What will it take to work?
Use a tripod to ensure the correct position of the unit. You can do without it in a room with a flat base, but when it comes to working on a construction site on bare ground, then the adjustable equipment will not be superfluous. But it will be inconvenient to work with the device even indoors without special supporting devices. For such purposes, ergonomic holders are provided. They can be attached to walls, floors and even ceilings.
You will also need a special rail. Its scale will allow marking the divisions on the target surface, along which the desired readings will be recorded. How to work with a level and staff? Traditional methods assume that two people will participate in the process - one is directly responsible for fixing the data, and the second is holding the rail. However, the latest models of laser electronic devices automatically process the data, taking into account the special bar codes of the bars. In this case, the user is only required to activate the corresponding function and correctly set the position of the scale.
Horizontal sighting axis and its check
Checking the cylindrical level. Measurements with unequal rail spacings.
To set it up, the following condition must be met: the instrument aiming line must be horizontal when the bubble is in the central part of the zero-point. To check the fulfillment of this condition, it is necessary to select 2 points (C and M), which are spaced 25-35 m apart. Rails are installed in them, and the level is fixed on a tripod so that it is in the middle, between these points. The device is put into action and a reading is taken along the racks, and then the difference between the levels of the location of the points (C and M) is calculated. As an example, let's say that the level reading for the first reading is 1.378, and for the second - 1.278 meters. Then the excess (PRSH) is equal to the difference of these figures - 0.1. Rearrange the tripod with the level as close as possible to point C and take a new reading along the staff. Let's say it is equal to 1.2 m. Then the theoretical indicator is equal to: for the first point - S-PRSH = 1.278, and for the second rail - M-1.2 = 0.078 meters. Then they take a new reading in M and compare the resulting figure with the theoretical one. If this difference is more than three millimeters, then it is necessary to carry out an adjustment.
Cylindrical level and slopes with the bubble position: a - side view, 6 - top view, 1 - ampoule, 2 - liquid, 3 - bubble, 4 - correction screw, 5 - ampoule slope.
Unscrew the protective cap on the eyepiece, using the adjustment pin supplied with the level, turn the set screw until the actual reading on the middle horizontal line coincides with the theoretical result (0.078 meters). Then the check is repeated.
If you install the level in such a way that the eyepiece of the tube with the horizontal positioning of the sighting axis is in front of the staff by two or three centimeters, then you can very accurately determine the height of the instrument from it. The lens must be covered with a cardboard or plastic cover painted black. In its center, you need to make a hole of two to three millimeters. The main observer looks through it at the rail, and the assistant places a movable part made of transparent material with a black stroke in the middle on it. At the direction of the observer, it is installed so that the mark is exactly opposite the hole in the lid. After that, a count is made on the staff.
Scope and device device
Using the latter, you can determine the elevations of points on the plane relative to some base level.During construction, the need for such operations arises constantly. After marking the axes of the future object, the site must be planned, that is, to make it even. Levelers will tell you where to remove the soil and where to fill it up. Determining the depth of the trench for the foundation - again, a level is needed. You cannot do without this tool when installing screeds or concrete floors, especially if they have a large area. Measurements made with a level will help make the base perfectly flat and avoid overspending of concrete or cement mortar.
Diagram of optical level elements ..
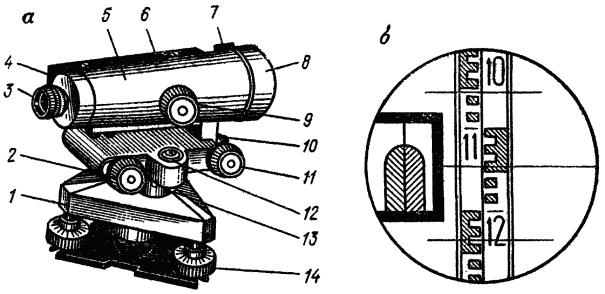
An optical level is a telescope mounted on a support - tribrach. The latter is equipped with three lifting screws that allow you to change the inclination of the pipe in two mutually perpendicular planes, achieving a strictly horizontal position. In this case, the leveling device is guided by the readings of the bubble level, which is also built into the stand. You will need a tripod to set up the level. It is best to use aluminum, which is both strong and lightweight.
The permanent companion of the optical level is the measuring rod. Before carrying out work, you need to get an assistant who will hold it while you take measurements. The scale is applied to the rail from two sides: on one side - in centimeters, on the other - in millimeters.
Working with the level
More often than others, an optical version of the level is used on construction sites. Working with the device consists in aiming the telescope at a special rail with divisions, from which the received readings are subsequently taken.
Recommendations: when buying a level, it is necessary to take into account not only its accuracy, but also such an indicator as optical properties.
 So, the greater the increase in the pipe, the more accurate the measurements will be. As a rule, modern models have 20-32x magnification, but if this is not enough, you can additionally purchase eyepiece or micrometer attachments.
So, the greater the increase in the pipe, the more accurate the measurements will be. As a rule, modern models have 20-32x magnification, but if this is not enough, you can additionally purchase eyepiece or micrometer attachments.
To use the device to determine the difference in heights of two points, you must adhere to a certain sequence. How to correctly use this tool in order to correctly make the necessary measurements?
- First of all, you need to set up a tripod. To do this, extend the legs to the desired height, first loosening and then tightening the screws holding them.
- For the device to take a horizontal position, fix the level on a tripod and tighten the screw. The tool stand should have lifting screws, which should be set at a medium height.
- The level should be set at the "zero-point" indicator.
- The time has come for focusing the telescope: the eyepiece must be adjusted to the vision of a particular person. Now the pipe with the help of the sight must be aimed at the rail, and then turn the screw until a clear image appears.
Tip: to quickly aim the device, you can use a model with a built-in visor.
If there is a need to set the level over a point, centering is carried out. First the screw is loosened, then the weight is suspended. Then the tool should be moved along the tripod head until the weight points to the desired point. It remains only to secure the loosened screw.
The very process of measuring and obtaining results is as follows:
Place the device in a horizontal position and fasten the rail vertically.
Please note: modern models of building optical levels are equipped with special compensators that automatically set the tool in working position. In addition, this system helps to ensure correct measurements even with strong shocks and shocks that often accompany the construction process.
Compensators are protected from mechanical damage by a reliable lock
In addition, this system helps to ensure that measurements are correct even with strong shocks and shocks that often accompany the construction process. Compensators are protected from mechanical damage by a reliable lock.

- Aim the pipe to the backsheet and set the level to the zero point position. Get a reading from the middle and rangefinder lines of the grid.
- Now the pipe should be aimed at the black side of the front rail and the readout should be taken again.
- Aim the pipe to the red side of the same front staff, then read off the middle stroke.
- It remains to point the pipe to the black side of the back rail and take the reading again.
The measurements obtained must be registered in a special journal. To work even in difficult weather conditions, the levels are equipped with a housing with rubber inserts that protect the device from moisture and dust.
Level setting
The level is an optical instrument
For its correct operation, its position in space is important. To adjust it, special mechanisms are provided. In construction, levels with built-in bubble levels are most often used, the adjustment with orientation to which allows you to achieve the correct location
In construction, the most commonly used levels are with built-in bubble levels, the adjustment with orientation to which allows you to achieve the correct location.
For the most effective adjustment, the level is equipped with three screws that change the position of the device along three axes: X, Y and Z. By turning these screws alternately, you can achieve the correct position
When carrying out adjustment manipulations, it is important to pay attention to the position of air bubbles in flasks with liquid. For best results, they should be positioned between the boundary lines
There is a circular bubble level at the top of the instrument
Two circles are marked on its flask: a large and a small one. After leveling the level, the bubble should be located strictly in the center of the small circle. This procedure is the most difficult step in setting up the level. To facilitate its implementation, you need to set the tripod to the maximum "level", since the margin of free adjustment of the device using three screws is limited. The next step in setting up the level is to adjust its optical lens.
A circular bubble level is located at the top of the instrument. Two circles are marked on its flask: a large and a small one. After leveling the level, the bubble should be located strictly in the center of the small circle. This procedure is the most difficult step in setting up the level. To facilitate its implementation, you need to set the tripod to the maximum "level", since the margin of free adjustment of the device using three screws is limited. The next step in setting up the level is to adjust its optical lens.
Setting up the tripod
To get the best results when taking measurements with a level, it is necessary to learn how to use this device. Working with it begins with setting up a tripod. The main criteria that determine the norms for the working position of the tripod are:
- vertical level;
- horizontal level;
- stability.
The presence of a vertical level in the position of the tripod on the ground allows to reduce the error of the final measurement result. This error can be expressed as a violation of the horizontal level. Thus, the vertical level of the tripod affects the display of the horizontal level in the eyepiece of the level.
The horizontal level of the tripod is determined by the inclination of the upper landing pad. The presence of a deviation of its surface from the horizon line at an angle exceeding the allowable value may lead to a change in the vertical level displayed in the eyepiece of the device.
The stability of the tripod position is of paramount importance.Depending on the condition of the surface on which the tripod is located, measures must be taken to ensure its stability.
As part of these measures, the soil or other surface is checked for looseness, holes, cracks or other imperfections. The stability of each tripod leg should be checked so that none of them fall into the ground, slide to the side, or otherwise change their position.
Knowing how the tripod works will help you to set up the tripod correctly. It consists of the following elements:
- landing site;
- adjusting screws;
- support legs (3 pcs.);
- clamps;
- support tips.
The landing pad is the plane at the top of the tripod. It is equipped with grooves with threaded connections, various clamps and adjustment screws. A rotary mechanism operates under it, which allows you to rotate the level without shifting the level of its position. This platform connects the tripod legs together.
The adjusting screws work in conjunction with the platform and other parts of the tripod. With their help, you can change the position of the landing plane in space. They allow you to achieve the correct level of its location - its parallelism to the horizon. Some of the adjustment screws are used to secure the position. They are used after completing the pad adjustment. Their presence allows you to limit its spontaneous movement and exclude deviation from the horizon.
The support legs of the tripod are the main elements of its design. They are fixed in one area - under the landing area, and diverge to the side with beams. Their outreach to the sides is limited by the fastening mechanism and straps connecting their middle parts. Each of the legs is telescopic. The extension and fixation of the position of the knees of the supports is carried out thanks to the clamps.
Clamps are simple mechanisms located at the articulation points of the knees of the legs. They work on a lever principle, which allows you to loosen or fix the clamp in one motion. This solution is optimal for this tripod assembly, as the screw clamps, which were used in earlier modifications, required more time and effort to use.
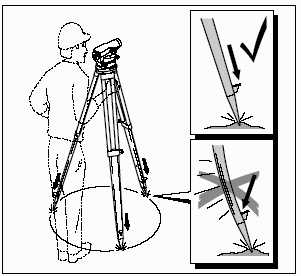
Tripod support tips are pointed metal ends equipped with a small “hilt” that prevents the tip from penetrating deep into the soil. The presence of these ferrules with a limiter increases the static structure. On a smooth surface, the pointed ends prevent the support feet from sliding, which prevents the level from shifting.
On soft and free-flowing surfaces, the tips sink into the soil, but the limiter prevents this sinking by controlling its depth. This avoids accidental subsidence of one or more supports at the same time. Often the tips are equipped with "paws", which serve to press on them with the sole of the foot. Thus, the tips are pressed into the soil by the operator of the device to the desired depth.
How to use the level, installation
The level set consists of a tripod, a staff with millimeter divisions on one side in centimeters on the other, and the level itself. Choosing a place for installation, it is best to place the device in the middle of the measured area.
Steps to install the level:
we set up the tripod: we loosen the clamps, extend the legs to a convenient height for us and clamp them with screws. Set the tripod head exactly horizontally.
install the level on a tripod, fix it with a screw that is on the tripod
we give the level an even horizontal position with the help of three lifting screws rotating them simultaneously (turning the screws I shift the bubble in the middle and adjust it to the center of the level with the third screw), eventually the level bubble should be in the "zero-point" position.
The level is adjusted, it remains for a small one to focus in the telescope.Focusing, aiming the telescope on the staff and turning the focusing screw, we achieve a clear image, the reticule is adjusted with the eyepiece ring.
Centering, set the level over the point, hang the plumb line by the fixing screw at the bottom of the tripod. We move the level along the tripod head so that the plumb line is above the point, fix it. this operation is needed if you are going to measure the distance from one point to another or using the optical beam of the level, for example, to set out the axes of a building.
How to use a level for flooring
Not knowing how to use the level, it is not possible to make even floors of concrete or cement-sand screed over a large area.
Working as a foreman in concrete flooring firms, the first thing I did on the new site was leveling the base. According to the survey, it is clear whether it is necessary to add sand or vice versa.
How to check the evenness of the base with a level? Let's say we have an object with an area of 540 square meters and we know the zero mark clean floor level.
After setting up the level, we start shooting. I took the marks of the base every six meters, both along and across the building, if you do it every three meters, then this will be a more accurate picture of the evenness of the surface.
Suppose, according to the survey results, we received 18 elevation marks with elevation differences from 1.57 m to 1.72 meters. We sum up all 18 elevations, we get the total of 30.51 m, divide by 18 equals 1.695 m, this is the arithmetic average elevation of the base from the level of the instrument horizon.
Next, we calculate the thickness of our floor, from 1.695m we subtract the mark of the finished floor 1.20m is equal to 0.495m. According to my measurements, it turned out that the base is lowered from the level of the finished floor by 49.5 centimeters.
How to use the level when constructing foundations
How to use the level if you need to determine the depth of the foundation indicated in the project. After installing the device, we calculate the horizon of the instrument. In my case, the geodetic mark is placed on the column, equal to 96.645 m.
We put the rail clearly on the mark and we get the data on the 0.850 m rail. We calculate the horizon of the instrument, to the geodetic mark 96.645 we add the mark from the staff 0.850 m, we get 96.645 + 0.850 = 97.495 m.
The design elevation 93.80 (bottom of the foundation) from the resulting instrument horizon we subtract the design elevation 97.495-93.800 = 3.695 m. It turns out that our foundation elevation from the horizontal beam of the level should be equal to 3.695 m.
If the level of the earth's surface according to the leveling survey is 1.250 m, then it turns out that it is necessary to remove the soil to a depth of 3.695 m - 1.250 m = 2.445 m.
How to use the level - step by step instructions for beginners
The practical application of an ordinary level is described by the following sequence of measuring actions:
Step 1: Setting up the tripod
The fastening screws on all three tripod legs must be loosened, after which each support is extended to the required length (this length can be different, because the level is often installed on rough terrain). The top of the tripod should be in a horizontal position, and then tighten the fixing screws on all three legs. Most of the devices are supplied with smooth corrective mounts on each "tripod leg", they are used to fine-tune the horizontal position of the upper platform.
Step 2: Mounting the level
The leveling pipe itself is mounted on a tripod with a few fixing screws, after which the level sensors have to work. By turning the adjusting screws, it is necessary to achieve an exact, central position of the bubble levels relative to the lines drawn on them. For convenience, first put the bubble in one "window", not paying attention to the other. Then the second level is adjusted, already tracking the position of the first, observing how it changes as it is installed.By gradually adjusting the position of the device, they achieve its exact horizontal position on the installation site.
Step 3: Focusing the optical-mechanical assembly
Before working with the optical level, it is necessary to adjust the eyepiece of the aligned telescope to the operator's vision. As you know, the acuity of the eyes of different people is different, even if they all do not wear glasses. Focusing a standard level is done as follows. The device is aimed at a well-lit and rather large object and operate with the settings until the thread mesh is displayed on this object as clearly as possible. Then this operation is repeated on rails installed in other, already less illuminated places. Experimenting with focusing on subjects with different illumination will help with further measurements.
Step 4: measure and record observations
With the instrument set horizontally accurately, aligned and focused, we proceed to the engineering survey. Two slats should be placed in front and behind our device. The front one will show the value of the measured height, the back one will calibrate the values. First, the level is aimed at the black side of the back staff, after focusing, the value is recorded along the middle and rangefinder lines. Then they focus on the front (main) staff, and the average value along its red side is fixed. This method is called centerline leveling, it is characterized by high accuracy of results and the convenience of multiple measurements.
Photo of the optical level South,.
In the photo - how to work with an optical level,.
Photo of the scheme of working with the level, snp.by
In the photo - working with a laser level,.
Photo how to use the level and rail,.
Selection guide
When looking for a model suitable for construction work, you should take into account not only the set of functions and the type of device. There are a few more criteria to consider:
- Accuracy. For professional devices, it is 0.5 ... 1.0 mm per 10 meters, for household appliances, it is optimal 1.0 ... 3.0 mm per 10 meters.
- Line range. In the construction of sports or industrial facilities, powerful devices are required that can give a beam at a distance of more than a hundred meters. For the construction of a private house, it is enough to use the simplest 20-30 meter ones.
- Line color. There are levels with red and green emitters. The first ones are the most common - for the convenience of finding them on the street, glasses with red filters are used. However, the green line is more pleasing to the eye. Otherwise, there is no difference between them.
- Power class. 1 - these are household appliances with a short beam, 2 class - more powerful, 3 - professional rangefinder devices.
- Alignment method. The most affordable are manual ones, the vertical and horizontal of which are set by a person. Easier to use self-leveling laser. It is enough to set it to the control point, press the button and the device itself will take the operating position, which will be signaled by an audible signal. This will cost much more than a manual one.
- The battery capacity determines the duration of the level.
- IP protection level. Levels are used in street conditions. Rain, dust, heating and cooling - the device must be protected from all these influences. IP54 is the optimal solution for construction conditions; for the street and in the field, you should not skimp on IP65 or IP67.
- Equipment. Filter goggles, signal catcher and other auxiliary items are designed to make it easier to work with the level, but you will have to pay extra for them.
The choice of a laser level should not be influenced by the price, since it depends on the set of functions, equipment and manufacturer's brand. The most reliable are BOSCH, Geo-Fennel, Matrix, Kapro, Makita and ADA.
How to use an optical level when building a foundation
The algorithm of actions is almost identical to preparing the foundation, with the only difference that in this case the foundation is already ready, if only it is necessary to level it. So, the sequence of work:
- Set up the level so that you can clearly see each corner of the foundation in a relatively narrow field of view (90 ° or less). This will help eliminate errors associated with turning the level at large angles. To minimize error, position the level above the foundation as low as possible.
- With an assistant holding the staff, shoot the outer corners a, b, c, d and record their heights. In our example, the highest angle is b.
- From the height of the highest corner, subtract the heights of the remaining corners and write down the difference - this will be the thickness of the shims.
- Use shims to bring the corners to the level of a high angle with a tolerance of ± 1.5 mm.
- Pull the lace between the corners. With the cord stretched horizontally, place steel spacers between the bed and the foundation under all joists, beams, and point loads.
- Place shims in the right places to roughly fit the cord to the cord.
These are general recommendations when working with a level at different construction stages of building a house.
Design and classification of standard levels
Layouts of the axes when checking the level: A - c - layouts of the axes when checking the level, d - the position of the level at the third verification.
This device has a simple design. The main optical-mechanical unit is located on the tripod, into which the lens system is built. This unit must ensure the horizontal line of the sighting beam, while only a minimum deviation is allowed. Lenses can produce a straight or inverted pattern. In the latter case, the measuring rod must also be turned over during installation on the ground.
Level sensors must be built into the upper part of the structure of all levels. Precise installation of the device on the ground determines the quality of further measurements. A qualified specialist will regularly check the values of these sensors, performing, if necessary, adjusting them with special tilt levers of the optical-mechanical unit. You can timely detect an accidental deviation of the device from the exact location on the ground and not re-measure.
Before using the level and the plank, you will need to familiarize yourself with the main types of devices for geometric measurements of excess height.
A meter with automatic installation error compensation is more accurate, but it is much more expensive. It is convenient to use it in the process of making measurements on problem soils: crushed stone, sand, etc. Devices with an electronic measurement system are used in the process of designing large-scale objects. This design is difficult to set up and operate.
According to the class of measurement accuracy, leveling structures can be divided into such main groups as:
- technical devices (marking H-10, H-12, etc.);
- precision devices (designations from H-3 to H-9);
- ultra-precise devices (designations from H-05 to H-2.5).
The numbers in the marking indicate the average measurement error in mm / km. It should be understood that even a technical device will give a deviation of about 1 cm per 1 km of distance to the object. This is enough to carry out accurate design and correct planning of a large number of construction works.
Excess measurement
Terrain relief - this is a set of irregularities in the surface of the earth; it is one of the most important characteristics of the terrain. To know the relief means to know the marks of all points of the terrain. Point elevation - this is the numerical value of its height above the level surface, taken as the beginning of the calculation of heights. The elevation of any point in the terrain can be determined from a topographic map, however, the accuracy of such a determination will be low.
The elevation of a point on the terrain is determined by the excess of this point relative to another point, the elevation of which is known. The process of measuring the elevation of one point relative to another is called leveling. The starting point for counting heights in our country is zero of the Kronstadt foot stock (horizontal line on a copper plate attached to the abutment of one of the bridges of Kronstadt). From this zero there are leveling moves, the points of which are marked in the Baltic height system. Then, from these points with known marks, new leveling passages are laid, and so on, until a rather dense network is obtained, each point of which has a known mark. This network is called state leveling network; it covers the entire territory of the country.
The marks of all points of the leveling networks are collected in the lists - "Elevation catalogs". These lists are continuously updated, new catalogs are published on new leveling lines. To find the elevation of any point in the terrain in the Baltic elevation system, you need to measure its elevation relative to some point, the elevation of which is known and is in the catalog. Sometimes the elevations of points are determined in a conditional system of heights, if there are no points of the state leveling network nearby.
Geometric leveling or leveling with a horizontal beam is performed with a special geodetic device - level; a distinctive feature of the level is that the sight line of the pipe is brought to a horizontal position during operation.
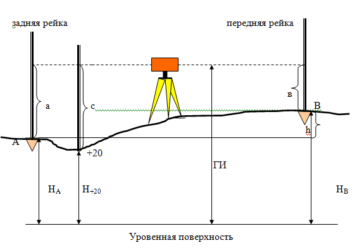
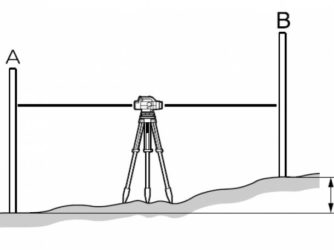
There are two types of geometric leveling: center leveling and forward leveling.
When leveling from the middle, the level is installed in the middle between points A and B, and rails with divisions are placed at points A and B (Fig. 4.29). When moving from point A to point B, the staff at point A is called back, the staff at point B is called front. First, point the pipe to the backsheet and take a reading a, then point the pipe to the front rail and take a reading b. The excess of point B relative to point A is obtained by the formula:
If a> b, the excess is positive if a x this error reaches 1.2 mm at 100 m distance.
Violation of the main condition of the level; when leveling strictly from the middle, this error is excluded.
The tilt of the staff. To reduce the influence of the tilt of the rail, it is recommended to slightly wiggle it back and forth around the vertical position; with readings less than 1000 mm, the rail cannot be swung. When the staff is wiggled, the readings on it change; the smallest count is correct.
An error in drawing divisions on the rail.
The total reading error on the checkerboard with the H-3 level is estimated at 4 mm per 100 m distance.
A level is a device for determining the difference in heights, checking the flatness of the surface by determining the excess of one point over another horizontal beam. Levels are divided into optical, digital and laser.