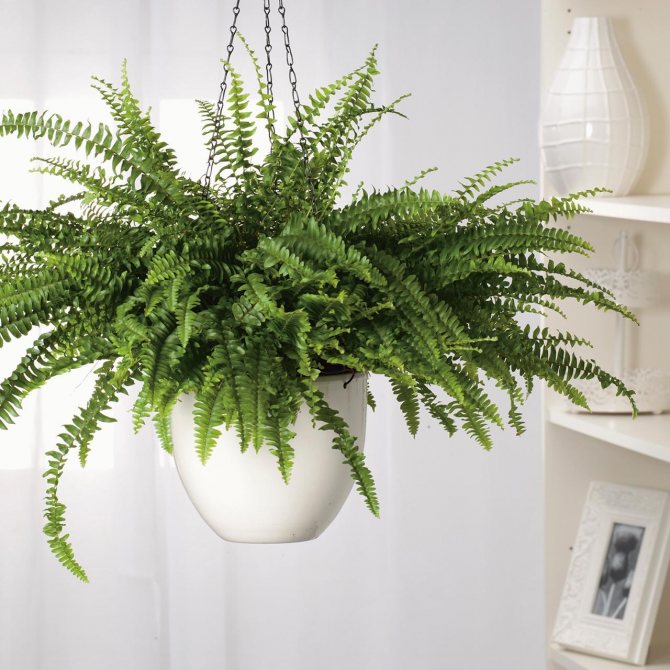
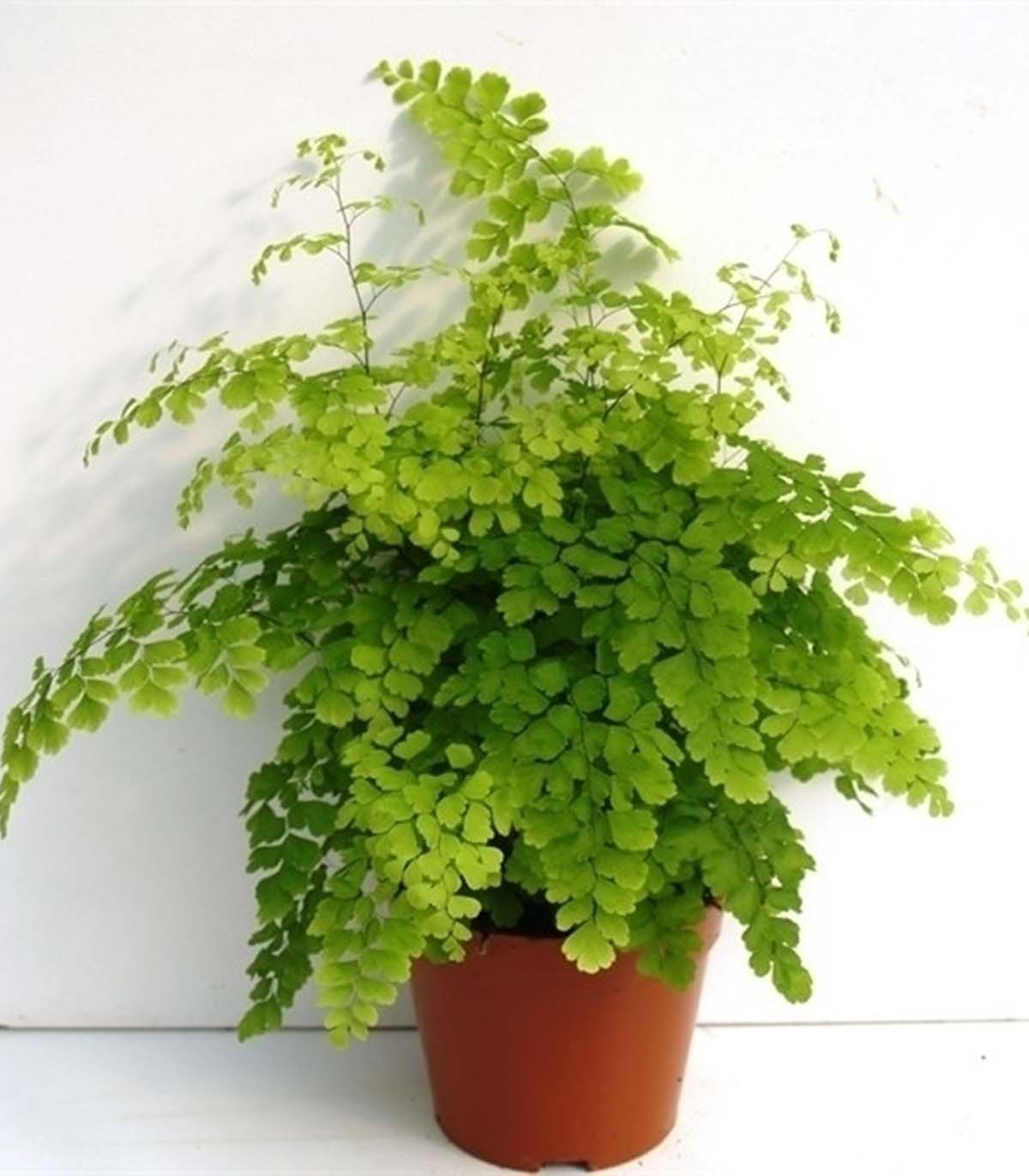
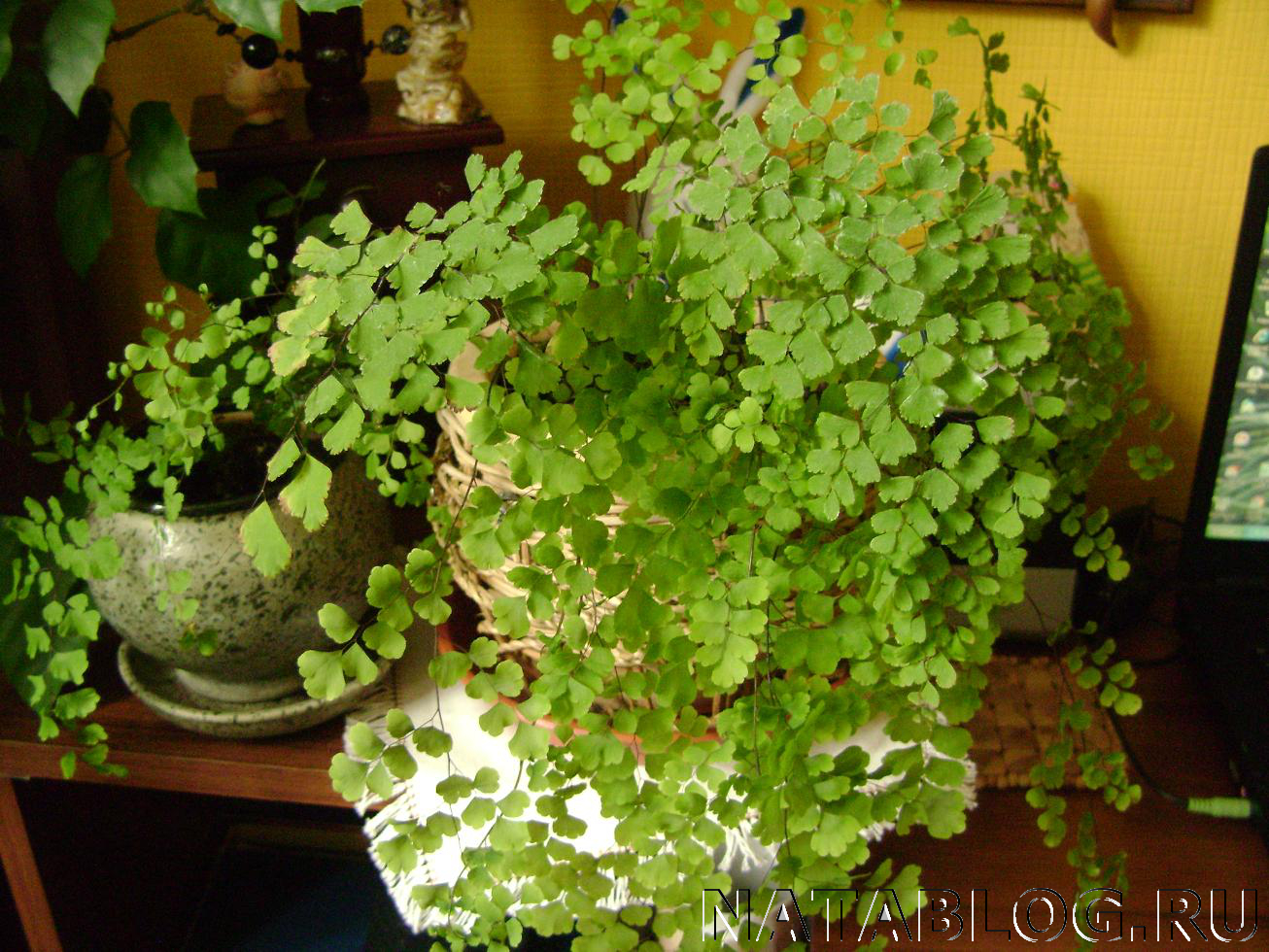How to care for a fern at home?
The active growth and beautiful appearance of the plant directly depends on the growing conditions and adherence to the rules for care.
Lighting and temperature control
 Indoor ferns need a well-lit place that is protected from direct sunlight. Many growers mistakenly believe that these plants are shade-tolerant. However, in the shade, the shrub will stop growing and may even die. Therefore, in order for the leaves to remain large and healthy, diffused but bright light is needed. It is best to place or hang the fern pot near the southwest window.
Indoor ferns need a well-lit place that is protected from direct sunlight. Many growers mistakenly believe that these plants are shade-tolerant. However, in the shade, the shrub will stop growing and may even die. Therefore, in order for the leaves to remain large and healthy, diffused but bright light is needed. It is best to place or hang the fern pot near the southwest window.
Shrubs feel good in rooms with an air temperature of + 15- + 22 degrees. However, some fern species belong to certain groups for which specific conditions must be created:
- For the pimpled polypodium and pellea, the air temperature in winter should be about +12 degrees.
- Asplenium, platycerium, nephrolepis and maidenhair are thermophilic plants, so the air temperature during their cultivation should not fall below +18 degrees.
It should be noted that all types of ferns like well-ventilated rooms, and do not tolerate cold air and drafts. In summer, plant pots can be placed in the garden or on the balcony, protected from direct sunlight.
Watering and humidity
 When caring for ferns at home, a certain watering regime is required. The plant needs a lot of water. Watering it is required regularly, as soon as the topsoil dries up a little. The optimal watering regime depends on the room temperature. In the hot season, the plant is watered several times a week.
When caring for ferns at home, a certain watering regime is required. The plant needs a lot of water. Watering it is required regularly, as soon as the topsoil dries up a little. The optimal watering regime depends on the room temperature. In the hot season, the plant is watered several times a week.
Prolonged overdrying of the soil is detrimental to ferns. You should know that a flower that has been in a dry earthen mixture for several days after watering will no longer recover.
Excess moisture for plant roots is also harmful. That is why ferns are planted in well-drained soils so that excess moisture immediately drains off. For watering shrubs, it is recommended to use soft water at room temperature. It is desirable that it be boiled or settled for several days.
Ferns are very fond of high humidity. They respond well to daily spraying. In hot weather and in rooms with batteries turned on, the plant must be sprayed several times a day or use a special air humidifier. It is also recommended that shrubs take a shower periodically.




If, during active growth, the plant does not receive the necessary nutrients, the color of its leaves will first become very pale, then they will begin to turn yellow and dry. Therefore, once a week at home, shrubs should be fed with special complex liquid fertilizers.
From late October to mid-February, the houseplant needs to triple the dormant period. If at this time the fern is kept in a cool room, then it will be necessary not only to stop feeding, but also to halve the watering.
Fern transplant
 Indoor fern care includes transplanting young plants annually. Mature plants are transplanted only after the roots have completely filled the pot.
Indoor fern care includes transplanting young plants annually. Mature plants are transplanted only after the roots have completely filled the pot.
The difficulty lies in the fact that the shrubs tolerate the transplant procedure painfully and can recover from it within several months. Therefore, it is recommended to use the transshipment method, replanting the plant from one pot to another without clearing the roots from the earth.
The best time for transplanting is spring.For the fern, you need to pick up a wide, low flowerpot and soil with an acidity level of 5.0 to 6.6 pH. For self-preparation of the earthen mixture, you will need to mix:
- peat - 1 part;
- humus - 1 part;
- leafy ground - 1 part;
- bone meal - 1/5 part.
At the bottom of the pot, which should be 5 cm larger than the previous one, drainage is poured first, then moss spreads, and the substrate is poured. The plant is planted, and its roots are covered with an earthen mixture so that there are no voids between them.
Immediately after planting and for another two weeks, the plant needs abundant watering.
Description, varieties and photos of domestic ferns
All ferns are perennial terrestrial epiphytic plants. They have short rhizomes and pinnately dissected leaves. On the stems covered with leaves, ground loops are also formed, which, when in contact with the ground, quickly give rise to roots. Below, on the leaves of the plant, sporangia are located.
 More than 10,000 species of aquatic, terrestrial, herbaceous and tree ferns grow in nature. Depending on the division, they can grow in forests, swamps or meadows. Among them there are babies and giants, the length of the leaves of which is more than half a meter. In moisture-loving plants, the leaves are delicate, strongly dissected and have a light green tint. Drought-resistant ferns are characterized by leathery leaves, sometimes with a waxy coating.
More than 10,000 species of aquatic, terrestrial, herbaceous and tree ferns grow in nature. Depending on the division, they can grow in forests, swamps or meadows. Among them there are babies and giants, the length of the leaves of which is more than half a meter. In moisture-loving plants, the leaves are delicate, strongly dissected and have a light green tint. Drought-resistant ferns are characterized by leathery leaves, sometimes with a waxy coating.
Types of indoor ferns
To date, many cultivated species of ferns have been bred, suitable for growing at home. The most popular of them are:
- Nephrolepis is the most unpretentious and well-known type of house fern. It is distinguished by a spectacular rosette, which is formed by openwork leaves with spores on the inside. The length of each leaf reaches 45-50 cm.
- Davallia or hare's foot is distinguished by reddish shaggy rhizomes that hang along the edges of hanging pots. The exotic plant is covered with lush green leaves.
- Platizerium is a plant whose flat leaves grow in different directions and are very similar to antlers. Its middle with brown leaves resembles a head of cabbage.
- Asplenium or kostenets differs from other fern species in undivided leaves wavy along the edge. He does not like very much when his leaves are touched.
- Blehnum or Derbyanka is similar in structure to a palm tree. In an adult plant, the crown reaches one meter in diameter and consists of hard fronds.
- Disconia as a houseplant can only be grown at a young age. Over time, it grows into a tall tree, the height of which can reach up to 3–6 m.
- Polypodium or millipede is distinguished by deeply dissected leaves located on thin stems. The rhizome of the plant crawls and clings to the surface, and the bush itself is able to grow in the air.
Growing and care
Selection and preparation of soil
The soil must necessarily pass moisture and air well. Here it is imperative to remember that in no case should the soil become waterlogged. This means that water should not stagnate in the ground. Therefore, stop the choice on loose soil, and a drainage layer of expanded clay is usually laid on the bottom. An increased acidity level (from 5 to 6) is also welcome.
Avoid oversaturation of the soil with needles or peat
The most important thing to know about caring for your fern soil is that it shouldn't be too wet. If the leaves of your fern have brown or brown spots, be aware that waterlogging has just happened.
If the spots are yellow, the soil is overdried, this should not be allowed either.
Watering and spraying
However, it will be difficult for a novice fern owner to determine what moderate watering is.
Pay attention to the soil. If its top layer has dried up, know that it's time for watering
Do not overfill the plant, otherwise it will quickly rot and die.
Spraying is a necessary procedure for growing healthy ferns. This should be done especially in winter, because at this time of the year the air in the apartments is especially dry. And the best environment for any kind of fern is humid! This procedure also includes fertilizing the planting with liquid fertilizers.
Do not forget about observing the correct temperature regime. This is not difficult to do. Consider: the best habitat for a fern in summer is street, forest. This means that the temperature of +20 degrees or more is absolutely optimal for him. but in winter it is not worth overcooling, the lowest threshold that a fern can withstand is +12 degrees. If it is not difficult to keep this temperature in summer, then in winter you need to try not to freeze the planting.
Lighting
Pay attention to how it grows in the forest. Under the trees, in the shade
This means that there will be nothing terrible if the sunny side is occupied by other plants that are more demanding on the presence of light. However, if you place nephrolepis on an area with diffused light, it will grow most beautifully and show all its advantages. The most important rule is not to leave the plant in direct sunlight or place it in dark corners.
Reproduction
Ferns reproduce by dividing the bush. You can, of course, try to grow nephrolepis from seeds (spores), but this is practically impracticable. It is much easier and more effective to divide the bush; it is recommended to do this during the spring transplant, so as not to disturb the plant once again.

The division process itself is quite simple. After pulling the bush out of the flowerpot, examine the base. You will see little rosette root babies there
So they must be carefully separated from the parent bush along with part of the rhizome. After separation from the bush, the small "cubs" of the fern need to create greenhouse conditions so that they can resiliently endure the rupture
Care features
Basic fern care at home involves regular watering and ensuring sufficient air humidity - most species cannot tolerate drought
It is equally important, when caring for a fern at home, to ensure optimal temperature conditions and lighting. It is necessary to correctly transplant and reproduce the fern
With illiterate maintenance, the indoor flower will quickly die.
If the plant is near other flowers, it is important to make sure that its delicate openwork leaves are not squeezed. Vayi are very fragile and require free space.
If the leaves are damaged or dry, they must be removed in a timely manner, allowing young fronds to develop freely.
Indoor fern is very fond of water. Prolonged drought can kill the plant. As soon as the top layer of the earth dries up, it needs to be watered. At the same time, excess moisture is harmful to the root system, and can lead to the death of the fern. With excessive moisture, the leaves become covered with yellow and brown spots, the root begins to rot, the plant dries up completely. You need to water it several times a week with settled water.
It is important to remember that if the home fern is dried out and then watered, the plant will still not recover.
Illumination
Indoor fern loves good lighting, it can die in the shade. It is best to place the plant on a southwest-facing window. With sufficient access to bright, diffused light, the leaves of the plant will be large, green and healthy.
Temperature
The average optimum temperature for a fern flower is from 15 to 22 ° C. But more specifically, the temperature regime must be selected taking into account the plant variety. There are types:
- thermophilic (nephrolepis, asplenium, platycerium) - should be kept in winter at a temperature not lower than 18 ° C;
- resistant to low temperatures (pimpled polypodium, pellea) - can withstand temperatures down to 12 ° C.
All types of indoor fern-like plants do not tolerate drafts, while they love fresh air. The room with the flower must be regularly ventilated.
The soil for the fern must be loose, allow air and water to pass through well, otherwise moisture will stagnate in the container, which ultimately will lead to decay of the roots. It is optimal that the soil contains a large amount of rotted leaves, slightly less needles and peat.
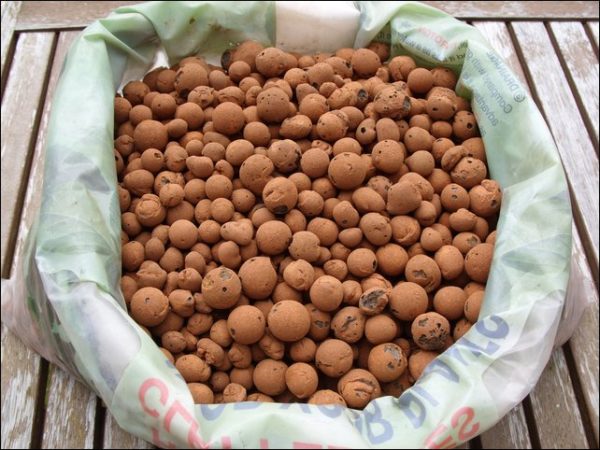

So that the water does not stagnate, a drainage layer of expanded clay is laid on the bottom of the pot.
For ferns, a soil with a slightly increased acidity level is suitable (pH value from 5.0 to 6.6). The acidity of the soil is easy to determine with the help of litmus paper. To do this, 2 g of soil must be mixed with 10 ml of distilled water, shake well, let the sediment settle. Then dip the litmus paper into the liquid above the sediment. At pH = 5, it will turn yellow, and at pH = 6, it will turn greenish-yellow.
Fertilization
Indoor fern usually grows normally and does well without additional feeding. But the fact that the leaves of the flower turned pale and became small indicates a lack of nutrients in the soil.
The need for top dressing often arises in the phase of active growth - in late spring and summer. You can fertilize a flower with liquid complex mineral fertilizers, for example, a solution, 1 liter of which contains:
- potassium salt - 1 g;
- superphosphate - 1.5 g;
- ammonium nitrate - 1.5 g
Organic ferns are used with great care - they can cause burns. Some growers periodically add tea leaves to the pot or water it with weakly brewed tea.
The fern plant is a fast growing plant, and therefore, at a young age, it is transplanted every year. Adult specimens are recommended to be transplanted every 2-3 years. Fern transplant is carried out in the spring.
In order not to harm the plant, it is advised to transplant it into a larger pot using the transfer method. During transplantation, the base of the rosette of leaves should not be deepened into the ground.
The soil is not cleaned from the roots of an indoor flower, so as not to damage the fragile roots. An exception is indoor flower disease, in which damaged roots need to be found and removed.

The fern is sensitive to the transplant procedure, and its recovery can take several months.
To transplant a fern, you can buy a ready-made soil substrate with an acidic environment in the store, or prepare the soil yourself. For this you need to take:
- leaf land - 1 part;
- humus - 1 part;
- peat - 1 part;
- bone meal - 1/5 part.
You can use another primer containing:
- 3 parts of sheet soil and peat;
- 2 parts of sod land;
- 1 part of humus and sand;
- 1/2 cup ash;
- a handful of sphagnum moss.
Transfer
The fern plant is a fast growing plant, and therefore, at a young age, it is transplanted every year. Adult specimens are recommended to be transplanted every 2-3 years. Fern transplant is carried out in the spring.
In order not to harm the plant, it is advised to transplant it into a larger pot using the transfer method. During transplantation, the base of the rosette of leaves should not be deepened into the ground.
The soil is not cleaned from the roots of an indoor flower, so as not to damage the fragile roots. An exception is indoor flower disease, in which damaged roots need to be found and removed.
To transplant a fern, you can buy a ready-made soil substrate with an acidic environment in the store, or prepare the soil yourself. For this you need to take:
- leaf land - 1 part;
- humus - 1 part;
- peat - 1 part;
- bone meal - 1/5 part.
You can use another primer containing:
- 3 parts each of leafy soil and peat;
- 2 parts of sod land;
- 1 part of humus and sand;
- 1/2 cup ash;
- a handful of sphagnum moss.
Indoor fern
This feature becomes apparent when considering the structure of the fern.Leaves, or more correctly, fronds, make up the aerial part of plants and, as a rule, are distinguished by a curly, feathery or multi-dissected form. Young, not yet opened leaf plates in ferns are tightly coiled into a spiral; as they grow, they unwind, become darker and denser. Fern rhizomes are located under the soil layer. This fully applies to:
air temperature at different times of the year; ambient humidity; lighting; frequency and volume of irrigation; application of fertilizing; transplantation.
How to care for a fern if this maximum is exceeded? The plant will need not only the usual protection from direct sunlight, but also frequent irrigation on especially hot days. Filling the entire free volume of the pot with moist sphagnum or placing the flower in a moist florarium will help. A useful solution would be to relocate the fern for the entire warm period under the open sky.
Read also: Even a beginner can provide good care for Thompson's clerodendrum, But with the onset of autumn, even before the first frost, the grower will have to find a cool place for the green pet under the roof. Some species are content with keeping at normal room temperature not lower than 17 ° C. But there are those who are more comfortable at 14-16 ° C. The minimum allowable temperature of the content is +10 ° C, if the air is colder, this threatens hypothermia of the rhizomes, which is especially dangerous in wet soil. At home, caring for an indoor fern will be greatly simplified if the pot is placed on the east or west window. Here, the plants are not threatened with sunburn, and the incoming lighting is enough for active growth and maintaining decorativeness. Do not forget that all members of the family react negatively to air pollution, smoke, and car exhaust. Therefore, not the best place for a flower is a smoker's room or a balcony overlooking a noisy street with heavy traffic.
Dryness of the substrate leads to the death of the leaves. Do not expect that the fronds that have lost their turgor and bright color will revive after the resumption of watering. Even with the resumption of proper care, they die off, which negatively affects the appearance of the flower. How to care for a fern that has lost its entire aerial part at home? You can reanimate a plant affected by drought by knowing the intricacies of the fern development cycle. Both already dead and still remaining green fronds are removed from the plant, after which the pot is transferred to a well-lit windowsill. With regular, but not too abundant watering, the fern can quickly recover. And a sign of awakening will be the tight green spirals of new foliage that have appeared over the substrate.
Complex fertilizing with the inclusion of organics and minerals effectively helps to maintain plants. They are carried out on a regular basis from mid-spring to autumn.
The best time to transplant indoor ferns is spring. Depending on the type of home plant, the procedure may have its own characteristics.
Read also: Do you have a sick room maidenhair? We know how to help Since among the ferns there are not only terrestrial plants, but also epiphytes, you will have to prepare for this stage of caring for indoor ferns at home in advance. To do this, select: a suitable size pot, basket or piece of wood for epiphytic varieties; a loose, necessarily light substrate that meets the needs of the culture.
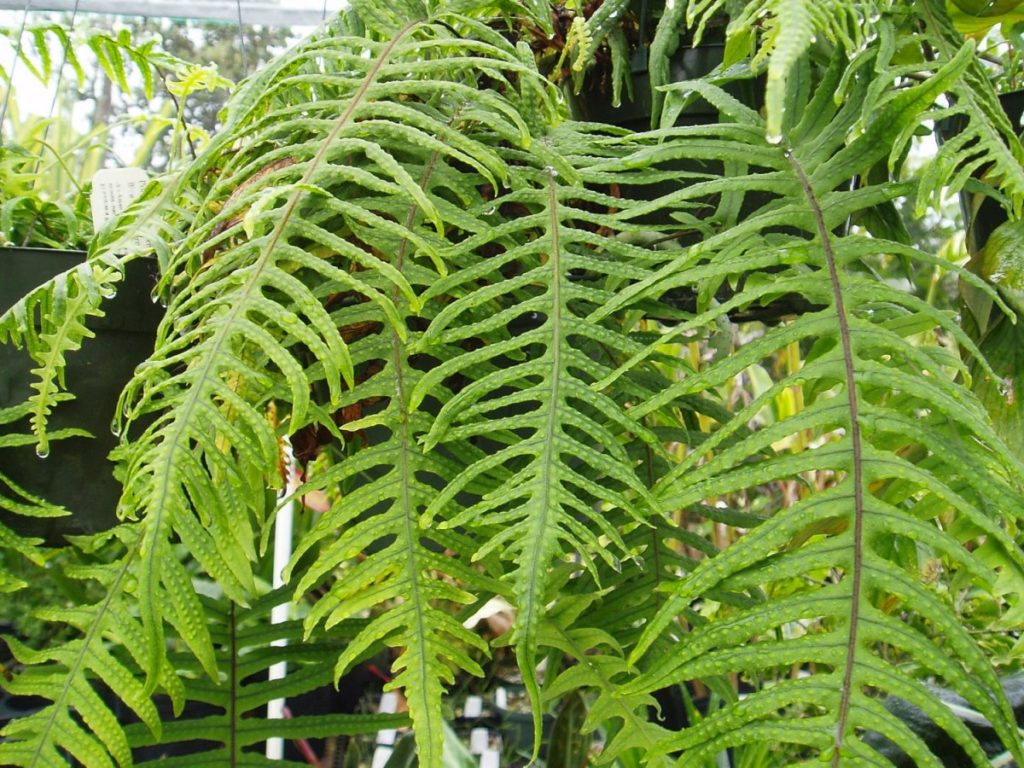
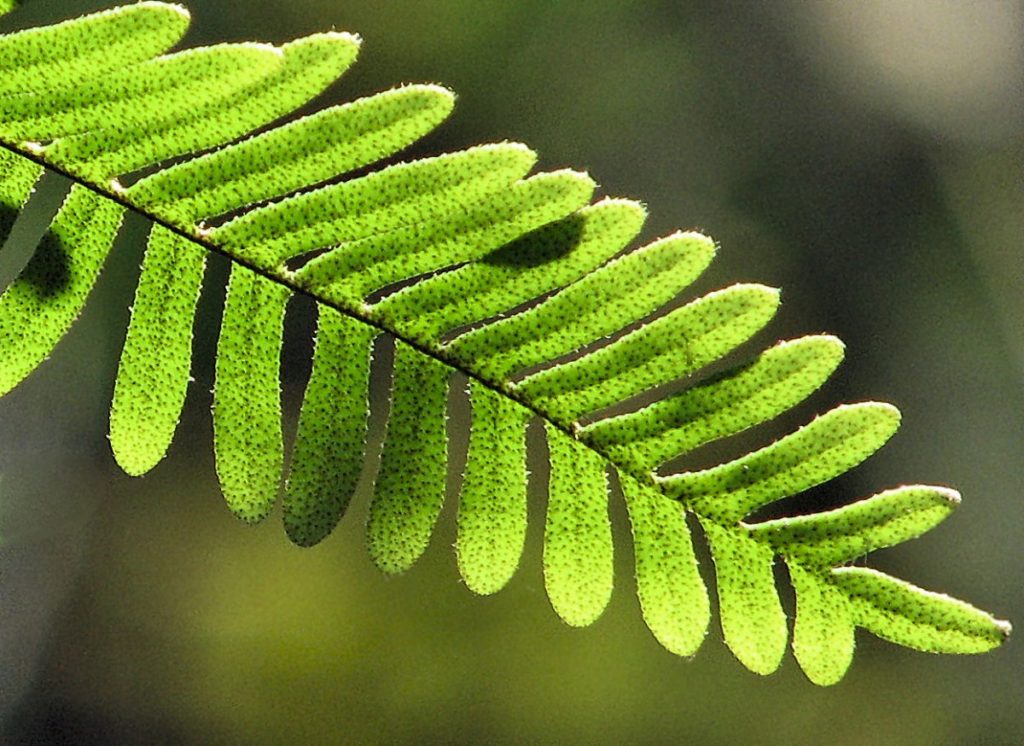
One of the rarest ferns - polypodium
Polypodiums, or Centipedes, are ancient ferns from the family of the same name, Polypodiaceae. Their name, like their appearance, has not changed for millennia.Polypodiums are often confused with Phlebodiums, and changing the classification with the transfer of individual species from one genus to another does not simplify the situation at all.
But polypodiums remain more rare, less extravagant and very special in nature rare ferns that deserve a special status and approach.
In Europe, centipede ferns are often referred to as sweet root. But still, translated analogues of the botanical name are much more popular. In nature, centipedes prefer to settle in the Southern Hemisphere. Some species are found in Australia with New Zealand, and in the south of India, and in South America. This forest plant, most often, chooses dense forests and jungles with high humidity and fairly secluded lighting, it grows on shrubs and trees.
The structure of this fern is often compared to water lilies, emphasizing how atypical a representative of the fern class the polypodium really is. But it is more appropriate to call it an original culture, and not look for analogies with aquatic plants.
Polypodiums are characterized by special rhizomes - creeping, scaly, horizontal rhizomes with rather thick adventitious roots. Rhizomes of polypodiums differ in size and character by rhizomes. In some polypodiums, the roots are thin, in others they are thicker and fleshy, but they are easily recognizable by their horizontal arrangement and characteristic scales on the surface. Polypodiums do not form a stem; leaf petioles remain very important organs for them.
All polypodiums grow fast enough, actively growing in indoor conditions and releasing several new leaves annually. They develop in a horizontal plane, gradually spreading, which should be taken into account when choosing a place and when looking for a container or method of growing. This is one of the fastest growing fern species for growing in rooms and greenhouses, capable of achieving maximum decorativeness by the third year of cultivation.
From the upper part of the rhizomes, in rows, on rather long, segmented petioles, large fronds of leaves develop. The maximum height of polypodium leaves is about 100 cm, although most species are limited to much more modest sizes up to 50 cm in height, and indoor plants are, most often, compact epiphytes up to 40 cm high.
Cirro-split or pinnately dissected, they are distinguished by their dense texture, asymmetric lobes and most often free veins. Segments are lanceolate or almost lingual, irregularly wavy, most often with a solid edge and a rounded tip. The leaves of polypodiums unfold very beautifully, from a peculiar shell-like shape, they stretch into a tight spiral, and then straighten their lobes.
In some polypodiums, the leaves are green, rather dark or brighter, in others they are covered with a bluish bloom or uneven, barely visible spots, with thinner or wider, curved or almost straight lobes. The variety of colors in the greenhouse and indoor culture is especially pronounced.
Sori of polypodiums are formed quite actively and almost over the entire reverse surface of leaves. They are located closer to the edge of the leaf plate, between the veins, large and rounded, not covered with a veil.
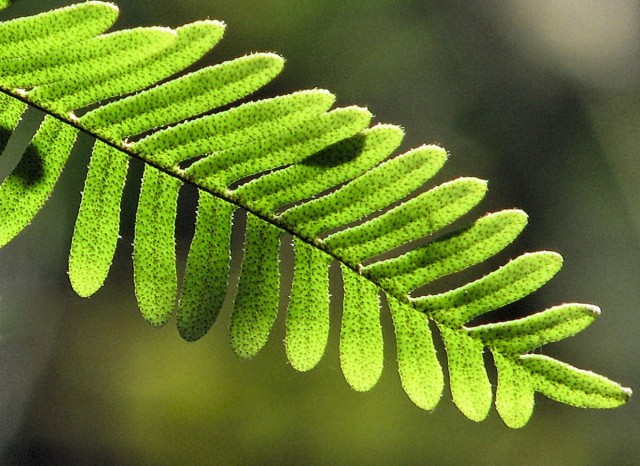 Centipede fern, or Polypodium polypodioides. Ransomed63
Centipede fern, or Polypodium polypodioides. Ransomed63
Views

Regardless of the species, ferns are fairly lush shrubs with long, curved leaves. The overwhelming majority of varieties have openwork, feathery and dissected leaf plates, but there are species whose leaves are whole. The main types of decorative indoor ferns are few. Not all relics are capable of being in confined spaces. The following varieties are chosen as indoor plants:
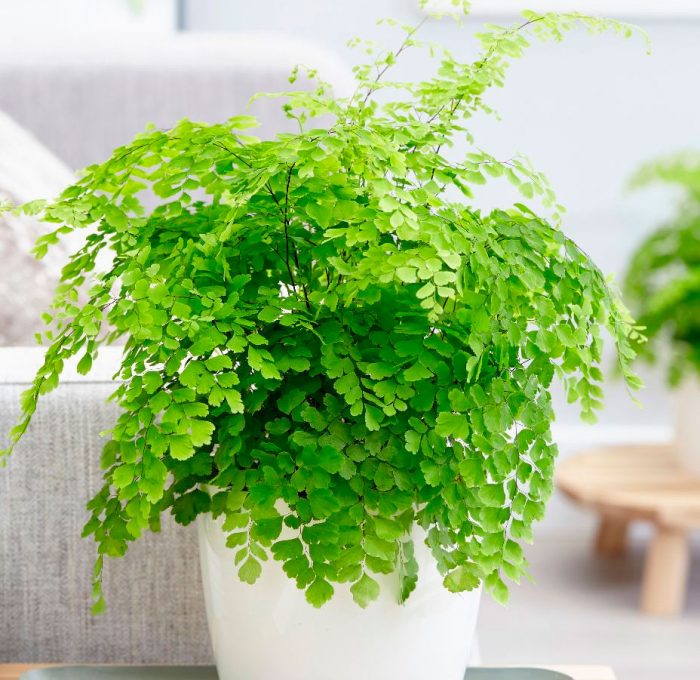
- Maidenhair - thin, fairly strong shoots and pinnately dissected fronds.Grows well in shaded warm and humid places. More suitable for growing in greenhouses, conservatories, and not in an apartment. Popular varieties are gentle, for the sake of, venus hair.
- Nephrolepis - lanceolate leaf plates, strongly dissected and pinnate. New shoots can form at the rhizomes of this relic. Most often, in apartment conditions, they keep nephrolepis of the sublime variety.
- Asplenium - grows well in shade, in high humidity conditions. In apartment conditions, they contain such varieties - nesting and viviparous, which have no noticeable similarity with each other.
- Blehnum (another name Derbyanka) is a sprawling relict plant, the crown of which reaches 1 m in diameter, and the fronds resemble palm leaves in appearance. Houses often contain Brazilian and humpback varieties.
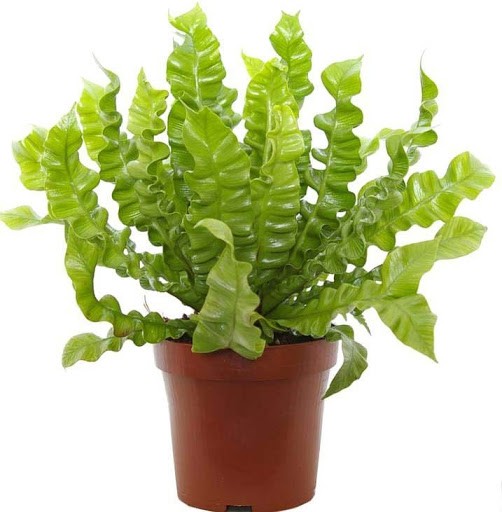
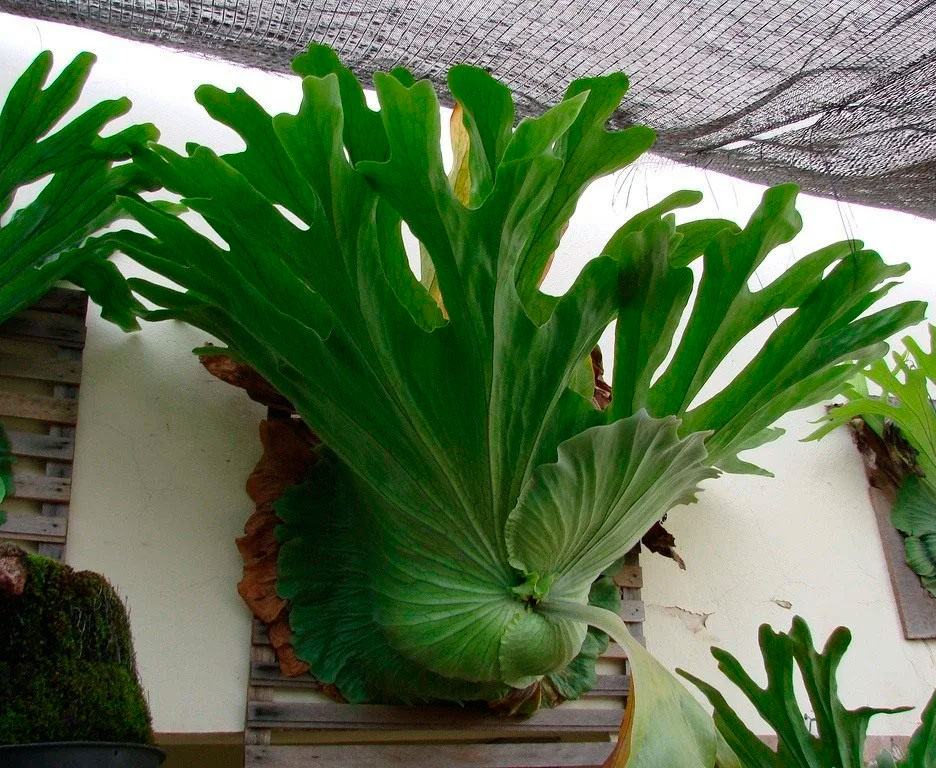
- Platycerium (flathorn) is a relic of an unusual appearance for a classic fern - its frond is large, resembling antlers in shape. The plant is relatively unpretentious to care for.
- Pylaea - unlike other species, this fern prefers not a wet, but a dry habitat. In indoor floriculture, varieties with the names green and round-leaved are popular.
- Disconia - the bush of this fern is not compact, adult relics can reach a diameter of 3 m, so this variety is grown only in spacious rooms.
- Polypodium (centipede) - fronds are strongly dissected, with blunt tips, and the rhizomes are distributed over the surface of the soil. This plant is capable of growing indoors with dry air.
- Davallia - this relic has a thick rhizome and therefore it is also called "squirrel legs".
Large plants look quite impressive in hanging pots, as well as on stands. Nevertheless, each of the varieties is very different from one another in size, shape and color saturation of the leaf plates. There are other varieties of domestic ferns, the names and photos of which you can see and choose the one you like best for growing.
Help! Fern leaves are sometimes used in floristry - for decorating bouquets and as part of flower arrangements. The plant recovers the torn off leaf plates quickly enough.
Flower propagation
Everyone knows ethnic fables about the fern flower that brings wealth and fortune. It is possible to find such an amazing plant only during one night a year during its flowering.







Due to its structure, ferns do not bloom. How does their reproduction take place? It turns out that ferns have one of the oldest methods of getting embryos using spores.

At home, this method is quite complicated due to the long appearance of plant embryos. When rare species appear, reproduction by spores cannot be canceled.

There are a lot of methods for increasing ferns. Some types can be easily propagated by crushing underground parts. Others provide an increment on a particular mustache.

And some, to accelerate growth and provide their own offspring with more opportunities for survival, became viviparous. Generated rosettes appear directly on the vayas. After the buds grow, they crumble and take root.

Description

Fern varieties grow in different climatic zones, they can survive in swampy areas, meadows, forests. Some species of this plant develop only by growing to trees. But ferns are most common in their natural environment in tropical forests. These particular species have become indoor ferns. Such home decorative flowers are not hardy, so they are not used for growing in open soil.
Help! There are varieties of ferns that can be kept in the garden, as they are able to survive in freezing temperatures. Their names and photos can be viewed on the net.
Indoor fern, regardless of cultivar or variety, does not produce inflorescences and does not set fruit or seeds. Reproduction of a domestic plant is possible only by spores or division of an adult mother plant, as in mosses, fungi or algae. In its natural environment, it is extremely hardy and unpretentious, but in the case of indoor cultivation, it is known as a relatively capricious plant. When caring for a fern is insufficient, at home it stops developing and dies.