Actinidia care basics
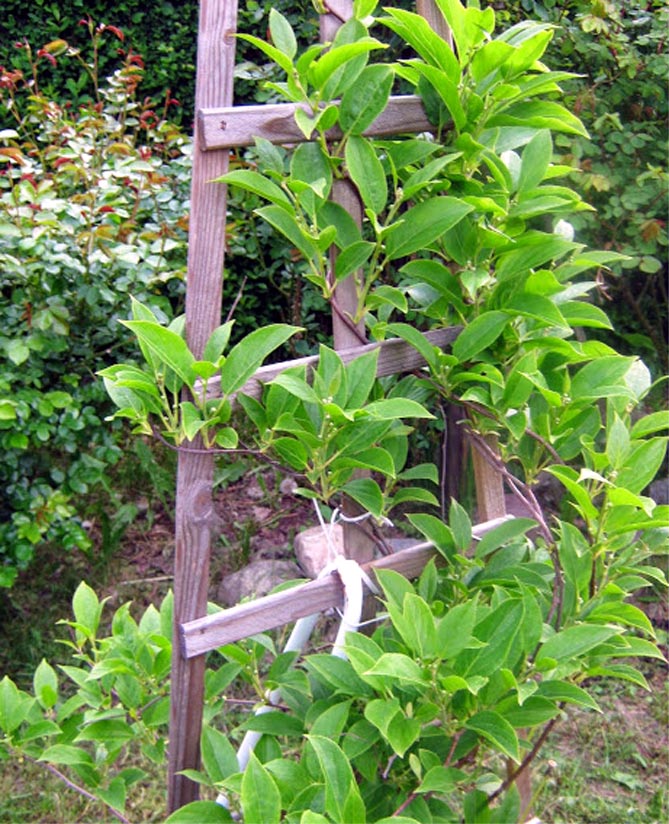
Proper planting and the complete absence of pests make it easier to care for actinidia. For better plant growth and increased fertility, it is advisable to provide it with supports - trellis (galvanized wire between the posts).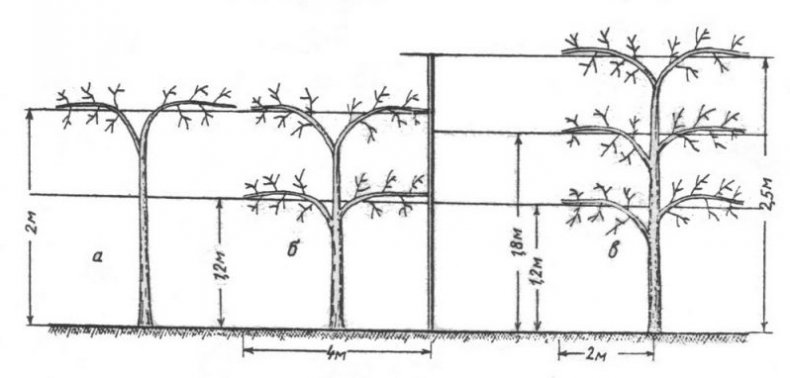
Important! Planted cuttings from lignified actinidia cannot be transplanted for at least two years - their root system should get stronger.
Watering and fertilizing the soil
Watering actinidia is moderate. Excessive moisture should not be allowed (the ground at the roots serves as an indicator). All actinidia like to spray their leaves with water dust (morning and evening).
Fertilizers are selected taking into account the preferences of the plant (slightly acidic and acidic soils) - potassium chloride, ammonium sulfate, ammonium nitrate, wood ash, etc. Chlorine-containing fertilizers, such as lime and fresh manure.
Before feeding the actinidia in the spring, after the snow melts, you need to shallowly loosen the ground near the roots (by 3 - 5 cm). Do not dig in - you can damage the roots. You need to feed:
in early spring (mulch with organic matter and fertilize - for each square meter - 35 grams of nitrogen, 20 grams of phosphorus or potash fertilizers);
middle - end of spring (ovary formation) (per square - 15-20 grams of nitrogen, 10 grams of phosphorus and 10 grams of potash). In summer, you need to constantly monitor the root collar, fill up the earth when it is exposed;
at the end of the harvest, before winter. Lianas are fertilized with superphosphate and potassium chloride
The roots are additionally covered with a layer of peat and leaves.
Important! Actinidia are sometimes affected by leaf spot and gray fruit rot. Young plants (shoots and especially roots) can be eaten by cats
For the preservation of the roots, the planted shoots are fenced off with a metal mesh.
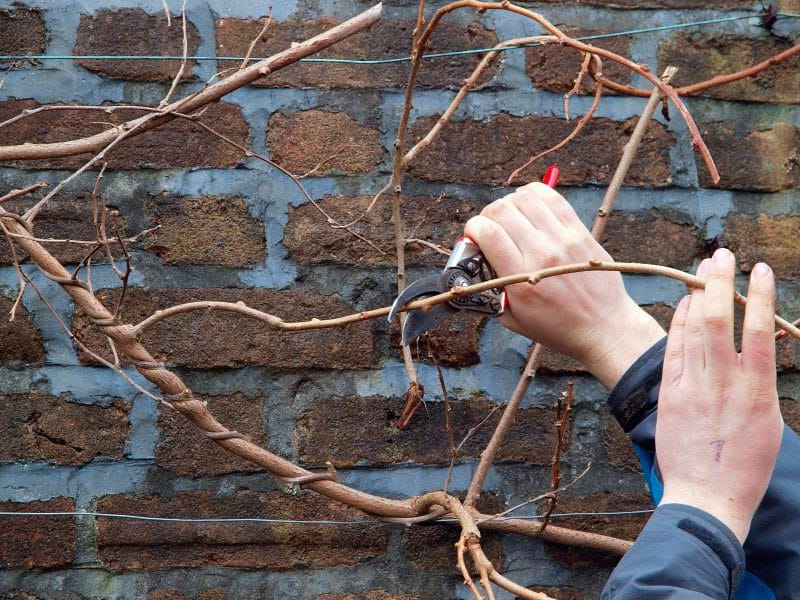
How to trim properly
Caring for actinidia involves pruning the plant regularly... Pruning is necessary for a young liana (for its correct formation) and an adult plant (the constant growth of a liana leads to thickening, darkening, and a decrease in yield).
Consider the following when planning your pruning:
- the most optimal time for the procedure is the summer months, immediately after the end of flowering;
- in the fall, about a month before frost (in different regions, frost periods may differ) - pruning is not recommended (awakened buds and young shoots will not ripen and frost will kill them). In the southern regions, sanitary pruning is carried out after the end of leaf fall;
- in early spring (when the juice moves along the liana), pruning is prohibited - any violation of the integrity of the plant is fraught with its death.
Important! Each variety of actinidia has its own specific characteristics that must be considered when pruning. For example, in a kolomikt over 8 years old, one old branch is cut off and replaced with a young shoot every year.
Kolomikt in the form of a bush does not bear fruit well and needs trellis. In the argut, the main vine serves all its life, but it needs to be thinned more intensively and cut shorter (short shoots bear fruit), etc.
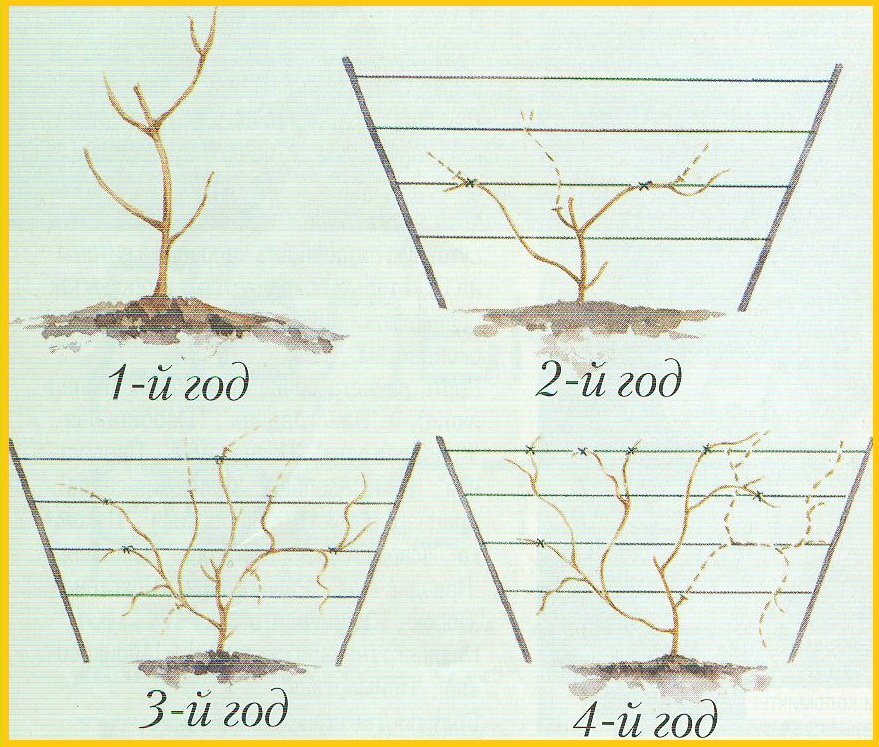
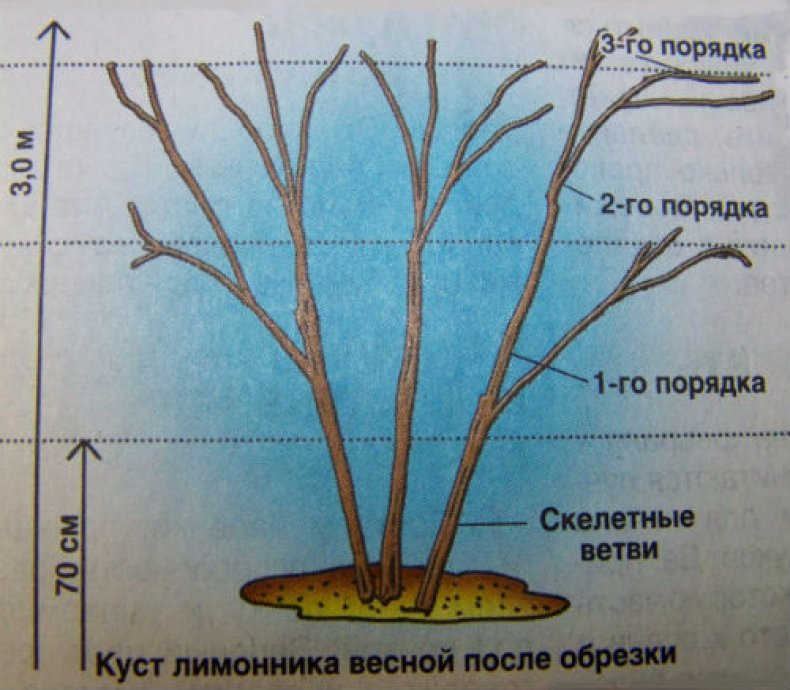
Pruning young actinidia is associated with plant formation.
- the first year - the aerial part is cut off, leaving 2 - 3 buds;
- the second year - all shoots are cut, except for 2 - 4 vertical (sleeves). After the end of the leaf fall, their apical buds are cut off;
- the third year - the strongest side shoots are selected and tied to the left and right trellises;
- the fourth and fifth years - further garter of the strongest and most fruitful branches, pruning of weak, thin, broken and non-fruiting branches.
Winter hardiness of actinidia

Actinidia varieties grown in our latitudes have a fairly high frost resistance (kolomikta can tolerate frost down to -35 ... -45 ° C).
For the first 2 - 3 years of life, young plants for the winter are best covered with a pillow of leaves, spruce branches or polyethylene.
The great danger for vines is not low temperatures in winter, but spring frosts (young actinidia sprouts, flower buds and buds are most sensitive to them)... A decrease in temperature below zero by 8 degrees can destroy the young shoot.
Planting actinidia near a residential building will partially neutralize the danger of frost, but there may be a problem from rainwater runoff from the roof.
Outdoor care: watering, support, weeding, feeding
With the beginning of the growth of shoots, actinidia must be tied to a support and not removed from it again. Further care consists in regular watering, weeding, feeding and shallow loosening of the soil.
Watering
During a drought, plants are sprayed with water in the morning and evening, watered abundantly, and then the soil is mulched. In dry summers, water the vines and sprinkle with water, preferably 2-3 times a day.
How to feed actinidia
Top dressing of actinidia will enhance the growth of shoots, help the plant to overwinter and increase the yield.
In the spring
With the arrival of spring, the earth around actinidia is dug up and 35 grams of nitrogen and 20 grams of potassium-phosphorus dressings are added per 1 sq. m plot.
Summer
The second time actinidia is fertilized during the formation of ovaries. For 1 sq. m. you will need:
- 20 g nitrogen;
- 10 potassium;
- 10 g of phosphorus.
In autumn
In the second half of September, the third feeding is carried out. This time potash-phosphorus fertilizer is applied in the amount of 20 g per square meter.
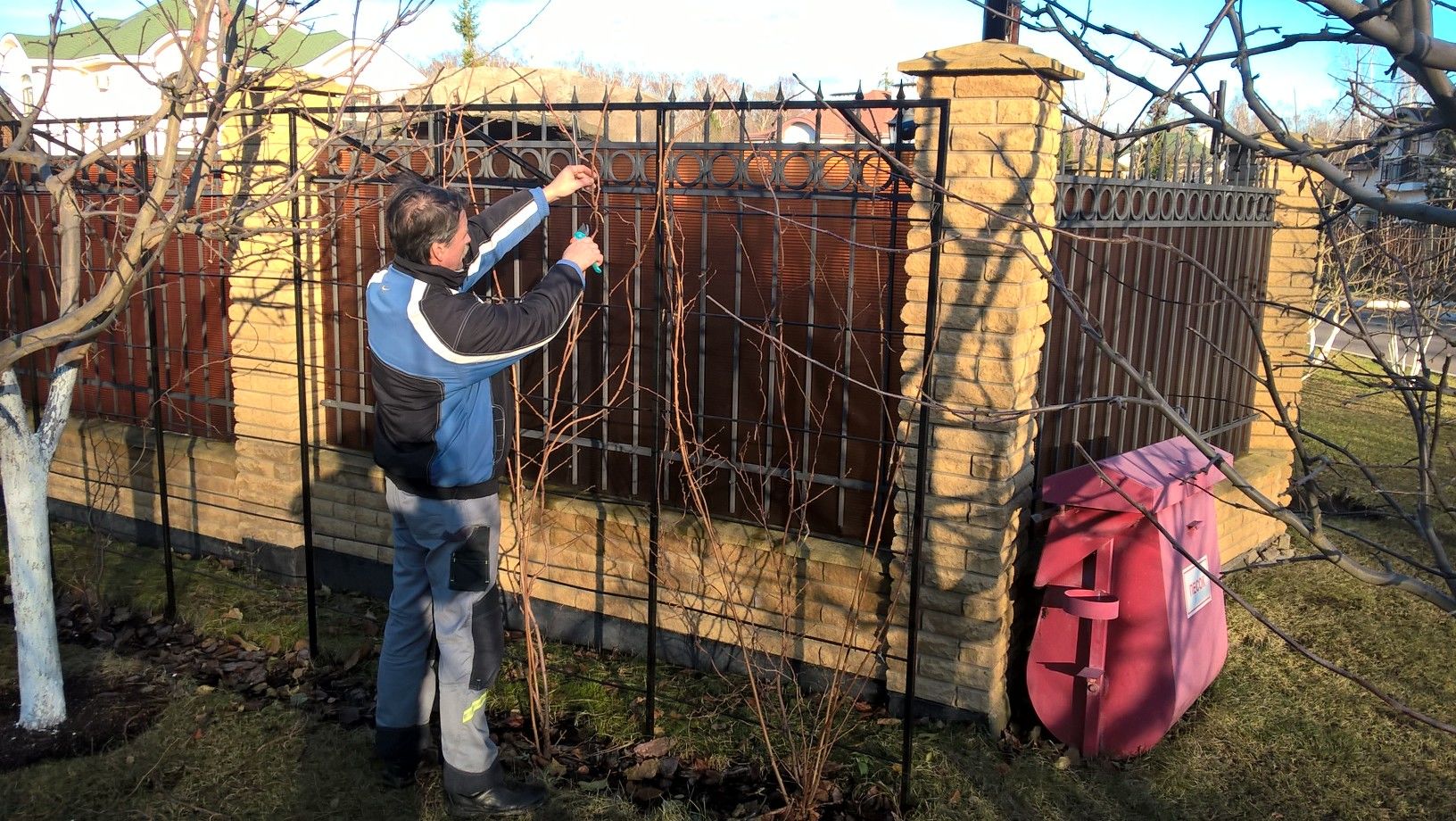
Support for actinidia
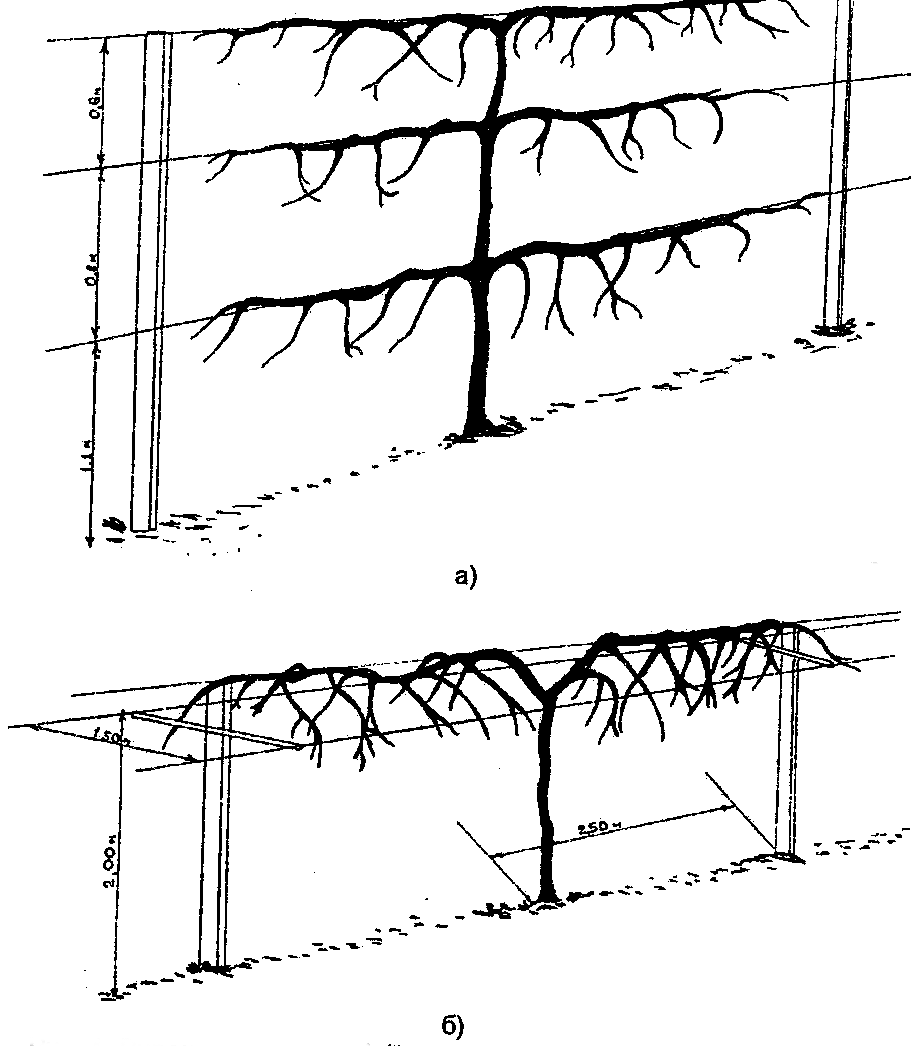
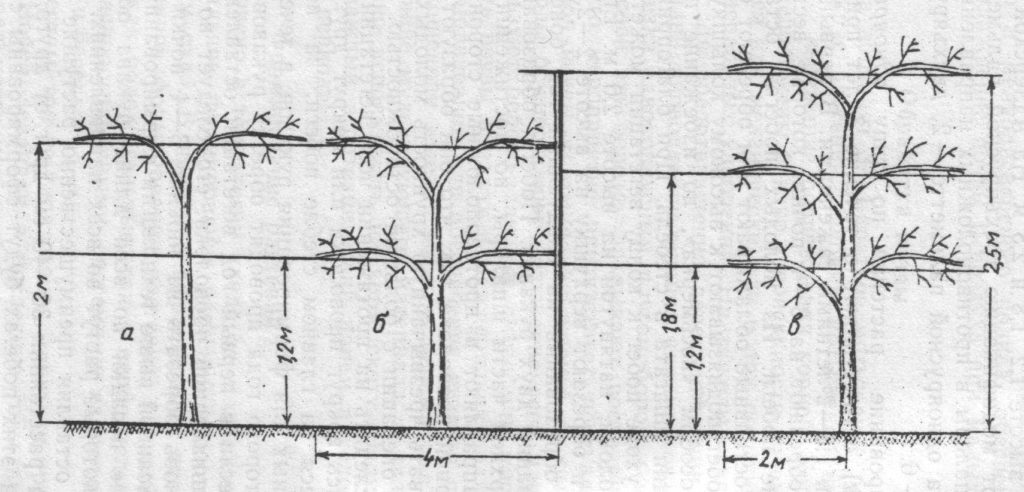
The most suitable support for actinidia is trellis shields 2 meters high and 3 to 6 meters long. For short trellises, two posts are placed, for long ones - three.
In the second year, the shoots on the support must be fanned out and tied up as necessary.
Pruning
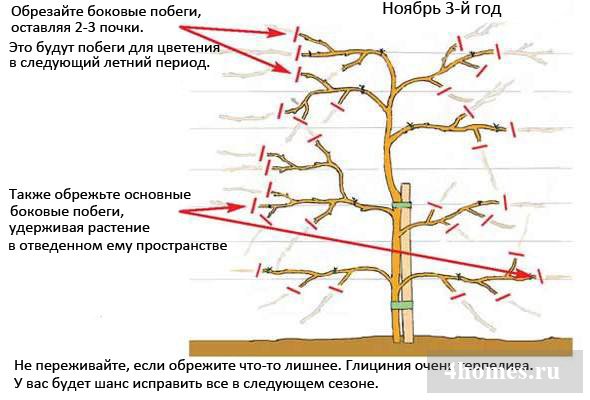
To improve further fruiting, the shoots are pruned annually. This is done in late autumn.
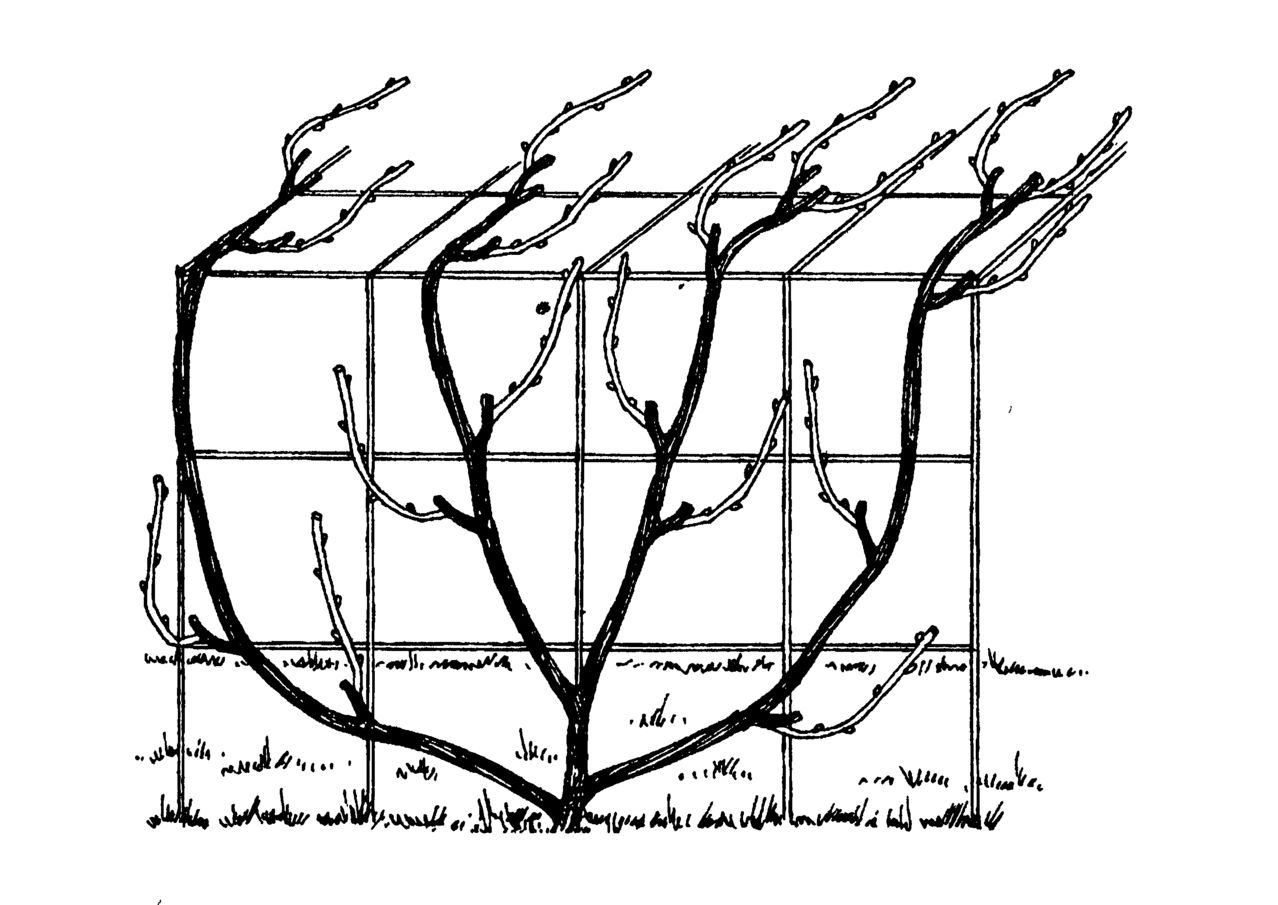
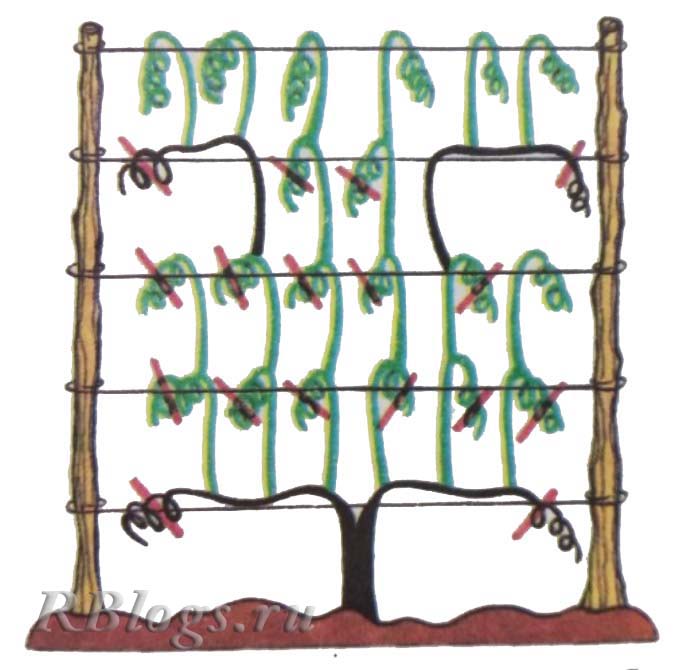
To do this, select the two strongest shoots on the plant and tie them horizontally to the support, directing them in different directions.
The rest of the shoots are cut out in October-November. The two main vines remain on the actinidia. Next year, new shoots will appear on them. They are tied up vertically on a trellis. These are fruiting shoots.
Fruiting shoots are shortened annually, leaving 4-5 buds behind the topmost berry.
Scheme: black - main vines, green - lateral fruiting shoots, red - pruning sites.
Preparing for winter
In the fall, in the first years after planting actinidia, to prepare for winter, it is advisable to cover the soil around the seedlings with fallen leaves.
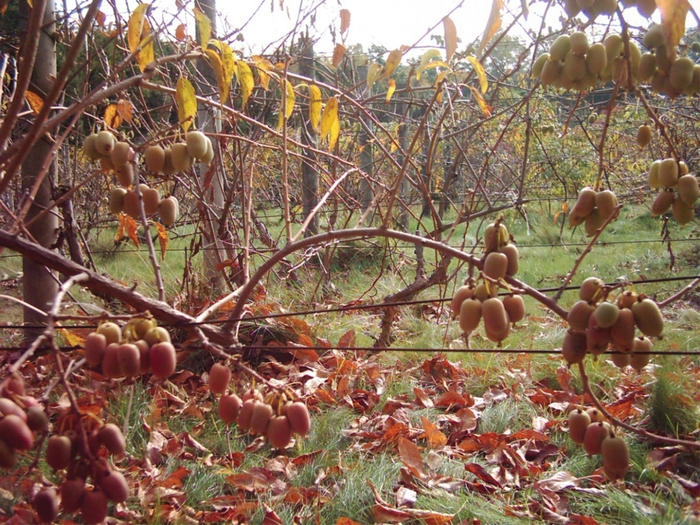
In the third to sixth year of life after planting, the plants usually begin to bloom and bear fruit.

Types and varieties
The genus Actinidia has 36 species, most of which are wild woody lianas from the subtropical and tropical forests of Southeast Asia. Only four hardy species grow wild in the Russian Far East:
- kolomikta;
- argument;
- polygamy;
- giralda.
There actinidia is called "Far Eastern raisins". The giralda species is very rare.
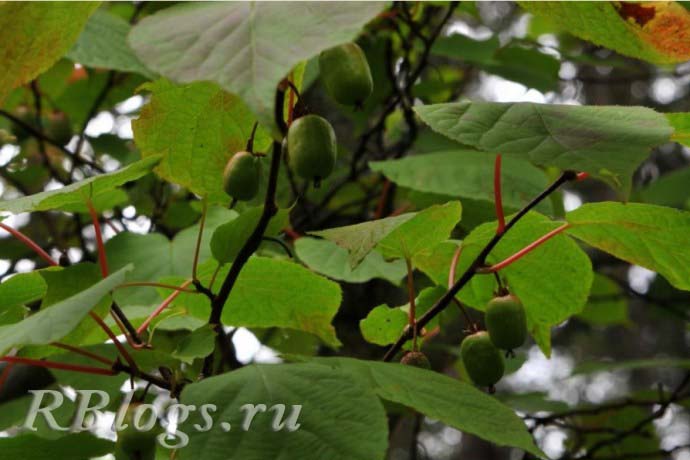

In amateur gardens, the most common actinidia kolomikta. This species is the most frost-resistant and unpretentious. The first varieties of this species were bred by IV Michurin: these are Pineapple Michurina and Klara Zetkin.
Actinidia argut
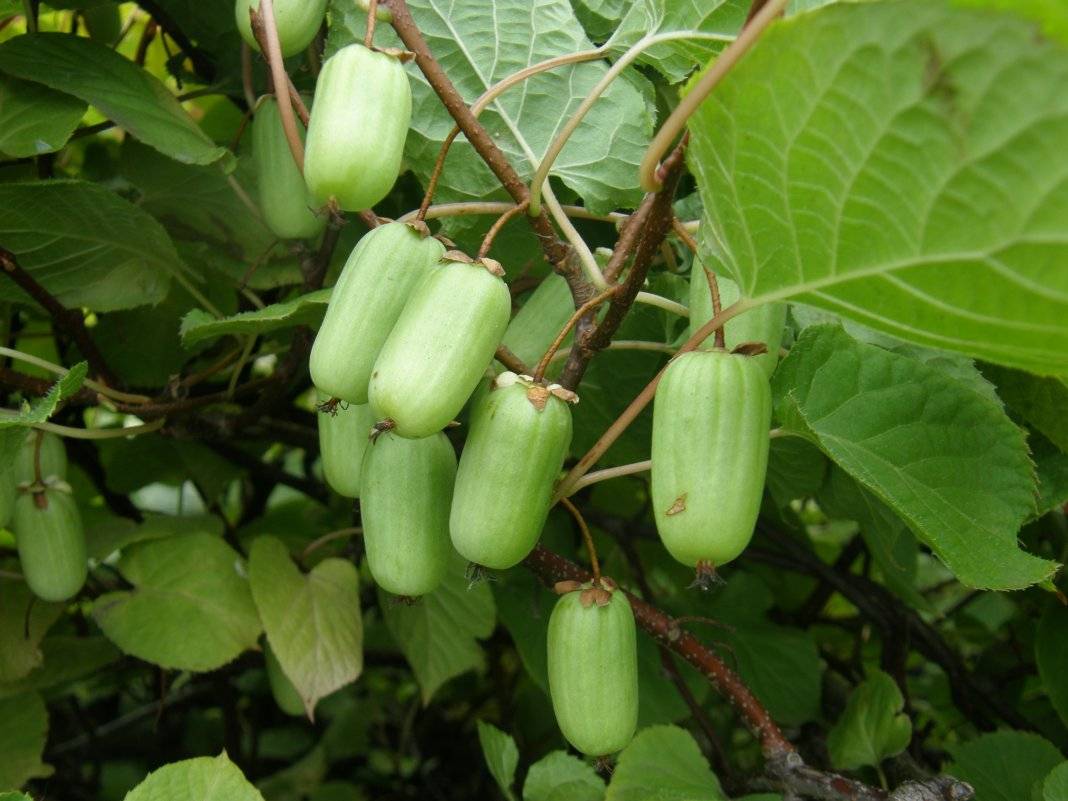
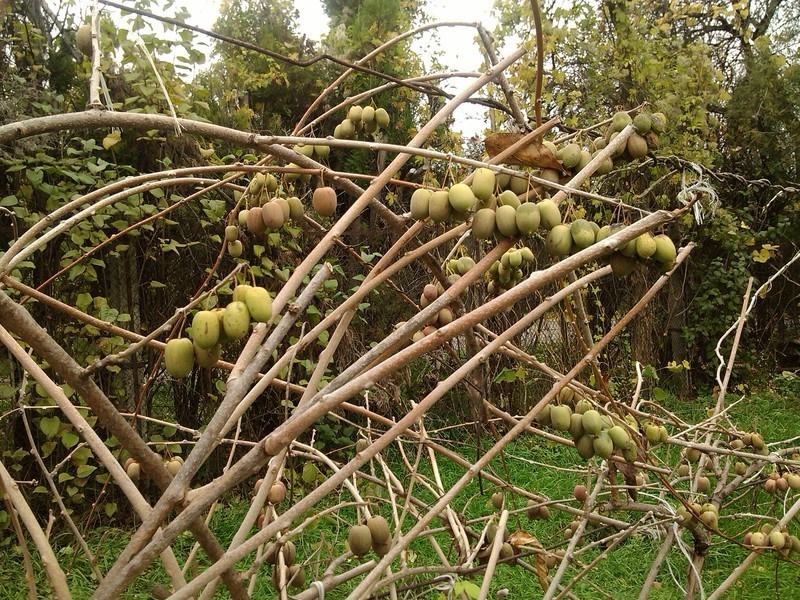
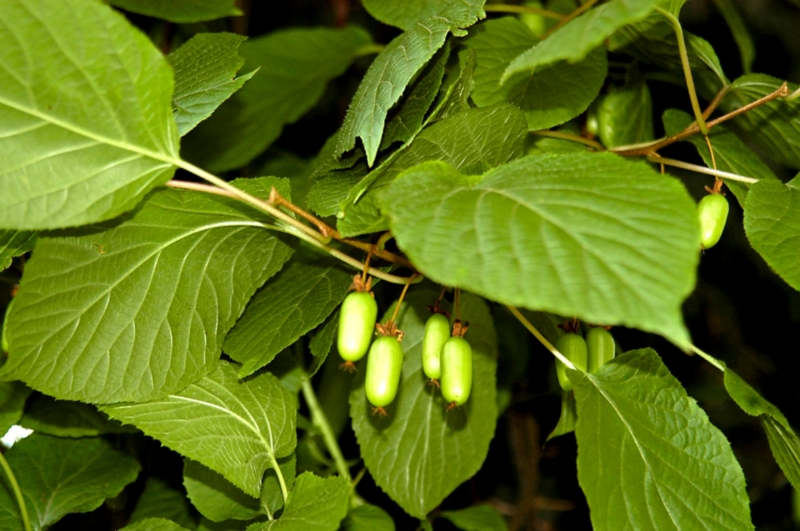
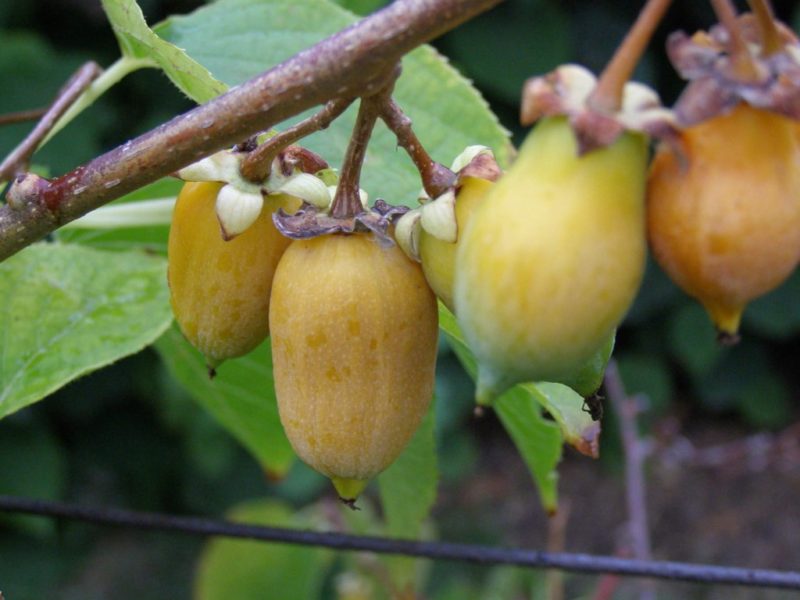
Of all the cultivated species, actinidia arguta develops the most powerful vine 20-30 meters long and 15-20 centimeters thick. Slightly pointed ovoid leaves up to 15 cm wide. Flowers are white, up to 20 mm, collected in a brush or single. Dark green oval fruits with a diameter of 15-30 mm, weighing about 5-6 grams.
Actinidia arguta is less cold-resistant than colomicta. In the Moscow region, it ripens late - at the end of August - early September. And in the southern regions of Russia, the arguta ripens in August and gives a large harvest.
Popular varieties:
- September;
- Curly;
- Kiev hybrid-10;
- Kiev large-fruited;
- Taiga emerald;
- Daughter;
- Balsamic;
- Goliath;
- Bureyanka;
- Sakhalinka;
- Ribbed;
- Giantess, etc.
Among the best varieties for the Non-Black Earth Region, gardeners singled out Ribbed.
Ribbed actinidia arguta is a winter-hardy vine with long brown shoots. The berries are large, cylindrical in shape, with a blunt base and a pointed "nose" top. The berries are 2 cm long, weigh 5.3-6.2 g. Ripen in mid-September. The surface of the berry is ribbed, yellowish-green in color. The taste is sour-sweet, with an apple aroma. Ascorbic acid content 251 mg / 100 g.
Actinidia polygamy
The diameter of the actinidia polygamous vine is about 2 cm, 4-5 meters long. Leaves are elliptical, oblong, pointed towards the top. Fruits weighing about 3 grams.
Actinidia polygamy occurs less frequently in nature than other species. In different regions of Russia, the varieties Orange, Kanareika and Perchik are widespread. In the conditions of the Moscow region, the actinidia polygamum is quite winter-hardy; it begins to bear fruit at the age of five to six years.
Actinidia polygamus stands out among its relatives: its orange fruits taste like sweet pepper and peppery aroma.
The Canary variety is recognized as the best for growing. It is a winter-hardy liana with annual shoots up to 183 cm long, brown or light brown in color. The berries are dark orange, large (average weight 2.7 g, maximum - 3.5 g), cylindrical, 2.1-2.6 cm long. The fruits contain 136-268 mg / 100 g of ascorbic acid, 14.2% sugars, 0.6% organic acids.
Actinidia kolomikta
Actinidia kolomikta has a very high frost resistance. The length of the liana can reach 5-10 meters, and in diameter - two centimeters. Ovate leaves are about 7-16 cm. The flowers are white, on male specimens they are collected in racemose inflorescences of 3-5 pieces, and on female specimens - single. The length of green fruits is from 20 to 25 mm.
Actinidia Giralda
The Far Eastern actinidia giralda is found in the south of Primorsky Krai. In the Moscow region, its cultivation is difficult.

Reproduction of actinidia
According to gardeners, the reproduction of actinidia does not cause any particular difficulties. There are several ways to propagate a plant. Among them:
- Root offspring;
- Green and lignified cuttings;
- Dividing the bushes;
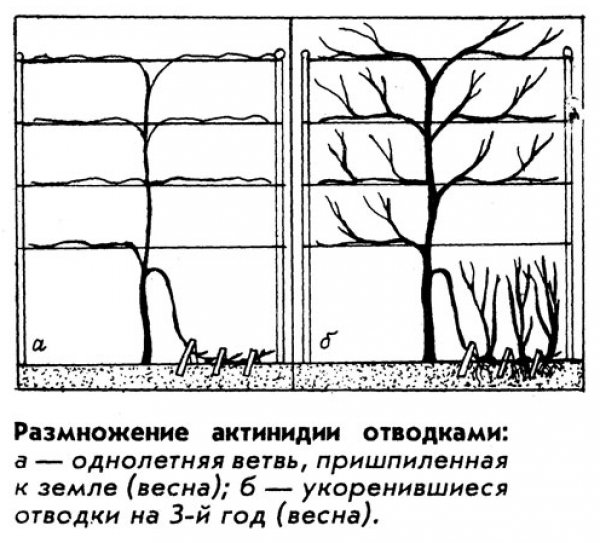
- Taps;
- Seeds.
Root offspring
Not all types of actinidia reproduce by root offspring. In this way, the actinidia of the Kolomikt and Polygam varieties can be propagated.
Fresh shoots that are close to the ground are laid out in special grooves. There should be peat and humus in the pits. Root suckers are systematically moisturized. As a result, shoots appear above the surface of the earth. They can be separated from the mother branch after a year.
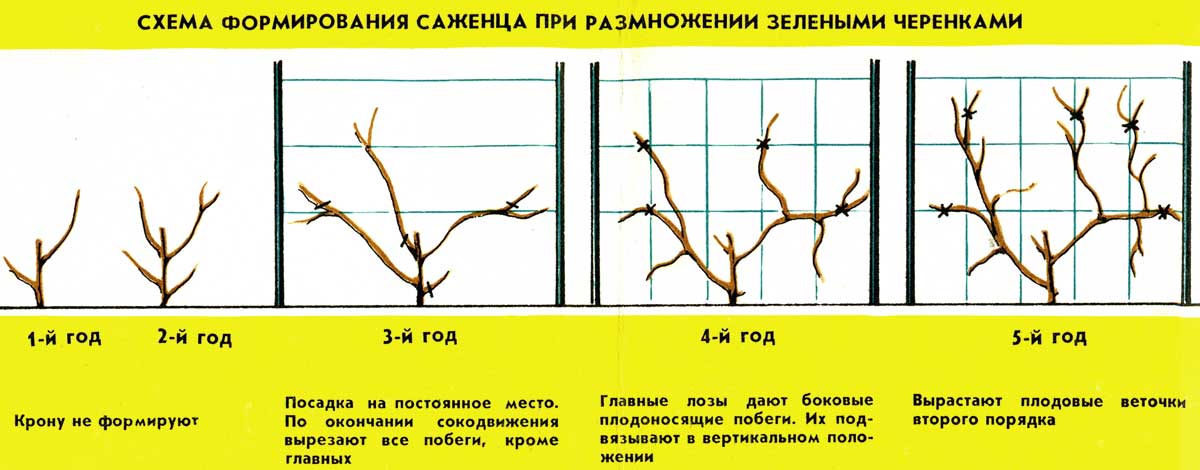
Green and lignified cuttings
Actinidia is propagated by green and lignified cuttings in order to obtain a large number of seedlings. Harvesting of cuttings takes place at the beginning of summer, when the fruits are poured. Strong shoots will do. Their average size should be about 60 cm. After cutting, they are left in a container with water. A few hours later, cut into pieces of 8-15 cm. Each of the cuttings should have several internodes, at least 3-4 buds. The cuttings are planted in a greenhouse, in a prepared slightly acidic soil with humus, river sand, and a complex nutrient mixture. You need to plant cuttings at a distance of 5-10 cm from each other. The angle of inclination of the cuttings is 60 degrees. For several weeks, they need hydration, which is carried out 4-5 times a day. Cuttings overwinter under a layer of dry foliage. In the spring, they can be opened and transplanted into the part of the garden that the summer resident chose.

Shoots of actinidia from cuttings
By dividing the bushes
By dividing the bushes, actinidia is propagated in early spring or late autumn. The bush is completely dug out of the ground.All dried, old branches are removed. Then it is divided into two equal parts. It is necessary to ensure that the number of roots, developed shoots is the same. Parts of the vines are transplanted into prepared planting pits.
Taps
One of the easiest ways is to breed by branches. To do this, one of the long shoots is partially bent to the ground, covered with soil, spilled, mulched with sawdust. The tip of the shoot should be on the surface, this is the only way to grow a new vine. After a few weeks, the cuttings take root, a shoot grows out of it. In the fall, it can be planted as a seedling.
Seeds
Seed propagation of actinidia is considered the most effective. The seeds produce hardy, healthy plants. But the method has its drawbacks. The first is that the fruiting of vines, which were grown from seed, occurs late: 7 years after planting. The second minus is that the sex of the seedling can be determined only after its flowering.
The seeds are harvested in the fall. They should be from healthy fruits. The planting material is placed in cheesecloth, washed well, then dried. 50-80 seeds can be extracted from one fruit.
In order for the seeds to have good germination, they must be carefully prepared for planting. The seeds are soaked for several days. During this time, they should swell. Then they are mixed with sand. The resulting mixture is moistened and left on the windowsill, periodically watered. In this form, they should be about two months. After this period, the seeds with sand are removed underground or in the refrigerator for another two months. After all the procedures, the seeds are ready for planting. They are planted in spring or autumn. Planting depth - 1 cm. Row spacing - 10-15 cm. Seedlings overwinter under a layer of dry foliage and straw.
Preparing for landing, choosing a seat
First you need to choose the best place for the development of the plant.
An important condition is moist, loose open ground. Acidity should be weak or neutral
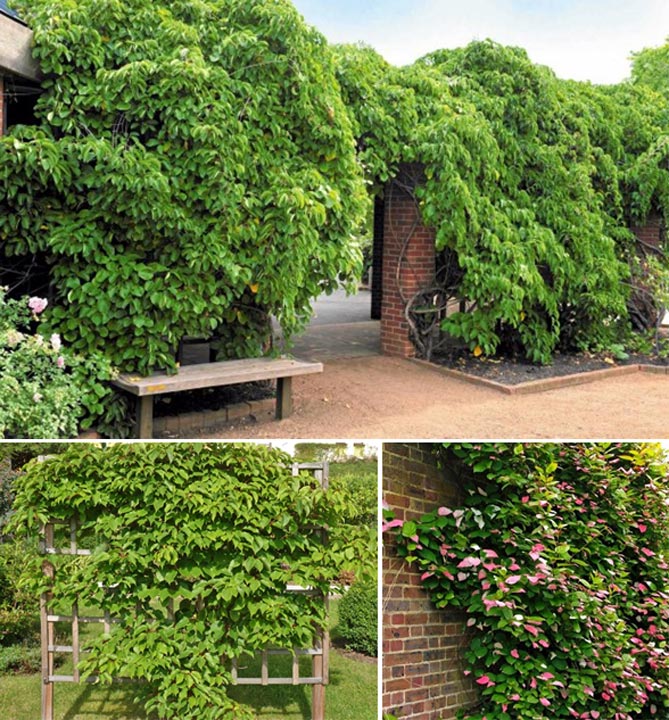
It is best to plant the vine in fertile land, where there is enough clay and sand. Culture loves the sun. Partial shade is also suitable for her. Another condition is the presence of support. Without it, actinidia will not be able to grow normally. You can install a trellis, an arch, a regular post next to it. Another option is to plant the culture right at home. In this case, she will be able to catch on the wall.

Before boarding
The right choice of seedling gives a lot. It is better to buy a small plant in a specialized store, nursery. The seedling must be healthy. Its roots are closed. Suitable age is one to two years.
Growing actinidia begins with preparation for planting. A pit is prepared a few weeks before the scheduled planting day. If several plants are planted, then several pits are prepared. The distance between them must be at least 2 meters. The hole needs to be dug quite deep - more than half a meter. The width is exactly the same. A drainage layer is built at the bottom. Pebbles, fragments of bricks will do. A soil mixture of humus, peat, garden soil, ash, ammonium nitrate is placed on the drainage, it is allowed to add superphosphate.
Note. Within two weeks, the soil mixture will settle
Ordinary soil is added to it. It is poured in the form of a slide. Actinidia will land on this hill.
On the day of planting, the seedling is examined. Remove all dry twigs, straighten the roots, remove broken or dried ones. After the root system is dipped in a clay mash, its consistency should be like thin sour cream.
Reproduction of actinidia
The plant reproduces well by layering, cuttings and seeds.
Layers
During active growth in late spring, the young shoot is bent to the soil in several places, pinned and sprinkled with moist soil.
The apex is directed upwards. After a year, the cuttings are separated from the mother plant, divided into seedlings, which are immediately planted in a permanent place.
Cuttings
From cuttings with 3 leaves 12-14 cm long, the lower leaves are removed, the rest are cut off by a third. Then they are planted obliquely into a wet substrate of sand and peat (3: 1) to a depth of 4-6 cm with a distance of 5 cm from each other and shaded. Provided that the soil is constantly moistened, the roots appear after 2-3 weeks.
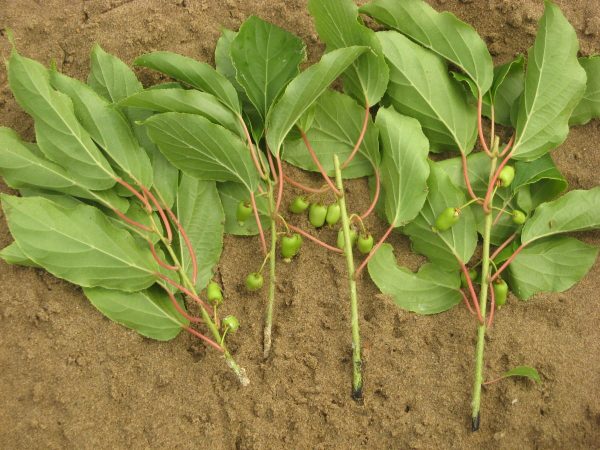 Actinidia cuttings for rooting
Actinidia cuttings for rooting
By the end of summer, a good planting material with a height of 20-25 cm is obtained with 100% survival rate. It should be covered with foliage or last year's dry sawdust for the winter. It is planted in a permanent place in the spring.
Seeds
Before sowing, the seeds require stratification - keeping in a refrigerator (at 3-4 degrees) in moist-calcined sand for 2 months. Then they germinate in the warmth (+ 22-24 degrees). Seedlings are shaded, in spring the seedlings are transferred to the street, in the phase of 4-5 true leaves they are planted in open ground.
Typical mistakes of care in the fall and preparation for winter

If you want to avoid actinidia diseases and get good growth, then you need to follow the advice and recommendations of specialists:
- The liana needs to be cut off only at a time when the process of sap flow is not in progress.
- It is not necessary to cover the actinidia early, as this can lead to the formation of fungi and mold, that is, to the death of the plant.
- Very intensive pruning can lead to the formation of a large number of wounds, which is undesirable for vines.
- Only dried covering material should be used, and it should be fresh every year.
- Be sure to water and fertilize actinidia abundantly in September and October.
If you follow all the rules and recommendations, then actinidia will live until next season and will delight you with an incredibly bountiful harvest. An ornamental plant needs appropriate care, without which you cannot enjoy the fruits.
Care
Caring for this shrub is similar to caring for other crops. But in this case, there are small nuances that should not be overlooked.
Watering
Watering actinidia is necessary only in extremely hot, dry weather, about once a week, one bucket of water for each bush. The plant will not interfere with both morning and evening spraying. If you do not carry out such procedures, then actinidia will not survive.
Mulching
To retain moisture and provide good growing conditions for plants, it is a good idea to mulch the soil around the bush with peat or old foliage. The mulch layer needs to be renewed every few months and replaced with a new one every six months. This method helps to preserve nutrients in the soil during fertilization, it serves as a kind of protection against moisture evaporation from the soil during hot weather.
Support
Support is required for actinidia. A height of 2-2.5 meters from the ground is suitable. It is advised to bend the support with a visor, approximately at the level of a person's height. Then the stems of the bush will grow and further curl at an angle to the existing support.
Pruning
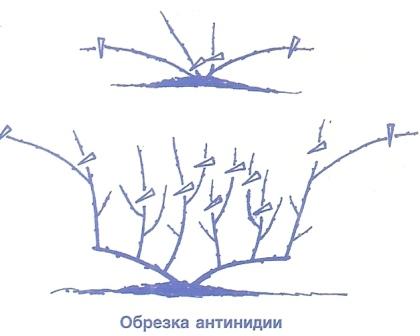
In order to get rid of excess density, which leads to a deterioration in yield, the plants are pruned.
At the beginning of September, you need to prune, shortening the shoots by a third of the length. This is called sanitary pruning.
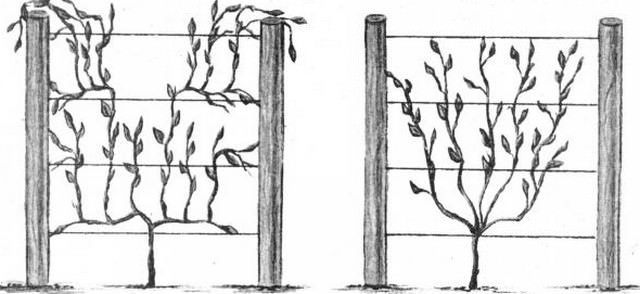
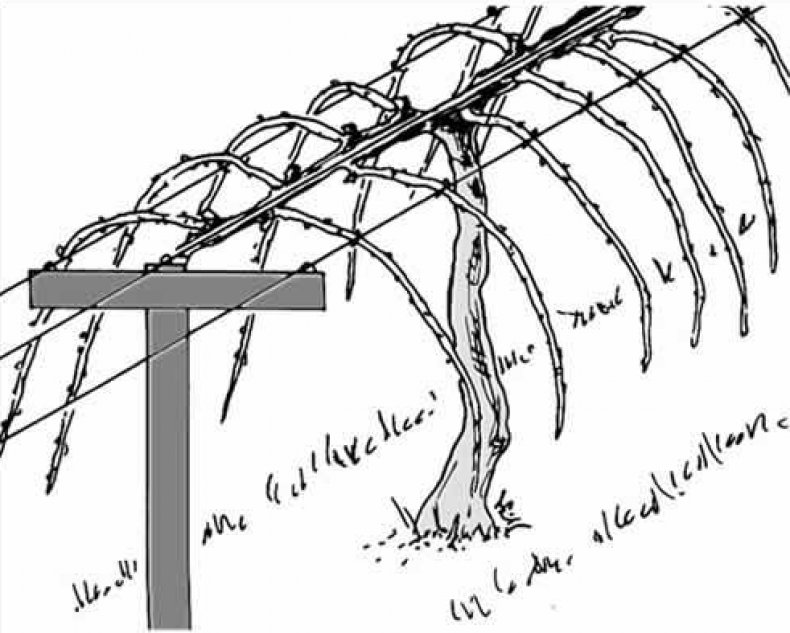
When the bush is 3-4 years old, in the summer it is necessary to carry out the formative pruning of the vine. A double-arm cordon is formed along a horizontal trellis: two shoots of the same level are directed in different directions and fixed, other shoots are cut off. In the coming season, shoots of the second order are formed on them, on which berries will grow, they need to be tied to a vertical guide.
When the age of the bush is 8-10 years in the summer, you need to make anti-aging pruning. It is necessary to cut off the shoots, keeping the stump 30-40 cm high.
In the spring, there is no need to prune due to sap flow.
Preparing for the winter period
Many gardeners advise, when preparing for the winter period, to remove the shrub from the support and put it in a plastic bag. But, if the winter period is favorable in the region, then you do not need to resort to this method.
Features of growing and care
Actinidia, although unpretentious, requires some care. For example, in the first 2-3 years after planting, the plant must be removed from the trellis, covered for the winter with straw, leaves, hay, garden film. Agricultural bags can be used instead of film. This is done in order to protect the vine from freezing.
But it's not just frosts that harm plants. Pets are not averse to feasting on young shoots. Therefore, it is worth taking care in advance that cats and dogs do not have access to seedlings. You can fence the actinidia with a plastic or metal mesh.
When weeding actinidia, it should be borne in mind that the root system of the plant does not go deep into the ground. In view of this, you need to carefully loosen the soil on the surface. This will provide air for the roots and prevent cracking of the soil.
Cuttings of actinidia
In mid-July, cuttings can be carried out. A non-lignified stem is selected. Cut into 2-3 buds. Of the leaves, only the upper ones remain. The lower leaves must be cut off. Cuttings are planted at an angle in sandy soil. In order for the plants to take root and begin to develop actively, you need to water the actinidia abundantly and cover the beds with a garden film. This creates a greenhouse effect. Within 2-3 weeks, the vine takes root in a new place. After this time, the greenhouses can be opened in cloudy weather, so that the plants gradually adapt. After planting, the cuttings are sprayed 3-4 times a day so that moisture remains inside the greenhouse. As the vines grow, watering should gradually decrease.
Video: cuttings of actinidia, features of care
Plant feeding and pruning
Liana is fed 2 times a year: in spring and autumn. Before the onset of cold weather, organic fertilizers and potash salt are applied to the soil. Since actinidia is sensitive to chlorine contained in potassium fertilizer, the dosage should be reduced. Instead of those indicated in the instructions, 30-40 g per 1 m 2 are introduced 10-20 g.
Complex types of fertilizers containing phosphorus and nitrogen are applied to the soil in spring. Such fertilizers include: Ammophos, Good Strength, Slox-Eco, Flower Happiness and others. You can buy them in garden centers, markets and online. The cost varies from 75 to 390 rubles.
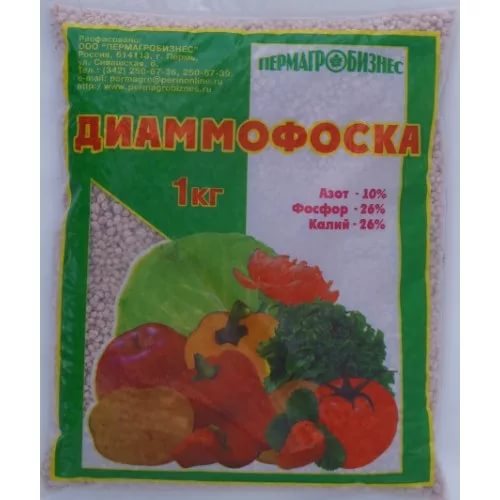

Complex fertilizer Diammofosk with nitrogen and phosphorus is suitable for feeding actinidia in spring
Actinidia pruning is best done in September, October. The old branches of the vine are removed with a pruner. It is better to cut them off in parts - this way it will be easier to pull them out of the trellis. It is worth carefully examining actinidia for damaged stems. Crossed branches are also cut to provide adequate ventilation between the stems. The cut branches are removed immediately.
Diseases of actinidia in Siberia
This vine rarely gets sick. With proper care, actinidia actively develops and bears fruit. Nevertheless, sometimes these plants are subject to such diseases:
-
powdery mildew;
- plant damage by fungi;
-
fruit rot.
Experts advise removing branches damaged by diseases and burning them to prevent the spread of the disease. For the prevention of diseases, it is necessary to spray the plants with 1% Bordeaux liquid after the buds appear on the vine. To destroy powdery mildew, you need to spray actinidia with a 0.5% solution of soda ash. After 8-10 days, you must repeat the procedure.
Each type of actinidia has its own pruning
During pruning, be guided by the peculiarities of the type of actinidia growing in your area:
- Kolomikta forms an ovary on short fruit branches and mixed-type shoots - do not cut them too much, otherwise you will be left with a nose next season. When the vine reaches 7-8 years of age, start rejuvenation: gradually replace the old lashes with a new young growth.
- Arguta gives the main crop on shortened generative shoots, so you can apply more intensive pruning to this vine. The arguta skeleton serves throughout the life of the plant, so there is no need to rejuvenate the main lianas of the vine. The exception is mechanical damage and freezing of the sleeve or shoulder.
- You also need to be more careful with pruning the polygamous actinidia: it, like kolomikta, forms fruits both on generative and generative-vegetative shoots.
The following video clearly demonstrates the actinidia pruning process:
As you can see, pruning actinidia is not as difficult as it might seem at first glance.
Pay attention to this event regularly, and your vine will not remain in debt - it will annually delight you with decorativeness and a generous harvest of exotic fruits.