Reproduction of Japanese fatsia
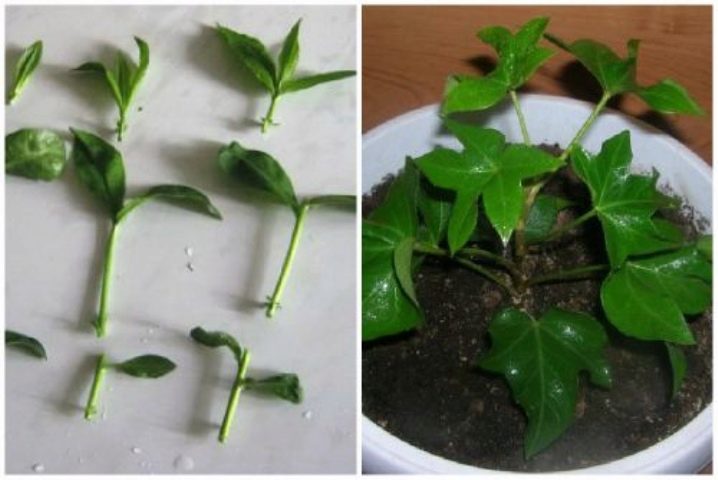
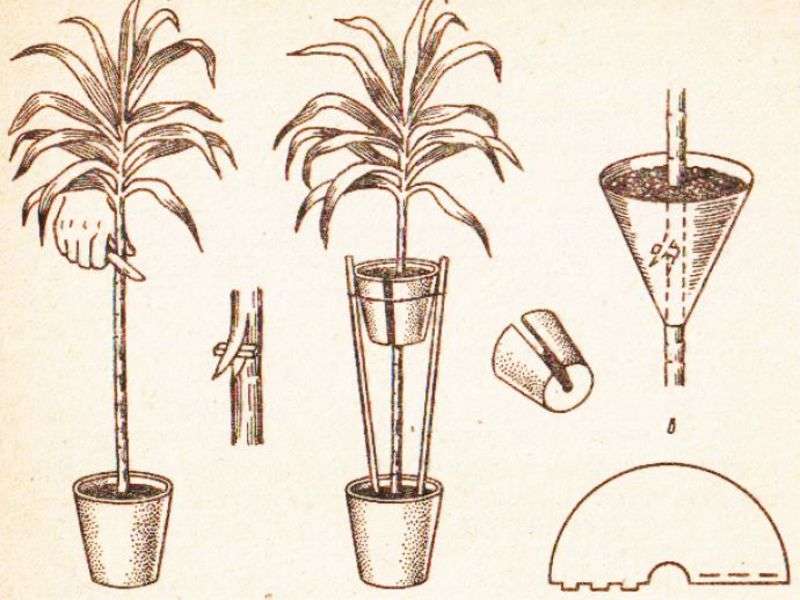
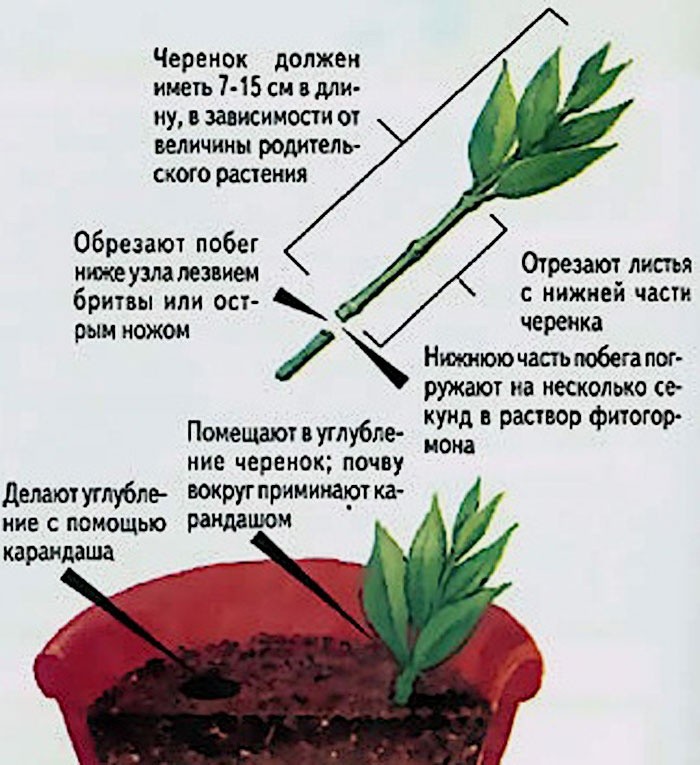
Fatsia japonica propagates by seed, cuttings and air layers. Cuttings cut in spring root well in water or wet substrate (peat, perlite, peat-sand mixture, peat tablets). The optimum rooting temperature is 22 - 26 ° C. Fatsia seeds are sown to a centimeter depth in a mixture of sand, turf and leafy soil. Sowing is desirable to keep at a temperature of 18 ° C. The hardened seedlings are planted in pots with a diameter of about 10 cm one by one. The method of layering is used for the reproduction of large adult specimens or for the rejuvenation of fatsias, the trunk of which has been exposed for some reason. To do this, in the spring, a light incision is made on the trunk, wrapped with moss dipped in a fertilizer solution, and covered with polyethylene. Moss should be moistened as it dries. Young roots will be visible through the polyethylene, which will appear in a couple of months. When these roots get stronger and develop enough, the cuttings are cut off and planted in a separate container.
If the remaining stem is cut almost to the root, and the "stump" is watered carefully, over time, a beautiful branchy bush can be obtained from the parent specimen, which will develop from the basal offspring. You can also try to get fatshedera yourself - a hybrid of fatsia and ivy
To do this, an ivy stalk is grafted onto the old trunk, which belongs to the same Araliev family. As a rule, such a grafting takes root well, and the plant acquires not only new decorative qualities, but also the vitality of an unpretentious vine. Fatskhedera tolerates heat and drought more easily, is more resistant to pests and diseases, and is less demanding on air humidity. From Japanese fatsia, it inherits the size and shape of the leaves, and from ivy - liana-shaped cascading shoots. This is a very beautiful and tolerant plant that is widely used for landscaping industrial and public premises.
Useful advice, informative articles for summer residents and gardeners. Planting, leaving, harvesting. Of course, there is a lot of information about flowers, berries, mushrooms. On the pages of the site "Useful grass.ru"
- Sanchezia: care and reproduction.
- Calathea: home care
- Aloe leaf yucca
What does Japanese fatsia look like, which family does it belong to
Japanese Fatsia belongs to the Fatsia genus. Family - Araliaceae, which includes shrub and liana-like plants. Differs in large green leaves and a significant length of the bush.

Fatsia japonica
Outwardly, the plant is very similar to a chestnut. Sometimes at home in Japan it is called so: "home chestnut", "Japanese chestnut". For this name, the plant owes its beautiful leaves. They very much resemble chestnuts, only much smaller in size.
The petioles are rather long. They have large leaves, reaching almost 30 cm in diameter. The plate itself is not entirely solid. It consists of 5 or 8 and sometimes 9 blades. It is no coincidence that fatsia from Japanese means "eight", because that is how many blades a leaf of a plant most often has. In general, the leaf blade resembles an ellipse or heart.
For reference! Fatsia is a genus of plants, within which there is only one species that can be cultivated at home.
The color characteristics are very different. There are both monochrome forms and variegated variants. Along the edges there may be notches and notches of the most bizarre and varied shapes.

Tall shrub with exquisite leaf shape
In terms of size, it is more of a shrub. But the stem is quite thin, although it reaches 1 meter (the maximum recorded is 2 meters).In the fatsia plant, the flower does not have the same attractiveness as the leaves. Inflorescences in the form of umbrellas of inconspicuous whitish or somewhat greenish flowers are usually cut off by breeders even before blooming.
If the inflorescences are left, after a certain time in their place you can find bluish-blue, even purple berries. Seeds do not always ripen in them, so there is no need and sense to leave them for the purpose of reproduction.

Inconspicuous umbrella-shaped inflorescences
Reproduction of fatsia by seeds and cuttings
It is unlikely that it will be possible to independently collect seeds from a room aralia: at home, the plant blooms extremely rarely. But you can buy them at the store. Fatsia seeds are sown in February-March. Before sowing, it is advisable to soak them for 2 days in an aqueous solution of a growth stimulator. The soil for germination should consist of equal parts of sand and peat. Drainage is poured into the bottom of the container to avoid moisture stagnation.
Instructions on how to get Fatsia seedlings:
- Spread the seeds over the surface, pour from a spray bottle and sprinkle with a layer of earth 0.5 cm thick.
- Cover the container with foil until shoots appear. Moisten the soil constantly and keep the temperature at 25 ° C.
- After germination, the container with fatsia is taken out to a lighted place, but away from direct sunlight.
- After the appearance of the third true leaf, the seedlings dive into pots with a diameter of 5-7 cm.
- After six months, transplant the seedling into a permanent pot, while trying to maintain the integrity of the earthen coma.
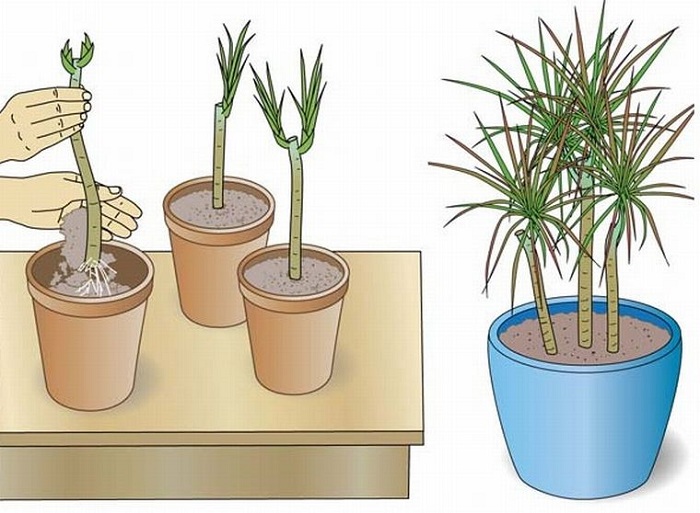
In the spring, the apical shoots cut off during the formation of the crown can be used for plant propagation. Cuttings 10–12 cm long, with 2-3 buds are suitable for rooting. The cut must be treated with a stimulant solution. Then, the cuttings are buried in a wet sandy-peat substrate, scattered in cups. Until the roots appear, keep the aralia in a warm, bright place, ventilate and moisturize regularly.
The result exceeds all expectations: in just 2-3 years, the aralia turns from a tiny seedling into a luxurious one and a half meter bush.
- a genus of the Araliev family, represented by only one species - Japanese Fatsia, or Japanese Aralia. This is a beautiful ornamental deciduous plant brought to Europe from South Korea and Japan.
Pests and diseases of room fatsia
Pests that can damage a home flower: whitefly, mealybug, thrips, aphids, scale insects, spider mites.
- When they appear, the stem cover and leaves are treated by spraying with fungicides - 3 times, we take a break for a few minutes. The best effective way is to use Actellik;
- A simple soap solution, which is sprayed several times a day, will also help.

Ailments of the southern pet:
- Sunburn (a representative of the flora is in direct sunlight): its leaves become wrinkled. Treatment: it is necessary to increase the humidity of the air, to make a shade for the shrub;
- Lack of moisture: leaves break and dry. Treatment: abundant watering and "shower" every day in the summer;
- Excess moisture: drooping and soft foliage. How to help: do not water for several days, remove the liquid from the pallet;
- Gray rot (the flower is kept in a damp, cold place): the stem decays, which takes on a brown color. Treatment: put in a more ventilated room, remove damaged parts.
Common varieties
Japanese fatsia is quite varied. There are about a dozen varieties that are grown for decorative purposes in indoor conditions.
First of all, the Fittshedera Lice variety is distinguished. The plant is remarkable in that it is an interesting hybrid of common ivy and shrub. As a result, the owner can get a five-meter liana. Its advantageous difference is that it is evergreen, the color of the leaves can be the most bizarre and interesting. The flowers are small and inconspicuous.
Fatsia of the Moseri variety (Mazeri) grows very slowly.The bush itself is undersized, but the crown of leaves is very dense and attractive. The plant is quite capricious, as it requires compliance with a constant temperature regime and humidity. It is difficult for many to maintain optimal microclimate parameters for Mazeri Fatsia.
The Samurai variety, on the other hand, is a very tall plant. It reaches 1.5 meters in height. The leaves look very attractive due to their special star-shaped shape and characteristic shine.
Fatsia variety Spider Web, with proper care in a comfortable home environment, looks very unusual. The foliage has a mysterious whitish bloom that resembles a cobweb. The crown itself is spherical, rather large. In some cases it reaches half a meter in diameter.
The variety of Fatsia Variegata is interesting for its leaves, which are located spirally relative to the stem.
Their color also attracts attention - it is rich green with delicate matte cream spots, stains. The spots are white along the edges.

Fatsia varieties Moseri
Diseases
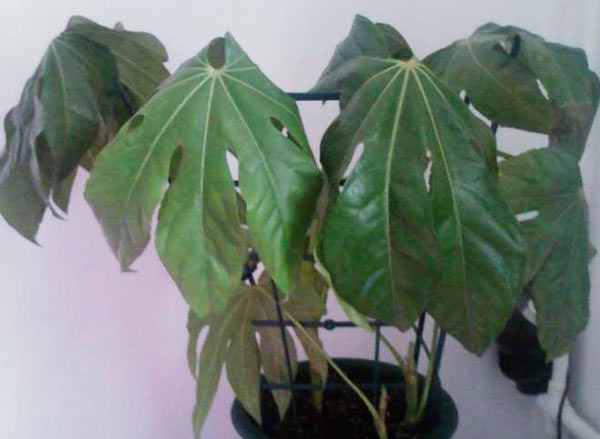

Fatsia is a flower that is quite resistant to all kinds of diseases. If you follow the rules of care, it will not give you any trouble. But, if you break them often, problems can arise:
From high humidity and excessive dampness of the substrate, root rot may appear.
The flower should be transplanted into a new substrate, having previously shaken off the old soil, having examined its roots. If you find that all the roots have softened and darkened, it is too late to treat the flower, throw it away. If most of the roots are white and firm, the plant can be cured. Rinse off any old substrate under the tap. Remove all damaged (rotten, dry and broken) roots with a sharp, clean knife. Remove wilted shoots and leaves. Treat the cut sites with potassium permanganate, then powder with crushed charcoal, and only then plant them in a new (or old disinfected) pot in a fresh substrate that is suitable in composition for decorative leafy indoor flowers. Water the soil with a fungicide solution (such as phytosporin). Place the pot in a bright, warm place, but not in the sun.
If the moisture content of the substrate is low, the tips of the leaves will dry out.
Do not wait until the earthy clod is completely dry. Water the flower in time as soon as the topsoil is a couple of fingers dry. Otherwise, not only the tips, but all the leaves will dry up and fall off.
Indoor air that is too dry can cause Fatsia leaves to become brittle and wrinkled.
The flower should be often sprayed with warm, settled water, wipe its leaves with a damp cloth or cloth. At times, you can have a cool shower in the bathroom by covering the substrate with plastic wrap or a bag. If the problem occurs during the heating season, try to set the pot aside from the radiator or cover the radiator with damp towels.
Excessive moisture in the soil will soften and turn yellow leaves.
Do not water the flower while the soil is still wet from the previous watering. Drain excess water from the sump, do not let it stagnate there. Use filtered, settled, warm water.
From hypothermia and waterlogging, the plant can also lose some of the leaves.
Maintain the ambient temperature within the normal range, 22 - 24 g. all year round, unless you hibernate in a cold room. But even there the temperature should not be lower than 16 - 18 grams.
If you often fill the soil, then a gray, sometimes brown tint may appear on the lower part of the stem. This disease is called Gray Rot.
If this happens, then the flower needs to be transplanted urgently. Moreover, the old soil should be completely removed from the roots, the dead and damaged roots should be cut off. Treat with some kind of fungicide or manganese. Only then plant Fatsia in a new soil and water it with the addition of the same fungicide. If the case is neglected, then you are unlikely to be able to save the flower.
What to do if Fatsia has stopped growing.
Perhaps he felt cramped in the pot. See if its roots are peeking out of the drainage holes. If so, transplant the plant into a suitable pot. If everything is in order with the pot, the possible reason is the poor soil. Remember the last time you fed a flower. Perhaps it's all about rare dressings.
Why the variegated leaves of Fatsia lost their brightness and turned uniformly green.
The reason is poor lighting. Variegated varieties need bright light all year round. In winter, they definitely need illumination using fluorescent lamps, fluorescent lamps or phytolamps for up to 10 - 12 hours a day.
The second reason is poor soil. Feed your pets regularly, and then they will delight you with their beauty.
Common plant problems
If the rules for caring for orchids are violated, different signs of soreness may appear on the plants.
- Soft and drooping leaves - excessive watering.
- Leaves dry and break - low humidity.
- Leaves shriveled - sunburn or low humidity.
- Leaf tips dry and break - poor watering.
- Yellowed leaves fall off - excessive watering.
If the care of the indoor plant fatsia is not good enough, it is attacked by the following pests: red spider mite, thrips, whitefly, aphid, scale insect.
The parasites settle on both sides of the leaves, which in turn curl and turn yellow. Pests should be removed with a soapy sponge or cloth. In advanced cases, treatment of the plant with Actellik will help.
Needless to say, Fatsia is a very capricious beauty, which only a very caring and diligent florist can tame.
However, as you know, "patience and work will grind everything," and love, attention and timely care will conquer even impulsive fatsia
And for the most curious, we suggest that you familiarize yourself with the video about Fatsia
Fatsia is a plant popularly referred to as "Japanese chestnut", "home chestnut". Unpretentious, persistent, has spectacular large palmate leaves. The crown is thick, lush, impressive in size, but volume does not interfere with harmonizing even small spaces. Interior designers love this plant very much. And even beginner growers will be able to cope with a shade-tolerant, persistent, undemanding plant.
Popular nicknames are well deserved. Fatsia leaves are really similar to the chestnuts we know, but more graceful in texture, in a reduced version. Among indoor crops, it is one of the most spectacular large-leaved shrubs. The luxurious crown grows quickly. The birthplace of Fatsia is Japan.
Be careful with care and cultivation, as Fatsia is a poisonous indoor crop. When working with shrubs, especially when transplanting, protect your hands from contact with roots and herbs.
Transfer
Fatsia belongs to the species that tolerate transplantation very poorly. After planting in another pot, the plant is sick for a long time and does not adapt well to a new place. However, the root system grows rapidly and eventually ceases to fit in the old container. Therefore, transplantation is often a forced measure and is performed every 2-3 years.
The problem could be solved by planting a young plant in a pot for growth, however, this method will not work either: the root system, once in a large container, will begin to actively grow, wasting all the strength and reserves of the plant to increase its mass. At the same time, the aerial part will receive less portions of nutrients and noticeably slow down in growth. Therefore, the transplant is performed in a pot, which is only 1.5 cm wider than the previous container.
The procedure is carried out by the transshipment method, while trying to preserve the earthen lump as much as possible. To do this, a layer of expanded clay is laid on the bottom of the new pot, which will serve as a drainage, and soil is poured on top.As an earthen mixture, a ready-made universal substrate or a home-made composition is used. It is prepared in the proportion 1X1X1X2 from the following elements:
- humus;
- peat;
- river sand;
- turf.
After transplanting, the bush is placed in the shade and not watered for 3-4 days. Then it is slightly moistened, rearranged to a permanent place and carefully transferred to the general care regimen. The procedure is recommended to be carried out in the first half of March, after the plant comes out of dormancy. If, after 2-3 years, the root system has not grown much and fits well in the pot, there is no need to transplant the plant.
Planting and breeding fatsia
Fatsia is grown at home without problems thanks to all existing types of reproduction. You can get a young and healthy evergreen plant by planting seeds, cuttings or cuttings. Consider each of the examples p>
From seed
Everyone can grow fatsia from seeds at home. Seeds are sown directly into prepared soil. The seed is sown to a depth of no more than 10 mm
In this case, it is important to maintain the optimal air temperature of about + 18 ° C or higher until the full emergence of shoots.
After the first two leaves appear on the sprout, the seedlings are ready to be transplanted into a separate pot. The sprouts are seated strictly 1 piece per pot, after which the container is placed in a bright and warm place, but without direct sunlight.
When propagating plants for better germination of seeds or for engraftment of cuttings, stimulants are used
root formation: "Kornevin", "Kornerost", "Heteroauxin", "Epin extra", "Chunky", "Etamon".
From cuttings
Cuttings of fatsia occurs with the help of young shoots. To do this, in the spring, material for cuttings is cut from the top of the flower. The finished cutting sits in a special substrate based on sand and peat, after which the container must be wrapped in a plastic bag to create greenhouse conditions.
If the air temperature is about + 20-26 ° C, the cuttings take root within a week. After rooting, the planting material is ready to be transplanted into individual pots.
Important! When propagating by cuttings, the plant desperately needs fresh air: for this, it is recommended to ventilate inside a plastic bag in the morning and in the evening.
From layering
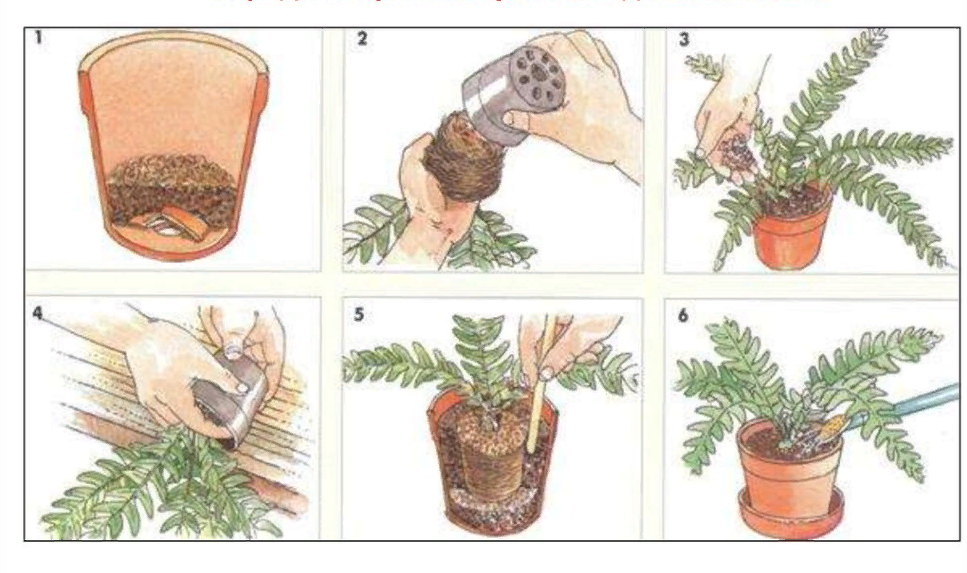
When the aesthetics of the flower is desired, you can rejuvenate the flower with the help of air layering. In the spring, a shallow hole is made on the trunk of the fatsia, which is wrapped in sphagnum moss, previously soaked in a special stimulating solution.
After that, the erected structure is wrapped in a plastic bag or film. With the constant maintenance of high humidity of the moss, aerial roots appear within six months. After another 2 months, the root tip is ready for cutting and planting in a separate pot.
Fatsia. Plant care, reproduction and pruning.


Fatsia is an oligotypic genus of plants that belongs to the Araliaceae family, which includes a small number of plant species. The scientific name of the genus was first used in 1854 by French botanists Joseph Déquinomy Jules Émile Planchon. It is derived from the Japanese name for the type species of the genus, Japanese Fatsia.
This plant has been known as an ornamental plant since Victorian times (19th century). It became widespread due to its unpretentiousness and rapid growth, which is easy to achieve with regular fertilization and timely transplantation. In a couple of years, Fatsia is able to grow 1 m in height from a very small specimen.

Fatsia is a low shrub with highly decorative leaves native to Japan, Taiwan and Vietnam, where it is widespread and can reach a height of 6 meters, forming a large spreading bush.In a home environment, Fatsia rarely overcomes the 1.5 meter barrier, but if you follow the basic rules for caring for a plant, then it will delight you not only with a lush bush with carved leaves, but also with flowering.
At home, Japanese Fatsia (Fatsia japonica) is mainly grown, but there are also garden species.
Reproduction at home
Japanese fatsia bushes can be propagated in several ways: cuttings, layering and seeds. Each of these methods has its own characteristics that affect the experience of the grower and the success of a new planting. You can choose any of them that you find more acceptable to yourself personally. We suggest that you familiarize yourself with each of them in detail.
When the cuttings take root (after 7–16 days), each plant is planted in a separate pot with a diameter of 9–11 cm. The soil is already taken as for normal cultivation.
The damaged part is wrapped in sphagnum moss dipped in a nutrient solution. The solution is prepared from any complex fertilizer for deciduous trees at the rate of 1 g per 1 liter of water. The moss is covered with a foil. Until aerial roots appear from the incision, the sphagnum moisture should be monitored. Be patient, the roots appear after a few months.
The remaining stem can be cut to a small hemp and treated as before for a flower. After some time, new shoots will appear in this place.
Seeds
The sowing is covered with a film on top to create greenhouse conditions and left to germinate at a temperature of 18 ... 20 ° C. The first shoots should appear 3-4 weeks after planting, the shelter must be removed immediately. As soon as the plants get a little stronger, they can be transplanted into separate containers.
An unspoken advantage over other ornamental plants is that samurai fatsia is able to adapt to almost any conditions of detention. But it is still necessary to adhere to the minimum recommendations for care.
When purchasing fatsia, it is best to opt for a young, weakly overgrown plant. At low temperatures, a pot of Japanese fatsia is wrapped with polyethylene several times, and warm air is pumped inside: a tropical plant does not tolerate drafts and cold. Upon arrival home, this packaging should not be removed for another 2-3 hours, allowing the Aralia to adapt to new conditions.
After that, it is recommended to make sure that there are no pests on the plant and, if necessary, treat it with insecticides. After 1.5-2 weeks, the fatsia is transplanted into another pot, which should be slightly larger than the previous one. In this case, the roots are completely cleared of the transport earth, simultaneously removing all damaged fragments.
The plant needs a loose substrate that is rich in nutrients. You can buy a universal soil in the store (a peat base with the addition of vermiculite and humus is best suited) or you can make it yourself. You will need to mix turf or compost soil and deciduous humus with sand in a 2/1 ratio. The acidic indicators of the soil are very important, the permissible pH values are from 5.0 to 7.0 inclusive.
Landing, transplanting
The container for the transplant is prepared 3-5 cm larger than the previous one, preferably clay or ceramic. For fatsia, a not too wide, but high pot is suitable. Its depth should be such that when laying a coarse-grained drainage, which fills about 1/3 of the tank's height, there is enough space for the full-fledged growth of the aralia.
The plant is pulled out of the old container and the roots are shaken off only slightly, without completely removing all the earth. The damaged and rotten parts of the roots are removed by treating the cuts with coal. When planting aralia, an old clod of earth is simply sprinkled on top and on the sides with new soil.
Fatsia loves abundant watering with settled water. In the spring-summer period, the soil is moistened as a couple of the upper centimeters dry.From mid-autumn and winter, watering is reduced, but make sure that the clod of earth is always slightly moist. If in winter the plant is kept in warmer conditions than recommended, then watering should be left the same, but the volume of water should be halved so that both the upper and middle layers of the earth can dry out.
When the soil is dry, the leaves of the fatsia wither, and it will be extremely difficult to fix this problem, even if the dry period lasted for a short time.
Description of the plant fatsia
Fatsia (Fatsia) - ornamental-deciduous, evergreen shrub or woody plant, belongs to the Araliaceae family. It is modest in varieties and species: as an ornamental culture, Japanese fatsia is grown with individual hybrids, forms and varieties. The crown is massive, but very beautiful, neat in appearance. In nature, it is a tree culture, and in indoor conditions shrubs up to 2 m in height are formed, but with proper care they are limited to a meter in size. The bush branches weakly.
The shoots are very thin to support the weight of luxurious leaves, they often need support, especially for variegated fatsias. The main pride of Fatsia is undoubtedly its leaves. They are large, up to 30 cm in diameter, finger-separated, planted on long petioles. The heart-shaped or round leaf consists of 5-9 leathery lobes. The color of the foliage is not limited to neutral dark green shades, but can have a border, variegated spots. But absolutely any leaves with a beautiful leathery texture and a characteristic glossy shine.
Bloom
Fatsia is capable of blooming in indoor conditions, but is exclusively an ornamental deciduous plant. Basically, it is believed that the flowering is unremarkable and only spoils the attractive appearance, most often the peduncle is cut from the plant, not even allowing it to bloom. Do the flowering of your choice. It represents nondescript small flowers of white or greenish color, gathering in miniature umbellate inflorescences.
In contrast to the large shiny foliage, the flowers seem airy, lacy, a bit like dandelions. After flowering, fruits will appear: small berries of a dark blue color, like a black mountain ash, but the seeds in them do not always ripen and lose their germination quickly. There is no need to prepare the plant for flowering, in general it will not spoil the appearance of the plant, but will give some tenderness and elegance.