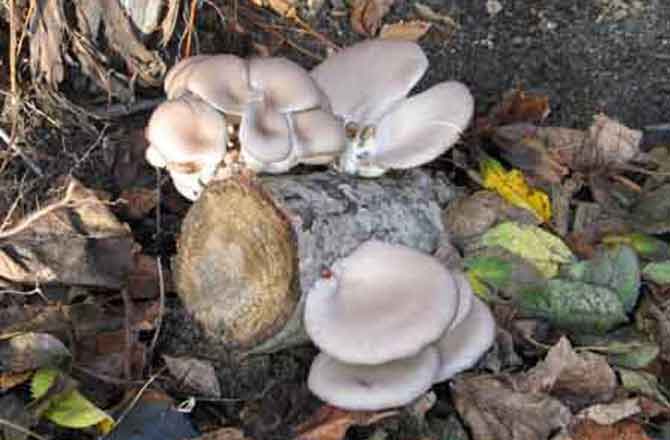
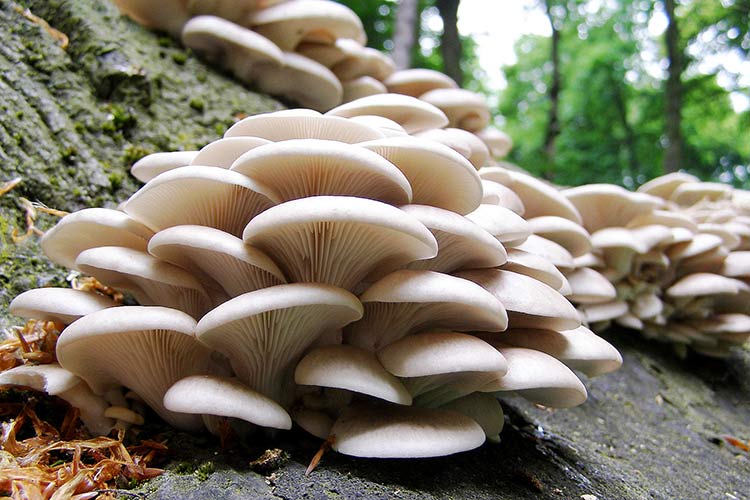
Storage of stumps with oyster mushroom crops
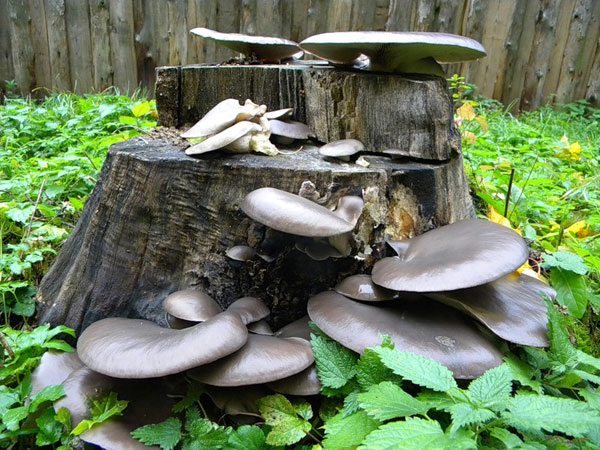
When oyster mushrooms are sown in freshly sawn chocks in early spring, it is necessary to ensure their safety until temperatures above zero, otherwise the mushrooms will freeze. Then we take out the stumps into the garden and set them on the ground.
How to save hemp with planting material
- Column storage. We hold the columns of the chocks upright in several rows, leaving narrow gaps between them and filling them with sawdust or damp straw. We cover the rows around the perimeter: a perforated film or burlap is suitable for shelter. Add another layer of straw or sawdust on top.
- Storage of individual chocks. We wrap the hemp in perforated polyethylene or burlap
We store stumps and columns in a basement or other room at a temperature of 15 degrees Celsius and good ventilation, avoiding drafts. We regularly moisten the air by spraying water. Shelf life - until the beginning - mid-May: as soon as they are covered with white bloom, they are ready to be taken out to the garden or garden.
How to grow shiitake mushrooms in the country
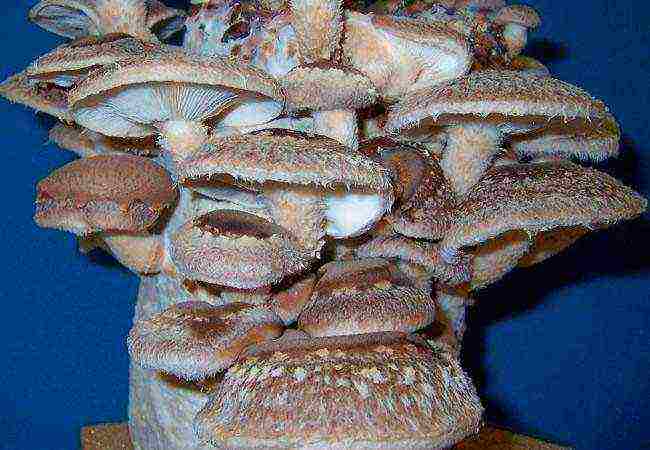
Shiitake mushrooms (Lentinula edodes) can be grown on logs or trunks of any deciduous tree, but oak or beech works best. You can test the hardiness of several strains. Thus, the strain of Japanese forest mushrooms "40 80" successfully overwintered in the open air at temperatures below minus 25 ° C. Harvesting and sowing with mycelium of Shiitake mushrooms of chumps is done in the same way as for oyster mushrooms. In conditions of daily fluctuations in temperature, shiitake bears fruit from May to late autumn better and more often than oyster mushroom.
The Chinese grow shiitake on long tree trunks. Set horizontally on the ground, the stems look good and yield a good harvest of mushrooms. The trunks of trees with a diameter of 7-15 cm are sawn into pieces 100 cm long
An important condition for growing shiitake is the water content in the wood of the order of 38-42%. If the moisture content of the wood is less, then the trunks are watered several days before the introduction of the mycelium.


How to grow shiitake in the country using stumps or logs? On the barrels, holes are drilled in a checkerboard pattern at a distance of 10 cm from each other along the length of the barrel and 7 cm between the rows of holes. The hole diameter is 12 mm and the depth is 40 mm. When growing shiitake on logs, the mycelium is introduced into the holes, the trunks are laid horizontally in high woodpiles for overgrowing with mycelium and covered with a film on top. In a greenhouse or in a shed incubated for at least a month at a temperature of + 20 ... + 26? С.
The stem is considered mature for fruiting if it does not "ring" upon impact, the mycelium has captured the outer edge of the sapwood and white mycelium zones are visible on the cross section of the stem. Before soaking, the trunks are tapped with a hammer or hit with the butt on the ground. When spreading shiitake on logs at the dacha, the trunks are soaked in water with a temperature of + 13 ... + 18 ° C for 12 hours. During soaking, carbon dioxide, CO2, comes out of the trunks in the form of bubbles. When the bubbles cease to stand out, it means that the stems can be removed from the water. The moisture content of the wood reaches 60%. At higher humidity, the intensity of mushroom fruiting decreases.
To grow shiitake on stumps, the trunks are buried in the ground horizontally by half their diameter. In this case, it is easier to maintain the moisture content of the wood. If the plantation is located not in a greenhouse, but on the street, the plantation is covered with material that helps maintain the moisture required for fruiting. 5-10 days after soaking, rudiments of shiitake mushrooms are formed in the places of the holes. Good quality mushrooms are formed at low temperatures (+ 10 ... + 16 ° С) and moderate air humidity (60-75%).
After picking mushrooms of the first wave, the trunks are kept for 2 months in drier and warmer conditions (+ 16 ... + 22 ° С).The moisture content of wood during this period decreases to the level of 30-40%. The next waves of fruiting are achieved by repeating the procedure for induction of fruiting by soaking the stems. If you have mastered the technology of how to grow shiitake mushrooms, you can use the trunks in this way for 3-5 years. The total mass of mushrooms collected during this time is 15-20% of the mass of wood.
Here you can watch a video of growing shiitake mushrooms in your backyard:
How to prepare stumps for mushrooms
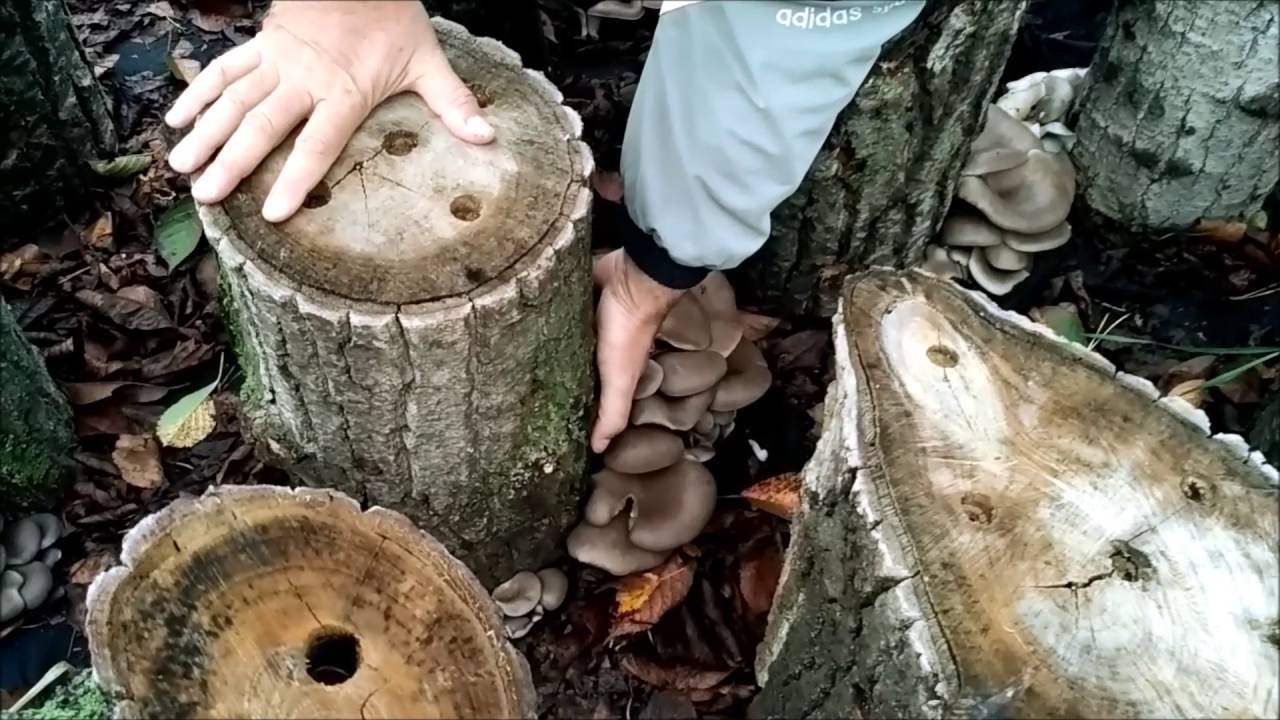
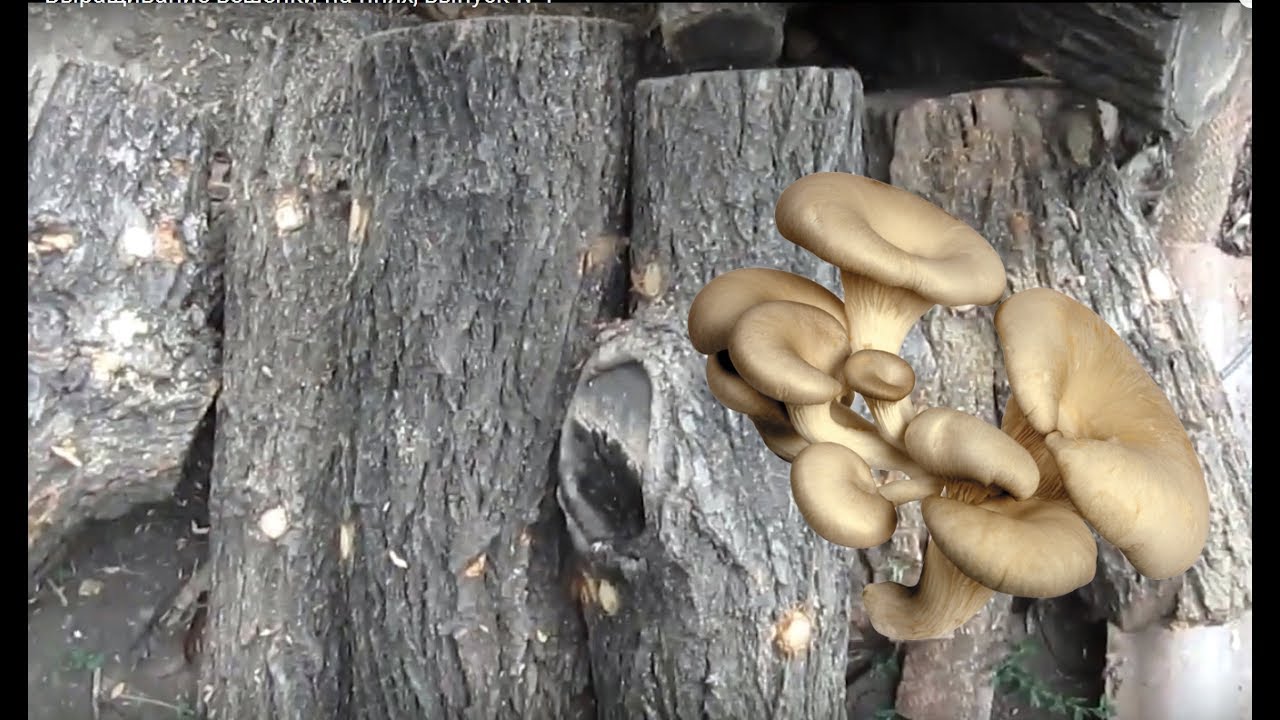
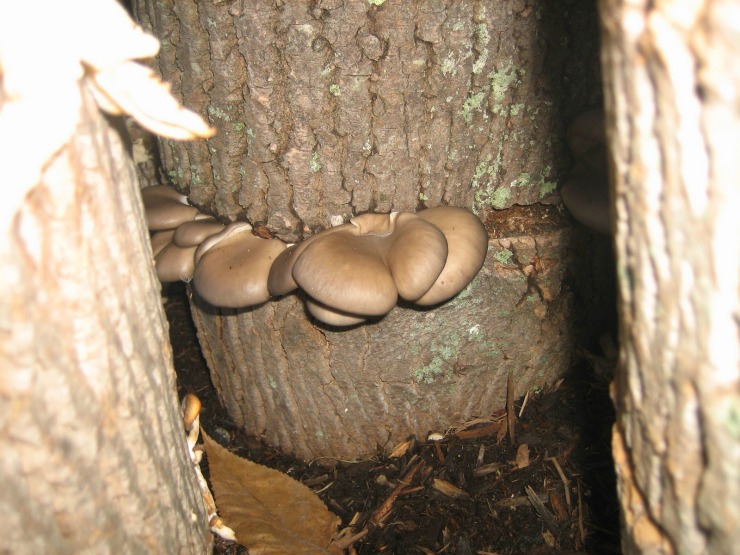
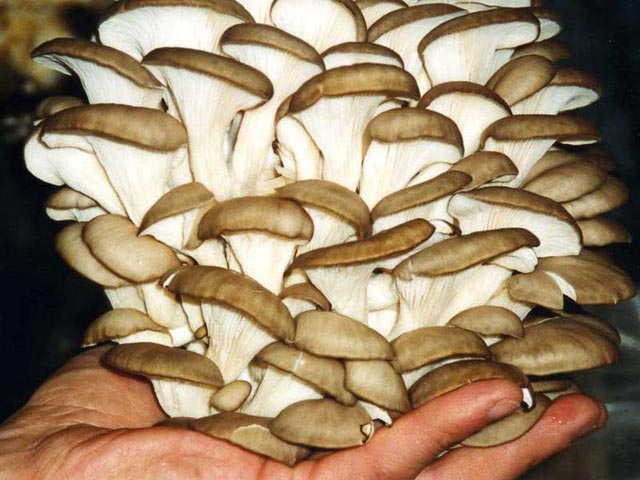
Common and royal oyster mushrooms, growing on stumps of which does not take much effort and money, grows well with proper preparation of the habitat. To obtain oyster mushrooms, aspen, birch, chestnut, beech, maple, ash, poplar and other chocks will do.
The main thing is that the trees are deciduous, not coniferous, and not have time to be amazed by mold. Their height can be up to half a meter, thickness 20-30 cm.
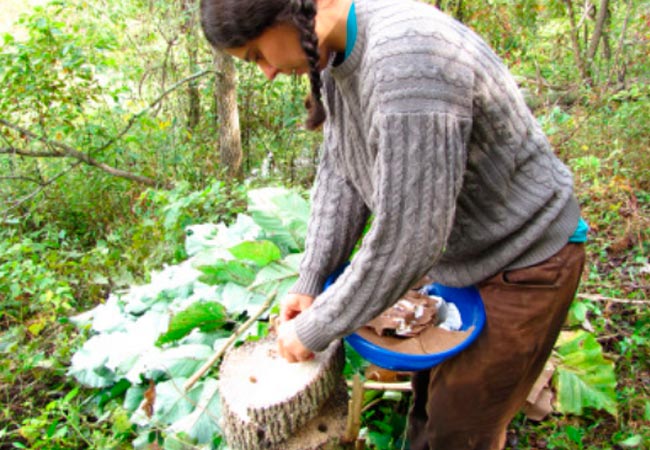

How to prepare stumps for mushrooms
If, after cutting down, there are not uprooted stumps on the site, we prepare them for sowing in April - May, but if the chocks were brought from the forest freshly cut, we prepare them already in March to get the harvest faster.
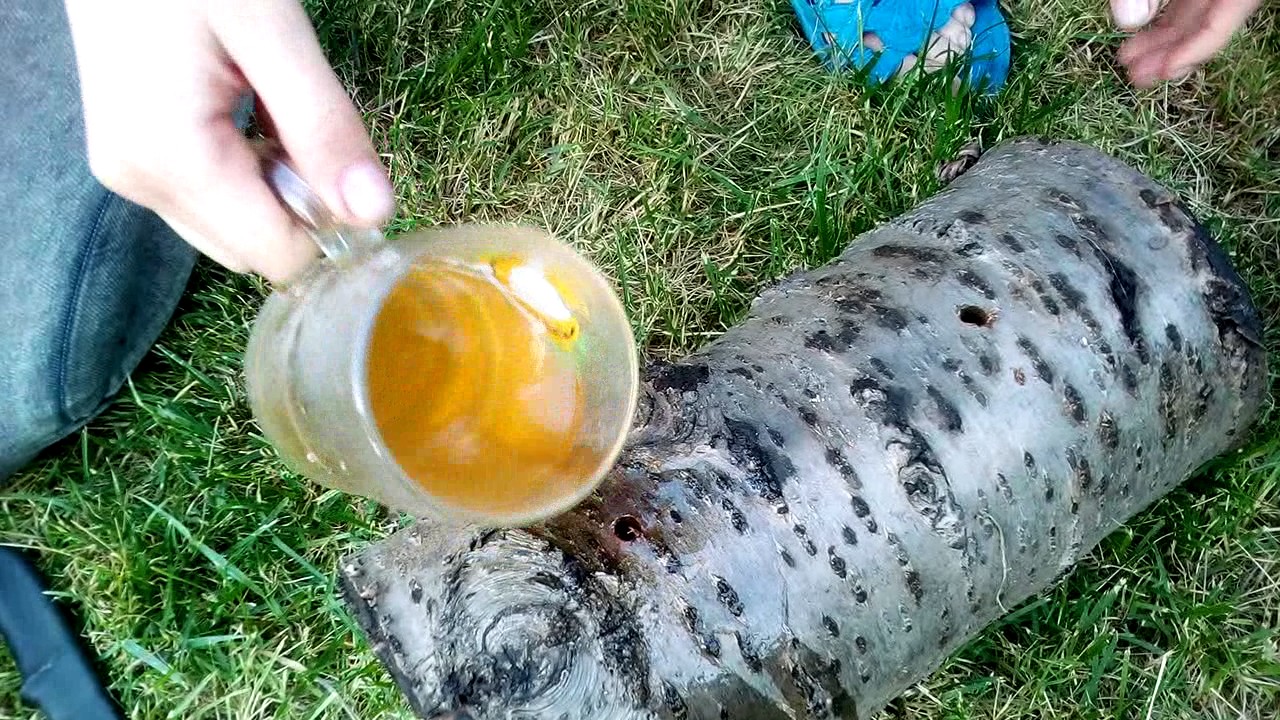
Before planting mushrooms, soak the hemp in rain or well water. It is necessary that the moisture content of the wood is at least 80%, so we keep them in water for three days.
Harvesting
Fruiting bodies should be harvested by curling before releasing the spores so that no hemp remains in the beds (straw). It is advisable to collect all the mushrooms from the block at once, then the next stream will appear simultaneously.
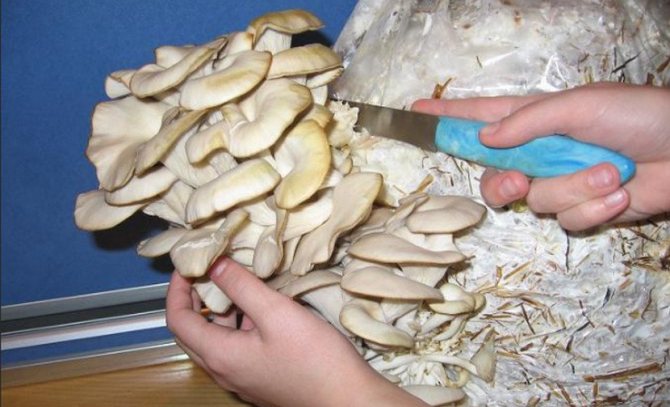

Fresh mushrooms should be packed in perforated plastic bags. Freshly picked oyster mushrooms can be stored at low temperatures (+ 5 ... + 10 ° С) for 1-2 weeks. without loss of quality.After harvesting, the premises must be disinfected - first with water, and then with a sulfur stick.
pay attention to information on freezing oyster mushrooms. Not many people practice mushroom cultivation, mainly due to fears of an unaccustomed activity.
Often the difficulties seem too great and the waiting too long. However, when an ordinary log or bag turns into a storehouse of tasty delicacies, all doubts are immediately dispelled.
Not many people practice mushroom cultivation, mainly due to fears of an unaccustomed activity. Often the difficulties seem too great and the waiting too long. However, when an ordinary log or bag turns into a storehouse of tasty delicacies, all doubts are immediately dispelled.
Preparatory work

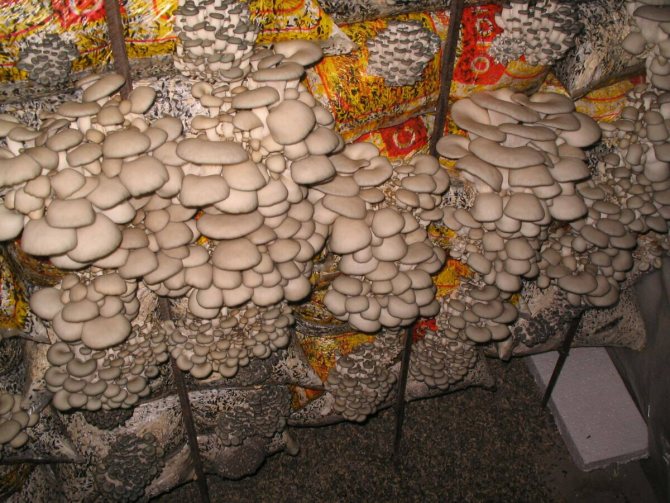
Oyster mushrooms are mushrooms that do not like the abundance of sunlight, drafts. A planting site should be chosen in the shade, for example, under a spreading tree. Place the stump so that on the hottest day, the crown shades the mushrooms. At the same time, the chosen place must be accessible for rain, otherwise you will have to water often. Other recommendations:
- you need to choose the northern part of the site for landing, for example, along buildings;
- you cannot place a stump under a canopy, otherwise the mushrooms will be waterlogged;
- for planting the mycelium, trimmings are needed, the diameter of which is at least 15 cm;
- you can not take stumps, the wood of which has obvious signs of destruction or rot;
- strongly dried driftwood should not be used, otherwise the crop will not be harvested.

Planting mushrooms in the garden and in the basement in autumn Mushrooms can not only be picked in the forest, but also grown at home: in the basement, garage, underground and in the garden. At…
Having chosen a place for planting, the gardener places the stump. There should be no mistakes, otherwise the mycelium will not receive the required amount of nutrients.
On a note! The stump must be placed strictly vertically. Its position should be the same as it was in nature. You cannot change the angle of inclination, make log cabins or turn it upside down.
Incubation and distillation of mushrooms
 In this form, the substrate should stand in a warm place for two months. It is convenient to control the development of mycelium through the glass of the jar.The completion of incubation is evidenced by the growth of the mycelium over the entire internal volume of the jar, as well as the clarification of the substrate itself (small brownish specks may also appear on it).
In this form, the substrate should stand in a warm place for two months. It is convenient to control the development of mycelium through the glass of the jar.The completion of incubation is evidenced by the growth of the mycelium over the entire internal volume of the jar, as well as the clarification of the substrate itself (small brownish specks may also appear on it).
Ripe mycelium is transferred into plastic bags measuring 20 by 35 centimeters, or 25 by 40 centimeters. The bags are tightly closed (by twisting them in the upper part) and again put away in the heat.
After a week, the top of the bag is unpacked and a piece of an old hose with a diameter of 2.5-3 centimeters and a length of 4-5 centimeters is placed in it. Through this opening, fresh air will constantly flow to the substrate. Just remember to cover the hole with a sterile cotton plug again to prevent pests from reaching the substrate. Keep in mind that the overgrowth is more active if the bags with the mycelium are in an upright position, with the cotton stopper up.
 Over the next two weeks in the warmth, the wood chips grow together into a single monolith and are strongly compacted. By this time, the piece of substrate is usually covered with growths of mycelium, in appearance, resembling popcorn grains. Immediately after this, the development of the fruit bodies themselves begins in the form of hard black beans (the so-called primordia). Then it is necessary to move the blocks to a place suitable for fruiting. d
Over the next two weeks in the warmth, the wood chips grow together into a single monolith and are strongly compacted. By this time, the piece of substrate is usually covered with growths of mycelium, in appearance, resembling popcorn grains. Immediately after this, the development of the fruit bodies themselves begins in the form of hard black beans (the so-called primordia). Then it is necessary to move the blocks to a place suitable for fruiting. d
If, after three weeks, dark bumps have not appeared on the blocks, you can stimulate their formation with the help of cold shock. This is done as follows: the substrate in bags is transferred to a cold (from 0 to +10 degrees) room for a period of at least three days. Then the blocks are pulled out of polyethylene, put in heat (at a temperature of +15 to +25 degrees) and a piece of film is thrown on top. A day later, another film is removed, and the substrate is transferred to a place prepared for fruiting.
Ensure that blocks show no signs of incipient mold such as blue or dirty green spots
Preparatory work
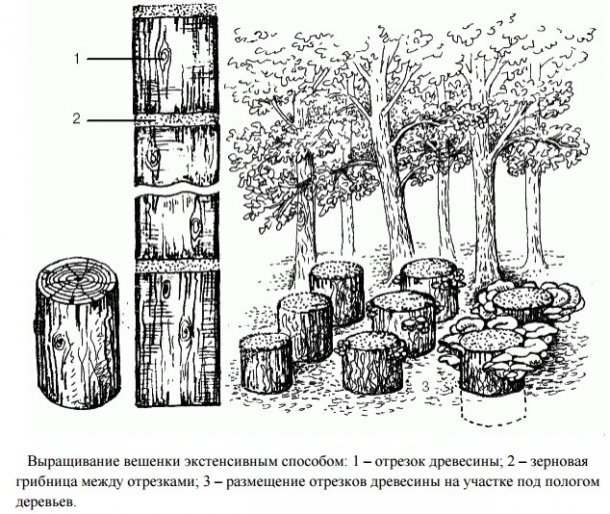
The most convenient way to grow oyster mushrooms is extensive. This means that it is necessary to artificially create conditions for mushrooms that are as close as possible to natural ones. The task is greatly facilitated by the fact that oyster mushrooms are unpretentious mushrooms - in nature they can be found on almost any tree.

Choice of location, choice of wood
It will not be difficult to choose the location of the mushroom farm, any dark and semi-dark place will do. Direct sunlight is contraindicated for oyster mushrooms. It is most convenient to create the necessary conditions in the country in the garden, or in the basement.
Important! If there is no shaded area, this is not a problem. An artificial canopy is also suitable for shading.
This is especially true for uncut tree stumps that cannot be moved.
The choice of timber for the farm is also very simple: any tree species will do. The stump can be both stationary and cut, with the ability to move to a convenient place.
Stump preparation and placement
The best time to start growing oyster mushrooms is spring, the period immediately after the end of the winter cold and the appearance of stable warm weather. As a farm, both a freshly sawn part of a tree and a dry one are suitable. The main thing is that there is no mold. The preferred chock size is 30-50 cm in height and 15-30 cm in diameter.
Despite the fact that the freshness of the wood does not matter, it is most convenient to use freshly sawn material. It has the necessary moisture, unlike dry. If only dry logs are at hand, they will need to be soaked for 2-3 days. For these purposes, a bucket, basin, bathtub, or any other sufficiently capacious container is suitable.
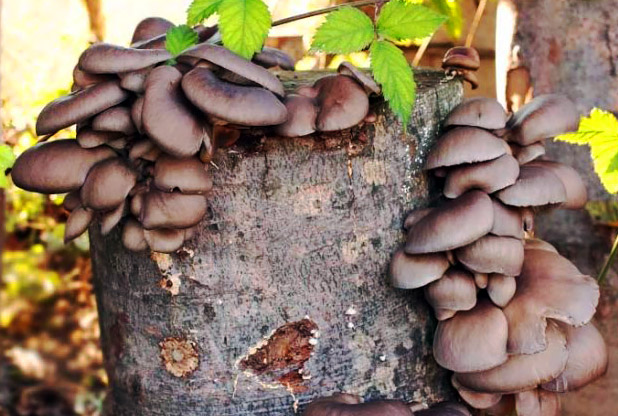
Did you know? Oyster mushrooms are not only delicious food, but also a very easy way to get rid of an unnecessary tree stump in the garden. In 2-3 years, the stump will turn into dust, making it unnecessary to use heavy equipment.
Substrate preparation
The substrate acts as a soil on which mushrooms grow.It is best to use two main components for the substrate: cereal straw and sunflower husk. Wood sawdust is suitable as an additional material - the main thing is that they are not from conifers. You can also add a variety of nutritional supplements such as soy or feather meal, brewer's grains, or malt sprouts.
It is important to remember that the content of additional components should not exceed 10% of the total substrate.

What oyster mushrooms can be bred at their summer cottage
Originally grown in nature, common oyster mushroom or oyster. Thanks to the efforts of scientists, special hybrids of these mushrooms have been bred, which are distinguished by higher yields. They are better suited for growing in artificial conditions.
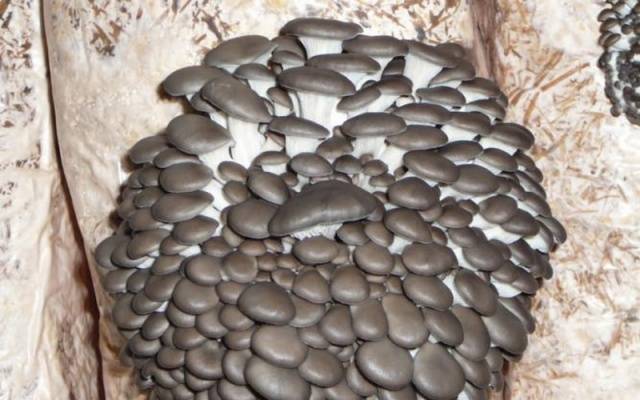

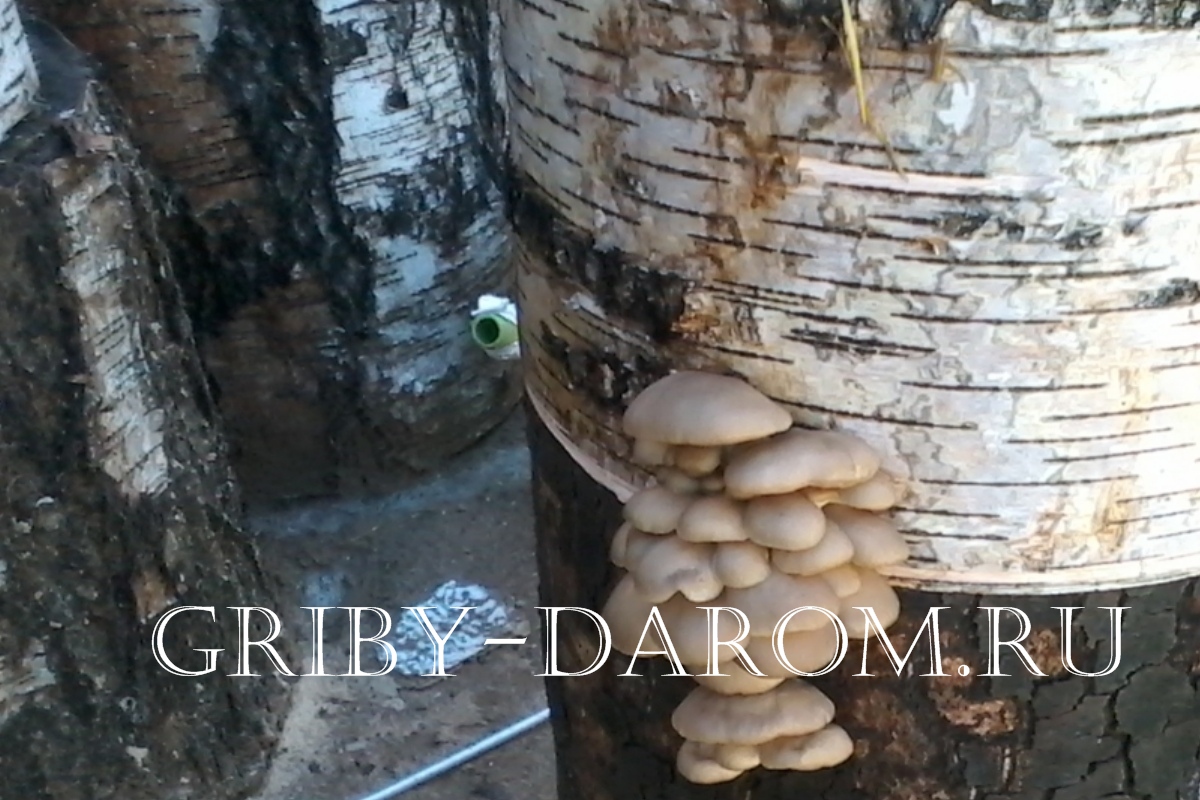
These mushrooms grow well both on artificial substrates and on stumps.
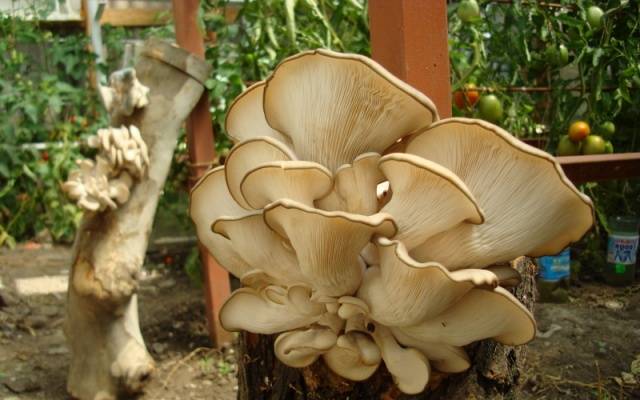

If you are going to grow mushrooms in small quantities, it is better to buy ready-made mycelium. When setting up a large plantation, it is more economical to grow it yourself. Unfortunately, manufacturers do not always sell quality mushroom mycelium. Therefore, there is a risk of wasting money and labor and ultimately being left without a crop.
A warning! When buying, carefully inspect the mycelium, checking its good quality.
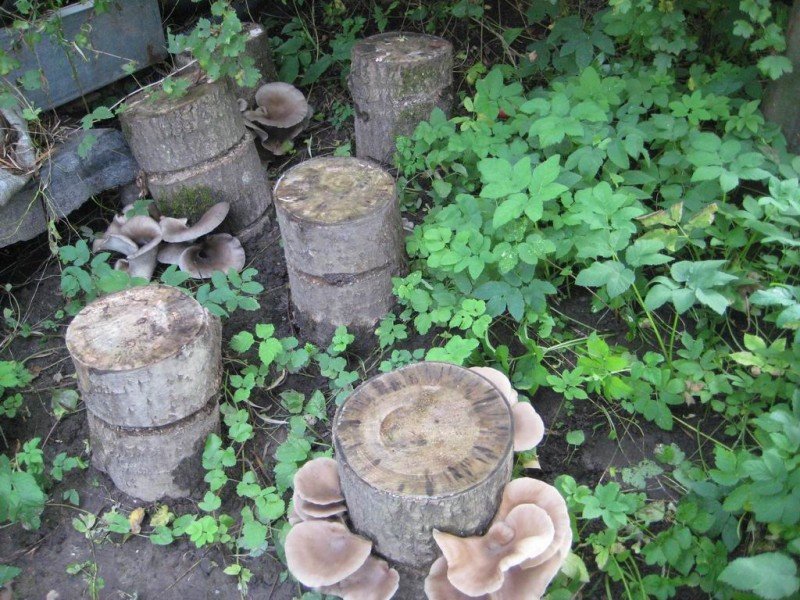
Growing methods on stumps
There are several ways to grow oyster mushrooms on stumps at home.
- Assumes the appearance of mushrooms in the trench. Dig a trench 15 cm deep. The bottom is covered with boiled wheat or barley. When grown, such a layer will serve as a pillow for oyster mushrooms. Grain mycelium, previously mashed by hand, is lowered there, approximately 350-400 g for each stump. Wood is installed directly on the mushroom spores and sprinkled with earth.
- Long logs are prepared. The bark is removed from opposite sides, a relatively flat and smooth surface is made. When growing, these logs are stacked horizontally on top of each other, so that it is the cleaned places that touch. Oyster mushroom mycelium is placed in the layers. Further steps are similar to the above method.
- When growing, the following methods involve the introduction of oyster mushroom spores inside the hemp, logs, or scattering them on the surface of the slices. The technology depends on the method of sowing the mycelium of the mushrooms and is described below.
Easy growing of oyster mushrooms on tree stumps
You can drill many, many holes and pour grain mycelium there. All other points of the instructions are unchanged. Start from the first point and follow it strictly right up to 11! Only instead of sticks you will have grains with mycelium.
Grain mycelium is best purchased from a professional laboratory. You are unlikely to sow all 6 kilograms from a pack, but you can take another bag of husk or straw, pour boiling water in the bathroom and make three or four mushroom blocks from the remaining mycelium.
What happens if you infect a stump with mycelium at low temperatures
Most likely, it simply will not overgrow. After all, mycelium develops very slowly at temperatures below 15 degrees. Chopiks themselves with fluffed mycelium can become prey for mold, because this is a good breeding ground.
If we are talking specifically about a stump that stands on the street, it is best to plant sticks there in the spring - at night temperatures above 12 degrees. Or in late August - early September, so that it will be warm for at least a month after planting.
Growing at home for beginners
First, it is advisable to prepare a room where mushrooms will be grown:
- It is necessary to make good ventilation, install standard room lighting in such a way as to be able to control the air temperature.
- Shiitake loves coolness, so the optimal temperature for them should be + 15-18 ºC during the day and +10 ºC at night.
- After preparing the premises, place the racks on the shelves.
- Further work should take place with gloves so that the fungi do not absorb germs and bacteria.
- You must purchase shiitake mycelium in advance (seeds cost from 100 rubles per 10 pcs.) And substrates (sawdust, dry leaves, hay, sunflower husks).
- It is recommended to boil the substrate for about one and a half to two hours, cool and squeeze. The mycelium bag must be prepared by rinsing it with a chlorine solution.
- When everything is ready, dry substrates are alternated with mycelium (each block should account for no more than 8% of mycelium). Tie the edge of the bag.
- "Pouches" must be spread out at a small distance from each other. With a sterilized knife, small cuts are made on the bag to allow air and humidity to get inside (up to 20 holes).
- A drip irrigation system is recommended for irrigation.
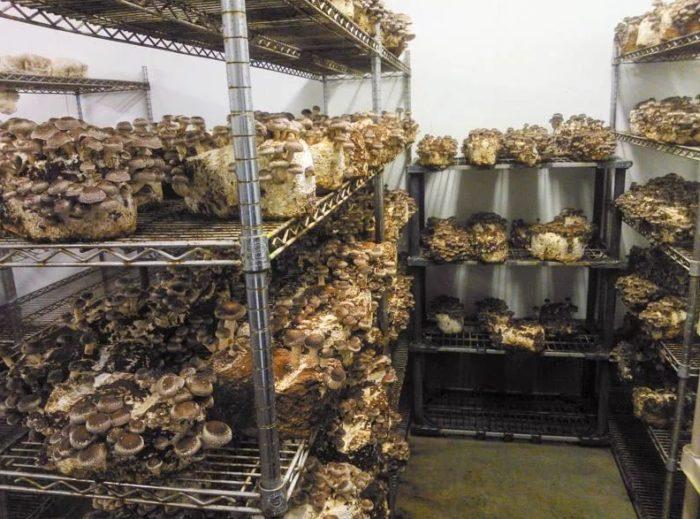

Next, you need to be very careful with regard to mushrooms. As soon as you see that the first crop begins to erupt, the temperature should be lowered to + 18ºC during the day and lowered at night. Shiitake need lighting for 5-6 hours a day.
Growing shiitaki in a greenhouse
In addition to home conditions, the mushroom can be planted in greenhouses, in garden plots. A kit for growing shiitake mushrooms costs from 2400 rubles. Ready-made packages are placed on the ground or on shelves. The temperature is maintained at + 18ºC, and irrigation increases in summer drought. Lighting should be present for 8-10 hours a day, the light should not be bright.
For edible lentinula, it is not necessary to build a separate greenhouse in the country. Shiitake plants bear fruit well in a greenhouse surrounded by other plants. A special structure can be built in the shade or protected from direct sunlight by fencing with an opaque roof on the south side of the house.

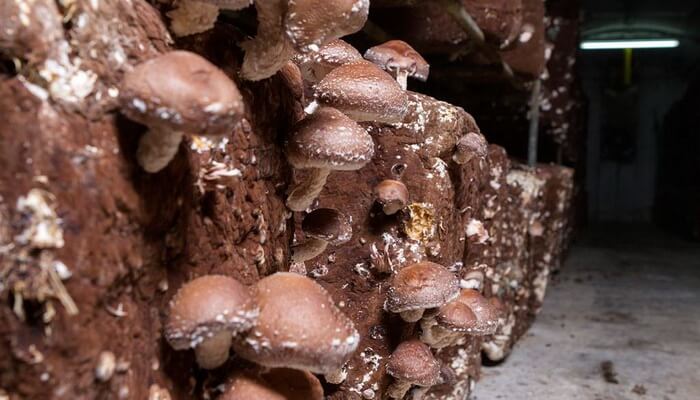
Straw cultivation technology: pros and cons
Straw mixes are very nutritious for more than just shiitake. Straw cultivation is an intensive method. Most often, barley or oat base is used as a substrate. Consider the pros and cons of this method:
Pros:
- mushrooms grow faster and more abundantly;
- it is an excellent nutrient material;
- budget technology for one-time fruiting.
Minuses:
you have to change the substrate more often;
other microorganisms can compete with fungi;
very careful attention to the conditions of the room;
requires sufficiently spacious and specially equipped isolated rooms.
But each technology has its drawbacks, so refer to the extensive method for comparison.
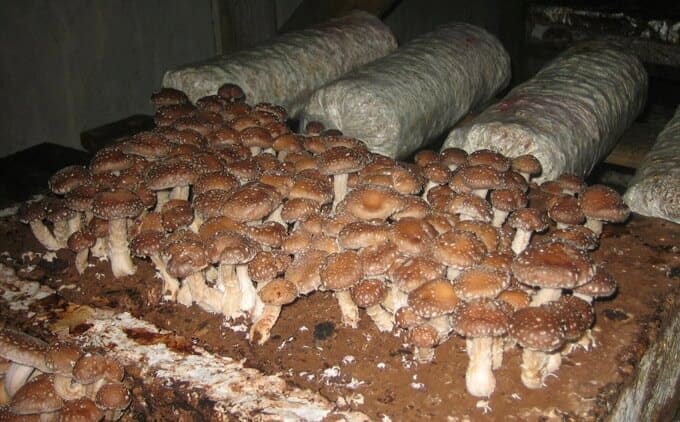

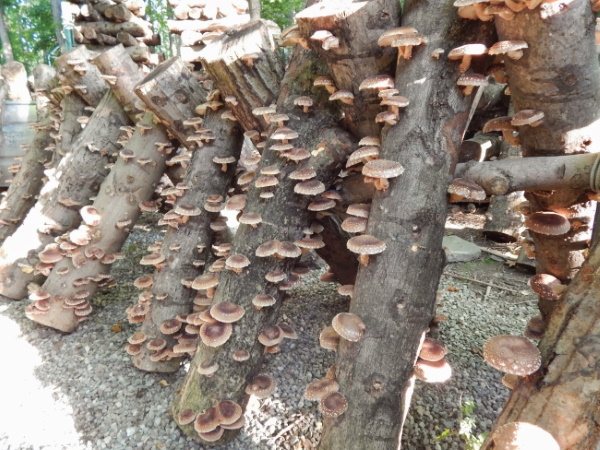
Features of growing mushrooms on stumps and logs
On tree stumps, lentinula grow slower and more capricious. Let's consider the basic requirements for this method.
Any low-grade wood is suitable for cultivation, but it is better to harvest those varieties on which shiitake spores grow naturally. Look for options with little signs of decay because fungi will wear down the tree and the growth medium will quickly deplete resources. This method is used to bring the fetus closer to its natural habitat.
When growing shiitake, the crop can be harvested from stumps or logs only after a year, and profit can be obtained in the second year of mushroom cultivation on the site, so mushroom pickers use artificial methods more often.
Extensive shiitake cultivation technology
Before growing shiitake mushrooms, they go to the forest and collect there trunks and thick branches of hardwood, for example, oak, beech, alder with a thickness of 50-200 mm. The trunks must be cut into equal lengths 1000-1500 mm, certainly covered with bark, the thickness of which should be within 1 mm, but not more, otherwise it will not transmit light.
The crucial moment is the correct preparation of the segments. It may seem paradoxical, but on the one hand, the fungus does not take root on a living tree, and on the other hand, for normal development, it requires a significant water content in the wood.
After cutting a fresh tree, they wait 1-2 months so that the mycelium can be planted. However, during this time, the wood will dry out too much.Japanese scientists testify that when the water level in the wood is below 32%, shiitake will not bear fruit. The mushroom will yield a harvest at a humidity of 35-65%, the higher this indicator, the better the result.

Shiitake stumps are harvested in the fall, because at other times of the year the bark peels off easily, and other wood-destroying mushrooms settle on the wood. In addition, the fruit bodies are laid under the bark, so its presence is necessary for the harvest.
The maximum nutritional value of oak wood occurs in autumn, when a third of the leaves turn yellow. At the same time, the amount of sugars that mushrooms can use increases. In autumn and winter, the nutritive value of the tree gradually increases and reaches its peak in early spring before the buds bloom.
Felled trees for growing shiitake mushrooms are most often left to lie in the forest for 1-2 months, after which they are sawn into pieces of equal length (1 m, sometimes 1.5 m) with a diameter of 50-150 mm or 200 mm. When choosing wood, you need to make sure that it is rot-free and completely healthy. Dark, white or red areas and dark stripes in the section indicate that competing fungi have already settled in the wood.
On pieces of wood 200 mm apart, holes are made with a depth of 15 mm and a diameter of about 20 mm. Grain mycelium is planted here and the holes are closed with wooden plugs, wax, etc., otherwise the risk of penetration of harmful microorganisms will increase.
An approximate scheme for cultivating a fungus in an extensive way is as follows.
The segments processed by the mycelium are stacked in a shady place. The areas must be clean, including from grass. The stacks are covered with branches for additional protection from drying out and exposure to direct sunlight.

To grow shiitake, it is important to create optimal conditions. The temperature required for the development of mycelium in the solid wood varies within 13-27 ° С, and the humidity - 78-85%
At this stage, light, in general, is not required, but it is necessary to provide access to fresh air, therefore the stacks are placed in a well-ventilated place.
The mycelium will completely grow over the wood within 6-12 months, which, of course, is largely determined by the conditions.
Sections infected with mycelium can easily overwinter in central Russia, not to mention the southern regions, if you cover them with straw mats or move them to the basement.
When the overgrowth stage is over, the segments are immersed in cold water for 24-72 hours. Then they are placed vertically or obliquely in a darkened place, but not in complete darkness, since the forming mushrooms still require light at this time. 7-11 days after soaking and storing the segments at an air temperature of about 20 ° C, the rudiments of fruit chalk are formed.
The total fruiting period is 3-5 years, while about 200-250 kg of mushrooms are harvested from 1 m2, i.e. 800-1200 g of mushrooms from one piece of wood.
The final section of the article describes how to grow shiitake mushrooms at home using intensive technology.
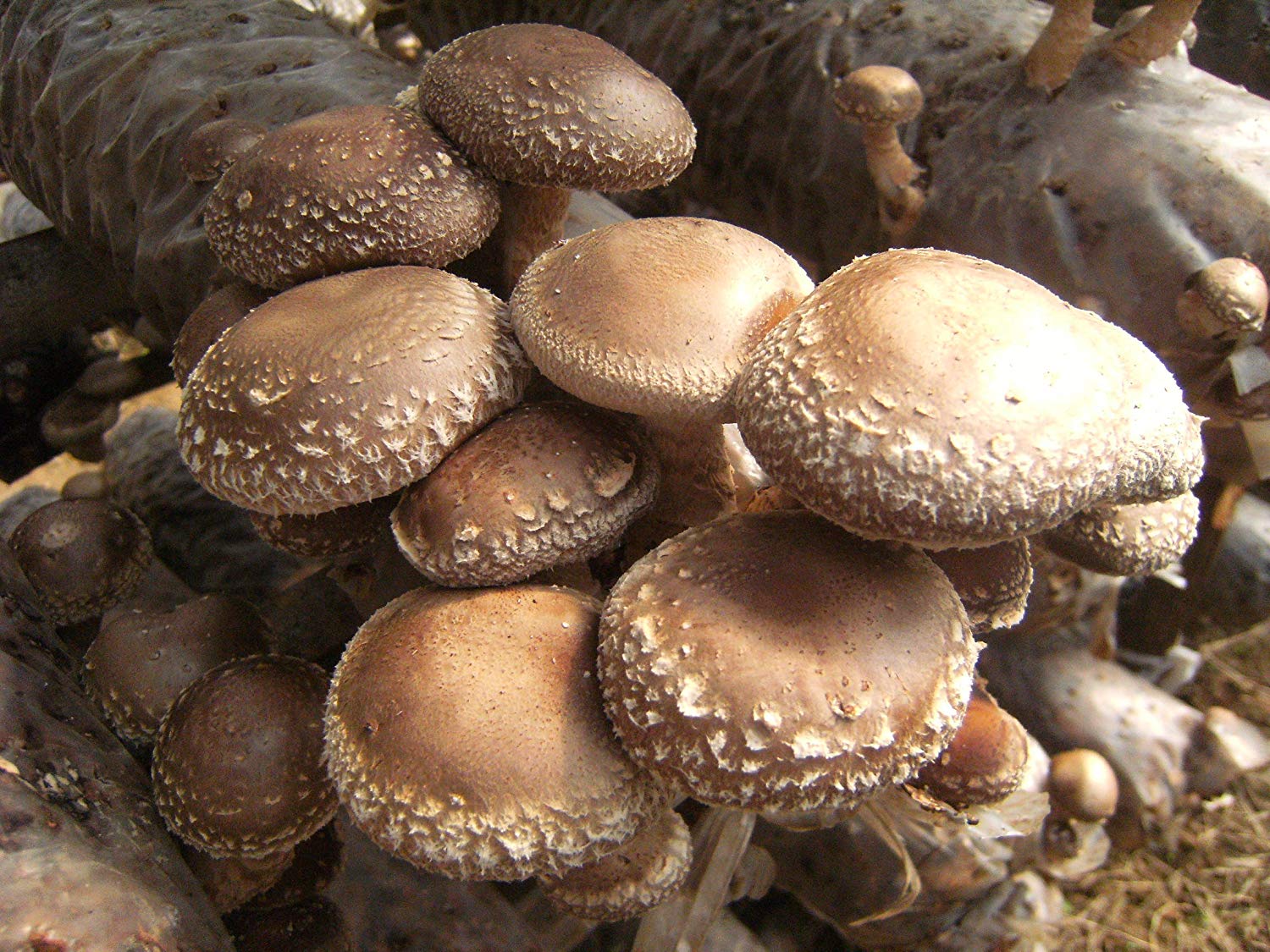
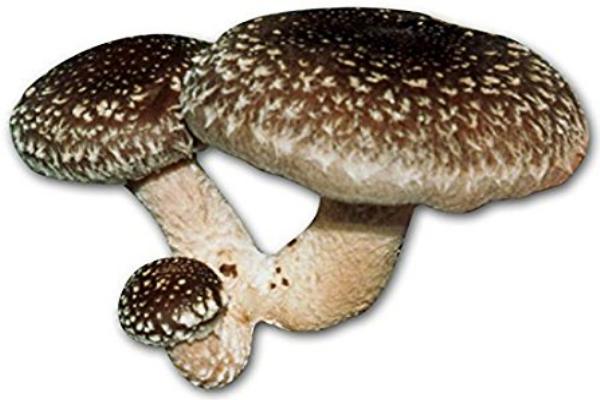
Where do shiitake grow and what do they look like?
In the wild, Shiitake grows in the countries of East and Southeast Asia: in the mountainous regions of China, Japan and Korea. In Europe, America, Africa and Australia, this mushroom does not occur in its natural wild form. In Russia, shiitake lives only in the south of the Far East; in Siberia and in the European part of the country, no foci of natural habitat of the fungus have been identified.
By the nature of their diet, shiitake mushrooms are saprophytic fungi that feed on organic matter from decaying wood, therefore they are found mainly on old stumps, wood cuts, and drying trees.
In Asian countries, this mushroom is considered curative and has been cultivated on tree stumps for more than a thousand years.
Outwardly, a shiitake looks like a hat mushroom on a short thick stem.The diameter of the cap can reach 20 cm, but on average it is 5-10 cm, in contrast to many xylotroph fungi. Shiitake grows alone without forming clusters of articulated fruit chalk. The cap of the fungus in the first phase of the growth of the fruiting body has a dark brown color and a pronounced spherical shape; as the fungus grows and develops, the cap flattens and becomes lighter.
The pulp of the mushrooms is light, delicate in taste, slightly reminiscent of the taste of porcini mushrooms; if the cap or leg of the mushroom plate is damaged, it darkens.
Fruiting and care
During the fruiting period, you will need eight hours of lighting with artificial lamps, a high percentage of humidity, frequent ventilation and a temperature not higher than 15 degrees.
If all norms are met, fungi will appear within two weeks from these slots. So that the remnants of the fruiting mushroom bodies do not rot inside, it is better to twist the mushrooms rather than cut them.
The substrate can be used to grow up to four oyster mushroom harvests. As a place for growing, you can use a loggia, basement, attics, etc. Oyster mushrooms do not like direct sunlight, so it is better to use darkened places. Compliance with a normal microclimate will yield a yield of 25 to 40% of the weight of the entire substrate.
Harvesting:
- It is better to harvest 5-6 days after the formation of the mushrooms.
- Optimally, the head should have a diameter of 40-100 mm, the stem 10-40 mm.
- At the very beginning of its development, the cap of the fungus is painted in a dark color, later it becomes ash-gray, and only at the end it sharply discolors.
- If the mushroom overripe, the cap begins to break, the leg hardens.
- The commercial appearance deteriorates, and with it all the taste and nutritional properties fall.
- You need to store fresh mushrooms at 0-5 degrees above zero for a week, and for about 6 hours at a temperature of about 20 degrees above zero.
- It is not recommended to selectively cut mushrooms! In general, cutting the crop should be neat and unhurried so as not to damage the mycelium.
- With the onset of cold weather, you need to cover the beds of mushrooms with straw if they are grown outdoors.
Some of the summer residents have been successfully building a business on growing oyster mushrooms for a rather long time. High demand and minimal growing costs bring tangible profits.
What you need to know before buying
Due to the abundance of offers on the market, it is not easy for novice mushroom growers to deal with the types of mushroom seeds. Let's consider the main criteria that should be considered when buying.
Oyster mushroom mycelium types
Today, five varieties of mushroom planting material are produced:
- Grain mycelium (live) - grown in sterile laboratory conditions on grains of any cereal. Plus - the highest germination and productivity. Minus - it is stored for no more than a month at a moderate temperature (up to 22º C), since it contains live culture.
- Grain (dried) - the same grain overgrown with live hyphae, but dried using a special technology. Plus - practically unlimited shelf life. Minus - slightly inferior in characteristics to the previous version.
- Dry powdery is a mycelium produced from biologically dried by means of complex technological processing. Pros - small volume of packaging, long-term storage, ease of use. Minus - the yield is lower than that of the first type.
- On sticks (dry) - planting material grown on beech and oak blocks, then biologically dried. Pros - ease of use, high germination, unlimited storage.
- Compost - it is extremely rarely used, it is produced mainly on order.

Oyster mushroom strains: what is it?
When choosing a mycelium, novice mushroom growers encounter two concepts - species and strains. In the first case, the name will be written in a standard way, for example, White Elf oyster mushroom Pleurotus cystidiosus. In the second, instead of the name, the abbreviation P-14, PPH or another is often written, which in this case means a variety of the pulmonarius species.
A strain and a species are not the same thing; one species can have many strains, that is, hybrid breeding forms that have some differences. All oyster mushroom strains are divided into three groups:
- summer;
- winter;
- universal.
As a rule, reputable manufacturers of the spore material give a detailed description of the proposed strain, indicating the duration and conditions of fruiting.

Criterias of choice
High-quality mycelium when growing oyster mushrooms on stumps is 50% of success. The remaining 50% is accounted for by all other factors
For the choice to be successful, it is important to consider three main criteria:
- Strain. For growing on stumps, universal strains that bear fruit in a large temperature range are suitable.
- Mycelium type. It is most convenient to use dry powdery and mycelium on bars. (uterine) can only be purchased if you are confident in the temperature conditions during delivery, since in the summer heat it retains its properties for only 36 hours.
- Manufacturer. Do not buy seed in random places where storage conditions are not met. The shorter the path of mushroom seeds from the laboratory to the dacha, the higher the probability of success, so it is better to buy directly from the manufacturer.
If, due to the abundance of offers, you find it difficult to choose an oyster mushroom variety, buy several at once for planting on different stumps.