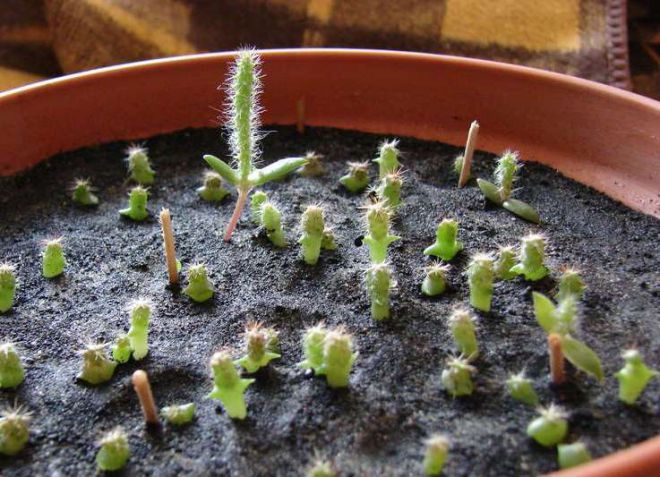
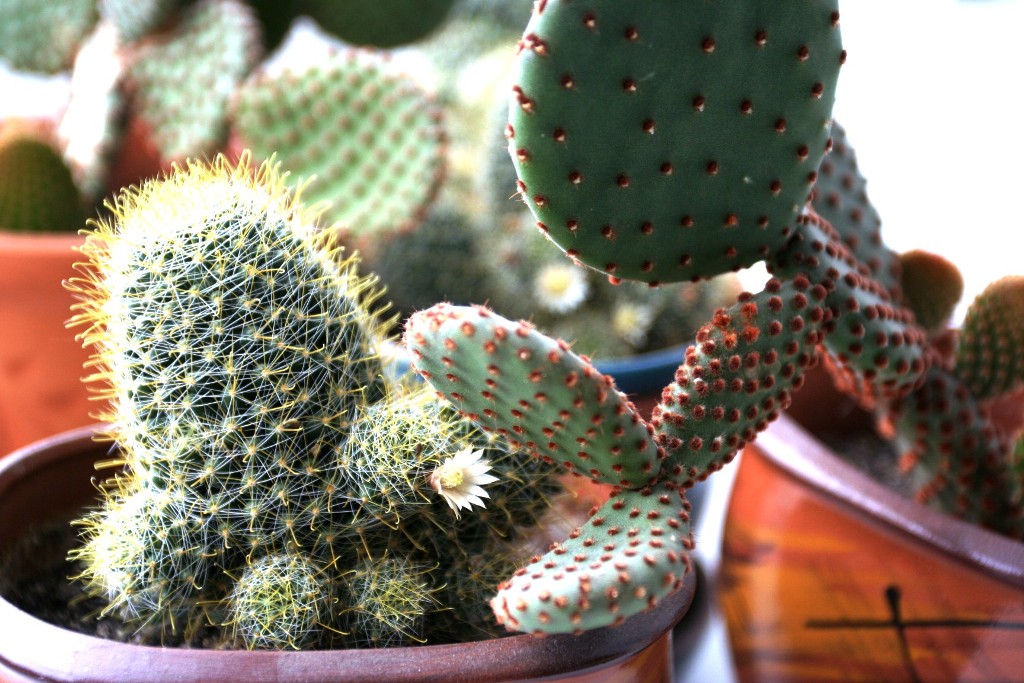
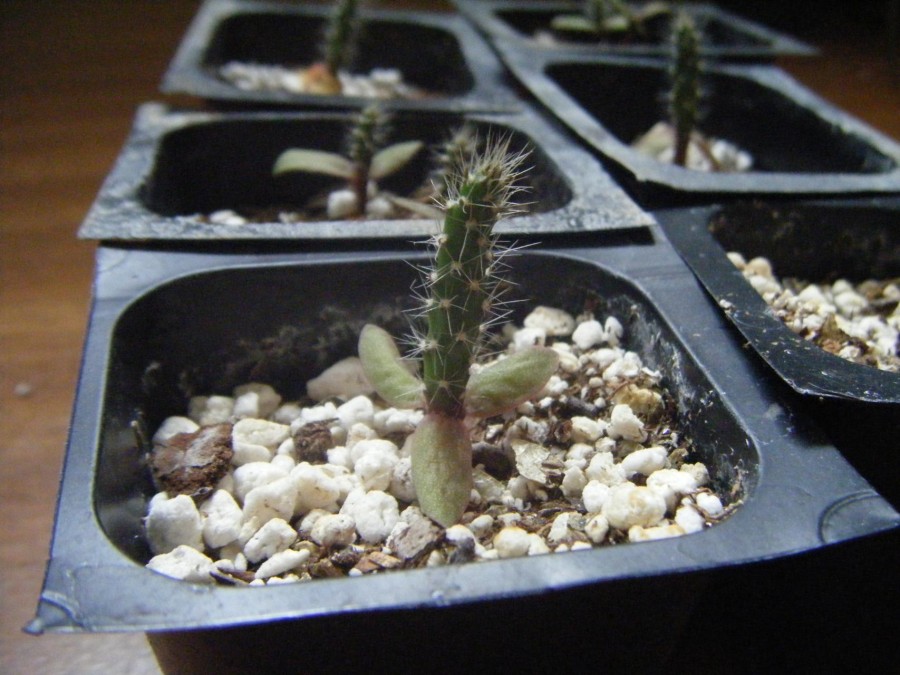
What do cactus seeds look like?
It is also the cheapest option for creating your own collection. Of course, you can buy already grown plants, but here a novice cactusist will have many pitfalls and disappointments. Purchased specimens can be affected by pests and rot, and cacti grown with the use of fertilizers stubbornly do not want to grow in ordinary soil. In addition, in cacti that have been in stores for a long time, with a lack of light, the stems are often hopelessly spoiled. Finally, the attitude towards these cacti will be completely different than towards plants grown by yourself. Before planting cacti, you need to get the seeds somewhere. The acquisition of planting material will not cause much difficulty. They can be bought in clubs of cactus lovers, borrowed from friends, ordered from private catalogs, and finally purchased online.
The rest of the semen is filled with a nutrient called endosperm. On the shell, a scar can be distinguished - the place of attachment of the seed and the micropyle - a narrow channel through which the pollen tube penetrates and fertilization occurs. When seeds germinate, the root lengthens and penetrates into the soil. At the beginning of germination, all the cells of the embryo divide, but after the formation of the seedling, cell division is localized at the tips of the shoot and root.
Seeds of rebutius, ailoster and some other genera have a short life. The term for germination of cacti from such seeds is limited to about one year. Conversely, in representatives of the genus Cereus and Mammillaria, seed life can reach 7-9 years. Longer-lived seeds are also known. In addition to biological reasons, the life span of seeds depends on the conditions of their storage. There are two independent rules for storing seeds: 1) with an increase in water in seeds by 1% (with an optimum of 5-14%), their life is reduced by 2 times. At the same time, below the optimum, the oxidation of seed fats occurs, above - the defeat by fungi; 2) with an increase in temperature for every 5 ° C (in the range of 0-50 ° C), the life of seeds is also reduced by 2 times. In other words, so that cactus seeds do not lose their germination capacity, it is advisable to store them in the optimal temperature and humidity range, without changing these parameters if possible. For cactus seeds, a good place to store the seeds is on the shelf on the door of your home refrigerator.
Next, you will learn how to plant cactus seeds and how to care for the sprouts.
Beneficial features
Opuntia is not only a cactus, but also a very useful plant. It contains a huge amount of useful elements and vitamins. For example, stems contain amino acids, protein, starch, and more. From the vitamin group, we can note the presence of vitamins A, B (1,2,3) and C.
Not only the stems contain a lot of useful things, but also the fruits of Opuntia. They are tasty, juicy, and rich in phosphorus, magnesium, protein and calcium, as well as glucose.
Thanks to all this, many medicines are produced from Opuntia that help fight various diseases, for example, disorders of the central nervous system, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes. In addition, with the help of Opuntia, people successfully fight obesity, skin diseases, rheumatism, etc.
In addition to medicines, glue, oil (something like sunflower or olive), detergents and cleaning products, as well as various cosmetics, which, by the way, are not so cheap, are made from Opuntia.
What a useful plant!

What does the plant look like and how does it bloom?



At home, prickly pear grows up to 1.5 m, but blooms rarely and reluctantly. There are also undersized species from 15 to 30 cm.
- The stem is articulate, dark green. Consists of flattened shoots (cladodia) drop-shaped.At the top of the cladodia, from 2 to 5 shoots grow - thus the prickly pear branches in the form of a bush.
- Leaves - rudimentary, succulent, subulate, up to 1 cm long, appear in the areoles of young cladodia. They are pressed to the surface of the shoots and die off over time.
- The root system is superficial, fibrous.
- Flowers - funnel-shaped, single, multi-petal, wide-open, from 3 to 6 cm in diameter. Painted in yellow, orange, red, pink and white tones. The stamens react to touch and immediately curl up. The buds are formed along the edges of the cladodia. The flowering period is from April to August. In different species - from a week to 4 months. Only adult plants bloom from 4-5 years of age.
- Fruits are fleshy, weighing from 70 to 200 g, 5-12 cm long. Ripen from the end of July. The pulp is juicy, tender, watery. It is similar in consistency and taste to ripe, sweet gooseberries and kiwi. In ripe fruits, the peel is pink-orange, red, purple.
- All types of prickly pear, in addition to thorns, have bunches of glochidia, which are located in the axillary buds of the stem and on the fruits.
Homeland of the succulent
In their natural environment, prickly pears are widespread in North and South America, including the West Indies. The main mecca of these large succulents is Mexico, where almost half of all varieties of prickly pear grows here.
Possessing high adaptive properties, some types of prickly pears have spread in various regions, practically all over the world, where the climate is tropical and subtropical. Moreover, some of the neophytes turned out to be very aggressive, literally filling the local flora. To combat cacti, which felt at home in new territories, in some regions it was necessary to use biological agents.

Propagation of cacti by seeds
Seed propagation of a cactus is not always effective. In many species of these plants, the seeds are very small, do not germinate well or are very capricious and require strict adherence to many conditions - from temperature, light and humidity to the composition of the soil.
But if your cactus seeds are fresh, large, healthy and you are confident in your skills and abilities of a florist, you can try to master this procedure.
You can sow cactus seeds in the ground, starting from February-March. For disinfection before sowing, it is better to soak them for a short time (8-10 hours) in a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate.
Soil for cacti is suitable from a mixture of peat and coarse sand (2: 1), previously calcined in the oven or spilled with boiling water. A drainage layer is necessarily poured onto the bottom of a disinfected small pot, and only then it is filled with soil mixture.
Cactus seeds are spread directly on the surface of a well-moistened and slightly compacted soil at a distance of at least 2 cm from each other. It is not necessary to sprinkle them with soil on top - this can only be done for large seeds.
The container with seeds is covered with glass or foil and placed in the warmest place, remembering to ensure that condensation does not accumulate on the inner surface of the shelter. The night temperature in such a greenhouse should be several degrees lower than the daytime.
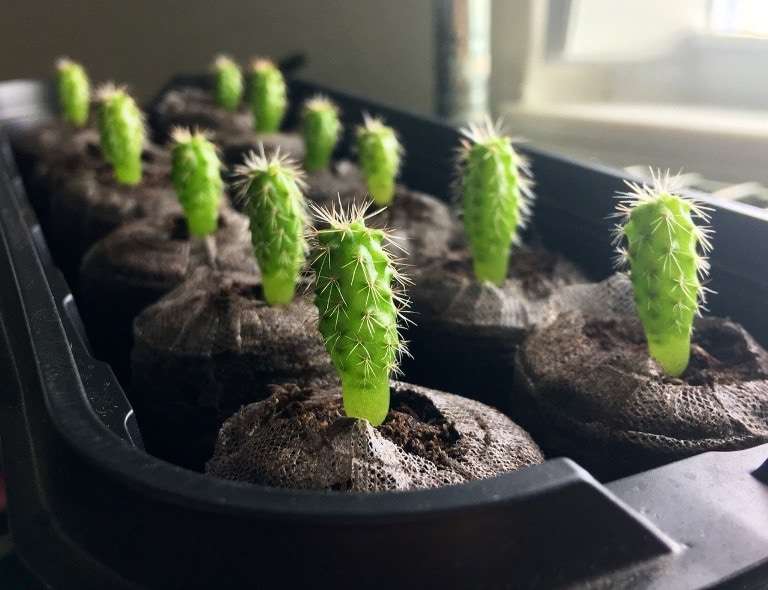
Seedlings will have to wait from several days to several weeks - depending on the selected type of cactus. As soon as the sprouts appear, they need to provide a sufficient amount of light, it is recommended to move the film or glass from time to time so that there is a constant flow of fresh air, and then completely remove it. Of course, a place with young growing cacti should be protected from drafts and direct burning sunlight.
As for the issue of watering the seedlings, here you need to be very careful and careful - both lack and excess of moisture are equally destructive for growing cacti. The soil should ideally be slightly damp at all times, but not wet.
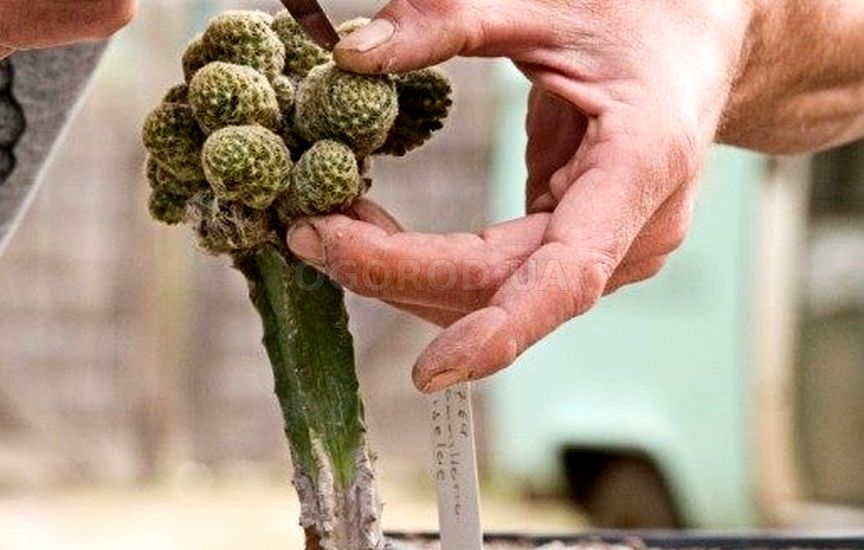
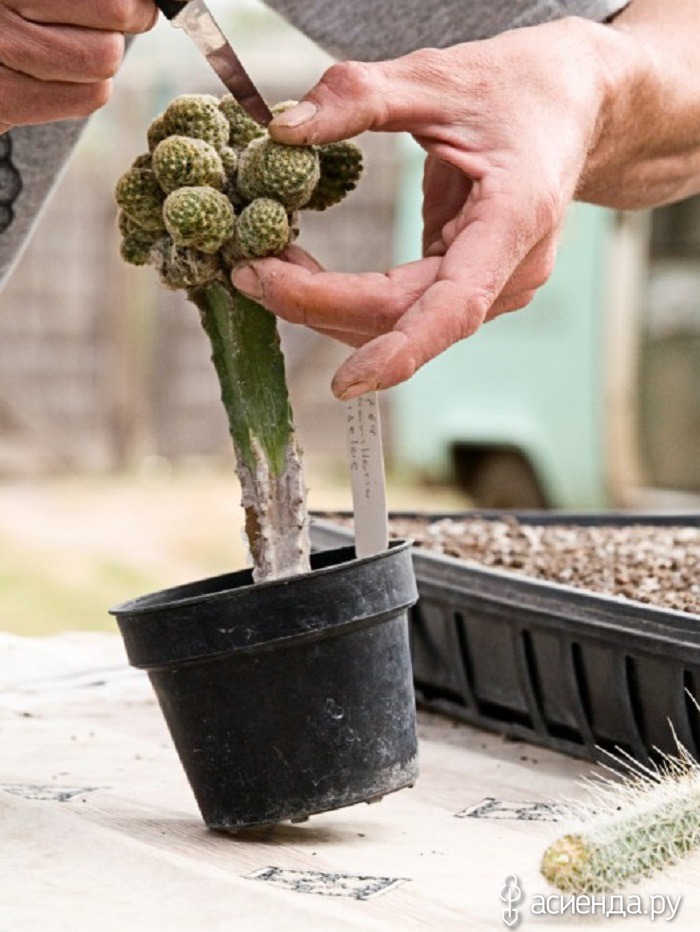
The grown cacti, in which thorns have begun to break through, can be transplanted into individual pots - the plants are carefully transferred with a lump of near-root soil, in no case, when planting, without deepening the root collars.
Seasonal care features
Spring
This is the time when the cactus comes out of dormancy and prepares to please the owner of amazing beauty with flowering. Gradually increase the air temperature to optimal values, resume fertilization and organize regular, but not too abundant irrigation.

Summer
Caring for cacti of this variety in the summer is reduced to the organization of full lighting, nutrition and irrigation.
Autumn
Gradually, they begin to prepare mammillaria for the rest period. They reduce the amount of fertilizers and soil moisture. Arrange light shading.
Winter
The quality of the growing season in the new season depends on good rest in the winter. Fertilization is stopped altogether, watering is rarely carried out, as the soil dries up. The temperature indicators in the room where the succulent will winter should not be lower than 15 degrees, otherwise the plant will get sick and will not please with abundant flowering with the arrival of spring.

Opuntia varieties
- Perhaps the most popular among lovers of home plants is the fine-haired prickly pear. During the flowering period, it is densely covered with bright yellow flowers of medium size. Even her golden thorns look very attractive.
- By the way, to the question of prickly pear - a houseplant or not: the garden queen of cacti can be grown both at home and in open space, since she is not afraid of winter cold. Under a thick layer of snow (just think!), It successfully survives frosts up to 35 degrees. If you live in areas with little snow, then cover the wintering prickly pears in autumn with a thick film.
- Indian prickly pear (fig) blooms very profusely, and in place of each flower wonderful edible fruits ripen, outwardly similar to figs. They taste like pear and strawberry.
- The Berger variety blooms with rich, bright red flowers.
- White-haired prickly pear pleases with small bright yellow flowers that smell amazingly nice. This cactus will also give you delicious fruits.
- Eeyore common in summer is covered with large yellow flowers.
- The Subulat species is very different among its congeners in its atypical form. Its thick stems grow strictly perpendicularly, their number increases over the years. The result is a lush bush of rectilinear stems.
- The main prickly pear is characterized by the splendor of its crown. Over the years, it takes on the appearance of a bush.
- How beautiful the Gosselin prickly pear looks! In adulthood, it is a dense bush. It blooms in large, very fragrant, bright yellow flowers. Its stems can be green or bluish in color. More precisely, the blue of the stems gives a light bloom. If you erase it, the surface of the stems will turn out to be green.
- The cactus queen, spread with her flat stems, spreads along the ground. In mid-July, these stems are covered with bright yellow flowers. Habitat - hot countries.
- Cylindrical prickly pear pleases with orange, pink or red flowers. It can reach a height of six meters. This happens if the plant grows outdoors. In the room, the variety reaches a maximum of 2 meters in height and does not bloom very densely.
Opuntia: home care
Opuntia is unpretentious in maintenance and care at home. Maintenance and care are no different from caring for other cacti.
Lighting and location
Opuntia is photophilous and requires bright lighting throughout the year. The plant does not tolerate direct sunlight. In winter, it is better to keep the cactus in a room with a low temperature, since the segments can stretch out from a lack of light. As a result, the plant will lose its decorative effect.
The prickly pear cactus does not tolerate frequent changes of scenery. The flower pot should be placed in a place where it can be for a long time
This is especially important during the period of bud formation. If the pot is rearranged or turned, the buds may fall off.
Watering and humidity
 The prickly pear cactus needs moderate regular watering during the growing season.During the dormant period, the plant is placed in a cool room and watering is stopped. At this time, the plant is watered using the bottom watering method, in which the pot with the plant is placed in a container of water. It is advisable to use acidified water. For this, a small amount of citric acid is added to the water for irrigation.
The prickly pear cactus needs moderate regular watering during the growing season.During the dormant period, the plant is placed in a cool room and watering is stopped. At this time, the plant is watered using the bottom watering method, in which the pot with the plant is placed in a container of water. It is advisable to use acidified water. For this, a small amount of citric acid is added to the water for irrigation.
Opuntia does not require additional air humidification. The plant is able to tolerate very dry indoor air.
Plant transplant and soil
The first transplant is carried out after the purchase of the plant. If the flower was purchased in the fall, it is better to postpone the transplant until the beginning of spring. Further transplantation is carried out as the plant grows, it is often not recommended to do it, since the cactus does not tolerate it well.
The plant needs a loose soil with a high sand content. For these purposes, you can use ready-made potting soil mixtures for cacti. The soil should be good moisture and air permeability. For its preparation, sand, clay, leaf and sod soil are used. Humus is not added to the soil. To plant a plant, you need a low, wide pot.
Main varieties
Golden-haired
This representative of the mammillaria came to us from Mexico. It has a dark green hue with a single stem reaching a height of 4-6 cm. Its shape is slightly flattened, slightly resembling a ball, about 6-8 cm in diameter. Elongated tubercles that do not touch each other are rarely located. The succulent root is fleshy and rather dense. The flowers resemble bells in appearance, have a diameter of about 3 cm. Their color is cream or beige, each petal has a pink longitudinal stripe.

Bokasana
The cylindrical shape and dense stem are characteristic features of bokasana. The stem has a dark green hue and a height of 4-6 cm. The dark spines with hooks at the ends are rather long, they are framed by a long white pile in the form of a bunch. During the flowering period, the cactus is characterized by pale pink flowers in the shape of a bell. If you follow all the care recommendations, the succulent blooms annually.
Wilda
The stem of this succulent is dark green and barrel-shaped. In the middle there is a hard spike, which has a hook-like appearance, it is framed by thread-like spines. A distinctive feature of the wilda is that many lateral children are formed on it. They do not fall off on their own, but continue their development on the mother trunk.

Zeilman
A wreath of small flowers with a bright pink hue adorns Zelman's mammillaria during the flowering period. Moreover, this process is quite long, with proper care, the cactus can bloom up to six months. The stem of the succulent is barrel-shaped, and the central thorn is surrounded by thin white spines collected in bunches.
Escaping
One of the smallest species with many side shoots. The stems are round and small. Hair-like needle-like spines tightly cover the stem of this mammillaria. Moreover, in the center they are golden in color, and white on the sides. White flowers adorn the shoot during flowering. The fruits that appear after this have a bright red hue. Moreover, they appear on the succulent even without pollination and become an additional decoration for the mammillaria.

Carmen
This highly branching cactus forms groups very quickly. The dense and elongated stem is up to 15 cm wide, and grows no more than 5 cm in height. There are brown or dark yellow spines on its entire surface. Carmen is adorned with numerous white flowers that appear on her in spring.
Luthi
The dark green pear-shaped stem and miniature appearance are characteristic of this mammillaria. Unlike other species, a small number of thorns are formed on it, and they are rarely located. But the flowers of Mammillaria Luthi are quite large, 2-3 buds appear on one stem. Their diameter is about 3 cm, and the color of the petals is dark purple or lilac at the edge and white at the base.

Zelman
In young mammillaria of this species, the stem has a spherical shape, then it stretches up to 7 cm in height, and has about 15 cm in diameter.At its base, there are many side shoots, located quite densely. The central spine is red. The Tselman cactus is one of the most beautifully flowering species of mammillaria, and the most undemanding to care for. This is a great option for your first floriculture experience. Its flowers are dark pink, large, located at the top of the stem. The flowering of the succulent is long - from the beginning of spring to the very fall.
Plumosa
The spherical stems of this cactus have a diameter of about 7 cm. In general, this mammillaria is one of the most attractive and decorative. However, caring for such a succulent is quite troublesome, so it is not as often used in home gardening as other varieties. It is decorated with tiny white flowers not exceeding 1.5 cm in diameter.

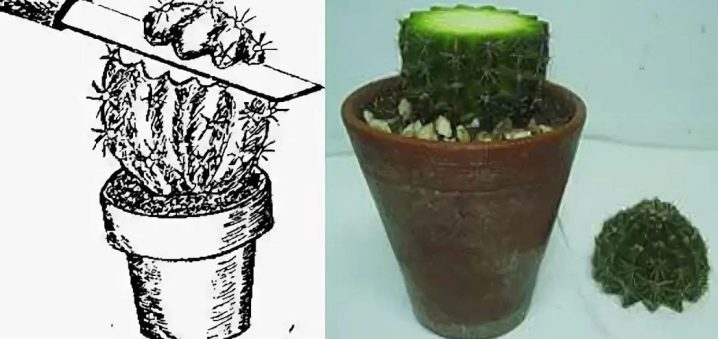
How cacti breed
The plant can be propagated in 2 ways - by children and by seeds.
The first method is considered the easiest and most effective way, most flower growers do just that.
Despite the fact that propagating cacti by seeds is much more difficult - the process is very laborious, but very exciting. It is very interesting to observe how small fluffy cones appear, which turn into miniature copies of future cacti.
Reproduction of cacti by children, cuttings or vegetative way
But consider the simplest and fastest way - vegetative. From an adult plant, they take a baby, which has already formed its own small roots, and transfer it to a small dish with a substrate - rooting occurs very quickly.
How to propagate a cactus by seeds:
- You should buy ready-made seeds in the store, since it is very difficult to get them from your own plants, and their germination capacity is minimal.
- The container for germination should be flat, with low edges, washed river sand is poured into it and moistened.
- Seeds are sown on the surface - without burying, and they equip an impromptu greenhouse, placing the crops under a film.
- Airing, once every 2 days, until the first shoots appear. High humidity must be maintained at all times.
- The appearance of small sprouts depends on the type of plant, some give distillation every other day, others have to wait for weeks.
According to psychologists, cactus lovers are stingy with emotions, but this is just a stereotype. In reality, they are vulnerable and sensitive creatures. An emotional person cannot but pore over a plant and take care of it so that it annually pleases with flowering.
How to transplant cacti correctly
Any plants need a transplant and cacti are no exception. It is produced when the container becomes cramped and there is no room for the roots to develop.
Cactus transplant rules
- The pot should not be too large - the plant does not tolerate waterlogged soil, which can form in a space free from roots.
- If you plan to transship an adult cactus, then you need to choose a pots 1 cm larger in diameter than the previous one. The roots should fit freely in the container.
- Before the procedure, the plant should not be watered in about 3-4 days. This is necessary so that the earthy clod dries out and separates well from the root system.
- As for young shoots, they need to be transplanted every year, up to 4 years of age, then the procedure is carried out as needed.
- It is better to transplant at the very beginning of the active growing season - in the spring.
- When transplanting, it is very easy to get injured on the thorns of a cactus, so it is wrapped in a dense cloth.
Step-by-step instructions for transplanting cacti
- At the bottom of the planter, a drainage layer is poured onto 2/3 of the container and a little substrate.
- The roots are lowered into a pot and carefully covered with earth.
- To compact the soil, shake the pots a little or tap on the edges - you cannot press the substrate with your hands, you can damage the delicate roots.
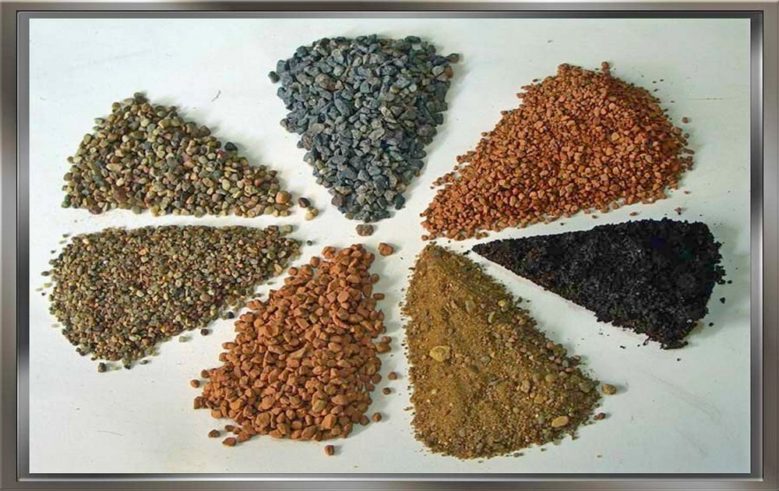
As for the soil, you can buy it or prepare it yourself.
Soil for cacti at home
- take 1 part of washed river sand;
- 1 hour of leafy earth;
- 1 part peat;
- 1 part charcoal.
Mix all components well until a homogeneous substrate is obtained.

Soil for cacti
Growing cacti from seeds at home: planting dates
Obviously, this is due to the poor quality of the seeds. A sufficiently high germination of seeds shows that in the absence of a cactusist's claims to create a cactus greenhouse or a cactus company, a relatively small amount of seeds will be required to obtain a decent home collection. The task is greatly facilitated by the exchange of grown seedlings with fellow hobbyists.
Table "Germination of cactus seeds":
|
View |
Sown, pcs. |
Rose |
|
|
PCS. |
% |
||
|
Acanthoclicium violocium |
10 |
7 |
70 |
|
Ariocarpus furfuraceus |
5 |
2 |
40 |
|
A. trigonus |
9 |
9 |
100 |
|
Astrophytum asterias |
10 |
10 |
100 |
|
A. capricome |
5 |
5 |
100 |
|
Aylostera muscula |
10 |
5 |
50 |
|
Bartschella schumanii |
20 |
5 |
25 |
|
Brasilicactus graessneri |
5 |
||
|
B. haselbergii |
20 |
1 |
5 |
|
Cleistocactus strausii |
30 |
15 |
50 |
|
Copiapoa montana |
5 |
4 |
80 |
|
Delaetia wontersiana |
5 |
3 |
60 |
|
Discocactus horstii |
11 |
7 |
64 |
|
Dolihothele longimamma |
5 |
4 |
80 |
|
Echinocereus viridiflorus |
10 |
4 |
40 |
|
Echinomastus durangensis |
5 |
4 |
80 |
|
Epithelanta micromeris |
5 |
5 |
100 |
|
Eriocactus magnificus |
10 |
2 |
20 |
|
Ferocactus glaucescens |
5 |
5 |
100 |
|
Gymnocactus knuthianus |
5 |
2 |
40 |
|
Hamatocactus hamatocanthus |
10 |
8 |
80 |
|
Islaya islaiensis |
5 |
5 |
100 |
|
View |
Sown, |
Rose |
|
|
PCS. |
% |
||
|
Leuchtenbergia principis |
5 |
4 |
80 |
|
Mammillaria microchelia |
10 |
8 |
80 |
|
M. Candida |
5 |
3 |
60 |
|
Melocactus bachiensis |
5 |
4 |
80 |
|
Neogomesia agawoides |
10 |
8 |
80 |
|
Obregonia dencgrii |
5 |
4 |
80 |
|
Parodia subterranea |
5 |
3 |
60 |
|
Rebutia krainziana |
10 |
5 |
50 |
|
Solisia pectinata |
5 |
3 |
60 |
|
Thelocactus hexaedrophorus |
5 |
5 |
100 |
|
Wigginsia sellowii |
5 |
4 |
80 |
Diseases and pests
Disease
Cause
How to treat
Anthracnose (brown spot)
Fungal infection that appears as moist, yellow-brown patches on the plant
The affected areas are removed with a sharp knife, a fresh wound is sprinkled with sulfur, and the whole plant as a whole is treated with fungicides
Rot
Illness caused by improper care: inadequate lighting and excessive watering
If rot has not yet struck the entire body of the cactus, the diseased areas are cut out and sprinkled with sulfur. If the root system is partially affected by rot, all diseased roots are also cut off and sprinkled with coal powder.
Watering the plants is resumed no earlier than three weeks later.
Mealybug
Appears when the temperature is too hot and the air is too important
Infected plants can be identified by spraying with infusion of garlic, tobacco, or green soap solution. Insects must be removed by hand prior to treatment.
We offer you to watch a video about the diseases and pests of prickly pear:
Diseases and pests of prickly pear
Pests of prickly pear
At home, prickly pears can be attacked by spider mites, mealybugs, nematodes, scale insects and whiteflies. Ticks, whitefly larvae, scale insects and their close relatives mealybugs are sucking pests that feed on the plant's cell sap. They are destroyed by spraying the prickly pear with a solution of acaricide - Actellic, Bankol, Decis or any other drug of a similar action. During processing, it is necessary to prevent the solution from entering the substrate. After 7-10 days, the treatment should be repeated.
As for root nematodes, it is very difficult to detect their appearance, but if you look closely at the roots of the prickly pear, you can see on them the swellings that form these root pests. With a sharp knife, these formations should be cut to a healthy tissue, after which the roots should be immersed in hot water at a temperature of 45-50 ºC for 10 minutes, but in such a way that the root collar remains dry. After the procedure, let the roots dry, treat the sections with crushed charcoal and plant the prickly pear in fresh sterile soil.
Diseases of prickly pear
Of the diseases, prickly pears can be affected by root rot, late blight, gray rot and wet smelly rot. The cause of these diseases is fungi, which are activated under conditions of regular waterlogging of the soil and overfeeding of prickly pear with nitrogen fertilizer. Sick areas must be removed, and the plant must be treated with a solution of a fungicide - Bordeaux mixture, Gamair, Oxychom, copper sulfate or other drugs of a similar effect. When spraying prickly pears with pesticides, follow safety precautions.