Diseases

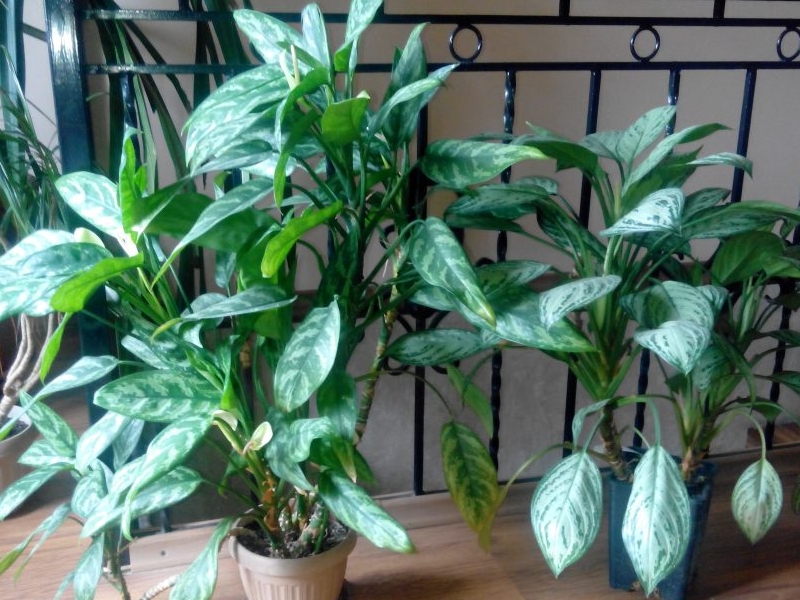
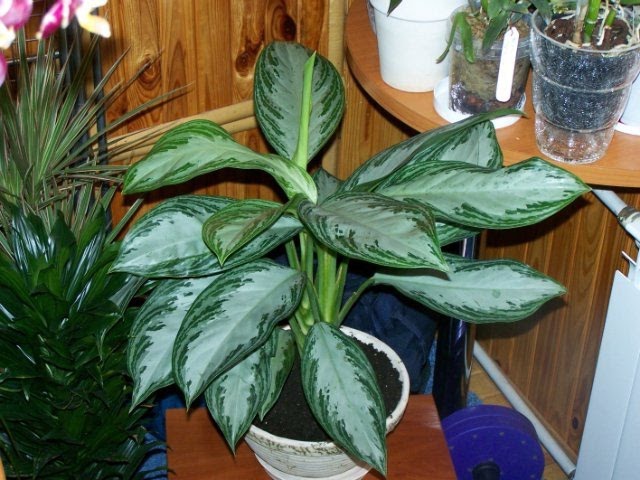
Lush Aglaonema Bushes
Common problems encountered by flower growers when growing aglaonema are discussed in the table.
| Problem | Cause | Elimination |
| Rotting stem | Excessive watering | You can save the plant if you re-root the top |
| Gray spots on the leaves | Fungal infection | Treatment with fungicide is recommended |
| The leaf plates curl and turn black | Low room temperature | Remove damaged leaves and move the plant to warm |
| Dry spots on the leaves | Direct sunlight | Aglaonem needs to shade |
| Slow growth | Lack of nutrition
Tight capacity |
The bush needs to be fed with fertilizer or transplanted |
| Dark spots on the leaves | Hard water containing chlorine was used for irrigation. | You can soften the water by adding citric acid to it, the proportion is 0.2 g per 1 liter |
| Yellowing of the lower leaves | Natural process | You can rejuvenate the plant by re-rooting the crown. |
| Spots on white leaves | Lack of sunlight | The pot with the plant must be rearranged to a more illuminated place. |
Popular aglaonema cultivars are shown in the following video in this article:
Aglaonema is a tropical ornamental deciduous plant that is appreciated for the varied color of the leaf plate. Caring for him is simple and even a novice florist can handle it. For the first acquaintance with this genus, it is better to choose specimens with green foliage, they are considered less demanding.
Aglaonema plant: room culture description
If you read the dry description of the culture in the reference book, it may seem that the plant is unremarkable. Aglaonema has erect stems or stems that lie down as they grow. When the aglaonema plant is young, the stem is almost invisible, then it lengthens, and the leaves on small petioles remain only at its top. Leaf plates, depending on the type and variety, can be variegated, edged or evenly colored. Oval, cordate or pointed leaves are quite dense, with a glossy upper side and a depressed central vein.
If the catchy inflorescence of anthurium became the reason for the appearance of this plant in the collections of indoor crop lovers, then the flowering of aglaonema is sometimes even difficult to notice. At the top or in the axils, peduncles also develop, crowned with medium-sized inflorescences with a white or cream cob and a light or greenish veil.
In nature, the reproduction of aglaonema takes place through root shoots or seeds, and at home, vegetative methods for obtaining new specimens are more often used.
Even at home, aglaonema blooms often and willingly, which distinguishes this culture from a closely related species - Dieffenbachia. It is this plant that resembles aglaonema most of all. But this impression is deceptive and develops only with a superficial acquaintance with the culture.
The main advantage of culture is bright, combining all shades from deep green to carmine foliage. It makes the aglaonema plant a bright decoration of any windowsill all year round, and maintaining its external attractiveness does not require special knowledge and efforts.
Description
Aglaonema (Aglaonema) native to the tropics of East India, as well as the islands of the Malay Archipelago, is related to a plant such as Dieffenbachia and belongs to the Araceae family. This is not to say that aglaonema is a particularly common home plant among flower growers, but in vain, because its appearance and useful properties make it quite attractive.
In the countries of Southeast Asia, Aglaonema was given a proud title - the flower of luck.This is because in 1986 the Malaysian was lucky enough to see the numbers on the foliage of the plant, which he wrote down and bought a lottery ticket with the corresponding number, it was a winning ticket.
Aglaonema is a perennial ornamental plant that grows slowly, producing about 6 new leaves per year and growing no more than 70 cm in height. Stems are fleshy, woody at the base.
The foliage is glossy petiolate with a base wide covering the stem, sometimes lanceolate and oblong up to 15 cm in length. Depending on the species, and there are about 50 of them (there are about 500 hybrids and varieties), the color of the leaf changes, there is one-color, striped and spotted, all species are united by a pronounced core vein on the leaves.
The plant blooms, but rarely, mainly in summer, with proper care, it can release an inflorescence-cob wrapped in a blanket, it is covered with unremarkable small flowers and has no decorative value. The fruits of the plant are bright red berries, they contain a seed that ripens for 8 months, it is suitable for reproduction.
The sap of the plant is poisonous, dangerous for the mucous membrane.
How to care?
Aglaonema is an unpretentious plant, but to create favorable conditions for its cultivation, it should be remembered that this is a shade-loving flower, which means that the conditions must be appropriate.
Illumination
An ideal place for growing aglaonema will be the sill of the east window, where direct sunlight will not fall on it. To grow a flower, you need to provide it with partial shade. If it is not possible to grow aglaonema on the east side, then it is necessary to artificially create partial shade. Direct sunlight will lead to burns and further death of the plant.
Temperature regime
The optimum temperature for growing aglaonema is between 20 and 25 degrees. The plant should be grown indoors without sudden changes in temperature and drafts. For the winter, the temperature can be gradually lowered to 16-18 degrees.
Watering
Water for watering aglaonema should be soft. Watering should be done after the top layer of the soil has dried.
Particular attention should be paid to watering during the growing season (spring, summer). In winter, you can water it a couple of days after the substrate dries.
Air humidity
Air humidity plays an important role in the cultivation of aglaonema, so it must be systematically sprayed with a spray bottle.
Aglaonema soil
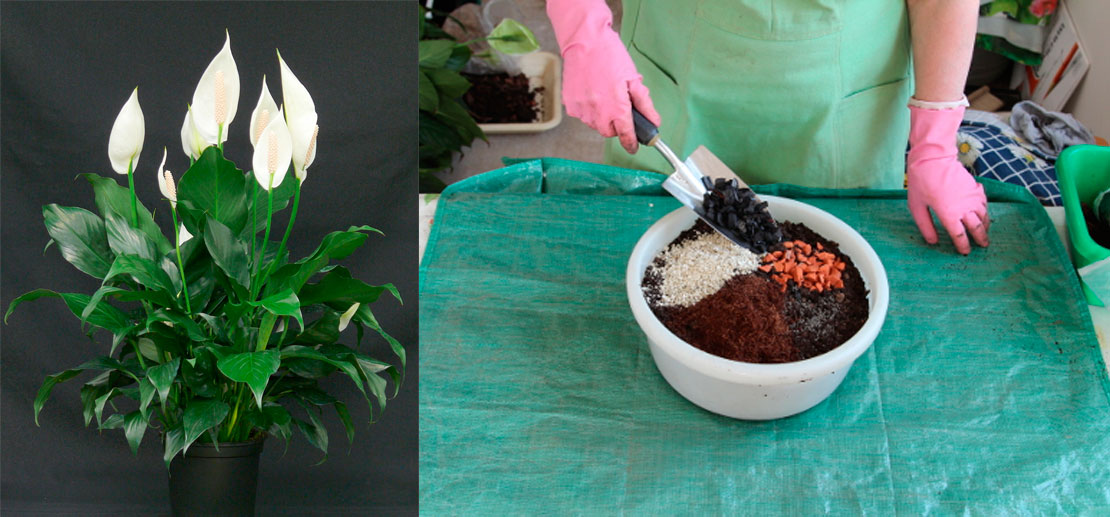
Aglaonema should be planted in a light substrate that conducts air and moisture well. You can buy a ready-made substrate or prepare it yourself. To do this, mix sheet soil, sand, peat in a 3: 1: 1 ratio. Charcoal can be added to the resulting mixture for better drainage.
Aglaneoma Silver Bay, Stripes, short and round
Aglaneoma Silver Bay has an impressive size, it grows more than one meter in height. It has an erect, dark green trunk, which is not visible due to the dense foliage. It is very slowly bare from below, while the plant is constantly branching from the roots. Therefore, Aglaonema Silver Bay retains its splendor and decorative effect for a long time. The attractiveness of this species lies in the fact that it is cold-resistant.
The long leaves of the plant (up to thirty centimeters) are pointed towards the top. In the middle of the leaf plate there is a gray spot with uneven edges. The same small spots are located over the entire surface of the leaves. The main color of young leaves is light green; they darken during growth.
Aglaonema Stripes. The decorativeness of the Strips aglaonema consists in light stripes that run from the center of the leaf to the edge. It gets along well in shaded rooms, for example, on the windows of the north side.
Aglaonema is short-covering. Variety with creeping or underground stems, only oval, highly elongated leaves with sharp tips are visible on the surface.They have a bright green color and a white vein in the center. In order for the plant to have a beautiful decorative appearance, it is necessary to plant several seedlings in one container, since it forms few leaves and has a slow growth.
Aglaonema is round. This species is considered one of the most beautiful of all Aglaonems. On the underground stem, heart-shaped sheets of black and red color are formed, along which a pattern of bright pink stripes diverges.
The subtleties of growing aglaonema at home
At home, different types and varieties of aglaonema feel great, often bloom and bear fruit.
Temperature
Likes moderate temperatures, in summer from +20 to +26 ° C, and in winter from +16 to +20 ° C. Try to avoid sudden changes in temperature. For the summer, it is best to take the plant outside, in a shady place or in a greenhouse. But before that, harden the plant and make sure that there will be no more frost.
She also does not like drafts. The ingress of cold air on the plant in winter is especially ops. The roots can freeze from the cold, and then begin to rot.
Light
They like partial shade or bright, diffused lighting, depending on the species. In nature, Aglaonems grow in the lower tier of the rainforest, where little light falls. Therefore, they all tolerate shading and partial shade well. But variegated species, it is better to place in a well-lit place, without direct sunlight falling on the leaves of the plant. So the color will be as attractive as possible, and from the sun, burns will not appear on the leaves.
- Variegated species like bright lighting, without direct sunlight,
- Solid colored species are best placed in the shade.
Watering and humidity
It is necessary to water with "soft" water - rain, snow or settled water. But do not overdo it with watering, since overflow is just as destructive for Aglaonema as the complete drying out of an earthen coma.
- In the summer, you need to water often and abundantly so that the substrate is always moist.
- In winter, we reduce watering, but make sure that the soil does not dry out.
Loves strong air humidity. Dry air has a bad effect on the development of the plant, the leaves, when unfolding, do not have sufficient moisture and, spinning up, are deformed - they lose their attractive appearance. Also, the edges of the leaves can dry out on the leaves.
- Frequent spraying and showering are beneficial. In winter, spray and bathe preferably with warm water.
- You can also put a bowl of water next to the plant, which will provide additional evaporation of moisture, especially if the plant is on a windowsill or near a radiator.
- Or put the pot itself on a pallet with wet expanded clay, moss or pebbles, while making sure that the pot is not in the water.
Top dressing
It responds well to fertilizing from universal flower fertilizers. Fertilizers need to be applied every 2 weeks from March to August. The rest of the time, the plant begins a dormant period, it slows down in growth and does not need feeding.
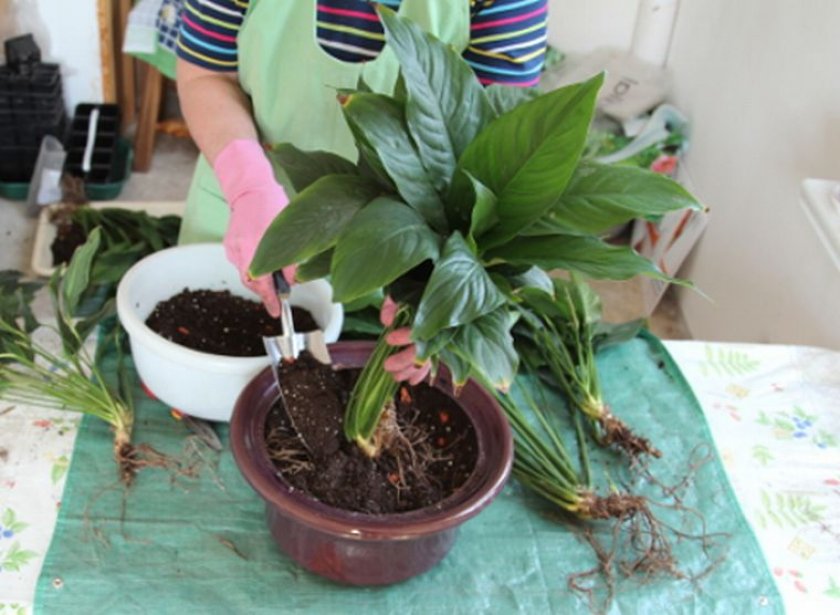
Planting and transplanting
Young plants need to be replanted each spring in a slightly larger pot with a new nutrient medium. So they grow and develop much more actively. Mature plants can be transplanted or reloaded every 2 to 4 years, depending on the need.
The substrate for Aglaonema is easy to make yourself, it must be nutritious and airy and moisture-permeable:
- You need to take 3 parts of leaf or garden soil, 1 part of peat, 1 part of washed river sand and 0.5 part of crushed charcoal. Mix all this thoroughly.
- At the bottom of the pot, be sure to lay drainage, at least 5 cm. Expanded clay, fine gravel, pebbles, foam broken into small pieces can be used as drainage.
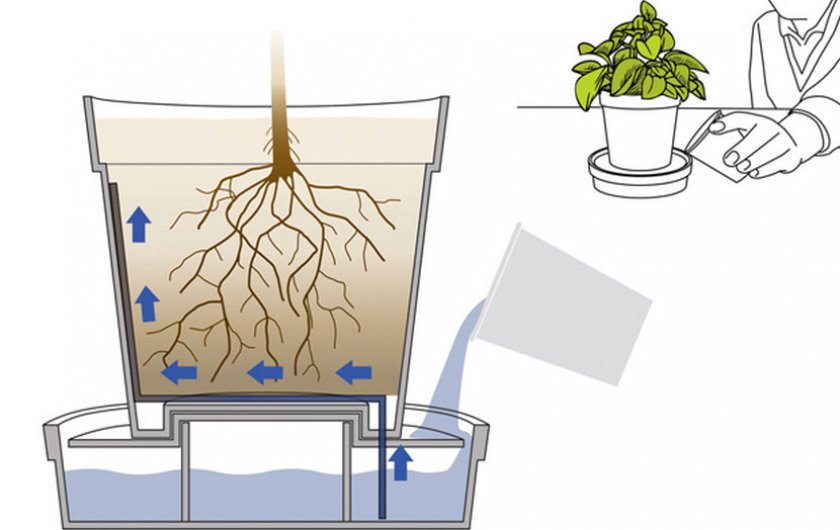
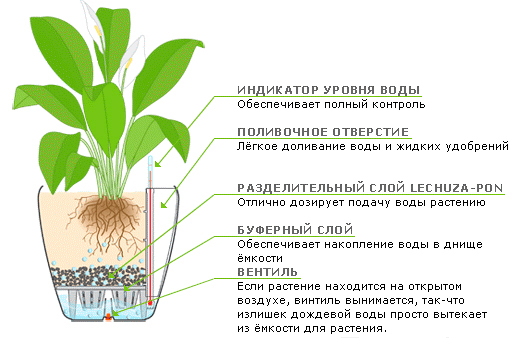
Aglaonema grows very quickly in hydroponics.
Breeding features
The fact that the plant is ready for reproduction is evidenced by the exposure of the trunk and the formation of individual plants in a flowerpot with the mother plant. The process is provided by the following methods.
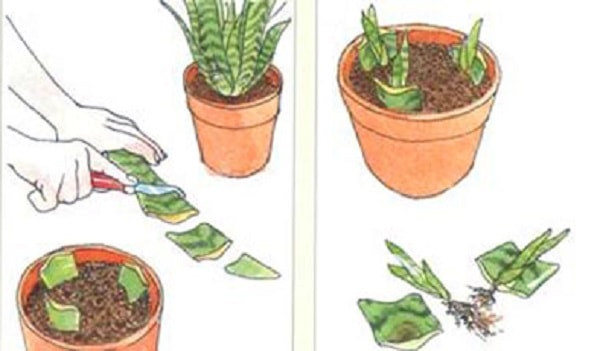
Division of the bush:
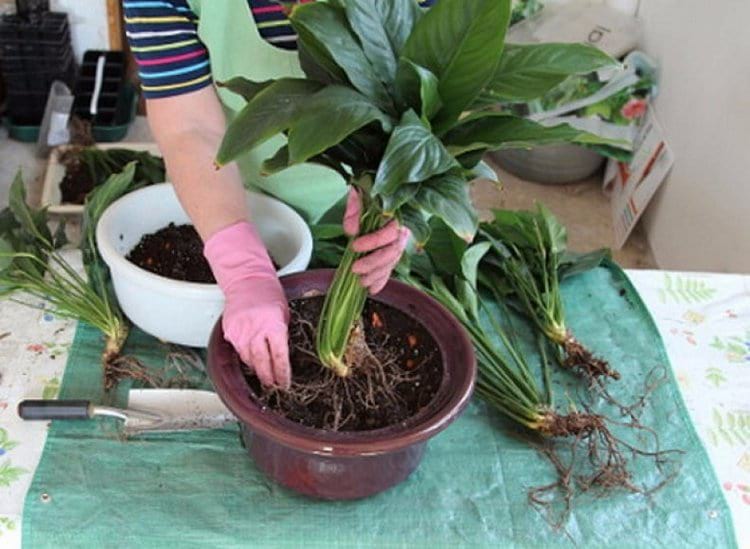
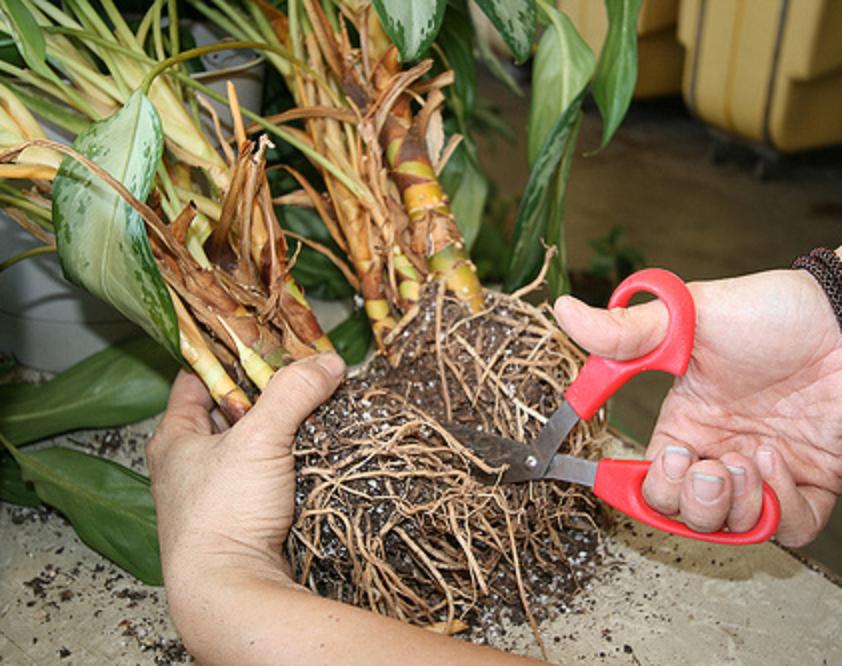
- the plant is taken out of the pot (in spring or summer) and the root system is examined;
- fragments with developed roots are separated from the total mass;
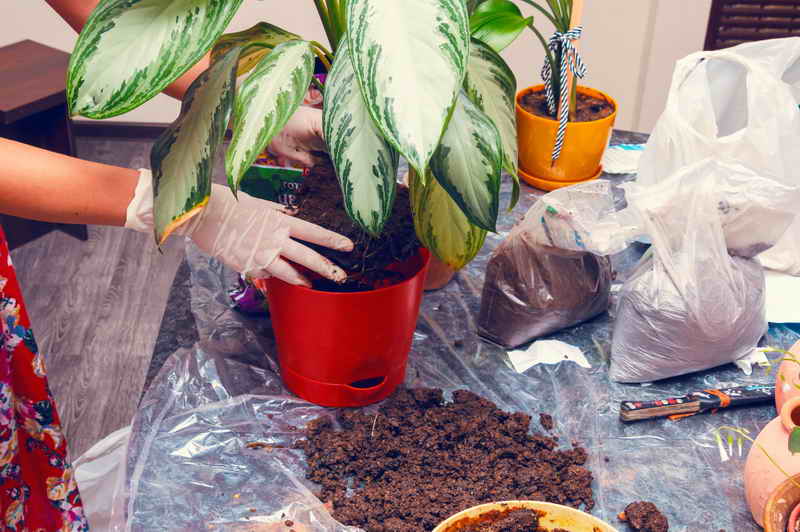
- delenki are planted in separate containers;
- watered and covered with a film, control that it takes root.
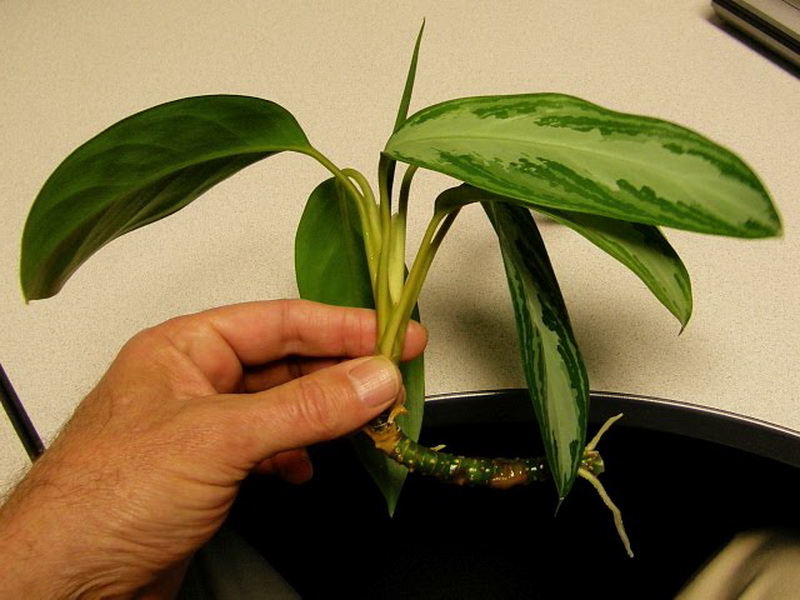
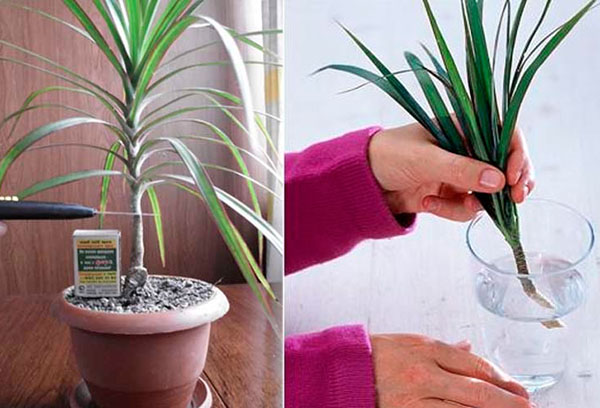
Propagation by cuttings is provided if the trunk of the plant is bare. You need to work according to the following algorithm:
- the apical shoot with a length of 10 cm is cut off, the cut is sprinkled with crushed coal and dried;
- the trunk is immersed 5 cm in the sand;
- covered with a film and kept under it for a month;
- the plant is watered and aired in the greenhouse.
Seed propagation is possible if the plant is self-pollinated and the fruits ripen on it. The seeds are taken out of the fruit, planted in a mixture of sand and peat, sprayed and covered with foil. The first shoots appear after a month, but there is no need to rush. You can transplant them into separate glasses after the formation of 2-3 leaves.
The following video will help you figure out the features of reproduction:
Aglaonema: home care, reproduction
In Europe, the plant began to grow back in 1885, and aglaonema is described in books on floriculture as difficult to care for indoor plants. Further, breeders have bred many unpretentious species, varieties, and now its cultivation has become quite simple.
Lighting
- Aglaonema tolerates shade remarkably, grows well far from the window, but the plant does not like bright light. You can understand whether the Aglaonema likes the place by the leaves, if they are at an angle of 45–90 ° to the stem, then the place is suitable, the lighting is normal. But when the angle is reduced, it means that the plant is hindered by excess light. You can place the aglaonema on the east window with indirect, moderate light.
- Ideal for a plant in the summer from 18 to 25 ° C, in the winter 15 ° C. Cold for aglaonema is destructive, foliage grows poorly, becomes shallow.
Watering and humidity
The frequency of watering depends on the illumination of the room, the less light, the less often watering. With poor lighting, the soil should be allowed to dry out to almost half of the pot, but with good lighting, the earth can dry out by no more than a third. With the correct location of the plant and sufficient light, aglaonema can be watered 2, maximum 3 times a week. It is better to use water that is settled, soft.
At low temperatures, it is advisable to avoid excessive soil moisture, this can lead to root rot. And under normal conditions, the plant is resistant to excess moisture.
This is not to say that aglaonema needs to be provided with additional sources of moisture, but sometimes spraying will not be superfluous, for example, you can carry out the procedure in the summer, twice a week, in the winter spraying can be dangerous.
Soil and fertilizer
- The main requirements for soil for aglaonem are moisture permeability and air permeability. A proven option is sand, leaf earth and peat (1: 2: 1) with the addition of palm fiber and coal (wood). From store options, a mixture for bulbous plants. Drainage is required at the bottom of the pot, the hole for draining excess liquid should not be clogged.
- You can feed aglaonema a little once every three weeks, alternating between organic and mineral liquid fertilizers.
Aglaonema transplant and additional care
- From time to time you can shower the plant, but only in the summer. You should wipe the foliage with a soft sponge and settled water, you do not need to use sprays to make the foliage shine, it can do harm.
- Due to slow growth, the plant does not need transplants, the aglaonema will inform about its need by the fall of the lower foliage and the rapid growth of the top. An emergency case requiring a transplant may be waterlogging, wilting of foliage, decay of the root system.Damaged roots need to be cut off and cut with crushed coal.
When planting, you can deepen the trunk of the plant, this is not dangerous, on the contrary, the growth of adventitious roots is stimulated in this way, which will lead to good branching, and pruning of old leaves has a beneficial effect on the appearance of lateral shoots.
Most suitable growing conditions
When thinking about what conditions are best for Aglaonema, you need to remember that its homeland is rainforest. And since the plant is rather low, it practically does not receive light - the crowns of the trees intertwine, forming a continuous “roof”.
Optimal conditions for growing aglaonema at home - table
| Factor | Optimal conditions |
| Lighting | Aglaonema categorically does not tolerate direct sunlight. Burns appear on the leaves very quickly in the form of dry spots. In the most beautiful ornamental varieties, the bright color fades. But even without the sun, the leaves become shallow and pale. Therefore, the lighting needs diffused (or even partial shade). During the day, the plant needs light for 12-15 hours. If you are unable to provide natural light, use ultraviolet lamps. With a lack of light, the growth of aglaonema is sharply inhibited, the leaves become smaller, turn yellow, the internodes are ugly stretched. Aglaonema can be safely left under the rays of the winter sun - it will not harm her. |
| Location | When choosing a place, be guided by the following rule - the darker the leaves of the aglaonema, the more shade-tolerant this plant is. And vice versa. Best suited for him is the sill of a window facing southwest, southeast, a place next to an indoor fountain or an aquarium. Also, the flower reacts very badly to tobacco smoke. |
| Temperature | In the phase of active growth, the optimum temperature for aglaonema is + 22… + 26 ºС, during the rest period + 15… + 18 ºС. A drop in temperature to + 10 ... + 12 ºС will not survive the flower. But if the air humidity and watering are sufficient, it feels good even at + 30 ... + 35 ºС. At any time, sudden changes in temperature and strong cold drafts are detrimental to the plant. Hot dry air, the source of which is radiators, is no less harmful. |
| Air humidity | Air humidity should be high, at the level of 90–95%. It is almost impossible to create such a microclimate in an apartment, so spray the leaves of aglaonema from a spray bottle every day. In late autumn and winter, spraying is carried out at intervals of 3-4 days. You can also put wet moss, pebbles, peat or expanded clay in the pan of the pot, purchase an air humidifier or put a container with water next to it. A good effect is given by placing the aglaonema in a group of other indoor plants, which, as it were, share moisture with it. The only thing you should not do is pour water directly into the pan of the aglaonema pot. The roots will rot very quickly. In winter, humidity can be reduced to 75–80%. |
Growing aglaonema at home
Light
Aglaonema flowers love diffused sunlight, but some species also love direct sunlight - these are plants with variegated colors.
You can empirically determine whether the lighting is chosen correctly: if the angle of inclination of the leaf in relation to the stem is 45-90, the lighting is normal, if it is below 45, it is worth slightly dimming the brightness.
Temperature
In home care, aglaonema does not require temperature control. This plant is very thermophilic (the birthplace of the tropics), therefore, even in winter, it does not require a decrease in air temperature. The optimal temperature regime in summer is 20-25 ° С, in winter - the air temperature should not drop below 16-18 ° С.
Like most indoor plants, aglaonema does not like drafts, from which it can die.
Watering
Aglaonema is native to humid forests, so a lack of moisture can be detrimental to the plant.In summer, it is advisable to water the flower every three days, but in winter, you should be from frequent watering - once a week is enough. It is better to use water for irrigation at room temperature and previously separated, but in winter cold water can be heated. In addition to watering, the flower must also be sprayed up to twice a week in the summer.
In winter, this process must be carried out with caution in order to avoid rotting of the root system.
For fast growth and beautiful appearance of Aglaonema foliage, the regime of proper watering and feeding plays an important role.
Air humidity
To create conditions close to the natural habitat of a flower, it is necessary to adhere to a humidity of 50-60%
It is very important in winter to protect the flower from the hot dry air that comes from the batteries. To do this, you can hang a damp towel on them or put a flower pot on a wide tray and pour water into it.
Spraying is carried out regularly, leaves are wiped from dust. Aglaonema does not tolerate spraying with special products designed to give shine.
Top dressing
During the period of active growth - from early spring to late summer - top dressing should be done 2 times a month. Mineral fertilizers should be alternated with organic fertilizers. In the fall, when growth slows down in aglaonema, the feeding is reduced. In winter, the plant does not need fertilizer.
Pruning, garter
Aglaonema are compact ornamental shrubs, but over the years they develop a tall stem, and the plant requires a garter to strengthen and prevent the stem from kinking. If you do not regularly prune old shoots, it may lose its decorative appearance, and simply stretch up to 1 m. The pruning sites must be treated with crushed activated carbon.
Transfer
Young aglaonema plants need to be replanted every spring, and mature plants as needed after 4-5 years.
Reproduction
There are three ways to reproduce Aglaonema:
- seeds
- cuttings
- division
For propagation by seeds, it is necessary to choose ripe berries, they are characterized by a bright red color, and with slight pressure, the seeds immediately remain in the hand
It is important to remember that seeds are extremely poisonous. Seeds need to be planted immediately, since over time their germination rate decreases.It is necessary to plant them in February-March in light soil, watered, wrap the pot with a film and leave in a warm place
After the seeds germinate, they must be transplanted - each boring in a separate pot. With the help of seeds, you can get a large number of plants, but they grow very slowly, and do not always look like the plants from which the seeds were collected.
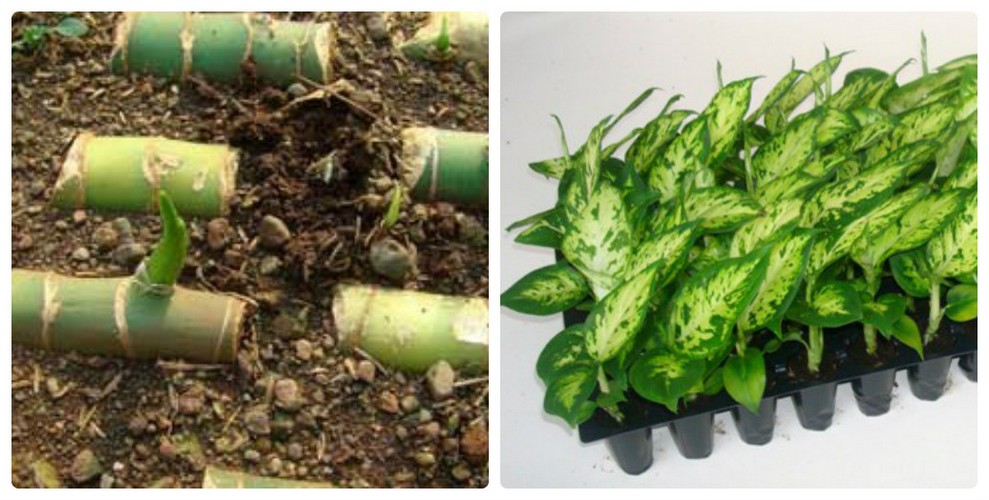
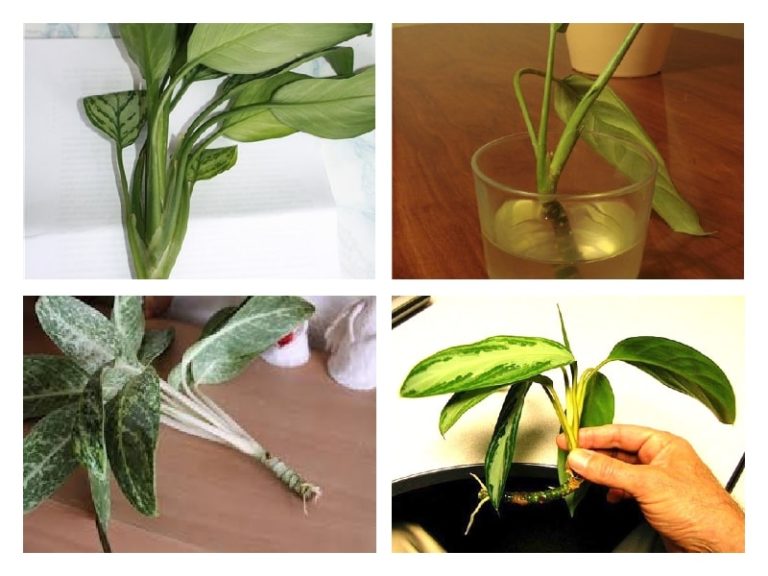
When propagating by cuttings, sections of the trunk or lateral shoots from old plants are used. The cuttings must first be rooted, for this they are dipped into water or into a layer of moss or sand. In any case, the stalk must be kept warm until the roots appear. Cuttings with leaves take root faster.
Division is the fastest and easiest way to reproduce. In the spring (May), young shoots with an already formed root system are separated from the total mass.
Aglaonema bloom
Aglaonema blooms very rarely and special care is needed for it to bloom. The flowers are small and represent an ear, which is shrouded from above with a green or white "blanket". Ripening of berries takes 2 months.
Caring for the agla mute at home
Temperature
Aglaonema prefers a warm and humid climate with a minimum temperature of 18 ° C. The optimal mode is from 22-23 ° to 27 ° C. Drafts are not allowed.
Lighting
Recommendations on the topic of how to properly care for aglaonema depend on the color of the plant:
- For a culture with a variegated color in yellow and red tones, diffused lighting or partial shade is recommended during the day, in the evening or in the cold season - maximum light.
- For green leaves, diffused light / shadow is desirable.
Watering
Aglaonema prefers moderate watering with a slightly dried earthy coma. Water to moisten the soil is used at room temperature. The approximate watering regime is every 3-4 days.
Spraying
It is allowed to spray the leaves with distilled or rainwater in summer and autumn, if the plant is properly cared for. Otherwise, spraying is prohibited.
Humidity
To maintain its decorative properties, aglaonema is kept in high humidity conditions. Average humidity is acceptable, but the plant will begin to lose its appearance.
The soil
Soil for aglaonema should be good for air and moisture. The proper conditions will be provided by leafy soil mixed with coal, peat, humus or sand. If it is not possible to make the substrate yourself, you can use a ready-made mixture intended for heather, azalea, violets.
Aglaonema care and maintenance
Top dressing
Aglaonema does not tolerate lime dressings, the plant is fertilized with a complex of minerals based on potassium, phosphorus, nitrogen, trace elements.
The following feeding options are most acceptable:
- One tablespoon of Agricola and Effekton is diluted in a three-liter container.
- One teaspoon of Agricola and a tablespoon of Fantasia per bottle of water.
- A tablespoon of "Lignohumate" and 1 teaspoon of "Leaf" for 3 liters of water.
Fertilize the plant from March to September after watering, in the cool part of the day - the measure allows you to prevent burns of the plant. Frequency - 2 times a month.
In winter
During the dormant period (September-February), it is important for aglaonema to maintain a temperature regime of 16 ... 18 ° C, stable watering. The plant is not fed in winter
Pruning
Aglaonema does not need pruning. As the flower grows, the stems become bare. If you cut off the top and process the cut with crushed charcoal or activated carbon, the plant will begin to actively branch. You do not need to throw out the stalk, it is better to root the sprout.
Popular varieties with different leaf colors
In greenhouses and houses in Europe, this plant appeared in 1885. Floriculture books of those times described the complexities of keeping the plant - it required high humidity and regular spraying. But the interest in Aglaonema was so great that a large number of unpretentious hybrid varieties were subsequently bred.
The Silver Queen. One of the most common aglaonema hybrids, it was bred in the 60s of the XX century. The length of the leaves reaches 15 cm, and the width is 8 cm.The color of the leaves is smoky-silver with a few green blotches. Very unpretentious in care, prefers partial shade. The bush usually reaches 70–80 cm in height.
Silver king. It is just as unpretentious in care as the variety described above, but shorter. The color of the leaves and cuttings is silvery-gray.
Crete. The cultivar belongs to the group of red aglaonems. The plant is slow-growing. The color of the leaves changes with age. If young leaves are completely red in color, then as they grow, spots appear on them, in color from rich green to olive. This variety is very picky about lighting. In a darkened room, the leaves lose their bright color and glossy shine. It reaches a height of 30–40 cm.
Aglaonema is humble. The variety has good shade tolerance. The leaves are rich green, about 20 cm long.The plant reaches a height of 50 cm.
Treiba. It is considered the most unpretentious variety. A short bush with narrow leaves about 15 cm long, covered with a silvery-green pattern.
Maria. The most popular aglaonema variety, which is more than 50 years old. A very shade-tolerant plant, it can grow even in rooms with artificial lighting. The lush bush reaches a height of 50 cm. The leaves are elliptical, green with silvery spots.
Aglaonema curly. It is a large - up to 120 cm in height - plant with an upright stem.The leaf plate is semicircular, up to 30 cm in length and 16 in width. The color of the leaves is silvery-matte, with the exception of the middle and edge of the leaf plate.
Siam Aurora. Another representative of the red group. Unpretentious, growing quickly. With additional lighting, the leaves are brightly colored. In the sun it "fades": the reds darken, and the greens acquire a yellow color.
Origin and appearance of aglaonema
Aglaonema is a perennial plant from Southeast Asia, it belongs to the genus of evergreen grasses and shrubs of the aroid family. Aglaonema is widespread in India, China, Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, Malaysia.
In nature, the habitat of aglaonema is tropical and deciduous forests, humid plains, river banks and swampy peat deposits. Aglaonema is very hardy, able to grow on poor soils, and tolerate a lack of lighting. Due to these qualities, Aglaonema is considered an ideal plant for growing at home and in the office.
Features of the maintenance and care of the aglaonema
Like all rainforest plants, aglaonems need warmth and humidity, they do not like cold drafts and scorching sun rays.
Lighting. Aglaonems with green leaves are not demanding on lighting. They can grow anywhere. Variegated forms need bright, diffused light. Aglaonema cannot tolerate direct sunlight, which causes leaf burns.
Temperature. In winter, the temperature should not drop below + 16 ° С, and drafts are completely unacceptable. The optimum temperature for growth is 20-25 ° C. Drafts, sharp temperature fluctuations are unacceptable for aglaonema.
Air humidity. Aglaonema prefers high humidity. In the summer, it is advisable to spray daily. It is necessary to regularly clean the leaves from dust. Do not cover the leaves with a gloss solution.
Watering. In nature, aglaonema receives daily abundant watering, but it grows in soil that is well permeable to moisture and air. During the growing season, the plant is watered abundantly, in autumn and winter watering is reduced, overdrying the earthen coma is dangerous for aglaonema. You should also avoid pouring aglaonema in the cool season.
Fertilizer During the period of active growth, aglaonema is often fed with liquid mineral fertilizer 2 times a month. Do not feed in winter.
Transfer. The plant grows slowly, so young plants are transplanted every year in the spring, then once every 3-5 years or less. Aglaonema gives good growth of leaves when its roots are limited by the small volume of the pot. There must be good drainage.
The soil. The soil for aglaonema should be light and loose, and water permeable. The mixture is made up of leaf earth, peat and sand (2: 1: 1) with the addition of crushed charcoal. You can also have the following composition: 1 part of peat, 1 part of leafy soil, 1 part of light turf soil and 2 parts of sand. Grows well in hydroponics.
How to propagate a plant
In the conditions of an apartment, flower growers practice several simple and effective methods of breeding a tropical beauty: dividing a bush, cutting and propagating by seeds.
Video: Aglaonema breeding methods
Division of the bush. The easiest and least time consuming breeding method, which is performed according to the following algorithm:
- The plant is removed from the pot and the soil is cleaned from the root system.
- Very carefully, by means of a well-sharpened, disinfected knife or secateurs, the shoots, along with the root processes, are separated from the adult flower.
- The seedlings are planted in a separate container with a nutritious substrate and covered with plastic wrap.
- The temperature in the room is maintained within the range of + 22 ... + 25 ° C, dim lighting, regular humidification and spraying are provided.
Important! The first days of May are considered the optimal time for the reproduction of aglaonema by dividing the bush. Cuttings
It is considered one of the most common methods of exotic breeding.It is as follows:
Cuttings. It is considered one of the most common methods of exotic breeding. It is as follows:
- In an adult flower, the top of the stem is cut off, the cut sites are treated with activated carbon.
- The top is cut into several pieces of 8-9 cm so that each of them has several full sheets.
- Cuttings are planted to a depth of 5 cm in a moist substrate of equal parts of peat and sand.
- The container with seedlings is covered with a film or a plastic bottle.
- After 3-4 weeks, when the cuttings take root, the shelter is removed.

Seeds. The cultivation of perennials by the seed method is considered the most time consuming and least effective, since it requires certain conditions and time. Seed material for planting can be bought in specialized markets or collected independently from a home plant. Seed germination is quite high, but they quickly lose quality during storage, which is why experts advise sowing fresh seeds as early as possible.
For this:

- The grains are washed well with warm water.
- The seeds are sown in a mixture of peat and sand, mixed in equal proportions, deepening each grain by 2 cm.
- The seeds are covered with a substrate, the surface is moistened with a spray bottle, covered with glass or plastic wrap.
- The container with crops is placed in a warm place with stable temperature indicators of + 25 ° C.
When the first shoots appear, the shelter should be removed, and the seedlings should be provided with traditional care.