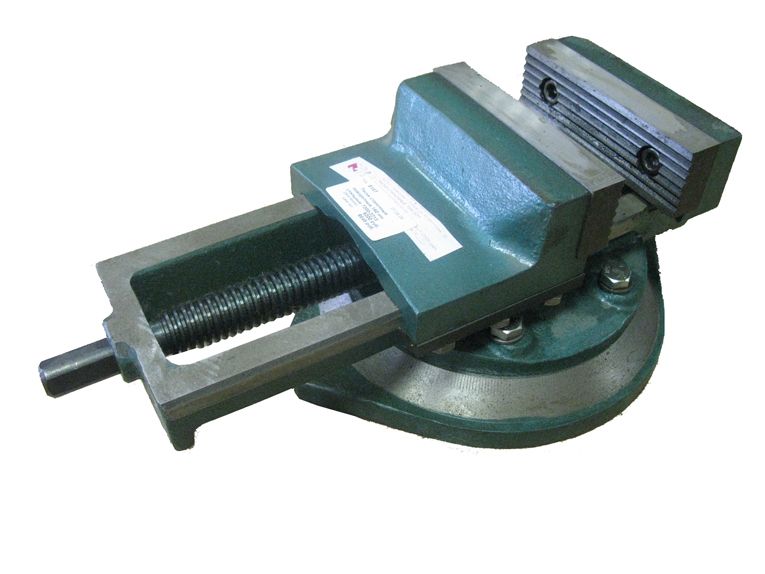
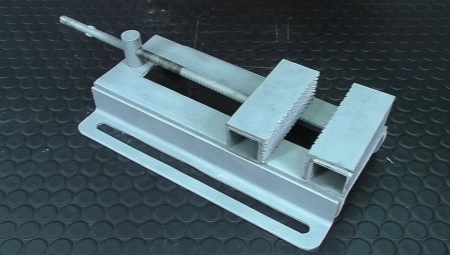
How to do it yourself
Many craftsmen prefer to make machine vices on their own, since this is a simple process that saves the family budget. Before you start assembling the device, you need to decide on the choice of material from which you plan to make the vice. It is best to give preference to a square (profile) pipe measuring 60X40 mm.
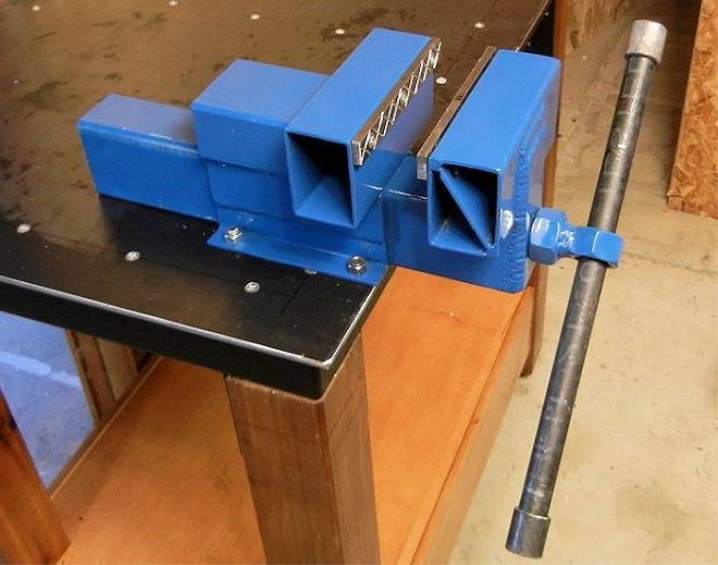
You will need to follow the steps in sequence:
It is necessary to cut a square out of metal, which will serve as the basis for the future device. On each side of the square, you need to make 4 holes, they will be needed to fix the vise to the machine.
Then, 2 sponges should be made from the pipe, in one of which you will need to make a hole and insert a washer.
The next step will be the manufacture of guides, thanks to which the plate can move along the axis of the stationary jaw. An ordinary metal corner is suitable as rails. It should be welded on both sides along the edges of the plate.
It is important that the corner then does not interfere with pressing the workpiece.
Next, you need to make a rotation mechanism by welding a clamp with a nut to the base. After that, a screw is screwed into the nut, it must be inserted into the hole in the plate so that the bolt does not pull it back.
The production is completed by fixing the vice to the drilling machine
This can be done with nuts and bolts. Since the vice is made at home, it differs in many ways from the store
Therefore, you need to pay special attention to their setting, which should not be in a hurry. Vise machines should be installed in the home workshop at a distance of 70 cm from each other.
A more detailed overview of how to create a vise for a drill vise with your own hands is presented in the following video.
What are they for?
If we talk about the use of a machine vise on a drilling machine of a floor or table structure, then the main task in this case is to create marked holes in the workpiece, regardless of materials, with maximum accuracy and compliance with all technical safety measures. In addition, the vice is often selected for a CNC lathe, grinder or fire machine.
For the same drilling machines, vices are not always present in the package when purchasing, although their presence does not greatly affect the cost of the model as a whole. Sometimes the machine vice in the case of a master's set is also called a drilling vice for the convenience of indicating the specifics of the work.
But the use of a vice also largely depends on the materials with which you will have to work in the future. For example, they are not needed for wood or plastic. A minimum of effort is required to secure the part in place. And in the case of plastic, excessive pressure can even deform the material.
A vise is essential when working with steel, cast iron or any other heavy metal. Their presence in the kit will allow not only to efficiently complete the task, but also to comply with all safety requirements.
Other clamps are sometimes used instead of a vice, but they will be less reliable. In addition, with due attention, you can make a vice for the machine with your own hands. Such a tool will fulfill its purpose no worse than the factory serial models, and in terms of cost, minus time costs, it will be much cheaper than an analog from the manufacturer. Before assembling, it remains only to understand the design of the desired vice.
Selection options
Depending on the specifics of the planned work, the compression mode is selected - point or coarse. The step length of the clamping mechanism depends on the thread of the lead screw.
The surface of the jaws is corrugated or smooth. The choice of this or that model is due to the texture of the workpieces being processed. A dotted or mesh pattern improves grip, but can leave unwanted marks on wood, for example.
The strength of the steel alloy from which the tool is made is an important quality indicator. Due to the peculiarities of the application of force, the characteristics of the material are the main criterion for the reliability of the joinery vice, therefore, when purchasing them, you should not save money by purchasing non-certified products.
How to choose?
First, decide what width of sponges you may need - it will depend on how thick the part can be fixed with a vice. Then you need to decide whether the vice will be removable or bolted to the locksmith's table forever. For non-removable equipment, significant weight will be a plus, and for removable equipment, you need to take into account your physique and the availability of a place where they will be stored. Many tasks are solved with a removable tool weighing 8-10 kilograms with a sponge spreading width of 100 millimeters.
All widening at the ends of the wrench needs a large diameter to prevent the screw from getting inside.
When compressing the jaws, the pads should be close to each other, the maximum allowable divergence is 0.5 mm. It is quite easy to check this - we first clamp a thin metal rod on one edge of the sponges, and measure the width of the sponges, then we clamp the same rod on the other edge, and also measure the distance. The difference between these figures should not exceed the maximum permissible 0.5 mm.
The lips are strictly parallel to each other, mobile - does not walk on the sides. Carefully inspect the bed for cracks, do not hesitate to tap on it. The lead screw must be thick - this indicates its safety margin. With a high quality of processing, the surface of the screw has a gloss. Inspect the screw for burrs and scuffs, you can even touch it with your fingers if in doubt. If they are, the quality of the instrument is poor, or they have already been used. After loosening the side screws, see if the pivot will rotate.
A high-quality tool cannot be cheap, but during operation you will not regret this money, because such equipment serves for a very long time and may well be inherited from you to children.
Sometimes there are remnants of earth from the mold or rust on the lower part at the junction of the base and the fixed sponge. This is removed with a metal brush, file.
Many craftsmen, to minimize operating noise, often stick a rubber gasket on the bottom of the vise base, or screw equipment with it to the workbench. This is not necessary if you do not use them all the time, but for permanent work, the advice is really useful.
You can endlessly discuss which grip is better, and which models will be more useful for performing certain tasks, but first of all, you need to focus on your needs and capabilities. Almost all the vice can be done independently based on your needs, or you can spend it once in a lifetime, but buy a good tool.
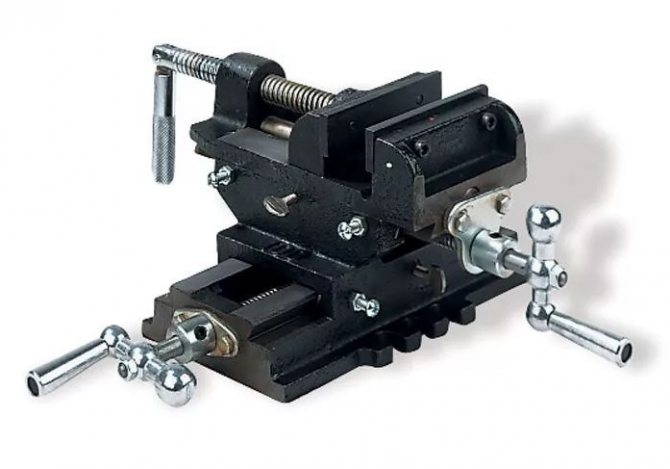
For an overview of the coordinate cross vise, see the following video.
Making at home
A machine vise is a tool designed for working with hard material, therefore, for reliability, their main and most important parts in the structure are made of durable steel or cast iron. The designs themselves may differ from model to model, depending on the type and profile of use. If a master makes a vise for the first time with his own hands, it is best to choose a non-rotating vise in order to gain the necessary experience and skills.
The only difficulty in reproducing some vices at home is the design features of the swivel and non-swivel models.
Pressure plates, strips and other parts, on which the strength and reliability of the tool depend, should be made of metal that can easily withstand wear during long-term operation. Fasteners and connections such as screws and nuts are also made of steel. During the assembly of some models, welding is also used, then it is imperative to remember about the stage of cleaning the seams. Slats for working with different types of workpieces and parts can also be of different shapes and contain a spring in the structure for comfortable work with dimensional parts.
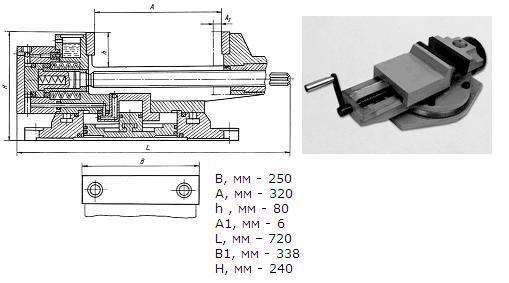
After the type and main parameters of the future vice have been determined, you can try to make them yourself. If we talk about sizes, then at home you can do:
- large;
- small;
- mini.
At the first stage, according to the drawing and the requirements of GOST, a workpiece of the required size is cut out - a standard 45 × 45 cm, then a few more for fastening the remaining parts. Long ones are installed with an edge inward, short ones - always outward and at right angles. After that, the entire structure is welded together.
After that, jaws are made and joined with the working screw using a nut. The entire assembly of the machine vice takes a minimum of time in accordance with the selected scheme. At the final stage, all seams are smoothed out, in addition, you can paint the tool with paint in order to protect the metal from corrosion for as long as possible.
Vise types
The main types of vice are locksmith, machine, carpentry and manual.
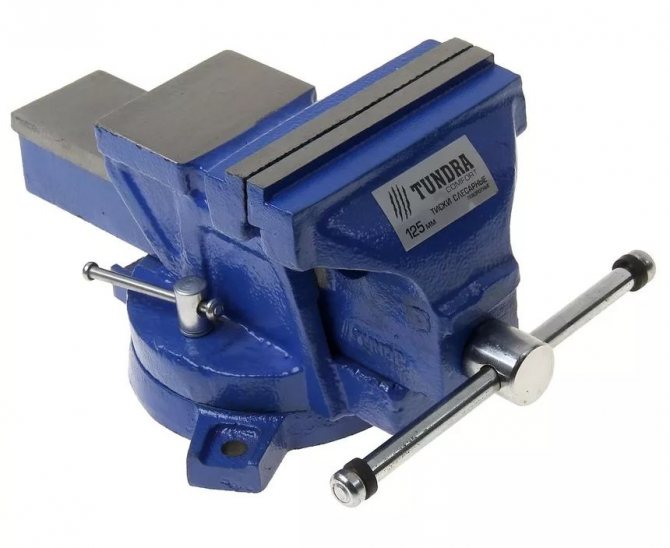
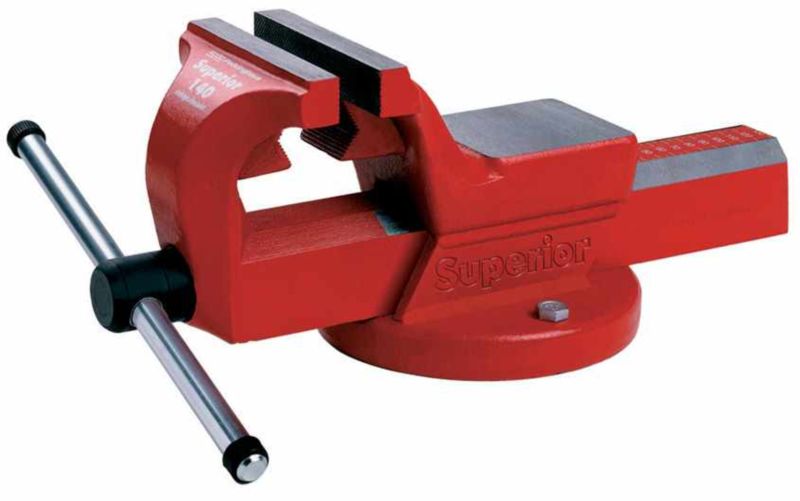
Locksmith vice
A solid metal tool that mounts on a workbench or table and bolts to the base.
- Chair and parallel vices differ in design.
- Available in stationary and swivel versions, which allows work at different angles.
- The width of the jaws is 45-200 mm.
- The length of the moveable lip stroke reaches 140 mm on average.
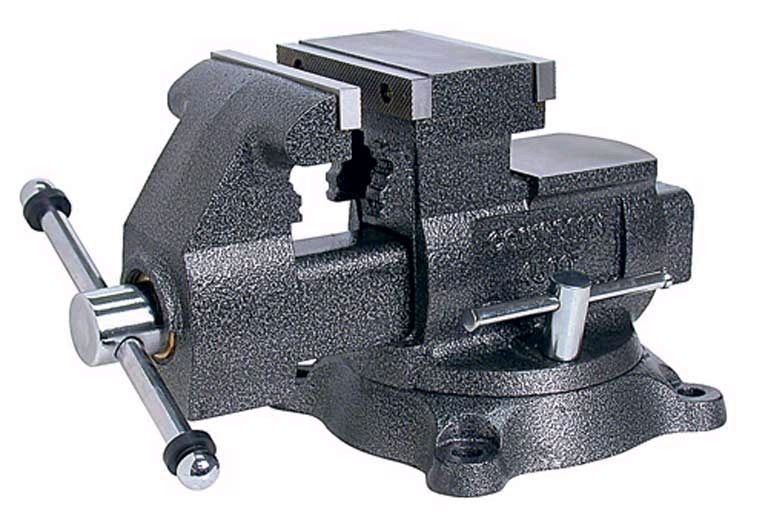
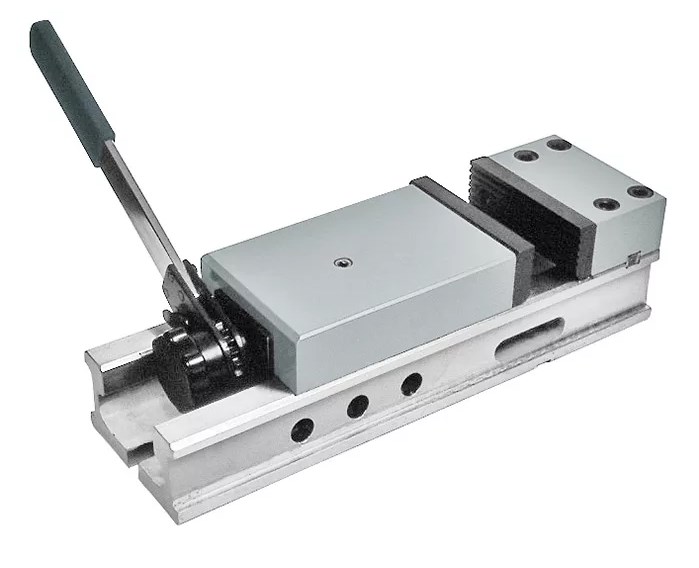
Parallel vise
- They are divided into swivel and non-swivel. The former rotate parallel to the base around the axis by 60 or more degrees. Fixed models are rigidly fixed, designed for work in one position.
- The movable jaw moves with the rotation of the screw parallel to the fixed part.
- The base of the tool is cast in cast iron and the moving parts are in carbon steel.
- The applied jaws of high-strength models are made of U8 tool steel, supplemented with a cross-shaped notch, and are fastened to the main jaws after hardening with screws.
Chair vise
Obsolete design type. Previously mounted on a chair-shaped base. Modern fixtures are fixed on workbenches.
- The construction is made of forged steel. Consists of a body complete with sponges.
- The working surface of the jaws is reinforced with screw-on hardened plates or a layer of U8A steel is welded onto it.
- The working surface is covered with notches inside for a firm fixation of the workpieces in the vice.
- The fixed jaw is equipped with a clamping foot, the rod is clamped with a bracket.
- The width of the jaws is 100-180 mm. The length of the opening is available in options for 90-180 mm.
- The jaws are displaced by the rotation of a rectangular screw, and are moved apart by inserting the screw into the tubular nut.
Models are most often equipped with an anvil plate. The bed is a structure of a base and a swivel disk, which are connected in the center with screws or additionally fixed with a return ring.
When the screws are loosened, the ring releases the blockage of movement.
According to GOST 4045-75, the types of locksmith vices differ from those presented. Three types are declared:
- general purpose;
- with swivel jaw;
- with additional pipe jaws.
The standard applies to models with a jaw width of 63-200 mm.Rotary and non-rotary manufacturing options with or without accelerated idling are assumed.
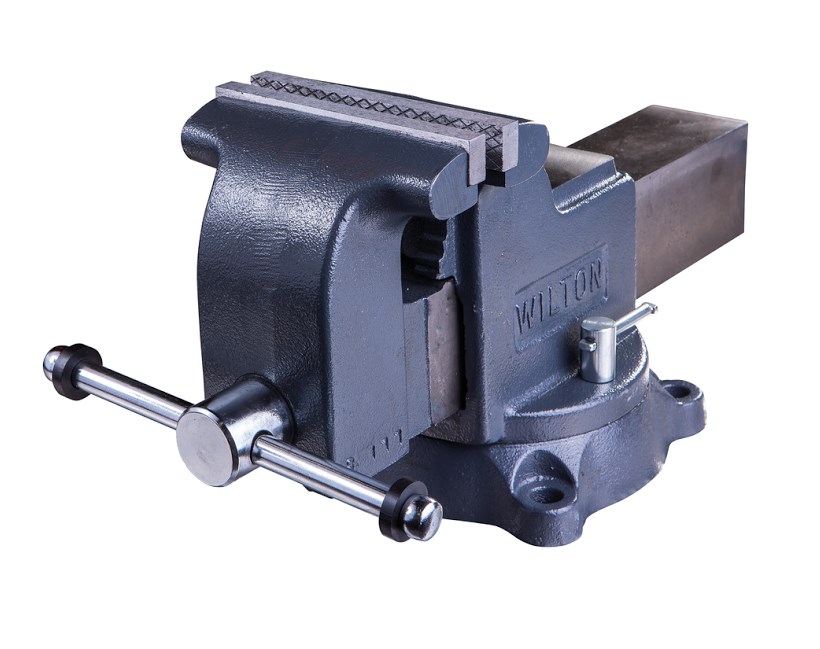
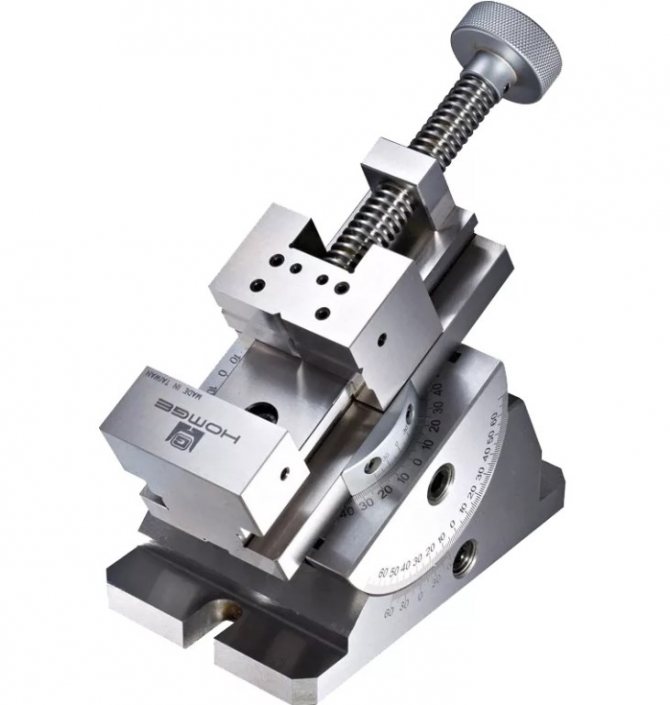
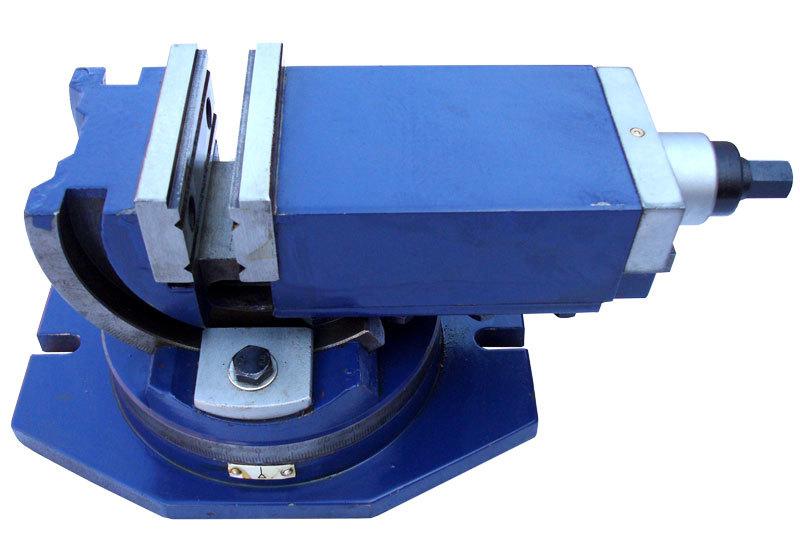
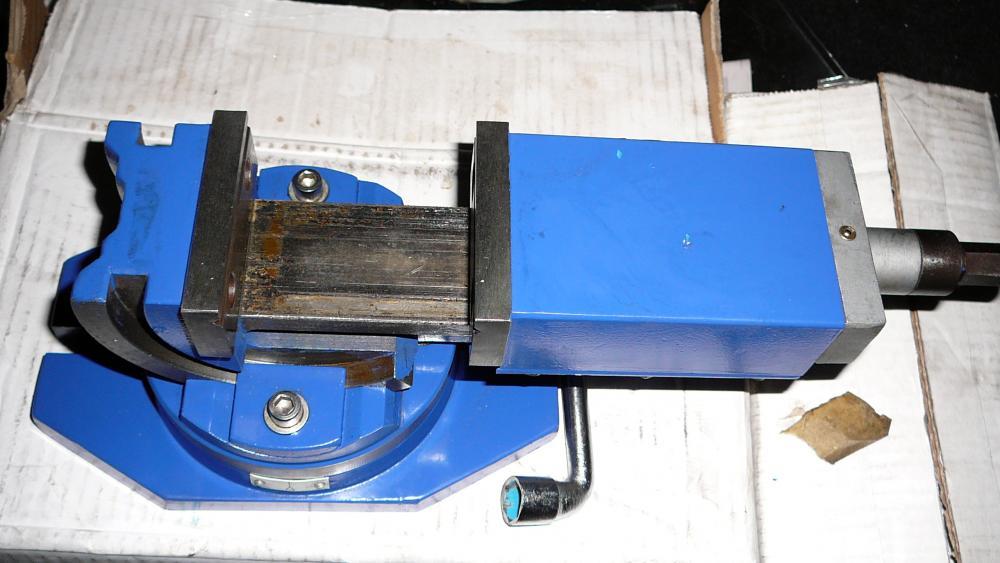
Machine vice
A tool of increased accuracy, which differs from locksmith models by the absence of backlash or its small take-off run. Designed for production work.
- They are fixed on industrial work benches for machining large parts.
- For the convenience of adjusting parts, they are often equipped with a rotary mechanism.
They are divided into basic and sine ones, in addition, a different number of axes is provided:
- Basic or stationary - the part is attached perpendicular to the tool.
- Sinus - the workpiece is fixed at an arbitrary angle.
- Multi-Axis - Supports rotation along multiple coordinate axes.
Machine vices are also available for domestic use, but are smaller than production models.
Hand vise
Compact tool for processing small parts, does not need to be attached to tables. There are two types that differ in the fixation system.
- With jaws - consists of a bridge with a screw, steel lips and a handle. The convergence of the jaws is achieved by rotating the handle. The cone is located on the back side, enters between the shanks of the jaws, causing them to be compressed.
- With levers - reminiscent of snap-nose pliers. They have a locking mechanism, which consists of two levers that clamp the jaws.
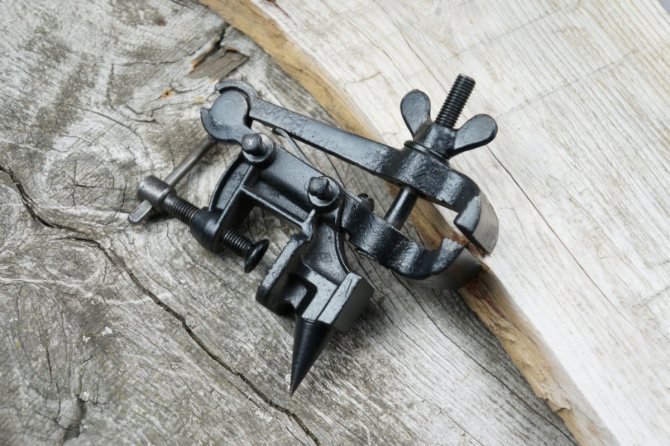
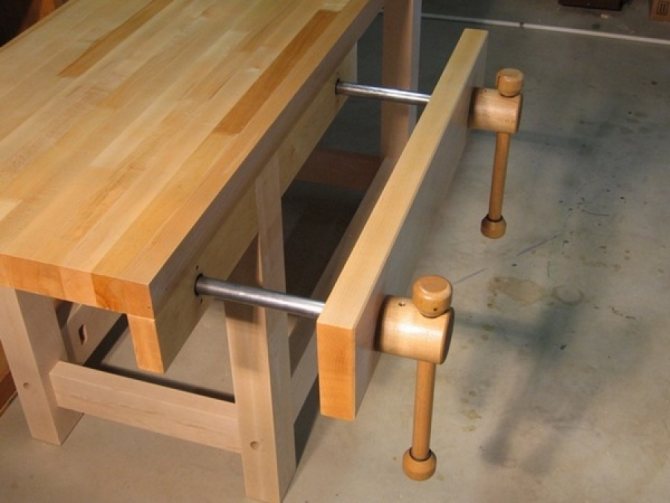
Holdfast
Used when working with wood and plastic blanks. Most often they are fixed with screws to a table or bed. Variations with front clamp available.
- Wooden shims are usually attached to the jaws to hold the workpiece without damaging the surface of the workpiece.
- Overlays are provided so that no marks remain on light or soft wood parts.
- Front mount models are suitable for vertical surfaces.
- There are models with a combined clamping device - a combination of cast iron and wood.
Some carpentry vise models are equipped with quick-clamping screws for easy positioning of the movable jaw and pre-clamping.
Production vise
This is not an entirely accurate term, under which one can combine the types of vices used only in factories and almost unsuitable for either the home craftsman or for small workshops. To clamp large parts or in mass production, hydraulic and pneumatic vices are used, in which the movable jaw moves not by the lead screw and the worker's hand, but by the pressure, respectively, of the liquid or compressed air supplied to the cylinder. Such devices can be both locksmith and machine tools (for installation on the machine table). Only in them, instead of a screw with a running nut, a hydraulic or pneumatic cylinder is used.
Sinus vise is designed for precise positioning of the part at a given angle, which is required for milling or drilling holes. Between the lower support and the cylindrical sleeve, a set of tiles or a spacer is placed on the movable part, the height of which is calculated or taken from the flow chart. Leaning the movable part on a stack of tiles, the worker obtains the desired angle of the upper part of the vice. By the way, the name of the vice was given by the sine used in the calculations.
Tool vices also "live" only in factories near grinding machines. They have two features: high parallelism of planes and perpendicularity of the sides, which is required for accurate positioning of the part on the machine. Their bottom plane does not have any fastening holes, since they are fastened by magnetization to the machine plate. To clamp the part, the movable jaw is rearranged into the desired hole and the part is squeezed by screwing the bolt with a wrench. All of these vices are practically inapplicable in a small workshop or home craftsmen. Nevertheless, they sometimes come across at flea markets, so we decided to mention them.
There is another very interesting vice - shrabkugels.The base of such a vice from below has the form of a hemisphere, with which it rests on a ring-shaped leather cushion. "Neck" provides a comfortable height for the hands of the master.
The peculiarity of this vice is that the lead screw has two threads (right and left). It is fixed in the frame with both ends so that it does not shift axially during rotation, while the lower parts of the jaws move along its own thread so that the jaws converge or diverge from the center of the device.
This achieves the transfer of force through the area of the bed and eliminates the fall of the device. A lot of blind holes have been made in the jaws on top. If it is necessary to attach a product of complex shape, wooden or plastic rods are inserted into them in such a way that they clamp the product lying on the sponges. At the same time, it will be firmly and carefully fixed: downwards - support on the jaws, to the sides - pressing with rods. Shrabkugels are used for jewelry and engraving.
Folding vise-stand
The difference between these vices from the "ordinary" ones is their versatility. The width of the clamp is such that at least the door leaf together with the frame can be fixed in a vice. The clamp is made with a foot pedal, its force is up to a ton. The floor version allows you to equip a workplace on any site. When folded, the vise is easy to carry and store. It is easy to find application of such a model when working with wood - in the conditions of a construction site or workshop, all of the above features will be very useful. But, of course, there would be a vice, and there will be something to “occupy” them. The vice is equipped with rubberized jaws; additionally, "toothy" jaws are offered for holding round logs with a diameter of up to 300 mm. If the vice is supposed to be used for working with metal, cast iron jaws with an anvil and grooves for fixing pipes and rods can be installed on them.
And one more type of interesting vice is manual. In the photo, the hand vise, released in the USSR, is unknown brand. Such devices were often called "jewelry", but were mainly used as handles for small taps or radio installers for soldering radio components. When the handle is screwed in, the cone moves apart the rear ends of the jaw levers, which is why they converge. They have angular grooves that, when converging, form a 1 × 1 mm square. An extremely durable tool for its purpose and size.