Pepper picking
Growing sweet peppers in the garden, even for an experienced gardener, is not an easy task. This culture requires a lot of attention and care. After all, everyone wants all the spring-summer worries not to be in vain, and, accordingly, autumn will reward with a bountiful harvest of multi-colored peppers.
Content:
What defines caring for a pepper? This means not only providing the plant with proper watering, weeding and fertilizing, but also pinching and pinching procedures.
What is pinching and pinching for?
Modern gardeners still cannot come to a consensus about pepper pinching. Some argue that sweet peppers do not need pinching, that it only harms it and reduces productivity. Others, on the contrary, believe that pinching is necessary and the amount of the crop will depend on this. We will be of the opinion that pinning is still necessary. This is what our parents and grandmothers did. This method of increasing yields has been tested over the years and has not lost its relevance to this day.
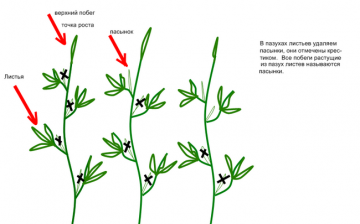
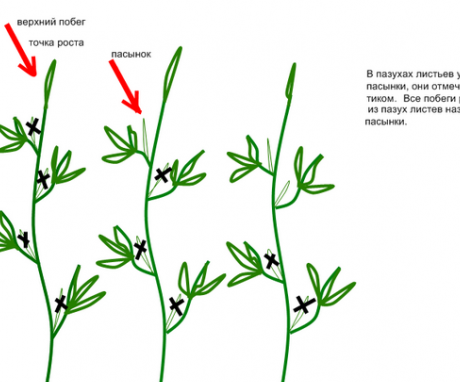
For any garden culture, pinching procedures and pinching in some cases they are simply necessary. The quality and quantity of fruiting crops depend on them. In plants, weak lateral shoots should be removed in a timely manner and the tops should be cut off. This is done so that the plant retains more strength for the formation of fruits.
A culture such as sweet peppers also needs pinching and pinching, although these procedures are not entirely simple and must be carried out correctly. If you do it inaccurately, the pepper can get sick, throw off the inflorescences and even die.
Pruning pepper bush should be carried out when it reaches a height of 20-25 centimeters. In this case, the bush will develop in breadth, lateral shoots will grow, which will have a positive effect on the yield of the crop. But the number of stepchildren should be limited and only the strongest stepchildren, located at the top of the stem, should be left. It is enough to keep the side shoots in an amount of no more than 5 pieces.
When should pinch not be done?
All the rules about pinning pepper are considered relative and this procedure must be done in accordance with the weather conditions and the growing conditions of the culture. Grazing is not always carried out, sometimes it can even have a detrimental effect on the plant. In what cases is pepper pinching not carried out?
- In hot and dry weather, pinching is not recommended. In the dry season, the plant itself will create at least some kind of shadow with the help of side stems and leaves. This will provide moisture retention and prevent the soil near the root from drying out, which is very important for crops such as peppers.
- Pinching is not carried out even if the plant sick... Removing side shoots will only worsen the position of the plant and can lead to its death.
- Pickling is not carried out even if the peppers are planted very rarely, far from each other. Peppers grow best in the neighborhood of other peppers. And they endure loneliness very badly.
- Pepper does not need pinching if it has grown to a height of no more than 20 cm.
The pinching procedure for pepper is forced, if possible, it should be avoided so as not to cause unnecessary stress to the culture. It is necessary to carry out pinching only in case of urgent need, when the plant really needs it. Some varieties of pepper are categorically impossible to pinch.
If there is not enough experience in growing sweet peppers, it is better not to carry out pinching and pinching procedures, so as not to permanently harm the plant.
How to pinch peppers correctly
It is believed that peppers should be pinched in rainy and hot summers. With sufficient moisture, the lateral shoots of pepper begin to actively develop, grow and carry only a burdening function for the entire plant. Because of them, the roots are poorly supplied with moisture and receive less sunlight.
But so that pinching does not harm the pepper, it should be carried out according to the following rules:
- when the plant reaches a height of 20-25 centimeters, the apical part of the main stem of the pepper is removed. After that, the lateral shoots begin to activate and grow rapidly, forming a compact bush shape;
- from the newly formed shoots, only 4-5 pieces of the strongest and largest shoots are isolated in the upper part of the stem, and the rest that are located below are cut off. The future harvest will be formed on the strong shoots left.
Peppers are a family culture. They do not like to grow up alone, but surrounded by neighbors like themselves. When planting peppers in the ground, this fact should also be taken into account, planting peppers 2 pieces per hole, and not far from each other. When pinched, neighboring peppers will provide support to each other and create favorable conditions for growth.