Landing rules
Planting groundcover roses and caring for them is not difficult, but if the bushes are not planted correctly, it is almost impossible to wait for abundant flowering and good growth, even if you buy high-quality planting material and good soil. Novice gardeners need to know the rules for planting a plant so that the flower garden looks well-groomed and elegant.
Site selection and organization
 The choice of a place for planting bushes is a responsible matter, so you need to take this very seriously. Roses are photophilous, so planting in shaded areas of the garden is not welcome, but direct sunlight can severely burn delicate flowers and they will wither and die. It should be planted on the western or southeastern side of the front garden, the sun shines there only in the first half of the day, and afternoon shading will be a good protection from the midday heat.
The choice of a place for planting bushes is a responsible matter, so you need to take this very seriously. Roses are photophilous, so planting in shaded areas of the garden is not welcome, but direct sunlight can severely burn delicate flowers and they will wither and die. It should be planted on the western or southeastern side of the front garden, the sun shines there only in the first half of the day, and afternoon shading will be a good protection from the midday heat.
Soil and landing
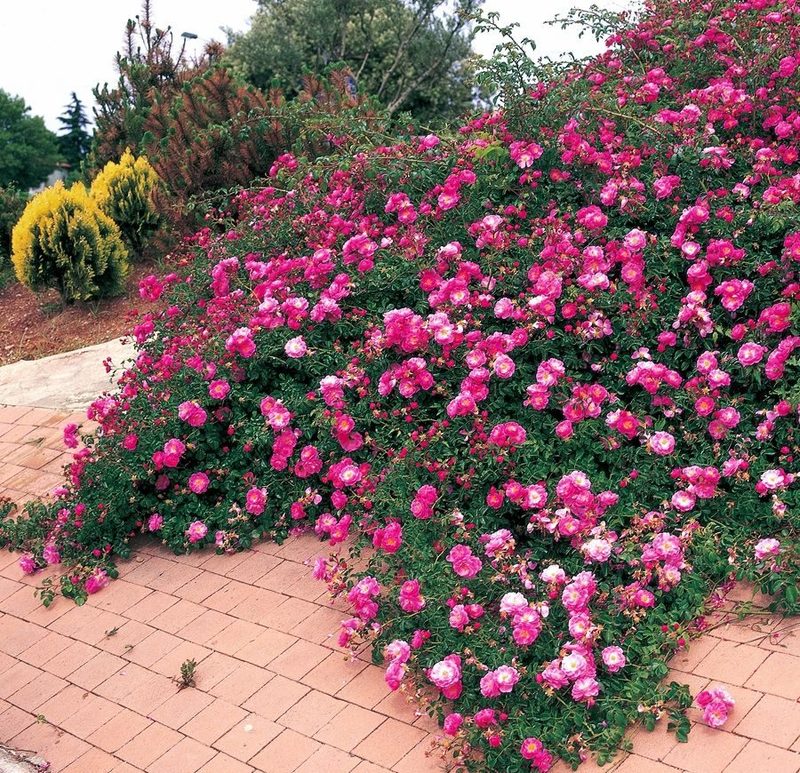 The soil for planting is prepared in the fall. The site is dug up, the roots of weeds and other debris are removed, and humus is added. Plants prefer a slightly acidic soil reaction within 5.56.5 pH, with acidic lime or dolomite flour is added. If the soil for some reason in the fall was not prepared for spring planting, you can do this 6 weeks before the start of planting roses, then the earth will have time to sink.
The soil for planting is prepared in the fall. The site is dug up, the roots of weeds and other debris are removed, and humus is added. Plants prefer a slightly acidic soil reaction within 5.56.5 pH, with acidic lime or dolomite flour is added. If the soil for some reason in the fall was not prepared for spring planting, you can do this 6 weeks before the start of planting roses, then the earth will have time to sink.
Landing. Plants are planted in holes about 60 cm deep and 50 cm in diameter.When planting several plants in a row, it is advisable to dig a trench of the same width and depth as the planting hole
It is important, when filling the hole, to water the soil layer by layer to prevent the formation of a void, and after planting, tamp the soil and water the seedlings abundantly. After the shoots grow up to 5 cm, it is necessary to undo and mulch the soil
Depending on the type of 1 sq. meter is recommended to plant from 1 to 3 bushes.
Adonis flower: growing, caring for and using the plant
Container types of roses are planted at any time, bushes with an open root system - in spring and autumn. In the northern regions they are planted from April to June, in the south - in late autumn.
Pruning
Creeping roses should not be drastically pruned. Although in the first year, the stems are shortened in order to cause tillering. It is necessary to form a bush for a constant limitation in size, which is considered optimal for the variety. To exclude the occurrence of mold or fungal diseases, you need to ensure that the bush is ventilated and sufficiently illuminated by the sun's rays.
Important! Shoots are cut at an angle of 45 °, the distance of the cut from the nearest bud should not be less than 0.5 cm.Provide pruning mainly of those branches that are directed to the middle of the bush and thicken it greatly
If several shoots grow from one bud, the strongest is left, the rest are removed. Ground cover roses should be rejuvenated 5–6 years after planting. All stems are cut at a distance of 20–30 cm from the root. All sections are necessarily processed with garden varnish, the bush is sprayed with a 1% solution of copper sulfate.
As beautiful as ground cover roses are, the care and cultivation of most of them is not a very time-consuming process, so this type of flowers has become popular lately. They are in high demand and look very impressive in various flowerpots and flower beds. In addition, they are often used to decorate nondescript areas.
Creeping roses are versatile, they can be grown and tied like curly. Planting such plants in the center of even the best grass lawn will give it much more originality.Small ground cover roses can be planted in wide containers and exhibited in the summer on the site, and in the winter brought into the house, turning it into a house plant for the winter period.
vote
Article Rating
Preparing for the winter period
Preparation for winter begins in late August - early September. They begin to gradually reduce the watering of the bushes, make potassium-phosphorus fertilizers. Pruning is not done to stop the growth of new shoots. Growing ground cover roses is less laborious than hybrid tea or climbing roses, they are frost-resistant, and do not need a special shelter. The exception is standard copies.

The crown of the bush is placed on spruce branches, covered with it or sawdust on top. Fix the rose in the desired position with iron staples. If necessary, if the variety is thermophilic, an air-dry shelter is constructed.
Shelter for the winter
An important condition for the preservation of planted ground cover roses is preparation for winter and reliable protection from frost. Many varieties of ground cover roses winter safely without additional shelters, but in case of unfavorable weather conditions, the plant may freeze, which will entail poor development and even death of the bush. To prevent this from happening, experienced gardeners recommend that you cover a ground cover rose for the winter.
It is quite simple to do this:
- Low-growing varieties are dressed up with spruce branches and dry branches and covered with a dense cloth or lutrasil on top. You can build an air shelter from metal arcs-frame and agrofibre.
- Of medium height, the branches are loosely tied in an upright position, wrapped with a tarp or other suitable cloth. The root area is covered with sawdust.
- Tall varieties are laid on the ground, with pre-thrown branches and spruce branches. This will help protect the branches from rotting. An air shelter is being constructed on top.
It is necessary to cover roses for the winter after the onset of the first frost, because in warm weather the plant can rot and rot. If warming has come, the shelter is ventilated during the day. In advance, leaves are removed from the bush and sanitary pruning of branches is carried out. It is also recommended to cut thin and weak branches, which, if dying from a cold snap, can be a source of infection for the entire bush. The shelter is removed in early spring, after which it is necessary to assess the condition of the bush, remove frozen shoots, spray the plant with Bordeaux mixture and feed.
The ground cover rose, the planting and care of the open ground of which are discussed in our article, are unpretentious, but they can decorate any area. They are often used in landscape design to "fill" empty areas, as well as in the design of garden compositions. Proper care and reliable shelter for the winter will provide the plant with a long life and excellent flowering.
Disease and pest control
Plants weakened by diseases hibernate poorly, bloom poorly and, in the absence of human help, may die altogether. Therefore, you need to inspect the roses from time to time.

Common diseases:
- gray rot;
- rust;
- powdery mildew;
- black spot;
- bacterial cancer.
All fungal diseases of the rose are effectively treated with fungicides. Spraying is carried out, having noticed the first signs of the disease, as well as in spring and autumn for the purpose of prevention.
For example, with black spot, brown or black spots with a light rim are formed on the leaves. Over time, they merge, causing the leaves to die. Disease spores are spread with the wind. For treatment, the affected bushes and the soil around them are sprayed with Bordeaux mixture or iron sulfate. Preventive treatment is carried out in April and autumn, before the onset of frost.
Bacterial cancer is not treated with fungicides; a symptom of the disease is light growths on the root collar and roots. Over time, they grow and darken, the rose dies. There are no chemical preparations for this disease, the diseased plant is dug up and destroyed.For prevention purposes, it is recommended to carefully choose the seedlings when buying.
Watering and feeding rules
Caring for ground cover representatives of the Rosaceae family is no different from caring for other types of roses
The main attention here is required to be paid to timely watering and feeding.
As a rule, bushes are watered in the morning, when the sun's rays do not touch the leaves. In the hot sun, it is extremely undesirable to water the plants: moisture that gets on the foliage will cause its burns. Foliar dressing and spraying carried out in the open sun can lead to the same result.
The queen of the garden treats overflows as negatively as she does underfills. Therefore, it is necessary to check the condition of the soil before watering. If the soil layer has not yet dried out to a depth of 3-4 cm, watering should be postponed. For the whole season, it is enough for ground cover roses to carry out 3 dressings. The first is carried out in early spring, 2 weeks after the buds open. Fertilizers such as Cytovit, Agricola, etc. are suitable. The second feeding is carried out after 30 days, and the third one - in the fall. For autumn feeding, only potash fertilizers are used.
Most ground cover varieties, especially undersized and short ones, do not need additional shelter for the winter, but during a winter that is too little snow or severe, the likelihood of freezing out the bushes is quite high. To reduce the risk of plant death, they can be covered with spruce branches. It is also recommended to build a simple frame from rods and cover it with lutrasil. The air layer will protect the bushes from frost. With proper care, the queen of the garden will delight with lush flowering for more than one year.
Most popular varieties
Halloween (Hello)
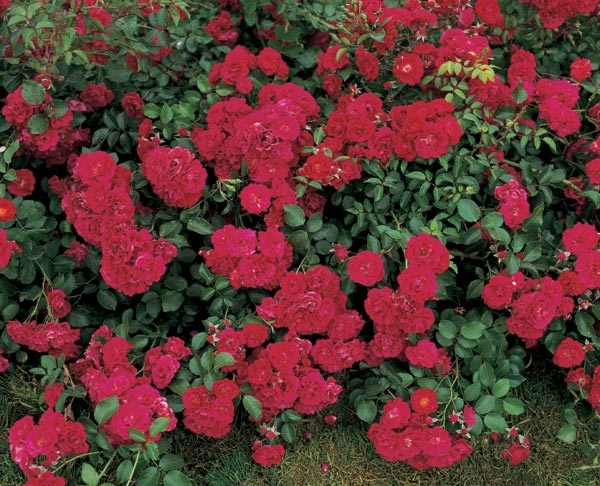 Halloween (Hello)
Halloween (Hello)
Low (about 50 cm), spreading bush. They are distinguished by large, densely double flowers, which, during flowering, change color from dark red to rich cherry. Flowers are odorless, but with the richest doubleness among ground cover roses. The variety is frost-resistant, immune, blooming profusely.
Swany
 Swany
Swany
The bushes are high, 75-80 cm. The crown is spreading, up to 2 m in diameter. The Swanee rose stands out with evergreen small shiny foliage and large umbellate inflorescences. Each contains up to 20 double, white with a pink center, fragrant flowers. Winter-hardy and very ornamental shrub.
Ahtiar
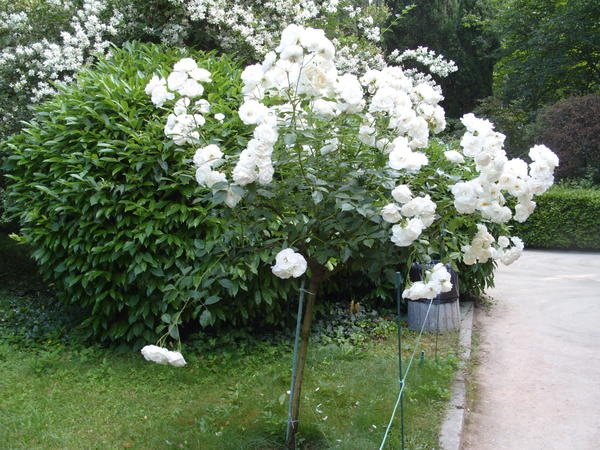 Standard rose Ahtiar
Standard rose Ahtiar
A tall shrub with long (1.2-1.5 m) falling arched shoots. Large double flowers are collected in inflorescences. This landscape rose is used to create curbs and green hedges, and is grown in a standard culture.
Ballerina
 Ballerina
Ballerina
Tall, up to 2 m, bush with a rounded dense crown. Winter hardy, drought and disease resistant. It blooms for a long time, continuously, until the onset of frost. Simple flowers are collected in clusters. The petals are white in the center, turning pink towards the edges. During flowering, the flowers increase in size, brighten somewhat. They have a delicate musky aroma.
Scarlet
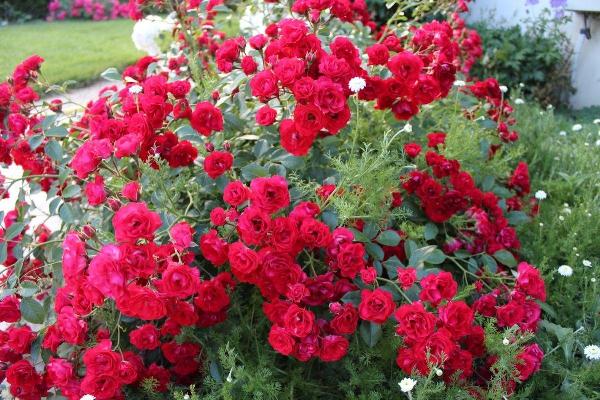 Scarlet
Scarlet
One of the most hardy and adaptable varieties. Bushes are low, up to half a meter. The foliage is dark, glossy. The flowers are double, deep red. Blooms profusely, all summer and autumn
Fairy
 Fairy
Fairy
Seedlings take root quickly, shoots grow actively and in a short time form dense thickets up to 60 cm high. White, sometimes with a pink tinge, double flowers are collected in a brush of 30-40 pieces. Bloom from July to frost.
Amber Sun
 Amber Sun
Amber Sun
Sprawling branchy bushes, 50-60 cm in height and in width. Drooping branches. Small semi-double fragrant flowers of all shades of yellow - from copper at the beginning of flowering to cream at the end. It is appreciated for long flowering, cheerful decorativeness, resistance to frost and diseases of roses.
Matador
 Matador
Matador
Low (up to half a meter) compact bushes. Scarlet semi-double flowers are grouped in brushes.One of the earliest flowering varieties, extremely disease resistant, hardy to environmental conditions. Often planted in hanging pots and containers.
Fiona
 Fiona
Fiona
Strong bush up to 85 cm, with long arched branches. Fragrant flowers are double, bright pink, medium-sized, collected in inflorescences. Blooms profusely from early June until frost. Winter hardy immune variety.
Ground cover roses - description
Most of the ground cover roses are dwarf plants that spread along the ground. Some growers successfully grow them in pots to decorate terraces, gazebos or walls of houses.
Ground cover roses have gained popularity due to long flowering, because with proper and regular care, they can amaze with a riot of colors and splendor of flower shapes all summer long. You can use plants as much as your imagination allows - decorate the yard building, create a chic hedge, decorate the flower garden with a bright original element.
The very first breeders of beautiful plants are the Germans, and they introduced some classification. The following groups are distinguished:
- with curly long shoots;
- with falling branches;
- with spreading creeping shoots;
- low bushes with a large dispersion;
- compact small bushes with short weaving lashes.

Planting and caring for a flower
Roses grow in one place for many years. They have their own requirements for the conditions of detention. Therefore, the place for the plants is chosen carefully. The decorative effect of the bushes depends on correctly performed work.
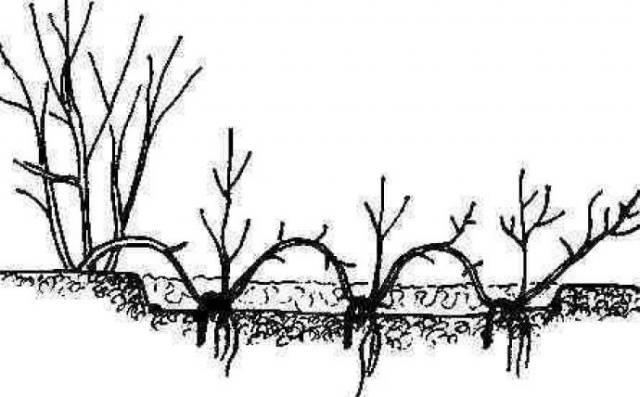
Site selection and preparation
The place is selected lit in the morning and in the evening, shaded at noon. From the scorching sun, the petals of the inflorescences can burn out. They are planted away from high walls and fences. If the soil is wet, drainage pipes are installed on the site.
Groundcover roses prefer to grow in loam. Peat, sand, compost are added to heavy soil. If the ground is too light, sandy, it is weighed down with clay, turf. Otherwise, moisture will quickly leave the root system deep in the ground. Limestone is added to the acidic soil.
Preparing the seedling
Thin, weak branches, broken roots are cut from the bush. An oblique cut is made above the bud located outside the shoot. In order for the root system to be saturated with moisture, it is placed in a container with water. Potassium permanganate powder is added for disinfection.

Terms and seating schemes
Ground cover roses are planted in the ground in spring or autumn. The period depends on the climatic conditions. In cold areas, planting is best done in the spring, so that the bushes have time to take root before the onset of frost. In the southern regions, landing is allowed in the fall.
The disembarkation is done as follows:
- dig a hole with a depth and diameter of 50-70 centimeters;
- a layer of drainage material is laid on the bottom;
- poured a mound of fertile soil;
- a seedling is placed vertically in the middle;
- covered with earth, watered abundantly.
The distance between the bushes is set depending on the variety of roses, as well as on their purpose in the design of the site.

Watering mode
Frequent watering is carried out immediately after planting. In the future, the land is irrigated after the top layer of the soil dries up. Water ground cover roses in the morning or evening. At least 10 liters of water is added under the bush. Overhead irrigation is not recommended as it promotes disease.
Top dressing
When leaves begin to appear on the shoots in the spring, the first feeding is carried out. A mixture of nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus is used. Before flowering, a complex mineral fertilizer is applied. If a rose blooms several times per season, then each time it is fed during the budding period. During the dissolution of the inflorescences, the soil is not fertilized. Potassium is introduced in the fall.

Mulching, loosening and weeding
Groundcover roses have sprawling shoots, so caring for them is a little problematic. The culture needs loosening and weeding of the soil, and this is difficult to do.Therefore, immediately after planting, the ground in the near-trunk circle is mulched. The covering material helps to retain moisture, prevents the growth of weeds.
Pruning and shaping the bush
A bush planted in autumn in the spring needs to be slightly trimmed. This stimulates the formation of many lateral branches. In the future, only shoots thickening the crown are cut off. In addition, they carry out sanitary pruning, removing dry, broken, diseased stems. Once every 5 years, the bushes rejuvenate, leaving cut shoots 25 centimeters high above the ground. Experienced gardeners do not recommend pruning for the winter.
Preventive treatments
To prevent the appearance of diseases and pests, dried foliage and plant debris must be removed from the root circle. It is advisable to dig the soil around the roses in the fall. For the prevention and treatment of diseases, fungicides are used. Insecticides will save you from harmful insects.

Preparing for the winter period
In the south, ground cover roses can winter safely without shelter. Especially if winter-hardy varieties are planted. In the northern regions, a frame is erected above the bushes, covered with lutrasil. If the shoots are long, they are bent to the ground. So that the stems do not rot, spruce branches are placed under them.
Site selection and boarding rules
Rules for planting ground cover roses.
Roses with creeping shoots are considered very undemanding, but a few basic factors that will be taken into account when planting a plant will achieve good bush formation and lush flowering. The development and growth of the bush is influenced by:
- illumination level;
- soil slope;
- ambient temperature;
- soil moisture;
- planting density;
- acidity of the soil.
In order for the rose to receive the required amount of light and nutrients, while simultaneously forming a large number of buds, it must be planted in such a way that in the morning the bush is in the sun, and in the hottest time of the day it is shaded by other plants. The location of the bush on the soil with a slope of about 10 ° will create a natural drainage of water, eliminating the need for a drainage arrangement.
But at the same time, it is undesirable to place bushes next to other massive garden crops: they will not only take moisture and nutrition from the plant, but also unnecessarily shade it. A rose planted in the shade, near the walls of a house, etc., forms shoots without buds, is affected by diseases, becomes weak and faded.
If the bushes are planted on flower beds raised 40-50 cm above the soil level, this automatically increases their frost resistance, since, according to the laws of physics, cold air accumulates in low-lying places without affecting the hills.
When planting a bush, great attention must be paid to soil moisture. Roses do not tolerate dampness well, therefore, the organization of a gravel-sand cushion in a pit intended for planting will significantly reduce the risk of death and disease
In this case, it is necessary to take into account the type of soil: loamy soil is considered optimal, creating ideal conditions for transporting oxygen, moisture and nutrients to the roots of the plant. Sandy, stony, clayey and other heavy soils are not very successful for planting Rosaceae. You can improve the condition of the soil by adding sand, compost, peat, turf, rotted chicken or rabbit droppings.
The time of planting rose seedlings depends on climatic conditions: for regions with warm weather, autumn planting is preferable, for areas with cold winters - spring planting. The acidity of the soil should vary between 5.5 and 6.5 pH.
In order to prevent overgrowth of weeds from forming under the plant as the plant grows, experts recommend carefully treating the entire area that the overgrown bush will occupy. The plant is planted in a hole 50 to 70 cm deep.With mass planting, you can dig a trench 50 cm wide.The required depth of the pit is determined as follows: the length of the roots of the planting material + 15 cm. After planting, the seedling needs to be watered well. Depending on the variety of plants, it is not recommended to have more than 1-3 seedlings per 1 m².
Best care tips
Groundcover roses are less demanding than other varieties. This gives a good chance to grow luxurious flowers, even for gardening beginners. At the same time, it is possible to achieve long flowering and active growth of bushes only if all the "whims" of the garden beauty are fulfilled. To do this, you need to know what conditions are necessary for this plant, as well as the useful nuances of successful cultivation.
Success secrets for ground cover roses:
Top dressing should be carried out only the next year after planting. The frequency of mineral addition is determined individually. In general, it is necessary to use 5-7 dressings per season. Groundcover roses are also very susceptible to foliar dressing, which can be alternated with regular ones.
In early spring, the bushes are fed with nitrogen fertilizers. For this, rotted manure, humus or ammonium nitrate are used. Before feeding, the plant is well watered.
Before the formation of buds, sodium humate or potassium sulfate is added. This will give the plant the necessary strength to bloom. During flowering, fertilizers are not applied, this can damage the bush. After flowering, old buds must be removed from the plant, and then well fed with potash and phosphorus complexes. For re-flowering varieties, it is necessary to use at least two dressings with a break of 10 days.
At the end of the season, three-fold feeding is carried out, the main purpose of which is to give the plant an additional margin of safety for a safe wintering. At the end of summer, organic matter is used, after two weeks - phosphorus complexes, after another two - potassium
It is important to finish feeding about a month before the onset of a real frost, so the timing can be determined according to your climatic region.
Roses are also pruned the next year after planting. This stimulates the formation of side shoots and the creation of an attractive bush shape.
The cut points must be treated with garden varnish, and the bush itself is sprayed with Bordeaux mixture to prevent infection of the branches.
A rejuvenating pruning of the bush is recommended about once every five years. To do this, all shoots are shortened to 20-25 centimeters, and the middle of the bush is thinned out. The disadvantage is the loss of decorativeness, but the next season the plant will thank the owner with lush flowering and active growth.
Watering garden roses must be carried out with abundant, previously settled water. On average, each bush will need from 10 liters of water. At the same time, waterlogging is not allowed, as a result of which the plant can rot and hurt.
Loosening the bush is desirable, but difficult for old plants. The root area is necessarily mulched, and care for it is carried out as far as possible. Strongly overgrown bushes are more expedient to simply spray and water, and loosening is carried out when pruning or feeding.
The video clip will tell a lot of useful information about growing ground cover roses.
Decorative and biological signs
Despite the fact that the ground cover representatives of the pink family were singled out into a separate group at the end of the last century, many experts consider this division to be arbitrary. And one should not be surprised, because some varieties of the group reach a height of 100 cm or more. The following signs are of great importance in the classification:
Various forms of ground cover roses: 1 - Short bushes with creeping shoots, 2 - Upright, wide bushes, 3 - Low, wide, highly branching plants, 4 - Roses with arched creeping shoots, 5 - Roses with long creeping shoots.
- active growth is not upward, but wide;
- long and abundant flowering;
- resistance to black spot and powdery mildew;
- frost resistance;
- the presence of a large number of small shiny leaves of dark and bright green color.
All currently known varieties are subdivided into 5 main subgroups:
- undersized (up to 50 cm), having horizontally spreading, rapidly growing branches;
- low (50-95 cm) with slowly growing hard shoots of an arched drooping shape;
- large (50-100 cm) creeping roses;
- tall (from 100 cm) with arched branches of a drooping shape;
- widespread (from 100 cm) with shoots directed upwards.
According to this classification, each rosaceous plant of the ground cover group can have shoots from 50 to 200 cm in length, and an adult and well-grown bush can cover an area of 60 to 300 cm².
Roses are especially popular due to their abundant flowering: at the same time on a bush there can be more than 300 loose buds, and for the entire growing season their number is more than 2-3 thousand. Usually simple, semi- or double flowers are collected in brushes and, depending on the variety, are painted in white, pink, red, yellow, orange colors and their shades. Long-term flowering of plants is often accompanied by a mild, but pleasant aroma.
