Types of transplanting roses in autumn
There are several methods for transplanting roses. Choosing a method is required based on the variety of the rose. More details about the technology and the benefits of each of them will be discussed below.
Classic method

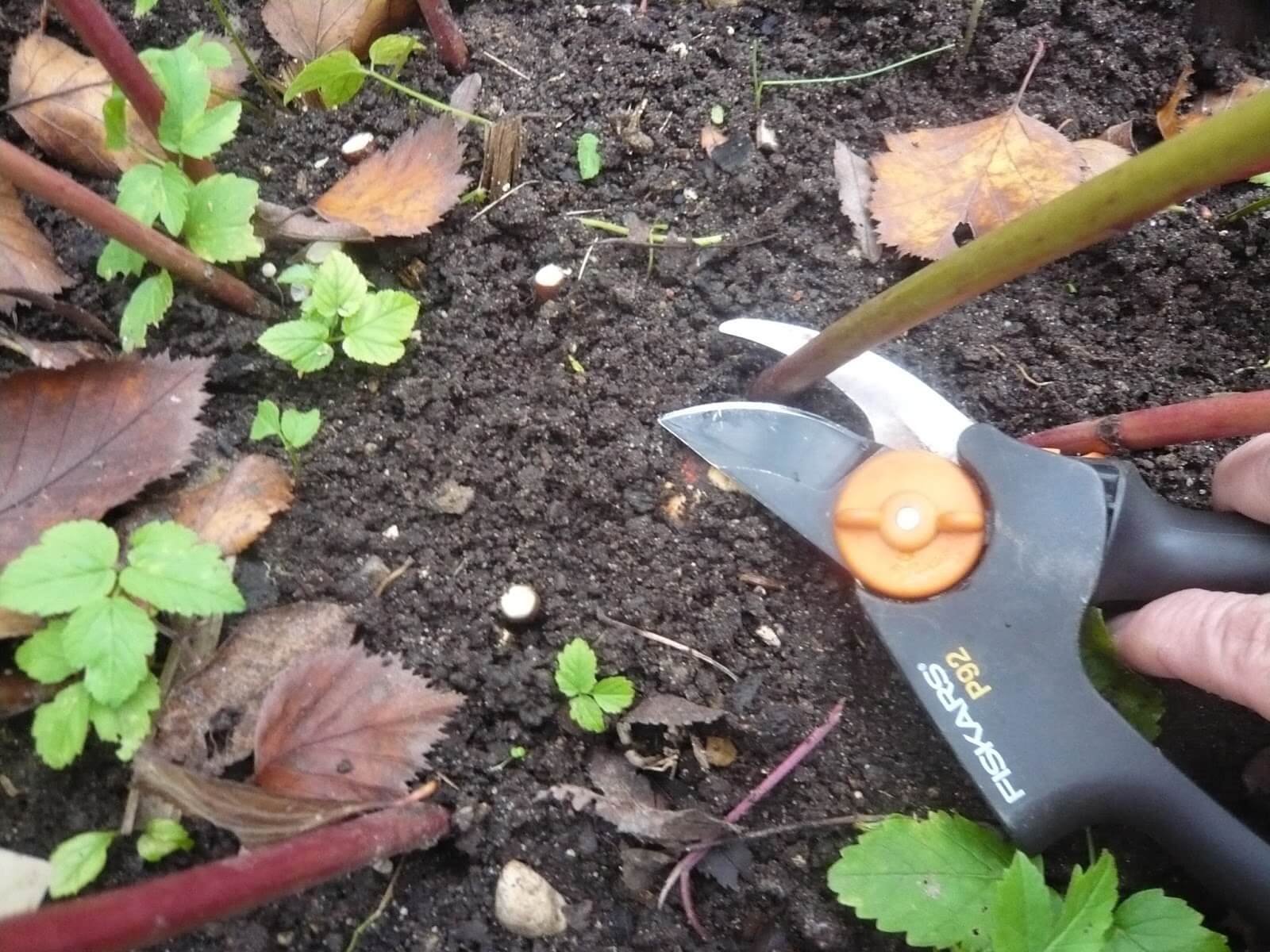
This transplant method requires special care with the root system.
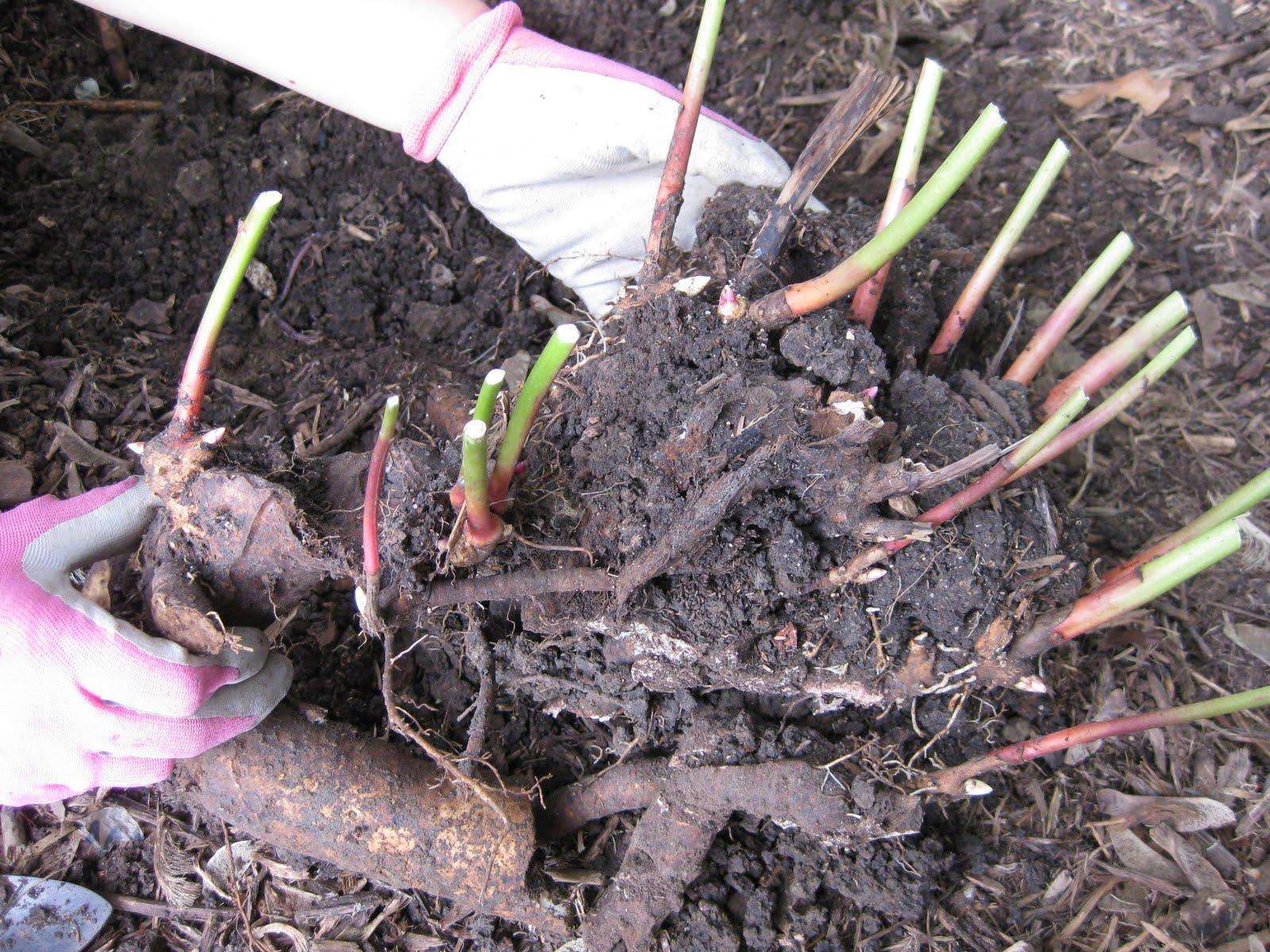
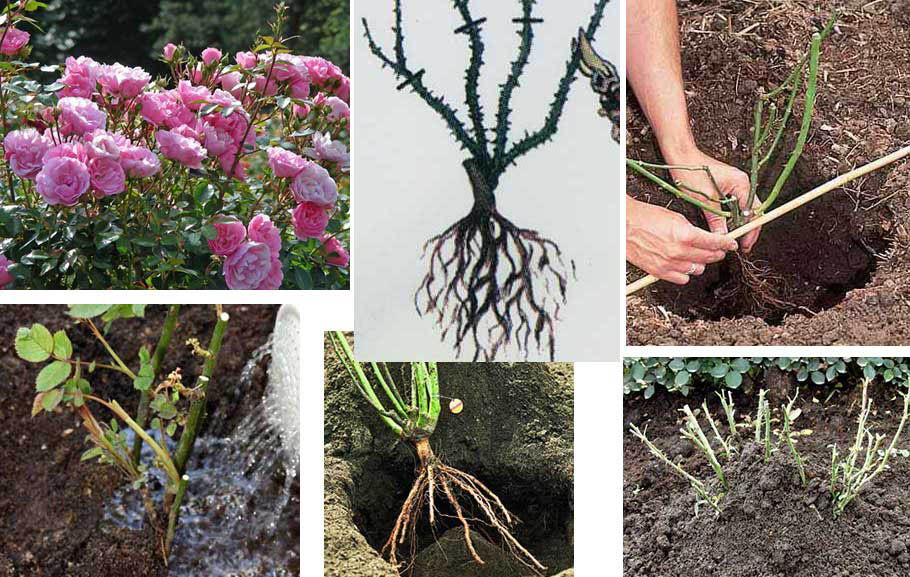
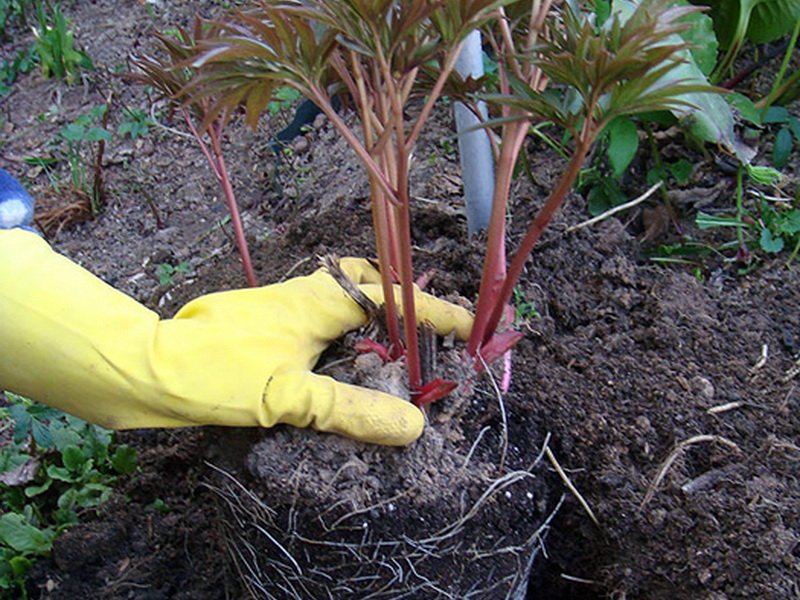
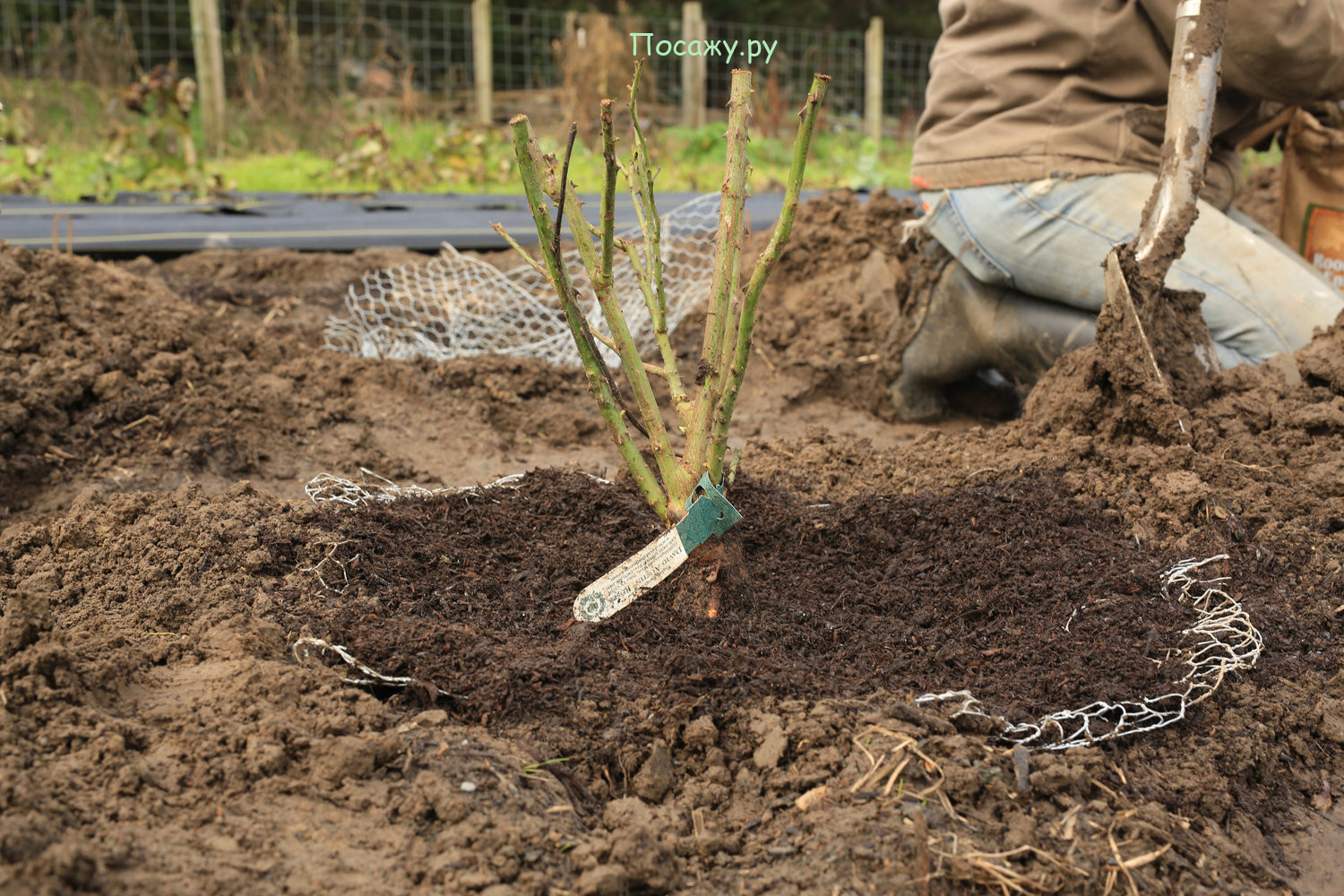
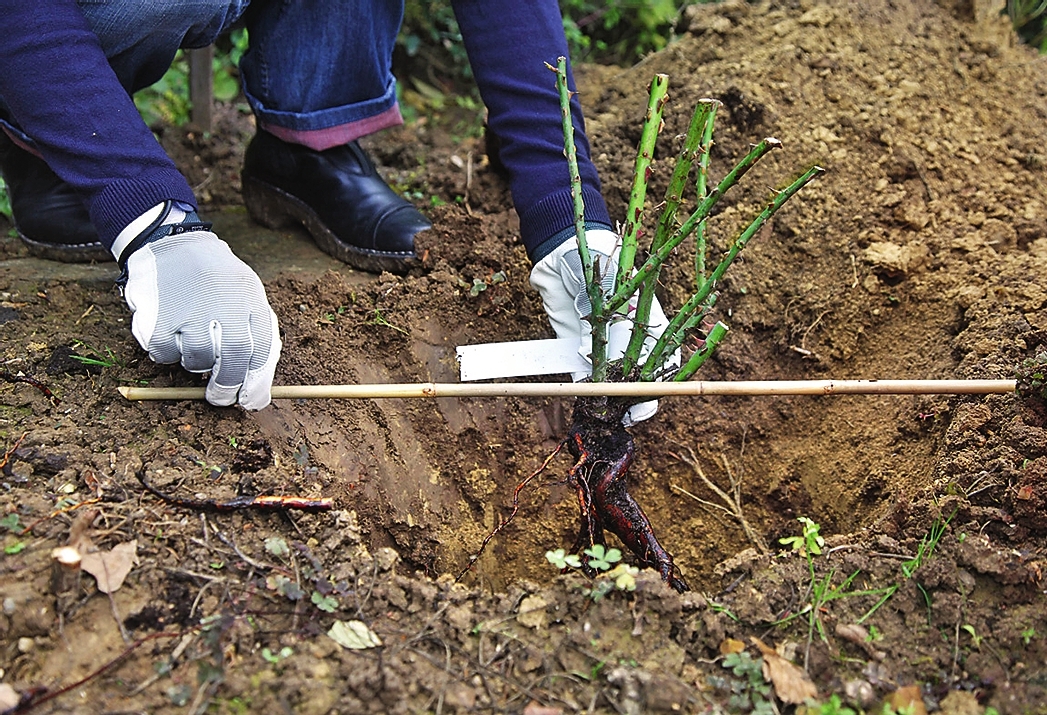
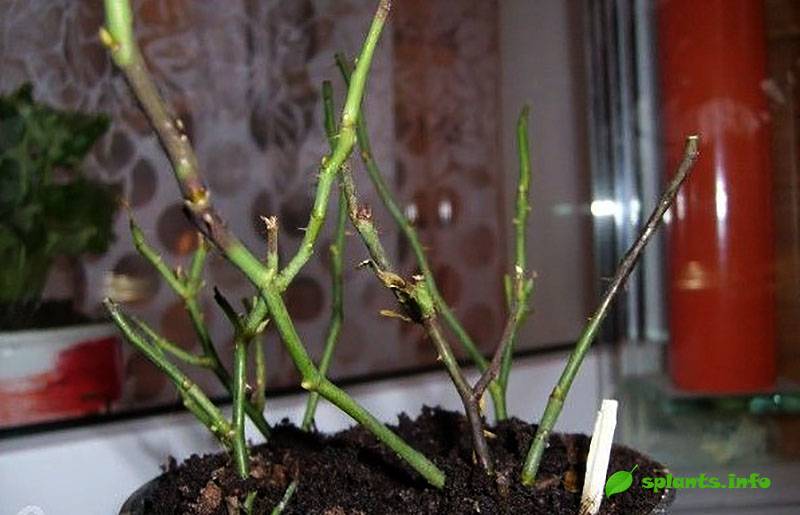
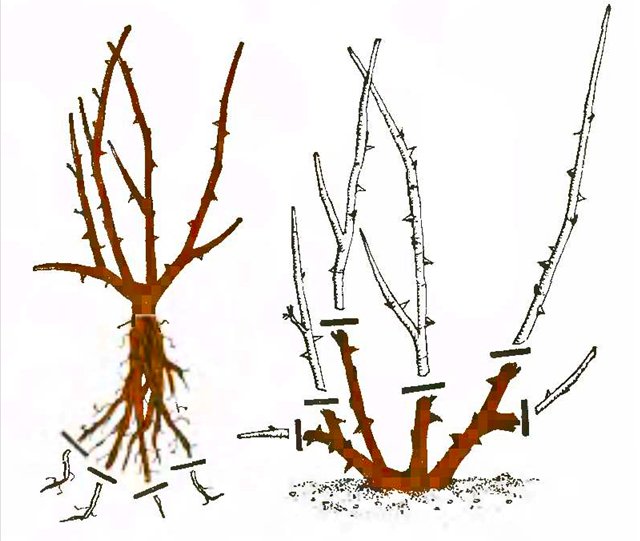
Transplanting bare-root roses is a classic method. The method is also suitable in the case when it was not possible to preserve the earthen lump during excavation. The root system must be carefully examined for diseased and dried roots. All damaged areas are immediately removed.
It is important to leave the length of the roots longer than the shoots. Next, the root system is placed in a container with rooting solution
The procedure is necessary in order for the plant to quickly take root in a new place. Can be planted in two hours.
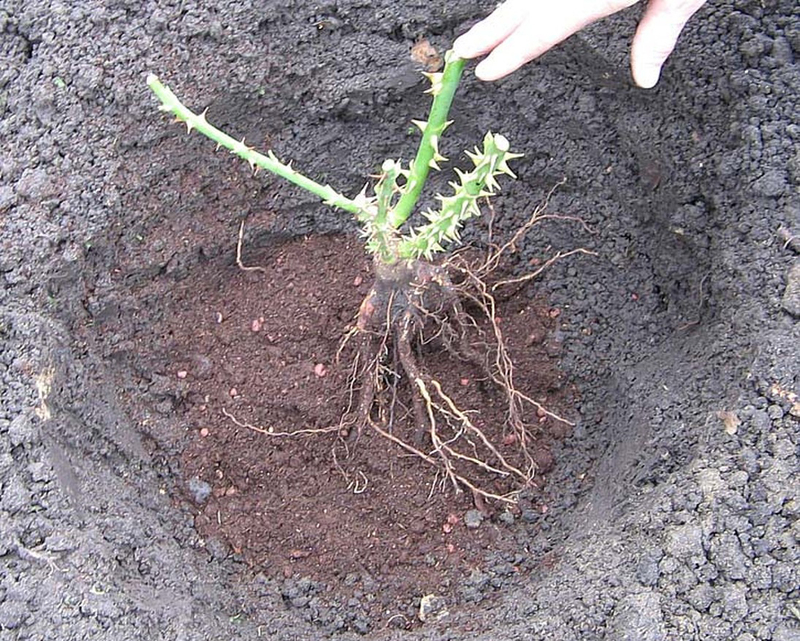
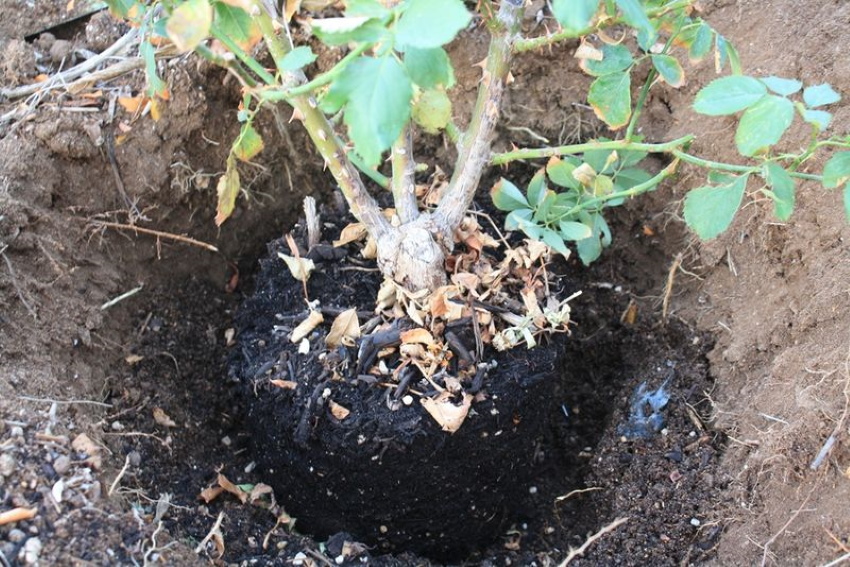
Then a hole is made with a small handful of fertile soil and the plant is carefully placed. Drainage can be placed at the bottom of the pit. It includes: river sand, small stones or gravel. Drainage will allow the roots to "breathe".
Next, you need to spread the roots well inside the flower bed. After that, the rose is watered and tamped into an intermediate layer of soil. Next, you need to water it again and fill the hole completely
It is important to compact the earth well so that there are no empty places and air congestion. In the presence of air, the plant may die.
In the event of the onset of the first frost, the roots are reliably sheltered from frost.
Method for beginners

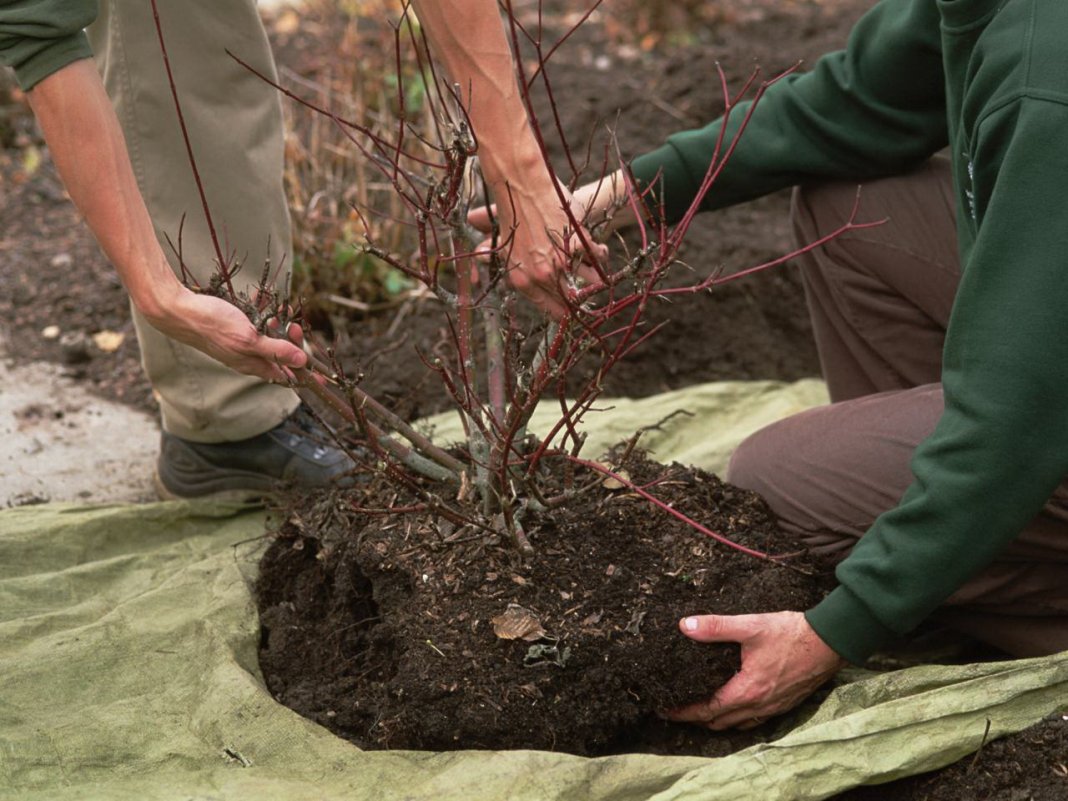
Transplanting a plant along with old soil is the easiest
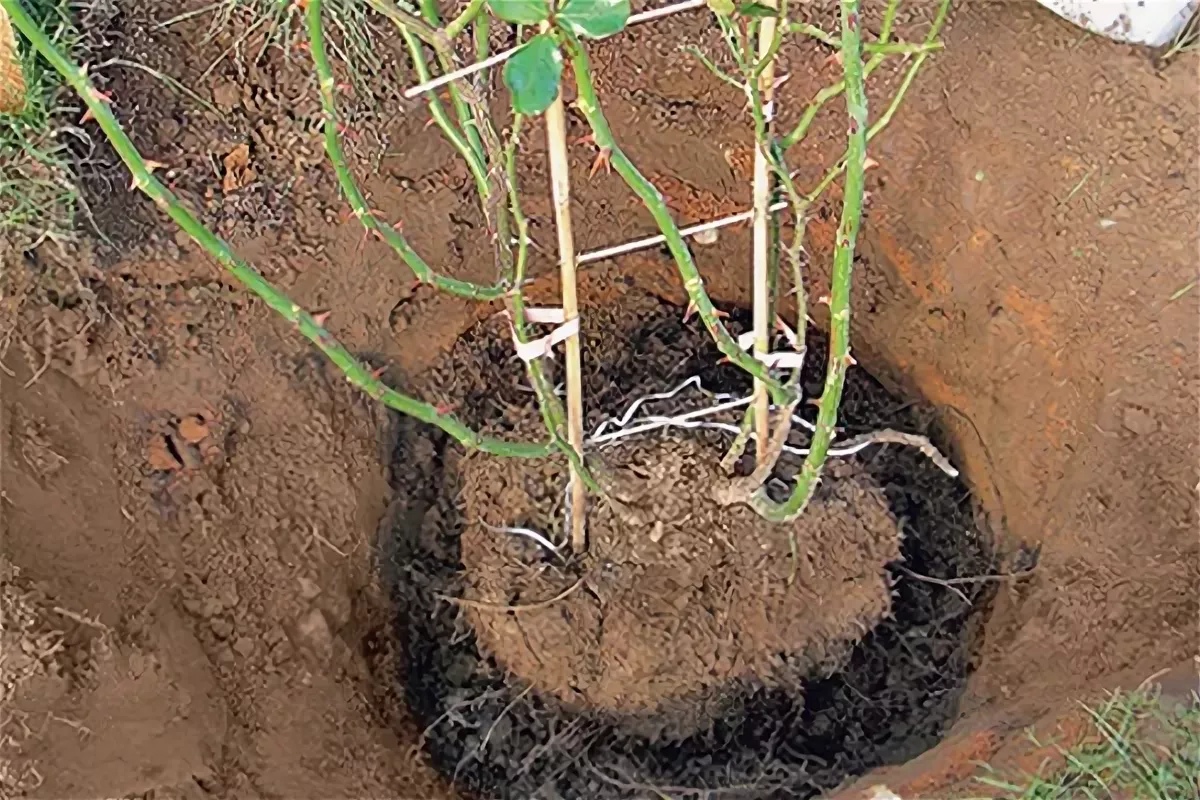
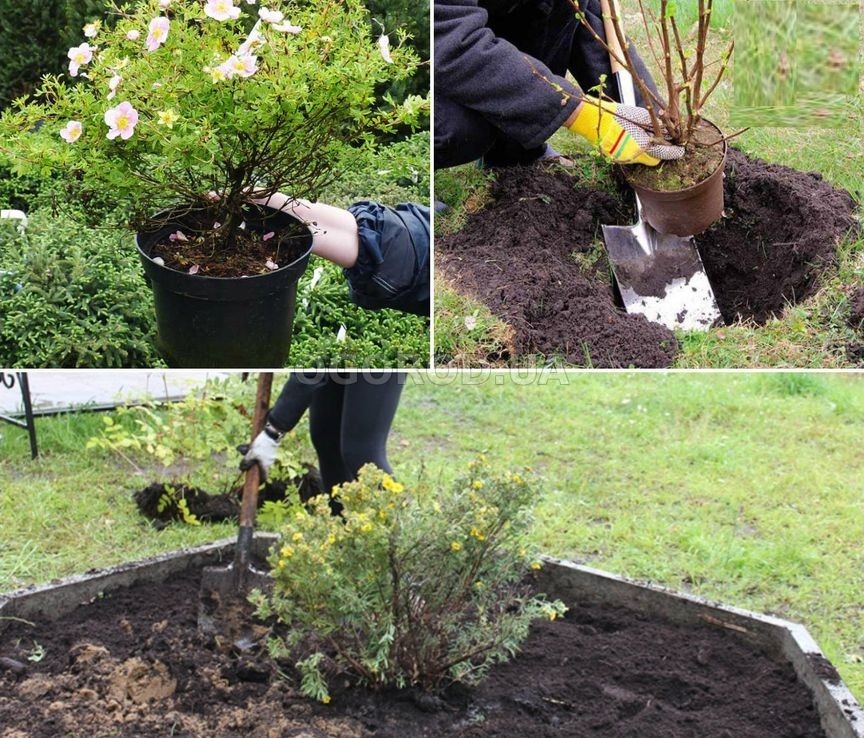
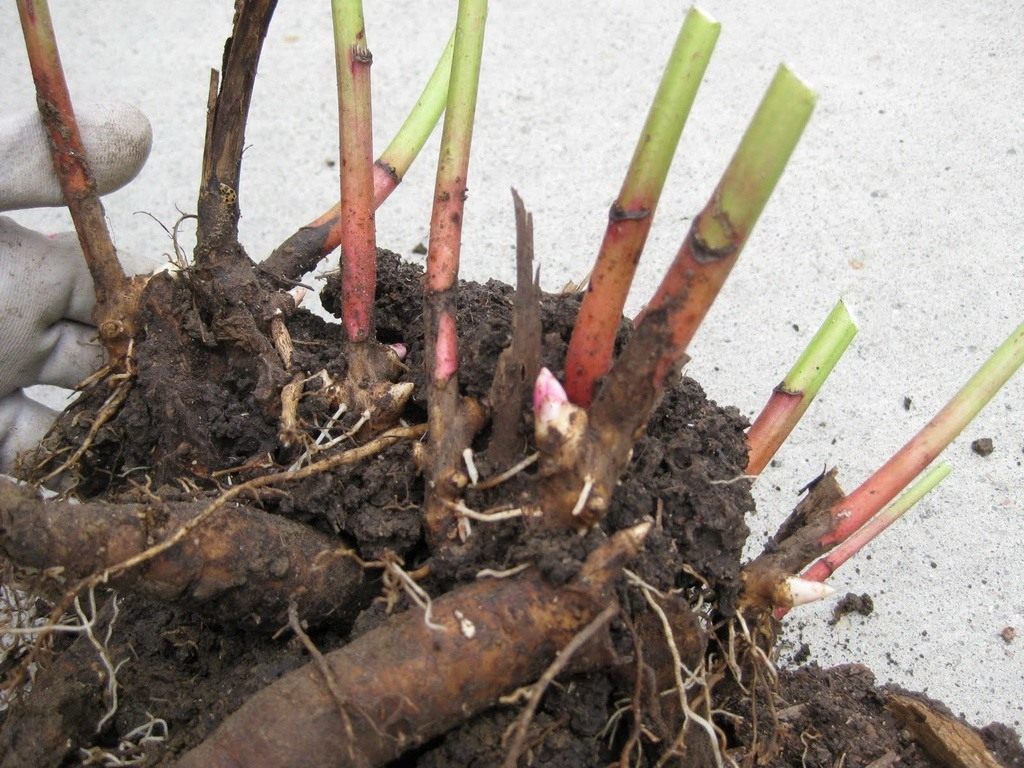
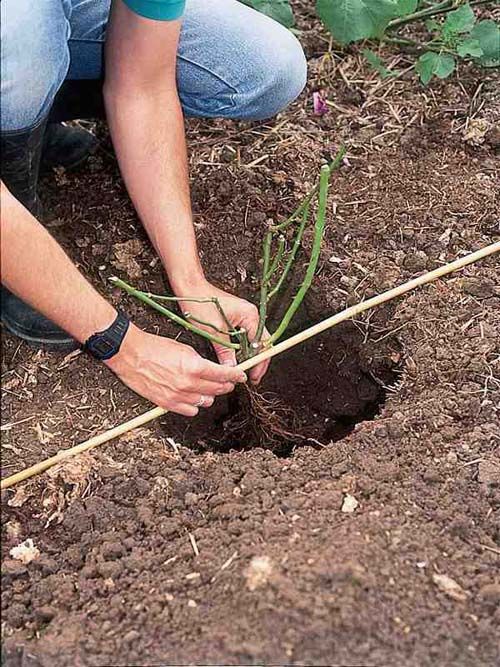
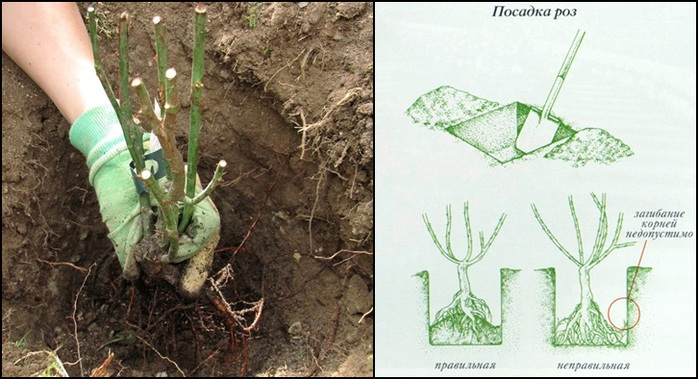
The method of transplanting roses with a lump of earth is suitable for novice gardeners. The principle is also called "wet" and does not require special skills and knowledge. There should be enough soil on the root system from the previous place
It is important to prepare a hole larger than the roots of the plant. Further, water is poured to the bottom
You can add humate and soil with trace elements. Next, the rose is placed, dripped in and watered again abundantly. After that, you need to add the remaining soil and tamp the surface well. Air congestion is unacceptable.
The advantage of this method is the absence of root damage. The plant is placed in a new hole in its usual soil, but from the fresh soil it will receive the necessary trace elements and substances. When transplanting with the "wet" method, there is practically no risk of dropping the buds. In the event that flowering continues during the transfer. When planting several bushes, you need to maintain a distance between the bushes of 60-80 cm. Thus, the roses will not interfere with each other.
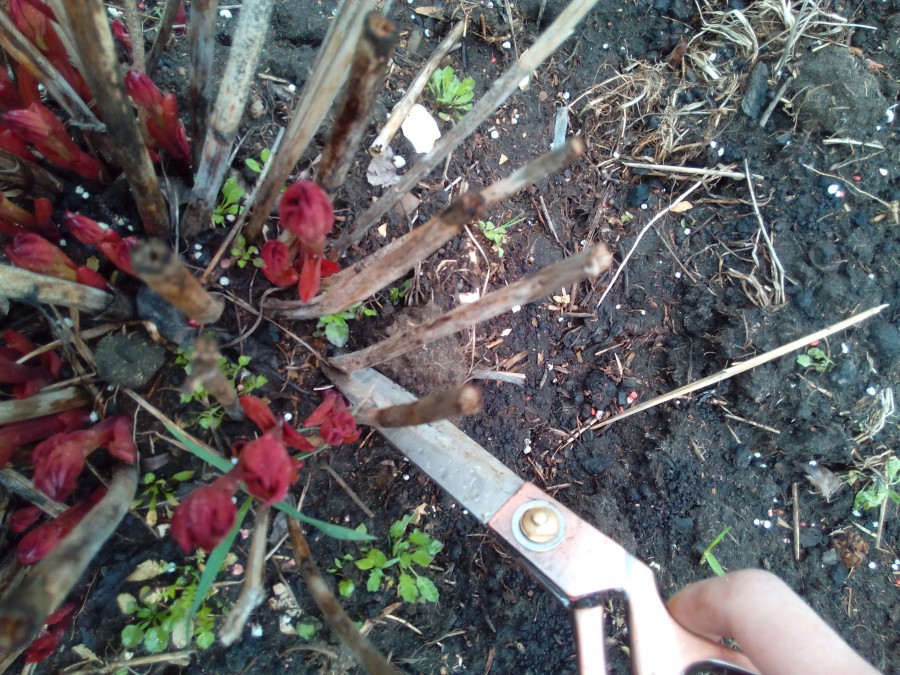
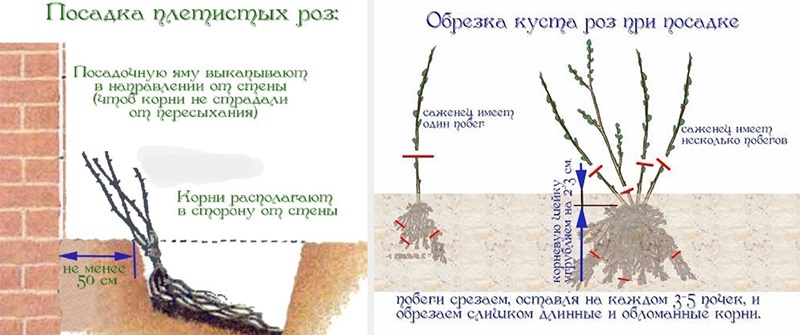
Pruning a bush
The bush is pruned 3 times:
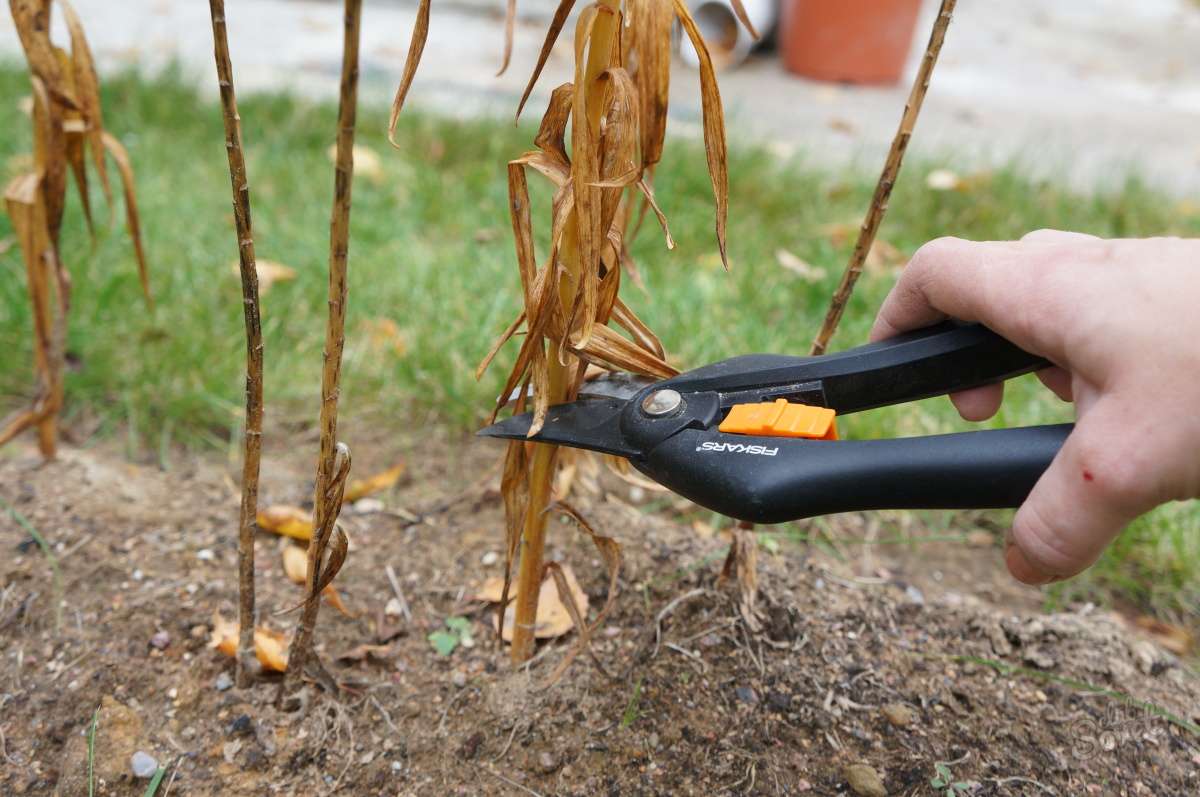
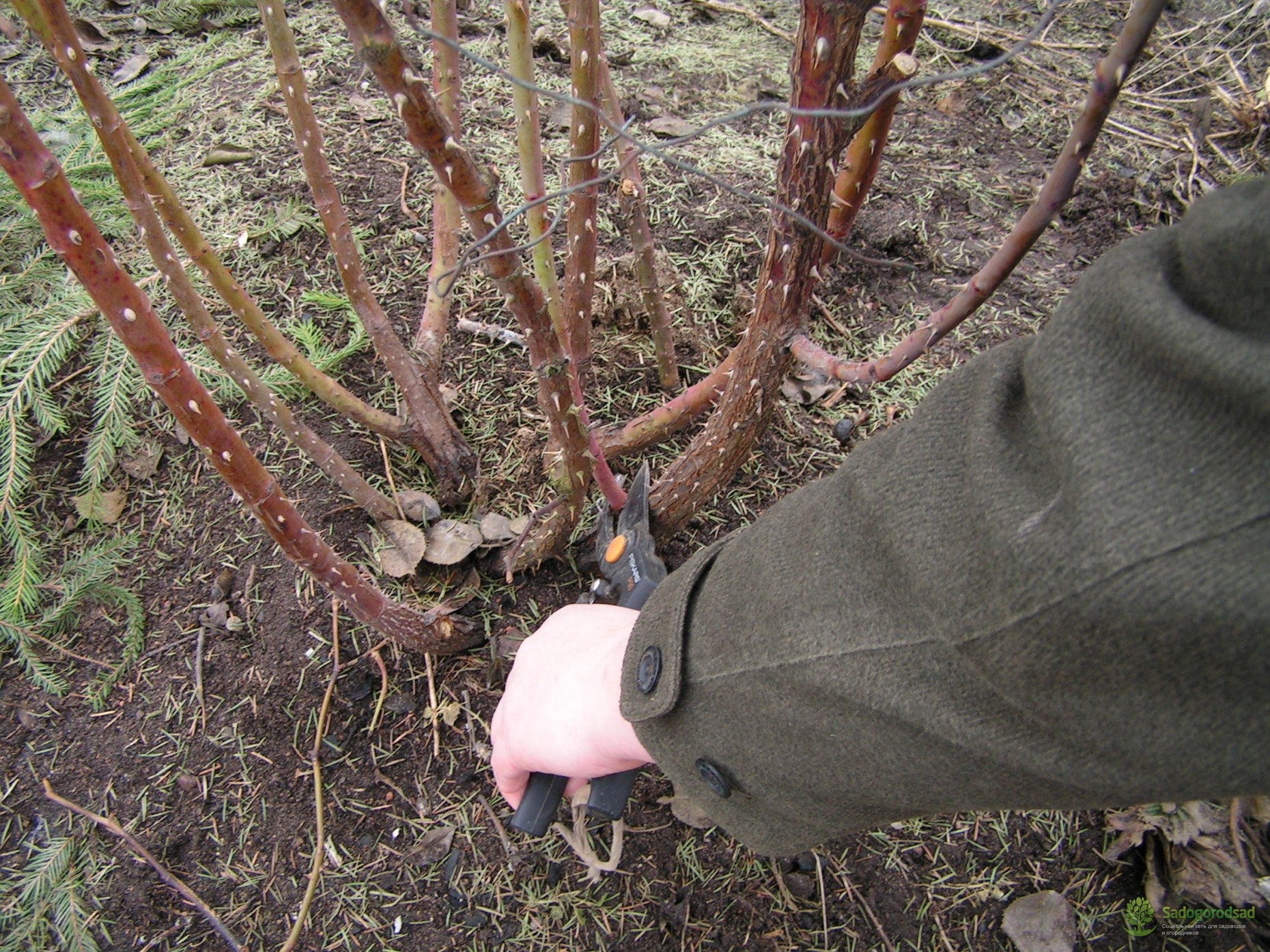
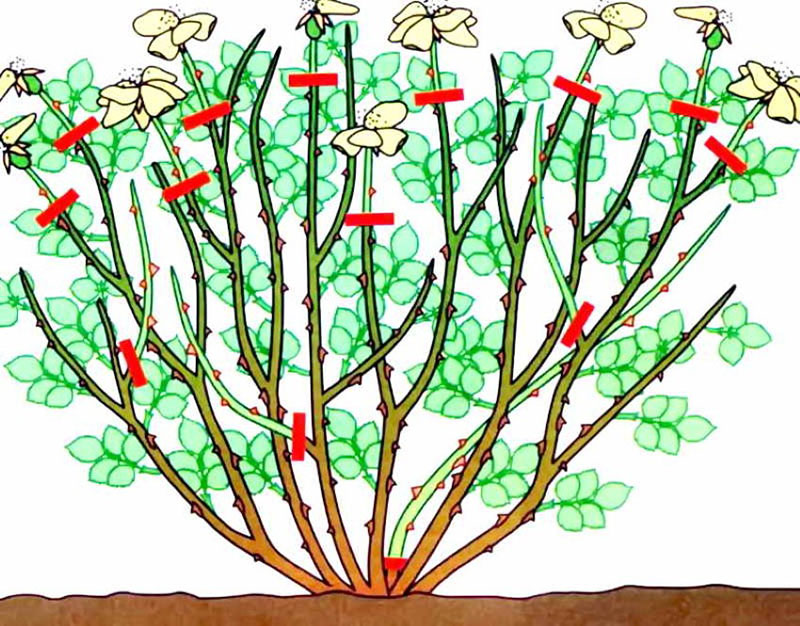
- In Spring: This helps to shape the plant, stimulate the growth and development of the side branches, which will make the rose more luxuriant. Produced before the appearance of the kidneys. It is the most important and radical pruning, thanks to which the bush takes the desired shape, dry or improperly growing (inward) branches are cut from it;
- In summer: pruning of dry and unnecessary branches, flowers and fruits is carried out. This is a sanitary procedure in which shoots are removed, leaving 2-3 buds;
- Autumn: prepares for winter. Weak branches are removed, which will deprive the bush of nutrition.
When pruning, it is best to remove old branches, leaving the youngest and strongest ones. You can determine the age by the color of the bark: the darker it is, the longer the twig lives.
Transplanted plant care
Subsequent care for a rose bush of any variety consists of regular watering, feeding and pruning, as well as observing a period of winter dormancy.Here are some valuable tips for growing a whimsical flower at home.
- Watering a rose in a pot is necessary after the top layer of soil has dried. In spring and summer, watering should be abundant, in winter, moderate and rare.
- It is better to take water for irrigation warm, filtered or rainwater, it should be poured only at the root.
- The bush is fed with organic and mineral fertilizers, adding them in the summer 1 time a week when watering, in the fall - once every 2-3 weeks.
- In summer, the temperature in the room should be kept at around 20-25 degrees, in winter - about 10-15 degrees.
- If the apartment is dry and warm, every day the plant is sprayed with warm water from a spray bottle.
- It is advisable to place the pot on a lighted windowsill, regularly airing the room during the warm season.
- Before wintering, the flower must be pruned, removing the remnants of foliage and the tips of the branches. To form a beautiful crown, 5-6 buds should be left on each branch in the fall.
You should also regularly inspect a room rose to prevent it from becoming infected with various diseases and pests. When aphids, spider mites or spots appear on the leaves, treatment with appropriate drugs or folk remedies must be carried out.
For those who want to study in detail the information on how to transplant a room rose correctly, the video below with practical recommendations from an experienced florist will help.

The room ones can undoubtedly be called flower queens. They are popular and require proper care.
Plants need not only general care: feeding, watering, access to fresh air, observation. Pruning is important for abundant and consistent flowering.
Further in the article, we will talk in more detail about the features of the room rose pruning procedure, and also provide step-by-step instructions.
Favorable time for transplant
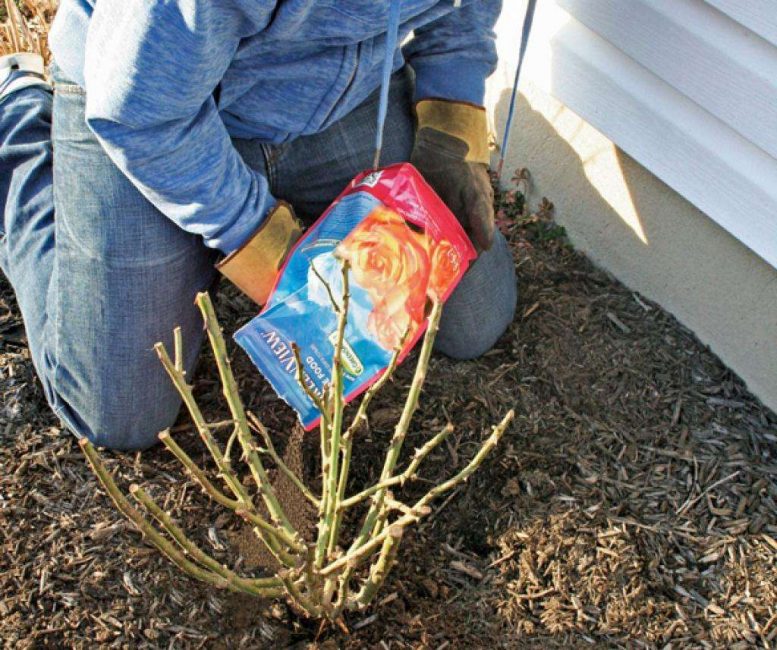
The best time of the year to transplant roses is early spring or early autumn. In spring, the weather should be warm, free from frost, but it is advisable not to postpone the matter until the summer heat. In the fall, all work must be completed by the end of September, otherwise the rose will not have time to take root in a new place and get stronger before winter.
Summer is not the best time to transplant adult roses, but if you create optimal conditions for the plant, the chances of success are high. You should not plant old bushes in an open sunny place, in the evenings, after sunset, it is good to spray the crown of the bush - this will help him to transfer the heat. 2-3 weeks before transplanting, you need to cut the shoots to 40-50 cm, be sure to remove the flowers and buds so that they do not take away the vitality from the bush.

Features of transplanting climbing varieties
Before digging up the roots, you need to disconnect the shoots from the support. If a rambler is to be transplanted, young shoots do not need to be cut off, and branches older than 2 years old must be completely removed. At the end of the season in August-September, the tops are pinched on the shoots of the current year.
For claimings, the situation is slightly different: before transplanting, the length of the shoots should be shortened by half.
Features of spring rose transplant
 Usually, the planting time falls in April, when the cold has already receded, and the first buds have not yet woken up and the plant is ready to spend its vitality on confident rooting in a new place.
Usually, the planting time falls in April, when the cold has already receded, and the first buds have not yet woken up and the plant is ready to spend its vitality on confident rooting in a new place.
However, the gardener must prepare for this responsible procedure in advance, three weeks or a month before the scheduled date for transplanting the rose bush.
Transplant equipment:
- tools (shovel, pitchfork, pruner, bucket, watering can);
- rags (burlap, natural fabric);
- spruce branches or screen for shading from the sun.
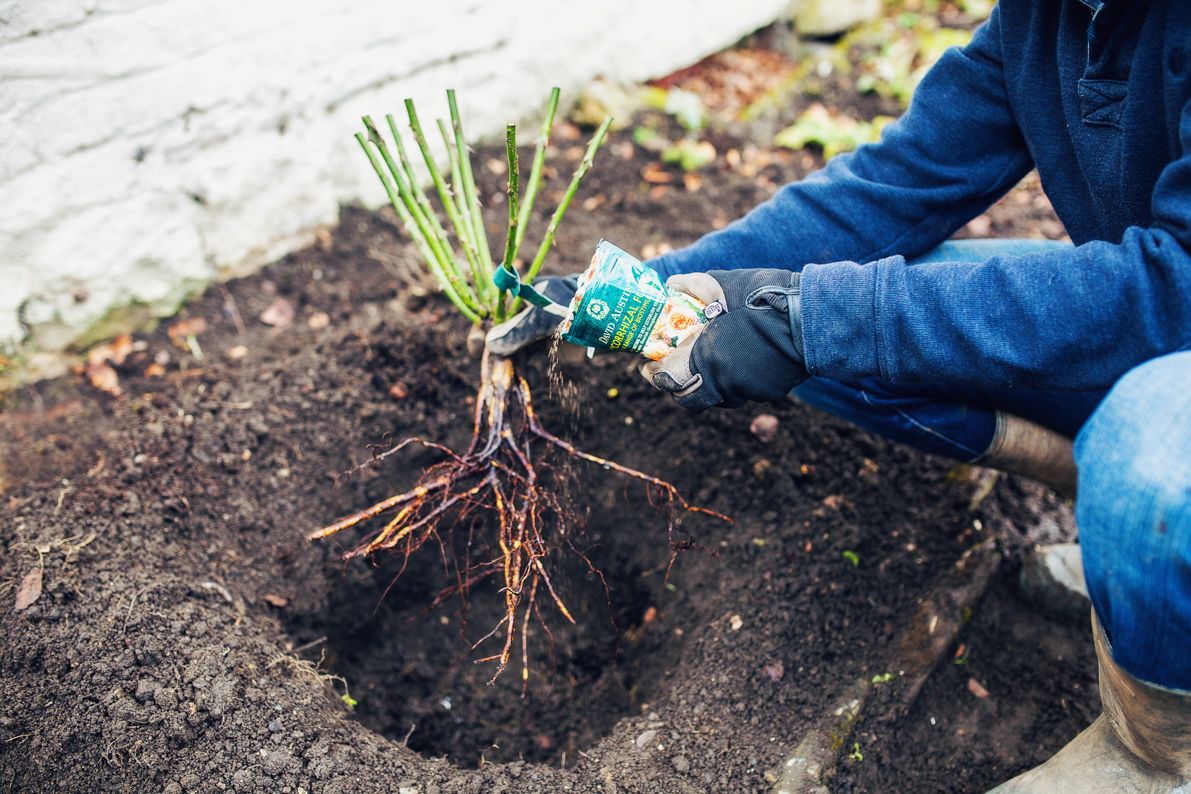
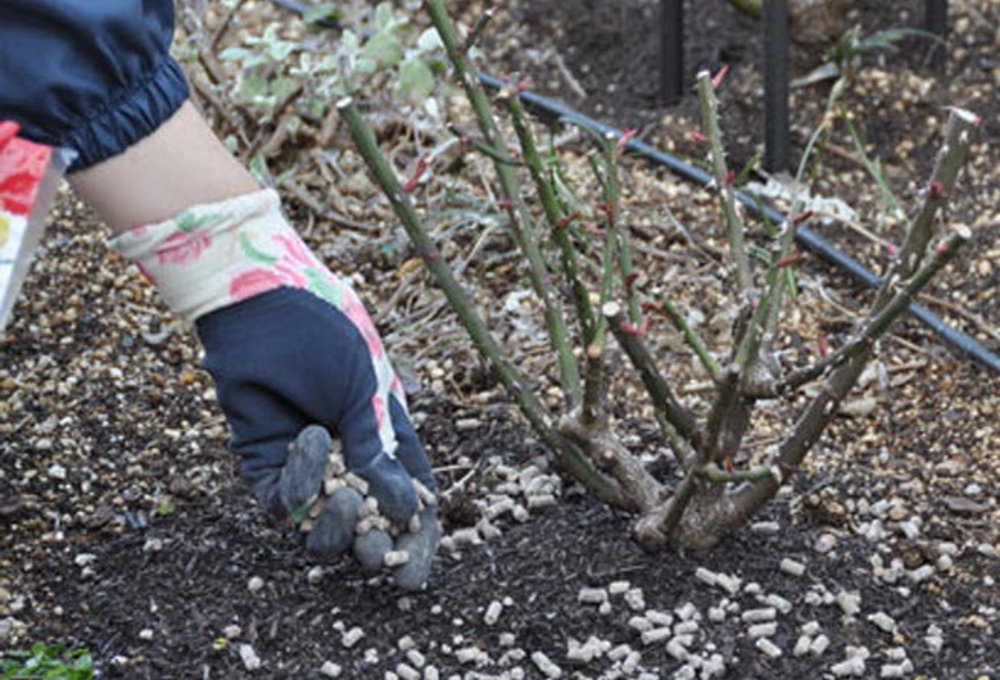
Fertilizers:
- Rotten manure (cow, horse or chicken), compost.
- Mineral fertilizers.
- Ash or lime, bone meal or egg shells.
- Nitrogen fertilizers.
The first thing to worry about before transplanting a flower princess is choosing a suitable place for her new residence.Loving the warmth of the sun and open space, the rose feels great on the southern slopes, sheltered from the cold wind.
At the same time, she does not like the proximity of buildings that create stagnant air. The rose is picky about other plants located in the neighborhood, which must be taken into account when choosing a site for transplantation.
Site preparation
 The accumulation of melt water in spring and stagnant rainwater are detrimental to the rose, therefore, when preparing a place for transplanting, you need to take care of good drainage and raise the site if the groundwater lies close to the soil surface.
The accumulation of melt water in spring and stagnant rainwater are detrimental to the rose, therefore, when preparing a place for transplanting, you need to take care of good drainage and raise the site if the groundwater lies close to the soil surface.
The soil before transplanting the rose is prepared in advance. A layer of loose, organic-rich soil with a weakly acidic reaction is created by no less than 40 cm.
To do this, mix the soil and well-rotted manure or compost in equal parts, add a little ash or lime and bone meal. As a result, the acidity level should be at a pH level of 6.5-7.
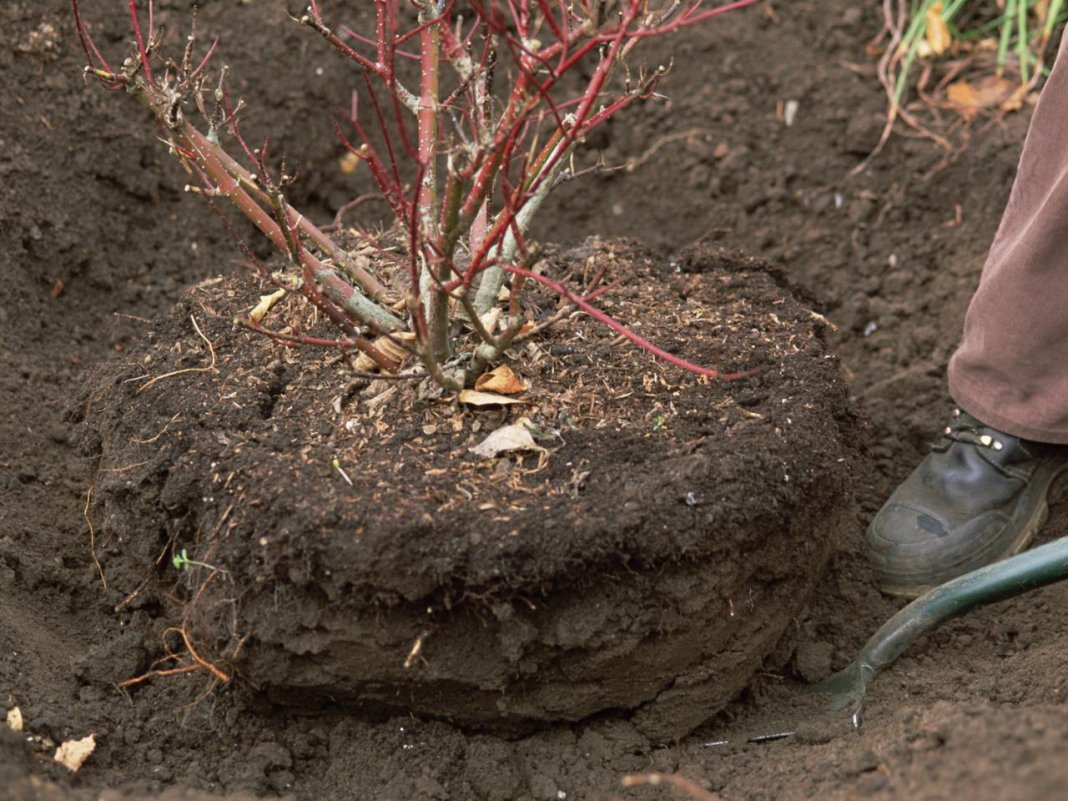
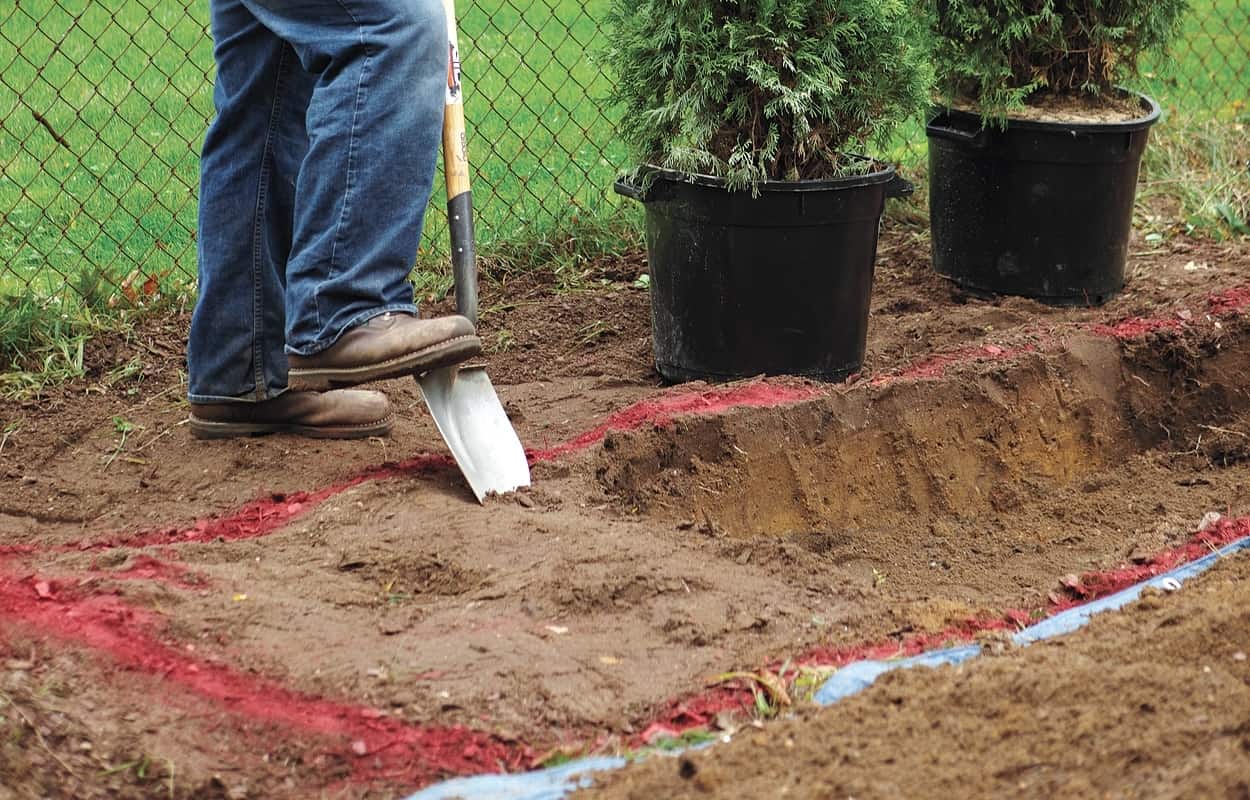
Pit preparation method
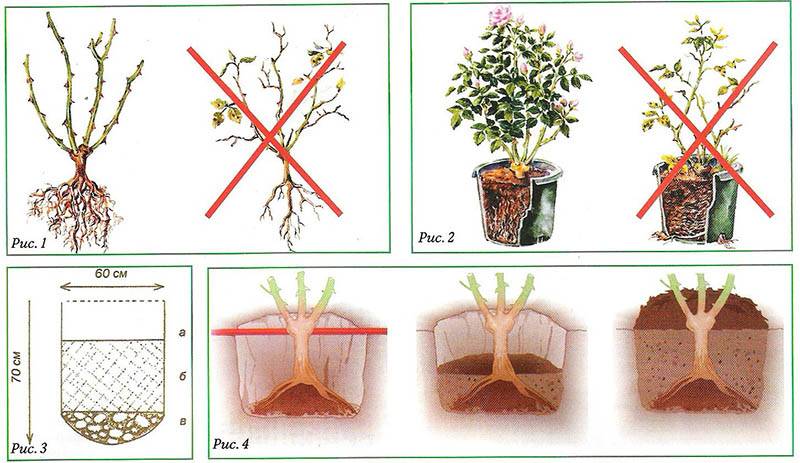
 The size of the pit or trench is made with a margin so that a lump of earth can freely fit into it, with which the rose will be transplanted. You can navigate by the crown of the plant - its projection onto the ground approximately corresponds to the area occupied by the root system.
The size of the pit or trench is made with a margin so that a lump of earth can freely fit into it, with which the rose will be transplanted. You can navigate by the crown of the plant - its projection onto the ground approximately corresponds to the area occupied by the root system.
It is usually considered a sufficient size of a hole 60 cm wide and 45 cm deep.
On sandy soils, the bottom of the pit is filled with a 7 cm layer of clay so that the soil dries out less. For clayey areas, on the contrary, the bottom is covered with coarse sand and gravel, preventing waterlogging of the future place of residence of the rose bush. The prepared pit should be allowed to settle for 2-3 weeks, after which the intended rose bush can be transplanted into it.
Soil and site requirements
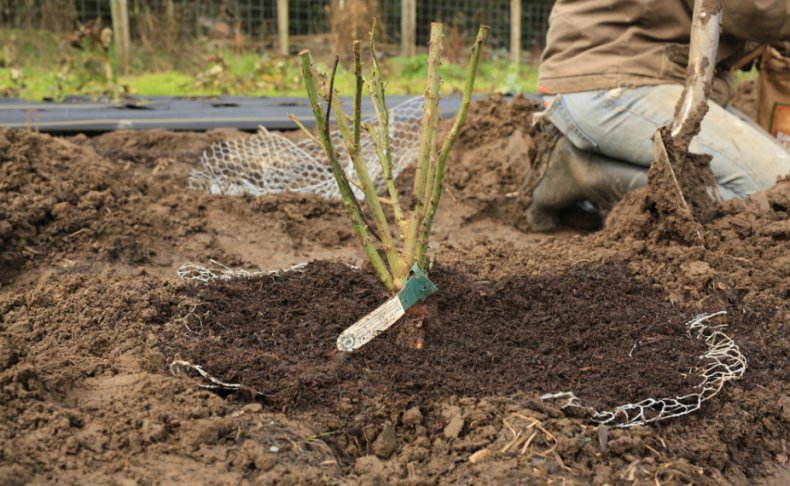

The new location should not be in complete shadow.
The plant will grow and develop properly in an open, sunny location in the garden area. Sunlight promotes the evaporation of excess moisture, so the flower in such conditions is less susceptible to fungal diseases. There should be no stagnation of moisture in the new place. It is recommended to choose terrain with a slope. A natural outflow of water is necessary so that there is no waterlogging of the soil and rotting of the roots.
When choosing a place for transplanting roses, it is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of the variety. There are plant species that can die from the aggressive sun at lunchtime. The petals become dull, flowering disappears, and the rose loses its appearance. For these varieties, prepare a place with light shading. You cannot completely deprive the plant of the sun. An area hidden from the sun under young trees is suitable. Plants should not interfere with each other's proper development.
The rose does not tolerate drafts. Cold winds can adversely affect flowering.
The soil is pre-fertilized and loosened. Sandy, clayey and muddy areas should be avoided. It is advisable if there have been no other plants on this site for several years. The content of nutrients in such soil will be higher. There will be an unfavorable neighborhood with rowan, bird cherry and cherry trees.
The earth must contain a sufficient amount of nutrients. The soil can be purchased ready-made, or you can prepare it yourself at home. For growing roses, you can make soil with different components. The easiest option is to mix a bucket of peat and a few tablespoons of bone meal. The more complex method includes garden soil, peat, a bucket of clay, several portions of ash and superphosphate.
Rose care after transplant
If you plan to transplant a rose to a flower bed with other varieties growing on it, then it is recommended to adhere to some rules:
- Plants should be at the same time of flowering. So they will not interfere with each other's growth and development.
- Watering can be carried out at once to the entire flower bed.This will have a beneficial effect on their overall growth and flowering.
The question often arises, if you start replanting roses in the month of August, is it possible to cut the entire flower bed at one time. It should be said that early pruning will not harm neighboring bushes, but it will provide better survival of new flowers. To ensure good survival, you can remove all young shoots for the first year. This method will help the bush take root better.

It is difficult for young transplanted roses to survive the first year. Their root does not have time to fully recover and therefore it is recommended to cover them for the winter. This is done using a special material, sawdust or spruce needles. Before preparing the bush for wrapping, the soil near the flower must be loosened and weeds removed.
Features of pruning in spring, summer, autumn and winter
The main pruning takes place in late winter - early spring. Then, when the flower begins to actively grow. This is the time to get rid of dried leaves and stems. Rose pruning also depends on the seasons. The houseplant is also affected by the change of seasons.
- In spring, branches damaged by dry air and pests are cut. Unaffected branches simply need to be shortened to stimulate flowering.
- In summer, pruning of dead wood (dry flowers, branches, leaves) is important. It is necessary to monitor the appearance of unnecessary shoots and cut them off. They can cause fungal infections. To stimulate new flowering, summer pruning is carried out in early August, but only for those plants that bloom several times a year. Indoor rose periodically should be outdoors.
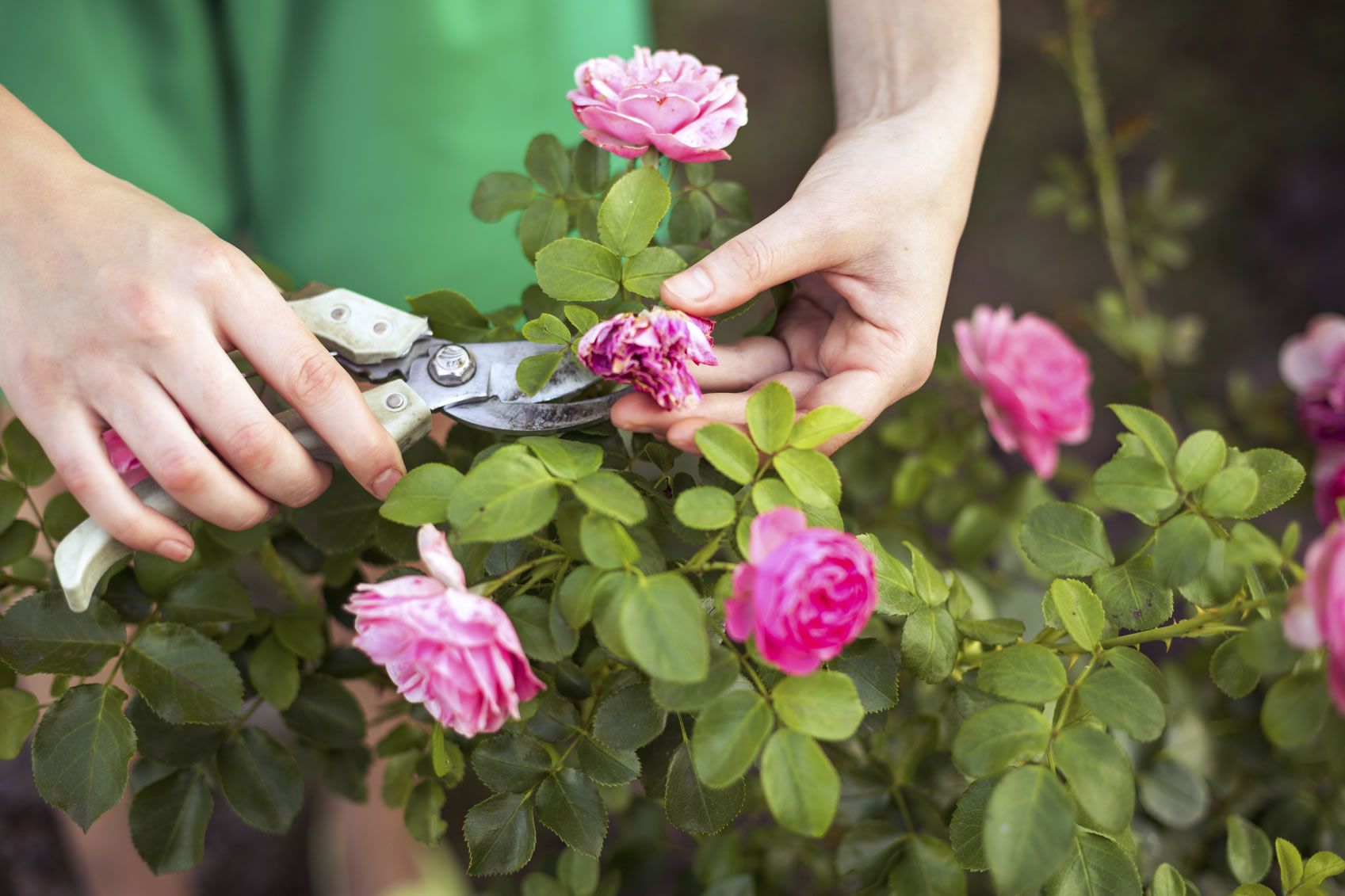
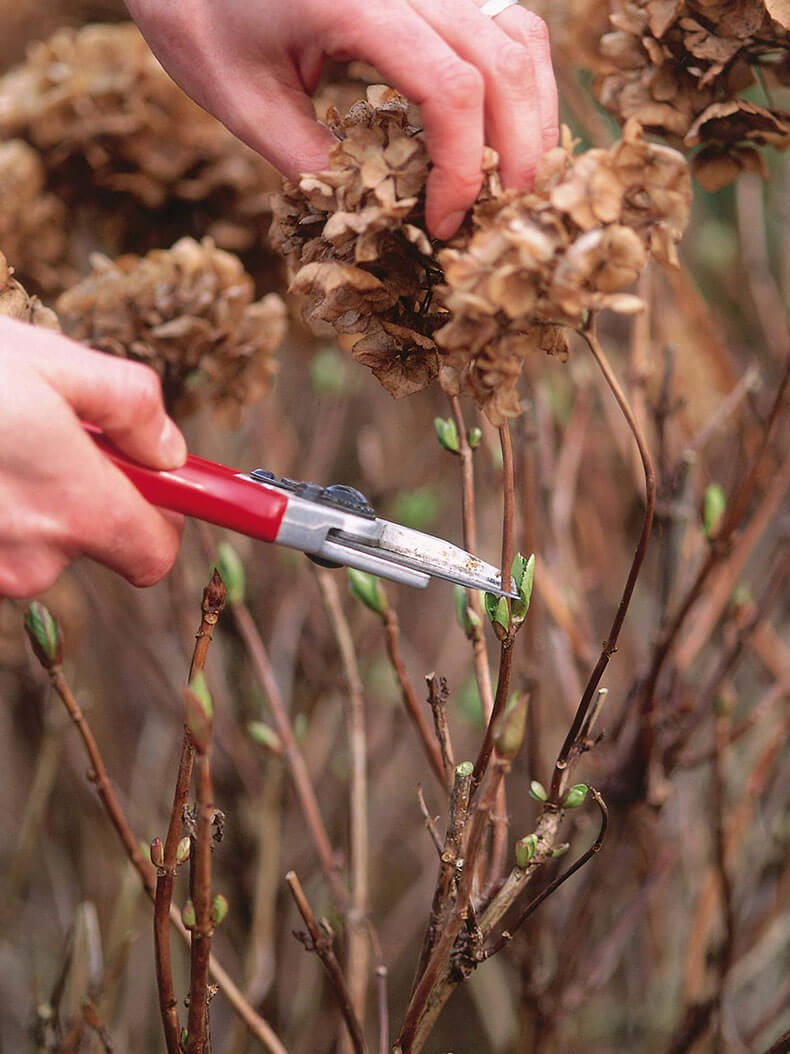
- In the fall, the top and wilted flowers are cut off. In some varieties, secondary flowering is stimulated. Pruning during this period is especially useful: there is a preparation of nutrients for the next season and nutrition of the root system.
- Winter pruning. To stimulate growth and flowering, the plant needs pruning for the winter. It is carried out after the flower has dropped its leaves. Those roses that need to be covered must go through this procedure. During such pruning, even before frost, the stems are shortened and unripe shoots are removed. In order not to infect the flower with fungal diseases, you will need a sharp, sterile knife. You need to cut off the branches, leaving 3-4 buds.
The main winter pruning is carried out at the end of February, when the buds have just begun to swell. At this time, the room should be cool. Then the injury will not harm, since the growth process slows down.
Secrets and features
Regardless of the variety, age and condition of rose bushes, there are uniform requirements for transplanting:
- using clean gardening tools to reduce the risk of infecting a weakened rose;
- provide an air shelter for the winter, flowers transplanted in autumn;
- transplant the bushes no more than once every 3-4 years;
- before transplanting, remove dry, diseased stems, buds and flowers.
In addition, there are special rules according to which different types of perennial flowers are transplanted.
How to transplant a blooming rose
It is possible to transplant a rose during flowering, but the procedure will require more time and effort. It is recommended to do this only if absolutely necessary. Old, large specimens can die due to severe stress. In small bushes, shoots are radically cut off, leaves and flowers are removed. This reduces the percentage of moisture evaporation, and all forces are directed to rooting. In the summer heat, frequent watering is required, the soil is kept moist until new shoots appear on the shoots.
It is recommended to spray, including biostimulants. Root feeding is carried out 3 weeks after transplantation.
Transplanting climbing species
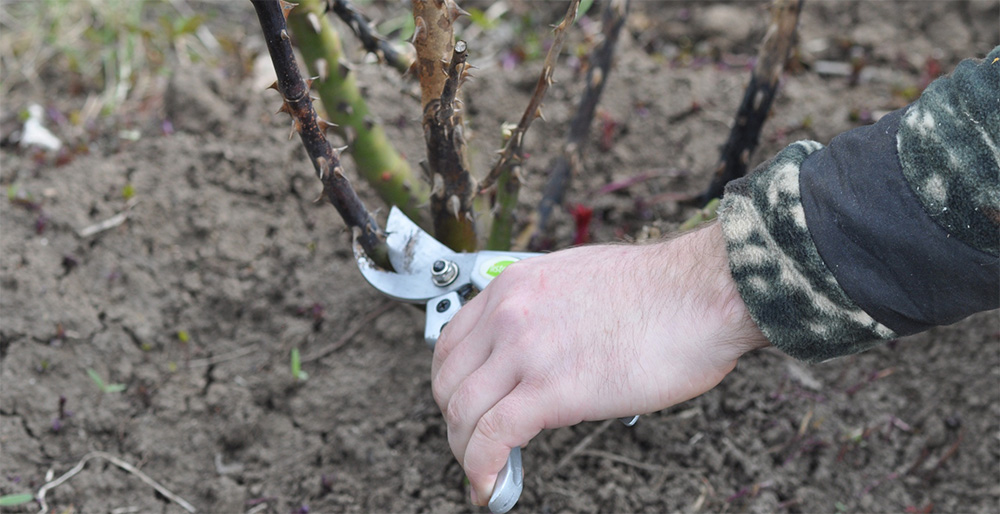
The main difficulty lies in the accurate release of the shoots of climbing and climbing varieties from the support. The optimal period to successfully transplant a weaving species is the autumn months.They begin to prepare the bush for moving in August. In young shoots, the top is shortened so that by the fall it is partially greyed. Old stems are cut by 2/3, diseased and dry branches are removed. The cut site is disinfected with ash or garden pitch.
Transplanting old bushes
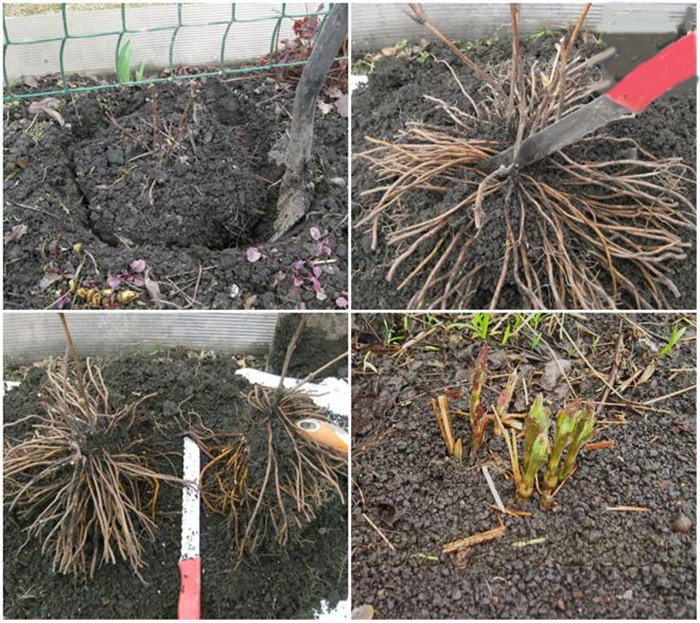
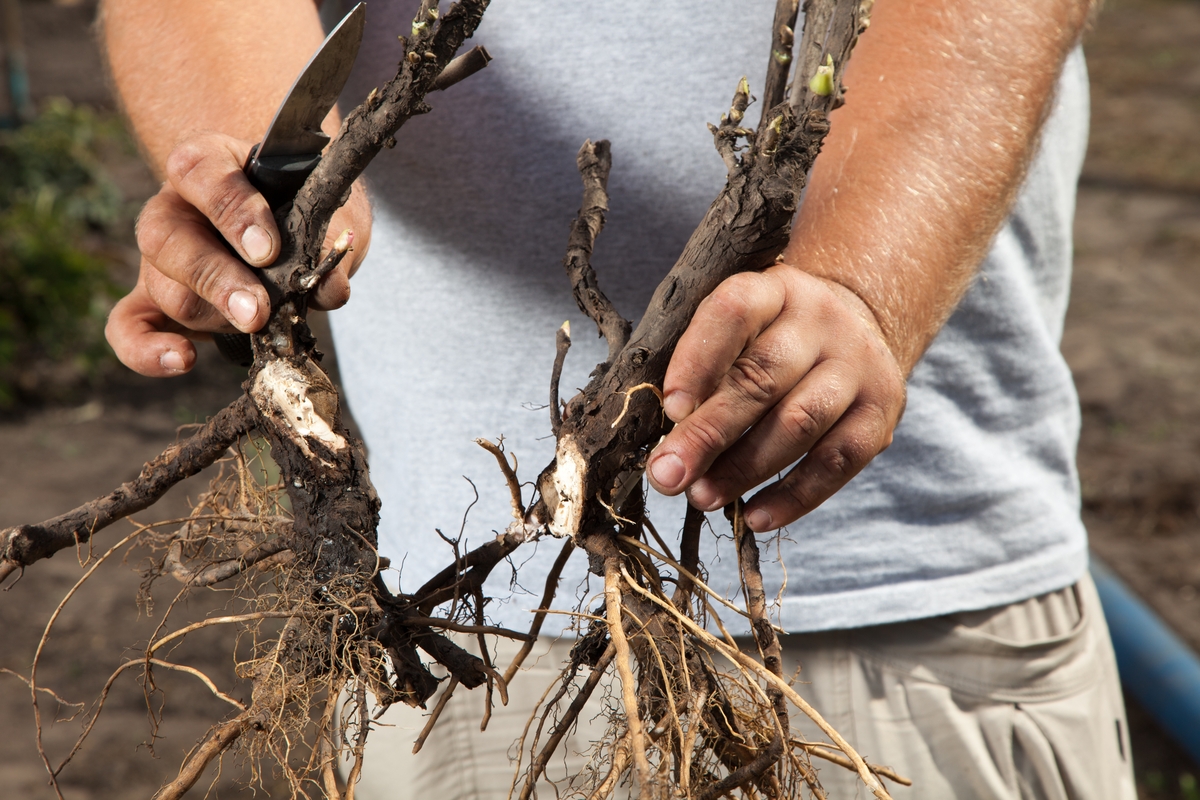
It is difficult to transplant a large or old rose to a new place due to the large size of the overgrown root system. It is easier to dig and move the flower together. It is recommended to transplant an adult rose in the fall or early spring. Growing conditions are selected as close as possible to the previous ones. Before proceeding with the digging, clean and sharp instruments are prepared, with which too long root processes are chopped off. The roots injured by the transplant are easily affected by pests and diseases, therefore, the soil and open areas are treated with a solution of potassium permanganate.
The rose has earned a reputation for being a capricious flower. Transplanting a blooming beauty to a new place is not easy, it takes an effort, ensure proper preparation and follow-up care. Due to the intense stress the plant experiences when transplanting, abundant flowering resumes one year after successful rooting.
Disease and pest control
Roses are whimsical plants that are often attacked by insect pests. Fragrant bushes have a large number of enemies. To minimize the risk of infection, it is necessary to carry out preventive treatment of the bushes, especially before flowering.
Rose aphid
The most common pest, parasites feed on plant juices, which begin to hurt, the stems and shoots are deformed, the buds become smaller and fall off, the leaves become sticky, curl.
In the fight against rosacea aphids, folk methods are often used:
- Planting with roses next to calendula, which attracts ladybirds - the main enemies of aphids.
- Spraying the bushes with a solution of laundry soap.
- Sprinkle plants with wood ash or mustard powder.
- Application of onion peel and garlic tincture.
In case of severe infection, insecticides should be used: Fufanon, Karbofos, Iskra.
Spider mite
It affects all types of roses, including indoor ones. It is difficult to notice the pest with the naked eye, the size of adults reaches 2 millimeters. The main signs of infection:
- The buds and inflorescences are covered with cobwebs.
- The leaves are covered with brown dots, turn yellow, curl, fall off.
- The plant lags behind in growth, loses or does not set buds.
Spider mite colonies multiply quickly, are able to rapidly move to other plants. The main insecticides are Actellik, Floromite, Iskra.

Leaf rollers
The leafworm is a small, pale yellow caterpillar that turns into a miniature butterfly in adulthood. It feeds on leaves and buds of plants. Leaf curling is the main symptom of infection.
To avoid infection, it is important to sanitize the bushes and disinfect the bushes for the winter. In case of severe infection, biological products are used: "Lepidocid", "Cesar", "Koragen"
Click beetles
The wireworm is a dangerous pest, the larva of the click beetle. It is found everywhere, capable of attacking all types of roses. It affects the root system of plants, lives in the soil. It will not be possible to remove the beetle immediately; it is necessary to carry out a long-term systemic disinfection of the soil. From insecticides used "Aktara", "Tabu".
Olenko and bronzovka
These beetles infect plant buds, which deform, shrink and fall off. Preventive treatment of shrubs must be carried out during the budding period and during the flowering period, use "Confidor" or "Aktara". From non-chemical agents, liquid smoke is used.
Powdery mildew
A fungal disease that can completely destroy the rose bush. The affected bush weakens greatly, the stems are deformed. Such a plant does not tolerate frost and spring temperature drops.The main symptom of the disease is the formation of a white-gray rough plaque on the leaves and stems of roses, then the plaque becomes brown, the leaf plates turn yellow. The disease spreads rapidly in conditions of high humidity and prolonged heat, and can spread to other plants.
As a preventive measure, varieties of roses with stable immunity to powdery mildew are chosen, weeds are removed in time, do not allow excessive moisture in the soil, disinfect the soil with a solution of iodine or potassium permanganate.
Rust
Fungal disease leading to cracking of plant stems. Over time, a kind of yellow-orange powder forms on the leaves, which passes into the buds, the rose loses its growth rate, some of the buds fall off. A rainy summer, humidity, lack of systemic care are the prerequisites for the onset of the disease. From folk remedies, spraying the affected bushes with infusions of nettle or wormwood is used. From chemicals used "Falcon" or Bordeaux liquid.
Chlorosis
Iron deficiency causes a dangerous disease of roses - chlorosis. If the soil lacks the required amount of organic matter, aeration is impaired, the concentration of phosphorus and manganese is high, there is a risk that plants will not receive iron. The first sign of chlorosis is that the leaf plates turn yellow, while the veins remain green. Iron deficiency is partially compensated by foliar feeding. To completely eliminate the problem, roses are transplanted or the soil is saturated with organic fertilizers.
Features of transplanting an adult rose instead of a dead bush

When one of the rose bushes unexpectedly dies in the rose garden, another, also an adult bush is planted in its place
When growing these beautiful flowers, sooner or later, it becomes necessary to transplant - immediately after acquisition, it must be transplanted into a larger pot with fresh nutrient soil, and garden roses have to be transplanted for various reasons:
it is not always possible to initially correctly plan the design of the site, or construction begins unexpectedly, and there is no other way out but to move the flowerbed with roses to another place;
when planting seedlings, the neighboring plants were not taken into account, from which the roses began to hurt and die;
due to sandy loam, excessively loose soil, the roots of the roses were buried, or on heavy clay soil they were squeezed to the surface;
the main ones on the site were not taken into account;
the soil under the mature bushes in the old rose garden was exhausted;
rose bushes have grown too much and have lost their decorative effect.
The latter option is possible with improper care of self-rooted roses, if you do not cut the roots of the bush in time and allow the stems to grow in different directions. At the same time, it is not at all necessary to dig the entire bush, it is enough just to cut off and transplant part of the bush, so you will rejuvenate the old bush, you will achieve more abundant flowering from it. In addition, you do not have to worry about how to root the rose before planting in a new place - it will already have a developed root system.
Video about the correct transplant of roses
In other cases, if the landscape design of the site was thought out in advance, and a place suitable for all parameters was chosen for planting roses, it will no longer be necessary to transplant the established rose bushes.
When one of the rose bushes unexpectedly dies in the rose garden, another, also an adult bush is planted in its place. At the same time, you need to carefully approach the choice of a plant - the rose should have suitable bush sizes, the color of its flowers should be in harmony with the environment. It is better to use the same variety, since planting, for example, a strong-growing variety among the weak-growing ones will negatively affect the rest of the plants.
Transplanting a new bush can be carried out in April or October, having previously dug up the old plant and completely replacing the ground with a new one to a depth of up to half a meter, within a radius of about 30 cm.For more convenience in carrying out all the necessary work, it is recommended to cut off adjacent rose bushes before transplanting. And in order for an adult rose bush to take root better in a new place, after transplanting in the first year, all buds that form should be removed from it.
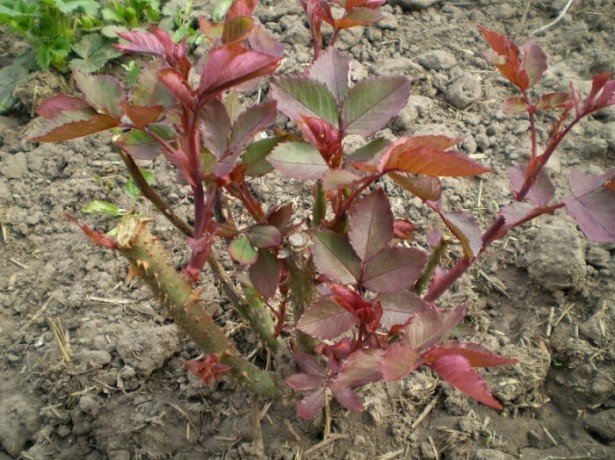

Rose transplant
How to transplant roses in the summer: a step-by-step algorithm
Before proceeding with the transplant, you should find a suitable place for the plant. It should be borne in mind that this flowering culture is warm and light-loving, most varieties can grow in partial shade conditions, but flowering will be scarce. It is strongly discouraged to plant it between shrubs, shrubs and trees, as the culture will experience a lack of sunlight. The most suitable solution is a large open space on the south side, it is desirable that it is the morning sun that falls on the bush. Bushes quickly take root in loamy fertile soils, excess moisture contributes to the development of adverse consequences, therefore, there must be a drainage layer at the bottom of the planting pit.

Before proceeding with the transplant, you should find a suitable place for the plant.
Before transplanting the rose garden, approximately three weeks in advance, it is necessary to start preparing the seat. As a rule, the hole in diameter varies between 50-60 cm. The bottom of the depression should be thoroughly loosened, and then a layer of compost should be added, and after the soil, otherwise the root system may suffer from direct interaction with organic fertilizer.
Just before planting, cut off shoots approximately 20 cm, and remove any damaged and weak ones. The transplant itself is carried out in several stages:
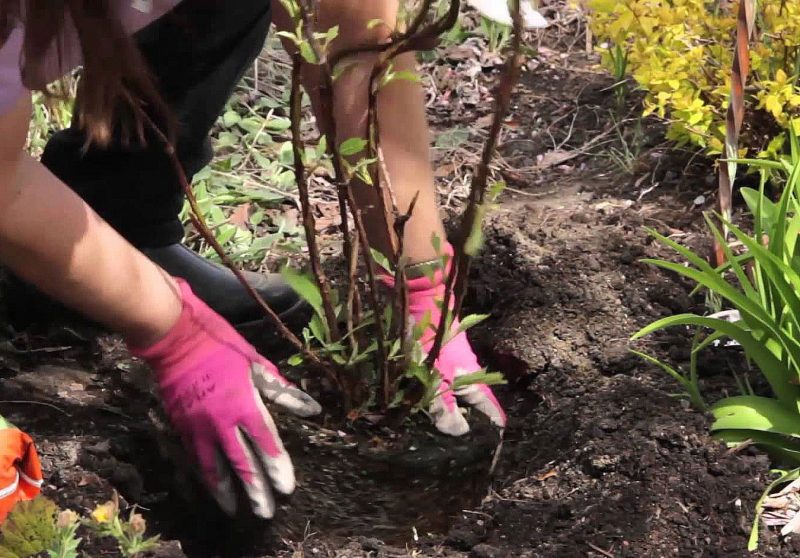
It is recommended to fill the bottom of the pit well with water; during planting, the soil should be loose and moderately moist.
The bush is placed in a planting hole in such a way that the neck, after burying, rises above the ground by about 2-3 cm.
The bush is lowered into a hole, the root system is evenly distributed, the plant must have enough space
Further, they are covered with ordinary soil, as they are buried, they are carefully tamped so that cavities do not form between the roots.
The transplanted bush is poured abundantly with water, after which a near-stem circle 15 cm in diameter is fertilized with a complex of mineral fertilizers. With the onset of autumn, it is strongly not recommended to introduce nitrogen-containing preparations.
Important! Re-transplanting is recommended no earlier than after 3 years, since adult plants react painfully to transplantation
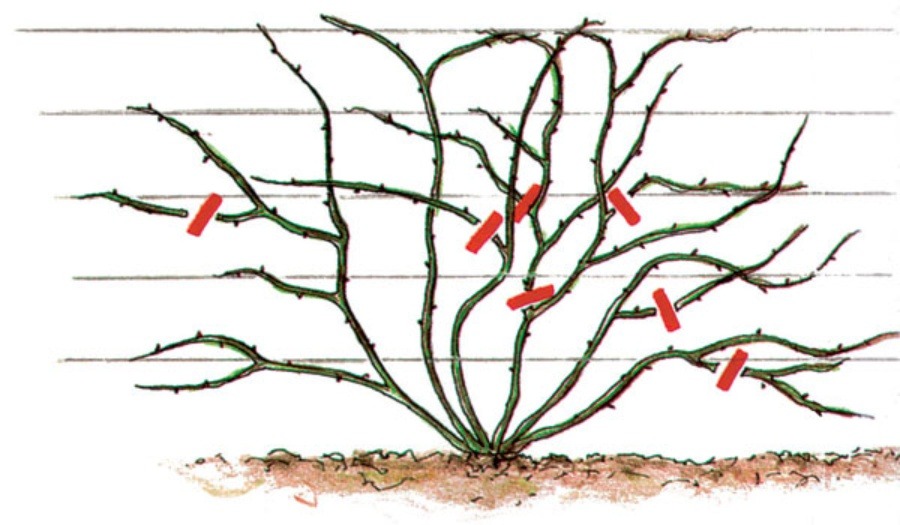
Transplanting climbing roses
A climbing rose is somewhat more difficult to transplant, and all because of the long shoots. When transplanting, it is strongly discouraged to place a bush near the walls of buildings, due to rain falling on the plant, and in winter, the likelihood that snow injures the culture increases significantly. It is also not recommended to assign them a place not far from the trees: the developed and powerful rhizome of the tree will absorb a lot of moisture and nutrients.
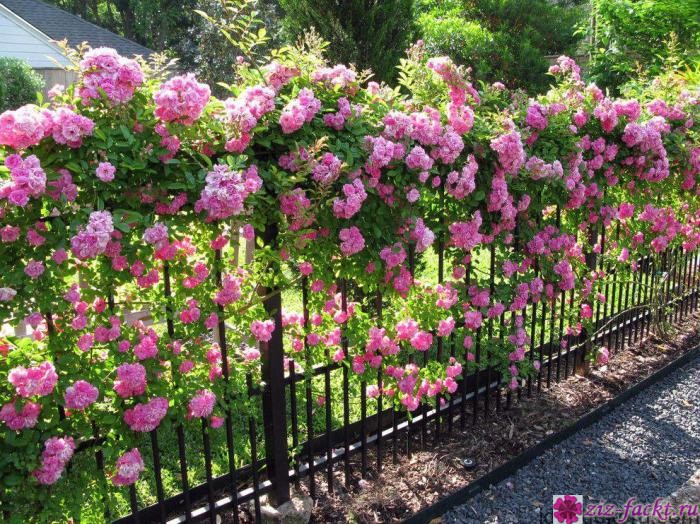

A climbing rose is somewhat more difficult to transplant, and all because of the long shoots
For transplanting, you will need to remove the plant from the support on which it is fixed
When transplanting, it is important not to injure the root system.
Having dug out a bush, it is gently shaken. Before transplanting, the seedlings are recommended to be treated with a disinfectant and stimulating solution.
Before transplanting, the seedlings are recommended to be treated with a disinfectant and stimulating solution.
- For better survival in a new place, the seedlings are dipped in a solution for a day, this is necessary for better survival.
- Pruning shoots.It is recommended to immediately remove the weak ones completely, the strong and powerful ones should be pruned, leaving about 15 cm. With the onset of heat next year, this will quickly build up the green mass.
- To minimize the likelihood of developing diseases, you will need to powder the bottom of the pit with charcoal.
The hole should be free enough so that the root system does not feel constrained there. The depth, as a rule, is at least 65 cm. If you need to transplant several plants, the optimal interval between them is at least one meter. When planting, the roots should be straightened; in no case should they bend up.
Transplanting roses in the summer, and even flowering ones, is not a good idea, but if necessary and troublesome, the procedure can be carried out with minimal trauma to the plant. Before carrying out the procedure, it is imperative that you familiarize yourself with the transplant rules.
vote
Article Rating
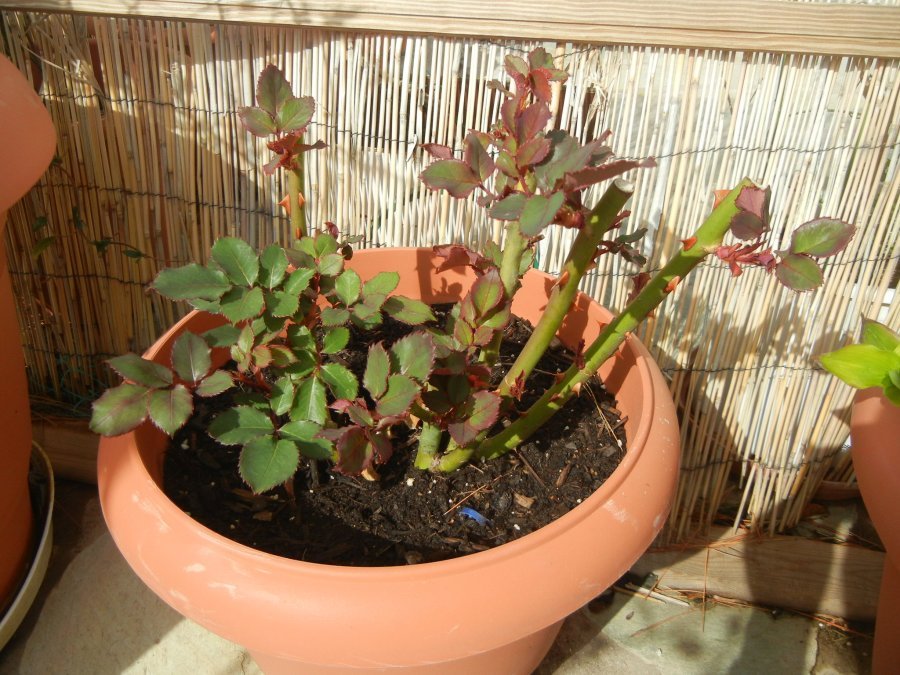
How to care for a rose in a pot
Every novice florist wants to know how to care for a rose in a pot, watering rules, and about the optimal temperature regime. And caring for a potted rose is very simple and consists of the following activities:
Correct lighting
The plant loves to bask in the sun, but it is important to remember that direct sunlight harms the plant: the buds wither and fall off, and the inflorescences quickly open and immediately fall off. In winter, when there is not enough natural light, it is recommended to use special phytolamps
Their light range should cover the blue and red spectra.
Air humidity should be within normal limits. The life span of a plant and the splendor of its flowering directly depend on this indicator. In summer and winter, air must circulate in the apartment near the plant. In addition, you need to spray the rose from a spray bottle several times a day. Wet expanded clay in a pallet, where a pot with a room rose is placed, will perfectly help to get out of this situation and provide constant moisture.
Watering. In the heat, the plant should be provided with abundant watering. From September, the rose needs to be rearranged to another place for the autumn-winter period. The frequency of watering at this time is reduced, the plant is placed away from the batteries in a cool room. It is recommended to drain excess water from the pallet. The flower can rot if it is watered a lot or, conversely, begin to dry due to lack of moisture. During watering, the water should be at room temperature.
Temperature conditions. It is not recommended to overheat the indoor plant, as this will lead to the development of diseases.
How to properly prune a rose after flowering in a pot? This is best done during the fall. The shoot is shortened to 5 buds. Thin and weak branches are also pruned.
Peace. As soon as the last flower falls, a dormant period begins, which lasts until February.
For some, it may seem that growing a rose at home on a windowsill is unrealistic. But everything is possible if you strictly follow the rules described above. Flower care begins immediately after purchase. If you miss even the slightest detail, you can not even dream of a lush bloom of a rose.