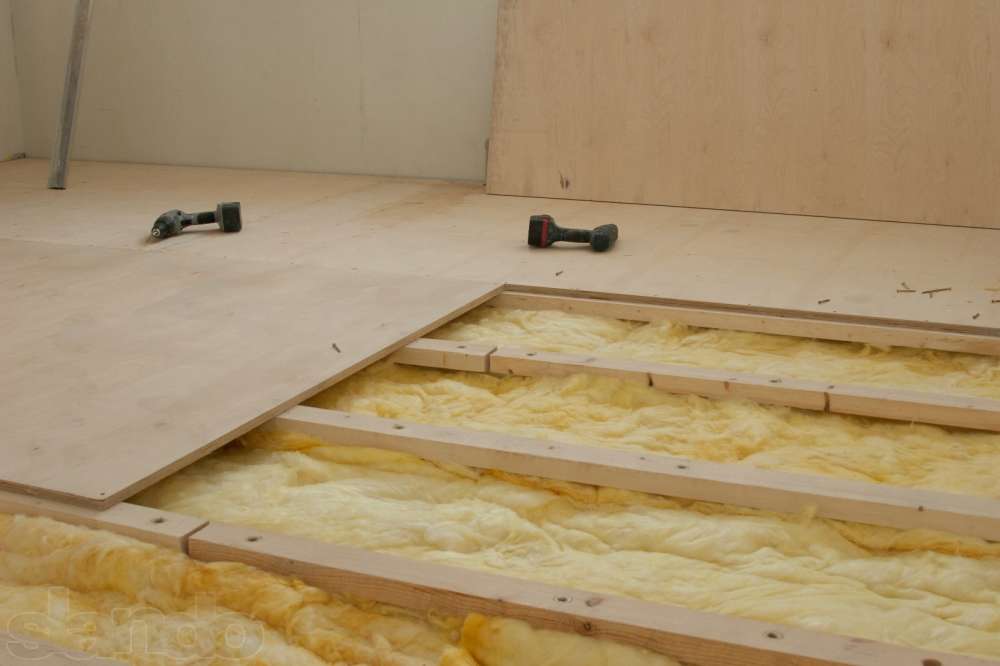
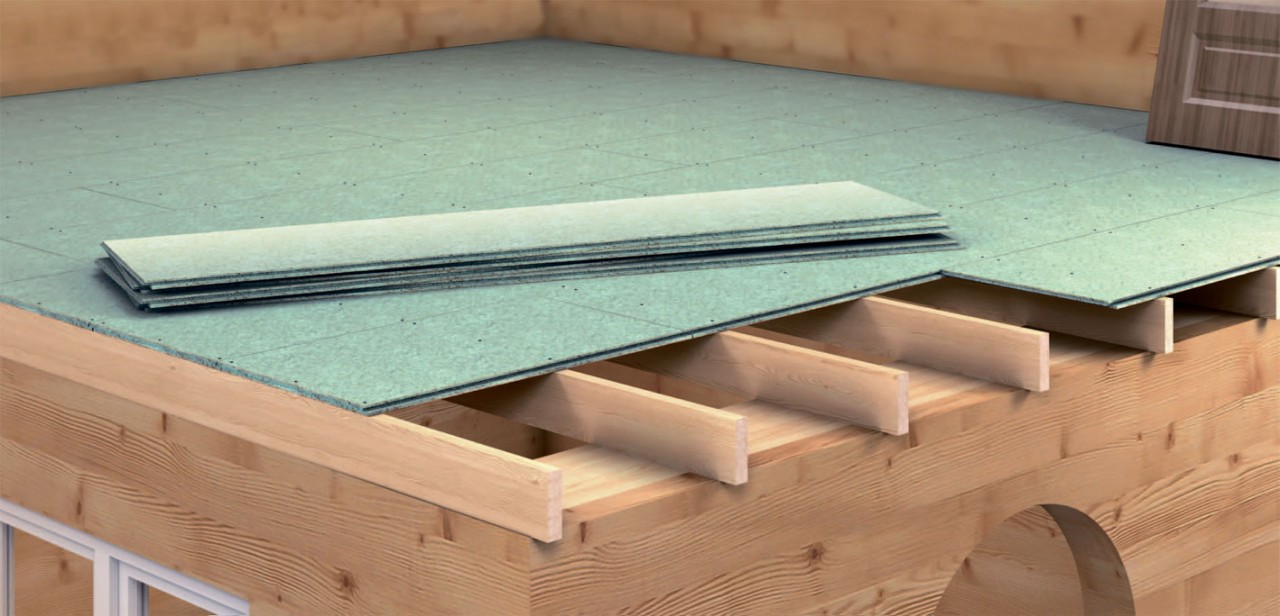
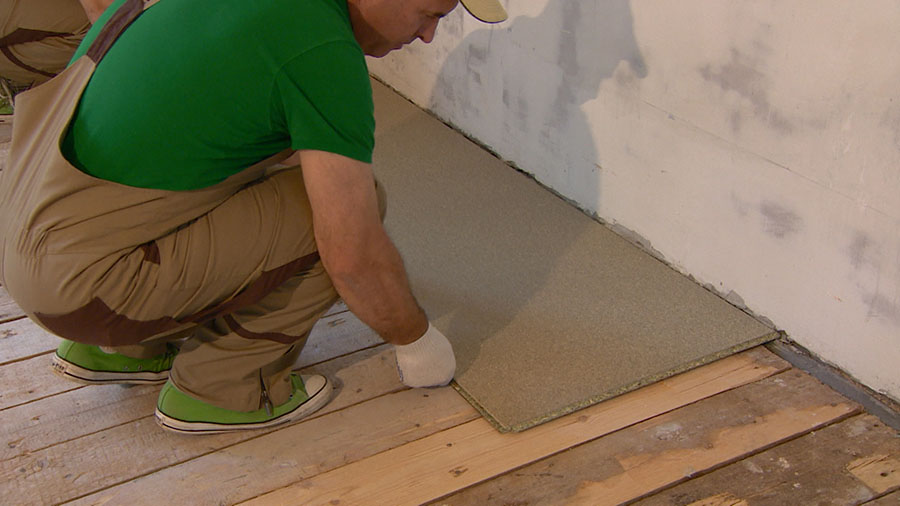
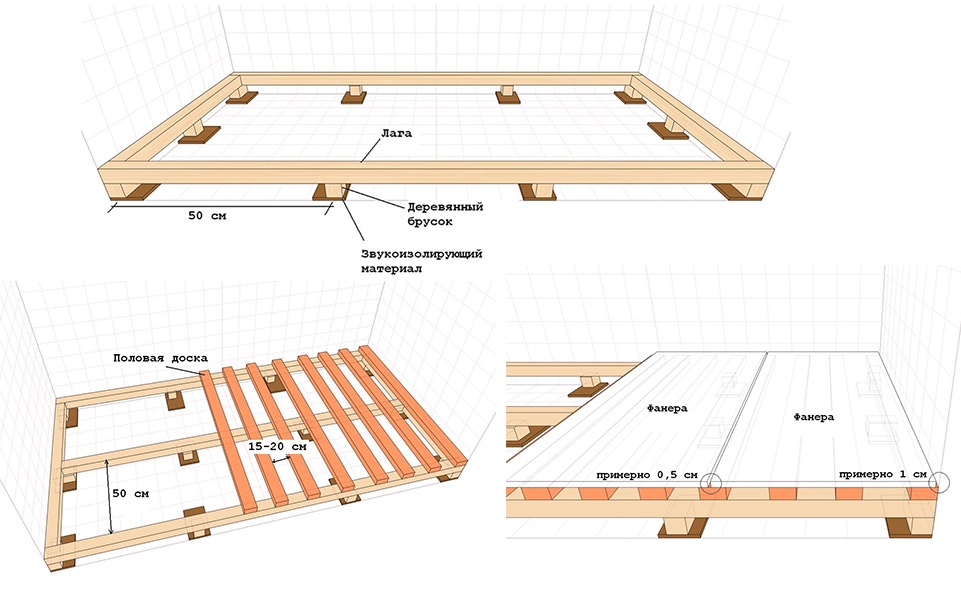
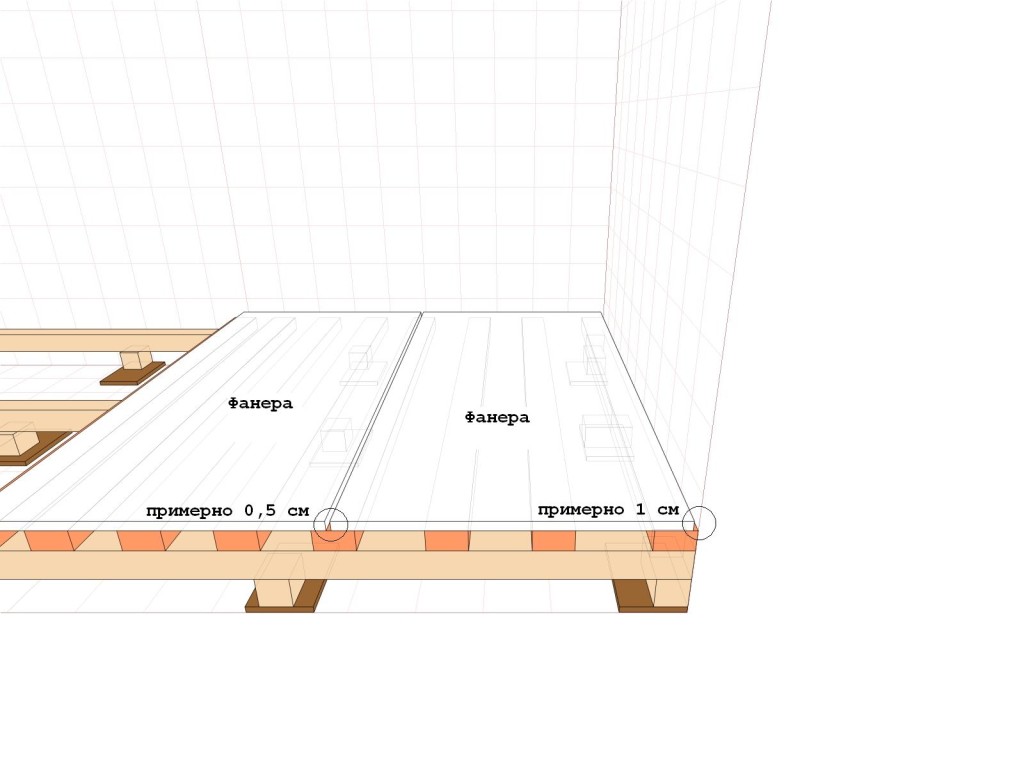
Plywood sheets are sawn so that the number of joints is minimal, taking into account damping joints of 3-4 mm between the sheets and 8-10 mm between the plywood and the wall. This will help to avoid swelling of the sheets, since during operation, under the influence of the microclimate and fluctuations in temperature conditions, the workpiece will increase by several millimeters in area.

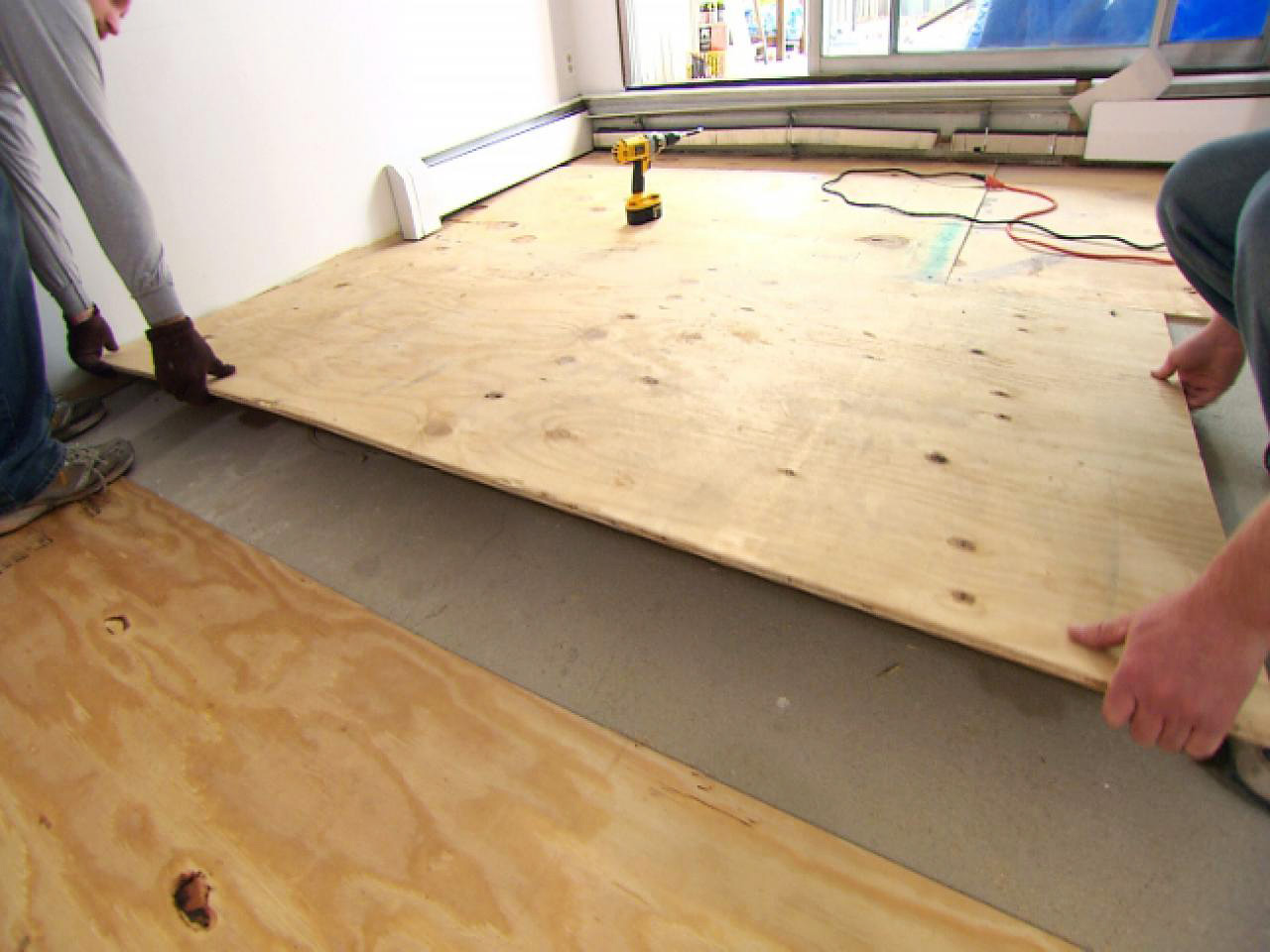
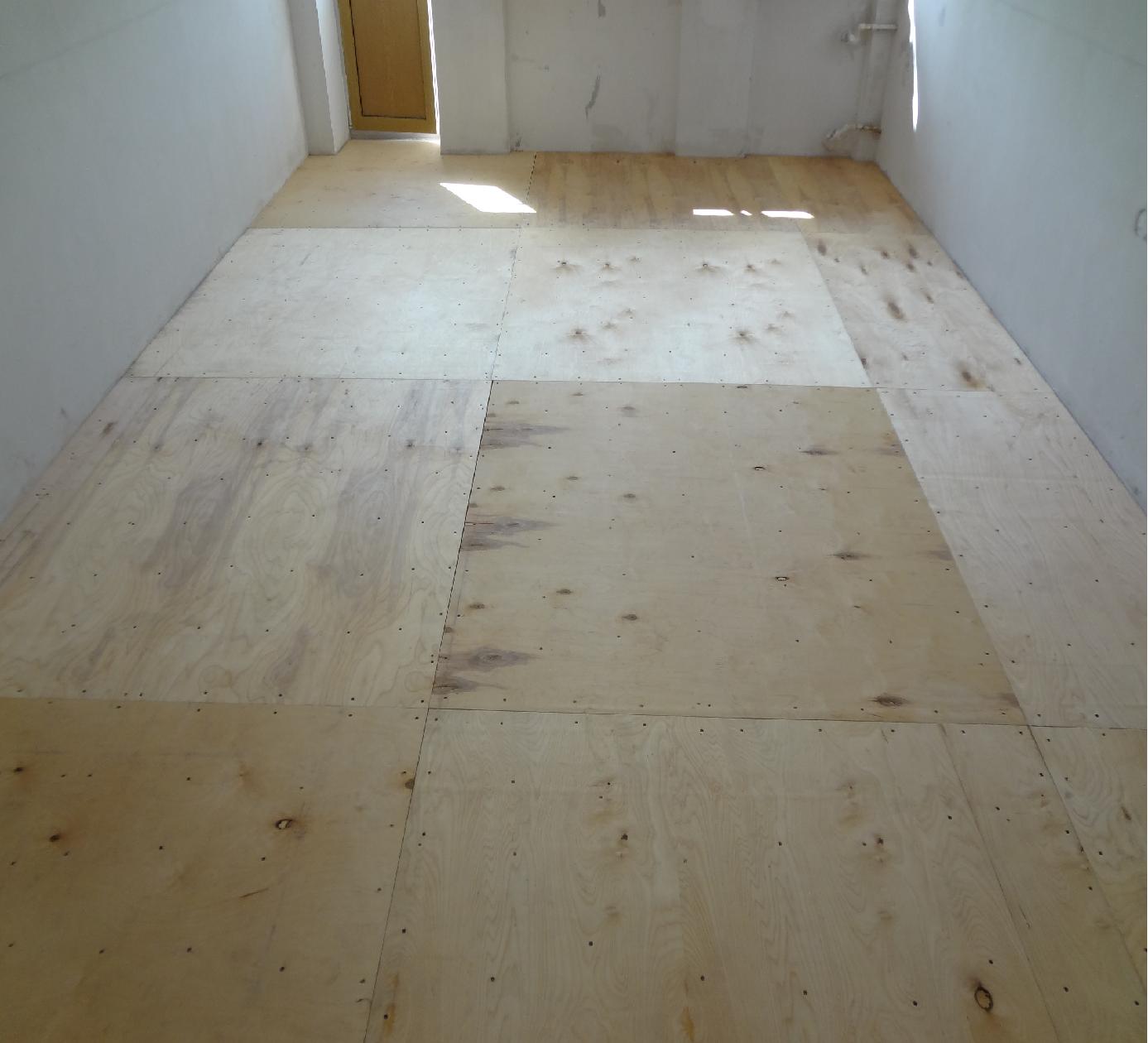
Laying plywood sheets

Fixing the sheet

Leave a gap between the wall and the plywood
Cutting is done with a jigsaw, while the ends of the blanks are carefully inspected for delamination and sanded. On large areas, for ease of installation, plywood can be cut into 50x50 or 60x60 cm squares. This technique will help to more accurately level the surface and eliminate possible laying defects.
The sawn sheets are numbered, and similarly to their numbers, a schematic arrangement of the workpieces is drawn on the wooden base.

Leave the vent open
Laying plywood
The assembly of workpieces has several features.
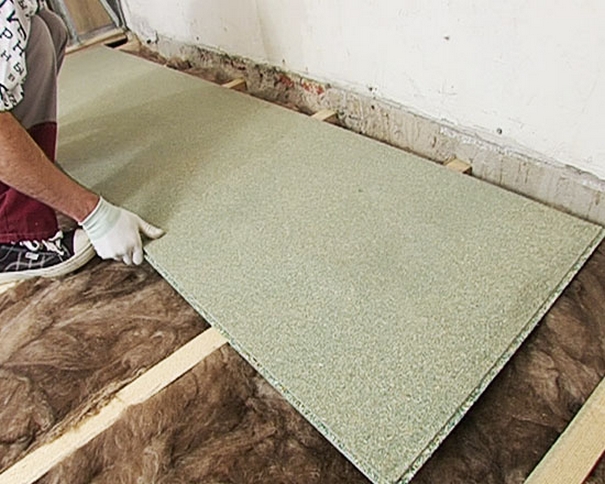
- If necessary, a backing is placed on the old wooden flooring, the strips are glued together with adhesive tape.
- Holes for self-tapping screws are drilled in advance, and then countersinked with a slightly larger diameter drill.
-
Self-tapping caps are embedded in plywood sheets.
-
Plywood installation begins with niches, podiums, ledges. Further, the sheets are arranged from the middle to the edges with a brick shift of the squares relative to each other.
-
Gaps and gaps in old flooring can be filled with glue, allowed to dry and looped.
At the end of the installation, you should check the quality of the coating, remembering that the ideal gap between the level and the plywood is 2 mm, the maximum is 4 mm.
Choosing the optimal plywood nomenclature for the floor
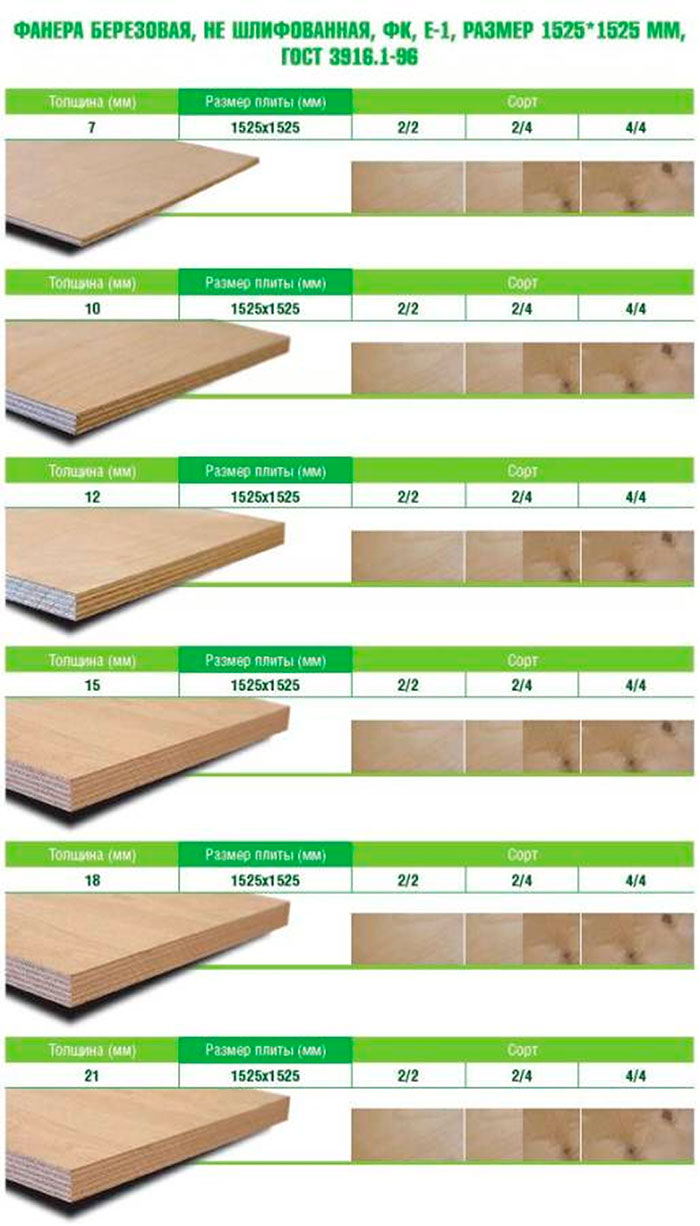
 According to GOST, depending on the appearance of the outer layers, plywood is divided into five grades: "E" (elite), I (no external defects), II (may have wooden inserts), III (the presence of wormholes, intergrown knots is allowed), IV ( low quality sheet, many visual defects).
According to GOST, depending on the appearance of the outer layers, plywood is divided into five grades: "E" (elite), I (no external defects), II (may have wooden inserts), III (the presence of wormholes, intergrown knots is allowed), IV ( low quality sheet, many visual defects).
After reading the above documents (GOST), we decide on the building material that must be chosen for the floor. Let's highlight the main information that influences our choice - which plywood is better to lay on the floor.
With the grade of the building material, everything becomes clear after reading the above picture. Excluding grade "E" - elite, grade I is the best, and grade IV is the worst.
According to the degree of mechanical surface treatment, plywood products are divided into:
- unpolished - NSh;
- sanded on one side - Ш1;
- polished on both sides - Ш2.
For all types of sanded plywood, the emission class is indicated:
- E1 - less than 10 mg of formaldehyde per 100 g of dry plywood mass;
- E2 - from 10 to 35 mg of formaldehyde per 100 g of dry plywood mass.
Plywood grades, depending on the type of glue, with which veneer leaves from hardwood and coniferous species are glued together:
- FB and FOF - for industrial construction;
- FC and FSF - for individual construction.
For internal premises, according to the documents (GOST), it is allowed to use the FC and FSF brands.
It is clear from the same document that FSF has increased moisture resistance, and FC - average. But on the other hand, in plywood products of the FK brand, a less toxic glue is used than in the FSF brands, in the binding adhesives of which there is formaldehyde. So, if you are not going to do a wet tidy, like in the navy, throwing buckets of water onto the deck, then the choice for the floors of living quarters is definitely in favor of the FC brand.
 You can lay plywood directly on an old wooden floor, if the floorboards themselves and the logs on which they lie are still strong and not rotted
You can lay plywood directly on an old wooden floor, if the floorboards themselves and the logs on which they lie are still strong and not rotted
What kind of plywood to cover the floor - hardwood or softwood? The price of coniferous products (for example, pine, spruce) is slightly less than that made from birch veneer, but the relative strength of coniferous sheets is also lower.
It is necessary to take into account the fact that at elevated temperatures resin can be released from the sheets of coniferous veneer, which in some cases is an undesirable effect. But at the same time, the presence of a natural antiseptic in the resin makes it more protected from rotting, fungal attack, and the building materials themselves, containing resins, are more moisture resistant.
But, nevertheless, more often than not, both the final and the rough flooring are laid from all the same from glued sheets of birch veneer of the FC brand.
And this choice is justified by the following advantages:
- safety for people;
- the best thermal insulation properties;
- the average density of birch wood is 700 - 710 (kg / m3), higher than, for example, for pine 430 - 480 (kg / m3) and for spruce 450 - 470 (kg / m3);
- easier to handle and bend;
- plywood products made of birch veneer can, if desired, be easily imitated under valuable species of wood (mahogany, walnut).
Thus, summing up the above information, one of the optimal options for the floor (on a cement screed or on logs) will be birch veneer plywood - FK-2E1SH1, the thickness of which is 12-16 (mm), and if the height of the floor base allows, then 20 (mm).
The designation of the selected plywood contains:
- product name - plywood;
- wood species of the outer and inner layers - birch veneer;
- brand - FC;
- combination of veneer grades of outer layers - 2/2;
- emission class - Е1;
- type of surface treatment - Ш1.
We purchase the required standard sizes of sheets of building material based on the area and shape of the room in which we will lay the flooring (while taking into account the optimal cutting so that there are no unnecessary costs).
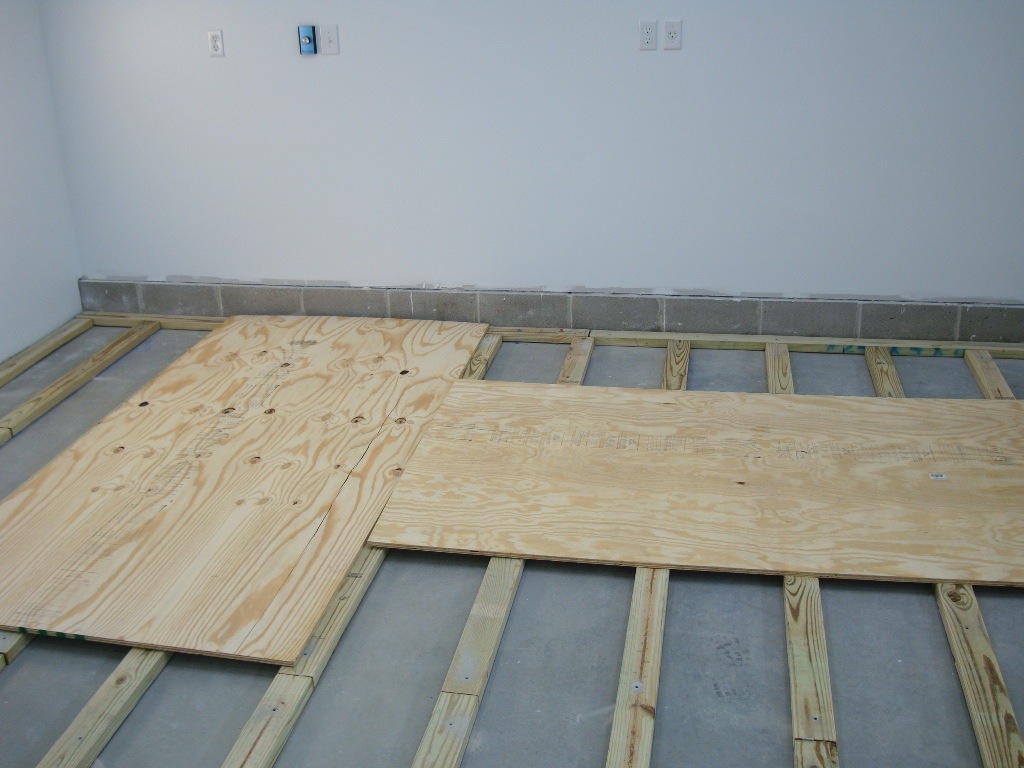
Table: Dimensions of plywood sheets produced according to standards
| Length (width) of plywood sheets | Limit deviation |
| 1200, 1220,1250 | ±3,0 |
| 1500, 1525, 1800, 1830 | ±4,0 |
| 2100, 2135, 2440, 2500 | ±4,0 |
| 2700, 2745, 3050, 3600, 3660 | ±5,0 |
Note: It is allowed to produce plywood of other lengths by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer.
Comparison of characteristics
To choose the most suitable option for a rough or final finish of a floor structure, it is necessary to take into account the main parameters of the product.
Environmental friendliness
Health safety is one of the main factors. Indicators wood-based materials comply with the standards that are reflected in the standardization documents.
- Plywood. Eco-friendly option. The most harmless products are those for which natural resins are used.
- OSB. Does not pose a threat, but only if the production technology is observed. It is better to choose trusted manufacturers.
- Chipboard. This variety causes the most controversy over health risks, since formaldehyde resins are used for gluing. Products must comply with the standards (marking E1 or E0.5).
- Fiberboard. Does not pose a threat, provided that quality raw materials are used.
- MDF. An environmentally friendly material made using urea resins. These products must also comply with E1 or E0.5 class.
Since the outside of all materials is finished, harmful fumes are minimized.
Strength
To choose the most reliable option, you need to take into account the density and structure of the product:
- OSB and plywood. Oriented strand panels withstand serious loads well: the layers are placed in different directions and are glued together extremely firmly. But a wood-laminated board can have a significant disadvantage - the possibility of deformation due to non-compliance with technology.
- Particleboard and fiberboard. Have sufficient hardness. The spheres of their use are somewhat different.Wood-based parts are very thick, and fiber-based ones are very unstable to bending, therefore they cannot be used for leveling voids.
- MDF. Relatively soft material that is not used in places with increased stress.
It is difficult to compare all products by this parameter, since they have different sizes.
Dimensions (edit)
The length and width of all varieties are approximately the same, so it is necessary to compare the thickness:
- Hardboard. The thinnest material. Its thickness can be up to 7 mm, but most often 3.2 mm.
- Plywood. Products with a thickness of 12–15 mm are selected for the floor.
- OSB. It can be of different sizes, but options from 10 to 22 mm are used for the floor. If you want to align the existing base, then a thickness of 1 cm is suitable, but in order to lay the material on wooden logs, the parts must be more durable.
- MDF. Due to its softness, the recommended board thickness ranges from 18 to 25 mm.
- Chipboard. For horizontal structures with increased load, a tongue-and-groove version with a thickness of 16–22 mm is used.
The thickness and structure of the parts also affects soundproofing and heat retention. If the noise pollution is very strong, it is recommended to give preference to medium density fibreboards of maximum thickness. They also serve as additional thermal insulation, which is similar to OSB.
Price
The difference in the price of materials depends on many factors: the method of production, the raw materials used, additional processing, size and even the place of sale.
- The most expensive is high-grade plywood.
- The cost of MDF is calculated from square meters and depends on the manufacturing method.
- The price of OSB-3 and 2 corresponds to wood-laminated boards of 3 or 2 grades of a smaller size.
- The lightest and cheapest option is fiberboard.
So that the total budget of work does not amount to too much, it is necessary to immediately determine the scope of each type of product.
Ease of installation
Laying wood-based panels is not difficult, it does not require professional skills and complex tools. The order of work depends on the specific situation:
- If a frame structure is being erected, then the OSB would be the best option.
- The light weight and thickness of the hardboard make the processing the fastest, but it is not suitable for serious leveling.
- Chipboard and OSB panels are cut and fixed in almost the same way. They are much easier to trim than MDF, which has more resistance due to its dense structure.
- The most laborious in terms of processing is plywood. It will take much longer to put the product down. It is more difficult to drill or adjust it to size due to the presence of layers of natural wood in the structure.
 All floor slabs are assembled on glue or lags, the only exception is the fiberboard cover: these sheets are not intended for flooring on joists, they need a flat and strong base
All floor slabs are assembled on glue or lags, the only exception is the fiberboard cover: these sheets are not intended for flooring on joists, they need a flat and strong base
Factors influencing the choice of plywood

Before making a plywood floor in a wooden house, you need to decide on the type of material. What to take into account when picking up sheets:
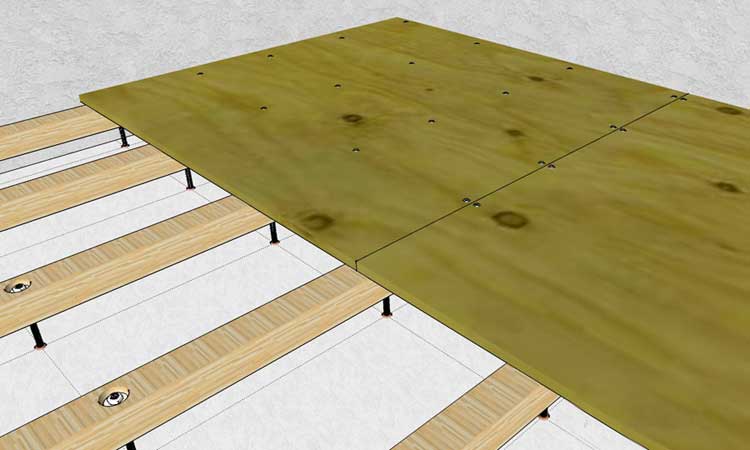
- Base type. For example, a concrete base has a high thermal conductivity; losses can be reduced with sheets of greater thickness (from 15 mm). But it is better to sheathe a subfloor made of plywood on logs with a material with a layer thickness of at least 12 mm.
- Room type (area of application). For residential areas, professionals recommend choosing the FC grade, it is produced without volatile chemicals.
- Thickness. Arrangement of plywood flooring on logs requires selection of parameters, since the service life of the subfloor depends on the thickness - the thicker the board, the less it will bend when walking. However, it is not necessary to bend in the direction of increasing the size - this increases the mass of the flooring, which also negatively affects the design of the log.
Important! Professionals advise to be guided by the distance between the lags (step). If the cell size is 0.5-0.6 m, the sheet thickness must be at least 15 mm
Considering all the factors, choosing plywood for a wooden floor is not difficult.
Thickness of sheets

The size range of plywood is varied: the length can reach 6 m, the width is 3 m, and the thickness starts from 3 mm. For roughing and finishing work on horizontal bases, the following are used:
- 1525 * 1525 mm with a thickness of 15 mm - this is the most popular product for mounting sheets on logs;
- 1210 * 2440 mm - used for leveling foundations in multi-storey typical buildings;
- 500 * 3000 mm - sheets for studio-type rooms.
As for what thickness of plywood to use for the floor along the logs, the type of prefabricated screed is taken into account, the load level:
- The degree of load. The greater the load on the floor, the thicker the sheets. Living quarters allow a parameter of 10 mm with a lag step of 0.4 m, but in commercial and other premises it is better to take plates of 22 mm thick.
- Finishing type. The materials of the final cladding also have their own weight, static load, which will press on the logs. If it is a laminate, then there is no big threat of an increase in mass, which cannot be said about an array of boards or tiles.
Types of plywood
Depending on the area of application, the material differs:
- building;
- furniture;
- constructional;
- industrial;
- packing.
According to the classification, material is distinguished:
- Scope of application. For the arrangement of the prefabricated screed, structural and building types are shown.
- Brand. Determined by the type of adhesive used. It differs as follows:
- FSF - sheets with increased moisture resistance, can be used in rooms with normal and high humidity levels. Adhesive resin composition with the addition of phenol-formaldehyde components;
- FC - products of medium moisture resistance, it is better to use in dry rooms. The adhesive composition is urea-formaldehyde;
- FBA - sheets practically do not tolerate moisture. Glue with albumin-casein components.
- Grade. It differs in the permissible number of wood defects, processing defects:
- E - extra class, in the manufacture of which oak, walnut, birch are used. Perfectly flat sheets without knots, chips and other defects;
- I - there are knots of a light or dark shade no more than 3-5 units / m2. There is no more marriage;
- II - knots (captive) with a diameter of no more than 6 mm in the amount of 6-8 units / m2 are visible, there may be cracks 0.2 cm long and up to 0.2 cm wide (fused or sealed);
- III - sheets with wormholes, knots up to 6 mm in the amount of 8-10 units / m2, cracks 0.3-0.6 cm long, 0.5 cm wide (sealed), dents, scallops;
- IV - grade with defects, chipping along the edge without restrictions.
Important! If you look at what plywood to use for the floor on logs of inexpensive cost, then grade 1-4 is suitable. But double marking of sheets is possible: 1/3, 2/2 - this means that one side corresponds to a high grade, and the other to a low grade
- The nature of the processing differs in grinding: Ш1 - processing of one side, Ш2 - both sides are ground, NSh - no grinding. You can use any slabs for the floor on the logs, but it is better to take one-sided grinding in order to get a perfectly smooth base for the finishing.
Having figured out what thickness of plywood for the floor on the logs is better, you should determine other suitable dimensions:
- FC brand;
- emission class E1;
- grade: for rough floor 3-4, for finishing 1-2;
- humidity 12-15%;
- number of layers (thickness) 8-12 mm.
Advice! Please note that with two-layer flooring, the thickness of the overall structure is divided by 2. However, the choice of price here matters: sheets plywood 15 mm thick are not much more expensive than a sheet of 30 mm, but laying and transporting lighter material is more convenient
Pros and cons of using plywood for flooring
Plywood covering has a whole list of technical advantages in comparison with other types of building materials:
- the material has minimum moisture indicators - up to 15%;
- when excessive mechanical stress occurs, plywood extinguishes most of it, preventing damage to the concrete floor;
- in the manufacture, natural veneer is used without the addition of harmful impurities that are present in chipboard and OSB boards. It is worth noting that more and more people are laying OSB on the floor, since this material has proven itself well;
- the material plays the role of thermal insulation from rough floors;
- unlike pouring a cement screed, laying wood slabs on logs is a less time-consuming process;
- plywood has high resistance to bending, so it can withstand very heavy loads;
- There are several grades and grades of plywood that makes it suitable for use as a rough and finish flooring.
Among the disadvantages of laying material on logs, the following points can be distinguished:
- poor resistance to large temperature changes;
- the material is afraid of moisture, so it is advisable to use it in dry rooms.