How can geotextiles be used in the country
Using geotextiles on the site, you can create unique design compositions and original reliefs.
Solution 1. Creating original garden paths
A well-kept garden cannot be imagined without winding paths, they are an essential part of a beautiful and modern garden. Geotextiles are used for their decoration. First, part of the soil is removed, then the groove is covered with crushed stone, and geotextiles are laid on top. Then it is covered with sand and compacted. At the final stage, paving slabs are laid.
Laying geotextiles allows you to avoid mixing sand with gravel and, as a result, soil subsidence. The tracks remain level and do not lose their shape over the years.
The durable nonwoven fabric can also be used for sandy or gravel paths. An insulating layer between the soil and the bulk material prevents the latter from penetrating into the soil and reduces its consumption. In addition, in this case, weeds do not germinate in the soil, and excess water quickly flows off the polymer surface, without creating swampy areas. Covering material protects embankments from landslides and flooding.
Solution 2. Waterproofing of reservoirs
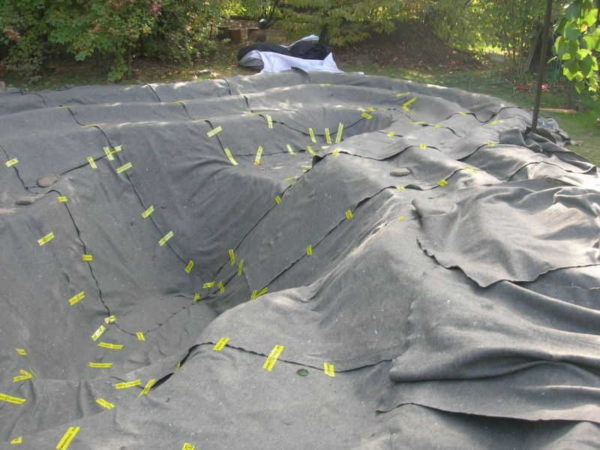
Decorative ponds are one of the stylish and luxurious elements of landscape design. To equip any body of water - from a swimming pool to an artificial lake - you need to create a special waterproof bowl.
During the construction, operation and cleaning of the reservoir, there is always a chance to damage the insulating layer. But not in the case of geotextiles! It can be laid either directly in the pit or by additionally covering it with a layer of insulation.
Solution 3. Registration of the local area
Geotextiles are also used to create playgrounds, recreation areas and decorate rocky gardens. A particularly successful find was the use of non-woven material in the construction of the patio. Rolls are laid directly on the ground, and a wooden flooring is mounted above them and a gazebo is erected. In this case, weeds do not germinate through the boards, maintaining a neat appearance of the recreation area.
Don't forget that geotextiles are breathable. Therefore, with the help of it, they construct and draw the boundaries of high embankments, reinforce the soil, create drainage systems, etc. The linen under the turf layer will prevent erosion as rainwater will enter the ground.
Solution 4. Protection of the foundation
Even a reliable concrete base of a private house can weaken over time and lead to displacement and subsidence of the entire structure. The most "evil enemy" of the foundation is groundwater, which imperceptibly erodes it. To eliminate the harmful effects and eliminate the mixing of soil containing moisture with gravel, geotextiles are laid close to the foundation. It prevents moisture from accumulating at the base and gradually destroying the building.
Solution 5. Rescue for gardeners and gardeners
Experienced summer residents have long known about the positive qualities of geotextiles. This material allows you to protect crops from weeds, increase yields and avoid mixing different layers and soil compositions.
Weeds are a real "garden plague". Germinating next to beneficial crops, weeds deprive them of nutrients, light and moisture. But if you want to take care of the protection of the plantings in advance, then be sure to cover the soil with a layer of geotextile, and plant the seeds and seedlings in holes specially made in it. This will save you the trouble of weeding and help keep moisture in the soil.
Many ornamental plants require special potting mixes for proper development and growth.And the soil on the site in terms of its composition, as a rule, is far from ideal. It is possible to distinguish between the two types of soil with the help of makeshift pockets lined with geotextiles and covered with fertile soil. This must be done so that the nutrient layer does not wash out and mix with the depleted soil. In addition, the roots of plants in this case will not penetrate into the infertile layer.
Also, geotextile protects plants from night frosts, saves from summer heat and scorching sun rays.
Geotextile is a versatile material that anyone can use. Its use simplifies gardening, facilitates plant cultivation and helps to improve the area. This is truly a miracle fabric that will solve many summer problems.
How to put geotextiles correctly
For a long service life, it is important not only to choose the correct geotextile, but also to lay it without errors.
Laying rules
When carrying out work, you should adhere to certain rules:
- the surface for laying the canvas must be well leveled;
- the packaging is opened immediately before starting work, since some materials are sensitive to sunlight;
- the required dimensions should be calculated and the strips should be cut taking into account the stock of material, but also so that there are as few scraps as possible;
- when calculating the dimensions, an allowance of 5–10 cm should be taken into account, which is necessary for a slight deformation of the geotextile after covering it with sand on top;
- if geotextiles are laid on a layer of gravel or pebbles, then a single layer is used, when laying directly on the ground - the canvas is placed in 2 or 3 layers;
- the geotextile is laid without tension, but the formation of folds should not be allowed;
- the overlap of the canvases should be at least 20 cm;
- the joints of the canvases with each other must be well fixed. They can be fastened with a construction stapler or soldered with a construction hairdryer;
- when applying strips at the joints, it must be borne in mind that the geotextile laid in the area located above should cover the material from the lower area;
- after filling crushed stone on geotextile, it is advisable to wrap its edges 15–20 cm from above in order to prevent contamination of the internal components;
- when fixing the material to the ground with long staples, the damaged areas must be glued with bitumen.
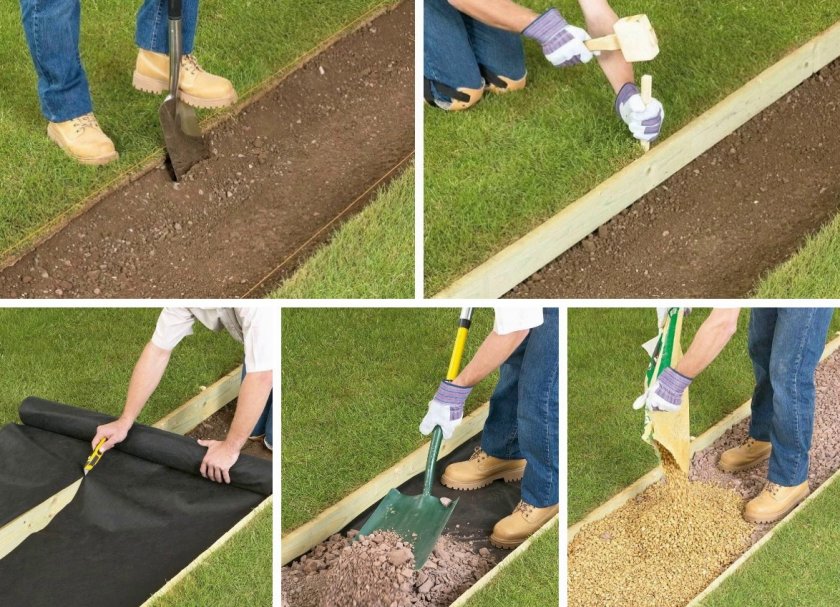

DIY step-by-step instructions for building a track
Laying paths using geotextiles follows a certain algorithm:
- Make a marking of the paths using pegs and a rope stretched between them.
- Dig a trench about 30–40 cm deep and level the bottom well.
- Fill in a layer of sand (preferably fine-grained river sand) up to 5 cm thick.
- Lay geotextiles on a sand cushion so that the edges of the material cover the slopes of the depression by 5–10 cm.
- Connect the joints with a stapler or solder with a construction hairdryer.
- Pour a layer of fine crushed stone 15 cm thick and level.
- Place another layer of geotextile in the same way as the first.
- Cover with sand 10 cm.
- Let stand for 2-3 days.
- Moisten a layer of sand or cover with tile adhesive.
- Lay the base covering.
Important! When using gravel or pebbles as the final coating, only one layer of geotextile can be laid, since these materials do not have a large mass, and will not cause a strong subsidence of the structure.
When assembling paths in the country, many owners are wondering: why spend money on geotextile if you can save money. Experienced developers give a negative answer to this question. The use of geotextiles by an order of magnitude increases the service life of any structure, helping to maintain its original appearance for a long time.
What is geotextile for?
The technology, which has proven itself in road construction, is successfully applied today in landscape design.The use of an additional layer with unique physical properties gives the coating the following qualities:
- Layers of different materials are separated. Natural migration of soil, gravel and sand is prevented.
- The layers do not mix, retain their qualities, which increases the service life of the coating.
- Prevents the growth of vegetation from under the laid tiles.
- Correctly selected fabric has a unique property - even the most tenacious weeds do not germinate through it.
- Preserves the structure of the soil at high humidity and precipitation.
- Prevents the washing out of soil, sand.
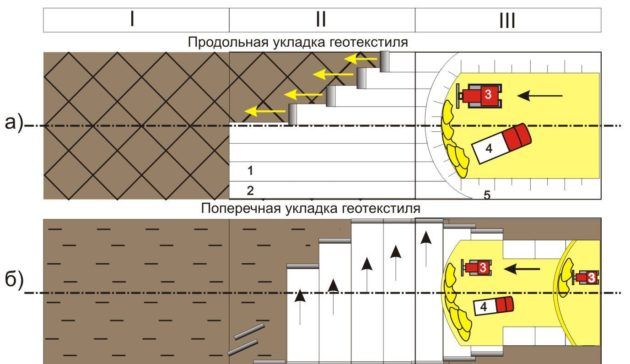 Types of laying geotextiles
Types of laying geotextiles
The latter quality is especially valuable if paving slabs are laid on areas with complex relief, where it is necessary to make ups, descents, and pave planes of complex configuration.
It is allowed to refuse to use geotextiles in cases where the installation is done on existing coatings, provided that they meet the strength requirements, do not have significant deviations in geometry (strong slopes, pits, bumps). Outdoor use of the material is recommended. With geotextiles, the reliability and service life of a DIY coating will be significantly increased.
Geotextile laying rules
Geofabric laying methods are very similar to each other, therefore they are all combined into one common technology.
-
It is necessary to start laying with soil preparation.
Before laying geotextiles on the ground, it is necessary to complete its full leveling and planning. This means removing all stones, roots, stumps and other foreign elements from the site. In order to identify all possible defects, it is recommended to carry out a trial rolling of the web, with the help of which all existing irregularities are revealed; - A roll of geotextile is rolled out manually or using attachments. The main requirement is the absence of folds on the material laid on the surface. It is strictly forbidden to move large fragments of the laid geotextile over the surface by dragging or move on the laid canvas of working equipment or builders;
- Laying the canvas. Initially, it is necessary to roll out the rolls on a specially prepared surface. Geotextiles can be laid laterally and longitudinally. According to the technology, it is easier to carry out longitudinal laying, but it will not be able to provide even strength over the entire width of the embankment. In order for all pieces of geotextile cloth to be firmly and evenly connected, they must be laid with an overlap, the width of which should be about 30 cm.If the surface on which the material lies is uneven, then the width of the overlap is increased to 50 cm.Transverse materials are laid by lining the next canvases, under the previous ... If the technology is not followed, then material shift may occur;
- Connecting geotextile layers. Despite the fact that geotextiles are laid with an overlap, sometimes an additional connection of the canvases is still required. Indeed, with gusts of strong wind, the canvas can shift and disrupt the general structure of the material. This can be fastening with metal and plastic staples, anchoring and welding.
If the fastening takes place by welding, then the overlap of the canvases can be left about 10 cm. Welding work should only be carried out using a low-temperature gas torch, which has a wide grip diameter. During operation, the burner nozzle must be located at a distance of 20 cm from the surface of the web. The next rolled roll is pressed against the already heated surface of the previous one. Welding is considered to be the most economical way of laying geotextiles today.
The edges of the roll are attached to the base of the soil with dowels; - After the geotextile is distributed over the surface, it is covered with rubble, sand or any other inert material. After leveling the backfill on the surface, it is compacted;
- The last step is compaction. After spreading the inert material over the web, it needs to be compacted. Sealing methods are static and dynamic. In this case, you need to know the quality of the lower soil and the material itself with which the geotextile was filled. The compaction is done with a special automotive technique or a rammer.
Special equipment can begin to move around the area where the geotextile is laid only if the backfill thickness is at least 200 mm. Otherwise, it is allowed to use only lightweight equipment, in order to avoid damage to the canvas.
Although other technologies can be used to lay geotextiles correctly, this one is the most common and effective. Of course, laying geotextiles at a summer cottage, making garden paths, is one thing, but laying geotextiles under a highway or expressway is quite another.
Which geotextile to choose?
The choice of material depends on its purpose. The most popular options:
- Needle-punched. This fabric is made by attaching microscopic fibers together. Moisture passes through its structure, so the material will not be flooded with weather.
- Doronit. Such geotextiles are suitable for the construction of a reinforcing substrate and have excellent filtration properties.
- Heat-set. The fibers of this geotextile are carefully melted together through heat treatment. This production technology endows the material with high strength. However, the heat-set variety has low filtration properties, because its structure allows moisture to pass through only in the transverse direction.
- Heat treated. The ingredients are fused and pressed together at the same time. As a result of such processing, an extremely dense and reliable material is obtained. Most often, this geotextile is used for waterproofing.
- Knitted with stitching. The fibers of this material are tied together with strong threads. Knitted geotextiles effectively pass liquid through their structure, but have low resistance to mechanical stress.
- Building. This material passes liquid only from the inside, so it can be used for waterproofing.
It is necessary to select material for arranging garden paths taking into account the following criteria:
- Density. The throughput of the geotextile fabric depends on this factor. The density of the drainage material should be between 150 and 300 g / m³. The pore size should then be 175 microns. If the density of the geotextile is lower, it will be less durable.
- Filtration coefficient. This indicator means the water permeability of the material. The optimum value for drainage material is from 100 to 300 m3 / day. The exact indicator is selected depending on the level of occurrence of groundwater, the volume of climatic precipitation and the degree of permeability of the soil. If the garden area is regularly moistened, it is recommended to take the cloth with the highest filtration coefficient.
- For arranging a garden or summer cottage, you can choose any type of geotextile. However, experts recommend giving preference to polypropylene material, which is made of smooth and durable monofilament. Such a canvas is characterized by increased resistance to silting. In addition, a thermally bonded look can be used as needle-punched quickly silts up and does not allow moisture to pass through well.
- It is undesirable to lay woven material under garden paths, because its fibers quickly rot in the soil.
- The tensile strength level of a garden geotextile cloth should be at least 1.9-3 kN / m. The resistance of the product to pushing through must be selected, guided by what material will be used for the drainage device, as well as how deep the drainage system will lie and how intensively the soil will move.In most cases, an indicator of 400-500 N is sufficient. When using large crushed stone, this indicator of geotextile should be higher. All the necessary information can be found on the product packaging.
- Financial savings. This factor is of great importance. When choosing a canvas, it is necessary to choose the right ratio of quality and cost. Most often, the price of geotextiles ranges from 10-20 rubles. for 1 m². The cost of imported high quality material can reach 200-300 rubles. for 1 m². At the same time, Russian products are not inferior in quality and reliability to many imported counterparts.
You need to buy material only from trusted suppliers or manufacturers who have certificates confirming the quality of products.
Examples of using
The field of application of geotextiles is wide, the following types are divided according to their intended purpose:
- Furniture. Not too dense material that is used for upholstered furniture mattress upholstery. Placed under the upholstery fabric, used to protect against dust during transportation.
-
Drainage. It passes water well, due to its special structure it is not clogged with sand, silt, and retains a high filtering capacity for a long time.
- Garden or agrofiber. The main difference is that it is light-stable, that is, it does not react to ultraviolet light.
- Packaging. A thin material from which covers are sewn for packaging (for example, for shoes).
- Building. There are many different materials in this group with different characteristics. The main ones are tensile strength and tensile strength.
Construction
One of the main functions of geotextiles is to separate different layers. These can be different factions, different materials.
When constructing a foundation of any type, a gravel-sand cushion is laid on the bottom of the pit. So that gravel and sand do not mix and perform their functions, geotextiles are laid between them. Its density is 160-180 g / m², but it can be more / less depending on specific conditions.
At the bottom of the pit, when constructing roads, droshky, platforms for cars, playgrounds, lawns, rubble is laid. So that it does not mix with the soil, geotextiles are also placed under the rubble. The density is selected depending on the purpose of the object and the planned load
You also need to look at how important water drainage is.
Drainage pipes are installed in the areas to drain water. They have small holes through which water seeps in, then enters the wells
To prevent the holes in the pipes from clogging, they are wrapped with geotextile membranes. For better filtration, the drainage pipes can be sprinkled with gravel. So that it does not mix with the soil, geotextiles are also used.
For all types of work, so that the materials do not "creep" and do not mix, it is necessary to take the width of the geotextile so that it rises to the entire thickness of the layer of bulk material and is still wrapped by 30-60 cm. doing more will be more reliable. This applies to both construction work and landscaping, gardening, etc.
In the arrangement of the site
Work on the site involves a large amount of land work. For the results to please for a long time, geotextiles are used.
- When forming flower beds and beds, fertile soil is often imported. So that it does not mix with the "native" soil, the layers are separated with this material. Also, it will prevent the germination of plant roots from below.
- When forming hills, hills, to keep the shape, layers of soil are laid with geotextiles.
-
When creating artificial reservoirs, geotextile is placed on the bottom. It is more durable, it will be better to reinforce the foundation pit.
- Separation of different materials when creating rockeries, rock gardens, etc.
- The gaps between the beds can be covered with geosynthetics by sprinkling gravel on top. So the view is solid, and clean, and the weeds do not germinate.When redeveloping, the geotextile is lifted, stones are removed. You can start further work.
- For shelter from the sun, protection from frost, instead of mulch, agrotextile is laid on flower beds and beds, which is the least dense geotextile.
This is only a part of the processes in which this material can be used. There is also a rare use in our country - when creating green roofs.
Arrangement of a garden path with geotextile
For the use of the material for the arrangement of garden paths, the following characteristics are the priority:
- improving the uniformity and functionality of the base layer;
- soil strengthening;
- protection and stabilization of the materials used;
- exclusion of the ingress of fine fraction (crushed stone) into soft soil.
The use of geotextiles for garden paths provides better bearing capacity of the finished structure by limiting and compaction of the layer of fractional material
In addition, due to the isolation of the layers, their cleanliness is ensured, which is very important for owners of summer cottages. The absence of dirt in this case contributes not only to a hygienic service, but also to greater frost resistance, as well as the performance of a drainage function

To the question: how to choose geotextiles for a garden path, it is worth looking for an answer after the final choice of building materials. For its arrangement with paving slabs, a separating layer of non-woven geotextile is used, which serves as the basis for the crushed stone pillow. The choice of material is based on several criteria:
- dividing;
- reinforcing;
- filtration characteristics.
Thus, subsidence and deformation of the track is excluded due to the formation of internal voids. Due to its high moisture permeability, moisture is completely removed from the base of the track. And its dense structure will not allow the roots of trees and shrubs to violate the integrity of the path.

Geotextiles for paths in the country can be selected according to the load on the area being developed. Usually, its level is moderate, therefore, it is appropriate to use polymer needle-punched textiles as a separator. It is worth immediately excluding the possibility of using organic or combined materials, which include cotton fiber. The short service life and low efficiency of these categories makes them unsuitable for durable construction.
The double-sided technical cover of the crushed stone layer will help to increase the operational life of the track, which is capable of compacting the material and eliminating soil contamination.
Geotextiles for garden paths: how to lay
After excavation, according to the preliminary marking of the site, the geotextile is laid with an overlap of 20 cm. If the pit is deeper, it is worth leaving large free edges on the sides, which must be brought to the surface. This helps protect the path from roots.

After laying crushed stone, it is manually compacted, followed by dumping of sand over the entire area. This is followed by a laying layer, which, in terms of composition, is equally suitable for both installation and grouting of tile joints.
The use of geotextiles for garden paths guarantees aesthetic and weather-resistant characteristics. Upon completion of the installation work, its free edges are cut at the level of the surface of the finishing layer, thereby achieving an exemplary appearance and shape consistency for long periods.
Types of geofabric
The characteristics of the canvas depend not only on the manufacturing technology, but also on the type of polypropylene. Each variety has its own area of application.
For various areas of use, their own types of geopolitics are intended:
- Construction - it is laid under the paving slabs and basements and foundations are waterproofed, the roadbed is strengthened.
- Furniture - the interior of furniture, mattresses are upholstered with it, furniture is wrapped during transportation to protect it from damage.
- Packaging - used for shoes, clothing, equipment and other goods for packaging.
- Garden - works great as a covering material for arranging greenhouses, protecting plants from frost in winter and sun in summer. It is spread around trees and bushes to prevent weeds from sprouting.
- Drainage - serves for winding drainage pipes or arranging drainage.
According to the manufacturing technology, two groups are distinguished: woven and non-woven material.
Woven
It is made by interweaving warp and weft fibers, as in fabrics. You can achieve different density of the fabric by changing the size of the gaps between the threads. For manufacturing, glass and polyester fibers are used. They are passed through special devices - calenders, where the fibers are partially fused. Fusion and impregnation with strengthening compounds significantly increases the durability and strength of the threads.
Knitted fabric with stitching is another type of woven fabric. It is created by weaving according to the principle of loop knitting and can be unraveled under mechanical action. This is the cheapest material, its use is optimal for light loads.
Thanks to the woven fiber fusion technology, the geotextile becomes more durable
Geotextile is used when separating various types of soil, for example, when arranging garden paths, strengthening various structures, reinforcing foundations for roads, embankments, and runways. On the garden plot, geotextile will help divide the beds, strengthen the slope for planting.
Non-woven
Geotextile is made by fusing synthetic fibers in a thermal or chemical way and, depending on this, can be needle-punched or thermally bonded.
Needle-punching is obtained from short continuous threads by piercing it with the finest serrated needles on a special press. The fibers in the form of a layer of cotton wool intertwine with each other and are compacted, catching on the needles, penetrate into the thickness of the canvas and form an elastic and durable structure. Outwardly, this material looks like a dense felt.
As a result of such processing, non-woven geotextile acquires special properties: it strengthens the soil and perfectly permeates water, draining the soil. Therefore, it is used in the arrangement of drainage systems. For greater strength, the geotextile is reinforced with a geogrid, which increases the service life of the needle-punched layer.
Thermally bonded is produced thermally by fusing polypropylene yarns when heated. As a result, a very elastic and load-resistant canvas is formed, which passes water only in the transverse direction and has excellent performance in reinforcing slopes, roads, and soil strengthening.

Non-woven geotextile has elasticity and resistance to stress
All types of canvases are produced in rolls with a width of 1.5 to 6 meters, the length is inversely proportional to the density of the material, most often from 100 to 350 meters.
Features of stacking material
Small areas or narrow paths can be made with one layer of geotextile. If larger areas are to be paved or the soil is too mobile, then two layers of material are recommended. The first is laid on the ground, and the second on the drainage. This technology guarantees that the coating retains its geometric and performance properties in all weather conditions. What else you need to know when preparing the soil in order to cope with the task by doing the work with your own hands:
- Square alignment. A preliminary marking of the territory is done using a level or a theodolite.
- Pegs are driven in along the perimeter, and a cord is pulled, relative to which the plane is examined.
- The bumps are cut off, the potholes and the pit are covered with soil.
- Getting rid of vegetation. The roots of trees are uprooted, a layer of grass is cut off.
- Elimination of the possibility of the formation of voids due to the decomposition of organic substances.
- Reduced risk of weed germination in tile gaps after placement.
- Compaction of soil.After completing the above operations, it is necessary to compact the soil.
It is recommended to sprinkle with sand on the ground, 2-3 cm thick. We lay geotextiles on this base. To prevent damage from sharp edges of rubble, a second sand layer is made over the fabric. It is aligned with a building rule or an even rail. Crushed stone and sand are laid out according to the marks.
A curbstone is installed and concrete is poured over the formwork. Then the second layer of geotextile is laid out, checking the horizontal position along the marks. The workpieces are cut taking into account the overlap (at least 20 cm) and a small approach to the vertical along the border.
Application
Geotextiles have appeared recently, but are already used in various fields: in construction, landscape design, horticulture and gardening, in the construction of footpaths, roads and runways. Hygiene products, disposable medical clothing and underwear are made of the same material, only of low density, and used as a rough upholstery for upholstered furniture. In general, the field of application of geotextiles is very wide, and it is worth knowing which type is suitable for what purposes.
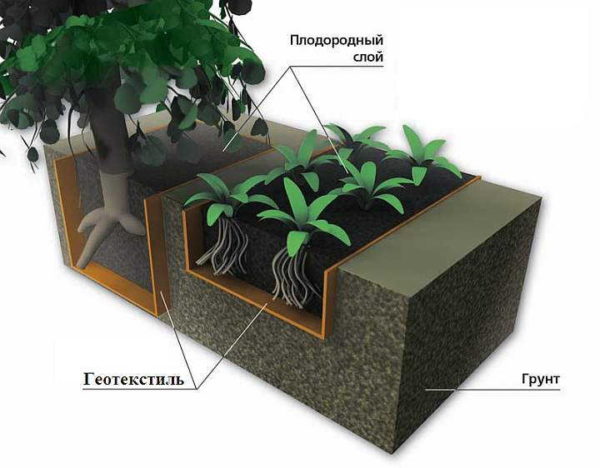
One of the uses - when arranging a site
Depending on the density
The cost of geotextiles can vary significantly. As you already understood, the price is formed depending on the material and method of production. But density also plays an important role. The same materials, but with different densities, have different prices. How do you know which geotextile is needed in a particular case? You can roughly navigate by this density division:
- Up to 60-80 g / m2 - agrotextile or covering material. Can be used to protect against germination of weeds (geotextiles against weeds). Non-woven polyester is usually used. To avoid confusion, they usually write this way - agrotextile.
- Density about 100 g / m² - for drainage, but geotextile is undesirable, as it quickly "silts up".
-
150 g / m² and more - for separation of fractions: sand and gravel. You can take more dense, but less - not worth it.
- Geotextiles with a weight of 100 to 200 g / m² are used for the construction of footpaths, under paving slabs, under lawns, to create alpine slides, etc.
- With a density of 200 to 300 g / m², they are placed under general-purpose roads, under a parking area for cars.
- Above 300 g / m² - for motorways, runways, etc.
These are only approximate boundaries. It is always worth choosing geotextiles, paying attention to specific conditions. For example, for hard and rocky ground, elongation at break will be important. The better the material stretches, the less the possibility of rupture when "fitting" irregularities and protrusions.

When arranging ponds, swimming pools
When choosing geotextiles for construction work and under roads / paths, parking lots, sites, look for a high breaking load (breaking strength). This characteristic can be neglected if you form relief irregularities, but there will be no load on them.
Depending on raw materials and production method
Thermally bonded geotextiles have high tensile strength, but drain water only in the transverse direction. That is, it can be used in areas with low groundwater levels, in well-drained soils. It is good as a separator of different fractions and materials when arranging sites, for footpaths made of various materials, and is suitable for changing the landscape. But all this is in areas with good drainage. It is not very suitable for drainage systems - water is not drained well enough.
Needle-punched is less durable, but water passes both in the longitudinal and transverse directions. It is suitable for laying on heavy soils that do not drain water well - loams, clays. The lack of strength can be compensated for by placing a geogrid underneath - another type of geosynthetics.It will take on the main loads, and geotextiles will not allow fractions to mix. This type can be used in drainage. The optimal density of drainage geotextiles in terms of price / quality ratio is 200 g / m².
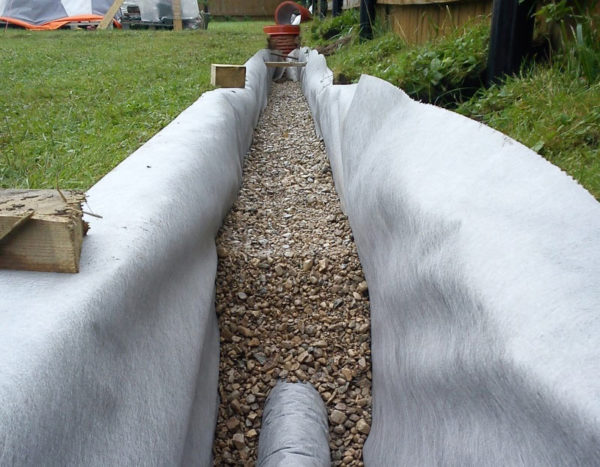

Drainage geotextiles. Properties: elasticity and strength, resistance to heavy loads and mold, long shelf life, ease of installation, fire safety and non-toxicity, resistance to ultraviolet rays
Woven geotextiles are very durable and have high tensile strength. It is ideal for embankments, landscaping, retaining walls. Moreover, it can withstand the load without question. It is not recommended to use it in drainage - the gaps between the threads are quickly clogged with small particles, which impairs water drainage.
Geotextile classification
In addition to the component classification, it is customary to distinguish types of geotextiles by type of production:
- needle-punched geotextile - consists of the smallest fibers of polypropylene or polyester, bonded in a special "needle-punched" way. The technology creates a structural fabric capable of passing moisture only across and along. During operation, the structure is not flooded with water and is not clogged with soil particles;
- Geotextile "Doronit" is a very elastic material and can act as a reinforcing substrate. It has excellent filtering properties, which are not affected in any way by high loading pressure or regular vibration. The isotopic nature of the material allows to ensure equal properties in all directions of the web;

- heat-set geotextile
- heat-treated geotextile - this material is produced by pressing the components with their simultaneous fusion. It turns out a very durable canvas, suitable exclusively for waterproofing;
- knitting geotextiles with stitching - here polypropylene and polyester fibers are stitched with strong threads. The resulting product passes moisture well, but is extremely unstable to external (mechanical) influences;
- construction geotextile - used for waterproofing any structures on the site. The material does not damp, does not accumulate moisture, and only passes water from the inside to the outside.

When to expect results
When cleaning the soil from weeds using geotextiles, the site remains completely clean of grass for a month. And the land located nearby turns out to be overgrown with weeds. After two months, the first shoots of the weeds are shown. There are not many of them, these are several pieces per square meter of soil. Basically, such shoots appear at the junction of the geotextile fabric.
From the seeds trapped in the sand, or crushed stone, a little more grass may appear. But, its growth quickly stops, as it rests against a layer of geotextile, and this grass dies off.
Experiments confirm that the use of geotextiles for weeds is quite justified. At the same time, the weeds lost their growth opportunities and died. After a year, garden crops can be planted on such an area where the soil has rested. And geotextiles can be used to protect against natural phenomena.
It is possible to lay garden hetextiles without the use of special equipment. And compact rolls can be transported in a car.
Laying track with geotextile
The pavement technology will largely depend on the type of soil and pavement material. For example, if gravel or pebbles are used, then one layer of geotextile will suffice. However, when paving with paving slabs, it is necessary to lay two layers of compacted geotextile.
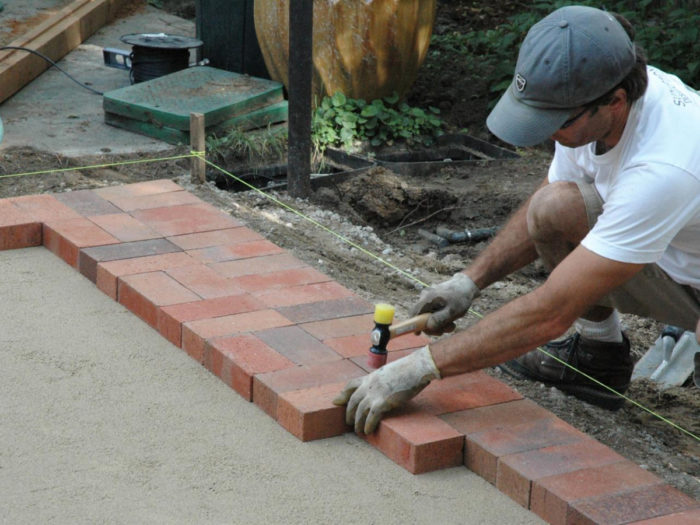 Laying track with geotextile
Laying track with geotextile
The utmost care will require the arrangement of the path on clay and sandy soils. In case of poor-quality work, the coating may sag after the first rain. The tiles must be laid on a dry mixture of mortar so that frost does not provoke cracking.Using concrete as a backing will hinder drainage and water will stagnate on the surface of the walkway.
Stages of creating a slab-crushed stone path
- Mark the boundaries of the track. To do this, lay out the tiles in the desired shape.
- Dig a groove 35 - 40 cm deep along the measured contour.
- Smooth out the bottom by removing debris and plant roots from it.
- Lay a layer of geotextile, leaving the edges of the canvas to protrude above the soil surface by about 5 cm on both sides.
- Pour a 15 cm layer of crushed stone on top.
- Next, lay another layer of geotextile.
- Pour fine-grained sand on top of the canvases in a ditch with a layer of 12 cm.
- Tamp the resulting "pillow".
- You can lay paving slabs or paving stones. For a more dense immersion in the sand, each element of the coating is compacted with a rubber mallet.
- Cut off protruding edges after installation.
- Inter-tile slots should be filled with sand carefully compacted in them.
- Now the laid track will only require edge trimming.
