How to prepare for planting?
Next, we will consider how to properly cut an indoor flower and plant a cutting, how to choose and prepare the ground and a pot for planting.
The earth
To root the cuttings, peat is used, into which you can add moss - sphagnum: peat will give the soil looseness and airiness, and the moss will maintain an optimal moisture level in the pot (how to properly prepare the soil for hibiscus and whether it can be purchased in the store, read here ). You can use a mixture of garden soil with river sand and peat in equal proportions. You can also root hibiscus simply in wet coarse sand.
Purchased peat-based soil is also used. The main condition is that the substrate must be light and breathable. The soil that is poured into the pot for the permanent habitation of hibiscus should consist of:
- 4 parts of sod land;
- 3 pieces of leafy land;
- 1 part humus;
- 1 part coarse sand.
As an option: sod soil, humus, sand in a ratio of 2: 1: 1.
Pot
Material
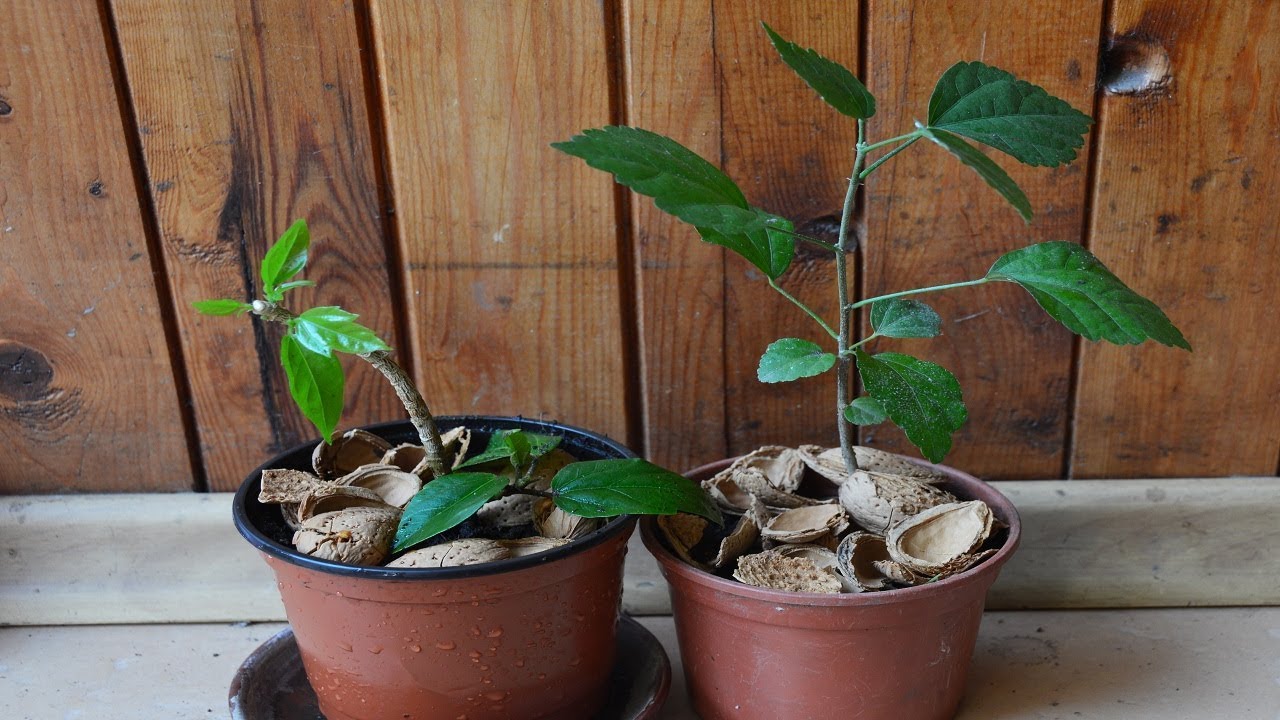
For rooting the cuttings in the ground, it is important to use transparent plastic containers in order to observe the development of its root system. If pots are not available, large plastic cups can be used, but remember that any container must contain a drain to drain excess moisture.
The size
Most often, for rooting in the ground, growers take containers with a volume of 200 to 500 ml, it all depends on the size of the cutting. Its diameter should be close to 9 cm. The hibiscus blooms when its roots grow freely in a pot. Therefore, after rooting, the indoor flower should be transplanted into a spacious pot.
Planting material
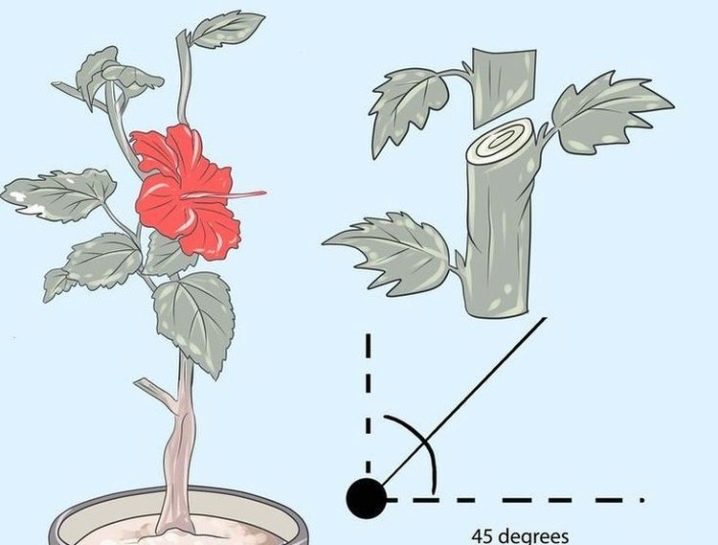
Cutting cuttings from hibiscus should only take place after the plant has faded. A young, developed shoot with semi-lignified bark is cut obliquely with a clean sharp knife or pruner. The stalk should be about 15 cm long and with 3 to 5 internodes.
The lower leaves from the cutting are removed completely, and the upper ones are cut in half to reduce evaporation, the upper part of the shoot is shortened by a straight cut. The lower part of the cuttings is dipped in Kornevin before rooting in the substrate.
Care advice
In order for a young plant obtained from a cuttings to fully develop and grow, it is important for it to create comfortable living conditions. This implies compliance with the following requirements:
- sufficient illumination;
- optimal temperature conditions;
- sufficient air humidity;
- timely watering;
- top dressing;
- prevention of pests and diseases.
Lighting
After rooting, young hibiscus is placed in a well-lit place (on a windowsill, a heated balcony), while excluding direct sunlight on its leaves. Moderate diffused light is considered the most comfortable for these delicate exotics.
Temperature regime
Tropical origin causes increased temperature requirements for hibiscus. Best of all, these exotics feel at a stable air temperature of about 21 ° in summer and 15 ° in winter. Temperature drops, cold snap and drafts are detrimental to these plants, since they cause a sharp decrease in their immunity and, as a result, the development of diseases.
Sufficient air humidity
The tropics and subtropics are zones in which high humidity constantly reigns. It is necessary for rooting cuttings, for young and adult plants. For hibiscus to feel comfortable, it needs regular spraying.
When carrying out this procedure, it is important to ensure that no water gets on the buds and flowers that are forming.Household humidifiers, as well as wide containers of water installed next to the pots, will provide constant air humidity.
Timely watering
Typical of the tropics, hibiscus does not tolerate drought. It is necessary to water it regularly, making sure that the soil mixture in the pot does not dry out. However, an excess of moisture in the substrate must not be allowed, otherwise it can cause root rot.
Top dressing
Young plants that have entered the phase of active growth and development require a lot of resources. To give them additional strength, top dressing is used.
Prevention of pests and diseases
It is very important to protect young plants grown from cuttings from diseases and pests. For prevention purposes, young hibiscus are regularly examined, and newly acquired plants are temporarily isolated from the rest.
Both the store substrate and the components of the soil mixture for do-it-yourself preparation should be checked.
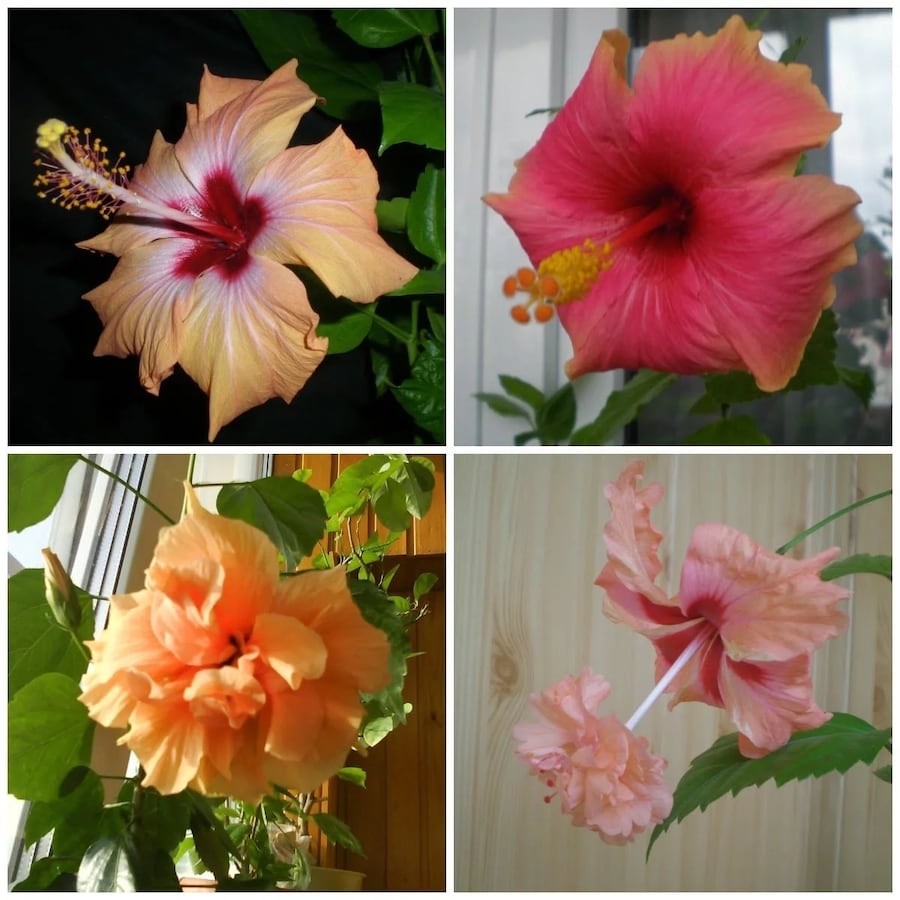
Description and photos of popular types of hibiscus flower
Most often, hibiscus are found as evergreen or deciduous shrubs, small trees 2-3 meters high. The stem of the hibiscus is bare, the leaves are located on the petioles. Large graceful brightly colored flowers can be from 5 to 30 centimeters in diameter. The color scheme of these beautiful flowers is very diverse. Hibiscus fruits are small bolls that split into five leaves. Inside such a box are fibrous or fluffy seeds, although in some varieties they may be naked.
Hibiscus lives for about 20 years. If the plant is properly cared for and favorable conditions are created for it, it can grow up to three meters in height.
There are garden and indoor varieties, there are about 250 species.
Marsh hibiscus. A plant with large, bright flowers that are decorated with carmine spots at the base of the corolla. With proper care, it blooms all year round. Gardeners love to use it for hedges. Syrian arboreal gibiscus. Many modern gardeners love this variety for its large (about 10 centimeters in diameter) bright flowers and use it perfectly as a hedge, decorating front gardens. Fertile land and abundant watering are essential for this plant. Leaves are ovoid, beautiful exotic flowers can be simple or double.
Home hibiscus are unpretentious, their beautiful flowers are used not only for decorative purposes, but also use their medicinal properties.
The most common in indoor floriculture is Chinese hibiscus (Hibiscusrosa-sinensis). Differs in large dark green oval leaves with jagged edges. It blooms for a long time: from late spring to autumn. Large bright flowers last for a maximum of two days. The color is usually bright red, but on sale you can find a variety of varieties of simple and double flowers in white, pink, orange, yellow.
The hibiscus is cosmatic. This is a herbaceous hibiscus species that grows well only in the south in the open field. Its leaves are similar to those of a sunflower. Large flowers with a burgundy spot on the throat, do not fully open, bloom one day.
Triplet hibiscus. This herbaceous annual is easily grown through seedlings. Interesting in that its beautiful creamy flowers open at 8 am and close at 9 pm. These flowers can practically be used to check the clock. Terry hibiscus. Large white flowers up to 15 centimeters in diameter bloom for just a day. This evergreen plant with bright green leaves looks very impressive and beautiful. Loves good light and abundant watering.
Changeable hibiscus or "crazy rose". It is notable for the fact that its beautiful flowers, similar to roses, during the entire flowering change color from white at the beginning of flowering, to crimson when they fade. It grows in height up to 3-4 meters.
Okra or edible hibiscus can also be grown from seed. It is an annual plant, reaching a height of 2.5 meters. Large yellow, orange or pink flowers are located in the axils of the leaves and, after blooming, form fruits that taste like asparagus and eggplant.
Growing indoor hibiscus at home
Hibiscus is quite hardy and not particularly picky about indoor growing conditions. It grows pretty quickly. With good care, it blooms profusely, it happens that it blooms even in the winter dormant period.
It is better to place it in a place protected from drafts, but well lit. It is necessary to periodically apply top dressing: throughout the growing season, about once every two weeks, mineral fertilizer (10 g per 10 l) is added to the water for irrigation. In early spring, at the same time as transplanting, the plants are pruned, which contributes to better branching.
Watering and lighting
Hibiscus prefers diffused sunlight. In summer, it is best to place it near the west or east window. If the windows face south, then it is better to put the flower away from the window or protect it from direct sunlight by hanging cloth (gauze, tulle), paper (tracing paper). On warm summer days, the plant can be taken out into the open air, but must be protected from drafts, direct sun.Hibiscus are moisture-loving, they need to be regularly watered and sprayed. In summer it is possible in the morning and in the evening, and in spring and autumn - once. Much also depends on the conditions of the plants and the season. In the winter period of dormancy, watering is usually reduced, and during the growing season and especially flowering, it is watered abundantly. The soil should always be moderately moist and loose. Water the flower with well-settled soft water.
Temperature regime for the hibiscus plant
The most acceptable air temperature for hibiscus in the warm season, during the period of active growth, is 18-25 degrees. In principle, it is shade-tolerant, but it blooms in the shade much less often. In winter, the temperature should not be allowed to drop below 10 degrees, otherwise the hibiscus will shed its foliage.
Hibiscus flower buds are laid at 12-17 degrees. In late autumn, when the dormant period begins, the hibiscus is rearranged in a darker place, away from heating, where the flower is located from November to March. When small leaves appear on the branches, even before the buds appear, the hibiscus is returned to its original place.
Air humidity
Soil for planting and growing hibiscus Hibiscus is unpretentious in this regard, but it is recommended to spray it regularly. Blooming hibiscus is sprayed with warm, settled water. In autumn and winter, it can be sprayed with warm water from time to time. Spraying is an excellent prophylaxis against spider mites.
The soil for the flower must be loose, breathable, and there must be drainage in the flower pot. Usually, the soil mixture for hibiscus contains pine, leaf, sod land, sand, humus, peat, and a little charcoal.
The acidity of the soil should be close to neutral: pH 6-7, maximum 7.8, minimum 5.5. If the acidity of the soil goes beyond these limits, it becomes more difficult for the plant to take up nutrients.
Top dressing and fertilizers
Nitrogen-containing and mineral fertilizers stimulate long-term flowering of hibiscus, therefore they are very useful in spring and summer. The plant is fed regularly every three weeks with water-soluble fertilizers that contain iron, copper, phosphorus, potassium, nitrogen, manganese, magnesium, etc.
Hibiscus transplant In the spring it is better to feed fertilizers with a high nitrogen content, in the summer - potassium and phosphorus. Complex special fertilizers for indoor plants "Ideal", "Rainbow" are perfect.
Young hibiscus are transplanted annually into larger pots. This is usually done in late April or early May. Transplant young hibiscus until the diameter of the pot reaches about 30 centimeters.
Mature plants are transferred to large pots every three to four years. If the acid composition of the soil is satisfactory, and there are no pests in it, then you can leave the flower in the same pot, simply replacing the top layer of the soil (about 5 centimeters) with a new nutrient.
In spring, you can trim the hibiscus growth by one third of its length to rejuvenate old bushes and form new branchy bushes. Annual pruning stimulates flowering.
Watering and spraying hibiscus
Water for irrigation needs rain or river water with low hardness. Watering the plant requires moderate, depending on the drying of the topsoil. If it's hot outside, watering can be done daily. The leaves must be washed from dust and thereby prevent the appearance of a spider mite. If the color begins to fall off en masse, there is not enough moisture. Chlorosis warns of watering with water with chlorine or iron. There is no violation if a beautiful flower falls off in a day. Another should bloom to replace it. A signal of danger is the massive fall of flowers and unopened buds. And most often the cause of the disease of hibiscus garden is improper watering.
Preparation for wintering is a crucial stage
Garden tree hibiscus sheds its leaves for the winter. In the middle lane, it grows no more than two meters. Hibiscus blooms from July until the first frost. The varieties that do not freeze out during the mild southern winter are considered frost-resistant. In the middle lane, shelter for tropical plants is necessary. For cultivation, varieties with simple non-double flowers should be used here.
In winter, the plant is watered abundantly, after the top layer has dried, it is spud high, but sand is added to the ground by a third. When stable frosty weather is established, the plant is covered with shavings, sawdust, dry foliage - a loose bedding about 15 cm high.
The branches, as far as possible, bend to the ground, are covered with dense non-woven material in several rows. A frame is built on top, on which insulating materials and coniferous spruce branches are subsequently thrown. The photo shows how the garden hibiscus hibernates in the garden.
In temperate latitudes, tree-like hibiscus can winter only with warmed roots, but it is necessary to prepare a frame for rescue in extreme conditions. In areas with a continental climate, garden hibiscus is guaranteed to be kept in cellars by digging out a plant with a large clod of earth.
Herbaceous hibiscus will overwinter if it is insulated after the ground part has died.
Graft
For vaccinations to be successful, you should consider:
- use a young Chinese rose plant for grafting cuttings;
- inoculated into the crown of the plant;
- one bush should not contain more than 5 grafts;
- it is recommended to vaccinate in the first summer months.
The grafted plants must be carefully looked after, provided with a well-lit place and ensured regular feeding.
In winter, grafted hibiscus requires additional lighting (about 6 hours per day) so that the vaccinations do not die off.
The use of grafts allows you to get several varieties on one plant.
Reproduction of hibiscus
Hibiscus is propagated by seeds, cuttings.
Hibiscus seeds are sown from mid-January to mid-March. Before planting, they are soaked for 12 hours in epine. Sowed into a mixture of peat and sand. The plate is covered with glass, the temperature is maintained at 25..27 ° C. Using a mini greenhouse or underfloor heating promotes better seed germination. Spray and ventilate periodically. When the seedlings form two or three leaves, they are dived into pots of the appropriate size. Seedlings bloom and bear fruit at 3-4 years of age.
It is easy to propagate hibiscus by cuttings. They are cut in June-August from the tops of a young growth with 2-3 internodes. The sections are treated with growth stimulants.Cuttings root well after 25-30 days in indoor greenhouses with soil heated to 22..25 ° C (a mixture of peat and sand or clean sand) or in pots covered with a glass jar, or in water. After the roots appear, they are planted in 7-10-centimeter pots with a soil mixture of humus (2 parts), leaf and turf soil and sand (1 part each), watered with warm water. It is good to add horn shavings and bone meal to the mixture.
For the correct formation of the hibiscus bush, pinch the smaller shoots. Young plants grow very quickly, so they may need to transplant into a larger pot within a few months after rooting. In the future, they need to be transplanted annually into fresh fertile soil. The transplant is carried out in early spring before flowering. Before this, it is useful to prune the plant, this stimulates abundant branching and flowering. The branches are cut two thirds or half of their length. With good lighting and abundant watering, flowering plants can be obtained in 1 year.
Features of transplanting indoor hibiscus
Transplanting a Chinese rose is not much different from traditional methods, although it has a number of features that are characteristic only of this species.
The method and technique of transplantation depends on factors such as:
- the age of the specimen;
- the state of the root system.
There is also a division into:
- emergency transplant, which can be carried out at any time of the year;
- regular transshipment, carried out in early March, before the start of the active growth phase.
An emergency transplant is carried out:
- after acquiring a new plant;
- hibiscus got sick, stopped growing.
The acquisition of a new plant is associated with the hassle of correctly transporting (in winter), adapting at home, and transplanting.
Transplanting the purchased hibiscus is the key to successful cultivation. The specificity of industrial cultivation of flora is to increase the demonstration qualities of plants. The purpose of the industrial substrate is to transport the plant.
A mixture of peat and vermiculite is used as a soil, which is not able to provide the root system with normal nutrition. Therefore, they use special formulations to stimulate growth, maintain flowering. Watering with plain water leads to chronic starvation and inevitable death of the specimen.
The transport substrate is not only useless, but also dangerous, as it contains a huge amount of undigested chemical compounds.
Hibiscus disease may require an emergency transplant, especially if its root system has been attacked by pests. In this case, the roots are freed from the old soil, trying to preserve the healthy part of the root system as much as possible. Well-developed roots are white.
An emergency transplant has its own characteristics:
- The roots are freed from the soil with a wooden stick.
- Old roots that are dark brown or greenish are not removed.
- The root system is placed in a pot close to the drainage layer to protect it from high soil moisture. The drainage layer should occupy at least one third of the pot's volume.
- Bottom watering is preferred until the plant fully adapts after transplanting.
Newly acquired hibiscus plants are not pruned before transplanting to avoid increasing stress levels.
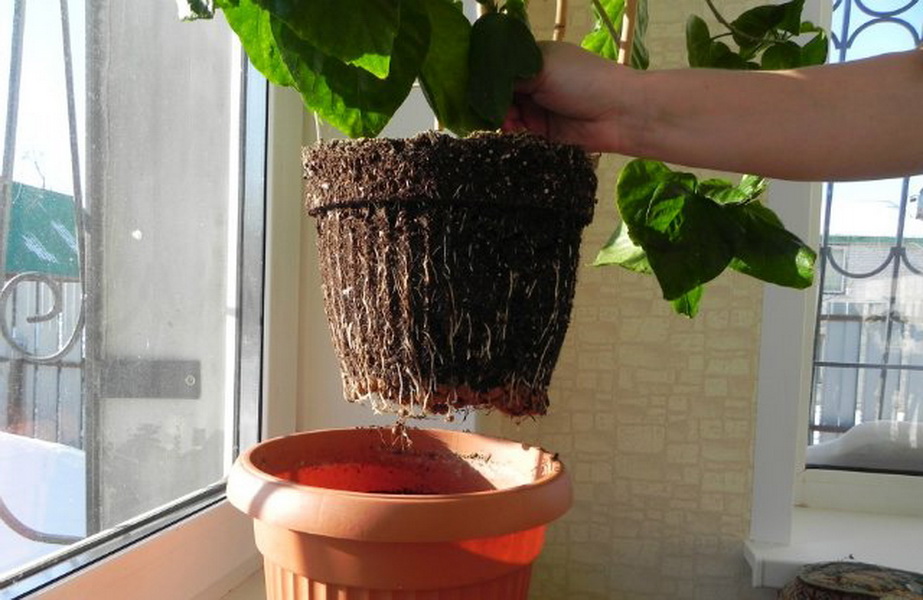
Regular hibiscus transplants are carried out exclusively by the transshipment method in order to maximally protect the root system from mechanical damage. The essence of the transshipment is that the plant is removed from the flowerpot along with an earthen lump. The earth lump is not destroyed, visually inspecting the condition of the roots and the degree of development of the substrate. The soil, entwined with roots, is not disturbed. Only the substrate that has not been mastered by the root system is removed. This is usually the top layer.
A couple of days before the upcoming event, a special preparation of the plant is carried out:
- The substrate is watered abundantly to facilitate the extraction of the earthen clod from the old flowerpot.
- The aerial part is cut in a decisive way, shortening the shoots by one third, or even half the length.
The necessary materials are also prepared:
- A flowerpot with large drainage holes, the diameter of which is two centimeters larger.
- Broken brick, expanded clay, small pebbles, pieces of foam, broken shards for the organization of a high-quality drainage layer.
- Industrial substrate or homemade earthy mix.
- A wooden stick, spatula, gloves, plastic or old newspaper to protect the desktop.
Experienced flower growers prefer to harvest earthen mixtures on their own.
Hibiscus develops well in a mixture of equal parts:
- leafy land;
- turf land;
- crushed peat.
It is recommended to add a small amount of river sand and vermiculite to improve aeration and moisture permeability of the soil. The drainage layer should occupy at least a quarter of the flowerpot, since hibiscus reacts negatively to overflow and waterlogging of the soil.
It is known that the soil for the Chinese rose must be heavy enough so that the root system can hold a large crown. It does not hurt to establish a support for the first time, until the roots get stronger. The support is removed when the substrate is compacted to the required degree and the plant becomes stable.
Reproduction
We will learn how to propagate hibiscus at home. The most effective method for propagating hibiscus at home is cuttings. The cuttings are rooted in the nutrient soil under polyethylene at a temperature of 20-25 degrees. Reproduction by seeds is sometimes used.
You can read more about all methods of plant propagation here.
Hibiscus propagates indoors by seed and cuttings.
The disadvantage of seed propagation of indoor hibiscus is that young specimens may not retain the varietal characteristics of the parent plant. However, in a sense, it is even interesting - a wide field for experiments opens up!
Let's take a closer look at growing hibiscus from seeds at home and how to care for sprouts.
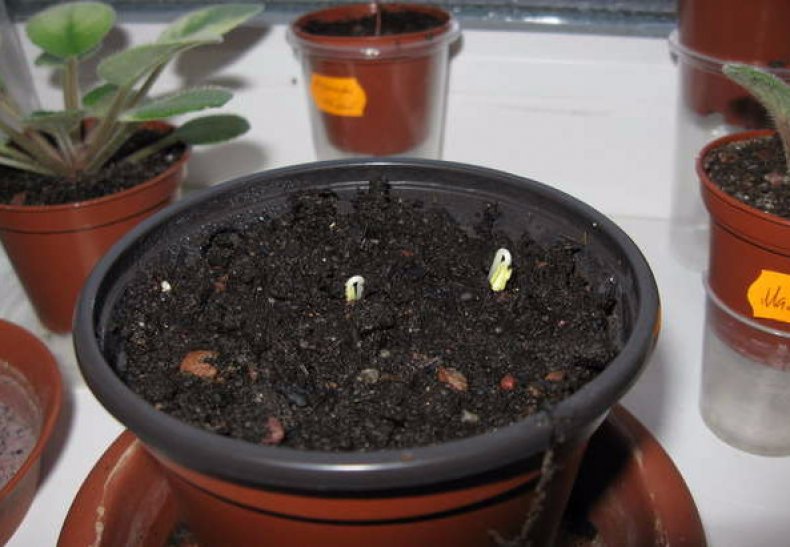
The most optimal time for sowing seeds is late winter - early spring (mid-January to mid-March). Before sowing, the seed should be soaked for 12 hours in a growth stimulant solution, for example, Epine or Zirkone. Then the seeds are sown in boxes or bowls filled with a mixture of peat and sand in equal parts. Seeding depth - no more than 3-5 mm.
The container is covered with glass and polyethylene and placed in a warm (25-27 degrees) place. For better seed germination, it is recommended to use the bottom heating. The "greenhouse" should be ventilated daily, and the soil should be moistened as necessary with a spray bottle.
When the seedlings have 2-3 leaves, the film or glass can be removed. A week after acclimatization, they can be dived into individual pots. To make the stem even, the pot should be rotated around the axis from time to time.
Hibiscus grown from seeds begin to bloom at 3-4 years of age.
Consider the propagation of hibiscus by cuttings at home.
The most suitable period for cutting hibiscus at home is late February - early March or late August. It is best to use semi-lignified cuttings. This is due to the fact that soft green shoots have a very high probability of decay, and very lignified ones will take root for a long time.
A stalk for propagation should have 2-3 internodes, it is desirable to shorten large leaves by half. It is recommended to treat the sections with a root stimulator, for example, Kornevin. There are two ways to root cuttings - in water or in a substrate.
In the second case, small greenhouses or individual pots are used, filled with sand or a mixture of peat and sand in equal parts.It is recommended to warm up the soil to 22-25 degrees.
Both when rooting in water and in soil, it is recommended to cover the cuttings with polyethylene or a glass jar. This "greenhouse" will speed up the rooting process, which usually lasts from two weeks to a month.
When the cuttings take root (and this can be determined by the appearance of new leaves), they can be planted in pots with a diameter of 7-10 cm in a permanent place. The earthen mixture consists of sand, leaf and sod land (1 part each) and 2 parts of humus. It is good to add some bone meal as well.
As a rule, hibiscus grown from cuttings bloom 3-6 months after rooting.
Photo selection of flowers and even hibiscus trees
Growing and caring for hibiscus can be carried out both in indoor and in garden conditions, so we invite you to enjoy the contemplation of beautiful and exquisite hibiscus flowers, from indoor plants in pots to full-fledged trees in the garden.
In summer, the hibiscus is watered abundantly as the upper earth layer dries up; sprayed regularly with water. During the rest period, watering is reduced: after the substrate dries up - on the third, fourth day; spraying is occasionally carried out, since the air is overdried by heating devices.
Optimal soil composition for planting and cultivation
Hibiscus is planted in a nutrient substrate from a mixture of humus, turf, peat soil and sand, in equal proportions, with the addition of small pieces of charcoal, horn shavings and bone meal; it is necessary to provide a complete, without stagnant water, drainage of the earthen coma.
The plant is fed, from March to September, with mineral and organic fertilizers, alternating once a week. In the rest of the year, a universal fertilizer is sufficient, once a month.
Reproduction and transplantation

Hibiscus transplant
It is not difficult to buy seeds and grow a full-fledged hibiscus from them, seeds are sown from mid-January to March. Before sowing, it is advisable to soak the seeds in a growth stimulator for 12 hours. They are sown in a mixture of peat and sand, under glass.
Ventilate and spray regularly. After the appearance of the third leaf, a pick is made into the corresponding pots. When propagated by green and semi-lignified cuttings - shoots with 2 - 3 internodes, February, March and August are most suitable.
For better rooting, the shoot can be soaked in water or a special solution of "heteroauxin" for 16 hours. Cuttings are well accepted in a mixture of sand and peat; rooting in water and the use of mini - greenhouses is possible.
When hibiscus is propagated by seeds, flowering will begin at 3-4 years, and when cuttings - after 1 year.
As a rapidly and vigorously growing plant, young hibiscus needs to be transplanted into a larger pot annually in spring.
The hibiscus is pruned before transplanting. Long branches are shortened by 2/3, short ones by 1/3. The plant tolerates pruning calmly.
It is advisable to reload adult hibiscus once every 3-4 years, but it is necessary to replace the top layer of the earth with fresh one every spring.
Diseases of hibiscus.

Bronze of leaves
Leaf bronzing is a virus that makes leaves tough, wrinkled, covered with rusty spots and tears. It is necessary to fight the disease by removing the affected leaves and special traps from carriers - thrips.
Ring spot is a virus that appears on leaves in the form of yellow ring spots and makes the plant unsuitable for propagation by cuttings. Extensive infestation can kill the flower.
Pests.
Hibiscus is affected by:
- shield;
- whitefly;
- spider mite;
- aphids;
- felted.
These pests cause dropping of buds, curling of leaves, significantly spoil the appearance and well-being of the entire plant.
Dry air and insufficient watering can provoke their appearance. The appropriate preparations sold in specialized stores will help get rid of pests.
Processing should be carried out in the morning or evening, after abundant watering. Hibiscus is quite tolerant to strong gas pollution and poor urban ecology.
Reproduction of hibiscus
The Chinese rose can be propagated in three ways:
- seeds;
- cuttings;
- vaccination.
To propagate this domestic crop with seeds, they are sown between January and March. First, they should be poured into Epin's solution for 8 hours. After that, river sand and peat soil are mixed. Seeds are sown into the resulting substrate, watered, then covered with a bag. Next, the seedlings must be placed in a warm room, where the air temperature is about 25 ° C. Every day, the room should be ventilated by lifting the film and making sure that the soil in the container does not dry out. When 2-3 leaves appear, the culture should be transplanted into a pot in a permanent place and placed on a windowsill.
To propagate hibiscus by cuttings, in the summer you should cut off the upper part on young shoots
In this case, it is worth paying attention to the fact that two or three leaves should be present on the cuttings. They are placed in water with a special growth stimulant
After about a month, the roots should appear at the cutting. Then they are planted in a container ten centimeters high, and the substrate for this is made from turf, humus, sand and leafy earth.
The Chinese rose can also be propagated by grafting. This plant does not have a dormant period, so it is grafted at any time of the year. As a rule, cleft grafting is carried out. To do this, prepare a stalk with rhizomes (stock). It should be about 3-5 months old. After that, you should find a cutting of the required variety (graft). He should have 1-2 leaves
Please note that these cuttings must be equal in thickness
First, the knife and hands should be disinfected with alcohol. Vaccination should be carried out as soon as possible so that the cut sites do not dry out. At the rootstock, the upper part is cut off, the top of the base is cut into a split about one centimeter deep. The top of the required variety is cut off with 1-2 leaves. An incision should also be made at the bottom. You need to insert the scion into the stock and wrap it tightly with tape. After that, the twigs are covered with polyethylene and placed under the lamp.
The bag must be removed every day to ventilate the culture. The first two days, the leaf plates will look sluggish, but after 5 days they will become elastic again. If this does not happen, then the vaccination should be repeated. After one month, the plant is exposed on the windowsill. First, the polyethylene is removed for a while, after which the time increases, and then the bag is removed. The ribbon is removed after six months, and the cuts are lubricated with garden varnish.
Types and varieties of hibiscus for growing at home
General information about the plant:
- in nature, the height of certain tree species reaches 10 m or more;
- genus from the Malvov family;
- there are shrubs, trees and herbaceous plants, annuals and perennials;
- in nature, hibiscus grows in the tropics and subtropics, in Europe and America;
- large leaves, large flowers, lush crown, bright greens, shades of petals - from white to deep red;
- a popular greenhouse and indoor culture is the Chinese rose. Photos help to understand why, when looking for an ornamental plant for decorating offices, it is Hibiscus rosa-sinensis that is chosen in large, bright red, with a scarlet tint, flowers, simple or double;
- a tree with a central trunk grows up to 2-3 m, sometimes taller, requires pruning and crown formation;
- the homeland of indoor hibiscus (Hibiscus rosa-sinensis) is the Malay archipelago;
- breeders have bred many interesting varieties of the Chinese rose with a varied shade of petals.
There are many types of Hibiscus in nature:
- Syrian tree hibiscus.
- Triple.
- Volatile.
- Chinese.
- Swamp.
- Sudanese.
- Cosmatogenic.
- Triple.
- Terry.
Some species change the color of the petals at different flowering periods. Previously, the Chinese rose had only bright red petals, but in recent years hybrid varieties with a different color of the buds have been bred: white, yellow, combined, with a bright center.
Landing in open ground
For planting seedlings, you need to find a permanent place, because hibiscus can grow for two decades. The place should be well lit. It is desirable that there are no drafts and wind in this area. The soil must be fertile and permeable. By the way, hibiscus can be grown next to roses, with which they get along well.
The size of the seedling pit depends on its root system. Deepening is made 2 times more earthy coma with roots. The bottom of the pit is treated with a thick drainage layer of broken bricks, a ten-centimeter layer of sand, a compost layer of 15 cm and a second layer of sand. For dusting, use soil mixed with sand and peat. The seedling is lowered into the recess so that the root collar is partially underground. The pit is covered with prepared soil.
Then hilling is carried out, with the help of which a notch is formed with the plant at the bottom. The plant is watered abundantly and wait for the soil to dry completely, after which the excavation is covered with soil and leveled with the surface of the site.
If hibiscus is planted in the autumn, the land around the plant needs mulching and mandatory tying with spruce branches.