Content
- 1 Brief description of the variety
- 2 The nutritional value
- 3 Requirements for soil and crop rotation
- 4 The risk of over-pollination
- 5 Agrotechnics of gymnosperms
- 6 Storage
- 7 Some gymnosperms
- 8 Characteristics and description of the variety
- 9 Features of agricultural technology gymnospermous pumpkin
- 10 Gymnospermous pumpkin varieties
The pumpkin in our country is known to everyone. Even as a child, her seeds were a favorite delicacy for many. And now the "fashionable" variety is gaining popularity - the gymnosperm pumpkin, known in Russia since 1911. But everything new, as often happens, is a long forgotten old. Now the seeds do not need to be sanded, although that was the beauty of it. Well, progress does not sleep - Israel created naked chickens so as not to pluck, but here are seeds without husks.
Brief characteristic of the variety
A hard pumpkin is the same gymnosperm. Planting and caring for them are the same, the requirements for soil substrates, as well as all agricultural techniques are similar, the only difference is that gymnosperms are more thermophilic. But this is one kind, so it is easy to confuse them outwardly. Accordingly, their cultivation technology does not differ significantly. This is the same plant, with a hollow, wicker-like stem, up to 5–12 meters long, with a very powerful root system characteristic of a dry climate, spreading in volume, sometimes over 3–5 m³. It grows very quickly - some varieties cover an area of up to 32 m in 3-4 months.
Gymnosperm pumpkin is more sensitive to planting time, since the optimum soil temperature for germination is not lower than 14–16 ° C, while for ordinary pumpkin it is 11–12 ° C. This is due to the fact that the embryo without shell protection at low temperatures quickly rots, so it makes sense to grow this culture through seedlings.
Depending on the variety, up to 80 female and over 400 male flowers can form on the plant. Seedlings 20–30 days old already give the first male flowers, and a week later female flowers also bloom with a small scatter. They appear on 3–11 leaf nodes, while the lower the first female flower, the more early ripening the variety. It is worth noting that gymnosperms have a slightly larger bud size.
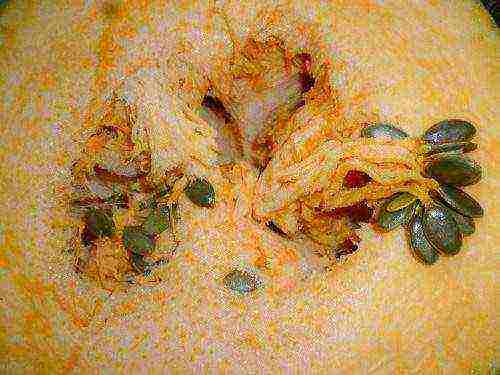
The fruits of gymnosperms usually do not reach the grandiose size of an ordinary pumpkin. They usually weigh 5–8 kg, rarely up to 16 kg, round in shape with a hard but thin crust, yellow with green unsaturated stripes.
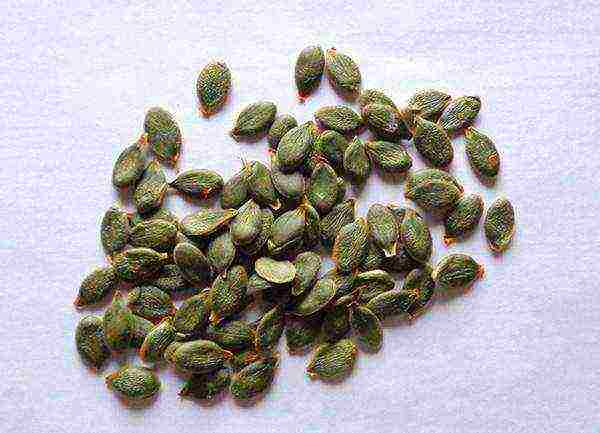

Danae gymnospermous pumpkin seeds
The nutritional value
In terms of nutritional quality, the pulp of gymnospermous and ordinary pumpkin differs little, since initially the first variety is technical varieties intended for extracting oil from seeds. However, some of them have pronounced taste differences from all others. For example, such sweet varieties as Apricot Pumpkin and Belorusskaya Gossemyannaya, which contain up to 5–8% sugar. As a standard, the pulp is used for making mashed potatoes, juices, for filling pies, as a component of rice, millet and other cereals.
But the main value of these varieties is seeds. The production of seeds without a shell is the main direction of breeding. They are used fresh or processed. Crushed roasted sunflower seeds are used as a condiment for confectionery. Flour from them goes great with salads and various sauces along with garlic, parsley, cilantro, dill and olive oil.

Ground roasted pumpkin seeds give dishes an unusual, original taste that can delight any gourmet.Porridge, homemade cakes and even a sandwich sprinkled with this powder will be a completely new dish for you.
Due to the fact that pumpkin seeds contain vitamins A and E (tocopherols), which work as antioxidants, they can be considered anti-aging. Up to 55% oil in their composition made it possible to classify gymnospermous pumpkin as an oil plant. Due to its optimal, balanced composition of fatty acids, it is a very valuable product.
Pumpkin seeds are used by traditional medicine, most of which are officially accepted. Their use is recommended as an additional remedy in the treatment of many diseases. Confirmation of the recognition of their beneficial properties is the drug "Tykveol", which has been in constant demand for a long time.
Requirements for soil and crop rotation
Like any pumpkin variety, the gymnosperm is the same thermophilic plant of a short subtropical day. Our latitudes are not too generous with sunny weather, therefore, well-warmed, sheltered from the wind areas, preferably on the southern slopes of the hills, are allocated for this culture.
Soils are required well aerated, rich in organic matter, humus, not lower than slightly acidic (pH 6.5 to 7.5). More acidic ones inhibit the development of plants. Pumpkin is very nutritious. According to research, the plant consumes 4.5 kg of potassium, 2.7 kg of nitrogen and 1.2 kg of phosphorus from the soil per ton of fruit, with a utilization rate of 50, 50 and 40%, respectively. Of course, such losses cannot be replenished with organic matter alone, so you should take care of a normal crop rotation, as well as regular feeding.
The most successful precursors to pumpkin can be potatoes, corn, cabbage, onions, carrots, beets, and a variety of spicy greens. Re-sowing the site with a similar crop, such as cucumbers, squash, zucchini, watermelons, is permissible no earlier than after 4 years. There are two reasons for this: pests and diseases common to all melons can remain from the last season, as well as a strong depletion of the land that requires replenishment.
The risk of over-pollination
And an important feature that gymnosperm pumpkin has - growing in order to get seeds from it is a very troublesome business. Since plants are pollinated by insects, the "range" of which is quite long, it is very important to know for sure that there are no closely related crops nearby, such as common pumpkin, squash or squash. Pollination from them will lead to the fact that the resulting pumpkin seeds for the next year will already have a shell, like an ordinary hard bark, and the fruit itself may be of a completely incomprehensible variety. Unfortunately, it will be possible to reliably learn about cross-pollination only a year after the harvest ripens.
Artificial pollination is more reliable, for example, using a brush, taking pollen from male flowers. It is advisable after that, so that pollinating insects do not penetrate the stigma of the pollinated flower, pull off its corolla with a soft rubber band or protect it with a plastic bag. To ensure pollination, this procedure should be repeated with each flower several times. In addition to obtaining good quality seeds, this method also allows you to increase the yield of fruits.
Agrotechnics of gymnosperms
If you want to use seeds of your own cultivation, then they need to be taken from fully ripe fruits. It is better to store in paper bags, but before that they should be rinsed and dried well. Sown seeds usually hatch after 5-8 days. Seedlings do not tolerate droughts, therefore irrigation of the site should be provided. The planting depth on irrigated lands is 5–6 cm. The planting pattern of bush varieties is 70x70 cm, medium-growing varieties - 70x140 cm, and large-growing ones - (180-210) x (100-180) cm.
Before planting, the seeds should be warmed up for 8-10 hours at a temperature of +40 ° C, then soaked for 12 hours in a solution of germination stimulants, for example, "Mitsefit" or "Vympel", in any available way (bobbiner, vermiculite).Sowing should only be done when stable warm weather has already been established without the risk of unexpected frosts.
For planting, a hole with a diameter of 30–40 cm is prepared, for which the top dry layer is removed from the prepared soil, and 1–2 liters of warm water are poured into the depression. 5-8 kg of humus, 75 grams of superphosphate, as well as a glass of ash or half a glass of potassium sulfate are placed there. All this is thoroughly mixed with soil to a depth of 15–20 cm, then 3-4 pumpkin seeds are planted into the resulting substrate with a distance of 3-4 cm to a depth of 5–6 cm, covered with soil, and mulched with humus or peat on top. After the seedlings hatch, leave a maximum of two of the strongest plants per hole.
Growing through seedlings
The need for later planting is the feature that distinguishes gymnosperm pumpkin. Growing it through seedlings makes it possible to neutralize this feature. This is the method recommended by seed producers as well, as it maximizes yields.
When planting seedlings, the timing should be calculated so that 3-4 weeks pass from the moment the seeds ripen to transfer to the open ground in steady weather without probable frost. The second, the control criterion, is that the seedlings reach a height of 15–22 cm, or the presence of at least two true leaves.
Since all melons do not tolerate transplanting well, it is reasonable to do without it by using peat pots measuring 8x8 or 10x10 cm. It is better to use a store-bought potting soil mixture for cucumbers as a soil. For self-preparation, you can use the following composition: a 2: 1: 1 ratio of peat, rotted sawdust and humus, respectively, as well as a teaspoon of Kemira Lux or Nitrofoski per kilogram of the mixture. You can add 1 part vermiculite. Mix all this thoroughly.
The optimum temperature for seedling growth is + 22-25 ° C with daily light for at least 12 hours. Immediately after the cotyledon leaves open, the plant needs to be fed. Quite good fertilizers for this "Ekofoska", "Uniflor Rost" or "Kemira Lux", dissolving them according to the recommendations on the label. Microfertilizers are not needed if you use ready-made cucumber soil mixture. It should be fed at intervals of 7-10 days, or 2-3 times for the entire seedling period. Before planting in open ground, the seedlings are hardened by airing or taking them to fresh air.
Before planting seedlings or seeds on the garden bed, the soil should be loosened to a depth of 6–7 cm and cleared of weeds. Seedlings should be watered daily until they take root. The soil in the bed must be constantly loosened to a depth of 6–8 cm in the holes around the plant, and 12–18 cm in the aisles, slightly huddling the stems, preventing the appearance of a hard crust on the surface. The soil should always be slightly moist, but not waterlogged.

Seedlings of gymnospermous pumpkin of the Styrian variety
It is advisable to do the first feeding within 7–10 days after planting the seedlings. As a fertilizer, diluted chicken manure (1:20), cow dung (1:10) or weed infusion (1: 5) are quite suitable. But one cannot do with organic matter when growing pumpkin. To any of these solutions, you need to add 45 ml (3 tablespoons) "Azofoski", 30 g of potassium sulfate, as well as, preferably, micronutrient fertilizer "Uniflor-micro". This mixture can be fed to the plant weekly at 1 liter per well. Be sure to feed after the appearance of two or three leaves, during flowering, and during fruiting, the amount of "Azofoska" is desirable to increase to 60 ml.
In the middle of summer, lateral shoots grow from the main lash, but it is better to pinch them. The roots formed in the nodes are lightly sprinkled with earth. When the ovaries begin to form, you can put grass or a piece of plywood under them so that they do not rot. When the required number of fruits is formed - for gymnosperms it is from 1 to 7 pieces, you should also pinch the main stem.
A sign of ripening - the stalk, leaves and shoots dry out, the pumpkin fruit acquires a color characteristic of the variety. Before the onset of frost, all of them must be removed by cutting them together with the stalk.
Storage
Dried and washed from the soil, the fruits are stored in a dry place until November - this is no more than 2 months from the date of harvest. Then they begin to dry out or even rot, and the seeds germinate inside, becoming unsuitable for consumption or as planting material. The mildest varieties, for example, Styrian pumpkin, can be stored for up to 3 months.
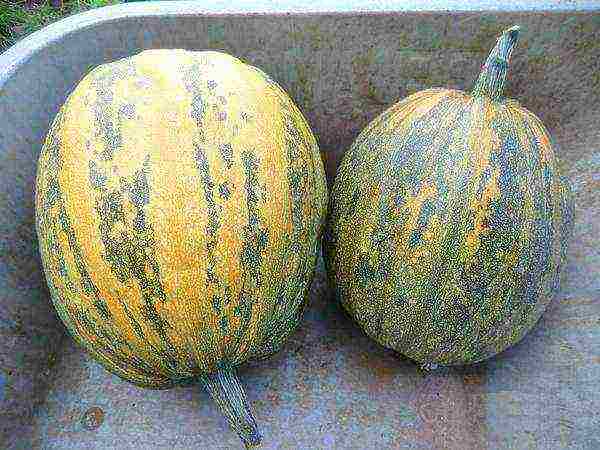

Styrian gymnospermous gourd harvest
A dark ventilated cellar with a humidity of 75–80% at a temperature of + 3–15 ° C can be considered the best place to store pumpkin. For the same purposes, you can adapt a closed loggia, garage, attic, shed with similar conditions.
Storing the pumpkin on the ground is not allowed. You need to lay the fruits on pallets, racks or shelves with the stalks up, and so that they do not touch each other. It is convenient to transfer them with dry hay or straw. During storage, the sun's rays should not fall on their surface.
Fruits showing signs of damage or decay cannot be stored. It is better to process them right away, and the excess can be kept in the freezer for a long time. The sequence of fruit disposal depends on the length of the stalk - first use the shortest one.
Some gymnosperms
All varieties of gymnospermous pumpkin were created primarily to facilitate the production of oil from seeds. The benefits of this are obvious. One of the most expensive technological processes of raw material purification is excluded, the oil yield increases. And varieties with different tastes of pulp were then bred purely out of gastronomic interests. It is used mainly for making juice, cooking, stewing, as well as fresh:
"Golosemyanka" - This is probably the same variety thanks to which the Russians learned about the existence of pumpkin varieties capable of producing seeds without a peel.
Description of the variety: ripens in 105-115 days. Strongly branched medium-growing, stem length 3-5 m, fruits slightly flattened, rounded, weight 3-4 kg, yield per bush 9-12 kg, resistant to low temperatures. Produces a lot of seeds. The planting pattern is 100x70 cm. The pulp is rather thin, not very sweet.
Pumpkin "Danae" gymnospermous - one of the most popular varieties of the middle lane.
Description of the variety: ripens in 120 days. Strongly branched, medium-sized, round fruits, average weight 5–7 kg, planting pattern not less than 100x100 cm, flesh is not very sweet, thin. Pumpkin variety "Danae" is an industrial crop used for oil production. It should be borne in mind that the pumpkin "Danae" gymnospermous was bred in Rostov for cultivation in the south of Russia.
Apricot pumpkin - was once quite popular, although few people knew about it. Due to its specific taste, strongly reminiscent of apricot, on the basis of its juice, "apricot juice" was made, which was sold throughout the USSR. The recipe is simple - they mixed mashed dried apricots with the juice of this pumpkin.
Description of the variety: ripens in 100–105 days, the fruit is slightly ribbed oval, the planting pattern is 100x100, the pulp is thick, slightly fibrous, light yellow sweet. It is considered a dessert variety.
"Olga" - gymnospermous pumpkin... Description of the variety: Ripens in 105-115 days, the stem is medium-growing, the fruit is round, weight is 4-6 kg, it gives a lot of seeds with a high oil content, the planting pattern is 150x150, the pulp is light, medium sweetness, relatively thick. Growing seedlings is recommended, with planting at 30 days of age.
There are two varieties on sale with this name. Simply pumpkin "Olga" is a small-fruited portioned table variety with an average weight of 0.7-1 kg and ordinary, skinned seeds, as well as a gymnosperm pumpkin "Olga", which sometimes causes confusion.
Eso pumpkin seeds are produced by the Czech company SEMO, which serves mainly Eastern Europe.Their products are distinguished by high germination and high-quality seed preparation, meeting all the requirements of European standards. However, it is worth noting that along with guaranteed germination and high quality, almost all of their products are not zoned for central Russia.
Description of the variety: "Eso" pumpkin fruits ripen in 100-110 days. It is a climbing plant that yields a large amount of seeds for processing into oil. The pulp is not very sweet, it is grown mainly for the seeds.
Pumpkin "Juno". Description of the variety: ripens in 100-110 days, climbing plant, the fruit has a soft skin, weight 4-6 kg, gives a large number of large black seeds. The pulp is not very sweet. The main nutritional value is represented by seeds.
Styrian gymnospermous pumpkin (Austria)... Despite the demanding temperature, it is successfully grown in our country. She was awarded gold, silver and bronze medals at various competitions in many countries, including Russia. It comes from the Austrian province of Styria, famous for its pumpkin seed oil with a pronounced nutty taste and smell, which is highly appreciated by culinary experts.
Description of the variety: ripens in 100–120 days, long-leaved plant, fruit weighing 4–8 kg, yields a large number of seeds, intended for processing for oil, planting pattern 150x150 cm. Fresh fruits can be stored for more than 3 months. The pulp is neutral or sweetish, grown from the seeds.
In this video you can see what the fruit of the pumpkin "Golosemyanka" looks like and its seeds without a peel:
How to grow gymnospermous pumpkin, popular varieties
4.6
(92%) voted
5
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the description of the most popular pumpkin varieties. Probably, there are no summer cottages in Russia, wherever the pumpkin grows. Its history goes back many centuries. It is known that pumpkin was used by the inhabitants of the Mayan tribe, knowing about its healing properties. This vegetable has a great advantage among all the others - it can be stored for a long time, and you can eat not only juicy pulp, but also the most useful seed for food.
Content:
General information and classification 
Decorative varieties
The pumpkin family includes 27 species. A huge number of varieties have been bred from each.
In our country, 3 types of pumpkin are most often grown:
- large-fruited
- nutmeg
- ambulance
By purpose, pumpkins are divided into:
- table varieties
- fodder
- decorative
We will describe different varieties for cultivation in different regions of Russia, taste, etc.
back to menu ↑ Butternut pumpkin 
Butternut squash
back to menu ↑ Spanish guitar 
Spanish guitar
back to menu ↑ Candied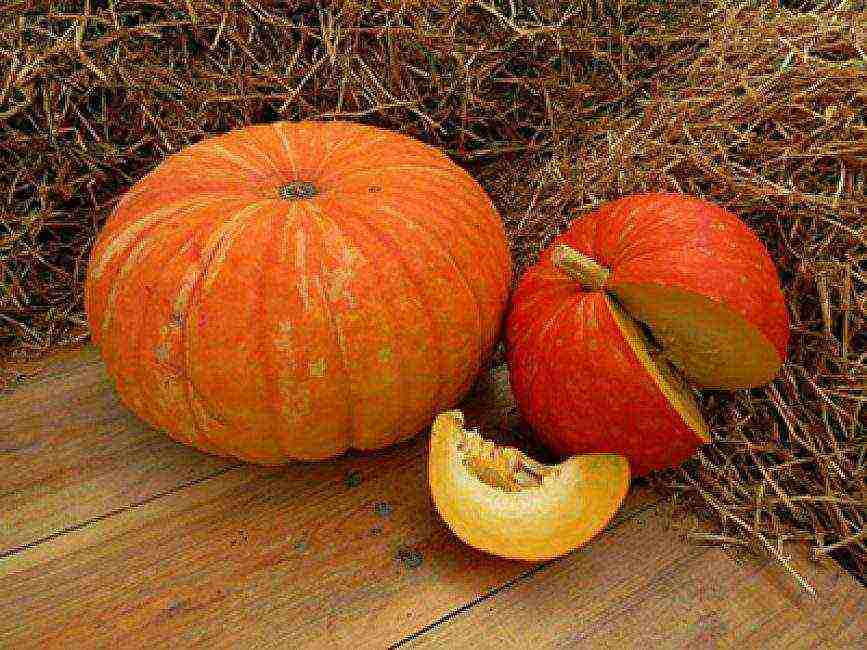 
Candied
back to menu ↑ Vitamin 
Vitamin
back to menu ↑ Marble 
Marble
back to menu ↑ Muscat de Provence 
Muscat de provence
back to menu ↑ Nut 
Nut
back to menu ↑ Varieties with large fruits 
Harvested crop
back to menu ↑ Pumpkin lantern 
Pumpkin lantern
back to menu ↑ Russian porridge 
Russian porridge
back to menu ↑ Varieties of hard-barked pumpkin 
Zucchini, squash also belong to this group.
back to menu ↑ Bun 
Bun
back to menu ↑ Gymnosperms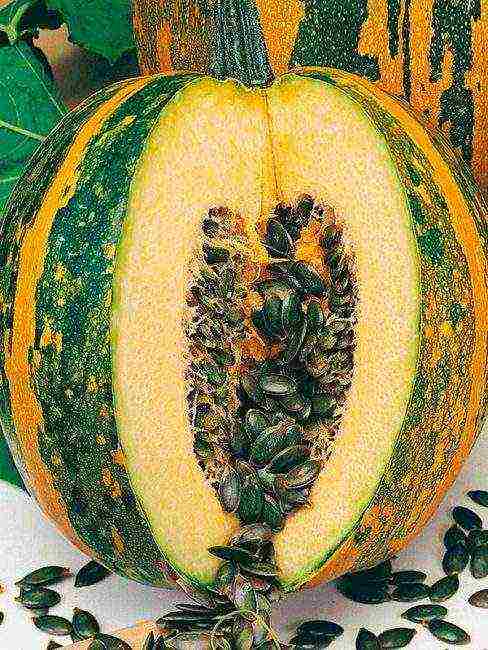 
Gymnosperms
The most famous varieties of gymnosperm pumpkin:
- Danae
- Olga
- Miranda
- Hamlet
- Gymnosperm 14
back to menu ↑ Varieties for Moscow region 
Moscow suburbs
back to menu ↑ Baby 
Chit
back to menu ↑ Sweet cake 
Sweet pie
back to menu ↑ Melon 
Melon
back to menu ↑ Champagne pastille 
Champagne pastille
back to menu ↑ Zorka 
Dawn
The variety is considered resistant to various diseases:
- fusarium
- anthracnose
- powdery mildew
- rot
back to menu ↑ Almond 
Almond
back to menu ↑ Russian woman 
Russian woman
back to menu ↑ Varieties for Siberia, Urals 
Siberian winter
Let's consider some varieties suitable for these regions of the country:
back to menu ↑ Medical 
Therapeutic
The plant is not resistant to:
- decay
- anthroknose
- powdery mildew
back to menu ↑ Pearl 
Pearl
back to menu ↑ Smile 
Smile
Also in the Urals, Siberia, you can grow varieties:
- vitamin
- Russian woman
- sweetie
- marble
- almond
- winter dining room, etc.
back to menu ↑ Sweet varieties 
Baked Sweet Pumpkin
Consider some of the varieties included in this group:
back to menu ↑ Winter sweet 
Winter sweet
The variety is considered:
- transportable
- drought tolerant
- suitable for long-term storage - up to 1 year
- resistant to the most famous diseases of pumpkin seeds - anthracnose, powdery mildew
back to menu ↑ Sweetheart 
Sweetheart
back to menu ↑ Gray Volzhskaya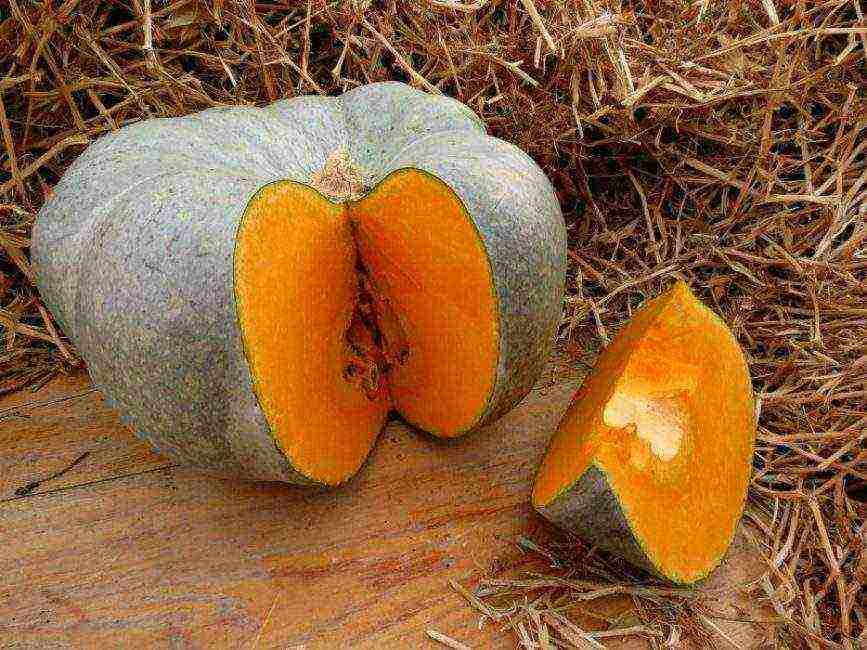 
Gray Volga
The seed nest takes up a significant part of the fruit. The variety is considered:
- transportable
- high-yielding
- drought tolerant
back to menu ↑ Honey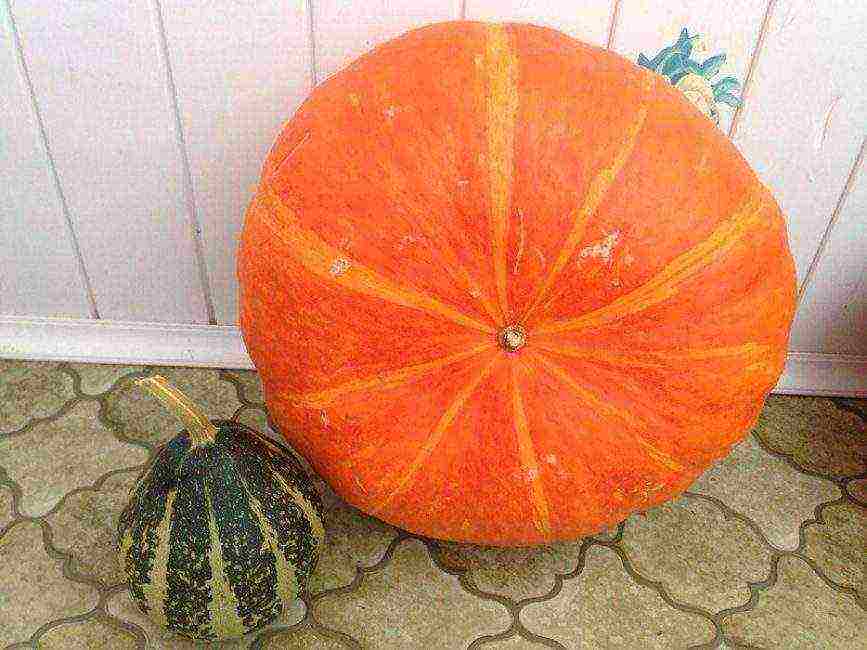 
Honey
Honey pumpkin brings together many varieties. The most famous:
- honey tale (princess)
- honey beauty
- honey dessert
back to menu ↑ Candy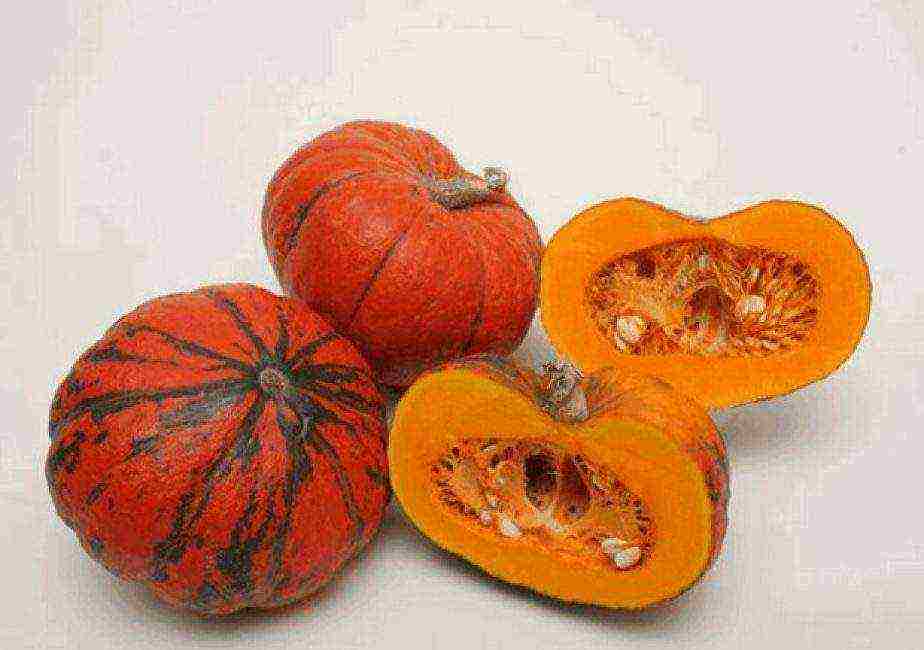 
Sweetie
back to menu ↑ Hybrid varieties
Hybrid pumpkins
Let's describe several pumpkin hybrids:
back to menu ↑ Blush F1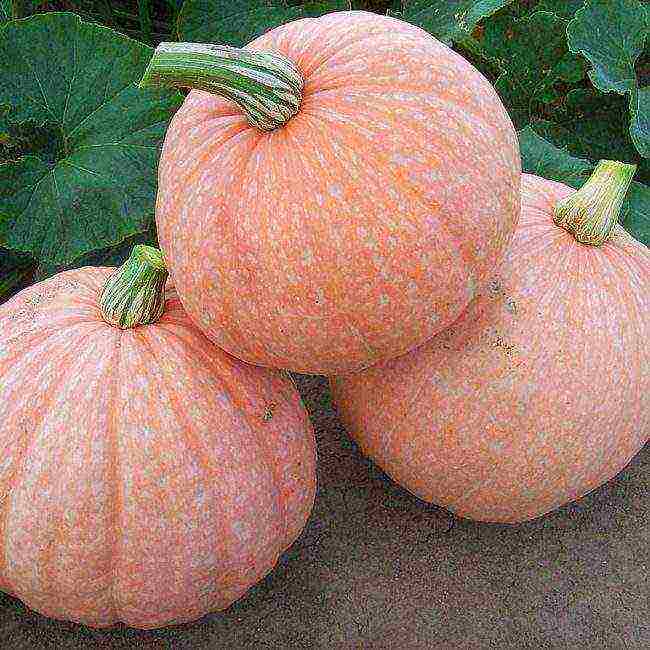 
Blush F1
back to menu ↑ Matilda F1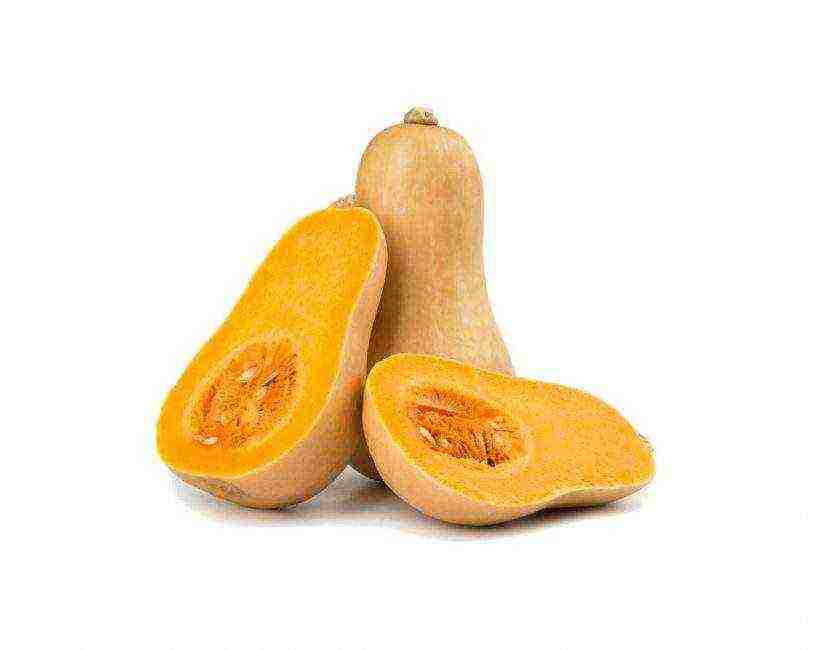 
Matilda F1
The seed nest occupies a small part of the pumpkin. The palatability of the pulp allows it to be used for various purposes:
- for salads
- baking
- stewing, baking, etc.
back to menu ↑ Butter F1 
Butter crumpet F1
back to menu ↑ Hazelnut F1 
Hazelnut F1
When choosing a variety, you must consider:
- area where the plant will be grown
- purpose: for storage, as animal feed, etc.
- taste qualities: for desserts, stewing, canning, etc.
8.9 Overall Score
From childhood, every inhabitant of our country knows that pumpkin is one of the most useful vegetables. It is used as a dietary product and is included in the diet of babies. There are many varieties in the world. Each of them has its own positive, negative qualities. We have described the best and most popular pumpkin varieties for you. If you disagree with these ratings, leave your rating in the comments with the reasons for your choice. Thank you for your participation. Your opinion will be useful to other users.
Relevance of information
Availability of application
8.5
Reliability of information
9.5
Add your review
.
Pumpkin is a popular agricultural crop grown in many parts of the world. This plant comes from America, and in different parts of it there were varieties of this plant. The demand for pumpkin is great, so countries that grow these melons can increase their economic potential by exporting pumpkin and pumpkin oil.
Among the wide variety of varieties, gymnospermous pumpkin occupies a special place, which can be used in cooking, medicine, and cosmetology.

It is important to store gymnospermous pumpkin seeds correctly, otherwise they begin to taste bitter
Description of gymnospermous pumpkin
The gymnosperm variety is not a separate subtype, it belongs to the hard-bore varieties. Its seeds are covered with the thinnest film containing fiber. The pumpkin is a round or cylindrical herb with ribs. The root system of this culture is powerful, extending to a depth of 3-5 meters.
One plant contains both male (430 pcs.) And female (80) flowers. They are larger in size than other pumpkin varieties.
This melon crop grows quickly: three or four months after planting the seedlings, you can harvest.

Growing a pumpkin on a trellis allows you to get a harvest already 3 months after planting
Growing pumpkin Preparing the field
For the pumpkin, it is of great importance what crops were grown in the soil before it. Growing a pumpkin plant will be successful on the site after such crops:
- Corn.
- Perennial herbs.
- Silage.
- Beans.
- Winter wheat.
- Beans.
- Peas.
- Potato.

Gymnosperms can be planted thicker than other pumpkins
You can not grow this crop after tomatoes, carrots, cucumbers and zucchini, since this is one family that has the same diseases and pests. These same plants cannot be grown in the neighborhood. When choosing a place for a gymnosperm pumpkin, you need to select an area that will always be illuminated and well warmed up by the sun. The place must be protected from the wind. The cultivation features depend on the pumpkin variety.
The most popular gymnospermous pumpkin Miranda, Olga, Hamlet, Golosemyannaya 14, Danae. You can buy seeds of varieties that grow not only in Russia, but also order from America and Europe.
Planting a pumpkin
In order to grow a huge harvest, you need to follow many rules, use a variety of agricultural techniques. Sowing gymnospermous pumpkin seeds is performed in the warm season, when the soil temperature reaches +15 degrees Celsius. For an ordinary melon plant, a +12 degrees mode is required, since their seeds are more protected than gymnosperms. Sowing technology depends on the size of the field. If you are in the cultivation of crops for sale, have a large field, use agricultural technology such as seeders. They ensure that the seed is sown evenly at the right distance. On a small plot of land, you can plant manually, observing the distance between the rows of 2 m.

Growing through seedlings will speed up your harvest
In early August, lateral shoots appear on the pumpkin, which are better to pinch.
The root system is securely anchored in the ground, nourishes the plant, taking nutrients from the soil. When the ovary forms, small boards or dry grass can be placed under the fruits to regulate the moisture regime, and rotting does not begin. By the time the pumpkin ripens and is harvested, you need to pinch all the shoots in order to normalize the optimal outflow of nutrients.
When the leaves dry out and the fruits reach large sizes, this indicates that the pumpkin is ripe. The surface of the fruit acquires a bright orange-yellow color.
Top dressing
For a rich pumpkin harvest, plants need to be fed regularly. It is necessary to select mineral and organic fertilizing taking into account the planned results, the composition of the soil in which the crops grow. Necessary elements for growing pumpkin:
- Nitrogen.
- Phosphorus.
- Potassium.

Side pumpkin whips should be removed
Depending on this, it is necessary to select fertilizers. During fall plowing, one hectare of field requires about 30 tons of humus, 70% of phosphorus fertilizer, 40% of preparations containing potassium. The rest of the minerals and useful trace elements will enter the soil with each watering. For gymnospermous pumpkin, you need to do three dressings:
- Before the plants bloom.
- During the flowering period.
- During the ripening of the fruit.
Watering mode
Gymnosperm pumpkin requires regular and abundant watering, the regime of which depends on the plant variety, and on climatic conditions, and on the soil. In places of drought, the melon crop grows poorly, and a minor drought can ruin the entire crop. Sowing seeds is carried out in moist soil. In the period from planting to flowering, humidity should be at 70%. During flowering and fruit emergence, the moisture content is 80%. At the time of ripening, you need to slightly reduce watering to 70%.

Gymnosperm variety firmokorya
Irrigation of crops should be stopped two weeks before harvest.
Prevention of diseases and harmful insects
The main danger for the harvest of gymnospermous pumpkin is diseases of melons and the invasion of harmful insects. Among the diseases are fruit rot, mosaic, powdery mildew. Plants can be attacked by melon aphids and wireworms. Some pests attack the root system of the plant, so it will definitely die.Other insects eat leaves and stems, and the crop can still be saved initially.

Variety Olga, except for seeds without shell. also has a great taste
If you notice pests or signs of disease, spray the pumpkin with special preparations to save the crop.
For the purpose of prevention, it is necessary to carry out the following agrotechnological methods and operations:
- Liming the earth.
- Carry out fall plowing.
- Observe the crop rotation.
- Weed rows regularly, remove weeds.
- When harvesting, remove plant residues completely.
- Create an optimal regime of air, temperature, moisture in the field.
Harvesting
The harvest period of gymnospermous pumpkin begins when the fruits are fully ripe. To do this, you need to choose a day without wind and atmospheric precipitation at the beginning of autumn, before a cold snap has occurred. In the north of the country, pumpkin is harvested in mid-September, and in the south - in the first days of October. From large fields, the crop is harvested by a special agricultural technique - a rake.

Variety Gribovskaya - the first type of pumpkin with bare seeds
On a small plot of land in the country or in the garden, you can collect plants by hand, cutting off the fruits from the stem with a knife. You need to leave the tail up to 5 centimeters.
It is recommended to store the crop in a dry and cool place, where the fruits will ripen, the bark of the plant will harden. Once harvested, the pumpkin pulp does not yet have a rich, sweet taste. After lying for several weeks, the vegetable can be used to prepare various dishes. Melons can be stored for a whole year and not deteriorate. Pumpkin porridge and pies can be cooked any season.

Danae gymnospermous pumpkin variety
During storage, the fruits of melons should be regularly inspected. If any of them become stained, start to rot, the spoiled place should be cut off, and the pulp itself should be used.

Pumpkin variety Hamlet - the largest
The weight of the pumpkin reaches 7 kg, the thickness of the pulp is 2-3 cm. Observing the recommendations of growing gymnosperms of various varieties, the conditions of watering, feeding, care, you can collect a rich harvest. The fruit can be sold or used for cooking, cosmetics and medicine.
Subscribe Be aware of new products on our site
A large family of pumpkin seeds is surprisingly diverse, and every gardener will be able to find "his" kind of pumpkin or variety. For those who love pumpkin seeds the most, the Golosemyanka pumpkin will definitely like it. This is a type of hard pumpkin, but it is not grown because of the pulp, but because of the delicious seeds.
Characteristics and description of the variety
This type of pumpkin owes its interesting name to the unusual structure of seeds that do not have a hard skin. Pumpkin kernels are covered only with a transparent film and they do not have traditional husks (see photo).

The plant can have a climbing or bush shape, is distinguished by powerful growth, and requires large areas of nutrition. The stem on the cut is not round, but faceted, covered with thorny spines. The leaves are large, five-lobed, evaporate a lot of moisture, so gymnospermous pumpkin needs abundant watering.
Male and female flowers are formed on one bush, so, like all other members of this family, gymnosperms need insect pollination. The flowers are large, the first to bloom are male, then, with an interval of about a week - female.
The fruits of this pumpkin reach medium size, most often their weight is from 5 to 8 kg. There are also champions - up to 15-18 kg, but this is rare. The shape of the pumpkins is round, slightly flattened, the color is from greenish-yellow to light orange. Spots or streaks may be present on a thin but dense and hard crust.
The pulp is fibrous, orange in color, in most varieties it is rough and not particularly pleasant to the taste.But today on sale there are varieties of gymnospermous pumpkin with tasty and juicy pulp, which contains a lot of carotene and sugar. True, gardeners prefer to grow nutmeg gourd for the pulp, and the gymnosperm is cultivated exclusively because of the seeds widely used in cooking, as well as in medicine (folk and official).
ON A NOTE!
This type of pumpkin, due to the high percentage of oil in the seeds, belongs to the group of oil plants.
Where are seeds used? They are fried and ground into flour, powder, so that they can then be added as a spicy seasoning to various dishes, as a component of many sauces. And just "clicking" pumpkin seeds is a real pleasure!

The fruits of the gymnosperm can be stored for up to 2-2.5 months. Perhaps the terms may be longer, but the thing is that after two months the seeds in the pulp begin to sprout. And such a pumpkin will be unsuitable for eating.
Features of agricultural technology gymnospermous pumpkin
Like all pumpkins, Golosemyanka needs warmth, an abundance of light and moisture, therefore, to get a good harvest and ripen fruits, you need to choose the right place for planting. In the south of Russia, there will be no problems with growing pumpkin, but in the middle lane, beyond the Urals and in the harsh Siberian regions, she will need good care and attention.
Seat selection
The garden bed is prepared in the fall, choosing a place warmed by the sun and protected from the winds. Hard-barked pumpkin is a plant that is demanding on soil fertility, and you need to pay attention to this. The soil should be permeable, loose, neutral in acidity. Culture grows poorly on acidified soils.
Digging up a garden bed in the fall, they introduce humus, manure (up to 5 kg), potash fertilizers (at least 20 grams) and superphosphate (up to 30 grams). The rates are given for one square meter.
ON A NOTE!
Many gardeners plant gymnosperms like other varieties in compost heaps or grow them in barrels.
Growing seedlings

Gymnosperm pumpkin is grown through seedlings, with the exception of the south of Russia, where fruits can be obtained by sowing seeds in open ground.
IMPORTANT!
Pumpkin seeds without a shell can rot during sowing, so it is imperative to germinate the seed and sow it only in well-heated soil.
It is recommended to warm pumpkin seeds at 38-40 ºC before sowing, and then soak them in a growth stimulator.
The timing of sowing pumpkin seeds for seedlings is the beginning of May, so that after 25-30 days the plants can be planted in the garden. For most of the territory of Russia, the most optimal time for planting pumpkin seedlings on the ridges is the beginning of June, since the threat of frost return has passed, and the soils will warm up enough. The soil temperature should be + 12-14ºC, otherwise the seedlings of the southern beauty will wither.
Pumpkin seedlings are grown in special peat pots. You can use purchased soil for growing cucumbers as a nutrient mixture, you can prepare it yourself.
The temperature when growing seedlings should be about + 22-23 ºC, and seedlings also need good long-term (at least 12 hours) lighting.
During the seedling period, the pumpkin is fed twice using the preparations of Kemira Lux, Kemira Universal and others.

ON A NOTE!
Plants must undergo mandatory hardening before planting. To do this, in about 8-10 days they are taken out to the balcony or loggia to adapt to the fresh air.
Garden care
When growing any pumpkin (gymnosperms will not be an exception), it is very important to maintain the planting pattern. The pumpkin needs space and a large feeding area, so the distance between the bushes of seedlings should be at least 70-100 cm.
After planting, the land in the bed is carefully shed, further controlling the level of soil moisture. The soil should not be allowed to dry out, but excess moisture is also harmful. A good effect is given by mulching with cut grass, it is also possible to use sawdust or peat.
 A remedy from which plants grow by leaps and bounds! Just water your plants with it ...
A remedy from which plants grow by leaps and bounds! Just water your plants with it ...
In the absence of precipitation, the pumpkin will have to be watered often and abundantly, trying not to get on the leaves of the plant. During flowering, they are watered especially carefully so that moisture does not get on the flowers, otherwise the pollen will be heavy.
For fertilizing, plants are used diluted with water:
- manure (1:10);
- bird droppings (1:20).
An excellent fertilizer is the herb infusion, which is prepared in a barrel and, diluted with water, fed to the pumpkin. An obligatory component is ash, which is introduced into the soil in the form of liquid infusions (watered at the root), or sprinkled on the soil near the plants.
ON A NOTE!
Mixing diluted manure or bird droppings with ash is not recommended.

Organic is good, but a voracious pumpkin needs a variety of nutrients. Therefore, it is also recommended to use ready-made fertilizer complexes, which contain all the components necessary for good pumpkin growth.
An important point is the formation of pumpkin bushes, and this should be given special attention. The lateral lashes on the plants must be pinched at the beginning of growth, leaving only one lateral and main stem. Sometimes gardeners leave only one stem, preferring to remove all other shoots.
The required number of fruits is left on the bushes - usually from 2 to 5, and when they are formed, the main stem is also pinched.
IMPORTANT!
Pinching the stem is done over 4-5 leaves after the last pumpkin fruit.
The harvesting time is determined by the color of the pumpkin, it should acquire a color characteristic of a particular variety and a drying stalk. But in any case, before the onset of the first cold weather and with the threat of even the smallest frost, the pumpkin must be harvested.
Gymnospermous pumpkin varieties
Having decided to grow gymnospermous pumpkin, the varieties of which are quite numerous, the gardener needs to pay attention to the description of the plant. The thing is that there are many varieties on sale intended for cultivation in the southern regions, from which it will be difficult to get a good harvest in the middle lane or beyond the Urals.
Golosemyanka
This pumpkin variety is suitable for growing in any region of our country. The main thing is to follow all the rules of agricultural technology and after about 115 days it will be possible to shoot green pumpkins with specks.
Golosemyanka's bush is powerful, with long, spreading lashes. Fruit characteristics: round, with a dense greenish crust. The pulp is yellow, without a special taste, however, it is not it, but the seeds that are valuable. They do not have a shell, are colored dark green, contain a large amount of vitamins B and E in the nuclei.
The largest fruits of this variety weigh about 6-8 kg. The variety is loved by gardeners, and is considered one of the most popular in the country.
Danae

This pumpkin belongs to the group of mid-season varieties, the fruits of which ripen at about 120-122 days. A yielding pumpkin, which not only has a large number of seeds in the fruit, but also has a juicy pulp. Its taste, of course, will be worse than that of the same butternut squash, but you can use it for some dishes.
Danae's fruits are oval in shape, with a green woody skin. Ripe pumpkins have orange stripes on the surface. The seeds do not have a shell, they are used in cooking, as well as for obtaining oil.
The Danae variety was bred by breeders for cultivation mainly in the southern regions.
Juno

This variety of gymnospermous pumpkin bears the name of the formidable and powerful ancient goddess. Juno is an early ripening variety (fruits ripen on day 100), unpretentious. Differs in very long and powerful lashes, high yield.
Fruits are round, relatively small in weight, on average - 3-4 kg. They have a soft green skin with bright orange stripes, juicy flesh. The variety is grown because of the seeds that do not have a dense shell. The pulp itself is unsweetened, has a thickness of up to 3-4 cm.
ESO
The pumpkin of this variety is the result of the work of Czech breeders, it has excellent yields, but is more suitable for growing in the south.
Description of the variety: ESO is an early ripening gymnospermous pumpkin, the harvest of fruits begins to ripen as early as 110 days after germination. The plant has long lashes, the fruits are round, have a yellow color with green stripes. The germination of seeds is excellent, there are a lot of seeds in the fruits, and after processing, a very high-quality oil is obtained from them.
Olga

This variety, judging by the reviews of gardeners, is excellent for growing in central Russia. The plant requires a large area of nutrition, therefore it is recommended to plant the Olga pumpkin according to the scheme 150x150 cm.
The bush forms lashes of medium length, which must be pinched. Shows the best results when growing seedlings.
Fruits are round, at first they have a greenish color with white spots, when ripe they turn dark orange. Their weight usually reaches 4-5 kg. The pulp is yellow in color, slightly sweetish, of medium thickness. There are a lot of seeds, while all the dark olive-colored kernels do not have a hard shell. The value of the variety is the high content of oil in the seeds.
Miranda

A gymnospermous pumpkin variety, bred in Poland. High-yielding, mid-season. Miranda is a semi-bush pumpkin, therefore it is excellent for cultivation in small summer cottages.
Fruits are of a beautiful greenish color, weighing up to 4 kg. The pulp is juicy, with a fairly high taste. Inside contains a large number of light gray seeds without a shell.
Styrian
It is impossible to do in the review without mentioning the Austrian variety of the gymnossemy - Styrian pumpkin. The variety is demanding in terms of care, temperature conditions (it gives excellent yields in the southern regions), but at the same time it is successfully grown in central Russia.
Fruits ripen in 120 days, the plant is very vigorous and long-leaved. Pumpkins grow on average up to 5 kg, but there are specimens under 8-9 kg. The pulp has a neutral taste and is usually not eaten. The main value of Styrian is its seeds, from which quality oil with a characteristic nutty aroma is obtained.

Styrian pumpkin needs a large area in the garden, abundant watering and good feeding. Once harvested, pumpkins can be stored for up to three months.
So, if there is a desire to grow a pumpkin not only for the sake of pulp, but also for obtaining tasty and healthy seeds, then the gymnosperm will be an excellent choice!
No related posts.


