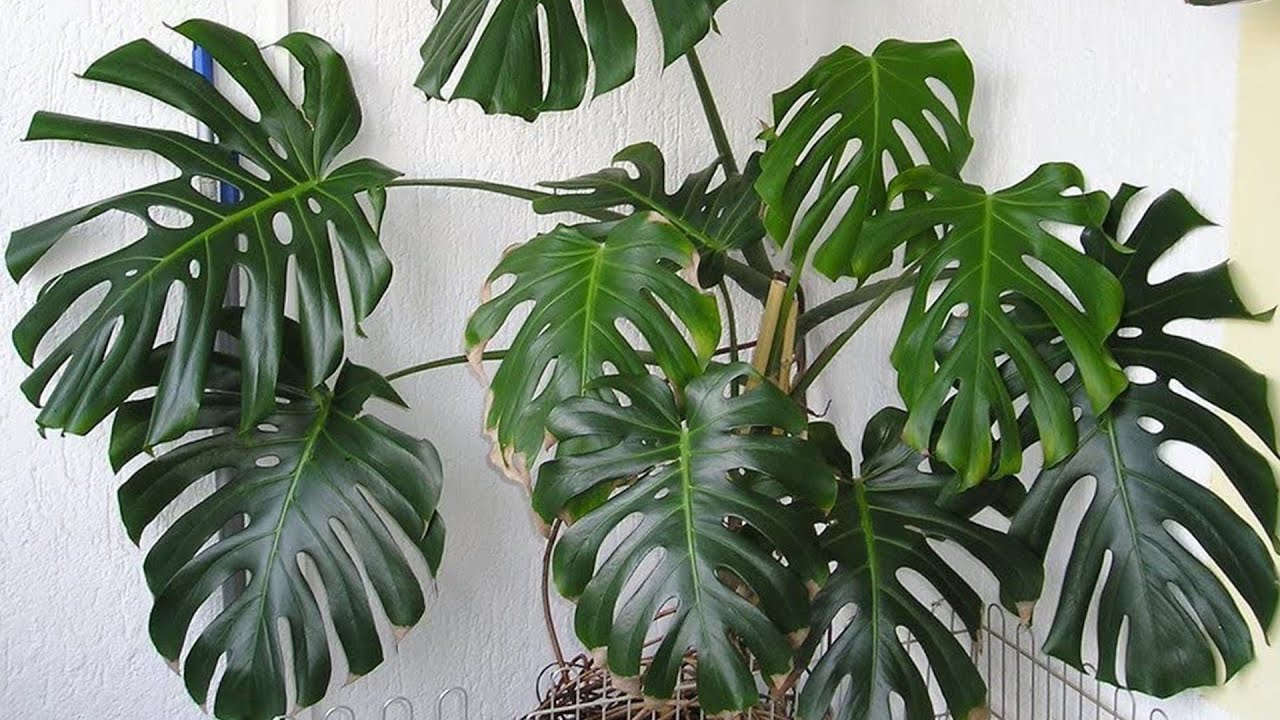
How to properly care for a monster?
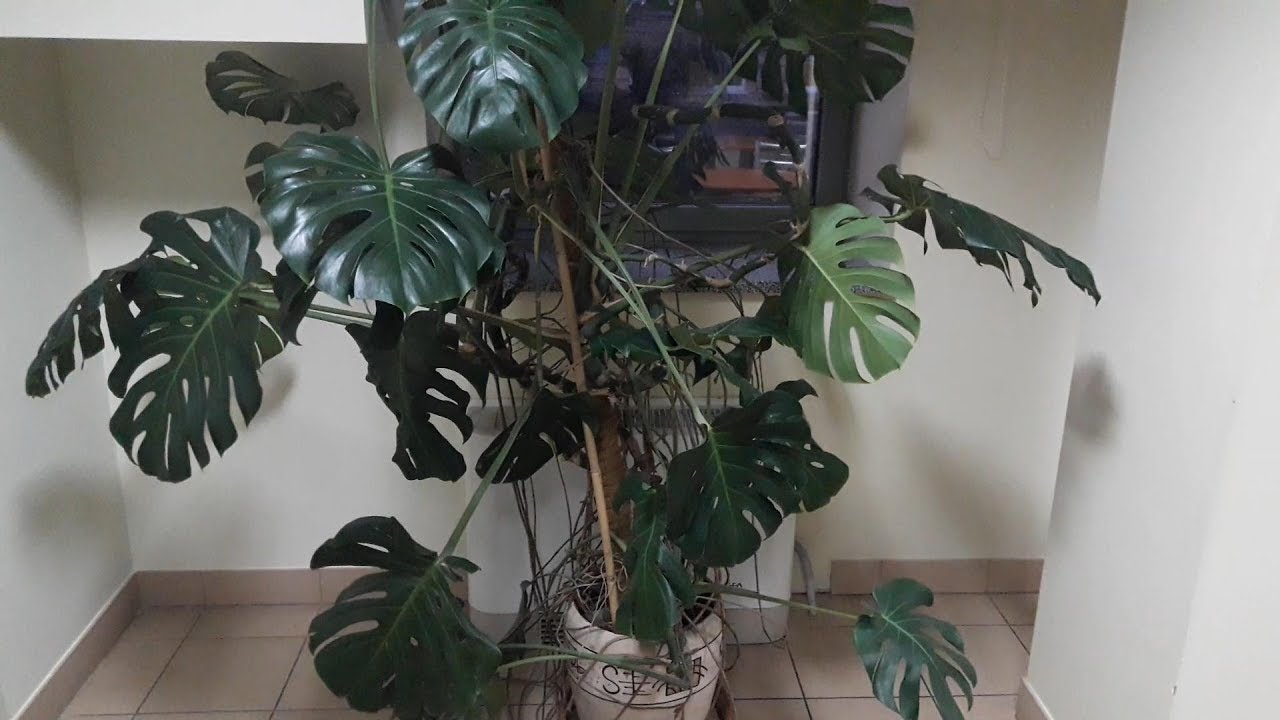
Bringing such beauty to the house, it must be borne in mind that this tropical plant grows large even indoors. This means, as it grows, it will take up more and more of your space, and the climb stops only by the level of the ceiling. Then the care of the upper leaves becomes more complicated.
Monstera home care
air layering monster
Monstera has a high ability to develop aerial roots that extend from the trunk of the plant. The plant throws out a lot of them, and these roots grow long. They are designed to anchor the plant to anchor points or in the soil.
Long ago, the pioneers of the rainforest mistook the aerial roots of the monstera for the long tentacles of an unknown monster. But in truth, these processes are very fragile and are of great importance for the life of the vine, you should avoid rough handling of them, exclude any damage. If the wall near the monstera is rough or textured, the roots may firmly attach to it. With sufficient length of these adventitious roots, you should direct them to the pot for rooting.
Liana, especially large and heavy, cannot do without support; for this, special supports decorated with coconut fibers are usually purchased. For growing plants, a smaller support is also suitable.
Suitable lighting level and temperature
In its natural environment, monstera grows in shady, but well-lit areas. After all, direct sunlight leaves burns on the sheets, and the lack of light slows down the growth of the beauty, up to complete suspension. Of course, this will not lead to death, but the appearance of the plant will deteriorate and decorativeness will decrease.
The temperature comfortable for the successful development of the monstera ranges from 10 to 24 degrees above zero. The plant is resistant to sudden changes in temperature. The warmer the air, the faster the monster grows, provided there is sufficient humidity.
In a cold room, the plant stops developing, goes into a dormant state until the air temperature becomes comfortable.
Irrigation and fertilization mode
Monstera comes from the tropics, which means it loves high humidity. It is necessary to periodically moisten the leaves of the plant, because they constantly saturate the room with moisture. Therefore, the leaves of the creepers are wiped with a damp cloth, and for a glossy shine they stir water with milk.
An actively growing plant needs not weak watering, you should not allow the state of dryness of the substrate. When entering a dormant state, minimal watering is recommended.
For good growth and maintaining high decorative properties, monstera are timely fed, using fertilizers with organic and mineral substances. In the summer, fertilizers are applied weekly, with the onset of cold weather - 1-2 times a month.
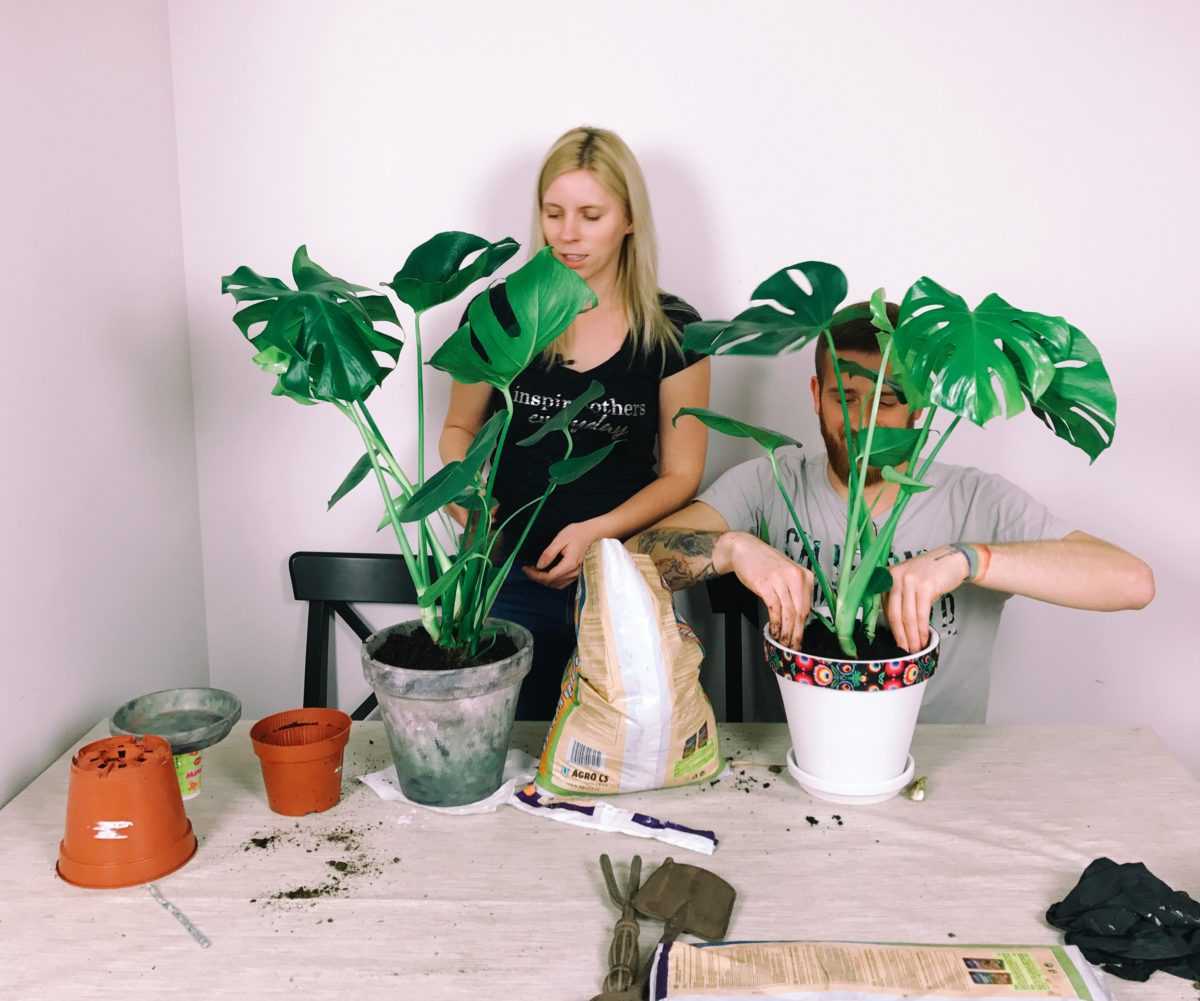
How to transplant?
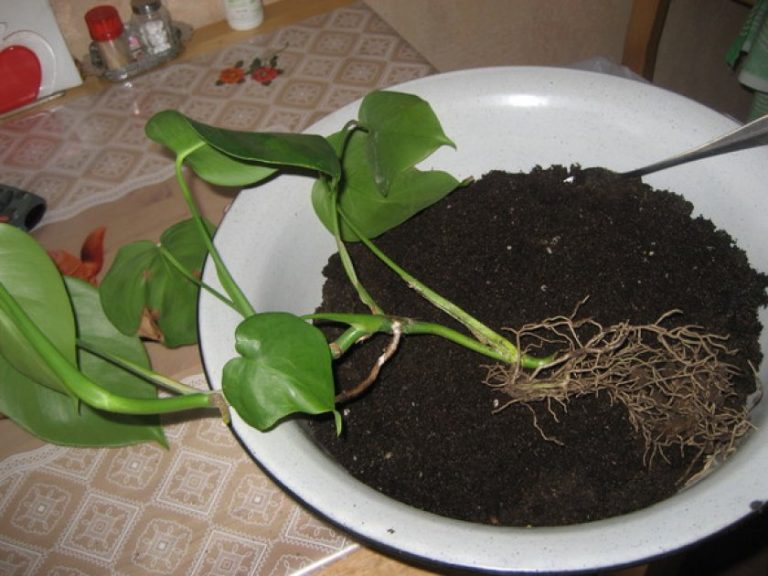
Monstera is distinguished by high growth rates, therefore the growing liana must be replanted annually, sometimes after two years
When transplanting, it is better to be extremely careful, because the vine is very delicate, plus you should remember about the fragile aerial roots
Upon reaching the age of 5-6 years, the plant acquires enormous dimensions, which means that transplants should be stopped. From now on, you can limit yourself to regular substitutions of the upper layers of the substrate.
For an adult plant, a wide and deep pot is needed, because the root system of the plant is very powerful and voluminous. In a cramped pot, the monstera slowly dies.
Good drainage is placed in the lower third of the pot, the remaining volume is filled with a mixture of the following components:
- peat 1 share
- turf 1 share
- humus 1 share
- sand 1 share
As you understand, everything is taken in the same proportions and mixed. Or they purchase a special substrate in the store.
Do you need pruning?
The monster is cut once at a young age to begin the formation of a voluminous spreading plant. You can repeat and final pruning for more branching.
It must be borne in mind that the trimmed vine is suitable for growing only in large rooms, while it needs good and strong support.
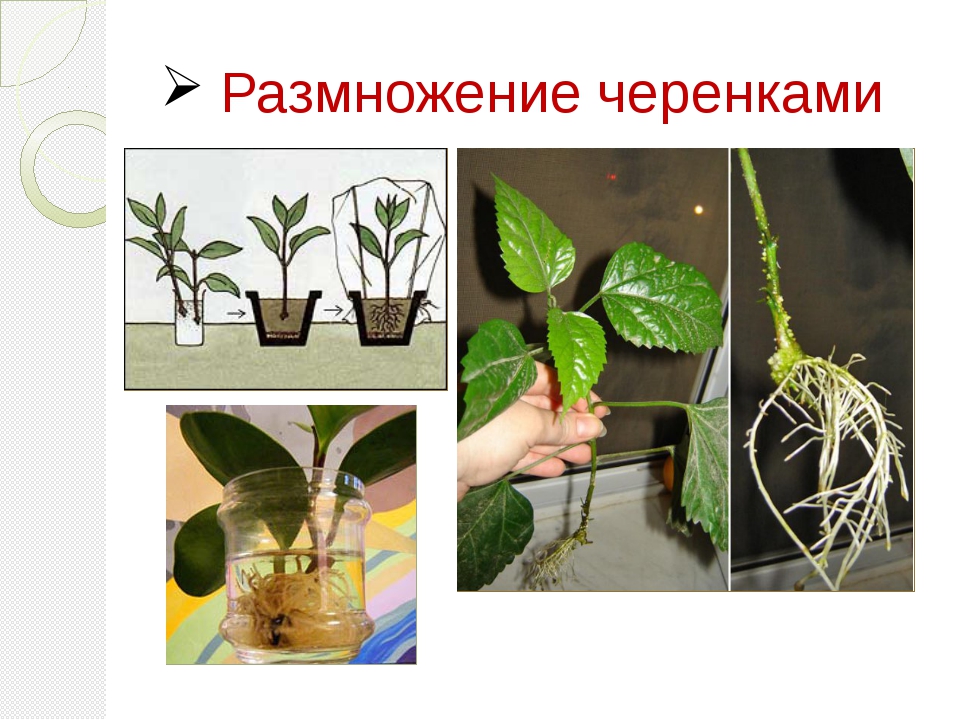
Flower reproduction methods
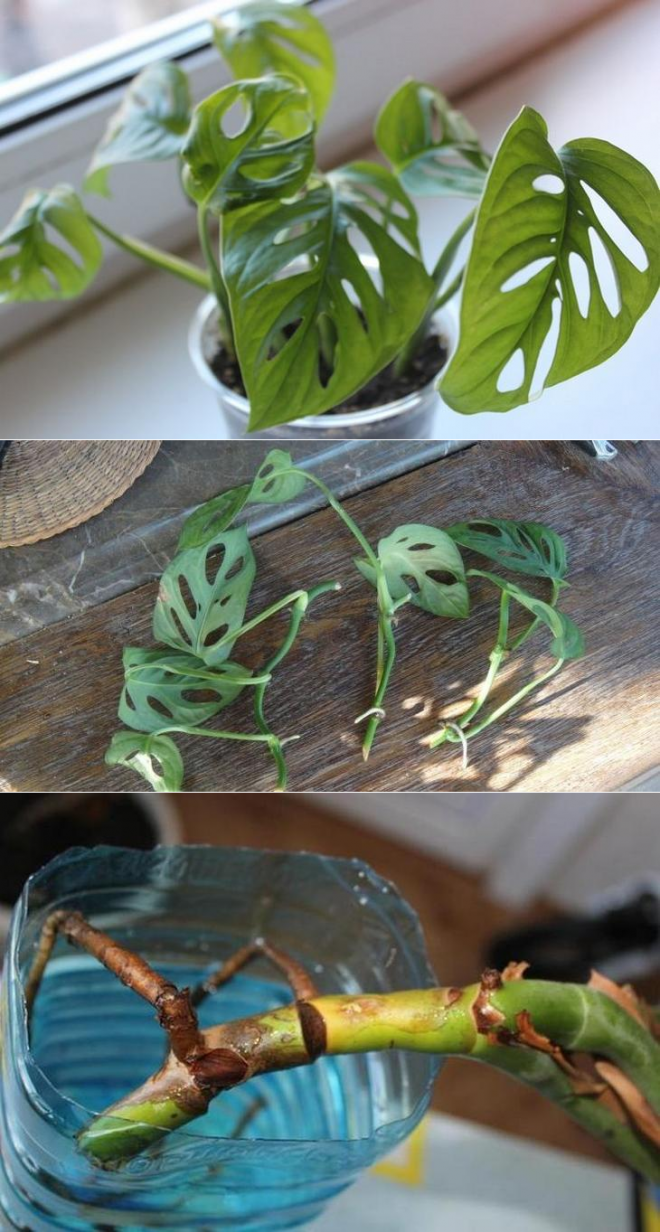
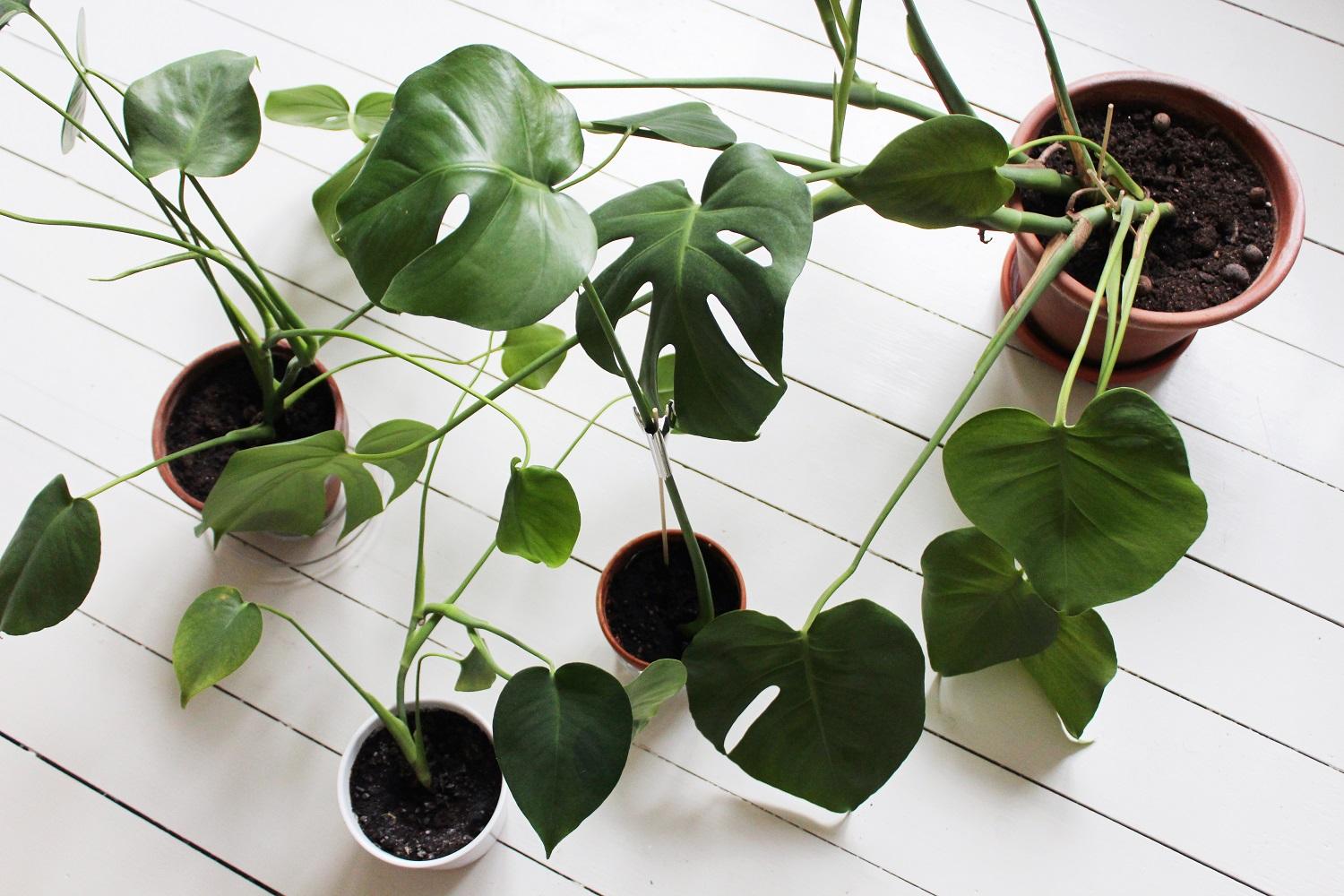
Monstera can reproduce both by stem cuttings and by leaves, aerial roots and seeds. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages.
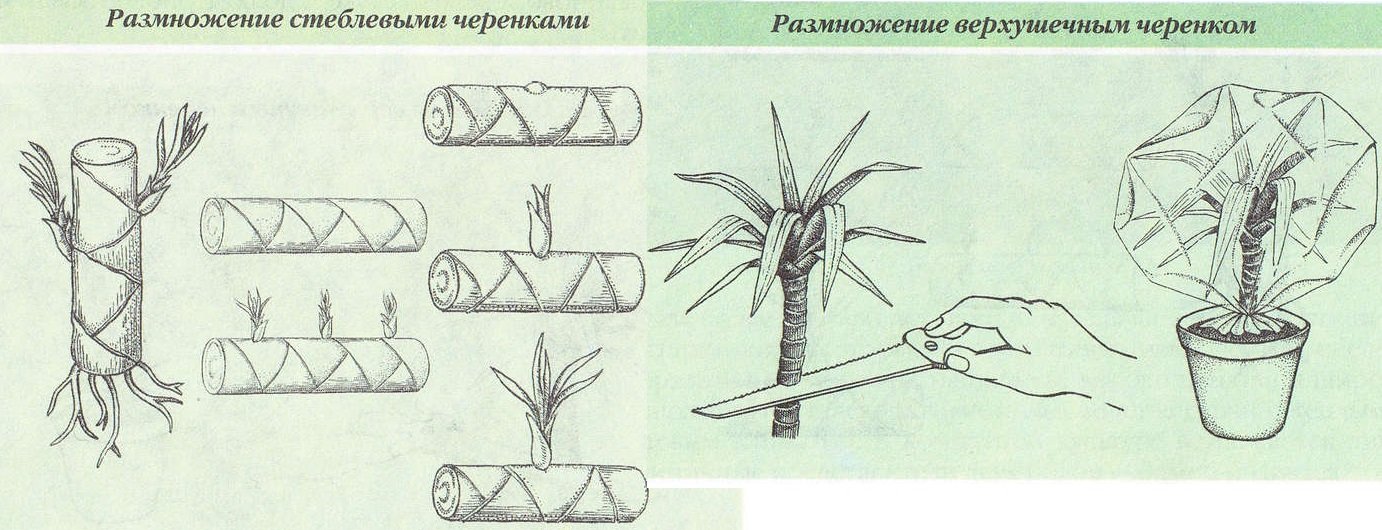
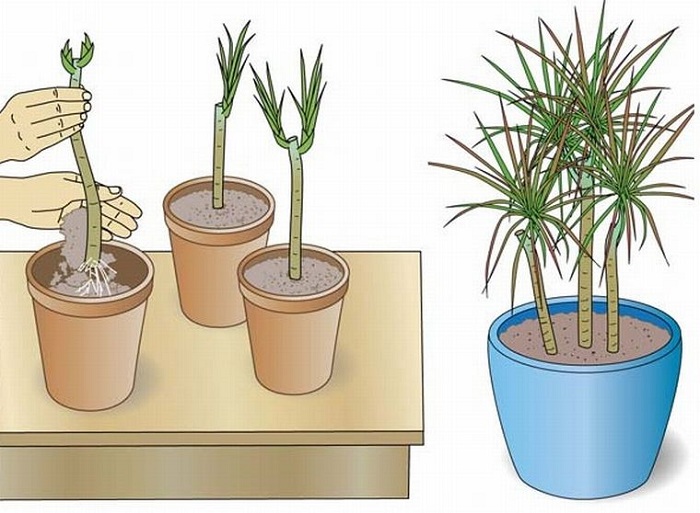
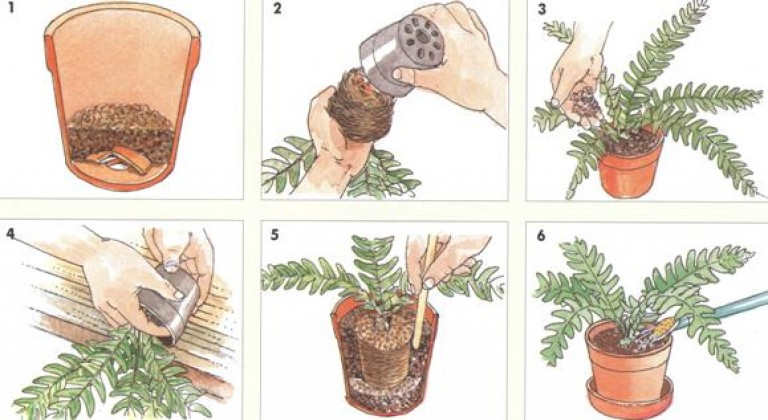
How to propagate by stem cuttings?
This method is considered the most common.
- To do this, you need to separate a part of the stem, on which at least 2 buds are present.
- The cuttings are placed on damp soil and sprinkled in. Instead of earth, the container can be filled with hydrogel.
- To accelerate growth, the container must be covered with a film. The result is a greenhouse environment with the required humidity level.
- The film needs to be removed every day to check the ground. The cutting should be periodically sprayed so that it does not dry out.
- When the first roots appear, the stalk is planted in a permanent place.
It is not recommended to use water for rooting stem cuttings. The roots will grow in it, but then they will not be able to normally adapt to the soil. As a result, the plant will often get sick.
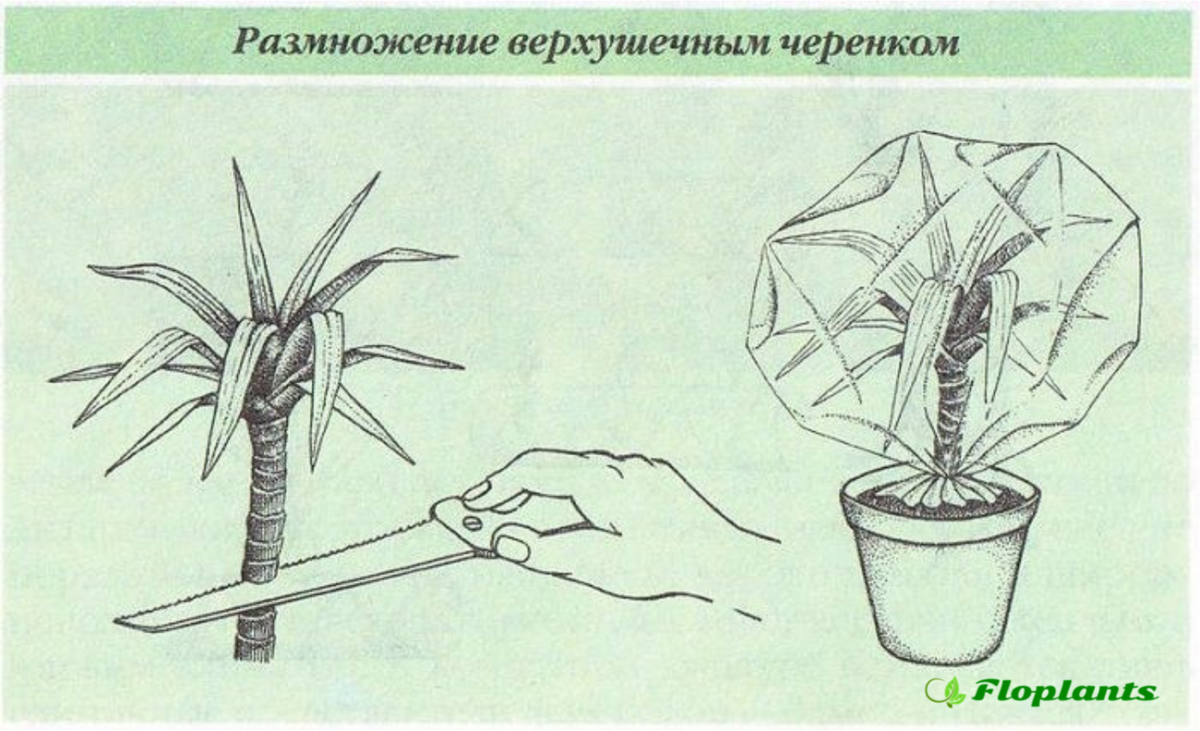
Apical cuttings
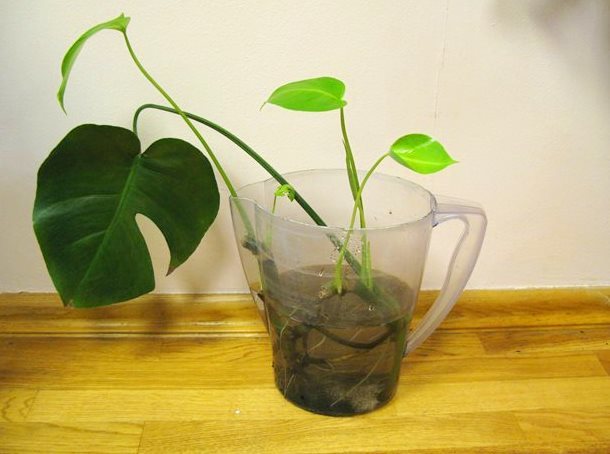
For reproduction in this way, an apical cutting is required, that is, the crown of an adult plant. It is cut off and lowered into the water. After a while, roots begin to appear. The transplant is carried out in the presence of 3 strong root processes.
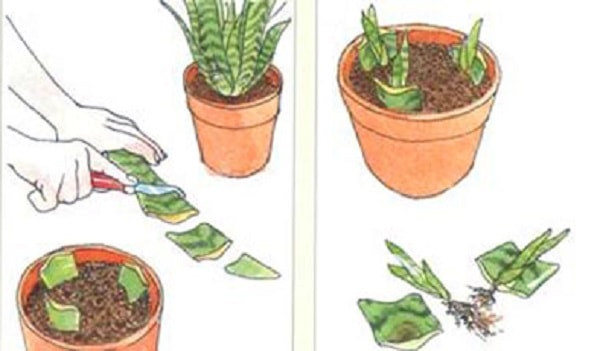
Leaves

This may not work as the leaves often wither. In the case of the formation of the root part, the flower is transplanted into the ground.
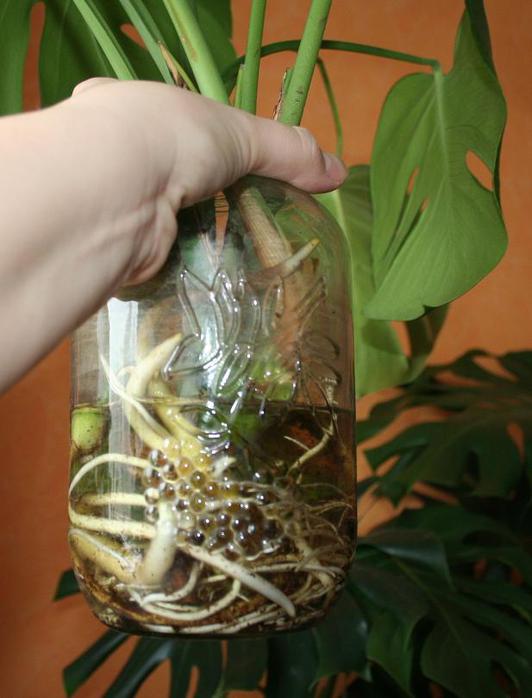
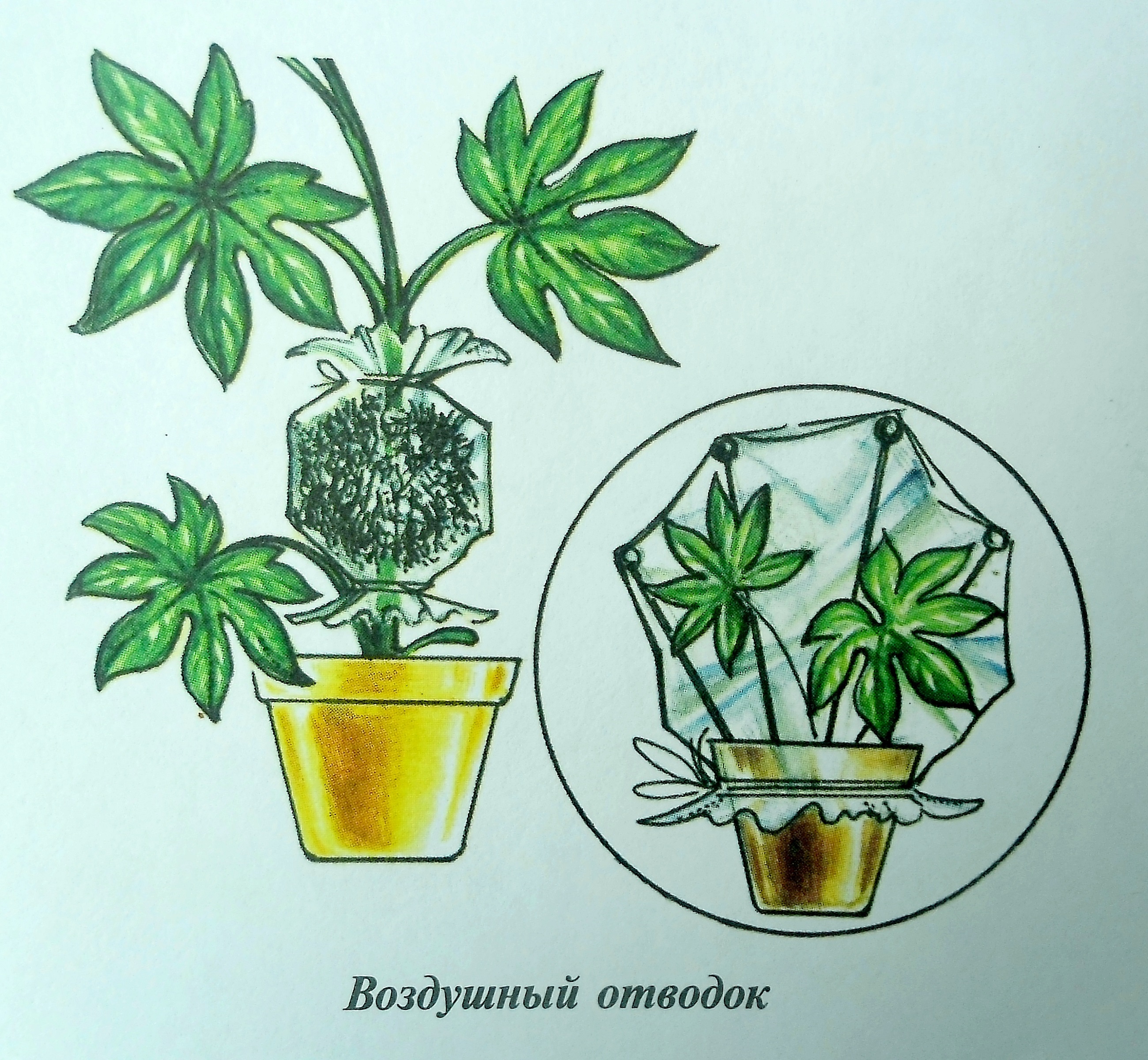
Air roots
Reproduction by aerial roots is a rather difficult, but reliable way. Algorithm of action:
- Selection of a shoot with a large number of small aerial roots.
- Wrap the place of the stem with the roots with moist sphagnum moss, and then with cling film. For fixing, you can use tape or wire.
- Permanent moss moisture. For convenience, a syringe is used. As a result, a small greenhouse is formed. After a while, new roots begin to form under the film.
- A cut of a shoot with a new root system.
- Transplanting the plant into a pot with soil for decorative deciduous plants.
A plastic water bottle can be used instead of moss. It is tied to the stem and the roots are placed there. The water needs to be renewed regularly.
Seeds
Seed propagation is not always successful. The main condition is the availability of fresh seeds. If they have been lying for a long time, then they may not rise.

For germination of seed, you need to use sphagnum moss.
After a month or one and a half, the first shoots appear. The first adult foliage is formed at 5-8 months. Seedlings are dived and planted in individual pots.
Disease and pest control
The main causes of diseases in monstera:
- Parasites;
- Insufficient or excessive lighting;
- Waterlogging of the soil;
- Cramped pot;
- Unfavorable air temperature.
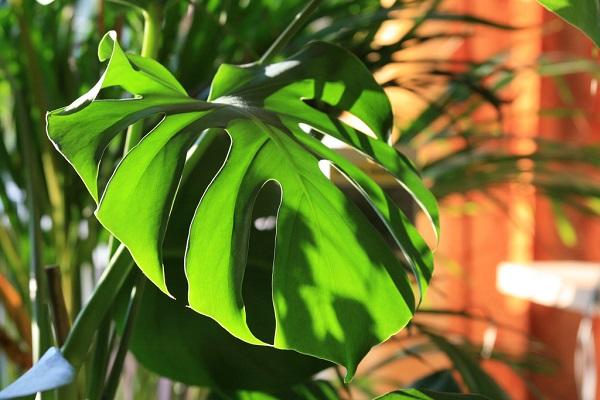

If the plant begins to appear white spots on the leaves, most likely the cause of the disease is an excess of light. A twisted stem and small leaves indicate a lack of light. In such cases, it is recommended to move the plant to another corner of the house.
The appearance of droplets on the leaves, the wilting of the plant indicates an excess of moisture. In this situation, it is necessary to stop watering and allow the earth to dry out. Insufficient watering leads to leaf fall, the appearance of brown spots on them. You can solve the problem by increasing the frequency of watering.
When pests appear, monstera leaves should be wiped with a cotton swab dipped in soapy water.High humidity affects the parasites, so the plant should be sprayed more often. Spraying should be combined with a decrease in air temperature - the plant can be left under the air conditioner for a while. You can process the monstera with a 0.2% rogor solution. If no method helps to get rid of parasites, it is necessary to cut off the affected parts of the flower.
Care errors and their elimination
Useful information is collected in the table:
| Problem | Causes | Elimination |
| Leaves turn yellow and dry | Moisture deficiency. Direct rays of the sun affect the leaves for a long time | Move the flowerpot to an area of moderate refreshment. Water on time and abundantly. In the warm season, wipe the leaves with a damp cloth |
| Rots | The flower grower fills the soil. The room is too damp and cold, the moisture does not have time to evaporate. No drain holes or holes in the bottom are clogged. Water stagnates in the pan | Provide moderate watering, especially in winter and autumn. Check the drainage holes: stones may be blocking access to the outflow of fluid. During the rest period, do not overmoisten the soil. Monitor the temperature regime at different times of the year |
| Does not grow | Little light and moisture. The soil is not nutritious enough. Lack of fertilizing for an adult plant | Eliminate negative factors that interfere with the growth of monstera |
| Leaves are small | Lack of lighting. Low temperature. An adult plant is not getting enough nutrients | Move the flowerpot to a bright and warm room. Feed with fertilizers for plants of the Aroid family. |
| Spots on the leaves | Settlement of spider mites. Sign of rotting roots | Normalize watering. Treat the leaves with soapy water and anti-mite preparations |
| Pale young leaves | The room is too hot, intense lighting | Lightly shade the plant in the summer when located in the southern room, make sure that the young greenery is not under the scorching rays in the heat. Stabilize the temperature at a level not higher than + 25 ° С |

Monstera pests and diseases
Diseases and insects
You and the monster will not have any problems in this regard: it is extremely rarely affected by pests, and it is resistant to diseases. And only the most careless owners can expose the plant to the attack of scale insects and spider mites, whose presence is not so easy to notice. If you still find pests, try wiping the monstera leaves with soapy water, but if this does not help, you will have to apply an insecticide treatment - Aktara or Fitoverm.
But what if the leaves of a monstera turn yellow and then become transparent? This is a sure sign of chlorosis, so you need to buy "Iron Chelate" and use it according to the instructions. In lazy owners who violate the rules for caring for a monster, the plant can get sick with fusarium, late blight, anthractosis, bacterial and stem rot, and spots.
Monstera turns yellow
Usually, monstera reacts to all mistakes and shortcomings in leaving by changing the color of the leaves - yellow spots on the leaves of the monstera are a sign that the plant is unhappy with your leaving. Why does monstera turn yellow? There are many reasons for this:
- if the leaves turn yellow in large quantities in winter, it means that you have overdid it with watering;
- if, along with yellowing, brown spots appear on the monster, it seems that this is a case of insufficient moisture;
- if the leaves not only turn yellow, but also fall off in large quantities, this is the result of too high a temperature and insufficient humidity in the room;
- leaves become yellowish-pale if the plant suffers from an excess of light.
What if the monstera turns yellow? Find out the cause and eliminate deficiencies in plant care.
Monstera dries
Sometimes only the tips of the leaves dry out in the monstera, and sometimes necrosis spreads along the entire edge of the leaf, which negatively affects the decorative effect of the plant. And in this case, the question of why the monstera dries can have several explanations:
- drafts or a jet of air from an air conditioner that falls on monstera leaves;
- too warm, too cool or too dry indoor air;
- stagnation of water in the roots, watering at night or, conversely, in direct sunlight;
- the lower leaves wither and dry quickly if the plant needs a transplant.
Monstera turns black
There are also several explanations for this phenomenon. The leaves turn black when the watering regime is unbalanced in the monstera: from a lack of moisture, the leaves first turn yellow, then darken, and from excess blackness appears on green leaves, and in the second case, rot can be either dry or wet. To find out why the monstera turns black, it is enough to observe it: if, upon observation, you find guttation, then it is necessary to immediately reduce the watering so that the leaves do not subsequently turn black.
Major pests
Pests on a monster can appear due to too dry or humid air. Often they are brought in from purchased or garden land, by the wind from the street or from a neighbor's balcony.
Shield
The ivy scale insect is a hard-to-kill insect that can completely destroy even an adult monster. It affects leaves, aerial roots and shoots. After laying the eggs, the females die, and offspring develops under the dense small shield with which they are attached to the plant. Wandering larvae very quickly move from one plant to another.
A sooty fungus willingly settles on the secretions of the scale insects, which is why all the affected parts of the monstera are covered with a black sticky bloom.
The main control measures: periodic mechanical removal of parasites with a sponge soaked in soapy water, spraying with insecticides: 1-2 ml of Aktelika per 1 liter of water. It is preliminarily recommended to treat the monstera with an alcohol solution (1 part alcohol to 4 parts water) to soften the scabbard shell. In difficult cases, plant breeders advise to water the soil under the monster with Aktara solution or spray the liana with dichlorvos.
Spider mite
Due to the invasion of the spider mite colony, the leaves of the monstera dry and turn yellow. On the reverse side of the sheet plate, you can see small dots and cobwebs. With a small degree of damage, the monster is washed with a strong solution of laundry soap. If the measure was unsuccessful, then chemicals are used: "Akarin", "Apollo", "Fitoverm".
Mealybug
If young leaves and shoots of monstera began to deform and dry, then the culprit may be a mealybug ("hairy louse"). Its presence can be determined by tiny white lumps (like cotton wool) located at the bottom of the sheet plate or in its mouths - this is a clutch of eggs. The insect itself is very mobile, well distinguishable with the naked eye.
At the initial stage, wiping the monstera with alcohol or soap solution can help. If the worm continues to multiply, then spraying with the preparations "Aktelik", "Fozalon", "Intavir" is used.
Thrips
Thrips, small oblong black insects (like tiny black sticks), cause a lot of problems for the monstera. Streaks and dots of a silvery color appear on the outside of the leaf plate, which gradually merge, leading to the drying out of the leaf. An effective measure is the treatment of monstera with the preparations Fitoverm, Karate, Agrovertin, Karbofos.
Requirements for soil, planting containers, transfer regime
Optimal soil composition for monstera:
- 3 parts of peat;
- 2 parts of humus;
- 1 part sand.
You can add 1 part of garden soil. It is better to purchase ready-made soil mixtures ("Gardens of Auriki", "Seliger-Agro"), so as not to risk the health of the plant.
For a young monstera (1-3 years old), a 2-3 liter pot is enough, and then you will have to pick up a larger container - 7-10 liters. On sale there are decorative buckets for 15-20 liters - this will be comfortable for an adult plant. At the bottom, at least 1.5-2 cm (depending on the volume of the pot) of fine gravel or expanded clay for drainage must be poured.
Until the age of 3 years, the monster is recommended to be transplanted annually. This is done to stimulate the development of the root system and intensive nutrition.
After 5 years, the vine needs replanting every 4 years, but for stable development, an annual replacement of the topsoil will be required.
Watering the monstera should be regular, carried out when the top layer dries about 2 cm.In winter, once every 10 days is enough, provided that the tub with the plant is located far from the heater and does not stand on a heated floor.
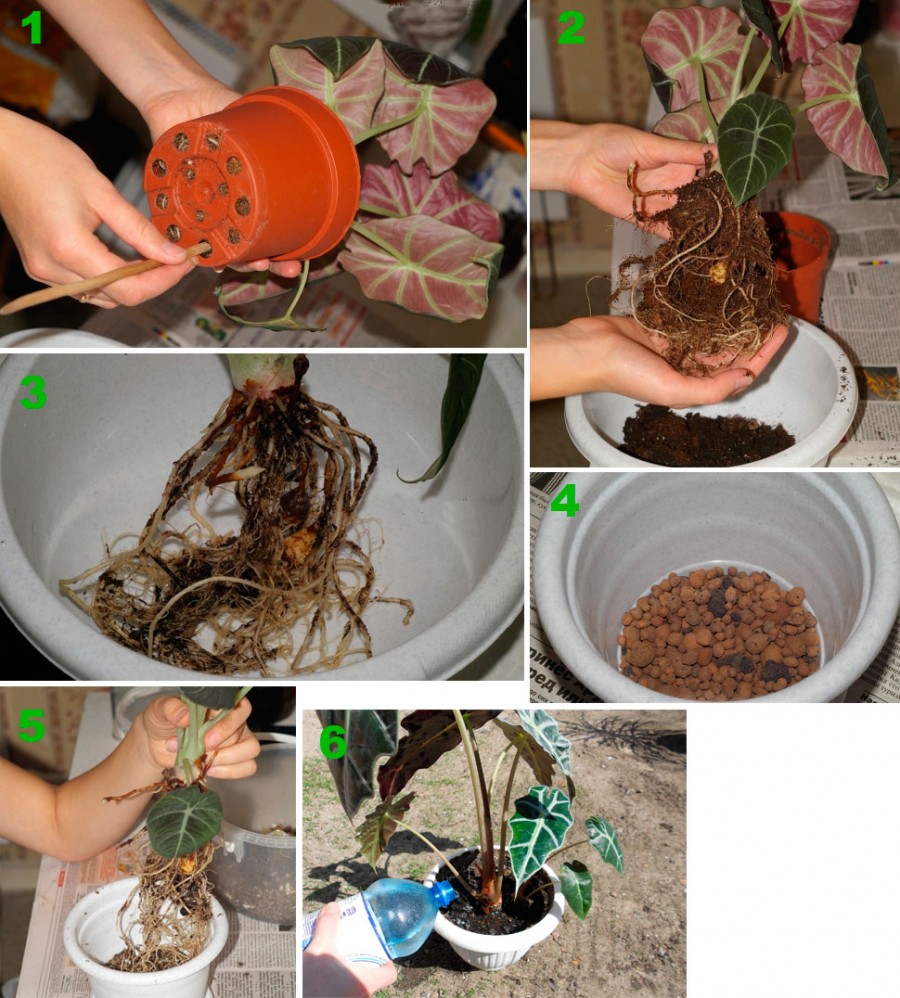
Transplant technique
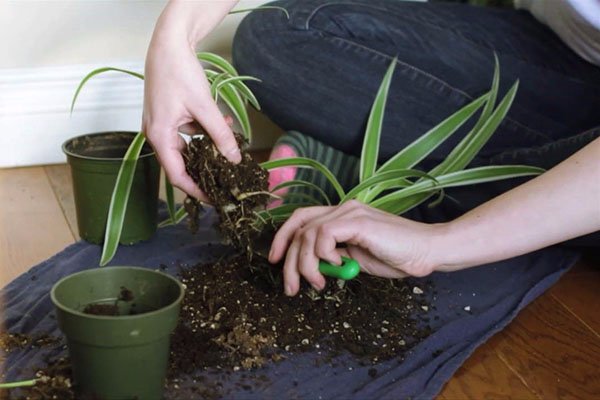
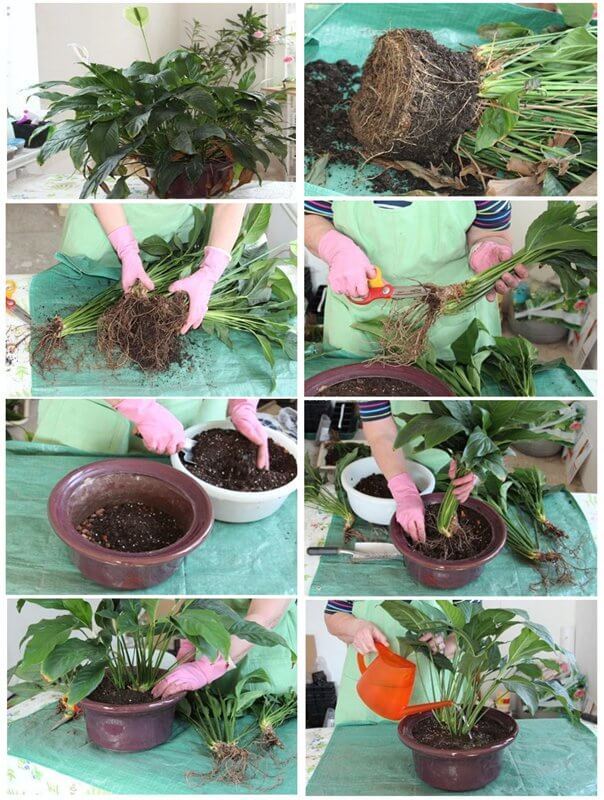
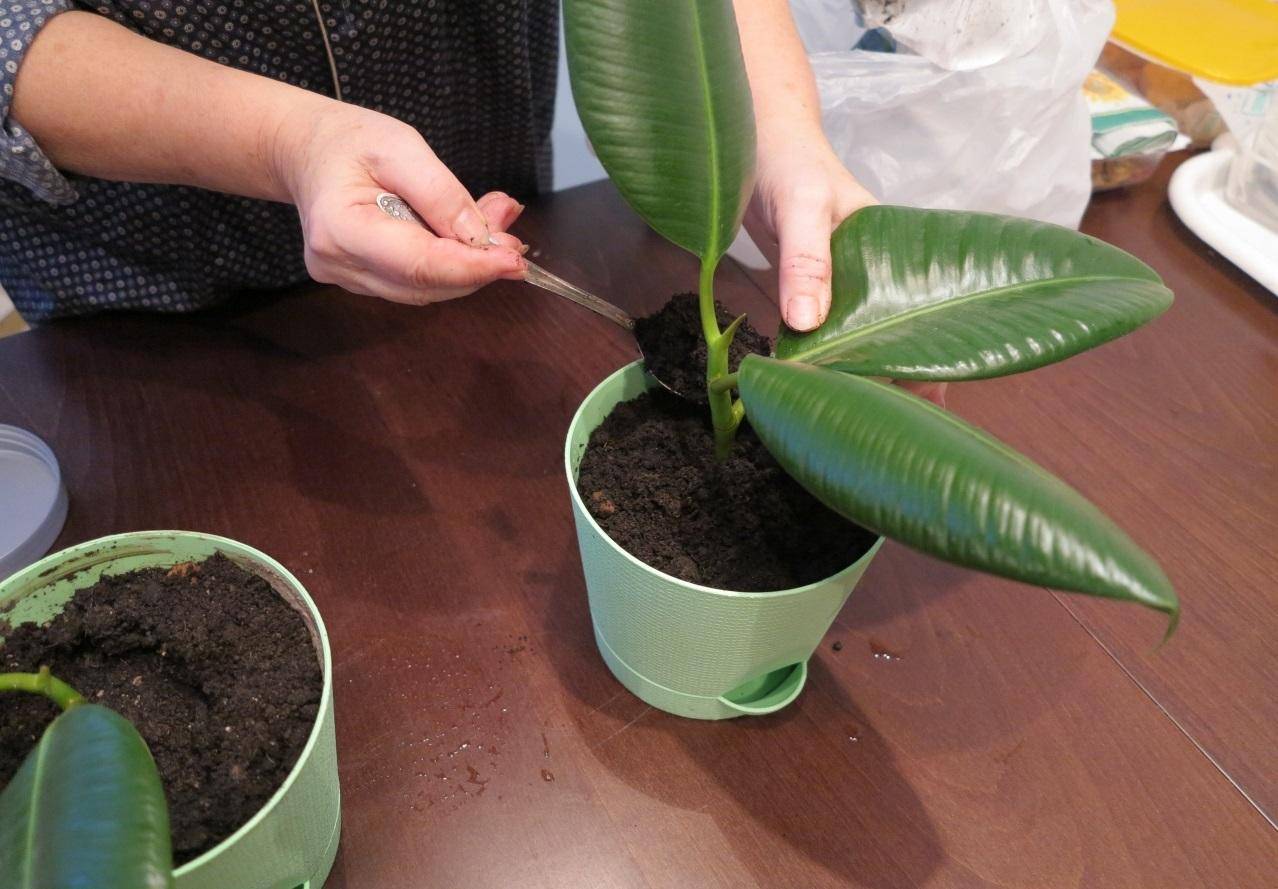
Monstera is transplanted by the transshipment method. To do this, the earthen lump must first be dried so that it easily moves away from the walls of the container. Some recommend abundant watering before transplanting, but in this case, the soil will stick to the walls of the pot along with the roots, which will inevitably lead to damage to them.
When transplanting a large liana, it is completely or partially removed from the mounts, neatly laid out on the floor. The pot is tossed to one side on a pre-laid piece of polyethylene. You need to grab the monster by the stems at the base and gently pull it out of the container. Previously, you can lightly knock on the walls of the pot, then the dried earthen lump will come out without problems along with the roots. It is more convenient to transplant the monstera with an assistant, who at this time will slightly shake the tub.
When the earth clod is released, it is carefully transferred to a new container filled with drainage (at least 1.5 cm) and soil (at least 4 cm). Soil is poured on the sides, compacted in stages
After planting the vines, the soil is shed with an emphasis on the perimeter. You should not strive for water seepage into the sump, it is enough to wet the lateral areas to activate the roots.

How to care for a monster at home
As mentioned earlier, monstera is a fairly unpretentious plant, but despite this, care (like reproduction) must be carried out taking into account a number of mandatory rules.
Watering a houseplant

Watering the monstera is the most important stage in its development. She loves moisture very much, but the plant has a clear seasonality of watering the soil. From early spring to late autumn, the flower should be watered abundantly. However, the top layer of the substrate should dry out between waterings. If the plant is poured, then it will begin to lose its decorative effect, forming black spots, and in rare cases, the root system will begin to rot. In the winter season, watering should be reduced, but be careful not to dry out the monstera.
Water for irrigation should be at room temperature and stand for several days before use. Also, the monster needs to be sprayed and regularly cleaned of dust.
Did you know? Monstera reacts to changing weather. Droplets slowly form at the edges of the leaves of the plant, which is why many florists say that the flower is crying in the rain.
Feeding monstera
All indoor plants need to be fed. If the monstera is not growing, then it is lacking in nutrients. Therefore, in order not to slow down growth in adult plants, they need to be fed twice a month. Mineral and organic fertilizers are suitable as top dressing, although young flowers may not be fed.
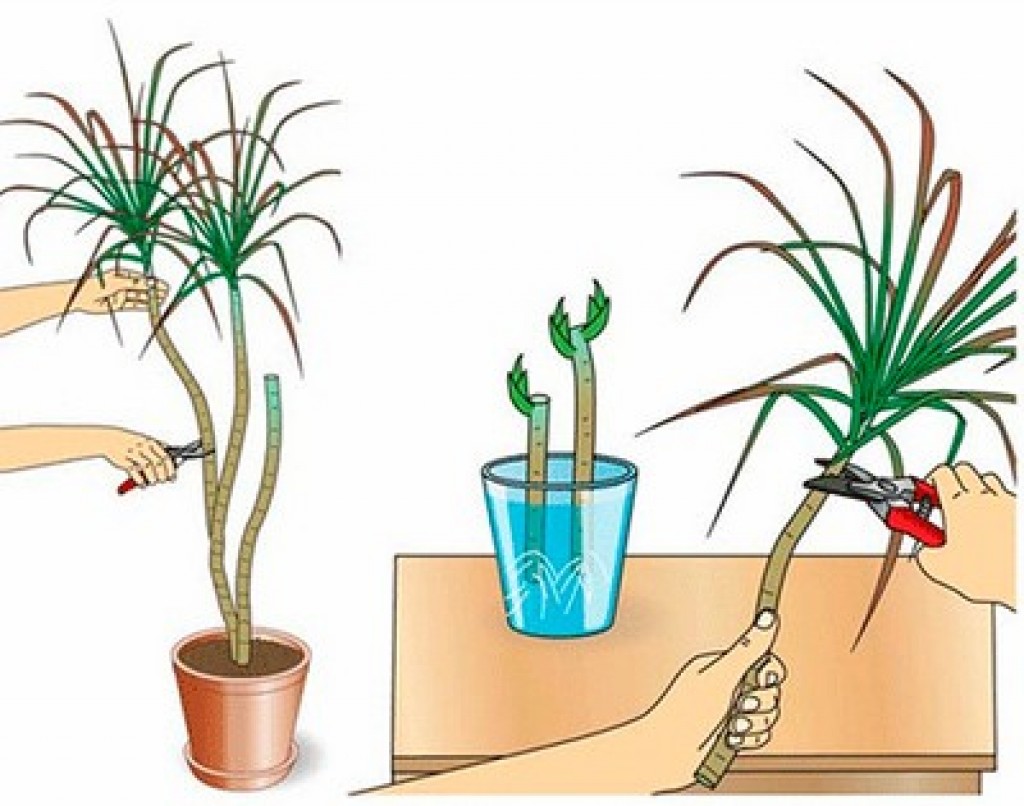
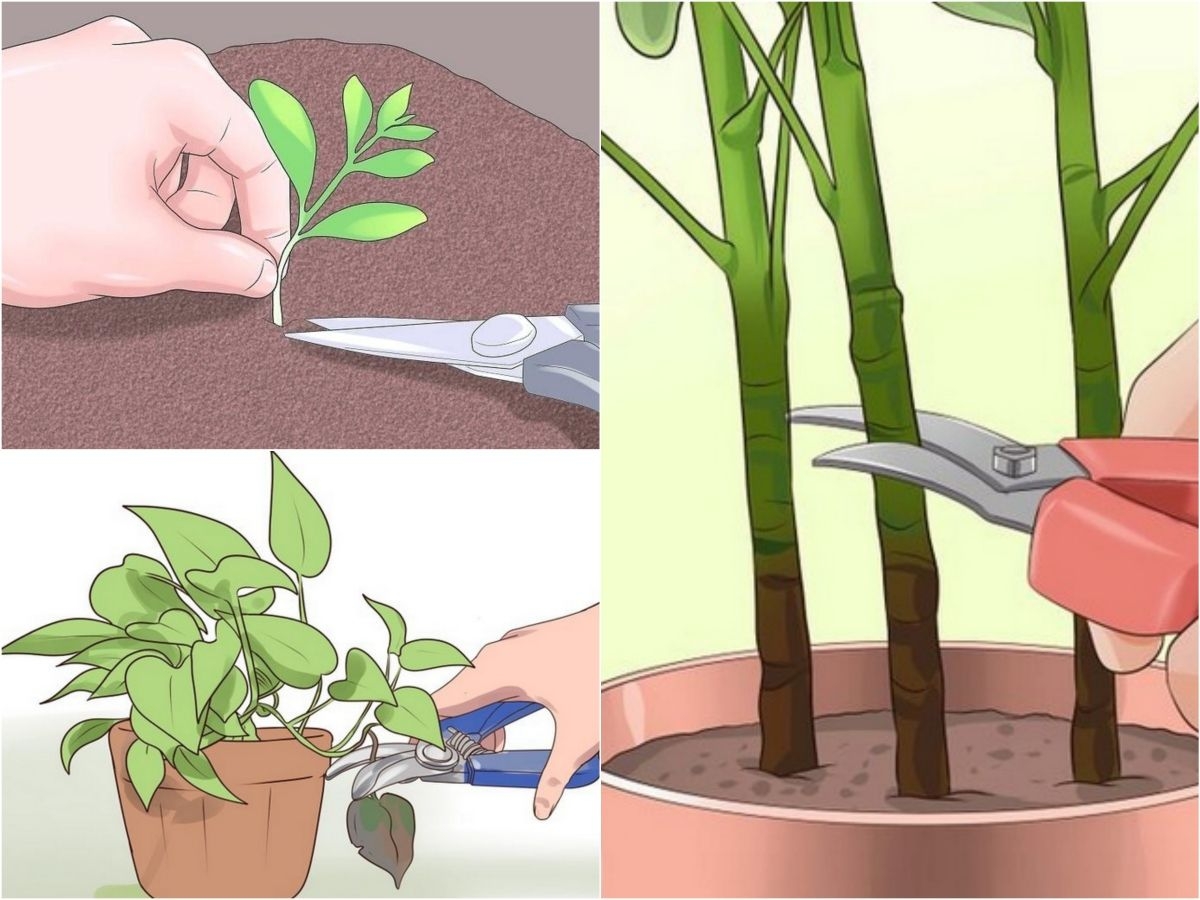
Features of monstera pruning

In order to stimulate the growth of new leaves, it is necessary to cut off the top. This is done in early spring, and when pruning, at least three nodes should be left on the top handle. The longer the cutting, the more it will take root. The cut must be made, departing from the flower node 1-2 cm, and it must be straight. After pruning, the stem should be sprinkled with charcoal powder, and if the cutting needs to be rooted, then the lower cut is made oblique.
All About Monstera Transplant
Monstera can be transplanted as soon as it is one year old. Young flowers are moved to another place once a year: in spring, at an air temperature of at least + 16 ° C.A three-year-old monster should be transplanted every two years, and a five-year-old - once every 4 years.
For transplanting, you should choose large pots. With each transplant, the size of the pot is increased by 2-4 cm. At the bottom of the container, it is necessary to arrange drainage from shards, pebbles, broken tiles or coarse sand. A young flower needs a slightly acidic or neutral soil, which consists of peat, deciduous, humus soil, turf and sand.
For perennial monstera plants, acidic soil is well suited. In addition, a support should be installed in the center of the pot, which helps the plant maintain the necessary conditions for the development of both the flower and its aerial roots.
When transplanting, carefully remove the flower from the pot and move it to a new container, slowly covering it with earth. After that, fill the pot to the top with earth and water well
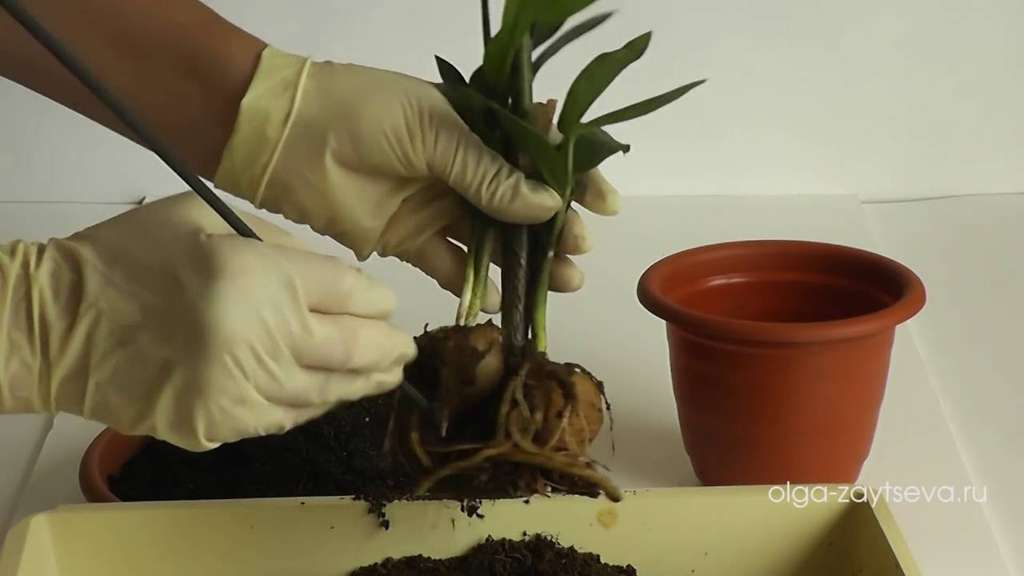
Some flower lovers have a question: "How to transplant to a monster with aerial roots?" With such a transplant, it is necessary to carefully wrap the aerial roots with wet twine and attach to the trunk. When they start to put out small roots, then part of the trunk of the plant with leaves can be cut off, planted in a container, covering the cut point with earth. Thus, a new, young flower will grow.
Important! If for some reason it is not possible to transplant to the monster, you just need to add earth to the pot.
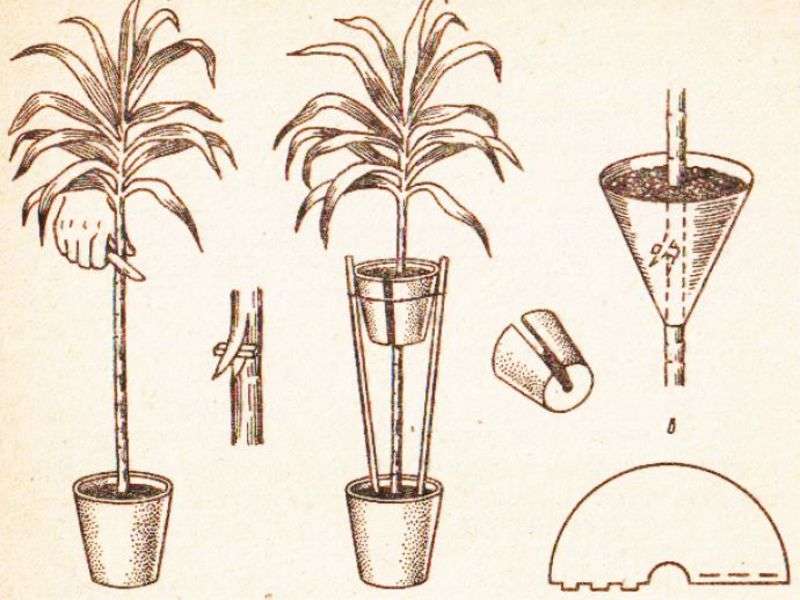
How to propagate a monster: planting cuttings and seeds
Breeding monstera is not difficult. Many growers willingly distribute already strong rooted cuttings. They are easy to obtain by cutting off the top with excessive growth of the liana, as well as when the short aerial roots of the upper part of the monstera are immersed in water (white layers grow from them). When adventitious roots appear, a part of the stem with a pair of leaves is cut off and planted in a prepared substrate.
In the root zone, vines often grow new shoots. They can be separated, dipped in a rooting stimulator and buried in moist, nutritious soil. From above, the seedling is covered with a transparent bag or jar to maintain temperature and humidity. When a new sprout appears, the shelter can be removed.
It is also possible to plant monstera with seeds, but it is extremely rare to get them on your own. The method is also problematic due to the rapid loss of germination and prolonged pecking.
Vine seeds are germinated before planting: they are wrapped in a wet soft cloth or placed in wet sphagnum moss. The temperature should be around 25 ° C. Monstera seeds germinate for a long time - 1-2 months. After pecking, they are seated in cups, not too deep.
Growing a monstera is not difficult if the plant has enough space and lighting. Some are confused by the need for periodic transplants, but practice shows that an adult vine can grow for years in one container.
It is important to provide her with good nutrition and hydration - this is the main care.
Monstera grows quickly, so with its help you can decorate the interior of the room in an original and useful way. To preserve decorativeness, it is enough to periodically wipe the leaves and spray the plant
The monstera will respond to the attention paid with lush greenery, will regularly disinfect the air and cheer up, despite all the myths about its harm
Transplantation and reproduction of monstera
Up to 3-4 years old, young vines need an annual transplant; 3-4-year-olds are transplanted once every 2 years; over 5 years old, with the annual replacement of the top layer with a new soil, - after 3-4 years. Monsters grow best in large pots with an obligatory drainage layer on a perforated bottom.
Soil for young plants at pH 5.5-6.0:
- turf - 1 part;
- peat - 1 part;
- humus - 1 part;
- river sand - 1 part.
For adult plants at pH 6.5-7.0:
- turfy - 3 parts;
- peat - 1 part;
- deciduous - 1 part;
- humus - 1 part;
- river sand - 1 part.
Reproduction of monstera is possible by cuttings, shoots, and less often by seeds. Vegetative propagation of this plant is simple and win-win. Best time: March to June. To do this, use lateral processes appearing in the lower part of the stems, with aerial roots, as well as stem or apical cuttings, that is, pieces of the stem, on which there should be at least a pair of leaves and aerial roots. Places of cuts are sprinkled with powdered black activated carbon, left to dry.
The prepared cuttings are deepened with aerial roots in a pot with drainage and soil for young lianas, sprinkled with a layer of sand on top, moistened and covered with a glass jar in the form of a miniature greenhouse, under which rooting and growth will be more successful. The new planting is kept at a temperature of + 20- + 25 C, watering under the root in the morning and in the evening with warm soft water without waterlogging. After rooting, the sprouts are placed in an intermediate container, and in the main large pot or tub they are transferred overgrown after 3 years.
An aging vine that loses its lower leaves becomes ugly. It is rejuvenated by the following method. The two uppermost aerial roots are wrapped first with wet moss, and then tied to the parent trunk with a washcloth or twine. When they are overgrown with many small roots, the top, about one or two leaves, can be cut off, treated with activated carbon powder and planted in a pot with moistened soil so that both the cut and the roots are completely in the ground. Two correct steps: the first - a young plant is obtained, and the second - the old stem will give new lateral shoots, which will lead to its branching and intended rejuvenation.

What will happen when placing a monstera in the bedroom
As mentioned, scientists have proven the plant is harmless, so it can be placed in the bedroom (as in any other room in the house). Bad superstitions are not backed up by anything. And even the loudest myth that monstera is an energy vampire is also unfounded. This has never happened before, and it will not happen in the future.
But if from a biological point of view the flower is harmless, then everything is extremely ambiguous with omens.
It is impossible to answer what will happen when the monstera is placed in the bedroom. Positive and negative signs are associated with the flower. Believe in them or not - everyone's personal choice. One thing worth noting is that if people are constantly fixated on negative thoughts and failures, then they will blame the monster for their adversity. On the other hand, many attribute positive changes in life to the influence of the monstera.
If the person is shy, you should not place the monster in the bedroom. People are afraid to wake up at night and see a huge shadow with large dissected leaves that resemble roots.

This cannot be denied, in the dark it looks terrifying.
Description of the plant
Monstera is an evergreen tropical culture of the Lian genus of the Aroid family, whose homeland is the southern regions of America. It has large, massive leaves in the shape of a heart with cuts, the color of which is deep green, may have spots, stripes of a lighter or yellow hue. Young leaves are devoid of cuts: only with a certain age do they develop holes, which are later transformed into long cuts.

The plant has a long stem from which roots can hang. Under natural conditions, the height of an adult plant can reach 6 m, at home - 4 m.It blooms in the form of a beige cob. After flowering, it forms a fruit - a berry that is suitable for eating. In total, there are about thirty types of monsters in the world. In the conditions of the house, in most cases, only a few are grown: a lovely, unequal or perforated monster.
Did you know? Many people mistakenly believe that the word "monstera" is translated as "monster, monster." However, in fact, from the Latin language "monstrum" means "amazing, bizarre".