Checking the planned pipe for the amount of natural draft
In fact, we have already determined the main parameters of the chimney - a sufficient section of its channel and height. But for devices with natural thrust, it will never be superfluous to check the strength of this very thrust. So that it does not happen that the built chimney suddenly refuses to fulfill its main functions.
Draft is, in fact, the pressure difference between the hot gases in the pipe and the outside air. It is this difference that stimulates the movement of the gas flow through the chimney channel.
It is believed that for normal operation of a natural draft chimney, this difference should be at least 4 pascal for each meter of pipe height (0.408 mm water column or 0.03 mm Hg). That is, for a five-meter pipe (our minimum), the thrust must be at least 20 Pa. This ensures both the normal evacuation of gases and the necessary air flow for continuous combustion of the fuel.
How to calculate this thrust. Naturally, it largely depends on the density of gases, which, in turn, are closely related to temperature. This can be seen by looking at the formula with which we will work:
ΔP = Htr × g × Patm × (1 / TV - 1 / Tds) / 287.1
ΔP - natural draft in the pipe, Pa.
Htr - chimney height, m.
g - acceleration of gravity (9.8 m / s²);
Patm - atmospheric pressure. A value of 750 mm Hg is considered normal. However, the area for which the calculation is carried out may have its own specifics. It must be understood correctly that sea level is considered the norm. And with an increase in altitude, this rate begins to decline. And - quite significantly. So, when calculating, you will need to be guided by the norm for your region of residence.
Atmospheric pressure is usually measured in millimeters of mercury. However, for the calculation in the SI system, it is required to translate it into pascals. This is not difficult if you know that 1 mm Hg. Art. = 133.3 Pa.
TV - the outside air temperature. Moreover, reduced to the Kelvin scale, that is, C ° + 273.
Tds is the average temperature of gases in the chimney. It is defined as the arithmetic mean of the input and output indicators, followed by conversion to the Kelvin scale.
287.1 - gas constant of air. It would be more correct to choose this value for the specific chemical composition of the exhaust gases. But in our case, the error will not be significant, strongly affecting the final result.
A few important notes on inlet and outlet temperatures.
You should always strive for its optimal values. Statistics show that most fires occur with sauna stoves, in which there is practically no heat removal, heat builds up in the steam room in a short time, and the chimney usually heats up to dangerous temperatures. Therefore, you need to be able to control the temperatures in the pipe using available means - gates, valves, devices for additional heat recovery (for example, hot water tanks).
In household and heating stoves, this is easier, but control is still necessary. In boilers, where the very essence of the work lies in the constant release of heat to the circulating coolant, these questions are not so acute.
The 900 ÷ 600 ℃ mode (entry and exit), found in some of the sauna stoves, is extremely dangerous in all respects, and should not even be considered! A reasonable framework (and even then - their upper limit) is 600 ÷ 400 degrees for household brick and metal stoves. Usually, they try to withstand in the range of 400 ÷ 200 ℃. For gas equipment, the lower limit may fall below 100 degrees.
If all the initial values for substitution in the formula are known, you can proceed to the calculation. To do this, we again suggest using the capabilities of a special online calculator.
Calculator for calculating the natural draft of the chimney.
If the obtained pressure difference falls within the norm (more than 4 Pa per meter of pipe height), then the check can be called successful.
The main parameters of the chimney have been obtained - you can proceed to the choice of materials and detailed design.
The proposed video will tell you about many other intricacies of self-designing a chimney:
Chimney section and height
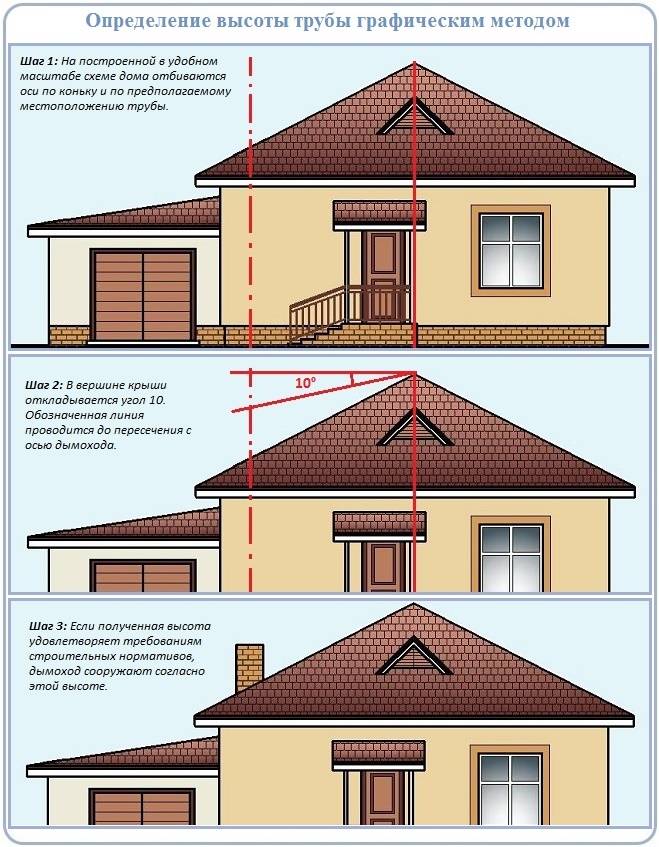
The chimney height is the parameter that largely determines the draft force.
There is a formula according to which the pressure difference directly depends on the atmospheric pressure, the temperature difference outside and inside, and also on the height of the chimney itself.
The greater the temperature difference, the greater the draft, the higher the atmospheric pressure and the height of the chimney, the greater the draft.
The owner of the chimney cannot influence the atmospheric pressure in any way, as well as the temperature outside. The temperature inside depends on the heat source. It rarely exceeds 1000 ° C.
In a short pipe, air entering from the outside will, on the contrary, facilitate the flow of smoke into the room. In a pipe that is too long, the pressure gradient will not be sufficient for good thrust.
Two air currents are created in the pipe, one tends inward, the other outward. The smoke in the chimney forms turbulences which must not interfere with the air flow. In order for the thrust to be maximized, the pipe must have a certain diameter. The bore diameter plays an important role in providing passive thrust.
In a narrow pipe, air creates turbulent flows and, instead of escaping outside, travels through the pipe for a long time. The longer the warm gas flows into the cold pipe walls, the colder it becomes. Cold smoke will not come out of the chimney. In a chimney that is too wide, there is also the possibility of rapid cooling of the smoke due to the excessive intake of cold air.
The optimal area of the chimney is considered to be at least 10 cm2, in the case of a round pipe - at least 15 cm in diameter.When installing fireplaces in which the combustion temperature of the fuel is slightly higher than in stoves and columns, one should focus on a minimum diameter of 10 cm. The maximum diameter will be depend on the size of the heater.
As for the chimney height, it depends on many parameters. In ideal conditions, when the roof is flat, does not have any protrusions, there are no trees and other buildings at its level and the air access to the chimney does not block anything, the chimney has a maximum height of 5m. In this case, its height is considered from the grate of the heater to the very top.
Smooth roofs are very rare in houses. They are often sloping, have various protective or decorative elements, and come into contact with trees and other buildings.
Under all these conditions, the chimney height is calculated separately.
In addition to the fact that the height of the flue ducts is regulated by the requirements of SNiP, its cross section and internal shape must be taken into account. These parameters also affect the normal functioning of heating devices and their efficiency.
According to the laws of physics, warm air - in our case, flue gases - as it heats up, rises up. And the closer it is to the outside, the more it cools, as a result of which traction is formed. Accordingly, a large chimney cross-section, it would seem, should create better draft. But in reality this is not always the case.
What is the expected way out? It is possible, by increasing the height of the pipe, to reduce its cross section. In this case, the draft will be so large that it can lead to a loss of efficiency of the heating boiler or stove. After all, the flow of cold air from below will be increased, due to which the heating of the heating device itself will be insufficient. This means that it will take more fuel consumption and time to warm up.
With a high chimney and insufficient inner diameter, the draft will also not be enough for the normal operation of the device. In addition, smoke and carbon monoxide gases can be thrown into the room. To prevent this from happening, and the heating devices worked with full dedication and performance, it is necessary to calculate all the parameters using a calculator or by inviting specialists.
Tips & Tricks
Sometimes in the house, in addition to the stove, a fireplace or a gas water heater needs to remove smoke. Of course, removing the chimney for every appliance is not an option. In this situation, experts recommend making a combined pipe with several channels; it is imperative to take into account the power of each device, as well as the type of fuel and the amount of products being discharged.
Taking into account the general recommendations of professionals, you can achieve high-quality work and design, namely:
- when installing a brick chimney, the masonry must be dense;
- so that there is no heavy load on the building, they provide a transition to pipes in the attic;
- it is recommended to install a metal and asbestos pipe only vertically;
- so that dirt and birds do not get into the chimney, a special umbrella is put on the top;
- if the height of the structure is more than 1.2 m, it must additionally be fastened with guy wires.
Varieties
By location, chimneys are as follows:
- wall - they are installed inside the main walls;
- indigenous - settle in the form of a separate structure;
- outdoor - installed on the facade of the house.
For brick buildings, experts recommend using wall chimneys, since they do not require the use of additional materials. A pipe of this type is produced independently along with the construction of the building. Heating equipment according to the gas removal method is divided into designs with natural and forced draft.
Single-wall chimneys are distinguished, which are made of stainless pipes with a thickness of 0.6 to 1.0 mm. They are installed inside the house or brick channels, their heat transfer provides additional heat to the house.
Double-walled pipes are made of two layers of stainless steel, between which a non-combustible insulation is installed. The advantages of this design include temperature savings and high gas flow rates. There is practically no condensation and the requirements for indoor installation are minimal. But such a structure is very high.


Traction: How To Achieve Perfect Fuel Combustion
The traction force itself is influenced by several important factors at once:
- chimney material;
- foundation height above sea level;
- flue gas temperature at the outlet of the furnace;
- cross-sectional shape of the chimney;
- smoothness or roughness of the inner surface;
- violation of the internal tightness of the chimney;
- temperature and humidity of the outside air;
- ventilation of a room with a boiler or stove;
- completeness of fuel combustion;
- the degree of contamination of the boiler (or stove) and chimney;
- type of burner used (modulating or discrete).
First of all, you need to determine the value of the static draft of the chimney, and it is measured in the value of ∆p. Here is the formula to calculate:
h = (∆p Tp Tn) / (3459 (Tp-1,1 Tn))
Tr is the average temperature in the pipe and Tn is the outside temperature. It is measured by default in degrees on the Kelvin scale, but you can also specify it in Celsius by adding +273.
Calculating the average temperature is not difficult
Usually it is reported in the technical data for the boiler, but it is also important to take into account the cooling. This is 1 degree for each meter of a brick pipe, 2 degrees for a meter of insulated steel pipe and 5 degrees for an uninsulated one.
At the same time, it is advisable to take the value of the outside temperature that is typical for summer as the most problematic time for traction:
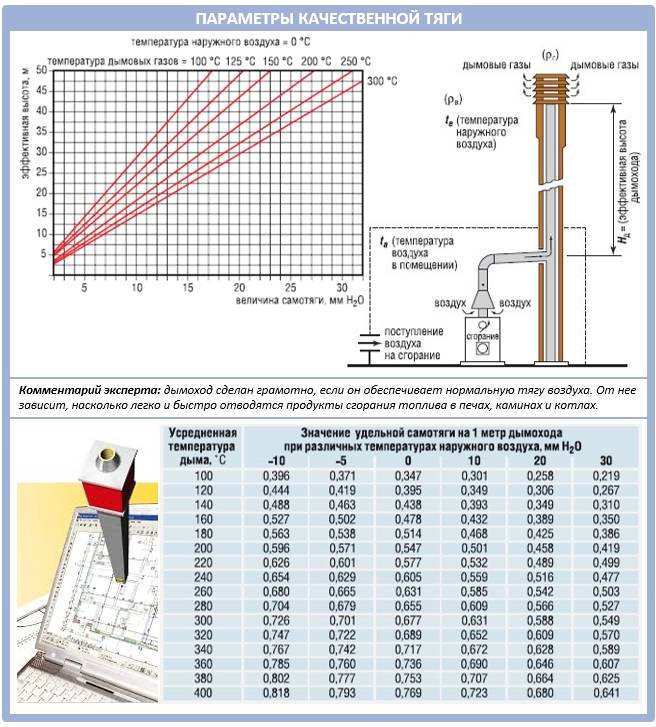
Make an aerodynamic calculation and find out the exact required height and diameter of the chimney. By itself, the magnitude of thrust means the difference in density of air and flue gas, multiplied by the height of the house. It is 5 meters of the chimney that provide vacuum and draft for the smoke.
But what if the height of the pipe cannot be set higher, and the thrust is still insufficient for certain reasons? This often happens when the flue gases cool down too quickly, especially during the cold season. Then, to restore traction, the desired section of the pipe is simply insulated.
Also remember that the real thrust is always less than static thrust due to the resistance of the gas movement inside the pipe walls. The narrower the flow area of the chimney, and the more bends, horizontal sections and the like in it, the worse the draft will be, because the draft is affected by the pressure loss along the entire length of the pipe.
Another problem with chimney height is the cold air from the fireplace. So, when he is not working, cold air is released from the street. This happens when the chimney head is below the end of the ventilation hood, or when the attic is too large and poorly insulated.
Chimney height.
Here we can do without complicated calculations.
Yes, of course, there are rather cumbersome formulas by which the optimal height of the chimney can be calculated with great accuracy. But they become really relevant when designing boiler houses or other industrial installations, where they operate with completely different power levels, volumes of fuel consumed, heights and diameters of pipes. Moreover, these formulas also include an ecological component for the emission of combustion products to a certain height.
There is no point in listing these formulas here. Practice shows, and this is also stipulated in building codes, that for any of the theoretically possible solid-fuel devices or structures in a private house, a chimney (with natural draft) with a height of at least five meters will be sufficient. You can find recommendations to focus on the indicator of six meters.
In this case, it is precisely the height difference between the exit from the device (for furnaces it is often considered - from the grate) to the upper edge of the pipe, without taking into account the worn umbrella, weather vane or deflector
This is important for those chimneys with horizontal or inclined sections. Let's repeat - not the total length of the pipe used, but only the height difference
The height of the chimney is precisely the height difference between its inlet and outlet, and not the total length of the chimney, on which there may be horizontal or inclined sections. By the way, you should always strive to minimize the number and length of such sections.
So, the minimum length is clear - five meters. Less is impossible! More? Of course, it is possible, and sometimes even necessary, since additional factors may intervene due to the specifics of the building (corny - the height of the house) and the location of the pipe head relative to the roof or adjacent objects.
This is due to the rules of fire safety, and the fact that the head of the pipe should not fall into the so-called zone of wind support. If these rules are neglected, then the chimney will become extremely dependent on the presence, direction and speed of the wind, and in some cases the natural draft through it may completely disappear or be reversed (“topple over”).
These rules are not so complicated, and taking them into account, it is already possible to accurately outline the height of the chimney.
Chimney prices
chimney
Basic rules for the location of chimneys relative to building roof elements
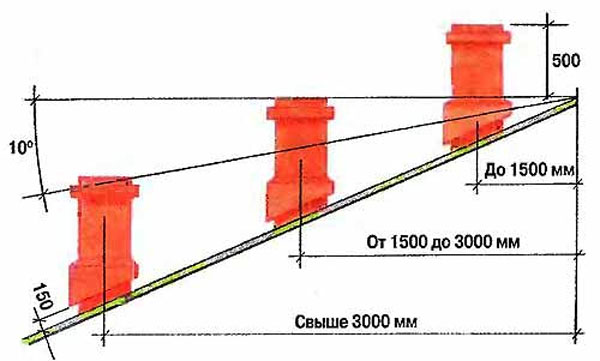
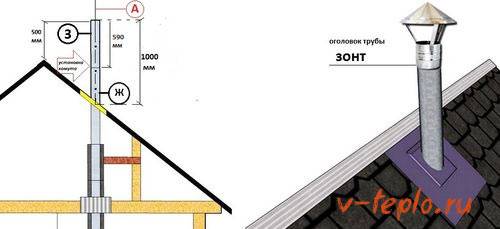
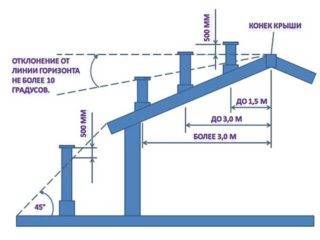
First of all, no matter what roof the chimney passes through, the cut of the pipe cannot be closer than 500 mm from the roof (pitched or flat - it doesn't matter).
On roofs of a complex configuration, or on a roof adjacent to a wall or other object (say, the edge of the roof of another building, extension, etc.), the wind support zone is determined by a line drawn at an angle of 45 degrees. The cut-off of the chimney must be at least 500 mm higher than this conditional line (in the upper figure - the left fragment) ..
The same rule, by the way, applies even then, for a year, there is a tall third-party object next to the house - a building or even a tree
The figure below shows how the plotting is done in this case.
Tall trees near the house can also create a zone of dense wind backwater.
On a pitched roof, the height of the pipe section protruding above the roof depends on the distance from the ridge (left fragment of the upper diagram).
- A pipe located at a distance of up to 1500 mm from the ridge must rise above it by at least 500 mm with its edge.
- With a distance from 1500 to 3000 mm, the upper edge of the pipe must not be lower than the level of the ridge.
- If the distance to the ridge is more than 3000 mm, the minimum permissible position of the pipe cut is determined by a line passing through the top of the ridge, drawn at an angle of -10 degrees from the horizontal.
To reduce the dependence of the draft on the wind, special caps, deflectors, and weather vane are used. In some cases, the use of a spark arrester is also required - this is especially important for solid fuel devices.
It remains to sit down at the drawing of your house (existing or planned), determine the place of the pipe and then finally stop at some of its height - from 5 meters or more.
Calculation of the duct diameter and duct height
The calculation of a rectangular or circular section of the ventilation duct is carried out in the presence of 2 parameters - the air flow rate and air exchange in the premises. With forced draft, the air exchange is replaced by the fan power. The parameter is written in the accompanying documents for the product. Air exchange is calculated based on the rate according to SNiP for a particular room. The flow velocity in the duct should usually not exceed 5 m / s, but sometimes it is increased to 10 m / s.
Standards
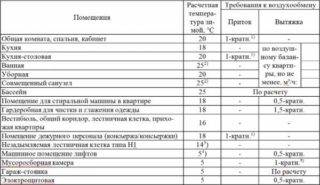 Air exchange rates in residential and utility rooms
Air exchange rates in residential and utility rooms
During normal operation of ventilation, the air in the room is constantly renewed. According to the requirements of SNiP and SanPiN, standards are established in residential and non-residential rooms, baths, toilets, kitchens, and other special rooms.
Minimum rates - frequency rate per hour or cubic hour for single-family residential buildings:
- residential premises with the constant presence of residents - at least one volume per hour;
- kitchen - 60 m³ / hour;
- bathroom, bathroom - 25 m³ / hour;
- other premises - not less than 0.2 air volume per hour.
The requirements for the "Code of Rules SP 60" are based on the norms for 1 person in premises with permanent residence:
- with an area of less than 20 sq. m / person - 30 m³ / hour, but not less than 0.35 volume per hour;
- with an area of more than 20 sq. m / person - 3 m³ / hour per 1 sq. m.
 In swimming pools, saunas, ventilation must be forced to prevent the formation of mold.
In swimming pools, saunas, ventilation must be forced to prevent the formation of mold.
"Code of rules SP 54" for residential multi-apartment buildings gives other conditions:
- bedroom, living room - 1 exchange per hour;
- cabinet - 0.5 volume;
- utility rooms - 0.2 volume per hour;
- sports facilities - 80 m³ / hour;
- kitchen with electric stove - 60 m³ / hour; 100 m³ / hour is added to the gas one;
- bath, toilet - 25 m³ / hour;
- sauna - 10 m³ / hour for each visitor.
According to the table
A special algorithm allows you to calculate the diameter of the ventilation pipe, based on the table in SNiP. The height of the ventilation pipe above the roof of a private house depends on the diameter and is determined by the cells of the table, where the width of the pipes is hammered in the left column, and the height is in the top line in mm. This takes into account the location from the ridge of the house, the shape of the ceiling, the distance of the ventilation duct from the chimney pipe.
By electronic calculator
A special calculator calculates the norms depending on the entered indicators: the area of the room, the height of the ceiling, the number of people, the type of room. The calculator takes into account the main indicators. It is advisable to carry out several calculations and select the maximum values for each of the premises.
Varieties of pipes for stoves and fireplaces
There are the following types of chimneys:
- Brick-built pipes are massive objects resting on the masonry of the stove; they must be laid out with a thickness of at least half a brick.
- Root pipes are free-standing structures in the form of risers; they should be made of asbestos-cement pipes with a diameter of 15-20 cm.
- Prefabricated pipes are individual blocks made of heat-resistant concrete.
- Wall pipes are structures mounted in a solid load-bearing wall, which saves space in the room.

Obtaining high efficiency from a furnace with this type of tube is not possible. If no other way of positioning the wall chimney is provided, appropriate types of work are carried out to equip a pilaster with a protrusion extending into the interior of the room. Installation is carried out with maintaining the required distances from the chimney to the outer wall:
- 2.5 bricks (from 20 to 30 - 650 mm);
- 2.0 bricks (from 20 and above - 510 mm);
- 1.5 bricks (from 20 and below - 380 mm).
The location of the chimney is determined strictly vertically without indents inside. If there is a slip in the structure, its dimensions should not be more than 1 m. A brick pipe often has a cross-section inside that is not less than 140x140 mm. The normal draft of the chimney is achieved due to the height of the chimney, equal to at least 5 m. If it is less than 5 m, the draft is provided by means of a deflector-diffuser.
Having equipped your house with stove and fireplace heating, you should install 2 chimneys. Different traction of one of the foci can lead to smoke. In a wooden house, in places where there is an adjoining brick chimney, a thickening of 1-1.5 bricks is provided. A highly flammable structure near the chimney must be closed from it with asbestos-cement or metal sheets.
What should be the chimney duct?
When constructing a chimney, it is extremely important that all dimensions are calculated and the material is selected correctly. And these parameters, in turn, will depend on the fuel that is planned to be used.
So, a brick structure is suitable for gas and solid fuel appliances. Its cross section and height must be carefully calculated (more on this later) in order for the entire heating system to function normally. In the case of improperly selected dimensions, the boiler efficiency will decrease, and the required draft will be absent, which can lead to the most unexpected consequences.
Note! All this is especially important in cases where the chimney is equipped for several devices at once - here it is better to entrust the calculations to professionals, since the risk of making a mistake is quite high. In accordance with generally accepted requirements, 1 chimney is capable of servicing no more than 2 heating devices, but only when its internal dimensions allow both of them to work at the same time. And the height of the cut channel in this case should be about 0.8 meters
In the case of large parameters, the efficiency of the device will decrease, and with smaller parameters, the draft will deteriorate, and combustion products can penetrate into the room.
And the height of the cut channel in this case should be about 0.8 meters. In the case of large parameters, the efficiency of the device will decrease, and with smaller parameters, the draft will deteriorate, and combustion products can penetrate into the room.
In accordance with generally accepted requirements, 1 chimney is capable of servicing no more than 2 heating devices, but only when its internal dimensions allow both of them to work at the same time. And the height of the cut channel in this case should be about 0.8 meters. In the case of high parameters, the efficiency of the device will decrease, and with smaller parameters, the draft will deteriorate, and combustion products can penetrate into the room.
As for the shape of the chimney, the cylinder is definitely considered the best. The height of the chimney relative to the ridge of the roof does not affect this, as well as the material used. And even pipes of the required diameter are built into channels made of bricks.This is explained by the fact that the combustion products rise in a spiral manner, therefore the optimal shape is precisely the cylinder. Only under these conditions is the maximum thrust possible.
Chimney cap
Earlier we talked about how to make and install a cap on a chimney on our own. In addition to this article, we advise you to read this guide.
And modern models of boilers, functioning according to the "stop-start", cannot do without such a pipe. Indeed, for them the main thing is to quickly heat up the system to the required indicator and put it into standby mode, which is why, in fact, such boilers are considered the most economical.
Swirls will be created in square chimneys, which again will lead to a deterioration in draft. But for wood-fired heating boilers, this form is suitable, since it increases their efficiency by slowing down the output of thermal energy.
The main types of chimneys
Common types of chimneys:
- Brick. As a rule, an asbestos pipe is installed in a brick mine. The key disadvantage of a brick chimney is the need to install a foundation for it. In addition, this design impairs traction and also contributes to the formation of debris and condensation products. This destroys the system and makes the room damp. Among the advantages are high heat capacity and fire safety.
- Ceramic. The most expensive and high quality option. They are made of refractory ceramics. A layer of thermal insulation of non-combustible material is required. Pros - they do not require frequent cleaning, have smooth walls and a round cross-section (provides good traction), have high levels of sealing and thermal insulation, heat-resistant, durable, easy to install. Disadvantages are the obligatory foundation and the high price.
- Modular in steel. They are assembled from tees, adapters, elbows, etc. Stainless steel structures often install channels made of bricks (the aforementioned sleeve). However, you can install such a chimney separately. The stainless steel must be resistant to acids and be heat-resistant so that corrosion does not appear in the chimney (wall thickness - from 0.6 to 1 mm). Galvanized steel is not suitable as zinc burns out quickly at high temperatures. Cons of steel structures - increased thermal conductivity leads to rapid cooling of gases, a large volume of condensate is formed, the service life does not exceed 15 years. Of the advantages - good traction due to the rounded shape, a separate foundation is not needed, and soot does not accumulate.
- Corrugated steel. They are a flexible pipe made of metal tape. They are used for casing curved brick structures. Easy to install, but short-lived.
- Steel sandwich structures. They are two pipes inserted into each other. The area between them is filled with a special non-combustible insulation. Cons - high cost. Pros - reduced thermal conductivity and slow cooling of gases, fast passage of smoke, minimum condensation, ease of installation.
- Asbestos-cement. Suitable if the emitted heating gases are not hotter than 300 degrees. Unsuitable for standard ovens due to poor heat resistance. Cons - fragility, lack of thermal insulation and unsatisfactory heat resistance, porosity, the need for frequent cleaning, weak rubber connection. Pros - lightness, round cross-section, low cost and easy installation.
- Polymeric. Manufactured from composite polymers. They are used for the sleeve of channels made of brick or concrete. Due to its poor heat resistance, it is not suitable for hot gases with temperatures above 250 degrees (ovens). Only for gas water heaters or boilers with increased efficiency. Cons - instability to high temperatures, fragility, lack of thermal insulation. Pros - flexibility and light weight, low cost, long service life.
We hope the material was useful to you. As you can imagine, calculating the height of the chimney is quite simple. These solutions are applied and you will always have warmth in your house.
Chimney types
Brick
Advantages:
- strength;
- high heat capacity;
- security.
Disadvantages:
- the construction requires a long time and money costs;
- the clay used, due to its porous structure, is capable of accumulating condensate during operation, which subsequently leads to the destruction of the chimney;
- with careless laying of bricks (the clay inside is not smoothed out), the accumulation of soot is accelerated;
- rectangular cross-section makes it difficult for smoke to pass;
- difficulty in maintenance and repair.
Asbestos-cement
Such chimneys can be used at a gas temperature not exceeding 300 degrees.
Advantages:
- cheapness;
- ease of installation;
- round section;
- relatively low weight.
Disadvantages:
- porosity of the material;
- not heat resistant;
- no insulation;
- it is difficult to make pivoting elements;
- often needs to be cleaned of soot.

Steel single-circuit
The best material for such chimneys is acid-resistant and heat-resistant stainless steel with a thickness of 0.6-1 mm. In reality, ordinary stainless steel and even galvanized steel are often used. The latter is the most unfortunate decision.
Advantages:
- relatively low cost;
- ease of installation;
- round section and smooth surface;
- light weight;
- ease of repair.
Disadvantages:
- there is no thermal insulation, which leads to rapid cooling and the formation of condensation;
- when passing through combustible materials, for example wooden floors, a large offset in diameter and insulation with asbestos fiber or other non-combustible material are required;
- relatively short service life (10-15 years).

Steel double-circuit
Double-circuit chimneys differ from single-circuit ones in that they are made of two pipes, between which there is a non-combustible insulation.
Advantages:
- keep the temperature, the rate of passage of gases is higher;
- requirements for internal installation are too low;
- there is little condensation.
Flaw:
very high cost.
Ceramic
The product is relatively young on the market, but has already gained popularity. It consists of three components: refractory ceramics, non-combustible heat-insulating insulation and a lightweight concrete protective box.
Advantages:
- very high temperature resistance (withstand up to 1200˚С);
- round section and smooth inner surface;
- tightness and thermal insulation at a high level;
- installation is quite simple;
- durability (ceramic pipe will last about 30 years).
Flaw:
high cost.
General Provisions
 Requirements for the placement of the chimney relative to the horizon and the ridge of the roof
Requirements for the placement of the chimney relative to the horizon and the ridge of the roof
The location of the highest point of the chimney is of great importance for fire safety and the efficiency of the heating system. Natural thrust is formed according to the laws of physics: warm air tends upward, and the vacant space is occupied by a new portion, since the vacuum is instantly filled. The more heated air, the more intense the draft, which is interconnected with the height of the chimney and its cross section. The purpose of all calculations and recommendations is to achieve such an upward flow rate so that heat loss is minimal, but at the same time, the combustion products do not have time to get into the room. Too much draft is not desirable, because heat will not be transferred to the air masses, and more fuel will have to be burned to maintain a comfortable temperature in the house.
Another aspect must be taken into account: an excessively high chimney will negatively affect the system for removing fuel combustion products, although it would be logical to assume that the higher the chimney, the greater the draft. This is really so, but the stream, rising higher and higher, gradually cools down, and the cold air tends downward. At a certain moment, an air lock of cold gas forms, which presses from top to bottom on the ascending warm stream and prevents it from rising higher - the thrust comes to naught. In addition, the situation is aggravated by the fact that when the gas cools down, condensate precipitates. It further reduces cravings.
It is advisable to place the chimney from the ridge at a distance of at least 50 cm and not more than 150 cm. The height of the chimney above the ridge is at least 50 cm. This placement is successful for practical reasons:
- at this level, snow accumulates in a smaller amount, therefore, the risk of leaks at the junctions is reduced;
- materials are saved during construction.
You can bring the pipe outside, removing it 1.5-3 m from the ridge, then the height of the chimney should be: maximum - flush with it, minimum - with a deviation of no more than 10 degrees from the horizon, if you draw an imaginary straight line through the highest points of the chimney and a skate. The last criterion is valid for the highest point of the pipe if it is located at a distance of more than 3 m from the ridge. The height of the chimney above the roof must be at least 50 cm. You should not remove the chimney at the level of the roof windows in order to avoid the entrainment of carbon monoxide gases into the room.
 The chimney pipe must match the oven outlet
The chimney pipe must match the oven outlet
Determining the location of the chimney relative to the ridge and its height is a necessary stage in drafting a heating system. But in addition to this aspect, it is necessary to take into account a lot of other conditions and initial data: the type of fuel, the power of the boiler, the properties of materials, the presence of additional channels that remove the combustion products from the fireplace, stove, climatic indicators, the predominant direction of the wind. After reviewing the requirements of SNiP for the height of the chimney, additional calculations need to be made. For example, calculate the cross section of the chimney. Calculations for complex projects with a large number of objects must be performed by professionals. Operating a faulty designed chimney can be life-threatening.
