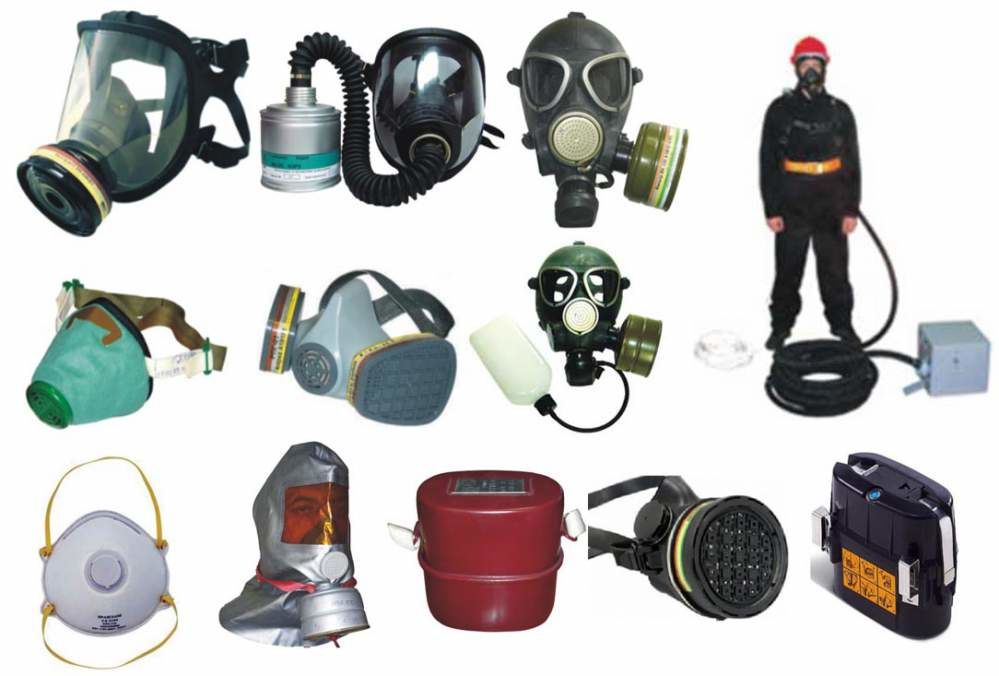
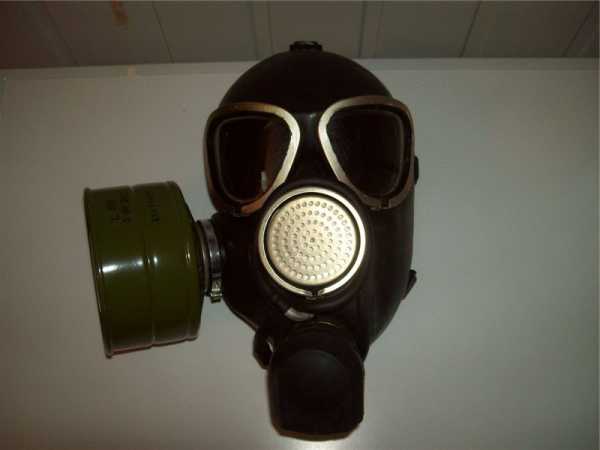
What is a filtering and absorbing gas mask box for?
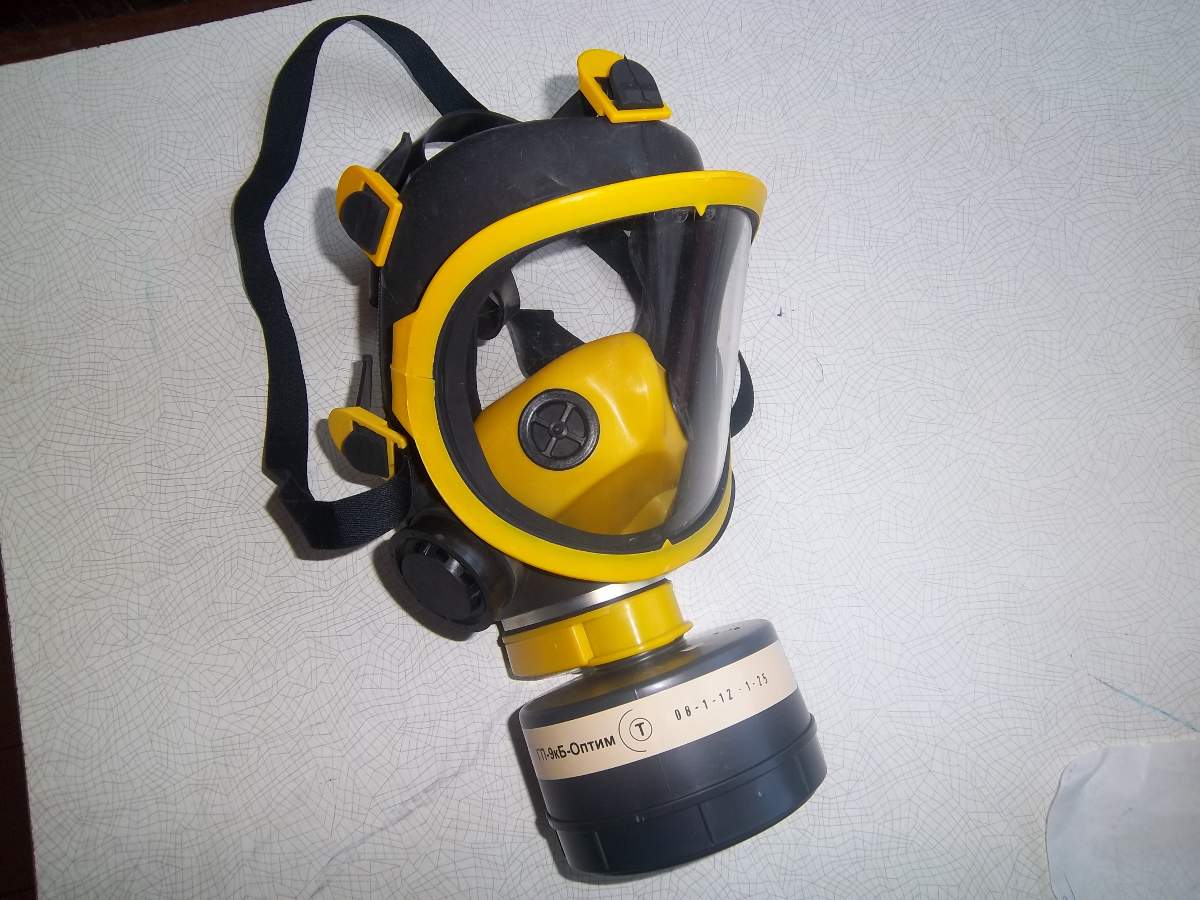
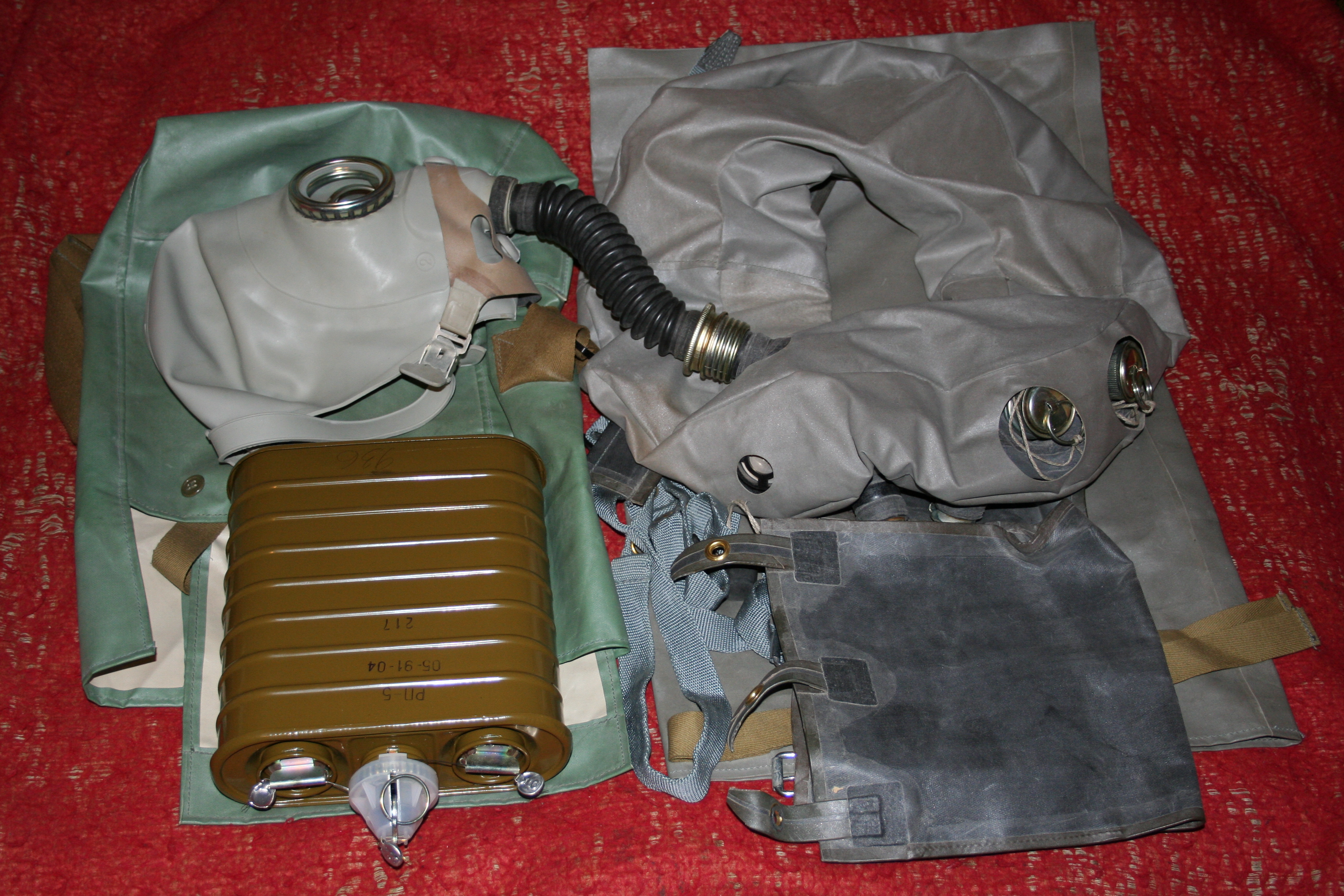
The filter box acts as a container in which the filter element is stored, which is responsible for air purification. It is made of metal and is threaded to the rubber mask.
Air purification in the gas mask box can be carried out in two ways:
- aerosol, by means of a special filter;
- steam, through the absorbing layer of the carbon catalyst.
The most common filter is for a gas mask, in the form of an absorbent of coal from apricot or coconut pits mixed with a mixture of metal oxides.
VIDEO ON TOPIC
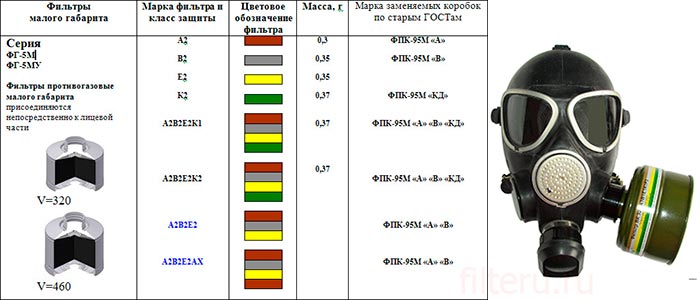
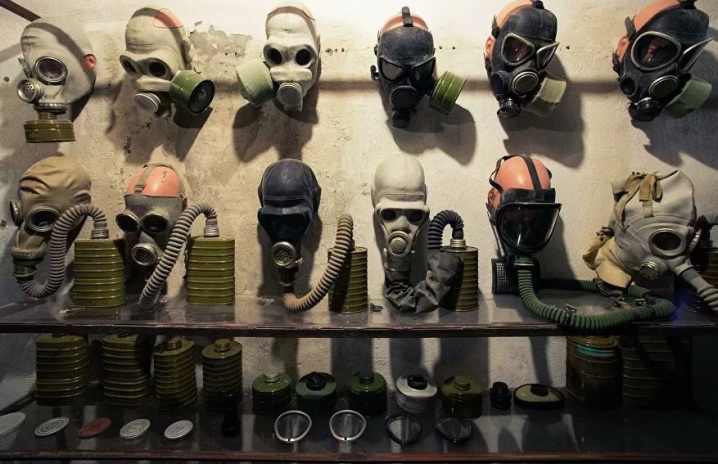
Gas mask filter boxes marking
The gas mask boxes show a lot of alphanumeric designations.
They carry all the important information, so if you want to purchase accessories for a gas mask, you need to understand them.
- Type A1 marking. IN 1. E1. P2. informs about what types of impurities and at what concentration, during what time the gas mask will protect the respiratory system.
- Internal factory markings. The code begins with it. Example "DON". These three letters indicate that the manufacturer of the box is this plant. Letter - class of substances, number - class of protection.
- Number 1 marks low efficiency filters,
- Class 2 indicates products of average efficiency,
- The number 3 can be seen on high efficiency filters.
Color markers. Sometimes the manufacturer glues a color marker to the side of the box. It informs about the type of substances that this filter is able to retain.
| Letter marking | Defence from: | Color coding |
| A | Solvent vapors and organic gases: benzene, xylene, gasoline, toluene, kerosene, alcohols, aniline, carbon disulfide, tetraethyl lead.
(boiling point from 65 degrees Celsius). |
Brown |
| B | Inorganic gases and vapors, namely: bromine, cyanogen chlorine, fluorine, halogen, hydrogen sulfide (except for carbon monoxide). | Gray |
| E | Acid gases and vapors: formic, acetic, sulfuric acid, hydrogen bromide, sulfur dioxide. | Yellow |
| K | Amines and ammonia. | Green |
| P | Aerosols in the form of fog, smoke and dust. | White |
| NO | Nitrogen oxides and aerosols. | Blue |
| CO | Carbon monoxide. | Purple |
| Hg | Mercury vapors and aerosols. | Red |
| AX | Vapors of organic solvents: acetone, isobutane, dimethylether (boiling point from 65 degrees Celsius). | Brown |
A common question is how long the filter in the box will last and when to replace it
The warranty period of the filter in the box is 3-5 years and depends on the conditions in which it is used. The protection time varies from 20 to 70 minutes.
If the gas mask is being used with odorless gases, it is easy to know when to replace the filter.
This is evidenced by the well-distinguishable smell of gas in the inhaled air. In other cases, you need to carefully study the instructions for the filter element and take into account the conditions of the working environment.
How to use?
For a specific gas mask, reliability is determined by the power of the gas protection and the level of tightness. In case of weak protection or leakage, hazardous agents can penetrate under the face mask. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully protect the geometry of the protective device, and if it is violated - immediately dispose of it. Although the exhalation valves are more reliable, they must be carefully cleaned after each use. The expiration date for a specific model is set by the manufacturer, but in most cases it is impractical to use them after 5 years.

Whenever possible, the wearing of gas masks should be kept to a minimum. Even the best versions of them are not able to provide completely physiological respiration. Before each use, it is required to inspect the mask so that there are no flaws, mechanical damage (punctures, cuts, tears, dents) in it. The norm of daily and session operation should not be exceeded, except for the most extreme cases and especially difficult situations. Wearing a RPE is permissible only in specially designed bags - bags, backpacks, household bags and everything else cannot be used.

Warehouses for gas masks:
- must exclude direct sunlight;
- are designed with the expectation of a minimum dust level (best of all - with self-leveling, concrete or asphalt floors);
- equipped with reliable ventilation;
- have basic and emergency lighting;
- should exclude the ingress of liquid water even into the room itself, not to mention the RPE;
- cannot be used simultaneously for storing toxic, corrosive, radioactive, flammable substances.

For information on how to properly use a gas mask, see the next video.
Classification by purpose
Modern types of gas masks are as follows:
- protecting respiratory organs from dust and aerosols;
- preventing the penetration of radiation, chlorine and other specific toxins;
- containing carbon monoxide (due to equipping with hopcalite cartridges);
- preventing damage by radioactive dust, microorganisms (including viruses and fungal spores).
Filtering
The very name of this category suggests that they stop toxic substances and thereby block their effect on humans. At the same time, the air from the outside, after being cleaned on a special filter, quietly passes on. Theoretically, the duration of stay in a contaminated atmosphere when using such PPE is limited only by hygiene standards. However, the problem is that an oxygen concentration of at least 17% in the ambient air is required. If this requirement is not met, wearing a filter gas mask becomes life-threatening. The filter is usually located at the front of the mask. It can constructively turn slightly to the side. The filter-absorbing box fits snugly against the face mask. In the most hazardous conditions, it is recommended to use devices equipped with a corrugated hose. Air purification is carried out using adsorption on a charge with a layer of activated carbon. Filtering gas masks cannot be used:
- if the chemical composition of toxins is not known exactly;
- there is a possibility of its abrupt changes;
- the concentration of corrosive substances can be very high.


Insulating
Such devices 100% block the path of toxic substances. They work confidently, even if the concentration of hazardous factors is very high. More precisely, there are also concentrations at which protection is impossible - but they are simply outrageous and do not occur in real practical conditions. No external breathing air is used. Wearable cylinders contain a combination of 70-90% oxygen and 1% carbon dioxide; such a mixture helps out not only with very strong air pollution, but also when working in an oxygen-free or low-oxygen atmosphere. Also, gas masks with isolation from the external environment can be worn:
- when the concentration of carbon dioxide is overestimated;
- with the spread of ammonia, chlorine and other substances that quickly exhaust the safety life of the filters;
- for work in an atmosphere guaranteed to pass through filter boxes;
- for performing various manipulations completely or partially under water.


Views
In accordance with GOST 12.4.011-89, protective equipment for use is divided into two types:
- for collective use - objects and mechanisms that ensure maximum normalization of environmental conditions, for example, reducing noise or the level of infrared radiation.They are applied to entire premises, they simultaneously affect a whole group of people in this room;
- for individual use, personal protective equipment are items that ensure the safety of the health of an individual person. The transfer of such PPE from one person to another for subsequent use is usually accompanied by special processing, some of these PPE are disposable and cannot be reused.
Depending on the purpose, they are divided into 11 classes, the types of personal protective equipment are allocated depending on the type of harmful factor from which they are designed to protect:
- devices for normalizing the air environment of industrial premises and workplaces;
- devices for the normalization of lighting in industrial premises and workplaces;
- protective equipment against an increased level of ionizing radiation;
- from the increased level of infrared radiation;
- from low or high levels of ultraviolet radiation;
- from an increased level of electromagnetic radiation;
- from increased intensity of magnetic and electric fields;
- from an increased level of laser radiation;
- from increased noise level;
- from an increased level of vibration (general and local);
- from an increased level of ultrasound;
- from an increased level of infrasonic vibrations;
- from electric shock;
- from increased levels of static electricity;
- from high or low temperatures of surfaces of equipment, materials, workpieces;
- from high or low air temperatures and temperature extremes.
In accordance with the classes, personal protective equipment includes:
- special protective clothing (overalls, semi-overalls, jackets, trousers, sheepskin coats, robes, coats, short coats, short fur coats, capes, raincoats, half-coats, shirts, shorts, vests, dresses, sundresses, blouses, skirts, aprons);
- hand protection (mittens, gloves, handhelds, fingertips, wristbands, oversleeves, elbow pads);
- PPE for feet (boots, boots, shoes, robes, slippers, etc.);
- PPE for eyes and face (goggles, face shields, etc.);
- items for head protection (helmets, helmets, comforters, caps, berets, hats, caps, kerchiefs, mosquito nets);
- items for the respiratory system (gas masks, respirators, self-rescuers, etc.);
- insulating suits (pneumosuits, spacesuits, etc.);
- hearing protection devices (plugs, headphones, earplugs, etc.);
- from falling from a height (safety belts, cables, etc.);
- dermatological (skin cleaners, creams, ointments);
- complex means of protection.
A narrower classification of PPE is also distinguished for certain types of hazardous work, for example, four types of PPE have been developed to work with pathogenic and biological agents:
- the first type is the most serious, protects the skin of the hands and respiratory and vision organs, allows the presence of glasses or a mask, or a filtering gas mask;
- the second type protects hands, respiratory and vision organs, glasses are not used;
- the third type is protection of hands and body surfaces without glasses and a respirator;
- personal protective equipment of 4 types presupposes protection of the body surface: a hat and a dressing gown are included.
The above classification does not include uniforms and corporate clothes, which are provided to employees in some enterprises. The fact is that the form does not belong to the means of protection.
To maximize the protection of personnel from harmful production factors, the use of PPE alone is not enough. The enterprise should use the latest equipment, effective ventilation and other measures to minimize harm to the human body, even in the most dangerous production.
How to put it on?
It is worth noting that there are various techniques and methods of putting on a gas mask (not only prescribed in the old civil defense manuals).But all options are aimed at the fastest possible application of protection. The classic version is as follows (if the gas mask is initially set to the "ready" position):
- stop breathing;
- close the eyelids at the same time;
- take off their hat (if any);
- remove the gas mask;
- take the helmet-mask with both hands by the thick part of the lower edge;
- put thumbs on the outside, and keep the rest on the inside;
- push the bottom of the mask against the chin;
- make a sharp movement and put on a mask as quickly as possible;
- remove all distortions, straighten;
- take a full noisy breath;
- open their eyes;
- resume breathing and carry out all the planned work.

Gas mask marking
To distinguish between brands of gas masks, special letter markings are used. It is an abbreviation indicating the features of the protective device and its model. Let's consider examples of markings for different types.
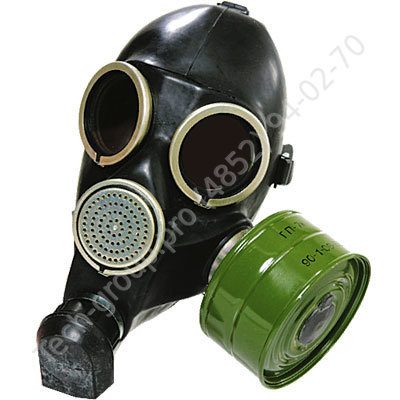
GP for adults:
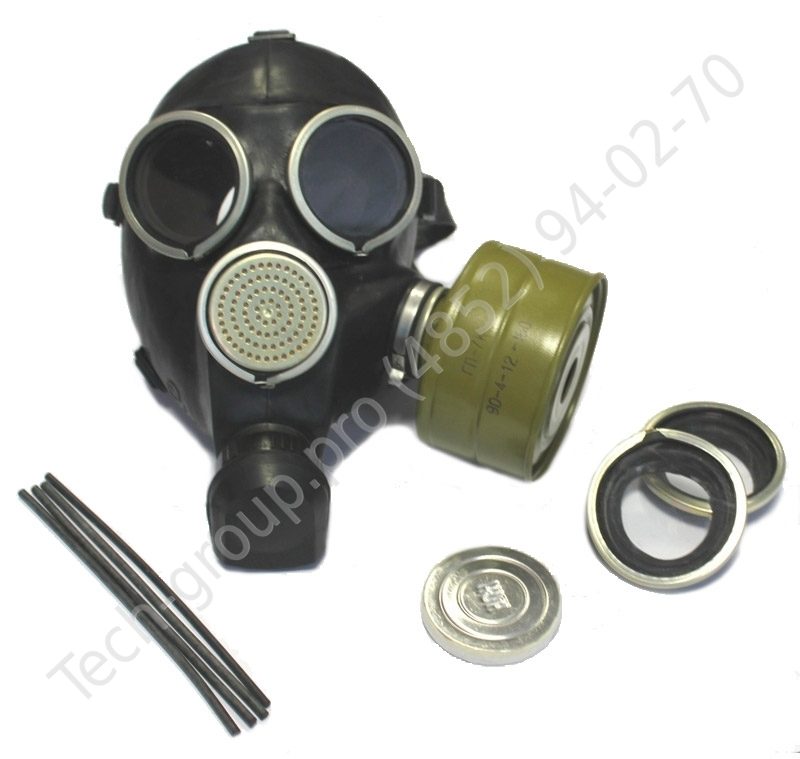
- GP-7 is the most popular means of protection for the adult population, which was discontinued more than 30 years ago. Its modified analogues GP-7V (the presence of a device for receiving water), GP-7VM (has glasses made in the form of a trapezoid and two inlets for filters), GP-7B (has a wide range of protection).
- GP-9 - has a large panoramic viewing window and a device for negotiations. They are used for protection against mercury vapors, ammonia, radioactive emissions.
- GP-21 - a lightweight gas mask with a wide panoramic view. Used for effective protection against hazardous airborne substances.
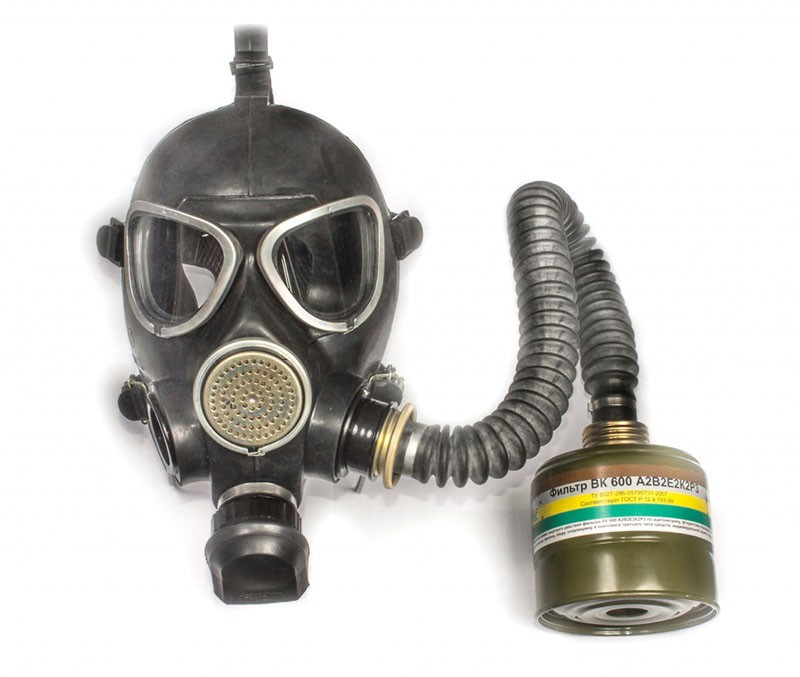
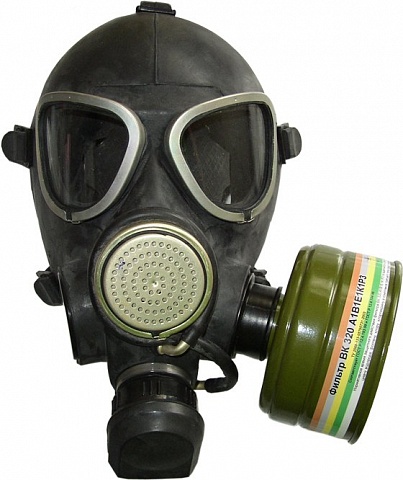
- UZS VK 320 or UZS VK 600 - have a universal adjustable size. The set uses filters of the first and third class of protection, which are superior in their properties to the standard ones in GP-7. Recommended for emergency use.
The marking of industrial gas masks differs from civil ones. For classification, an alphanumeric code and color marking are used, which indicate the type of harmful substances and the level of protection.
Filter coding in letters means:
- A - organic compounds and gases with a high boiling point (over 65 degrees), marked in brown;
- АХ - vapors with a low boiling level (less than 65 degrees): gasoline, butane, acetone, kerosene, etc., (color - brown);
- B - gases of inorganic origin (gray);
- P - microbes and air suspensions (white);
- E denotes in yellow - this category includes acid gases, including HNO3;
- K - from ammonia and its derivatives (denoted in green);
- CO (purple) - from carbon;
- SX - hanged hazard class of toxic substances, for example, sarin, faosten; (the marking is purple)
- Hg - from vapors of mercury vapor (red).
To indicate the degree of protection, numbers from one to three are used, where:
- 1 - this is a low-efficiency protection;
- 2 - protection with an average coefficient;
- 3 - a product with a high protection index.
Other features of the labeling of gas masks:
- Contains information about the manufacturer, for example, Breeze, DON, DOT, IZOD.
- The length of the hose used is indicated on the hose protectors, for example, PSh-1, PSh-20ERV, PSh-40RV.
PPE for coronavirus
The developing coronavirus pandemic forced the use of personal protective equipment not only when working in hazardous industries, but also during normal activities and even at home.
Coronavirus infection spreads:
- by airborne droplets;
- air-dust;
- by contact method.
This means that from person to person the infection is transmitted through direct contact, when infected particles of biological fluids released during sneezing, coughing and even breathing of a patient fall on the mucous membranes of a healthy person, but also through indirect contact - through the surfaces of objects that the patient touched.
All this makes the coronavirus highly contagious and easily transmitted from person to person, the purpose of personal protective equipment in a pandemic is to slow down the spread of infection from person to person.
In this regard, the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation recommends that all employers who take their employees to work during a pandemic period, especially if this work involves interaction with a large number of people, provide employees with appropriate PPE:
- masks;
- gloves;
- antiseptics for frequent hand treatment.
The use of these PPE is justified because:
- the mask will not completely protect against potential infection, but will significantly reduce the level of viral load that the employee will receive when infected, in addition, it prevents the spread of the virus from the employee himself if he is already infected, but tolerates asymptomatically;
- gloves will prevent the virus from getting on the skin, and then on the mucous membranes;
- an antiseptic damages the protein envelope of the virus, killing them - this is the effect of ethanol, which is part of alcohol antiseptics, antiseptics with an alcohol content of at least 60% should be preferred.
Knowledge of what PPE is, their types, and application for coronavirus do not exclude the need to keep a social distance of at least 1.5 - 2 meters. The distance from one potential carrier to another is the best protection against the spread of coronavirus, as well as adherence to the rules of personal hygiene.







































