Philodendron diseases and pests
The most common disease of the philodendron vine is stem rot. There is a nuisance from overly abundant watering, which is accompanied by flabbiness and softening of tissues. If the problem is detected early, it is possible to salvage the remnants through re-root. To do this, the stem should be cut 3 cm higher than the place of rot lesion and placed in water or soil to root. It is better to hold the cut site in a weak manganese solution.
Typical pests for the philodendron are the cobweb mite, thrips, aphids, and the isoptera.
Putinnik sucks the juices of the plant, after which ugly yellowish spots appear on the surface. On the back of the leaf, there is a lot of whitish dandruff, which is the integument of the tick. An increase in humidity in the room can be called a preventive measure; in serious cases, only special acaricidal substances will help.
Aphids are visible on branches and stems at once. Symptoms are an altered tip, foliage folding, a sticky coating with a sooty fungus. Soap solutions recommended by many rarely help. It is better to use Intavir immediately.
Thrips are noticeable by gray spots on the leaves, and scabbards by brown growths, which is a pest carapace. Washing the foliage and branches with a soapy substance will help from the last two pests, after which the soil needs to be treated with Aktara - an insecticide.
A defenseless plant cannot in any way be to blame for human problems, you just need to take it for granted and not blame the flower for celibacy. And then make beauty at home with the help of the climbing philodendron, and take care of the flower with love and joy. And then personal happiness will catch up with a spark of kindness and care.
- Hydrangea diseases: their treatment, photos, pests and measures to combat them
- Elderberry: photo and description of the bush
- Ito hybrids - the most modern types of peonies
- How does the reproduction of peonies
- When to transplant astilbe
- Late planting of peonies in autumn
- The main methods of selection, preparation and storage of grape cuttings cut in the fall until spring
- Autumn feeding of fruit trees and shrubs
Reproduction
This flower can be easily and simply propagated by vegetative methods: stem pieces, cuttings, apical shoots, air layers. Sometimes seed propagation is used, but this method is laborious and time-consuming, it is usually used in greenhouses and greenhouses.
Cuttings
Cuttings begin in the spring, when the plant begins to grow actively. Philodendron breeding stages:
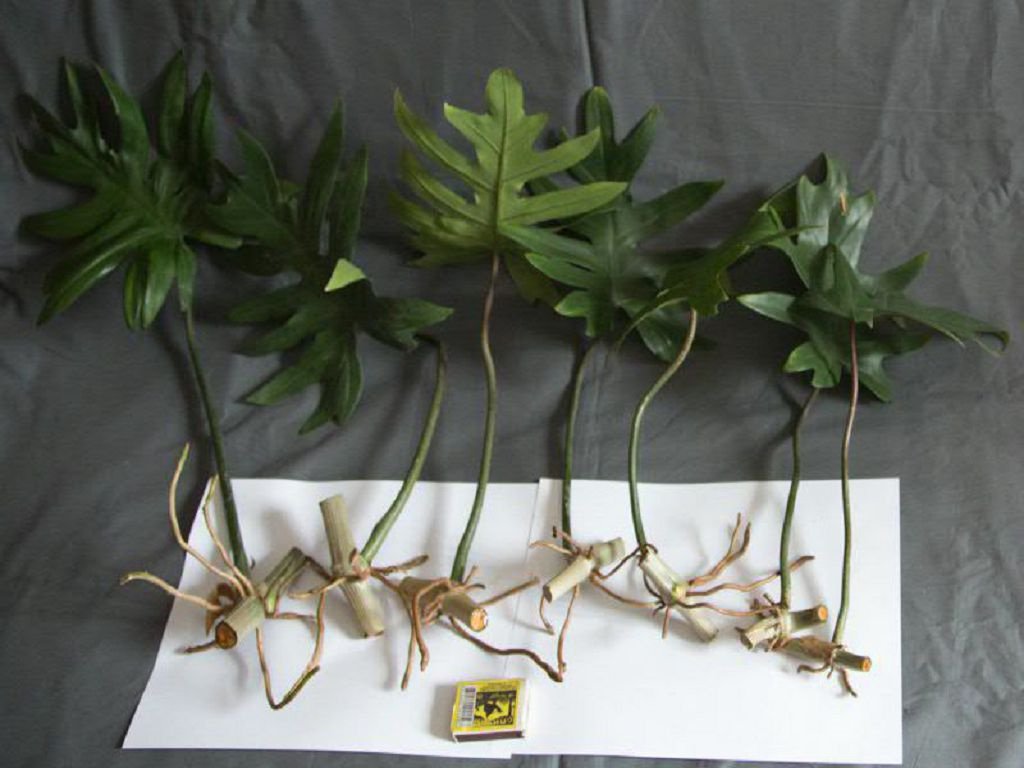
- Selected cuttings are prepared: the tops or side shoots with growth points are cut off, for large vines, the stem is cut into pieces with two internodes.
- The resulting cuttings are soaked in Epin's solution (1 ml per 2 l of water) overnight to stimulate growth and root formation.
- Small pots are filled with a mixture of sand, perlite and peat in a 1: 1 ratio.
- Stem cuttings are placed horizontally in pots, buds up. Other cuttings are planted vertically. Lightly sprinkle them with soil 1-1.5 cm.
- The pots are covered with a bag and left in a warm (22-28 degrees) and bright room. Make sure that the substrate is constantly wet, if necessary, water it, and ventilate the cuttings.
- After 3-4 weeks, roots are formed, the cuttings start to grow. After that, they are seated in permanent pots.
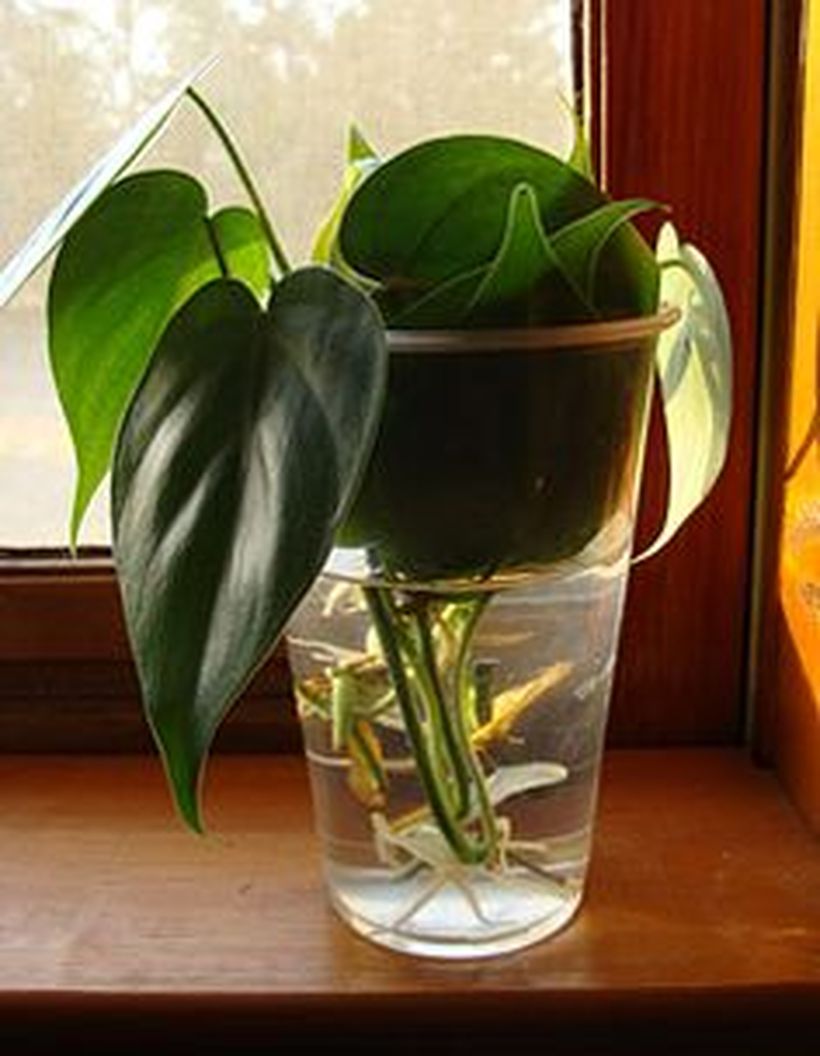
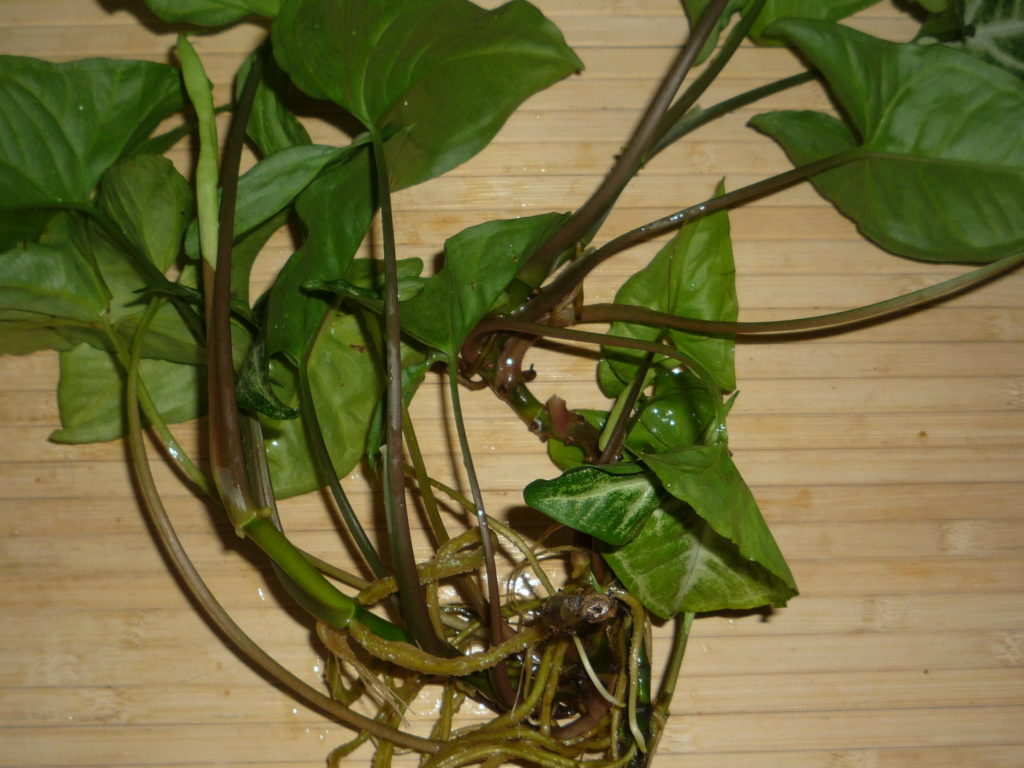
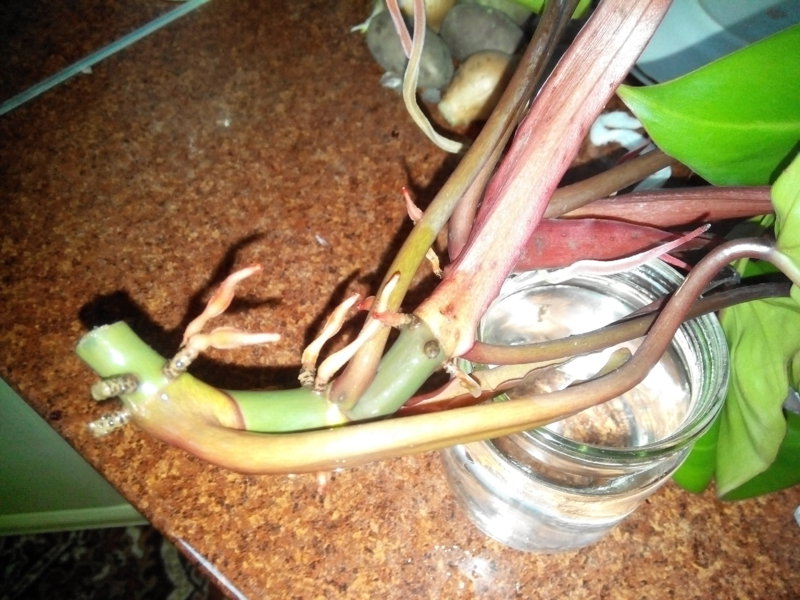 It looks like a rooted stalk of a philodendron
It looks like a rooted stalk of a philodendron
Air layering
It is very easy to obtain air layers in herbaceous vines. The shoot is laid on the ground and pinned in several places in the area of internodes.The soil in containers with layering is kept moist. After 1–2 months, full-fledged roots appear, after which the stem is cut into pieces between the rooted segments. Young plants are planted in separate pots.
How to root the top of a giant creeper
It is somewhat more difficult to propagate large ligneous vines in this way, but it is also possible. This is done like this:
- In the spring, two shallow annular cuts are made on the lignified shoot at a distance of 1.5–3 cm from each other. Remove the bark ring between the incisions.
- A piece of sphagnum moss is moistened with a growth stimulant solution (for example, Epin at the rate of 1 ampoule per 1.5–2 liters of water). The moss is wrapped around the bare trunk, covered with foil and fixed at both ends with rubber bands or electrical tape.
- Periodically moss the moss with clean water, making sure that it does not dry out. After a few months, roots will begin to form under it.
- In 1-2 months after the appearance of the first roots, the moss is removed. The trunk is cut 1–2 cm below the annular notch. The resulting young specimen is planted in its own pot.
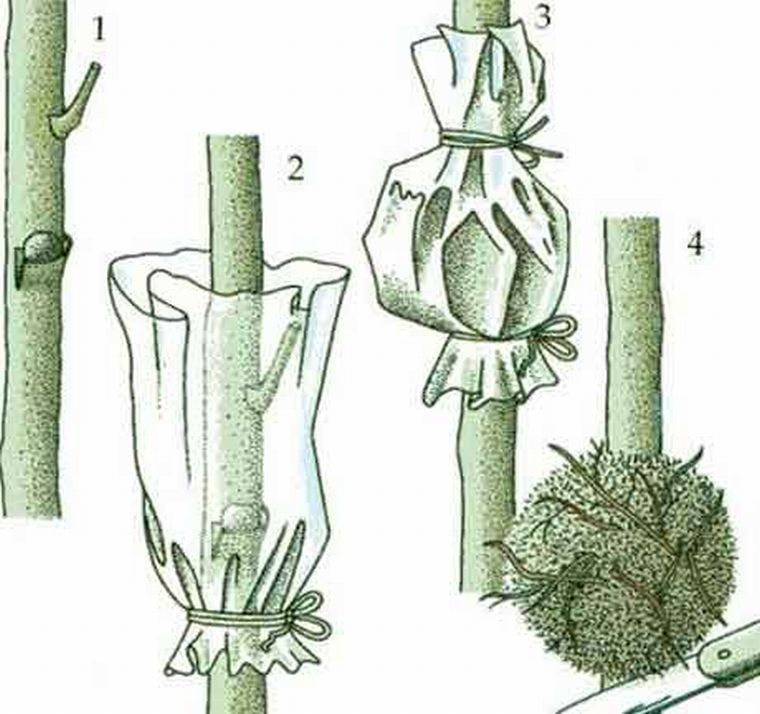 This is how woody lianas propagate
This is how woody lianas propagate
Care features
Easy to grow plant. For full growth, they adhere to the following rules of care and maintenance.
Lighting. Some species are shade-tolerant. It grows more actively in bright diffused light. Direct sun action is undesirable. In the rooms on the east side, they are placed near the window, on the south, they are pushed into the interior of the room. Variegated varieties are more demanding on lighting.
Temperature. The optimum range for all varieties is 22-30 ° C. Many people cannot stand a cold snap below 18 ° C. The soil temperature should be the same as the air temperature. They do not keep them on cold windowsills. In winter, they are fenced off from cold glass with heat-insulating material.
Watering. Moisture-loving plant. In summer, watering is plentiful, as the top layer of the soil dries out. The substrate must not be allowed to dry completely. In winter, watering is limited - once a week is enough.
Humidity. The humidity requirements are high. It is recommended to regularly spray the plants and the air around them, place the pots in trays with wet expanded clay. The use of special humidifiers is encouraged. The increased humidity is combined with regular ventilation.
The soil. Use light, well-drained soil mixes. A mixture of garden soil with peat, pine bark and perlite is suitable. It is allowed to use ready-made soil mixture for Saintpaulias. Useful additives are charcoal and sphagnum.
Transfer. Annual for young plants in active growth phase. Adults - less often, as the root system grows. The germination of roots through the drainage holes is a signal for transplantation. Additionally, the transplant is carried out with salinization and acidification of the soil.
Top dressing. Fertilizers are applied weekly in low concentration - 2-3 times lower than the dosage specified in the instructions. Responds gratefully to the introduction of organic matter. In winter, feeding is not stopped, but their frequency is reduced to 1 time per month. For variegated forms, preparations with a high nitrogen content are not used. Overfeeding young plants is not recommended.
Hygiene. The large leaves of the philodendron quickly become covered with dust. Wipe them regularly
They act carefully - despite the large size, the leaves are very fragile! Young, not very overgrown specimens are useful to periodically bathe in the shower.
Interesting! Philodendrons are characterized by guttation. The complex word hides a phenomenon familiar to many - the leaves "cry". Guttation is associated with high air humidity, often intensifying before rain.
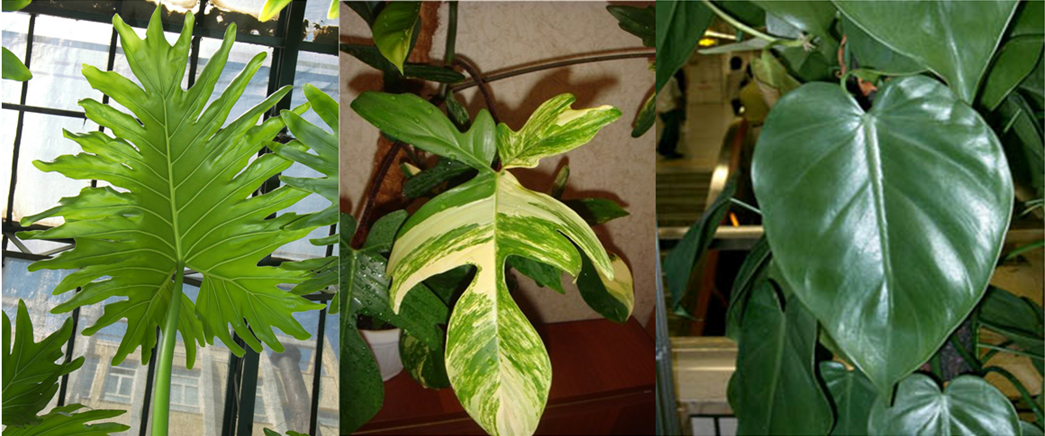
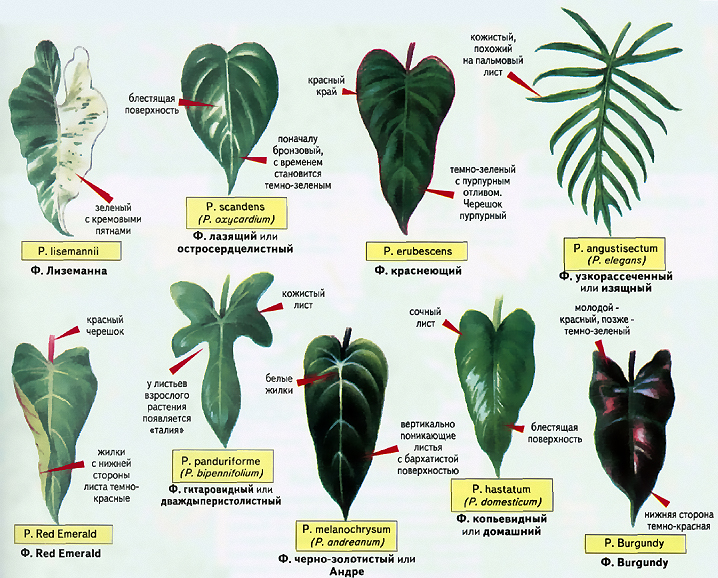
Varieties
There are about 500 varieties of philodendrons in the wild, but not all of them are grown indoors.They have their own characteristics and differences not only in external characteristics, but also in the features of care, requirements for lighting, soil.
Atom
This variety of Philodendron is a compact plant, perfect for indoor cultivation. The stem is straight, the maximum height reaches 30 cm. The leaves are five-lobed, with characteristic wavy edges and a bright green color.
Warty
On the surface of the leaves of this variety, there is a characteristic bristle. Their shape is heart-shaped, their color is dark, and their size is rather large.
Elegant
This philodendron reaches a maximum height of 0.7 m and has very large leaves. Their shape is thin and long. In indoor conditions, this species does not bloom, but has sufficient decorative qualities to decorate rooms.
Cobra
A distinctive feature of this variety is the whole leaves with a pointed tip. When growing the Philodendron Cobra, additional supports are required. He does not tolerate direct sunlight, which should also be taken into account by the florist.
Xanadu
The Xandu variety has feathery leaves, the length of which reaches 0.4 m. The trunk grows up to 1.5 m in indoor conditions. In the wild, its height reaches 4 m.

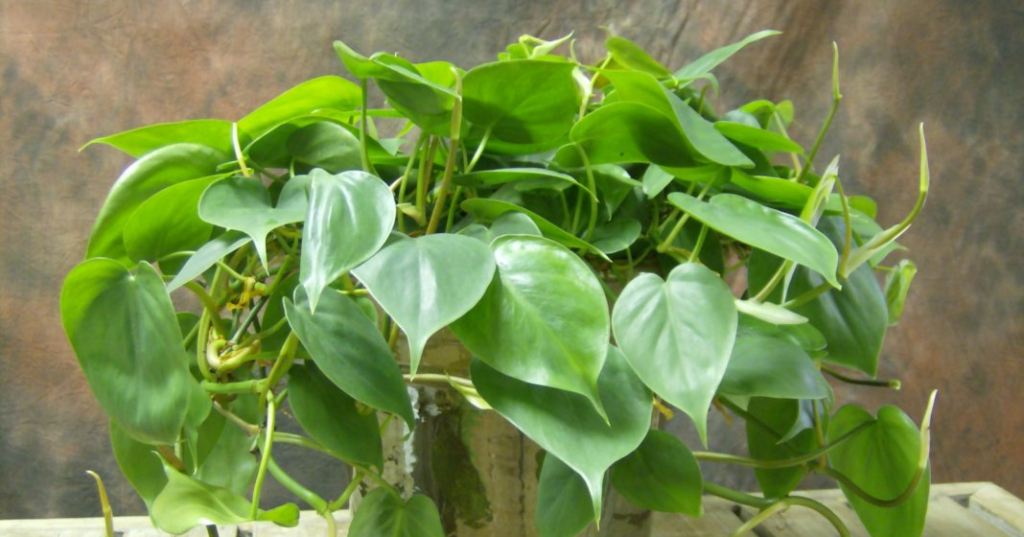
Climbing
Philodendron Climbing has heart-shaped whole leaves of a dark green color. The height of an adult bush reaches 2 m. Excellent for growing in hanging pots.
Jellyfish
This variety differs from its counterparts in its fast growth and amber color of the leaves. The stem is of an unusual burgundy color. Jellyfish is a subspecies of the blushing philodendron, from which an unusual color scheme is inherited.
Sello
The variety is double-feathery. The height of an adult plant in indoor conditions reaches 3 m, and the length of the leaf is up to 1 m. The leaves are triangular, pinnate, dissected.
Hastate
This philodendron is a liana, the leaves of which are spear-shaped and can be painted in the following colors:
- green;
- bluish green;
- silvery green.
Martius
Philodendron Martius is a small bush, the maximum height of which reaches 0.3 m. The leaves are heart-shaped, light green in color. In the wild, the plant forms flowers and fruits.
Ilseman
A decorative liana with a stem length of up to 1.5 m. It needs a support, which would be covered with moss. It is appreciated for its high decorative qualities, provided by the unusual color of the leaves. Their color is uneven, there are white or grayish-white stripes, strokes.
Decorated
The variety of Philodendron Decorated is a decorative perennial vine with dark green leaves and characteristic white veins. The leaf plate is ovoid.

Blushing
This philodendron owes its name to the large leaves that turn red at the base. Their length sometimes reaches 30 cm, and the width is 20 cm. The trunk of the plant is woody. This variety is most popular with flower growers, because it does not require much attention, it is unpretentious in care. The flower tolerates a lack of sunlight and a lack of moisture.
Lobular
The two-meter liana of the Philodendron Lobate has increased flexibility and impressive thickness. When growing at home, additional supports must be installed.
Guitar-shaped
This variety also requires the installation of additional supports if it is grown at home. It owes its name to the unusual shape of the leaves. Initially, they are heart-shaped, but as they grow, they stretch out and become like a guitar. The leaf plate is divided into 3 blades. The stems are flexible enough.
How to create a microclimate at home for a flower - table
| Factor | Optimal conditions |
| Location | Move the plant out of drafts and direct sunlight. The sill of a south-facing window will not work. |
| Lighting | Philodendron prefers diffused light. Varieties with green leaves can exist even in partial shade, but this is unacceptable for variegated plants. In the shade, the plant stretches out, the leaves shrink and turn pale. Climbing and blushing philodendrons tolerate the absence of light best. |
| Temperature | The plant does not tolerate heat well. The optimum temperature in summer is no higher than 25 ºС. The philodendron will not survive "cold weather" below 12-15 ºС. The flower reacts extremely negatively to sudden changes in temperature. |
| Air humidity | The moisture content of the plant needs to be created high, at the level of 85-90%. In the heat, spray the philodendron additionally several times a day, wipe the leaves with a damp soft cloth. Every 25-40 days it is useful to arrange a warm shower for him. Also, the flower needs additional moisture in winter - radiators dry the air greatly. Purchase a special humidifier. |
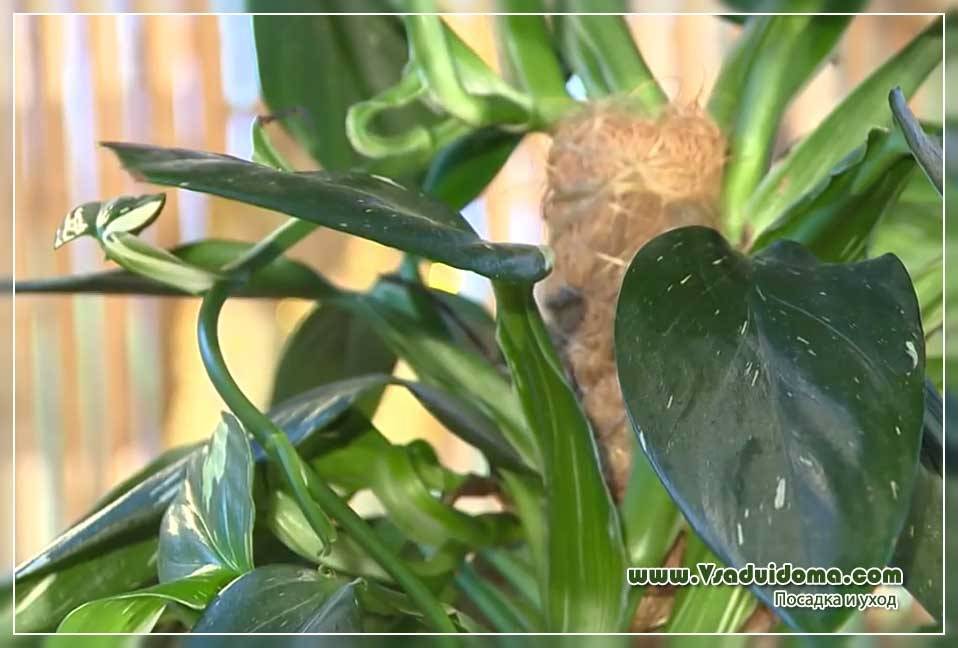
| Support presence | Young philodendrons can do without props, but adults are in dire need of it. This is provided by nature. Give preference to wood structures or supports wrapped in natural coconut fiber, and best of all - hollow tubes filled with sphagnum moss. After all, metal and plastic cannot be constantly kept moist. |

Philodendron definitely needs a support - this way you will save space
Diseases and pests
A plant in a tropical climate is susceptible to various diseases and viruses. The following diseases are most common:
- bacterial infection of the leaves;
- red border.
In all cases, without treatment, the plant dies.
Fungal diseases quite often appear on vines:
- root or gray rot;
- dropsy or spotted foliage.
If the plant begins to lag behind in growth for no apparent reason, a withered color of the leaves appears and the stem begins to wither - this is a viral disease.
It is much easier to deal with pests. By the way, they often appear on vines. The most common are:
- scale insects appear in the form of brown larvae on the stem, sucking out all the juice to the base.
- thrips;
- the appearance of mites is affected by too high temperature, low humidity. Their appearance is not difficult to notice. A large yellow spot may appear on the leaf. In order to prevent it, it is necessary to conduct weekly water irrigation and wipe the leaves from dust. The ideal solution would be to purchase a humidifier.

Humidifier
Growing a philodendron at home (with video)
Philodendrons need protection from direct sunlight. This plant should be placed in a well-lit area. On especially sunny summer days, the plant needs to be shaded. The air temperature in the room where the plant is located should be very high - not lower than 20-25 ° C. In winter, the room temperature should not fall below 15 ° C.
When caring for flowers, remember that philodendrons do not like drafts.


Philodendron loves uniformly moist soil and does not tolerate stagnant water. The plant needs high humidity all year round. This can be achieved by placing a container of water near the pot, and spray it once every two weeks.
When caring for philodendrons at home in the spring-summer period, it is necessary to apply complex mineral fertilizers once every two weeks. During the rest period, fertilize once a month.
During the period of increased growth and development (March - October), plants are fertilized with flower fertilizers for decorative leafy plants.
Overgrown shoots should be pruned every spring.
Reproduction is carried out by apical or stem cuttings or shoots, often appearing in the lower part of the stems, at a temperature of 24-26 ° C.
The main pests are thrips, scale insects and spider mites. Excess moisture in the soil and watering with too cold water lead to root rot.
When growing a philodendron, the following problems are possible.
Rhizome decay. Reason: excess moisture. Make sure that the water in the sump does not stagnate.
Yellowing of the leaves. Reason: lack of moisture. You should water the plant more often and monitor the humidity in the room.
The appearance of spotting on the leaves. Reason: exposure to direct sunlight. The plant should be shaded.
It should be remembered that these plants are poisonous, their juice can irritate the mucous membranes of the eyes and nose.
In decorative floriculture, philodendrons are used mainly for vertical gardening.
Watch the video "Caring for a Philodendron" to get a better idea of how to grow this vine:
Philodendron cultivation problems
A non-capricious philodendron, if you choose suitable conditions and establish minimal care for him, grows well and pleases the owners with bright lush greenery. However, breaking the established order threatens to get into trouble.
As a rule, all problems of philodendron cultivation are associated with a violation of care and optimal conditions for growth. You can recognize trouble by changing the color, size and tone of the leaves:
- Decrease in leaf plates and their pallor, elongation of shoots, leaves signal a lack of light.
- Plants respond to excessive watering or lack of moisture by yellowing or browning the foliage, which gradually dries up and disappears.
- If the flower is regularly watered, but its greenery looks sluggish, the cause may be an excess of light or root rot. In addition, the active summer sun is the cause of real burns, on which tissues die and dry.
- Root decay, often caused by cold or draft, results in brown or black spots on the leaves.
- Being in dry air, the philodendron begins to deform the leaves, rolling them up in a boat.
In order for the plant to always be healthy and beautiful, one should not forget about top dressing, timely transplantation into correctly selected soil.
Philodendron - home care

Temperature
The optimum temperature for growing indoor philodendron is considered to be +20 - 25 degrees. In practice, it can withstand higher temperatures, but subject to more frequent spraying. In winter, the temperature of the content of the philodendron can be lower, but at least +15 degrees. The main requirement is no drafts at any time of the year! For the same reason, it is not recommended to take it out in the summer to fresh air.
Lighting
There are not many philodendrons that can grow in shaded areas. Philodendron climbing and F. blushing. That's probably all. All other types of philodendron love bright, diffused light. This is especially true of its variegated species, which lose their color from lack of light. They need to be provided with all the maximum possible light. At the same time, make sure that direct sunlight does not fall on the plant.
Watering and humidity
Philodendron does not tolerate prolonged drying out of the earth in a pot. Water it regularly and abundantly. The large leaves of the philodendron actively evaporate moisture, so the soil dries out faster than most other indoor plants. With cool winter contents, watering is reduced. Excess moisture combined with low room temperature can lead to decay of the flower roots.
Maintaining high air humidity is the main condition for caring for a philodendron. Spray it as often as possible. There are no restrictions on this. Dry air leads to the fact that the leaves of the philodendron change shape, become smaller.
Take only settled water for irrigation and spraying.

Top dressing
Regular feeding is required by the philodendron mainly during the period of active development, that is, from March to September. During this period, feed him twice a month with fertilizer for decorative - deciduous plants.It is ideal if it contains an equal content of the main nutritional components (nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus). The increased nitrogen content in the fertilizer stimulates the rapid growth of the philodendron, and if there is a desire to quickly get a large plant, then the emphasis should be on fertilizers with a high content of this element. The dormant period of the philodendron is practically not pronounced. Therefore, in winter, provided that it is kept in warm conditions, it can be fed once a month, but with a less concentrated fertilizer. Its concentration should be reduced by a quarter of the concentration recommended in the instructions.
Philodendron transplant
Until 3-4 years of age, the philodendron is considered a plant still young, requiring an annual transplant. Upon reaching adulthood, less often - once every two to three years. Particularly large species, upon reaching the maximum size, at home, you can not replant them, but only replace the top layer of the soil with a fresh one every year. The philodendron has no particular preferences for the composition of the soil. The only thing is that it should not be alkaline, but have a slightly acidic reaction. Also, the soil for the philodendron should be good for moisture and air. For some species of philodendron, orchid soil mixture is successfully used, enriching it with peat, grassy soil and perlite. But much more often they take a specialized soil mixture or prepare it themselves.
Philodendron Earth Recipe:
- Two parts of sod and leaf land;
- Part of humus (greenhouse) land;
- Half a piece of sand or perlite.
As for the transplant technique itself, a transplant with complete removal of the soil from the roots is not needed. It is enough just to transfer the flower along with a lump of earth into a slightly larger pot and pour fresh earth into it.
Reproduction of philodendron
It reproduces exactly like a monstera. This means that almost any part of the philodendron is suitable for this. But the easiest way for novice florists is to propagate a philodendron with an apical cuttings. It is possible to propagate in this way only in the warm season, because for the success of the operation, a sufficiently high temperature is required, not lower than +25 degrees (higher is possible)
The second important condition for the reproduction of a philodendron at home is high air humidity. It will be ideal if, during the rooting process, it is possible to create greenhouse conditions for the cutting by covering it with a transparent cap or a large PE bag
For rooting, you can use a light mixture of leafy soil with plenty of sand. But rooting in clean, wet sand gives good results. You can also put a philodendron stalk in a container with water and wait for the roots to appear. In general, everything is like a monster's ...
Philodendron care
Philodendron is a rather unpretentious plant. However, in order for him to feel comfortable and actively develop, a number of simple conditions must be observed.
Watering and the required air humidity
The philodendron needs regular watering. It is undesirable to allow the soil to dry out. Watering the flower infrequently can affect its appearance. In this case, the leaves of philodendrons become small and lose their attractiveness.
The air when growing philodendrons should be sufficiently humid. The flower reacts to its dryness by crushing the leaves and losing their decorative properties. Therefore, in hot summer and winter, when the heating is turned on, the philodendron should be regularly sprayed - at least once a day.
How to fertilize philodendron

Fertilizers for ornamental foliage plants are perfect for philodendron
In the summer, the plants need to be fed with ordinary store-bought fertilizers at least weekly; in the winter, monthly feeding is enough. If the vine is large, in the summer you can add humus once to the top layer of the substrate.
Philodendron is fed only after careful watering, otherwise excess salts in the soil can harm it.When choosing a fertilizer, it is recommended to purchase complex fertilizers. If you want to accelerate the growth of the flower, you should feed it with formulations with a high nitrogen content.
The plant does not tolerate excess fertilizers - its leaves rust and wither. If too much fertilizer is added, then the philodendron does not need to be fed for at least 2 months.
A plant bought in a store should start feeding in 2-4 weeks, and if you have grown it yourself, then when the first shoots appear. Plants that have been transplanted do not need to be fed for the first six months.
If the philodendron is not transplanted on time and fed irregularly, the leaves will begin to shrink, and the tips will turn yellow and dry. The plant begins to grow more slowly, underfeeding negatively affects the thickness of the trunk.
Errors in care and how to fix them - table
| Problem | Symptoms | What to do |
| Lack of nutrition | The leaves turn yellow, but there are no signs of wilting. | Feed the plant more often. |
| Excess light | The leaves turn pale and look lifeless. | Philodendron loves light, but reacts poorly to direct sunlight, so if necessary, it should be shaded a little in summer. |
| Lack of light | The leaves turn pale and become small. | Place the pot in a more illuminated place, but do not forget that the light should be diffused. |
| Dry air | Dry brown spots appear on the leaf plates, the leaves may begin to fall off. | Spray the leaves of the plant with water from a spray bottle periodically. |
| Excess moisture | Roots and stems begin to rot when the temperature drops. | Put the flower in a warm place and dry the soil. |
| High air humidity | The appearance of drops at the tips of the leaves. | It is harmless to the plant. |
Secret number 4. Add a couple of degrees to the minimum temperature
In the recommendations for growing philodendrons, you can often find the minimum allowable temperature of 13 degrees. It is better not to bring the situation to such a decrease. Limit the temperature range in winter to just 16 degrees. And then you will prevent most of the problems and difficulties that can arise in the cultivation of philodendrons.
As for the air temperature from spring to autumn, the room values for philodendrons will be comfortable (from 20 to 25 degrees). Higher rates, however, are not. In order for philodendrons to maintain a high decorative effect in the heat, you will have to make efforts to control more abundant watering and an increase in air humidity. But the main thing is to protect plants from temperature extremes. Do not place any heating devices near philodendrons, protect plants from air conditioners and even ventilation in cold weather.
Just by stabilizing the temperature and observing the minimum indicators, you guarantee yourself that the leaves on your philodendron will not shrink, and growth and development will occur evenly.
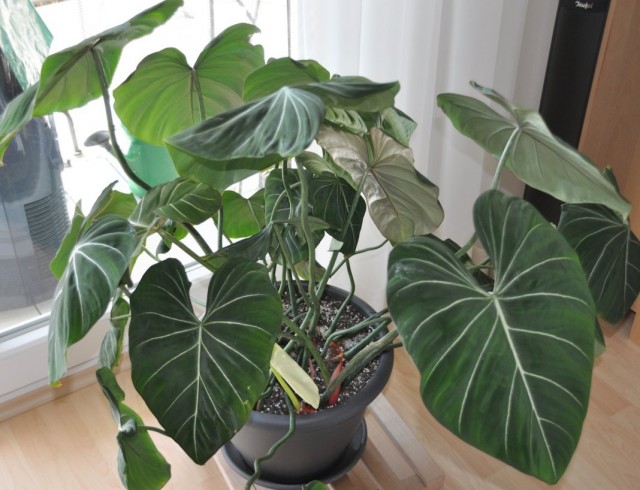 Philodendron gloriosum
Philodendron gloriosum
Diseases and pests
At home, the plant is not susceptible to pests. But with poor dust removal, a mite, mealybug or scale insect may appear.
To eliminate pests, use a soap solution, a weak mixture of potassium permanganate or chemicals. For this, "Aktara", oil emulsion, "Agravertin", "Iskra-bio" are suitable. Diseases manifest themselves only with improper care.
The video shows the signs of damage to the "Philodendron" by the shield:
"Philodendron" has over 400 different subspecies. At home, it is smaller than in the wild. Not susceptible to pests. Requires good care. Loves bright natural light, top dressing and abundant watering.