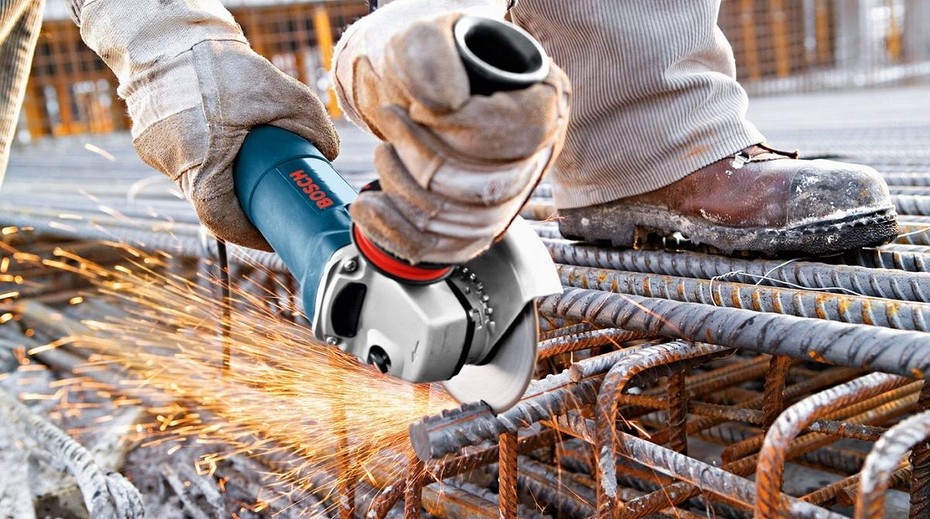
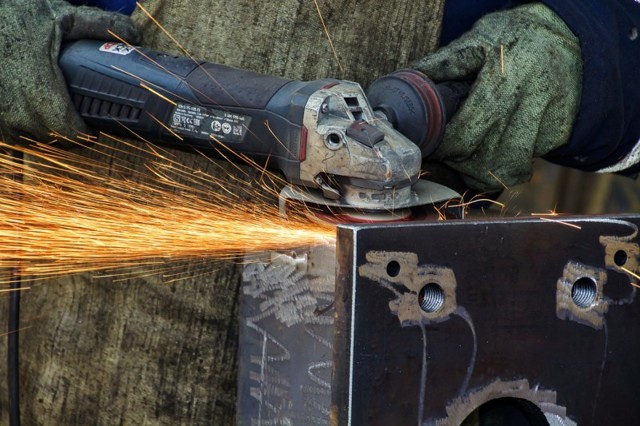
Basic rules for safe work when cutting metal with a grinder
The layout of the most dangerous sectors when working with a grinder, taking into account the rebound and destruction of the disc.
The most necessary condition for cutting is strict adherence to the rules of safe work.
Grinder manufacturers are constantly trying to minimize the risks of injury and injury by inventing and improving various protection systems. But no one cares about the worker like he does.
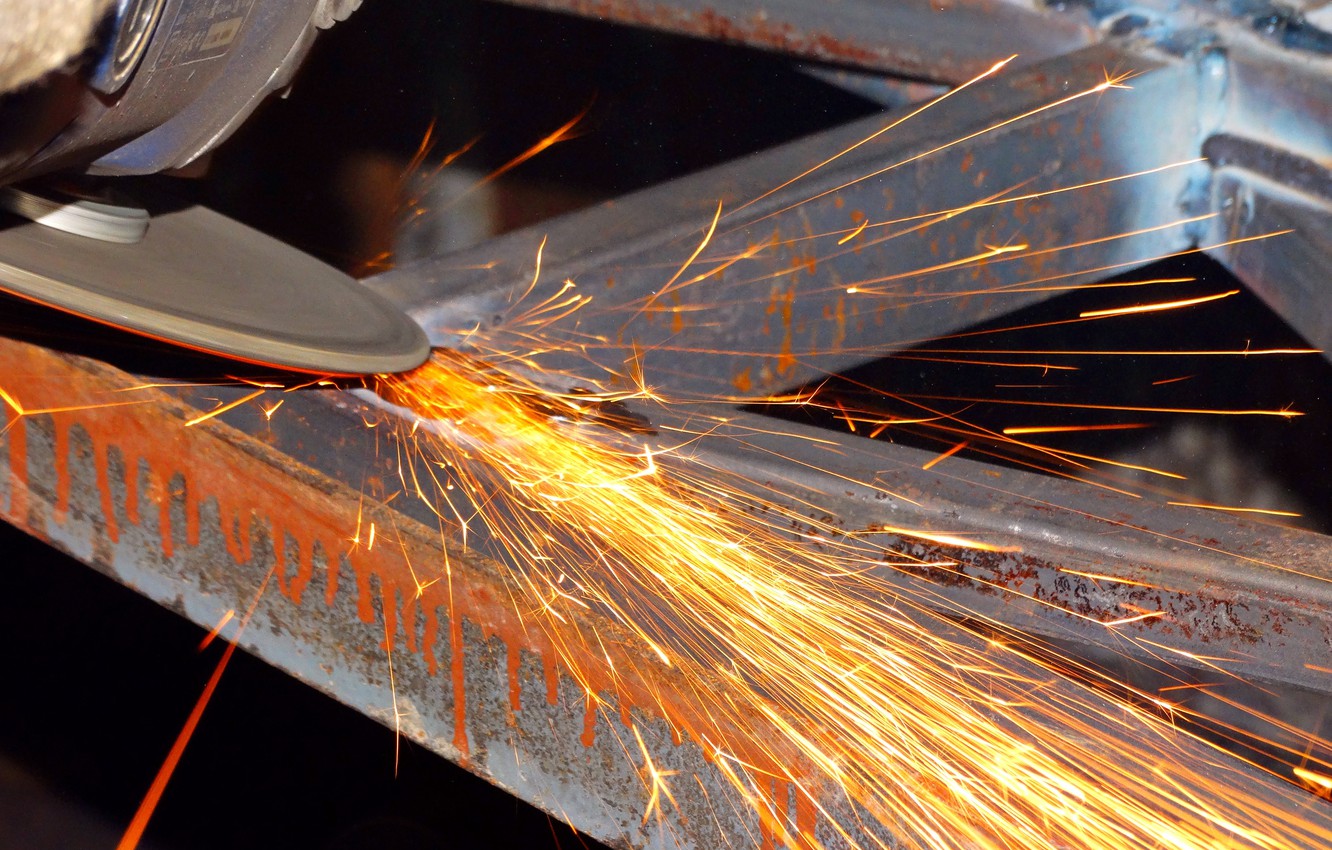
The main dangers that arise when cutting metal are the flight of fragments of a broken disc, the flow of sparks and the smallest abrasive particles, the inability to hold the tool in your hands.
If the disc breaks or gets jammed, the grinder can break out of the hands at the most inopportune moment and with great force, therefore, even before starting work, the direction of its possible movement should be foreseen.
Safety rules cannot be neglected even when performing small work.
Before starting work, you should:
- Protect face, eyes, hands and, if possible, all body parts.
- Remove all combustible materials and objects that are in the direction of the discharge of sparks.
- Fasten the part to be processed by the grinder, if possible, in a vice. Do not hold the workpiece with your free hand or press it with your feet.
- If you install a new disc, you need to "spin" it with a grinder at maximum speed, placing it further away: the disc may turn out to be defective and fly to pieces.
- Install, adjust and secure the protective cover.
It is best to protect your face with a special shield when working with a grinder.
During work, you should:
- When replacing discs during rest, you must disconnect the grinder from the network.
- Use goggles or a face shield to protect your eyes and face - professionals use both for extended work.
- Hold the grinder firmly during all work.
- To replace a disk, you need to wait until it comes to a complete stop.
- Wear protective gloves. It is undesirable to use cotton gloves, they do not provide sufficient protection, they can ignite, and the threads wind up on the grinder's spindle or disc.
- During work, you need to position yourself so that the face, and, if possible, all parts of the body are not in the plane of rotation of the disk.
At the end of the work, you should:
- wait until the disc rotation has stopped completely and only then put the tool on the floor with the disc facing up so as not to damage it;
- disconnect the grinder from the network;
- make sure there is no smoke or other signs of fire.
A typical mistake that is made when cutting metal: if the diameter of the new circle is larger than the size of the protective cover, it is removed. The casing is a protection in case the disc breaks and shatters in the process.
Instead of a disc, many put cutters, saws or other scrap materials. Doing this is strictly prohibited.
Working principle of diamond cutting disc
Most diamond discs are used on angle grinders up to 12,000 rpm. The maximum number of revolutions that the best wheels can withstand is 13,900 rpm, but there are not too many tools that can develop them when cutting.
Only the diamond itself is in contact with the treated surface - it protrudes above the surface of the rim and, when rotating, abrades the material into fine dust. The multi-layer structure of the cutting edge ensures that the wheel is always ready for work - abraded or ejected diamonds are replaced by others that are in the lower layer of the rim.
Excess heat is carried away through the blade body, but, nevertheless, it heats up to high enough temperatures, which requires adherence to certain safety rules for dry cutting.
The longevity of the wheel and the effectiveness of its use depend on the size of the diamonds. Large ones provide work efficiency, but wear out quickly, small ones cut very accurately, but slower, their service life is 25 - 30% longer than that of a tool with large crystal fractions.
Unscrewing methods if the disc is jammed
What to do if the hold-down flange is stuck? This nuisance, when the nut is bitten, often occurs if, while working with thick and durable materials, the tool is jammed in the workpiece. In this case, the abrasive wheel often breaks, and the spindle continuing to rotate tightly tightens the clamping flange. There are several ways to spin the grinder if the disc is jammed.
With a gas wrench
This method is considered not entirely safe, since the stopper can be broken, although in most cases, it is possible to unscrew the nut. To avoid breaking the spindle lock, do not apply too much force to the gas wrench. The retainer is designed to withstand the force of a standard wrench.
An overly tightened flange can be unscrewed using 2 gas wrenches. To do this, break off the protruding ends of the abrasive wheel with pliers so that you can reach the bottom flange with the first gas wrench. Next, tighten both flanges with wrenches and turn them in opposite directions (taking into account which thread on the spindle is right or left).
Disassembly of the gearbox
In the event that the retainer is broken, you will have to disassemble the gearbox to remove the tool from the angle grinder. Use pliers to break off the edges of the remaining abrasive wheel so that you can get to the bolts holding the gear cover. After that, unscrew the fasteners and open the gearbox. The cover will be removed together with the pinion shaft. Further, this shaft should be clamped in a vice, having previously laid aluminum gaskets between the steel jaws, and using a gas wrench, unscrew the flange (do not forget to determine the direction of unscrewing).
Heating nut
The nut can be heated with a gas torch, hot air gun or blowtorch. The heated flange can usually be unscrewed with a standard grinder wrench.
Sewing off a jammed circle
If, after applying the first 3 methods, the nut does not loosen, then the remaining abrasive wheel between the flanges can be ground off. To do this, follow these steps.
- Use pliers to remove the rest of the circle around the edges of the nut as much as possible.
- Clamp a piece of sheet metal as thick as the disc itself in a vice, turn on the grinder and grind off the rest of the circle on the end of the sheet metal.
But the use of a stationary abrasive wheel requires great care, because when grinding the remnants of the tool, the geometry of the flange can be damaged. If this happens, you will have to trim the nut.
Using a penetrating lubricant
Liberally spray the flange-shaft connection with WD-40 fluid. It tends to penetrate into inter-threaded spaces and small cracks. After applying the liquid, wait about 5 minutes and try to unscrew the fasteners with a standard wrench.
Using a puncher
Some owners of grinders, in a situation where the clamping nut is jammed, install a “chisel” or “jackhammer” nozzle into the hammer drill, insert it into the hole of the flange at an angle and turn on the jackhammer mode without rotation. Accordingly, the stop button must be pressed. Just a couple of gentle clicks with a perforator are enough (so as not to break the shaft retainer), and the nut will begin to turn.
Cut the pressure flange with a hacksaw
This method can be called radical, since you will have to buy new fasteners, and it is used if the nut is not unscrewed by any other methods.To cut the flange, hold down the stop button so that the shaft does not rotate, and using a metal hacksaw, cut the retaining nut.
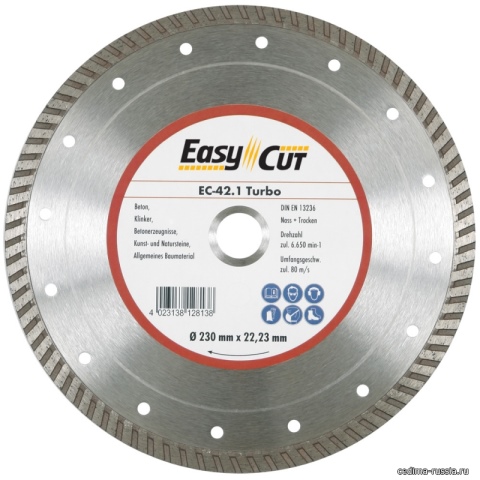
Varieties of diamond discs
Diamond cutting discs have certain differences in design and manufacturing technology.
Types of diamond discs by structure
By structure, dry cutting discs are divided into:
- solid;
- segmented;
- turbo;
- turbo-segmented.
Solid diamond discs. Equipped with a continuous cutting band, running along the circumference, into which artificial diamonds are interspersed in several rows. For cutting ceramics and other materials, where cutting accuracy is the main parameter, wheels with a solid edge are preferable.
Segmented diamond discs. Segmented ones are divided by radial slots into several working sections of the same size, they are more resistant to mechanical and thermal stress and are used more often than solid ones, although they are somewhat more expensive. They are more productive than solid ones, but the cut after them is not as accurate. They are best used for rough cutting of concrete structures.
Turbo diamond discs. Turbo disks are distinguished by the presence of oblique (and not only) notches on the sides of the rim. It somewhat increases the mechanical strength of the wheel and significantly increases the intensity of heat removal, which makes it possible to speed up cutting from 50 to 100%. Like segmented blades, turbo blades are suitable for fast cutting of all mineral materials of a wide range of hardness - from sandstone to concrete and granite.
Turbo segmented diamond discs. Even more powerful are discs divided into segments with a turbo side notch. They are characterized by high performance and versatility.
Difference of discs by the arrangement of diamonds
Artificial diamonds are fixed in the working rim in a specific order. There are circles with their even distribution, when there are the same number of crystals in any of the selected length units or segment.
But there are also circles in which diamonds are arranged with a certain period (the so-called sandwich). They are more productive with less tool force, more efficient cooling and even force distribution.
Diamond blades for dry and wet cutting
According to the cutting method, diamond discs are classified into dry and wet cutting discs. The former provide an accurate cut and are "cleaner" in work, but require the use of dust extraction devices - when cutting, very small particles of solid materials are formed, which irritate the eyes and respiratory tract. Water-cooled wheels operate with a constant flow of liquid that binds and washes away dust, but they cannot always be used. This is due to some bulkiness of the hydraulic system and the formation of drips.
Dry cutting wheels can be used in water cooled machines, but wet cutting wheels cannot be used without cooling - they overheat and deteriorate quickly.
Basic safety rules for working with metal
How to cut correctly metal? The basic rules for this process:
- The specialist should equip himself with goggles when working with angle grinders, take shields, in order to avoid sparks, small particles of metal from getting into the eyes.
- It is advisable to secure all parts of the body. Hands must be put on protective gloves, not cotton, they are highly flammable.
- To cut metal with a grinder, it is necessary to remove nearby objects, especially highly flammable ones.
- The workpiece must be fixed in the machine or vice. Do not hold it with your hand, do not pinch it with your feet.
- When installing a new disc, rotate it at maximum speed, you need to keep the grinder away from you.
- If the disc turns out to be defective, it can fly into small parts and injure.
- The protective cover of the angle grinder must be adjusted, securely fixed. It is installed to protect the eyes from the emission of particles.
- The master must remember that when replacing disks or during rest, the device must be turned off from the network.
- Do not try to change the disc while the grinder is on.
- You only need to move around the work area with the grinder turned off.
- If the light turns off accidentally, you must turn off the grinder to avoid unexpected turning on.
You should not put cutters, saws instead of a disc, it is strictly forbidden to do this. Safety rules must be observed and the possibility of injury must be minimized.
How to choose the right grinder
The grinder should fit comfortably in your hand.
The correct choice and quality of the grinder itself determines the quality of work and the safety of the worker.
When choosing a machine, you should be guided by its main parameters: power and diameter of the cutting abrasive wheel
Its weight is also of no small importance, since it is often necessary to work "on weight", and dimensions so that you can perform work in inconvenient and hard-to-reach places.
Most buyers at the sight of powerful grinders are somewhat frightened that it is more difficult to cope with it than with a low-power one. This is a misconception. Low-power grinders are more likely to jam discs, i.e. they are physically unable to “pull out” the disk under heavy loads. The situation of how the disk and the machine itself will behave after reducing the load is unpredictable. Most likely, the grinder will be torn from the hands. The consequence of this will be a break in the disc, damage to the machine and injury to the cutter. Therefore, it is better for novice craftsmen to purchase a grinder for a 125 mm disc with a power of 800-1000 W and a spindle speed of 10,000 rpm. This power is sufficient for cutting iron.
For cutting metal, there are machines for a 115 mm disc powered by batteries, but, as practice shows, with their high cost in solving household problems, they do not justify themselves.
The handles of the grinder should be rubber or made of a material that will dampen vibrations from the machine.
But none of the technical characteristics reflects the convenience and safety in work.
The grinder should lie comfortably and securely in your hand so that when working with metal you can focus your attention on it, and not on how to hold the tool in your hands. It is desirable that the grips are rubber or vibration-damping material with indentations for the fingers.
Low-powered grinders, as a rule, do not have an additional handle.
If, when choosing, any inconvenience was found, you should look for a grinder of another model.
Specialist recommendations for some types of work
Next, we will tell you how to work with an angle grinder with various metal products.
Chainsaw chain sharpening
Photo number 12: sharpening the chainsaw chain with a grinder
The chain is sharpened on the boom of the chainsaw. For work, use a grinding disc with a thickness of 2.5 mm. The first tooth to be processed should be noted. With competent actions, you can update the chain 4-7 times before it finally fails.
Pipe cutting
Photo no.13: pipe cutting with a grinder
It is better to start cutting thick metal with a grinder from the edges. Starting in the middle can cause the disc to jam and bend. During processing, apply force to the bottom of the cutting tool, which ensures effective cutting.
Cutting moldings
Photo number 14: cutting corners with a grinder
For cutting metal corners, you can use worn discs or a small diameter tool
It is important to remember that the work is phased: first, one part of the molding is cut, then the second.
Circular saw wheel sharpening
Photo No. 15: sharpening a circular saw circle with a grinder
Start by securing the angle grinder with clamps, leaving access to the rotating part of the tool. Then bring the saw blade to the grinding wheel without applying too much force. The circle must run tangentially along the product. When working, observe the observance of the sharpening plane.
Views
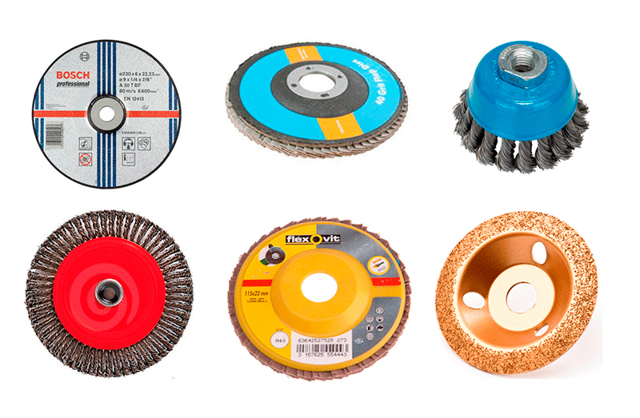
Depending on their purpose, nozzles for angle grinders can be classified into several types.
Cutting discs are perhaps the most popular model of cutting discs. They are used for cutting all sorts of materials. In turn, cutting discs can be subdivided according to the material for which they are reassigned.
Cutting discs are some of the most durable. They vary in size, thickness and diameter.



- Discs for stone outwardly do not differ in any way from circles for metal, but their composition is different. These discs use different abrasive materials.
- Diamond blades are one of the most versatile attachments for all materials. Ultra-strong crystals that grow into the composition of the circle are able to cope with metal, and with stone, and with concrete. These discs can differ in the size of the spraying (fine and coarse), as well as the cutting edge (solid and individual cutting sectors).
This completes the classification of cut-off models. Next, it is worth considering the types of grinding discs and polishing wheels. These models differ in their coverage. They may contain sandpaper, felt. And also the grinding discs can be spongy or cloth.

It is also worth noting such types of discs for the grinder as sharpening and roughing (or stripping). There are also some varieties among them. For example, a disk with twisted cones. These circles are a round steel wire brush.
Sharpening consumables are usually small in diameter. They are used, as a rule, for cleaning welded seams or for sharpening tools. Diamond grinding wheels are distinguished by the fact that work with them is carried out exclusively by the peripheral part of the wheel.
It should be said about the materials from which the cutting wheels are made. They can be diamond, carbide, abrasive and metal wire wheels.
- Diamond blades are diamond-coated and are usually made of steel. On carbide discs, instead of diamond spraying, high-carbon steels are used, to which nickel and chromium are added.
- Abrasive discs are made of thick latex paper with a reinforcing mesh between the layers. These discs usually have the most affordable price.
- Wire discs are intended for stripping work. Cutting hard materials with such circles is quite difficult.