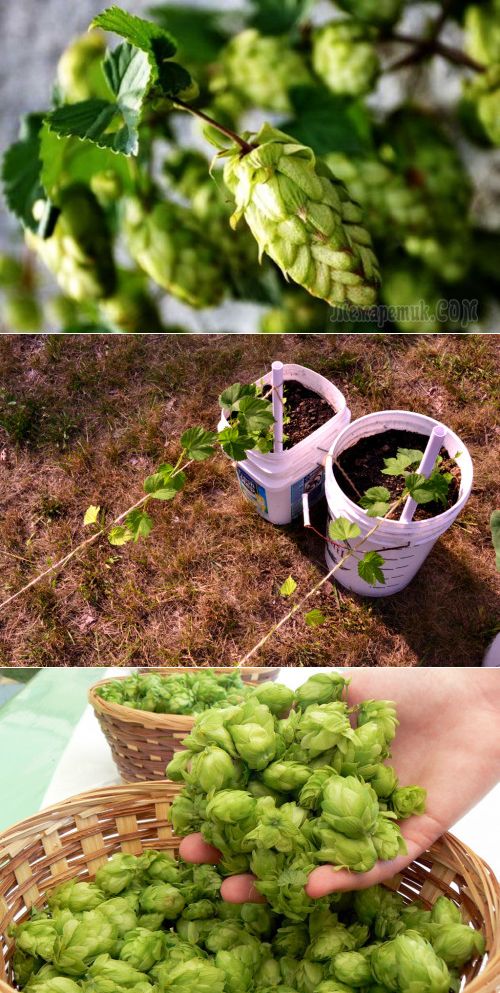
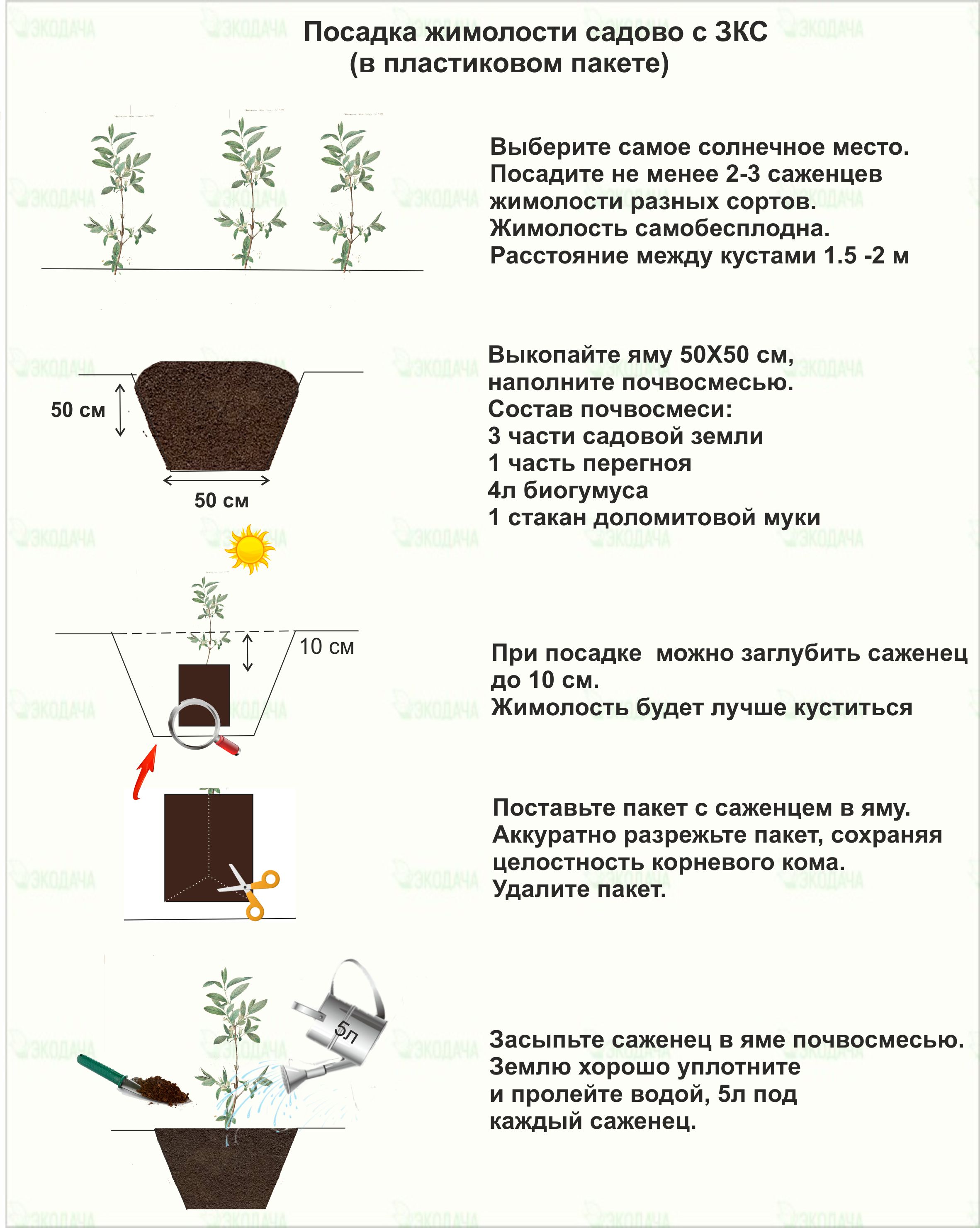
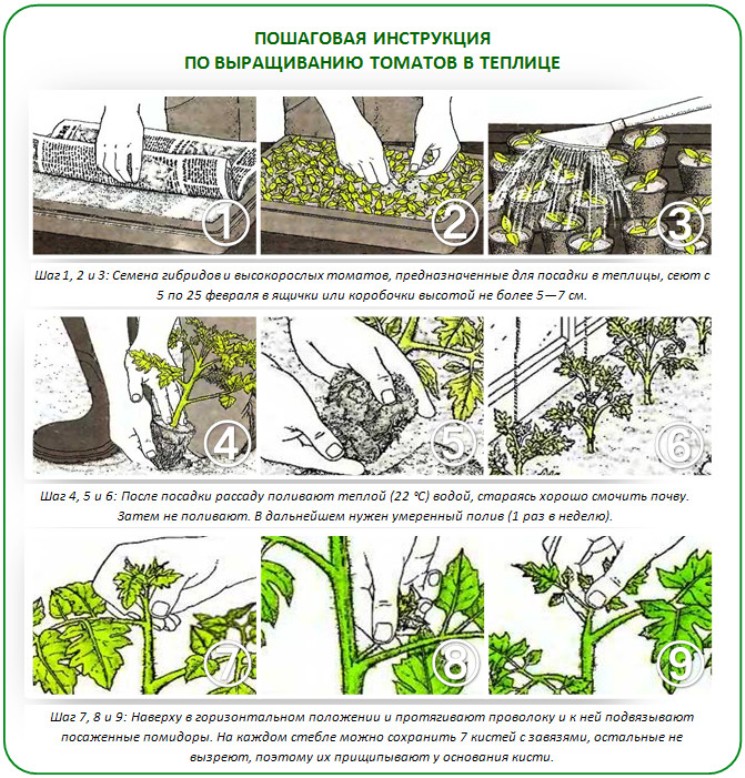
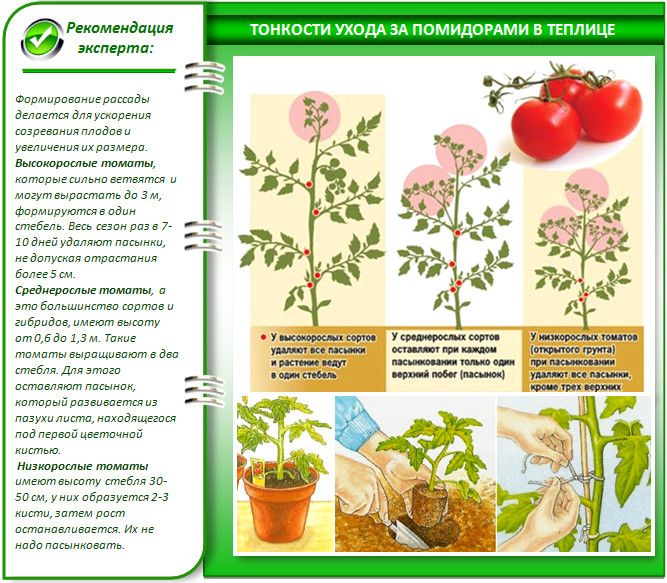
Soil requirements

It is believed that with proper handling and proper fertilization, almost any soil can be used to grow hops. Nevertheless, both quantitatively and qualitatively, the yield will depend precisely on the nature of the soil. So, for example, the best in quality, but insignificant in quantity, hops are obtained on sandy soils; on clayey, moist loamy and fertile soils, on the contrary, quantitatively large yields are obtained, but in quality they are inferior to "sand hops".
When choosing a site, you need to pay attention to the level of groundwater: if they are too high, the root system will rot, since hops are plants with deep roots in the soil. For the same reason, purely calcareous soils are not suitable for planting, which are characterized by excessive density and low permeability for roots (but at the same time, the presence of a small amount of lime is favorable for hops and is considered rather as a favorable factor)
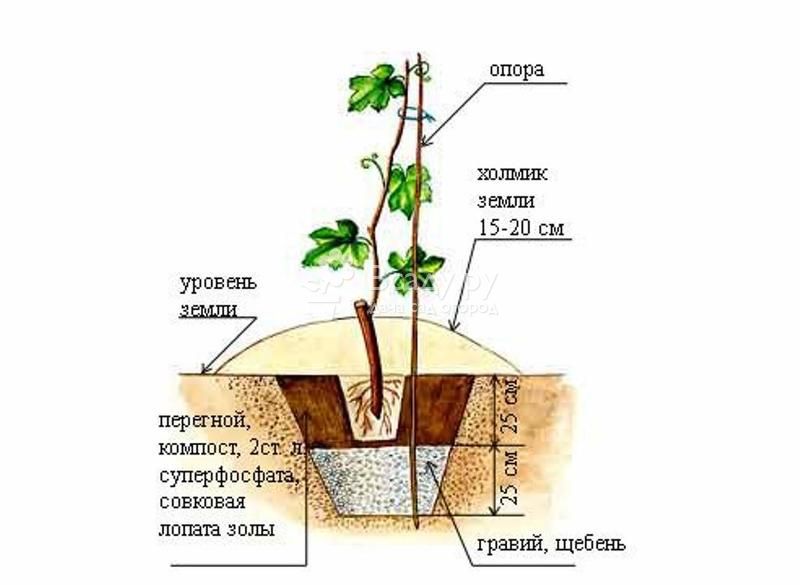
Soil cultivation should be deep enough - up to 1 m. Most often, for these purposes, a bayonet technique is used for the pass - digging up the soil in such a way that the top layer of the earth is turned over with the sod side down. Sometimes only local treatment is allowed in the form of preparing planting holes or ditches corresponding to the rows of plants.
On very wet soils, planting ditches are dug, on the contrary, in the aisles, and the plants are placed on the ridges formed by the excavated soil. All these preparatory work, in view of their cumbersomeness, it is desirable to carry out in advance, in the fall.
Plant care
Growing hops at home is a time consuming process influenced by the smallest details. The plant is susceptible to many pests and diseases.
Therefore, they carry out sanitary pruning: root leaves are removed from the shoots (1 meter along the shoots). Such pruning is carried out after 3-4 months of active growth. After planting, you can mulch with peat.
Watering
Hop lianas are responsive to abundant watering
It is important to provide the plant with moist soil. Make sure the water does not stagnate
It is enough to water once a day in summer. Watering can be done less frequently after harvest.
Top dressing
Growing hops at home obliges you to provide full feeding in caring for it. It is carried out as standard for all perennial plants: in autumn and spring.
In the rainy season - in the fall, it is important to apply a sufficient amount of manure and compost, and in the early spring - to fertilize the soil with potassium-phosphorus or mineral additives
Did you know? Hops for beer began to be used later than the direct production of the drink began. Now beer cannot be imagined without this element, which, by the way, was added for the sake of increasing the shelf life. Hops are a natural preservative.
Weeding and soil care
Weeding is carried out neatly due to the close location of most of the roots. Usually weeds are removed and the earth is slightly loosened - so it is saturated with oxygen, and the shoots become stronger. This should be done infrequently, but as needed.
Support
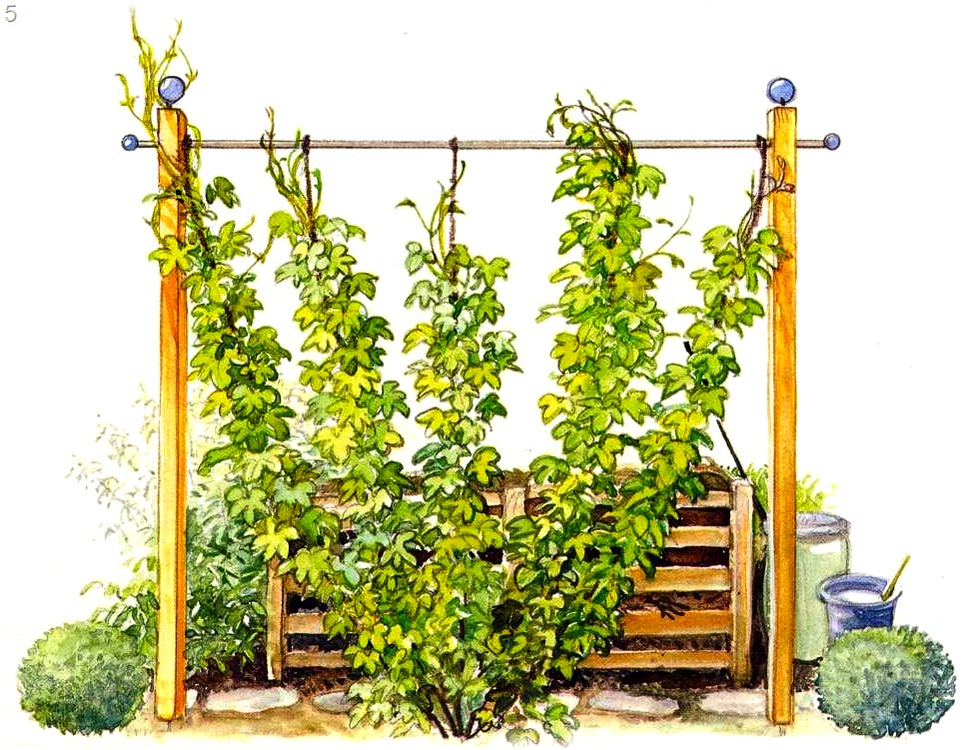
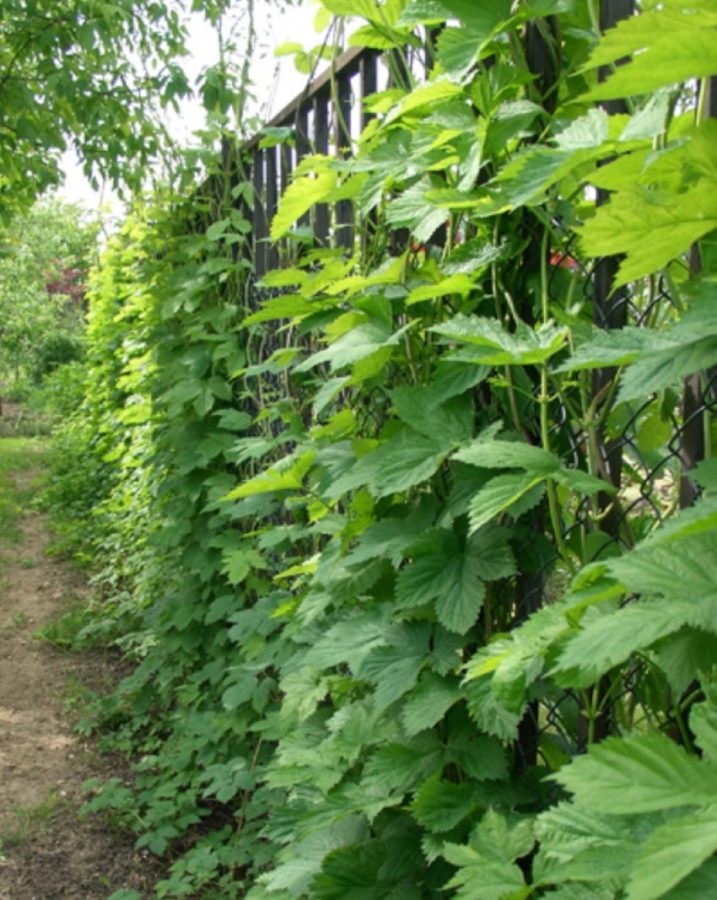
Many have seen what the plant cones themselves look like, but few know exactly what a hop plantation looks like. Since the plant does not have a vine, but powerful shoots, a strong and high support is needed. Places, for example, mass-grown are like vineyards.
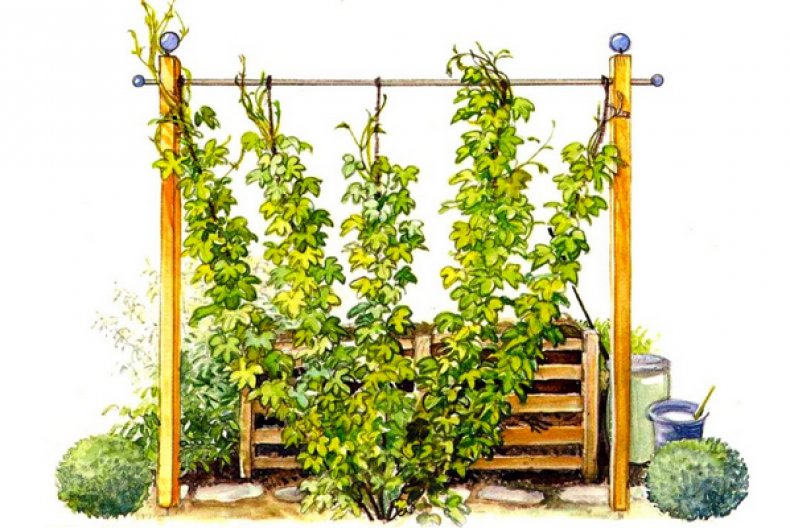

But the fact is that hop shoots can be up to 10 meters in length. Therefore, the support must be strong. Summer residents make it on their own.
It is possible to make a support on the south side of your house. To do this, it will be enough to lower the string from the roof and fix it to the ground.
Hop care
Hops love moist fertile soil.Under natural conditions, it grows in oak-ash forests, hiding behind bushes and in ravines. The soil should be rich in humus.
Basic conditions for growing hops on the balcony:
- Large pot (since hops have large roots).
- Installation of a support around which the shoots will curl.
- Regular watering every 3 weeks.
- Annual shoot pruning.
If you need a large number of plants for your own needs or for sale, the question arises: how to grow hops over a large area:
- For planting, you need to find a sunny place, good drainage must be provided on the site. A support for growth is installed near almost every plant. The ideal location is the south side of the house. In addition, hops are highly decorative.
- The soil should be loose, with a pH of 6.5-8. A layer of sand can be laid out to a depth of 30 cm. Each hole is made at a distance of more than 1 meter from one another. Compost or soil for seedlings is laid out at the bottom of the hole.
- The rhizome, that is, a creeping underground stem, deepens by 5-10 centimeters in a horizontal position, the roots look down. Now the earth can be tamped, and the hole can be covered with hay, and watered abundantly.
- The upper part of the plant dies off every winter, and the perennial part, the rhizome, develops underground. Hop roots are capable of withstanding severe winters.
- When the first shoots appear, they need to be cut off after two weeks. Only the strongest shoots remain, in the amount of 3 pieces. Tying is done when an individual hop vine has grown to 40 cm.
- Hops grow very quickly; in good spring weather, the shoot can lengthen by 15 cm.
During the period of active growth, it is desirable to introduce a large amount of nitrogen. This is not a mandatory procedure, compost will be enough for normal development, however, nitrogen will save the plant if the leaves suddenly turn yellow or shrink.
To make the cones ripen faster, the plant is sprayed with a 40% solution of ammonium nitrate. If an alfalfa weevil or fleas appear, then the shoots are treated with chlorophos. 40% phosphamide will help get rid of the spider mite, 80% polycarbacin or 80% cineb, 80% curozan will cope with other diseases. Viruses can be killed with zinc sulfate.
How to propagate vegetatively
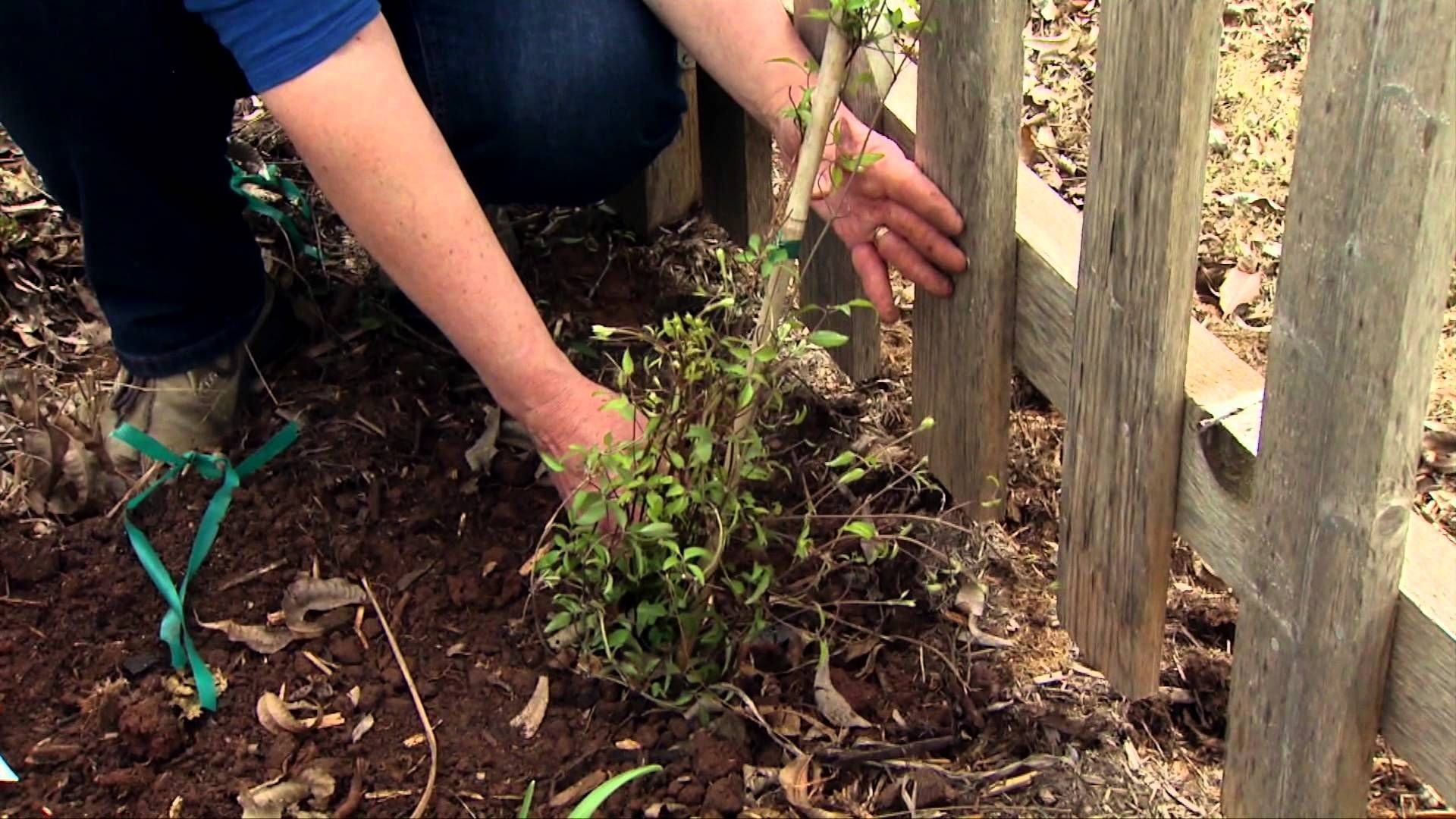
A perennial crop can be propagated vegetatively. This is most often done by dividing the rhizome. Sometimes root suckers are used. In the first case, in the spring, after the formation of young shoots with a sharp shovel, it is recommended to separate a fragment of the rhizome. This should be done directly in the ground. Rhizome cuttings should be cut. Their length should be 10-15 centimeters. Each fragment should include 2-3 pairs of buds. It is best to give preference to one-year-old roots. Their diameter should be no more than 2 centimeters.
The plant should be rooted in an inclined position. It is recommended to do this in wet sand. It is also permissible to use moss. Nurseries usually sell parts of the hop rhizome. If you want to get a varietal plant, use an exclusively vegetative breeding method. The culture takes root pretty quickly. The efficiency of the method reaches 95-100%.
Basic rules of care
Hop care includes timely shoot removal, watering, feeding, and pest control.
Removal of shoots, pinching
An important step in the care is the removal of shoots. When the sprouts grow to 15-20 cm, they are cut off. Up to 5 strong shoots are left on each bush. When they reach 50 cm, they are put on a support. Usually, 3 stems are started on one support.
Excess shoots should be removed as the culture grows. Do not forget that as hops grow, they oppress neighboring plants. So that the plot in the country does not turn into impassable thickets, the growth of hops should be constantly monitored.
Caring for the plant involves pinching - shortening the side shoots. This operation increases the yield of the cones.
Crop care involves frequent watering, since the plant is moisture-loving
But it is important to ensure that the water does not stagnate in the holes. Waterlogging negatively affects the condition of the roots
If the plant grows in dry climates, it is better to install an automatic watering system. Moderate constant soil moisture contributes to the growth of green mass, which provides decorative hops.
To avoid the appearance of downy mildew on the leaves, they cannot be wetted during watering.
Pest and disease control
Care also includes timely pest control. They rarely attack hop crops, but sometimes the following insects can be found:
The complex of measures for the destruction of pests includes spraying plants with appropriate preparations (solutions of "Kuprozan", polycarbacin), destruction of dead stems in autumn, digging up the earth between crop plantings. When spraying, it must be borne in mind that most of the insects accumulate on the lower (back) side of the leaf.
Effective and simple ways to destroy pests are infusions of tobacco and wormwood, a weak soap solution.
If brown or yellow spots have formed on the leaves, and their underside is covered with a white-gray bloom, then the hops are infected with powdery mildew. This is the most common cultural disease. The damaged foliage breaks off, and the aboveground part is sprayed with a fungicide solution.
Further care of the plant includes weed control, loosening the soil, hilling bushes.
Plant care during dormancy
In the fall, after the foliage withers, all dried shoots are cut off from perennial hops. After trimming them, fertilizers are applied, and the uterus is covered from above with a layer of earth (at least 30-40 cm). Hop rhizomes easily endure winter, and resume growth with the onset of spring.
If the crop is annual, like Japanese hops, it is completely dug up and disposed of.
What to feed?
Fertilizers are used for feeding:
The manure is applied 10-15 cm deep. It should be added in the fall so that it decomposes during the winter.
Of nitrogenous fertilizers, it is recommended to use urea, ammonium sulfate and ammonium nitrate. Urea is introduced before planting hops at the rate of 20 g of fertilizer per 1 m 2. Ammonium nitrate - 15 g per 1 m 2 of soil. If fertilized with ammonium sulfate, then its single dose should not exceed 30-35 g.
In the group of phosphate fertilizers, phosphate rock and superphosphate are recommended. For flour, a single applied dose is 50 g, superphosphate for a one-time feeding is enough 30 g.
Potash fertilizers include potassium salt, potassium sulfate, and potassium chloride. 25-35 g of these fertilizers are added to 1 m 2 of soil. Phosphorus and potassium fertilizers are applied when the plant reaches 4-5 m in height or after flowering.
A deficiency of these fertilizers will slow down the growth of the plant and the maturation of its cones. But you should not overdo it with feeding: the increased content of trace elements reduces the disease resistance of the culture.
So, in order for hops to please the eye for more than one year, and its healing capabilities to maintain health, give strength, you must adhere to simple tips for growing and caring for it.
How to grow the well-known hop plant in your country house from seeds? After all, sometimes you need to quickly decorate an unsightly building, fence, veranda, porch or gazebo. The ideal option for this is a powerful vine with beautiful leaves and cones. How to plant, how to care, what varieties are there? Can this crop be damaged by diseases and pests? You can get answers to questions after reading the article and viewing the photos.
Hop propagation
Hop propagation is also straightforward. Most often, it is propagated by vegetative methods. Fragments of rhizomes with living healthy buds are separated without digging the mother plant out of the ground.In the spring, as soon as the first shoots appear from the ground, small pieces are carefully cut out with a shovel and planted in a prepared place.
Rhizome cuttings are harvested before the start of sap flow. To do this, the rhizome is dug up, divided into fragments with living buds and planted in a new place. Such cuttings can be grown on a separate bed, and transferred to permanent residence in the fall. By the way, hops live for about 30 years.
For propagation by layering, the selected vine is tilted to the ground in the middle of summer, pinned and sprinkled with soil. In this position, the plant is left until spring, when it will be possible to dig out the resulting new rhizome and plant it in a new place.
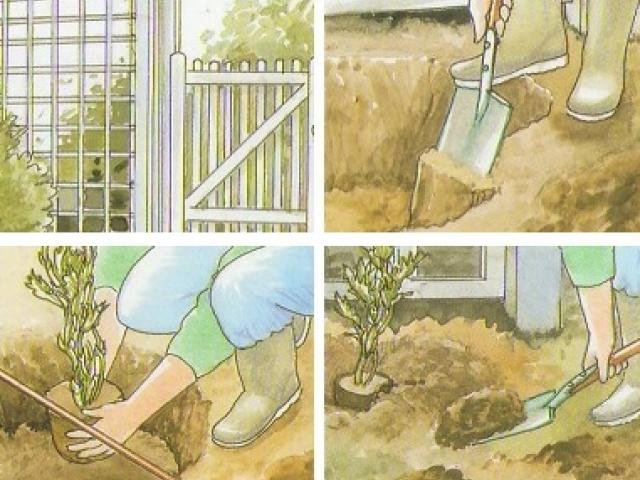
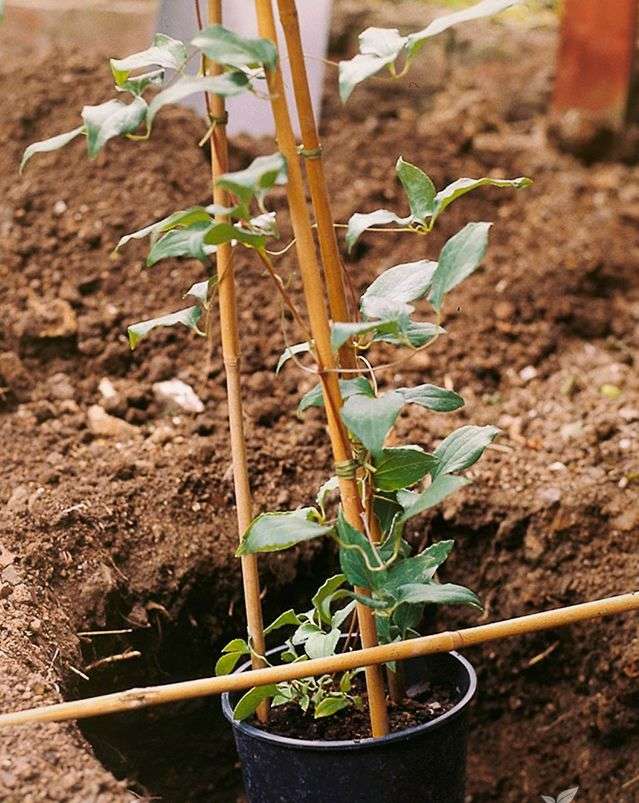
In the fall, a place is being prepared for future plantings. Dig holes up to 50 cm deep and half fill them with rotted organic matter (best of all with manure), add earth on top and leave it until spring.
When planting in spring, the seedling is placed in ready-made holes, covered with soil, tamped well, watered. If there is no difference, male or female plants are needed, and also, when the "sex" of the seedling is already known, they are placed at a distance of about 1 meter from each other, and the row spacing should be maintained about 3 meters. If you plan to thin out the plantings, you can make holes more often.
In the first three years after planting, to ensure health and rapid growth, young plants should be regularly watered and fed with a solution of complex mineral fertilizer. Top dressing should be alternated: once the fertilizer is applied to the soil, then foliar dressing is performed on the stems and leaves with half the fertilizer concentration.
Already in the first year of life, ordinary hops can give many shoots - it is better to cut off weak ones immediately so as not to deplete the plant. Then in the second year there will be fewer shoots, and the flowering will be more abundant. In the third or fourth year, the rhizomes grow; from this time, constant monitoring of the vine is required so that it does not turn into a real disaster for your garden.
Seed propagation of hops is usually used when it is necessary to grow an unusual variety or when large plantations are planted at the same time.
For seed propagation, containers or boxes are filled with prepared soil and watered well. Then the seeds are sown. The seedlings are transferred to the open ground and the young plants are cared for, as well as the adult hops. The hops will begin to grow rapidly in the second year, and the bumps will appear on it in a couple of years. Not a very convenient feature of seed reproduction is that, as a result, you can get too many male plants, that is, be left without bumps. Therefore, experienced hop growers plant hop seedlings closer to each other, and then remove excess sterile plants.
Hop seeds, collect and store "according to science"
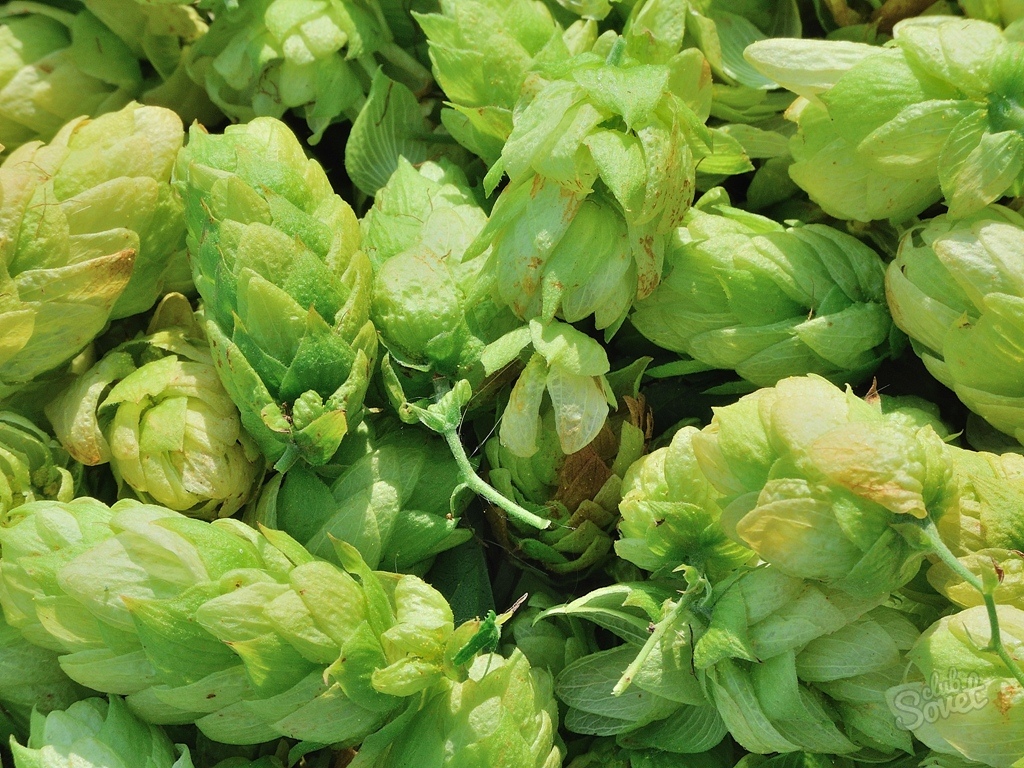
 Hop inflorescences are panicles hanging from vines. Flowering begins in June. The fragrant garlands of blooming hops look beautiful on the plant, and in August the seeds begin to ripen. Summer residents are advised to start harvesting a few days before full ripening, when the hop cone is just beginning to turn yellow, then the seeds will not be able to spontaneously spread over the site.
Hop inflorescences are panicles hanging from vines. Flowering begins in June. The fragrant garlands of blooming hops look beautiful on the plant, and in August the seeds begin to ripen. Summer residents are advised to start harvesting a few days before full ripening, when the hop cone is just beginning to turn yellow, then the seeds will not be able to spontaneously spread over the site.
The fluffy hop cone contains more seeds. After harvesting, the cones are dried in the shade, spreading out in a thin layer. A properly dried hop cone retains its firmness and aroma. It is not recommended to hang hops in bunches, as the seeds are sprinkled and the substance lupulin is lost.
Dried raw materials are stored for three years, but it is better to use it immediately for its intended purpose. The aroma of raw materials is specific, bitter and tart, and with proper storage, it does not lose its properties over the years.
Hop care
Spring. Shoots emerging from the ground grow very quickly. A tiny sprout in one day stretches 20 - 30 centimeters, and sometimes more.
Summer. During the summer period, the liana grows up to 3.5 - 4 meters long. It happens that up to 8 meters. First, the shoots are directed upward along the support.But as soon as it ends, the movement continues in the same direction, clinging "to the air" and winding on its own stems. Because of this, numerous "air loops" appear. The top of the liana becomes heavier and becomes more windy. It becomes difficult for her to withstand showers and strong gusts of wind. This leads to the fact that part of the green hedge sooner or later breaks off the support. It should also be borne in mind that the fragile supports and fasteners holding the heavy tops of the hop shoots break easily. To avoid the fall of the hop hedge, it can be run only on very reliable supports, tie it up and prevent the appearance of "air loops". As soon as the height of the shoots reaches the upper support bar, all the ends of the shoots must be cut off or directed downward.
Hops often suffer from powdery mildew. Aphids may appear on young shoots. Towards the end of summer, the decorativeness of the hops decreases: the foliage begins to turn noticeably brown. True, such a disadvantage is often not striking due to the abundance of cones. Hops are dioecious plants that are pollinated by wind and insects. Plants with male flowers have loose paniculate inflorescences.
I'm used to it, but I can't stand it for more than three hours in a blooming hop forest - you breathe in the ubiquitous hop pollen, and your head starts spinning. A friend of mine, a very talented herbalist, asked to pick flowers with me. Much younger than me, short, thin. He climbed onto an elm tree, where at a height of four to five meters the hops formed a luxurious tent - one of them would be enough for several baskets. An hour later I looked - at first the sack fell to the ground, and this comrade of mine fell on top of it. Fortunately, I landed successfully. They just laughed (RB Akhmedov "Plants are your friends and foes").
Female bushes have capitate inflorescences, in which the covering leaves grow and cover the nuts. This is how the famous fruit cones of hop cones look, which, first of all, are welcome to brewers.
From time to time you have to weed the weeds that have grown at the foot: nettles, dandelions, runny, etc. Hops easily tolerate both waterlogging and drought. He is calm about the different composition and structure of the soil.
Autumn. The entire aerial part of perennial hops annually dies off. Dry whips look ugly: the wind flutters them, they turn black from rain and snow. It should be borne in mind that in the future, during the spring fall, dry hop flares up like gunpowder. Therefore, it is better to cut off the entire aerial part, and not just the dried stems. This painstaking work takes a lot of time, since you have to remove dried shoots from all the cracks of the fence. It's better to finish before the cold and rainy weather sets in.
Hop collection
Hop ripening directly depends on climate, soil properties and weather conditions, but in most cases it occurs in late August - early September. Technical ripeness, i.e. the suitability of cones for practical use and storage is determined by the following criteria:
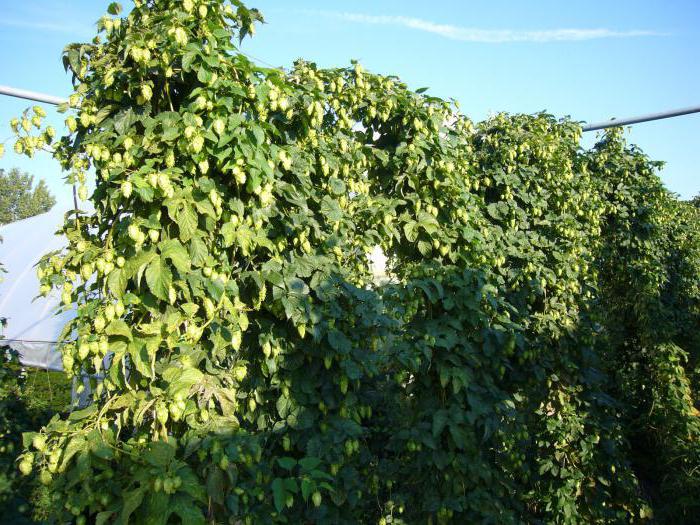

green fruits become yellowish or golden brown in color;
the bumps become denser;
the scales of the cones lose their softness and moisture, in dry weather they emit a slight rustle;
the fruits acquire a characteristic bitter odor.
Overripe buds often acquire a reddish or brown tint, easily crumble or reveal scales, which is why they lose their aroma. Unripe hops yield hard-to-keep buds, and early harvesting will drain the plant more than late harvest.
Hops are harvested in good weather, as the cones soaked in rain darken, quickly mold and become unsuitable for practical use. If there is a need (for example, only poles are used as supports), the lashes are cut, the pole is taken out of the ground and, together with the plant, is taken to the place where the cones are collected. When using a wire system, harvesting takes place directly on site.
So that the cones do not crumble, they are torn off in such a way that small petioles remain - about 1.5-2 cm long. The sorted buds must be dried thoroughly: in good weather this can be done outdoors, but in most cases the hops are dried indoors, scattering them in a thin layer on the floor. The hops are mixed periodically, increasing the layer thickness as it dries. To speed up this process, mechanized hot air drying is used.
Hops are stored in paper or cloth bags: when packing, it must be tamped as tightly as possible in order to protect the cones from damage, discoloration and loss of aroma.
Plant characteristic
Hops are a prominent representative of the Hemp family. There are 3 types of it:
- cordate;
- ordinary;
- Japanese.
This plant has annual and perennial varieties, some of which can grow in one place for up to 20 years. It has a twisted green or light red stem covered with fine hairs. In thickness, it reaches 15 mm, and the length reaches 10-12 m. It has a powerful root system, the bulk of the roots is in the upper layer of the soil.
Flowers are collected in inflorescences of 30-50 pieces and are formed only on female plants. Hop fruits are small brown nuts that ripen from mid-July to September. The seeds are also small and light: 1000 seeds weigh only 3-4 g. The leaves are heart-shaped, and in the middle of the stem they are much larger. Their upper side is dark green, and the back is much lighter and has glands.
It is used in pharmacological, perfumery and cosmetic, bakery and medicine industries. It is used for decorating fences, arches, buildings, creating a hedge in the country. The most popular is the ordinary type of hop, since its planting, care and cultivation does not require special rules, it is outwardly more attractive and has a lot of useful properties.
How hops are propagated
Planting hops is a protracted process, but shoots emerge quickly. There are several ways of reproduction: seeds, cuttings, seedlings. Usually planted in May, because the vegetative period of a representative of the Hemp family lasts 120 days.
It is important that during the planting period the weather is dry and the temperature is above + 10-12 ° С
Important! For hop shoots, trellises are required at least 7 meters high.
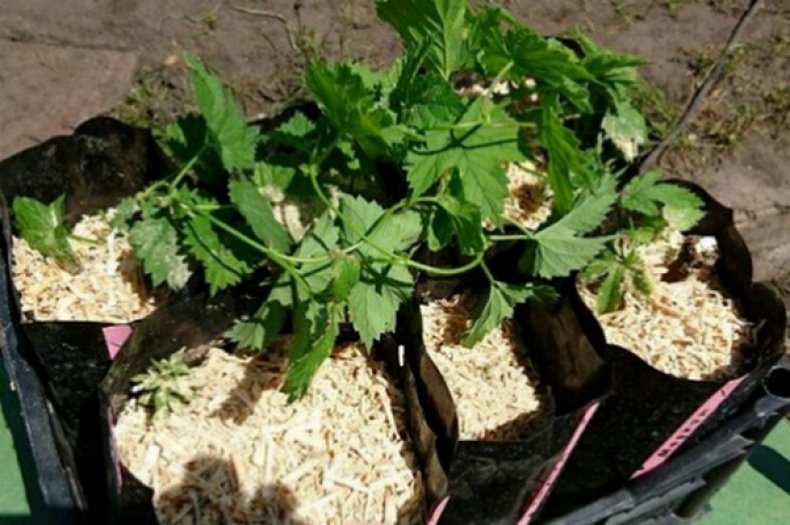
Seeds
Hop seeds are very small. The weight of 1000 pieces is only 4 grams. The seed sowing procedure is standard as for all perennial plants. Only in this case, seed stratification is usually not carried out, because the shoots of the plant are removed for the winter.
However, sift the correct amount of seeds into the soil, water and cover tightly. When young shoots begin to appear, open the seedlings and maintain the room temperature at + 20-24 ° C.

Seedlings are planted in early April as hops grow rapidly. The seedlings will get stronger quickly enough, and at the end of May they can already be planted.
Interestingly, in a region with a humid climate, seeds are planted directly in open ground. And the plant gives the results the same as when growing seedlings.
Vegetative ways
The most convenient way to plant hops is with cuttings and seedlings. In this case, you will need to plant the ready-made material in the previously prepared ground. Moreover, the likelihood of normal plant development is higher this way.
After all, the seeds have already been tested before you and rejected. How to plant cuttings and seedlings has been described above. Those who have been growing hops for many years recommend planting them in a vegetative way.
Did you know? Culinary experts in Belgium often use hop leaves in their dishes.

Types and varieties of hops
Common hops (Humulus lupulus)
It is this type of hop that we are familiar with and is used in baking bread and in brewing. It is he who has healing properties and is endowed with essential oils.This vine is perennial, it is dioecious and has a long creeping rhizome. From personal experience, I can say that the rhizome is able to overcome many obstacles underground from the place where it is planted to open soil. Actually crawl under paths and various types of masonry. A curly stem from 7 m can both attract a gardener for dense landscaping, and cause a lot of trouble if you thoughtlessly choose a planting site. The stem itself is tetrahedral, it has sharp small thorns. Leaves with a rough surface and yellowish glands.
 Common hops (Humulus lupulus)
Common hops (Humulus lupulus)
At one time, I decorated a fence with a small sprout of this type of hop, as a result, it began to unauthorizedly flood everything around. There is too much of it and it is poisonous. You can scratch heavily on its stems, wounds heal for a long time and "burn" very much. My baby, running past, caught the stem with his face, cheeks, forehead and part of the nose were badly scratched, the scratches healed for a long time and caused a lot of trouble when bathing the child, especially in the first days. Common hop varieties Currently, hop varieties used in brewing are gaining popularity, but they are usually not zoned. Let us dwell on the varieties that today are in the greatest demand among gardeners.
Hops 'Pivovar' is a medium-term variety with a growing season of about 115 days, recommended for the forest-steppe zone. This variety is weakly affected by diseases, resistant to soaking, freezing and perfectly tolerates drought. It is used for the preparation of hop-containing preparations, as well as in the beer industry. Has a delicate aroma. A massive, wide-cylindrical plant about 6.5 m long. When planted along the fence, it will not form a "hat". Also won't give you a lot of buds. The cones themselves are medium in size and elongated cylindrical in shape, but at the same time wide and quite dense. Attached to the shoot low. The leaves are medium in size, waviness is felt on the surface, the color is green.
'Triumph' hops are medium-sized rounded cones. They are attached low and have a medium density. The plant is quite tall, cylindrical in shape. The ability to form a "cap" is average. It has a delicate aroma, so it can be used both in brewing and for obtaining concentrated granules. For a gardener, it is good because it will regularly grow in one place for 15 years, while it does not freeze, it is resistant to drought and soaking. But it can be affected by a spider mite.