Principle of operation
Optical levels, which are also called optical-mechanical, are still found today at some sites, but are gradually going out of circulation for two reasons: firstly, they do not protect against possible operator error, and secondly, they require two people to service at once. The operator can track the difference in levels through the telescope - a beam of light passes into it, while the tube itself rotates in a horizontal plane. The second person is needed in order to hold the measuring stick while the first one takes readings.


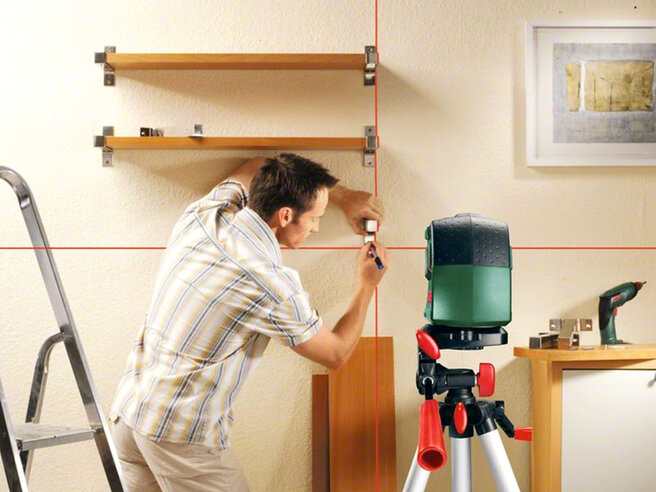
It is much easier to work with a laser level, if only because a colored ray visible to the human eye emerges from it, which replaces an imaginary line in the optical unit. Thanks to this principle of organization of work, any deviation of the beam from a straight line, if it suddenly happened due to the reflectivity of the surface, will be striking.
Most modern laser levels can do even more - if necessary, they project vertical and horizontal lines onto the surface, draw corners, and so on. Some models also allow remote control - such a unit can be serviced by one person on the site, provided that it works with a partner.


A digital level is also either optical-mechanical or laser, but the work with it is substantially computerized. The design assumes the presence of its own processor and memory, in this case the device itself acts as a partner for its operator - a second person is not needed to use it. The on-board computer of the unit allows you to more accurately assess the differences and more correctly evaluate the geodetic picture, in addition, it clearly submits all the collected (and already calculated) information to a special screen.
Among other things, the device is also able to remember the data that it recorded, which is very convenient for modeling and design. The whole principle of operation of such a level is built on modern technologies: even the divisions on the rail are applied in the form of a barcode so that the computer can read them automatically.


Leica instrument overview
Electronic levels from Leica (China) are presented in a wider range than analogues. They are designed for different types of work. Each device is equipped with a processor and large memory. The disadvantage is the weak body of the device, the level requires careful handling.
Their feature is to minimize human participation in the measurement process and maximize productivity.
Detailed characteristics of the devices are presented in the table below.
| Parameter | Sprinter 50 | Sprinter 150 / 150M | Sprinter 200M / 250M | DNA03 / 10 | LS15 / 10 |
| Increase | 24x | 24x | 24x | 24x | 32x |
| Accuracy, mm | 2.5 | 1,5 | 1,5/0,7 | 0,3/0,9 | 0,2/03 |
| Min. focal length, m | 0,5 | 0,6 | 0,6 | ||
| Objective diameter, mm | 36 | ||||
| Working temperatures | -10 ... +50 ° С | -20 ... +50 ° С | |||
| Assembled device weight, kg | 2,55 | 2,55 | 2,55 | 2,85 | 3,7 |
| Working hours in hours | unlimited, 4 AA batteries, 1.5V | 12 h |
We can say that an electronic level is an indispensable assistant for a modern builder. These are high-precision, automated devices that have their own software and help the owner to take the necessary measurements in a short time.
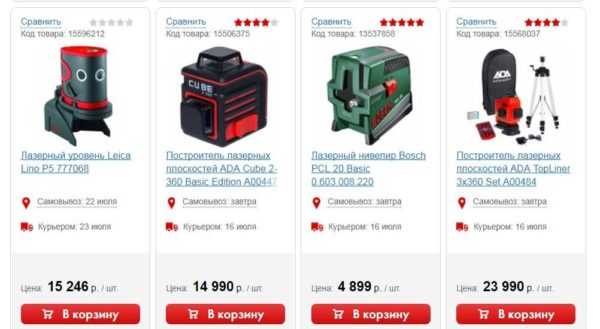
Inexpensive level Bort BLN-15-K (98296808) for finishing work in the apartment
- self-leveling with an accuracy of 4 degrees;
- the price is only 2200–3500 rubles;
- 360 ° rotation;
- works from the network.
Inexpensive laser line level from China. It builds lines with a range of 15 m. There are two beams: vertical and horizontal. The angle between them is 90 degrees. The color of the beam is red. One of them can be disabled. Installation accuracy 0.2 mm per meter. The device is self-leveling with an error of up to 3 degrees. There is an illuminated bubble level that allows you to more accurately set the horizontal plane. The device can be rotated 360 degrees. A geodetic scale is provided. The laser class is the second. The price is only 2200–3500 rubles.
The Bort BLN-15-K (98296808) model is powered by three AA-class rechargeable cells.The kit comes with a charger, which allows them to be recharged. It can be operated from the mains through a charger. Also included is a carrying strap and a padded inner case. There are also safety glasses, although it is not clear why they are.
Household appliance for apartment renovation. Also useful for building a house, especially since it is inexpensive.
Buyers like the device for its rich set, mains power, self-leveling, low error, accurate measurement. The main advantage is low cost. There are complaints about an uncalibrated bubble level - in this case, it becomes meaningless.
Pros:
- the price is 2200–3500 rubles;
- rotation of the limb by 360 °;
- self-alignment;
- the horizon level is set with an accuracy of 4 °;
- 2 beams with 90 ° crosshair;
- power supply from the mains through the charger;
- convenient case.
Operating principle
The operation of the device is based on the formation of projections of laser beams. The latter are focused using an optical system, which allows you to project lines and points on the desired object. Similar landmarks are used for marking when performing various works.
At its core, any laser level is an optical electromechanical device that visually displays planes, lines and individual points on different surfaces. They are located strictly vertically or horizontally, as well as at a specific angle.
The functions of radiation sources in the levels are performed by powerful LEDs. These semiconductors create a monochromatic stream with increased density and specific wavelength.
Level accessories
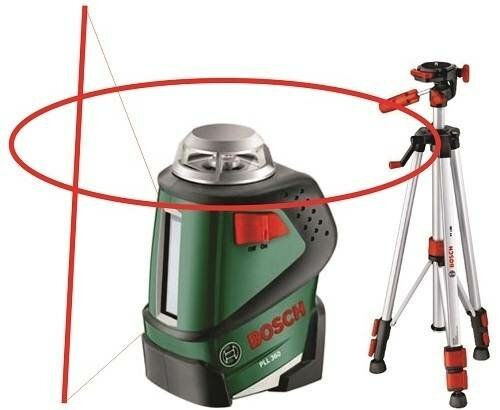
Additional accessories of the device include tripod stands and measuring rods.
The tripod consists of light alloys or aluminum, serves to install the device in the desired position and at the desired height
When choosing a tripod, you should pay attention to its maximum height, mount (it must be ergonomic and firmly fix the device in the required position), as well as strength and weight.
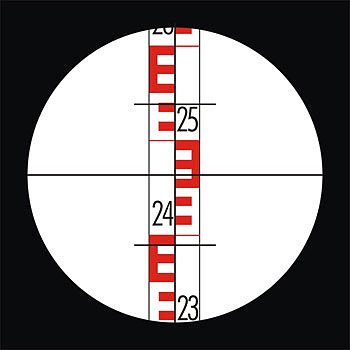
The rake deserves close attention. It should be of sufficient length (staffs of different sizes are produced) and have a scale of values that can be clearly seen in the eyepiece of the level from a long distance.
All models of measuring rails are marked with the letters PH and the numbers following the letter designation. For example, RN 3-2500 means the following: a leveling rod with an accuracy of 3 mm, a length of 2500 mm.
Some slats are of a folding telescopic type and are marked with the letter "C".
When choosing a leveling rod, proceed from the fact that their length ranges from 1 to 5 m, and the measurement accuracy depends on the material from which the rod is made. Invar is a special alloy that is not very susceptible to expansion when exposed to temperature.
Definition and classification
A level is a measuring device with the help of which the difference in the levels of the location of points in space in relation to a conditionally specified surface is calculated. They are often used by topographers or surveyors in the study of the relief, as well as by builders, when it is necessary to strictly observe certain parameters during the construction or repair of objects.
These devices are needed wherever it is necessary to perfectly align the surface vertically or horizontally, or to give a certain object or structure one or another slope level.
They are classified according to two criteria: the principles of their work and the accuracy of measurements.
There are three groups of devices in terms of the accuracy of reading the parameters:
- high-precision - a square-law error is allowed in measurements per square meter of a double stroke in the amount of 0.2-0.5 mm;
- exact - the permissible square-law error is 0.5-1 mm per square meter of double stroke, respectively;
- technical - the error rate is 2-10 mm, respectively.
To perform an elementary marking of the terrain and determine the differences in the relief, as well as its binding to the desired points, you can use simple devices of a technical type. But more accurate devices will be required to determine the parameters at all stages of construction work.
As for the classification of levels according to the principle of operation, they are as follows:
- Geometric. Such devices emit a sighting beam and bring it to a horizontal position. With their help, the difference in the position of points on a particular terrain is established. These points must be marked using special rails. Geometric leveling can be simple or complex. In the first case, it is carried out from one point, in the second - from several, which progressively change;
- Trigonometric. In another way, they are also called theodolites, and they are used to establish elevations between marks by means of an inclined beam. The tilt angle and distance are measured between the device and the control point, and then, according to the formula, the desired value is determined. This is quite difficult, at large distances or intersected surfaces, the result may be inaccurate;
- Hydrostatic. These devices consist of two containers of liquid connected to each other. The difference in heights at various points is determined by the level of the liquid. Full vessels are connected to each other by means of a sleeve and a hose and are placed at control points. The amount of excess of one point over another is determined by the difference between the height of the liquid column in each of the vessels. This method, although highly accurate, is limited by the distance of the length of the hose or sleeve;
- Optical and mechanical. With the help of such devices, the parameters of the points are determined by means of a light beam and laths marked in a special way. The devices have an optical tube for observation, as well as a device for leveling strictly horizontally. But in order to carry out measurements with their help, you need to have a number of specialized skills and knowledge;
- Laser. These are high-precision devices in which a narrowly directed beam is projected onto the surface by means of a laser. They are very easy to use, with their help you can work not only with points, but also with planes;
- Digital. Levels of optical or laser type, displaying information in digital form, are able to memorize it, and in some cases even partially analyze it. These devices are accurate and can be operated by one person, but they are expensive and sensitive to mechanical damage.
There are also special methods of leveling, they are carried out using devices such as:
- radars;
- barometers;
- sonars;
- stereoscopes, etc.
However, all these methods are almost never used for domestic needs.
Characteristics of devices
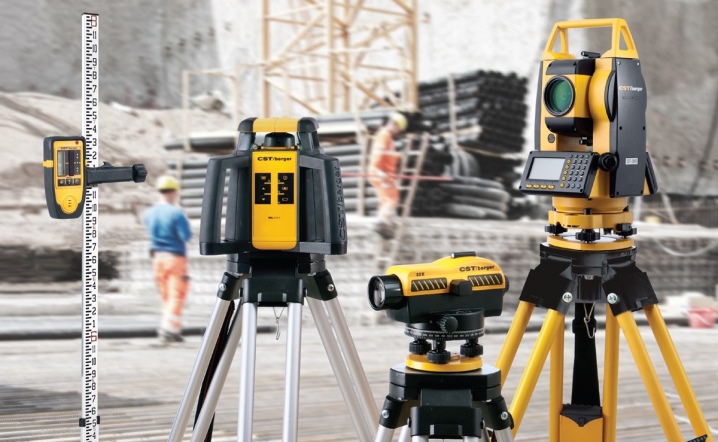
So let's take a look at both devices in turn and start with the theodolite.
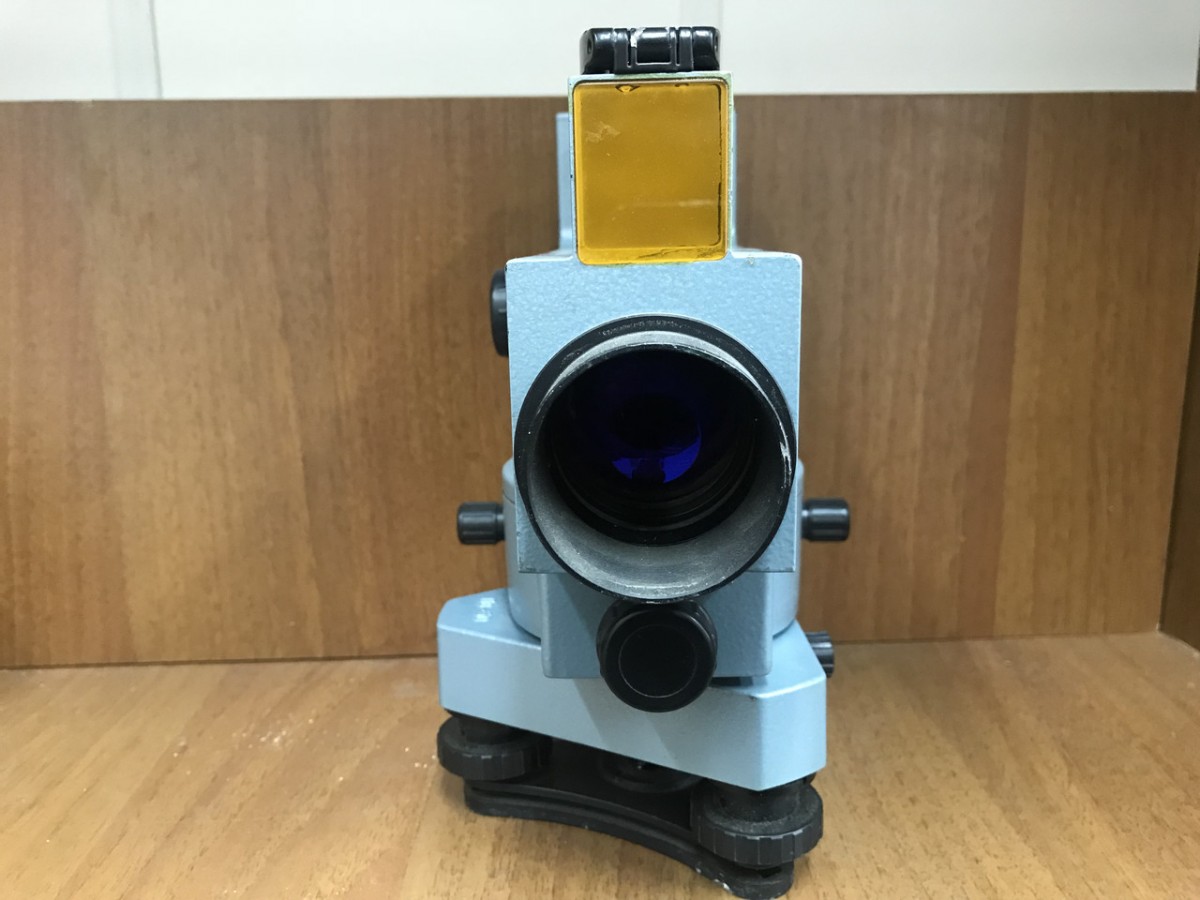
Theodolite is an optical device from a geodetic group, designed to measure angles, vertical and horizontal. The main components of the theodolite are:
- limb - a glass disk with a scale image on which the degrees from 0 to 360 are indicated;
- alidada - a disk similar to a limb, located on the same axis around which it freely rotates, has its own scale;
- optics - objective, lens and reticule necessary for aiming at the measured object;
- lifting screws - used to adjust the device in the process of pointing;
- level system - allows you to install the theodolite in a vertical position.

You can also highlight the body, which houses the above-mentioned parts, a stand and a tripod on three legs.
The theodolite is placed at the apex of the measured angle so that the center of the limb is exactly at this point. The operator then rotates the alidade to align it with one side of the corner and record the reading in a circle.After that, the alidade must be moved to the other side and the second value must be marked. In conclusion, it remains only to calculate the difference between the readings obtained. The measurement always follows the same principle for both vertical and horizontal angles.
There are several varieties of theodolite. Depending on the class, they are distinguished:
- technical;
- accurate;
- high precision.

Depending on the design:
- simple - the alidade is fixed on the vertical axis;
- repetitive - the limb and alidade can rotate not only separately, but also together.
Depending on the optics:
- phototheodolite - with a camera installed;
- cinetheodolite - with an installed video camera.
Now let's talk about levels.
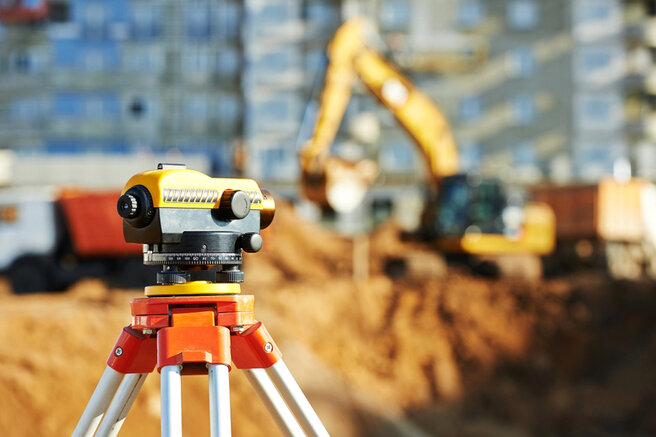
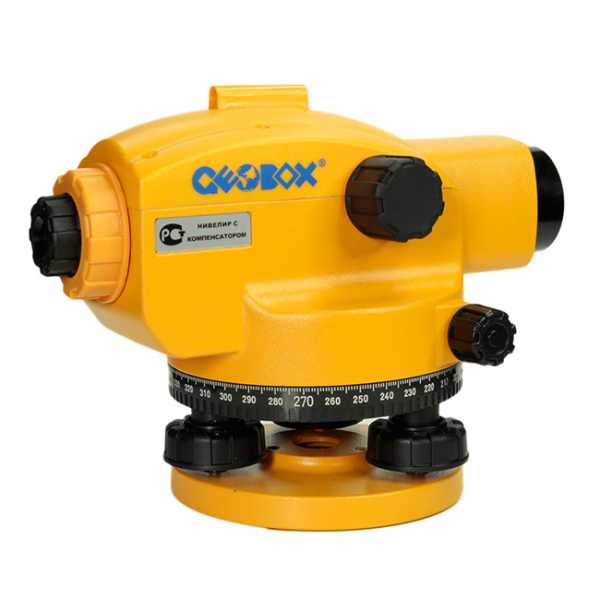
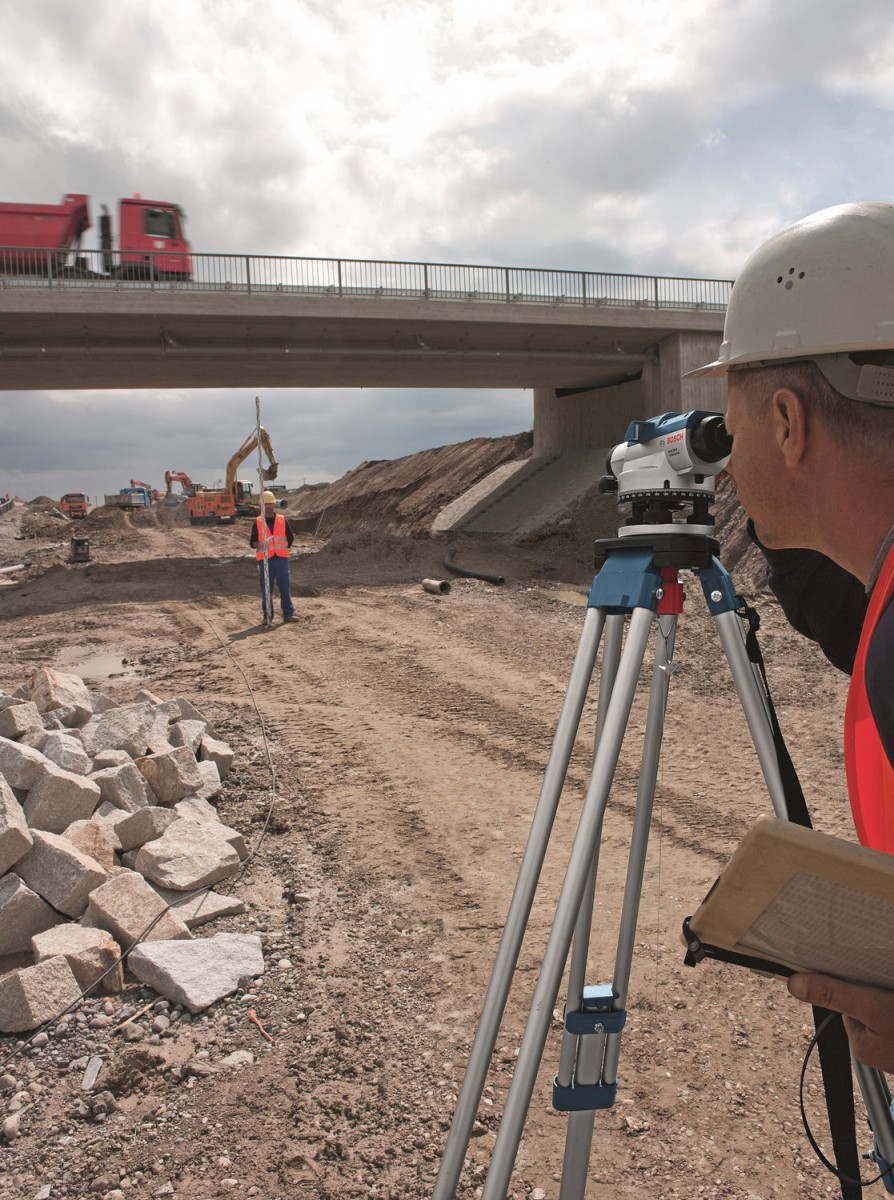
Level - an optical device from a geodetic group, designed to measure elevation points on the ground or inside erected buildings.
The design of the level is in many ways similar to the theodolite, but has its own characteristics and elements:
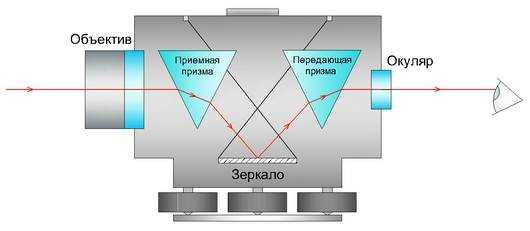
- optics, including a telescope and eyepiece;
- a mirror fixed inside the pipe;
- level system for installation;
- lifting screws for setting the working position;
- expansion joint for keeping the horizontal axis.

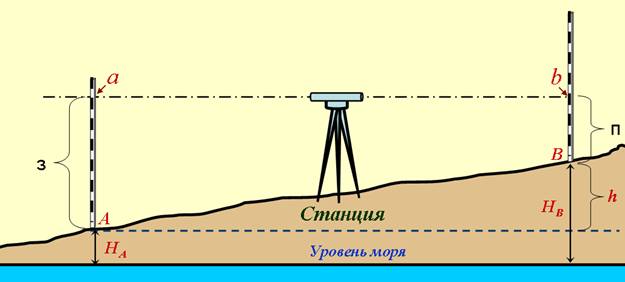
The level measures the height as follows. The device itself is installed at a point called an overview. All other measured points should be clearly visible from it. After that, in each of them, an Invar rail with a scale is placed in turn. And if all points have different readings, then the terrain is uneven. The height of a point is determined by calculating the difference between its position and the position of the survey point.
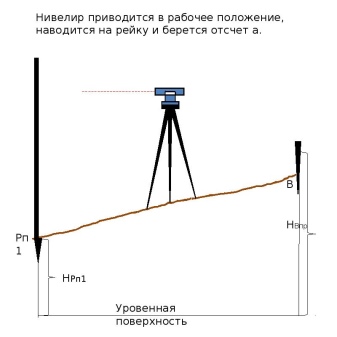
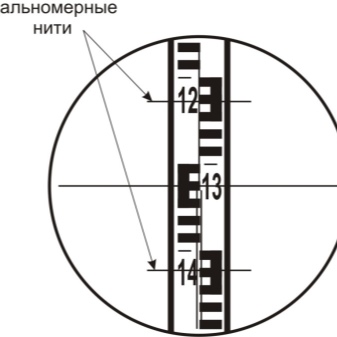
The level also has several varieties, but not as many as theodolite. These include:
- optical instruments;
- digital devices;
- laser devices.
Digital levels provide the most accurate results as well as ease of use. Such devices are equipped with special software that allows you to quickly process the recorded readings. Then they are saved on the device itself, thanks to the built-in memory.
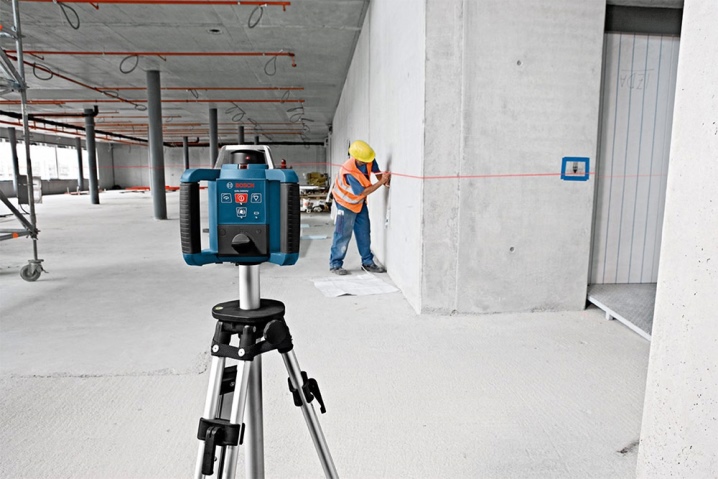
Today, a variety of laser levels is widely used in construction. Their distinguishing feature is the presence of a laser pointer. Its beam is passed through a special prism, which is used instead of a lens. As a result, two such rays form perpendicular planes in space, intersecting with each other. They help to level the surface. Therefore, laser levels are often used for repairs.

Technical specifications
The most important in the level are six structural details that are needed for competent and accurate measurement of heights.
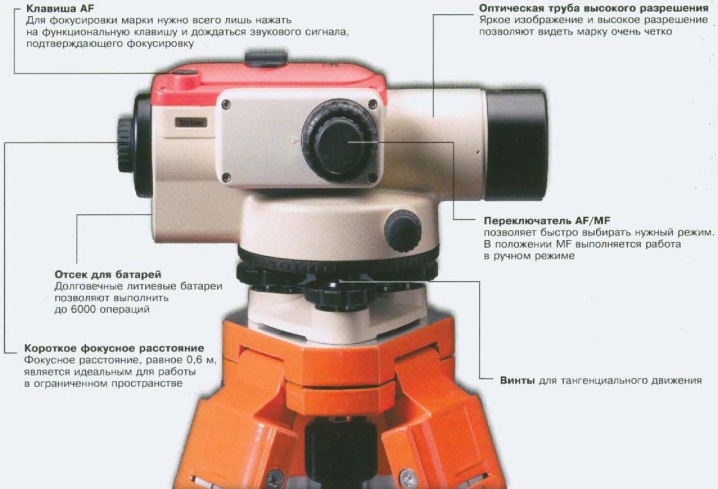
- The optical system is one of the most important elements. Lenses allow you to build a beam of a certain thickness and project it over long distances.
- The adjusting mechanism is required for setting the level on the ground. Modern sophisticated models are equipped with an automatic deflection angle detection system, which further simplifies the operation of the device.
- Control elements - are available for all types of laser levels, however, rotary devices have a variety of functions. But despite this, it is quite simple to understand the control - just read the instructions.
- Light emitter - represented by a built-in LED that projects a beam on a plane. High power LEDs are used for long distance measurements. However, they consume the power charge faster and cause the machine to heat up. One level can have from one to three LEDs at the same time.
- Batteries - are needed for long-term operation of the level, since the rotary instruments are autonomous. This role is usually played by finger-type batteries or removable batteries, the charge of which lasts up to 10 hours of continuous operation.Powerful levels simultaneously require several power sources: separately for the electric motor and LEDs.
- Rotation controllers - allow you to adjust the speed of rotation of the moving head for a specific task.

Also, the rotary laser level has additional accessories in the set, including consoles, targets and glasses, which facilitate the operation of the device.

Each model of the level has its own technical description, which details its characteristics. These include:
- extreme accuracy;
- the magnitude of the error;
- maximum distance;
- beam color;
- available features and capabilities.
Now that you have an idea of the parameters of the laser level and its structural elements, we can proceed to describe the operation of the device.

Similar parameters
A person who is not versed in measuring technology can easily confuse a theodolite with a level. And this is not surprising, because, as we have already said, both devices belong to the same geodetic group of devices used for measurements on the ground.
Also, confusion can be caused by external similarity and the same elements that make up the devices. These include the visual system, which includes a reticule for guidance.
Perhaps this is where any significant similarities end. Theodolite and level have many more differences than you might initially think. Nevertheless, in some situations and under certain conditions, these devices can replace each other. But we'll talk about this a little later. Now let's look at the most important issue, namely the distinctive features of theodolite and level.

Review of the best models
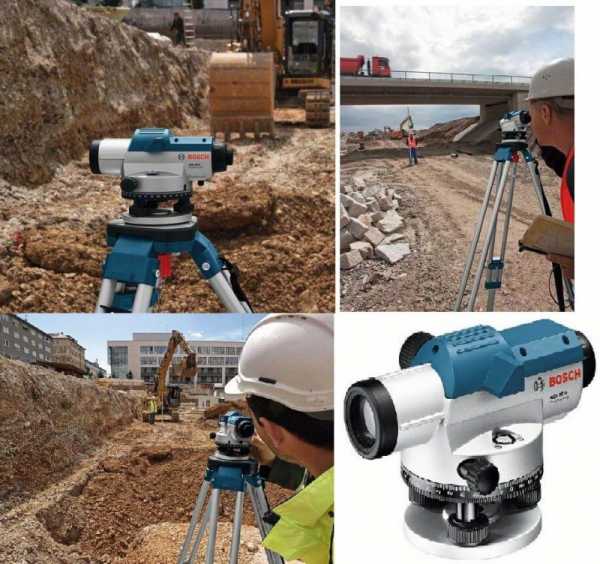
Speaking about the best manufacturers of levels, first of all it is necessary to mention the German company Bosch, which is known all over the world for the production of high-quality household appliances and other electronic devices. In fact, the scope of this firm is much broader: it also includes automotive, industrial, construction technology, etc.
But it cannot be said that the Germans monopolized the market for measuring instruments. Some manufacturers are not much inferior to them in terms of the quality of their equipment.
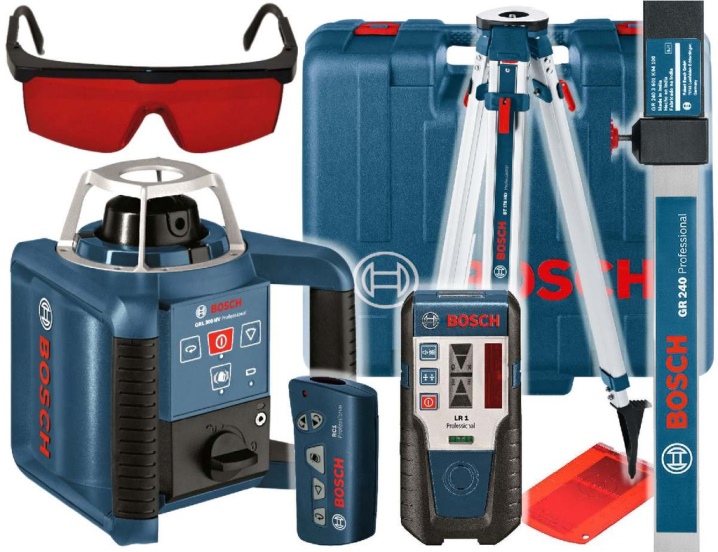

Here are the best models of rotary levels.
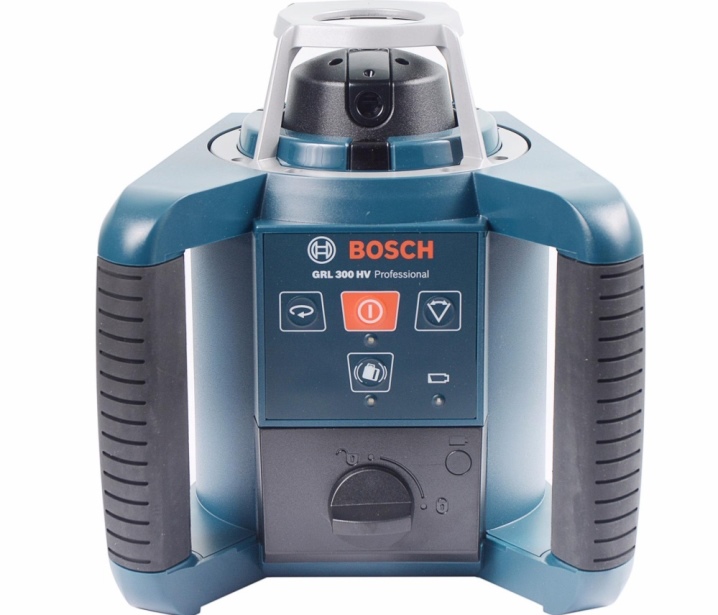
Bosch GRL 300 HVG Set is the most popular device in many areas. Contains almost all functions available today. Very accurate, the margin of error is minimal. The projection length of the plane is 150 meters. The wavelength is approximately 530 millimeters. The cost starts from 90 thousand rubles.






We also recommend paying attention to the levels from the manufacturers Hilti, Infiniter and Control. They have good characteristics and a very reasonable price.


How it works during filming
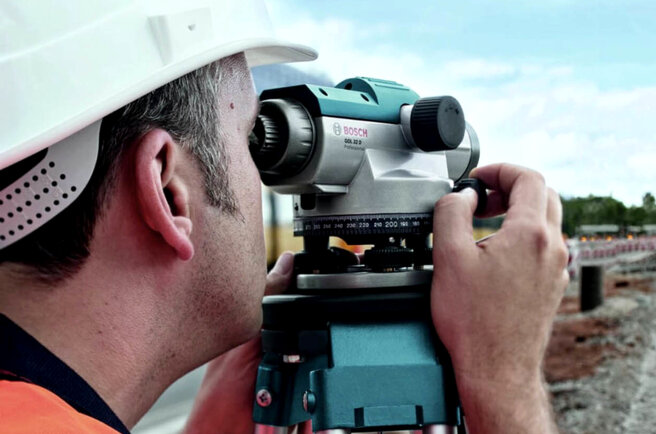
In order to avoid mistakes and understand the principle of operation of the device, you need to know how it works from the inside and what types of it exist. The most common optical instruments have varying degrees of measurement accuracy. They usually consist of a telescope with a special cylindrical level, with which you can control the horizon of the optical axis.
The image is projected through the optical prism system into the optics of the tube and then continuously monitored. In order to properly configure it for measuring work, you need to carefully read the instructions. Thanks to special screw mechanisms (azimuth, support and elevation), you can ensure the maximum accuracy of the exposed horizon. The device is placed on a special tripod with an axis of rotation.
To make the measurement results more accurate, and errors in determining the distance between different points are minimized, you should use digital-type levels.But for them, you need to have rails with special barcodes, thanks to which automatic data registration using microprocessors is provided.
The principle of operation of this level can be seen on the Internet in special videos. If there are no such slats, then these types of levels are used by analogy with conventional optical ones.
But remember that before using even the simplest optical level, it should be subjected to the following checks:
- level at the pipe;
- round level;
- horizontality of thread nets.
In addition, the level can also be checked for the vertical of the network of the device's marking lines with the level at the pipe.
Important indicators are also the price of the level division with the pipe, as well as its brevity. This allows the suitability to be determined.
The work itself can be performed using optical, as well as water or laser levels.
Optical Leveling Instructions
For correct installation and adjustment of the optical device, it is important to properly study the instructions
Setting up the tripod
First of all, you need to set up a tripod. By loosening the screws, the tribrach legs are set to a comfortable height for measurement. Then the screws are tightened again. The device is fixed to the tripod head. We also horizontally align the device with the bubble level.
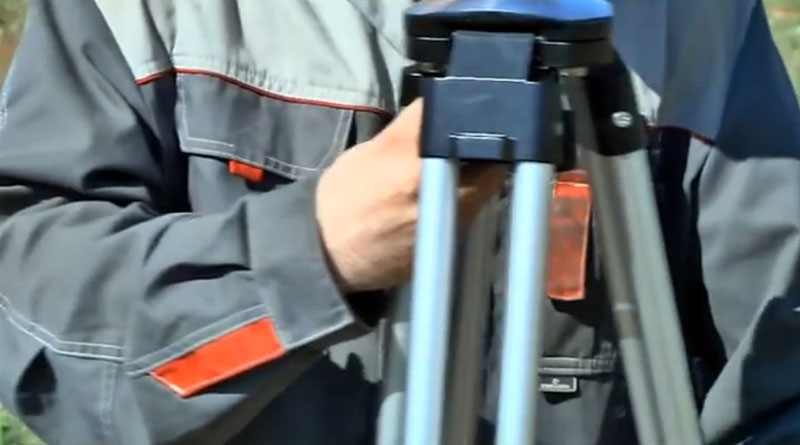 Setting up the tripod
Setting up the tripod
Installation of the device
The device is installed and secured by means of the fixing screw, which is located on the tribrach. Preparatory work involves adjusting the optics, mounting the level in a horizontal position.
 Mounting
Mounting
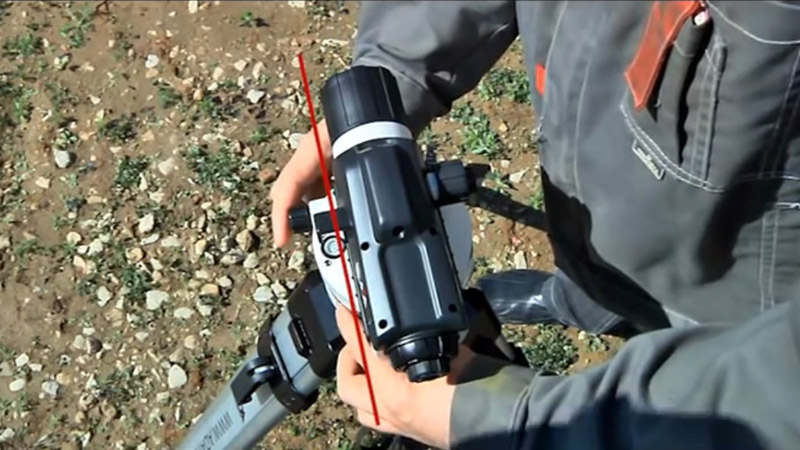
Focusing the optical-mechanical unit
Begin by leveling the instrument horizontally. To do this, the two lifting screws turn at once, the level bubble is positioned in the center. This point is called "zero point".
Next, you should go to focusing the optical level. The telescope is aimed at any surface. The eyepiece ring is rotated so that a clear view of the reticle will be achieved. The device is transferred to the rail, the focusing screw helps to adjust the corresponding visibility of the scale.
Centering is carried out during the installation of the fixture over the point, working by the "forward" method. The fixing screw is loosened, the plumb line is suspended.
The device moves along the tribrach head until the plumb line points to the required point. The screw is tightened.
 Focusing the instrument
Focusing the instrument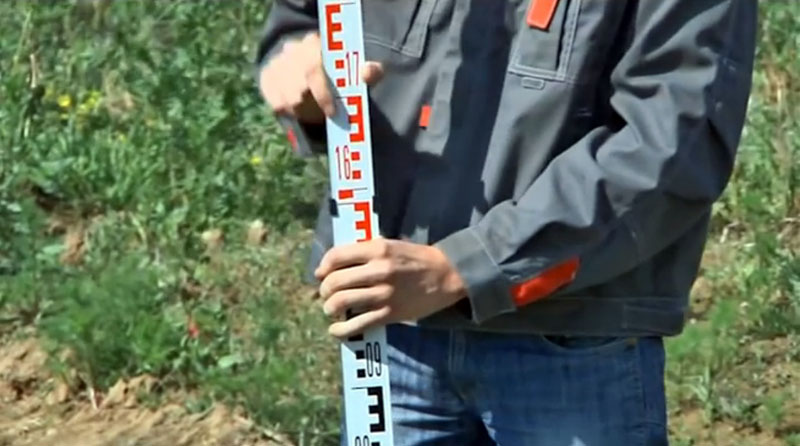  Installing the rail
Installing the rail
Measurement and recording of observations
After mounting the fixture in the center between two points, you should proceed to measurements.
A measuring rod is installed on the control point. Its exact location is controlled with the help of the vertical lines of the sight.
 Capturing observations
Capturing observations
Focusing
The taking of readings of the device is preceded by the focusing procedure. For focusing, a special element is used - a ratchet, which rotates to guide the focusing lens. When a sufficiently clear image of the measuring rod is obtained, it is also necessary to achieve a clear image of the reticle.
The middle thread of this mesh will determine the height. To make it clear, you need to rotate the eyepiece knee to the desired position.
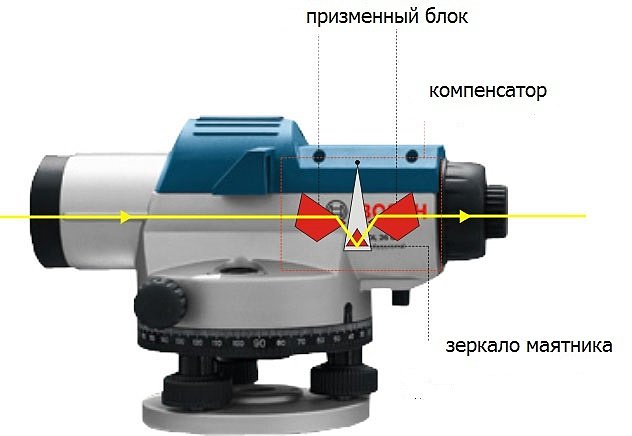
In optical levels of classical design, you can see the bubble ampoule of a cylindrical level through the telescope. Focusing on the bubble, the pipe is brought to a horizontal position by rotating the guide screws.
If the problem of horizontal alignment is solved with the help of a compensator, there is no need for a cylindrical level on the telescope, but there is a setting level on the body of the device. With its help, you must place the device on the stand level, adjusting its position with the screws, and only then focus.


Types of devices
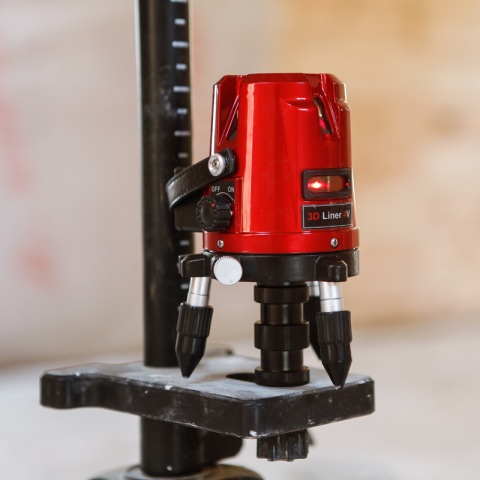
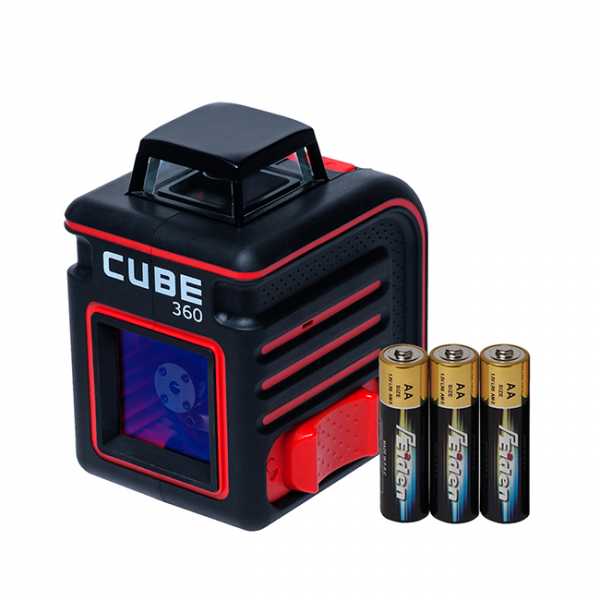
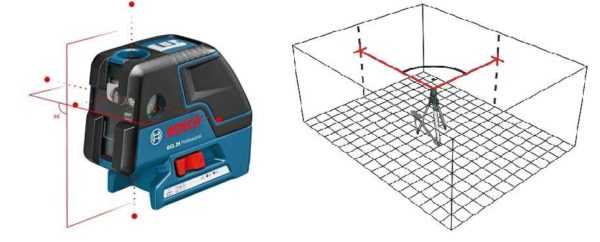
There are three main groups of laser levels, differing from each other in purpose, design complexity and number of beams.
Point (axis builder)
The device is capable of projecting a point without forming a straight line. To apply horizontal markings, it is necessary to successively mark two points at different ends of the wall and draw a line between them or pull a cord.
The point has maximum clarity on the plane, so the range of the axis builders is noticeably greater than that of other views
You have to take some additional steps, which complicates the measurements somewhat, but the accuracy and the ability to determine the distance using a laser rangefinder, as well as the presence of up to five beams (in the most advanced models), increases the accuracy of the work.
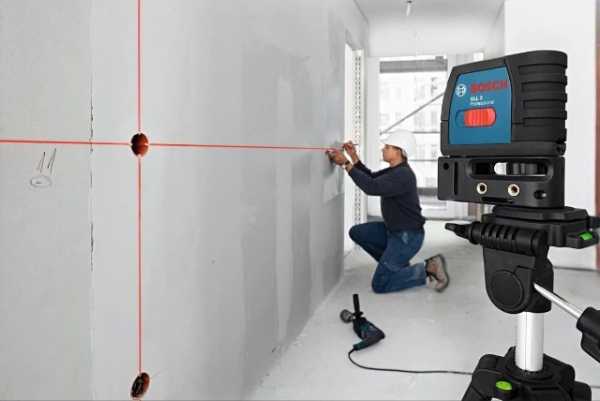
Crossliner (line builder)
This type of leveling allows you to build a light line on a plane. The beam is passed through a prism that unfolds it by 120 °, due to which a straight thin strip appears on the surface.
It is convenient to work with a crossliner when the planes are uneven, have a complex relief or a lot of elements that make traditional marking methods impossible.
Separate models of such devices allow you to simultaneously obtain horizontal and vertical main lines, and up to 5 additional ones. The possibilities of the level allow not to apply any markings on the wall or floor, but to work directly along the projected light axes.
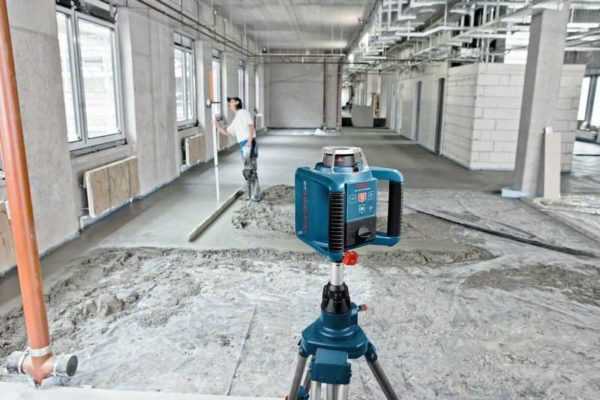
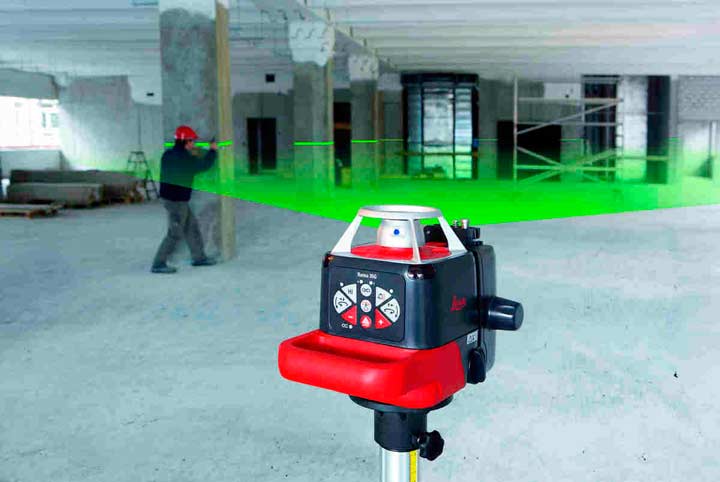
Rotary plane builder
In this case, it becomes possible to obtain one or several planes (usually one horizontal and two vertical).
The rotary level is indispensable for leveling the floor, pouring the screed, installing a stretch ceiling and other work with planes that require precision and high quality
The light beam rotates around its axis, projecting a continuous light strip around the source, which builds a plane. This allows you to determine the degree of slope of the floor or ceiling, to control the verticality of walls or partitions.