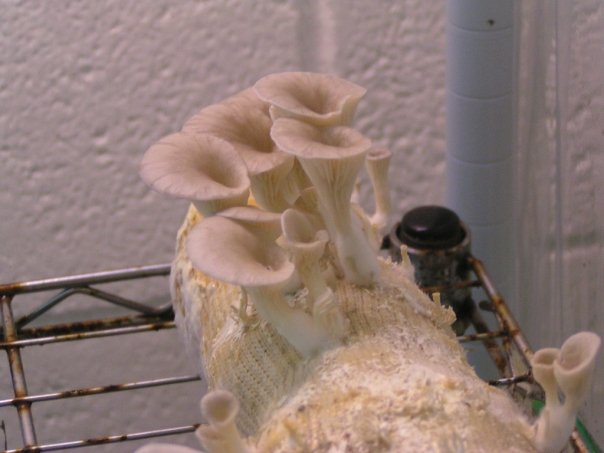
Oyster mushroom (Pleurotus pulmonarius) - Mushrooms of Siberia

Current title
| Index Fungorum | Pleurotus pulmonarius (Fr.) Quél. |
| MycoBank | Pleurotus pulmonarius (Fries) Quélet |
Systematic position
Fungi, Basidiomycota, Agaricomycetes, Agaricales, Pleurotaceae, Pleurotus
Etymology of the species epithet
Pulmonarius, a, um patient with lungs; healing for the lungs.
Synonyms
- Agaricus pulmonarius Fr., Syst. mycol. (Lundae) 1: 187 (1821)
- Dendrosarcus pulmonarius (Fr.) Kuntze, Revis. gen. pl. (Leipzig) 3 (2): 464 (1898)
- Pleurotus araucariicola Singer, Lilloa 26: 141 (1954)
Other names: Whitish oyster mushroom, Spring oyster mushroom, Beech oyster mushroom.
Habit
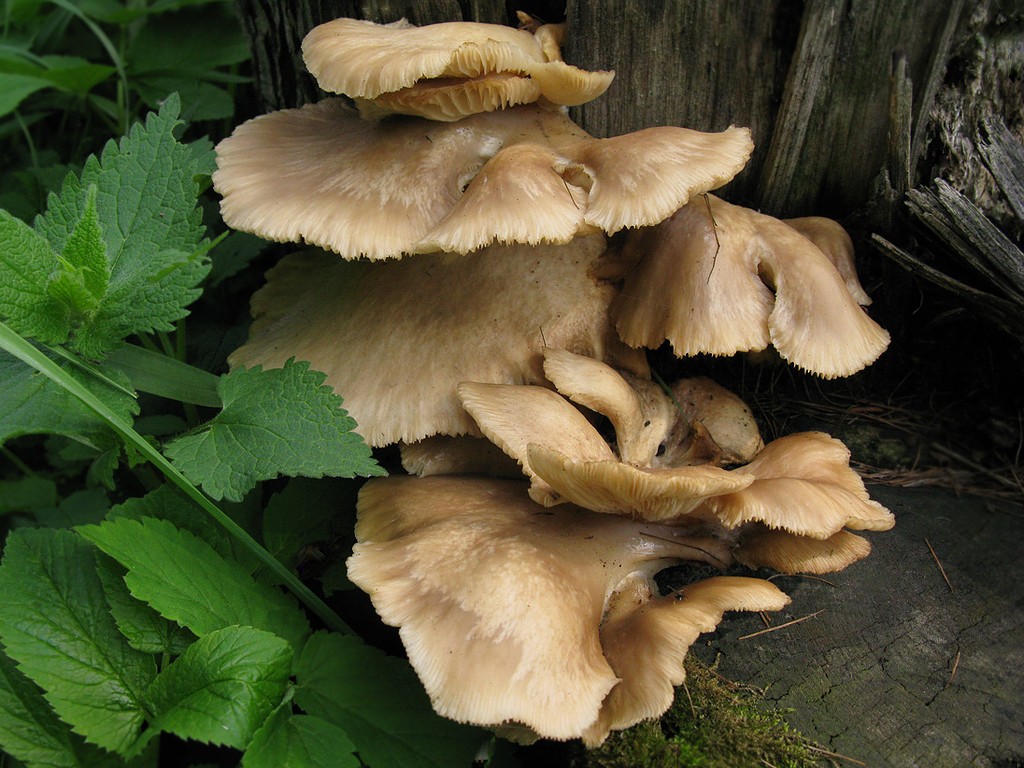
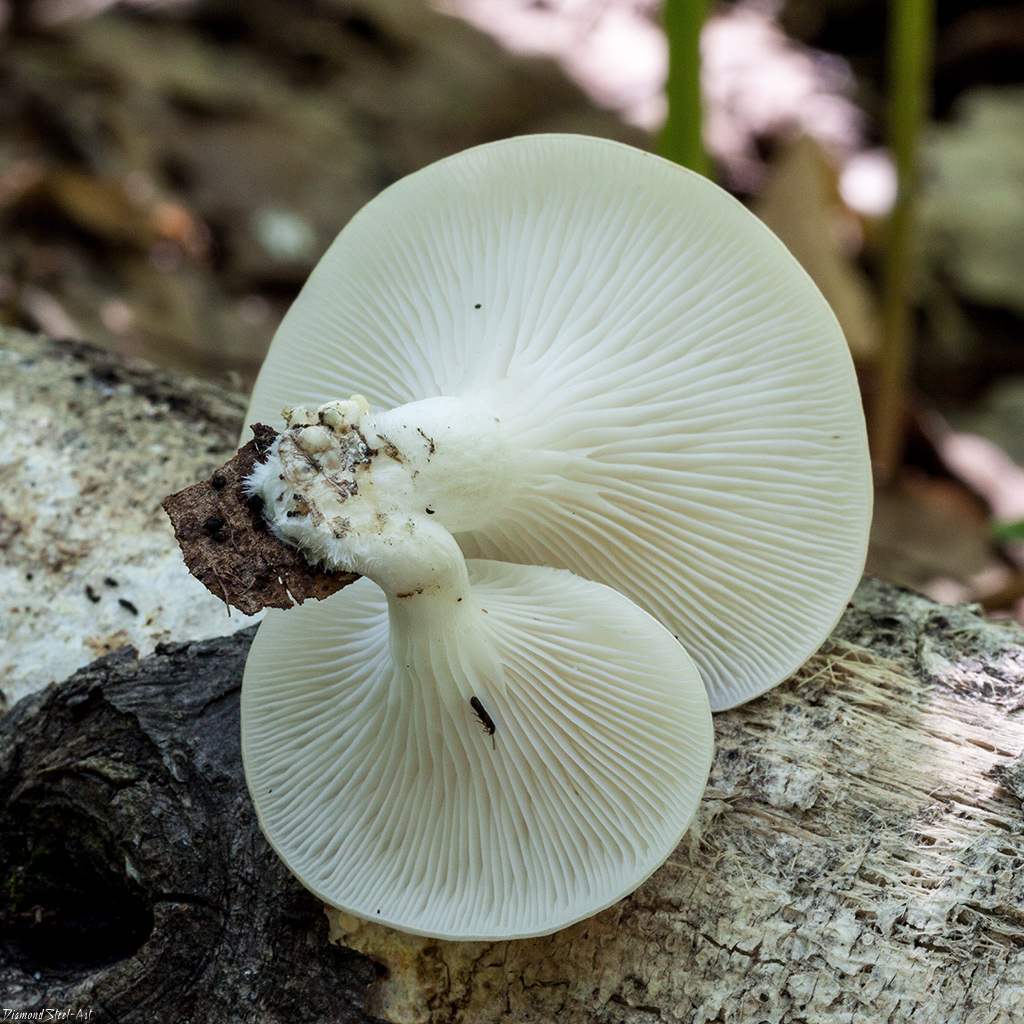
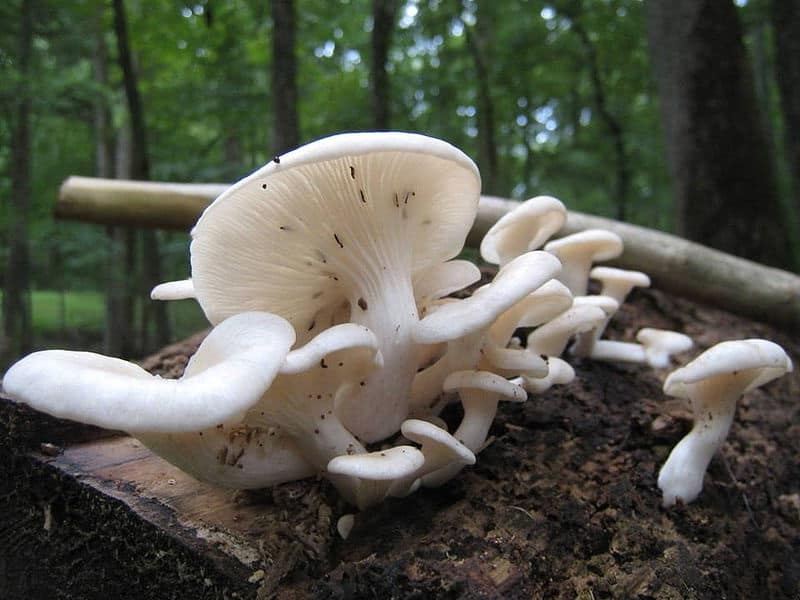
Hat
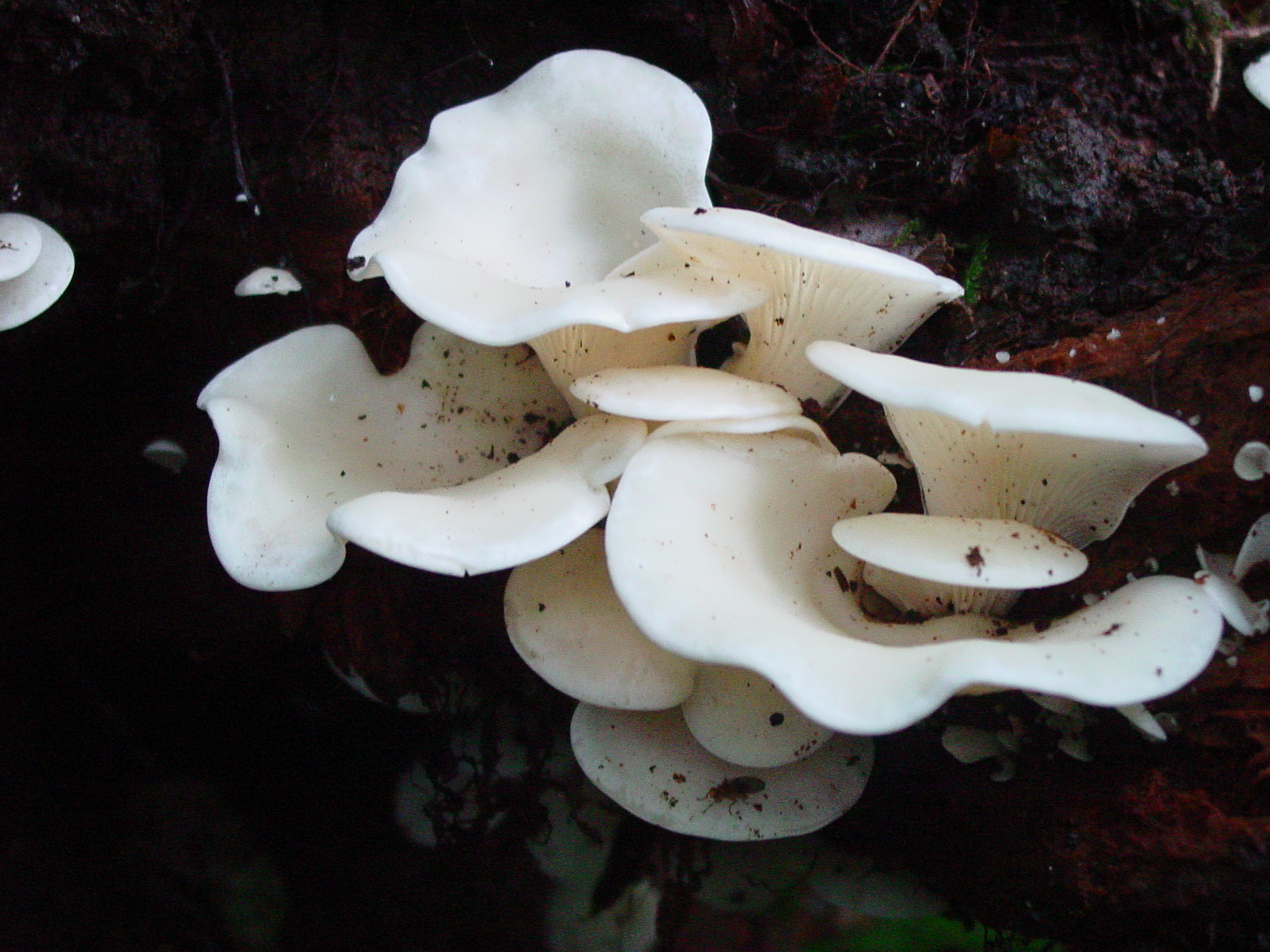
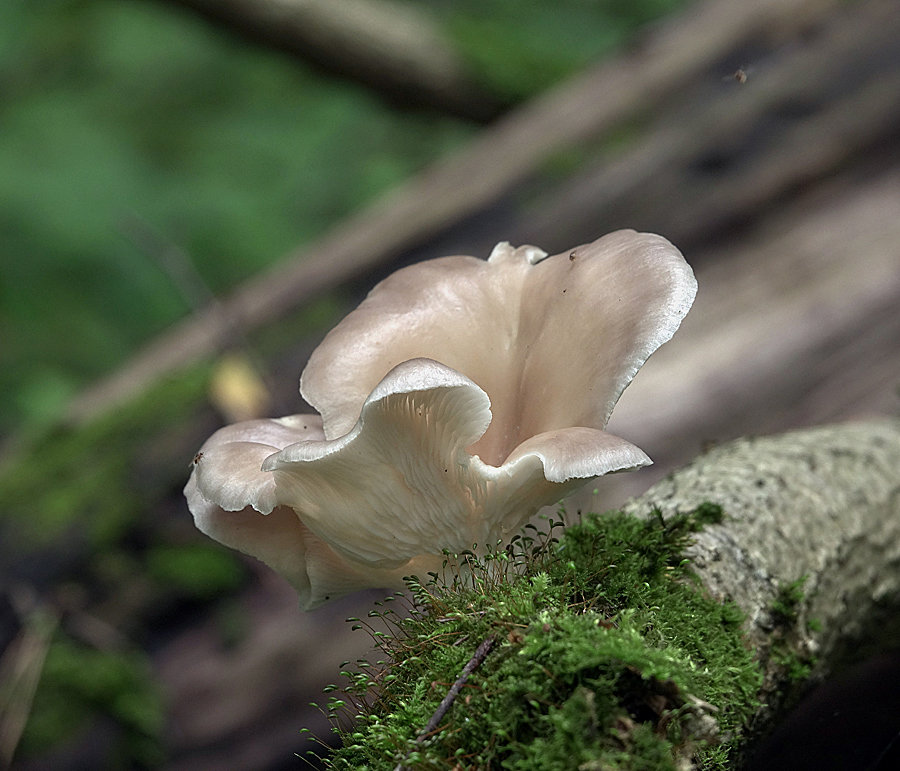
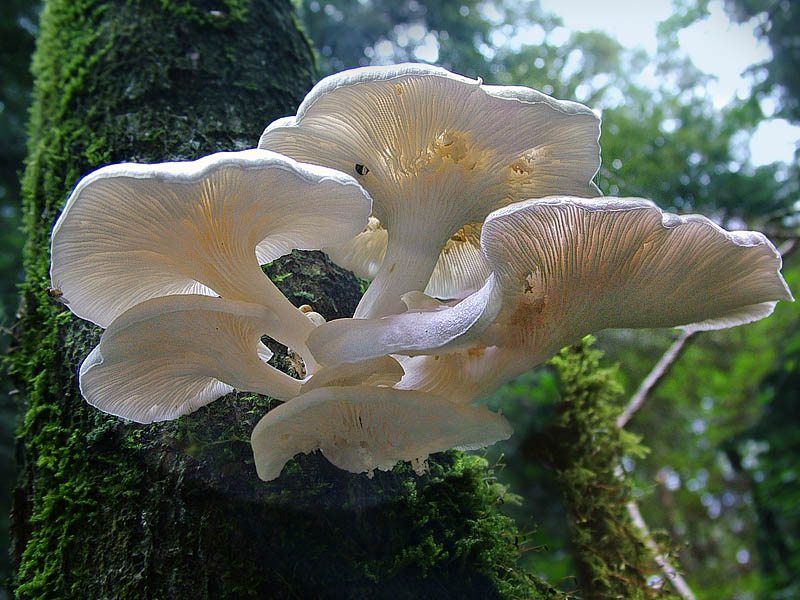
The cap is 3-10 cm in diameter, ear-shaped, lobed or irregular in shape, slightly concave-outstretched or convex, with a straight or wavy sharp edge, sometimes slightly turned up, smooth or rarely scaly, often with radial hygrophane zones, white, cream, grayish, ocher, or the color of coffee with milk.
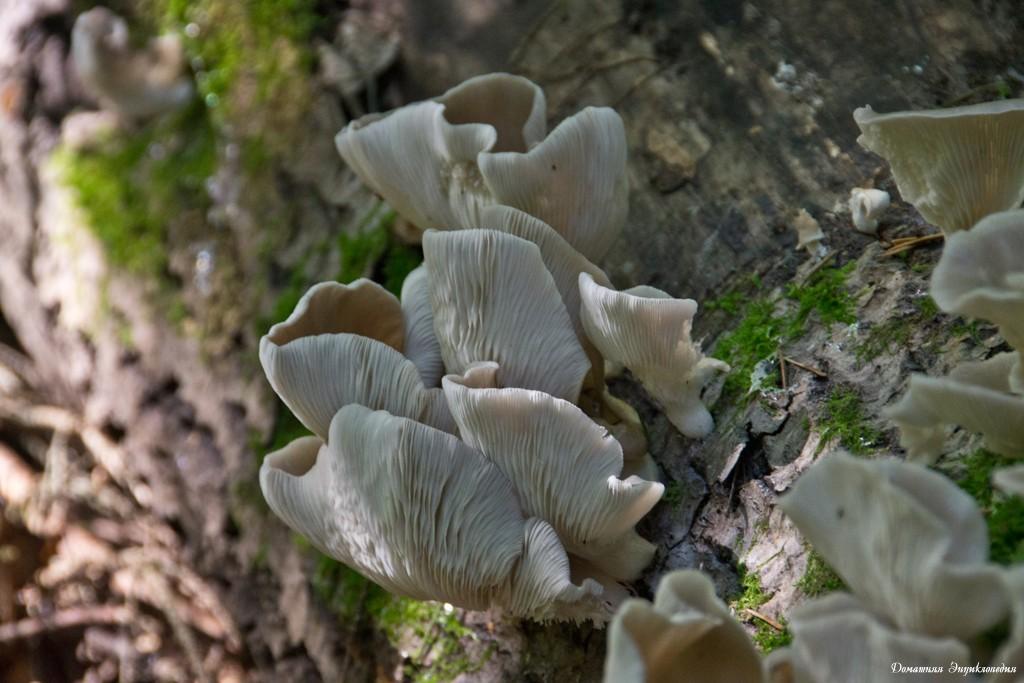
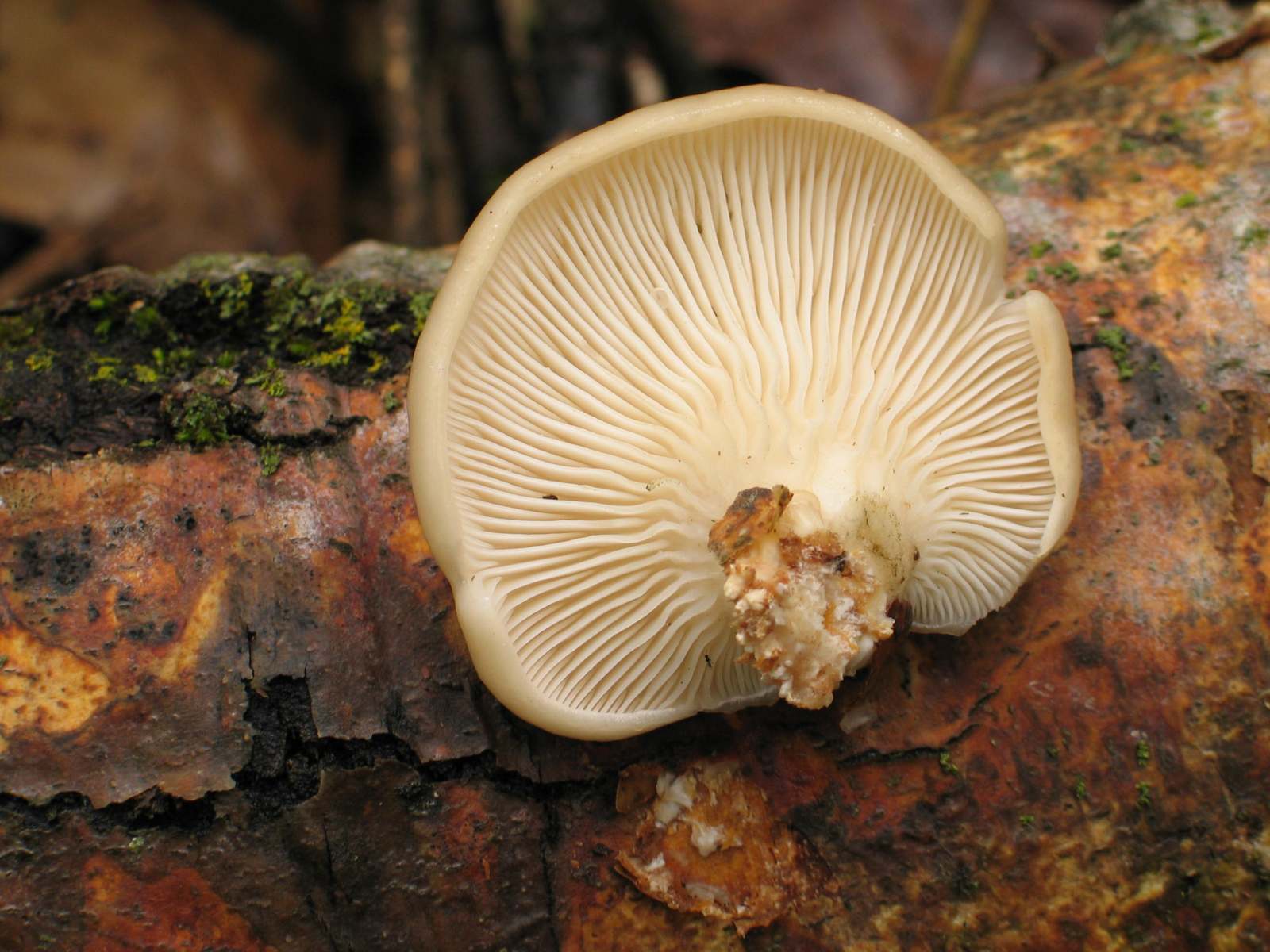
The plates are descending, frequent, narrow, with plates, with rare anastomoses and an even, wavy or finely toothed edge, white, grayish or creamy, often with greenish or lemon-yellow spots.
The blanket is missing.
Leg
Stem 1 - 4 cm long, 0.5 - 2 cm in diameter, short or completely absent, lateral or eccentric, cylindrical, solid, white, pubescent at the base.
Pulp
Microscopy
Spores 7.5 - 12 × 3 - 4.5 µm, ellipsoidal, sometimes slightly almond-shaped, unequal, smooth, thin-walled, not amyloid, white, yellowish or grayish in mass.
Basidia 20 - 30 × 5 - 8 μm, clavate, 2 or 4 spore, with a buckle at the base.
Pleurocystids 20 - 50 × 2 - 4.5 µm, cylindrical with a slightly swollen apex.
Cheilocystids were not found.
Ecology and distribution
Substance: Woody plants (living trees, bark and dead wood)
Grows in groups, rarely singly on dying or dead deciduous trees. Recorded on alder (Alnus), birch (Betula), aspen, poplar (Populus), willow (Salix).
Fruiting
May - September.
The divisions correspond to the decades of the month.
Nutritional properties
Edible
Should be harvested with care due to its resemblance to pleurocybella, a potentially poisonous fungus. Similar species
Similar species
- Oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) - has fleshy fruiting bodies with a brighter color.
- The protruding pleurocybella (Pleurocybella porrigens) is an outwardly indistinguishable fungus from the Marasmiaceae family. Differs in a mealy, not mushroom smell, a slightly more fragile habit and growth on coniferous wood. Until recently, it was generally accepted as edible, but studies conducted after a series of severe and fatal poisoning in Japan in 2004 identified a potential toxin - the unusual amino acid pleurocybellaziridine.
Notes
Causes white rot.
Oyster mushroom, as well as Oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus), is cultivated on an industrial scale.
Distribution in Western Siberia
Everywhere in birch and birch-aspen forests.
Related materials
- Zmitrovich I.V., Malysheva V.F., Malysheva E.F., Spirin V.A.Pleurotoid fungi of the Leningrad region. - SPb .: "VIZR", 2004. - 124 p. - S. 96.
- Bas C., Kuyper Th. W., Noordeloos M. E., Vellinga E. C. Flora Agaricina Neerlandica. Critical monographs on families of agarics and boleti occurring in the Netherlands. Vol. 2. Pleurotaceae, Pluteaceae, Tricholomataceae. - Rotterdam - Brookfield: A. A. Balkema, 1990 .-- 160 p. - P. 21.
- Beug M. Pleurocybella porrigens toxin unmasked? - North American Mycological Association. Url:
Oyster mushroom use
How is edible mushroom used? Naturally, for food.
Oyster mushroom is edible without any "conditional". Can be fried without boiling. You can cook soup. Or, boiled, use in salads.
I fried. It turns out very tasty. Looks, in my opinion, is also quite nice and appetizing. It is a pity that it is not enough.

Oyster mushroom can be fried without pre-boiling
Since I find few mushrooms, the question of harvesting for future use has never been raised. Can be frozen - either fresh or lightly boiled.
Oyster mushroom, along with other types of oyster mushrooms, is one of the few cultivated mushrooms. Oyster mushrooms are grown on a substrate of deciduous shavings or on straw. This process is far from simple and very costly. Special rooms are needed, maintaining the temperature regime.
In any case, I would not recommend to somehow react to the advertisements of various "Mushroom Farms", "Mushroom Baskets", etc., which have flooded the Runet.The buyer of these "miracles" does not expect anything but lost money.
As they say, this is a real "scam and scam". Why - I, in my opinion, quite reasonably expressed myself in the article "Mushroom Farm" - a real expert review. "
According to experts, pulmonary oyster mushroom is a medicinal mushroom. This, in particular, writes the Moscow mycologist M.V. Vishnevsky in the book “Medicinal mushrooms. Great Encyclopedia ".
Oyster mushroom preparations have an antioxidant effect, are useful in diabetes mellitus (lower blood sugar).
But in folk medicine, pulmonary oyster mushroom has never been used. The mushroom is not harvested in our country as a medicinal raw material.
Harm and contraindications
Unlike other mushrooms, oyster mushrooms do not accumulate heavy metals. Therefore, she has few obvious contraindications. These include individual intolerance to the product and acute pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
In large quantities, mushrooms can cause a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen and upset. There are other recommendations for their use:
- You can't eat mushrooms raw, they contain a lot of chitin.
- It is better to boil them in boiling water for a few minutes before use.
- The optimal intake for women and men is considered to be 200 g of fried or stewed oyster mushrooms, 100 g of salted mushrooms.
- You cannot salt raw oyster mushrooms.
- You cannot buy them from your hands without knowing where they were grown.
Pediatricians advise to exclude any mushrooms from the children's diet. It is permissible to give oyster mushrooms to babies after 7 years in crushed form and no more than once in 14 days. Thus, medicinal mushrooms will be beneficial if collected and consumed according to all the rules and taking into account the recommendations of a doctor.
What does it look like
In the Caucasus, this mushroom is called kagarchik, Ukrainians call it gliva. The name "horn-shaped" appeared due to the special shape of the cap. Also, the mushroom is called abundant oyster mushroom due to the growth of large families.

In the photo, horn-shaped oyster mushroom Pleurotus cornucopiae
Its external characteristics include the following features:
- The hat resembles a funnel or horn, sometimes it grows in the form of a tongue or leaf. It reaches 100 mm in diameter. In young specimens, its edges are wrapped inward.
- The color of the cap is usually white, brown or grayish. In many ways, the color depends on the region of growth and the age of the oyster mushroom.
- Its flesh is tight and fleshy; as the mushroom matures, it coarsens. It has no special aroma and taste.
- Under the "headdress" are visible rare white plates that stick around the entire leg to the very bottom, forming a braided pattern.
- Reproduction cells are white, oval in shape.
- The stem grows in the center or to the side of the cap. It can be up to 15 mm wide and 80 mm high. The base is narrowed.
Oyster mushrooms are successfully cultivated on an industrial scale. They are grown on plantations not only in Russia, but also in other states.
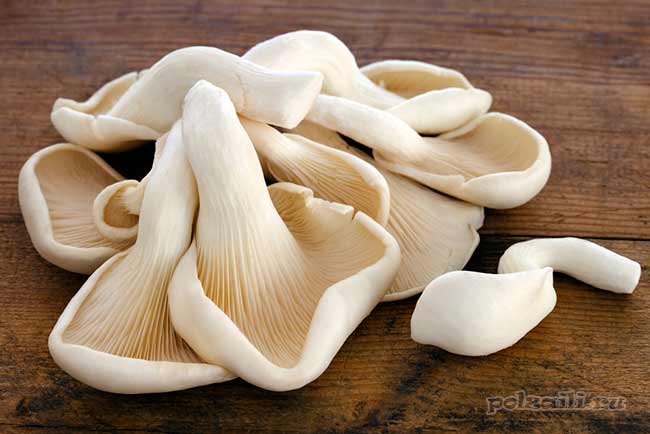
How is it cooked
Oyster mushroom is an edible species. It does not have a rich mushroom taste or aroma, however, in combination with other products, it becomes very tasty.
Kagarchik is used for frying, stewing, salting and pickling. It is dried in powder form and put as a seasoning in various dishes. This spice has a bright bready aroma. Only young specimens are eaten. The old ones are too tough.
Spaghetti with mushroom sauce
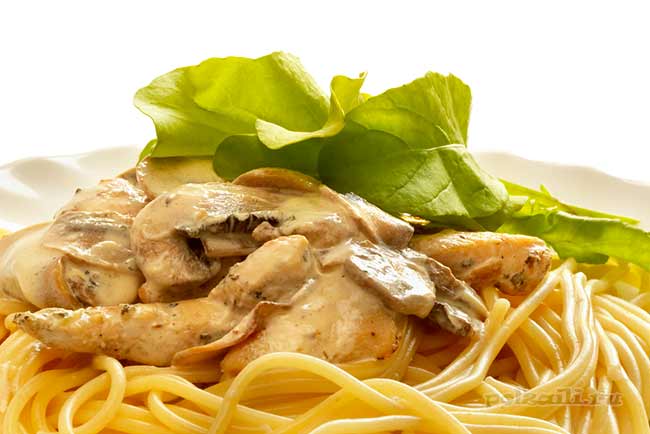

- a pound of mushrooms;
- 400 g spaghetti;
- a quarter glass of olive oil;
- three cloves of garlic;
- a teaspoon of chopped thyme;
- a glass of fatty cream;
- black pepper;
- Parmesan for serving;
- some salt.
Prepare the dish as follows:
- Boil the pasta in a deep saucepan until cooked.
- In a frying pan, heat the oil and lay out the pre-processed chopped mushrooms.
- Cook them for about five minutes until golden brown.
- Reduce heat and add minced garlic to it.
- After 6-7 minutes, put thyme, herbs, salt and pepper.
- Add the cream and remove from the stove after a minute.
- The pasta is placed in a serving dish, sprinkled with mushroom sauce on top and sprinkled with cheese.
Any kind of oyster mushroom is suitable for this dish.
Where grows
Oyster mushroom grows on the remains of deciduous trees, which are located in hard-to-reach places. It is often found on oaks, elms and maples. It can be found in dense thickets, in areas of deforestation. The mushroom grows in the Russian Federation, China, Ukraine, Japan and the Caucasus.
The species bears fruit in numerous families from early May to late September. The mass of all fruit bodies found in one meadow can reach one kilogram.
Oyster mushrooms are successfully grown at home. If you adhere to the technology and recommendations, you can get a good harvest. These mushrooms are capable of multiplying on almost any basis. Usually they use straw of cereal crops, reeds, sawdust of deciduous trees.
Oyster mushrooms are quite resistant to diseases and pests.
It is important to maintain the right climate for the growth of mycelium, then in one place you can harvest for 5-7 years
Oyster mushroom - description and photo
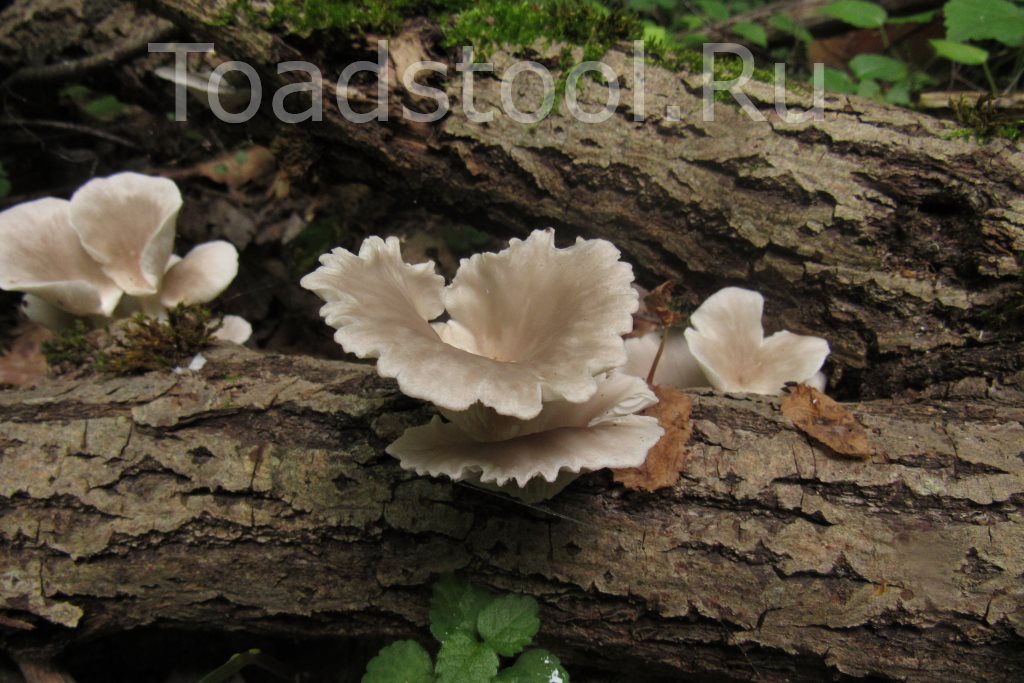
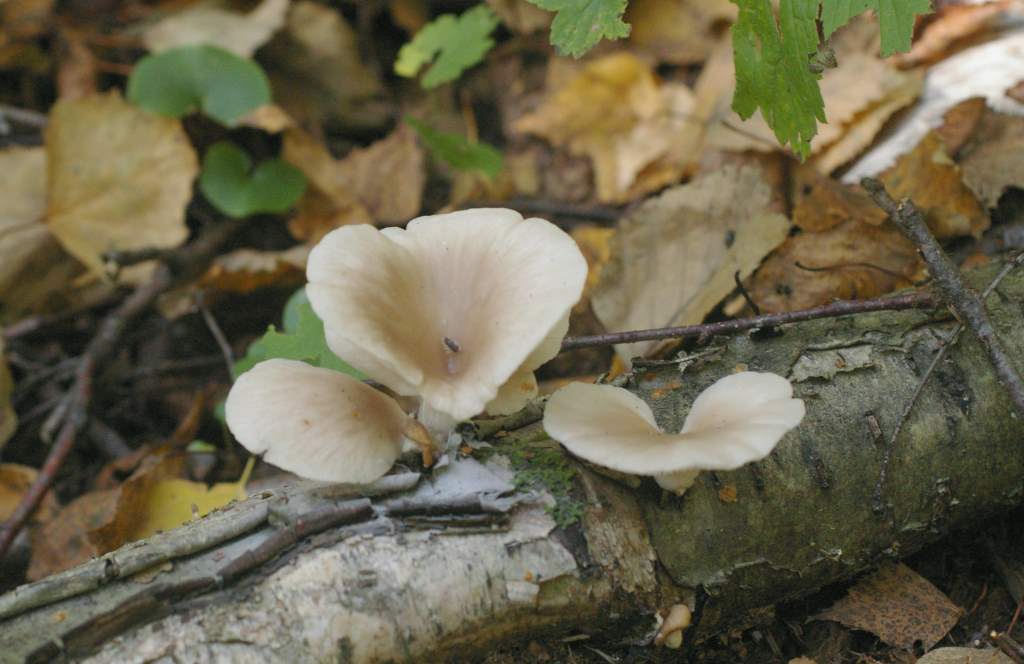
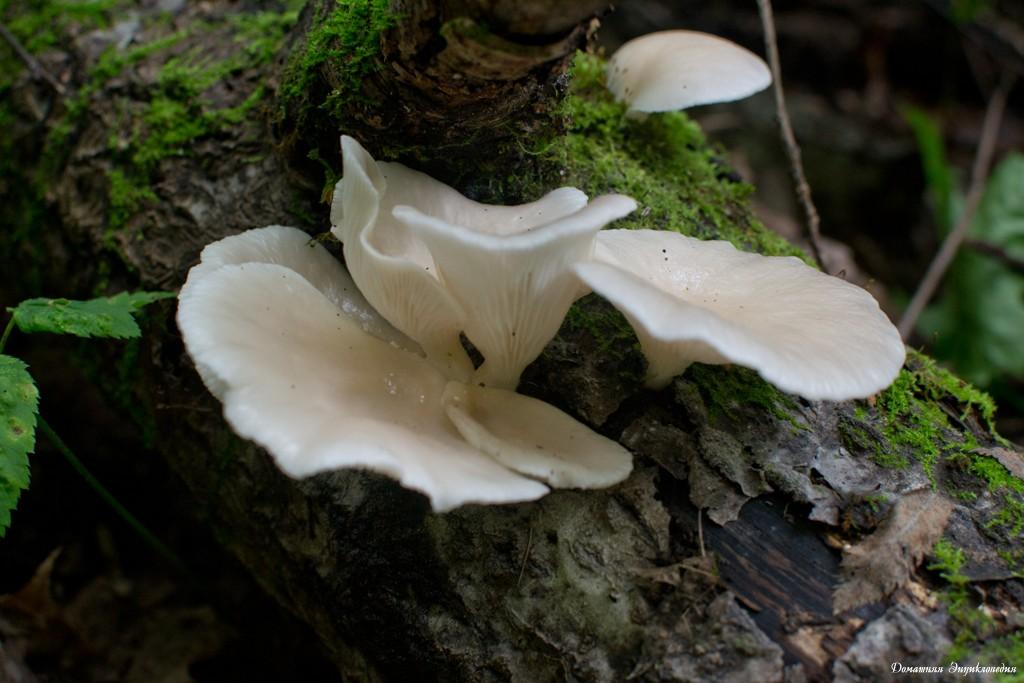
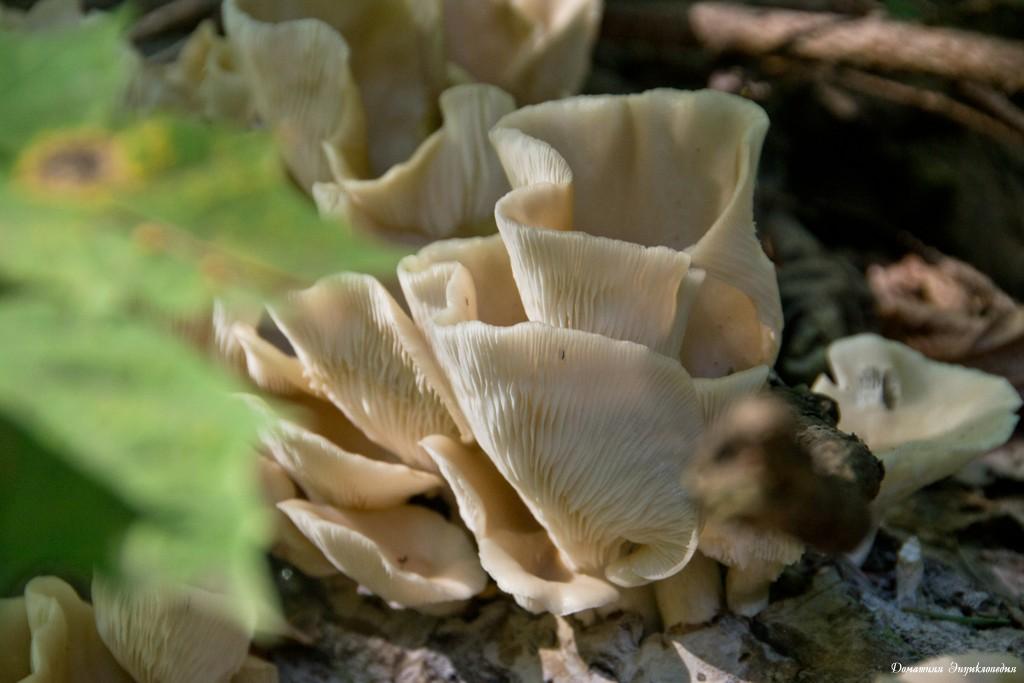
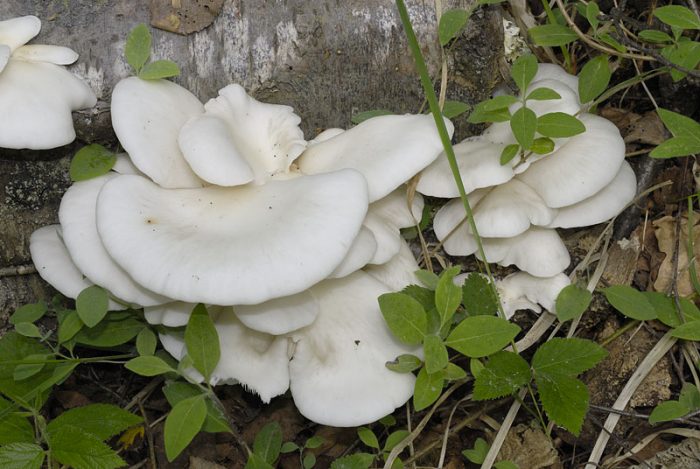
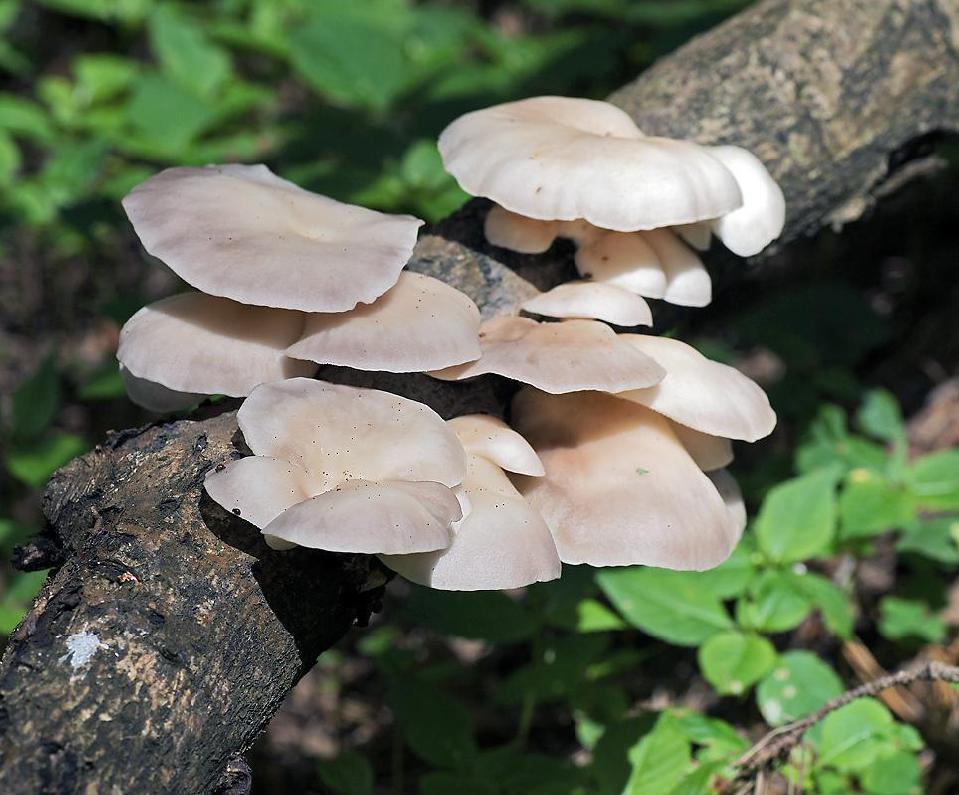
Oyster mushroom (Pleurotus pulmonarius) is a mushroom from the Veshenkov family (according to other sources, from the Polyporov family). It is very widespread in the forests of Europe and Siberia.
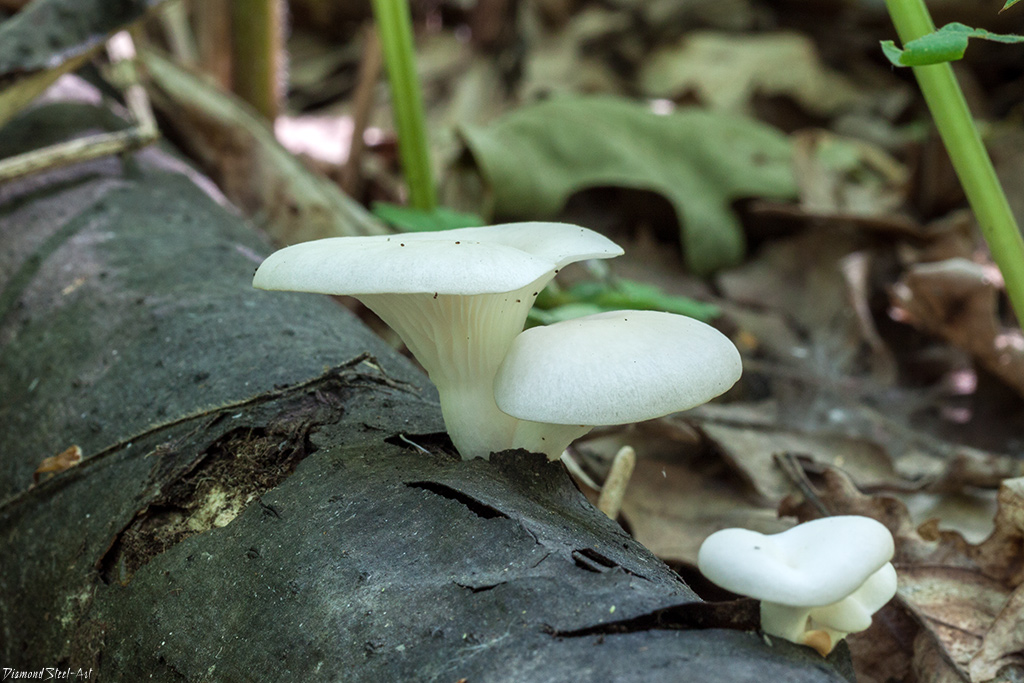
The wide range of the fungus does not mean at all that the fungus is abundantly represented everywhere. Somewhere it occurs more often, somewhere less often. For example, here, in the east of the Vologda region, I do not meet pulmonary oyster so often. And oyster oyster mushroom (ordinary) and generally has not yet come across in nature.
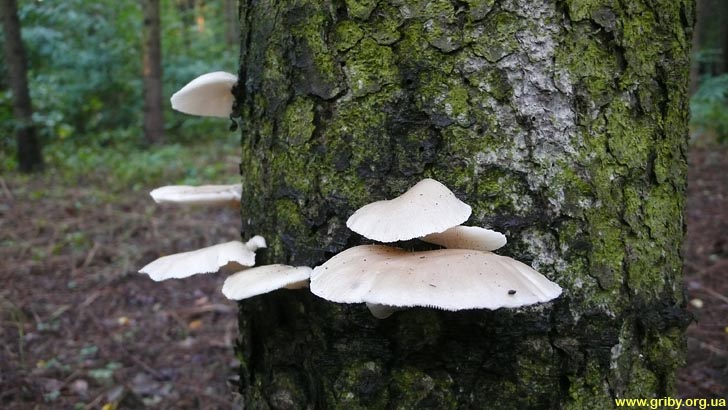
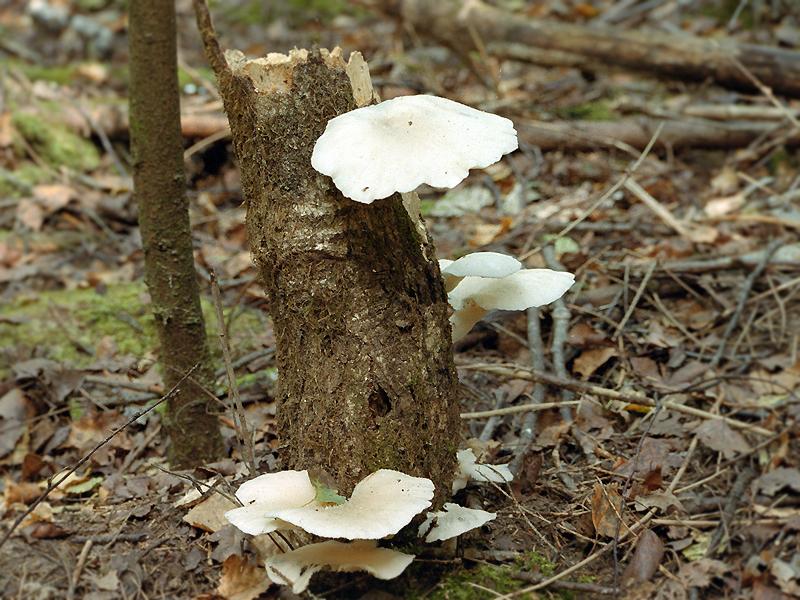
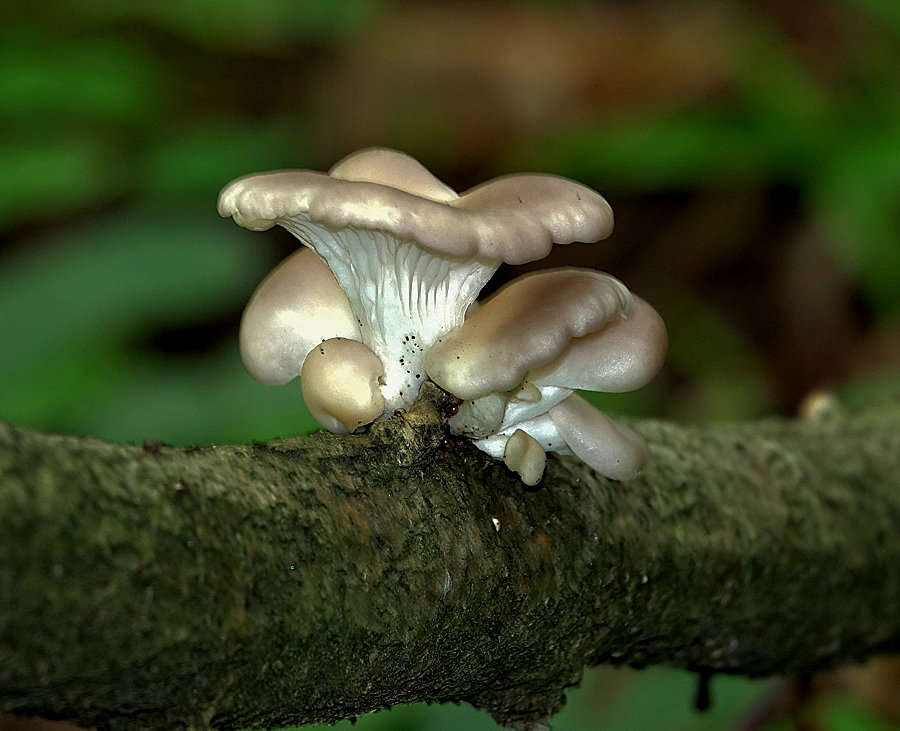
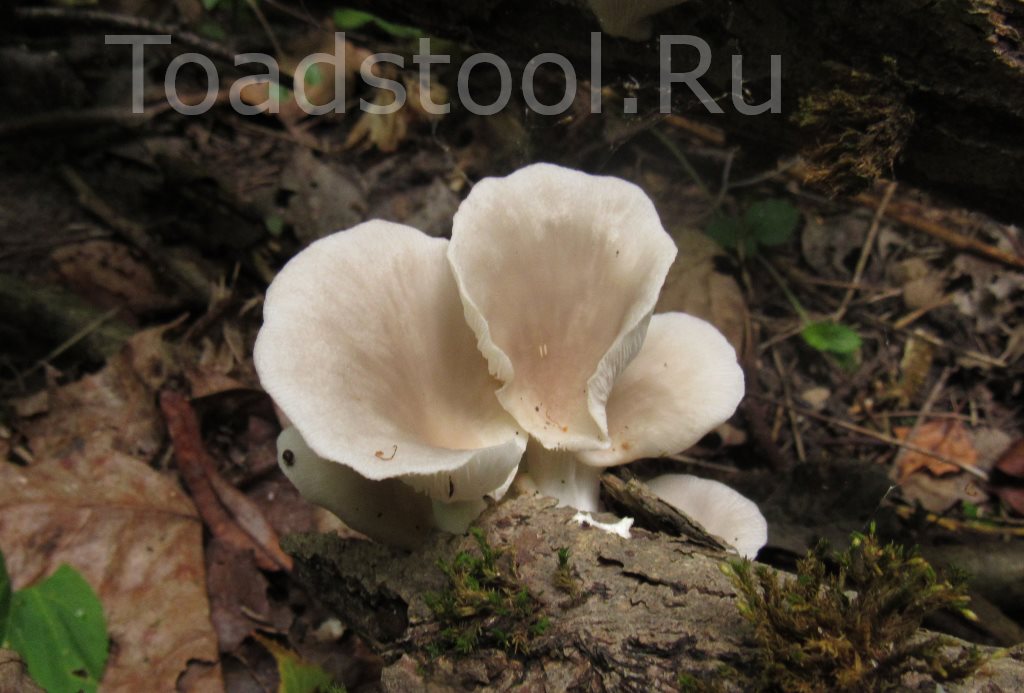
Most often I find one or two mushrooms. Only in July of this year it was possible to simultaneously find several fruiting bodies of pulmonary oyster mushroom and finally to truly "take a sample". Oyster mushroom grows on dead wood: on half-dried and dry trees, stumps, dead wood.

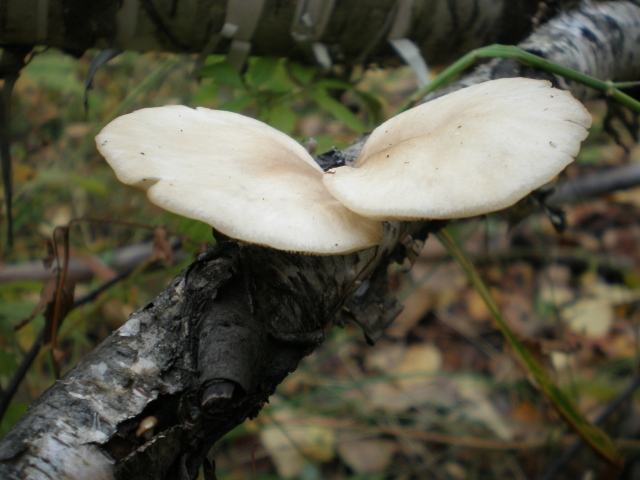
Oyster mushroom on the trunk of a fallen aspen
Prefers hardwood - birch, aspen, willow, poplar. But it can also grow on conifers.
Sometimes it may seem that the fungus grows in the soil as well. In fact, the oyster mushroom "assimilates" the deadwood already hidden in the soil and forest litter.
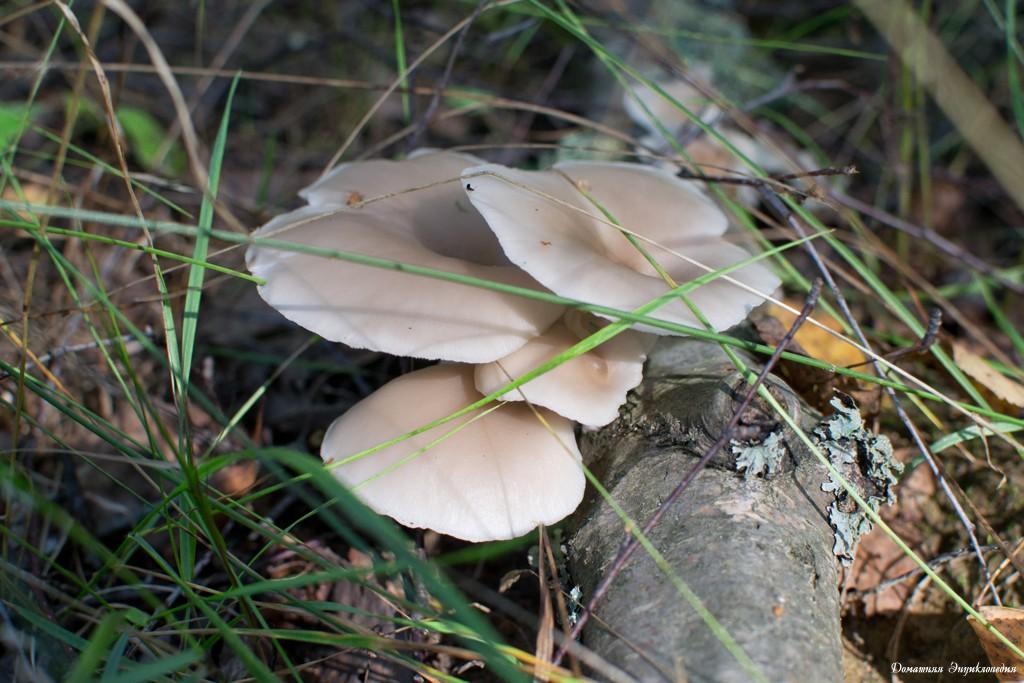
Fruiting bodies appear in May. This gives rise to the assumption about the origin of the name from the word "spring". If only because they pay more attention to oyster mushrooms at this “mushroomless” time.
But the formation of fruiting bodies occurs until autumn, until October. And it is preferable to collect pulmonary oyster in the summer.
What are the main distinguishing features of pulmonary oyster mushroom?
The shape of the cap of this mushroom is fan-shaped, sometimes ear-shaped. The leg almost always grows not in the center, but on the side.
The hat is rather thin and fragile. Its size is from 5 to 10 cm, but it can be slightly larger.
The leg is short, firm and even stiff. Sometimes the leg is practically absent.
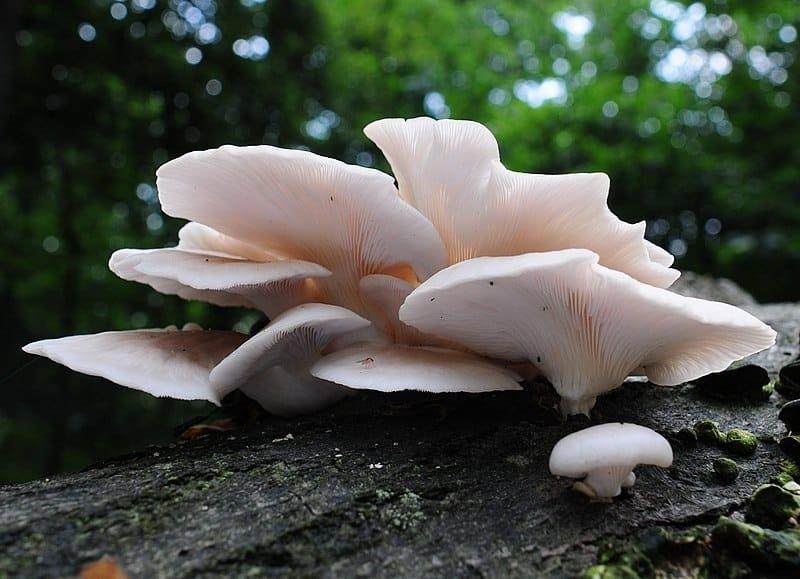
The skin color is almost white, beige or cream, with yellow color. The older the fruit body, the more yellow in its color.

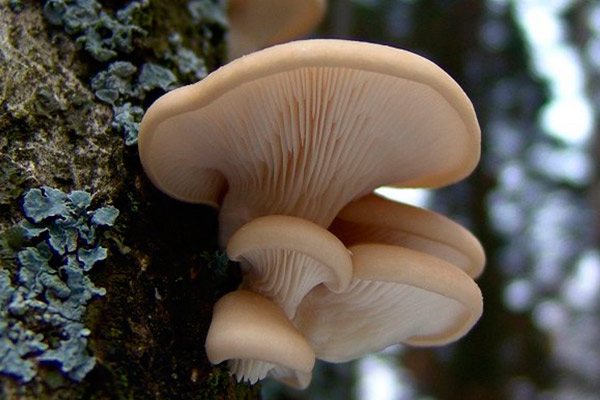
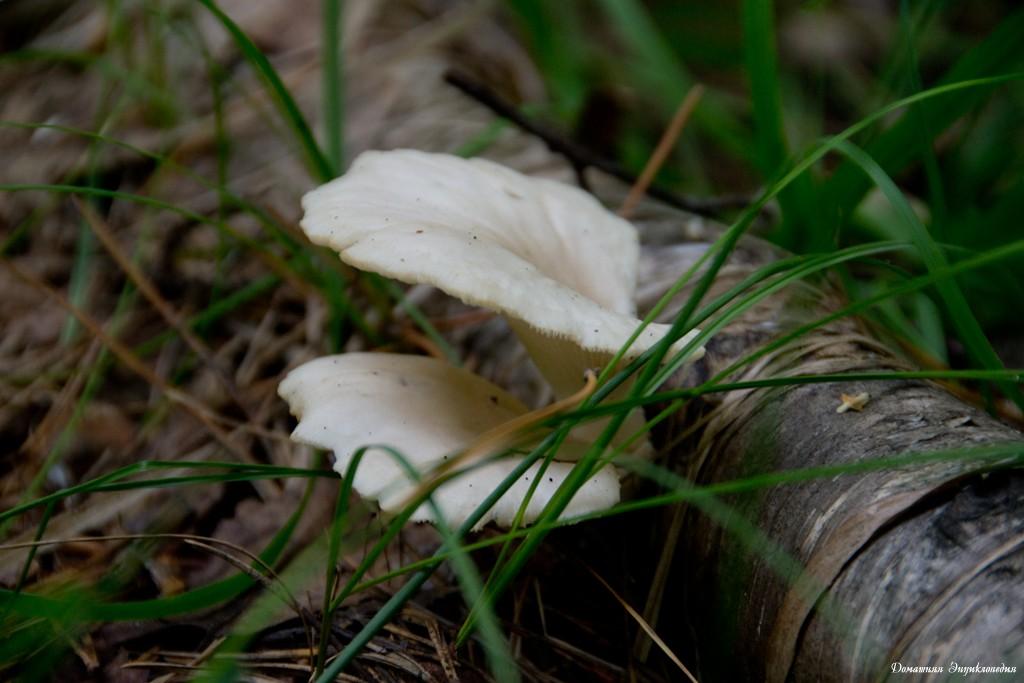
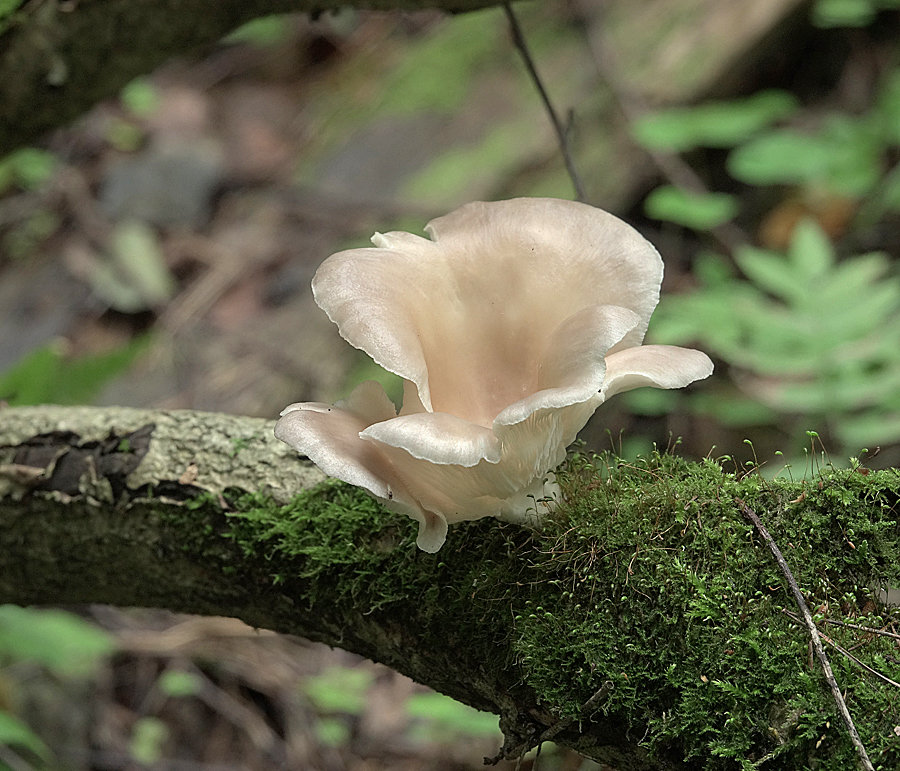
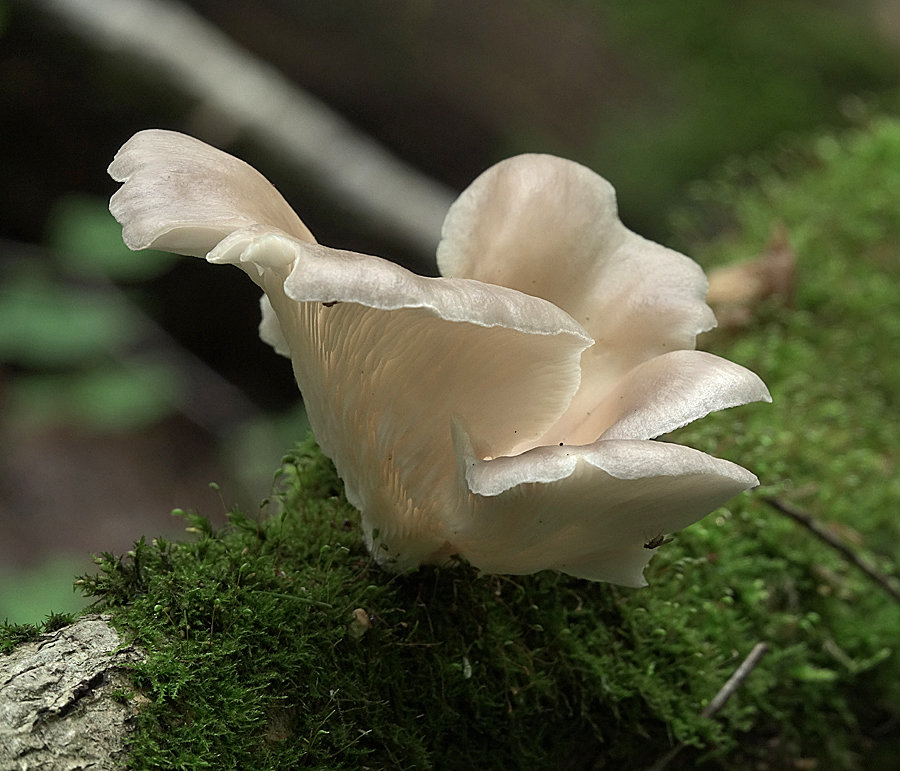
Another oyster mushroom, quite large
The edge of the cap, especially in young mushrooms, can be tucked up. A funnel-shaped depression appears on the cap of the young fruiting body. Later it is no longer expressed. With the growth of the fungus, the edge of the cap often becomes lobed.

The edge of the cap of the oyster mushroom is often lobed.
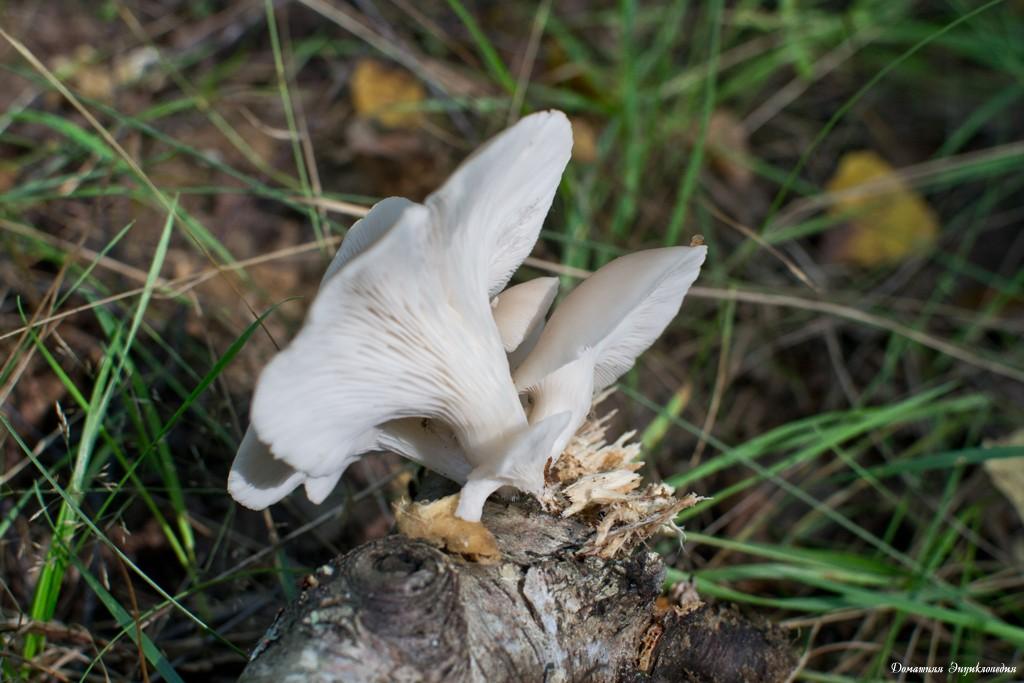
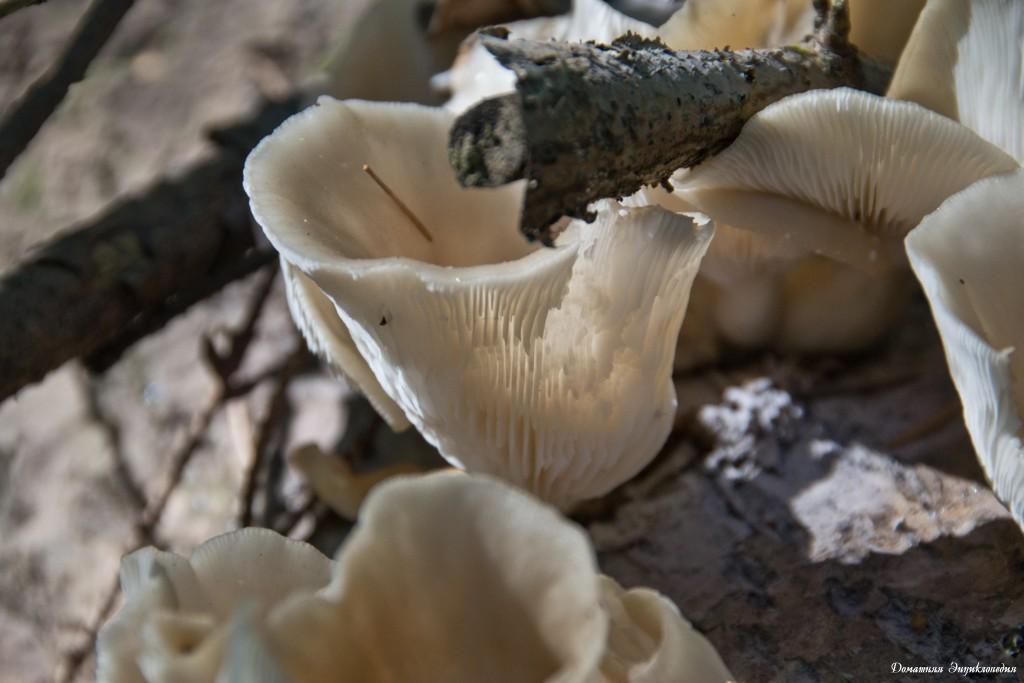
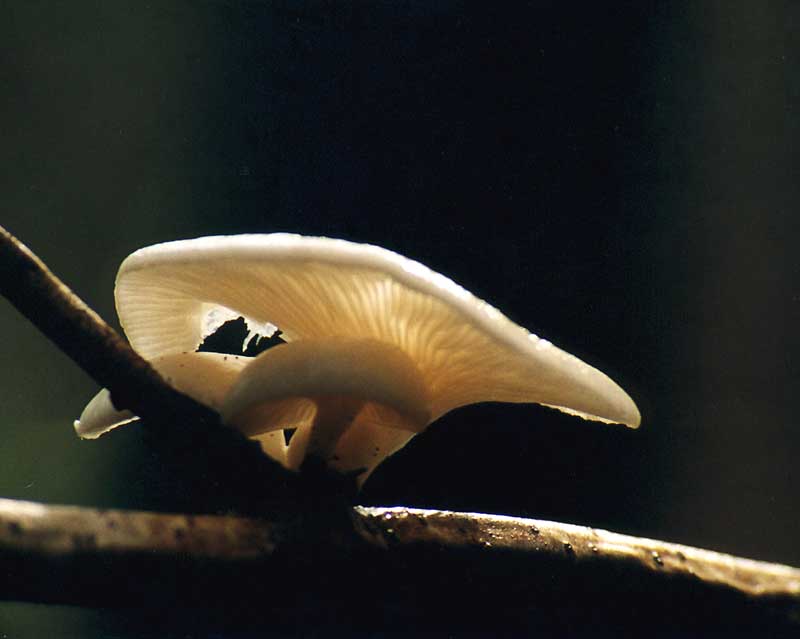
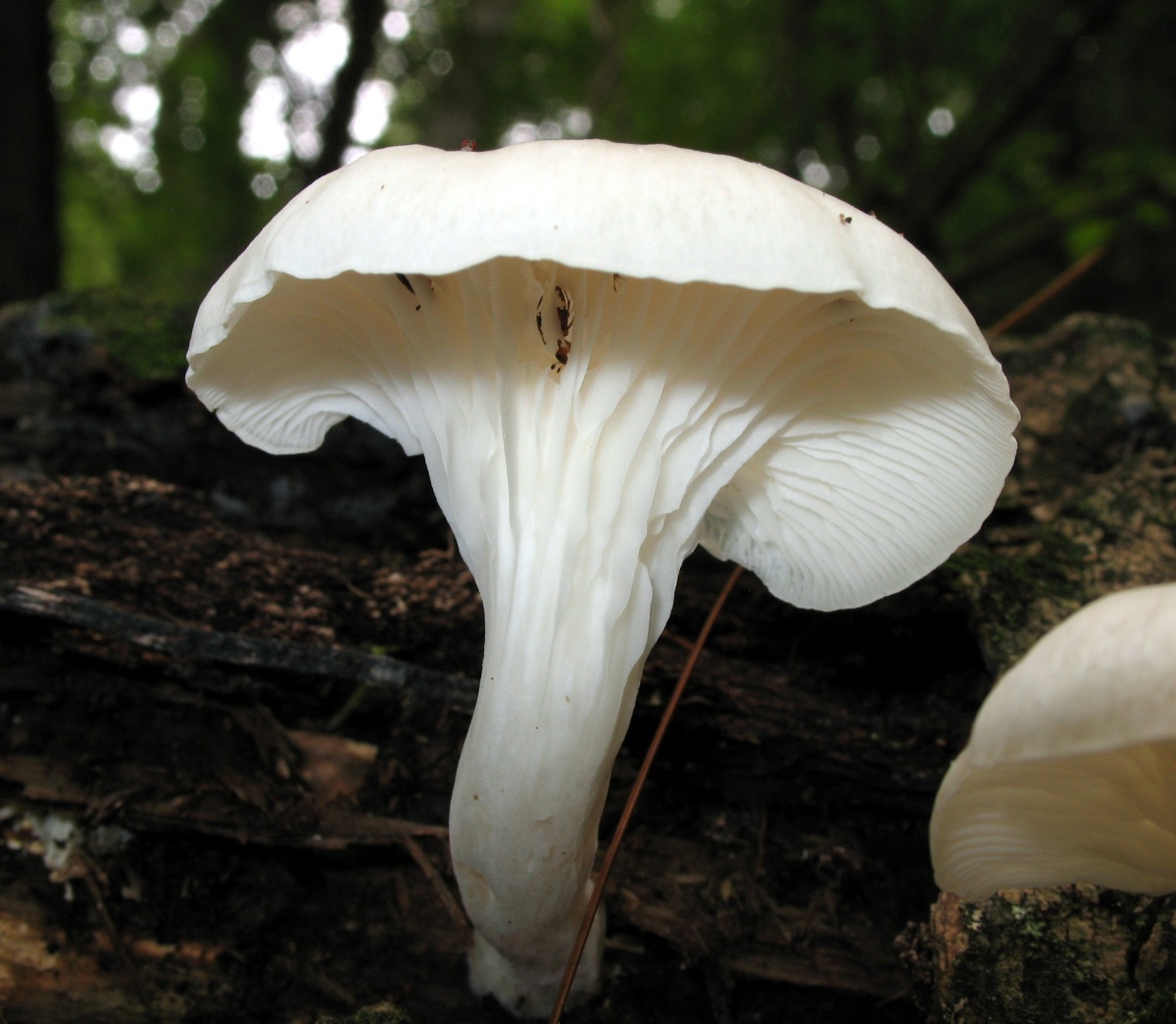
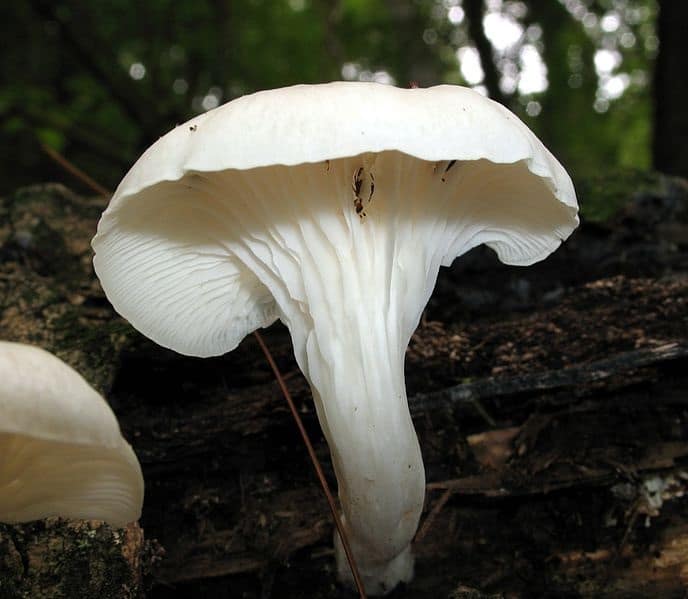
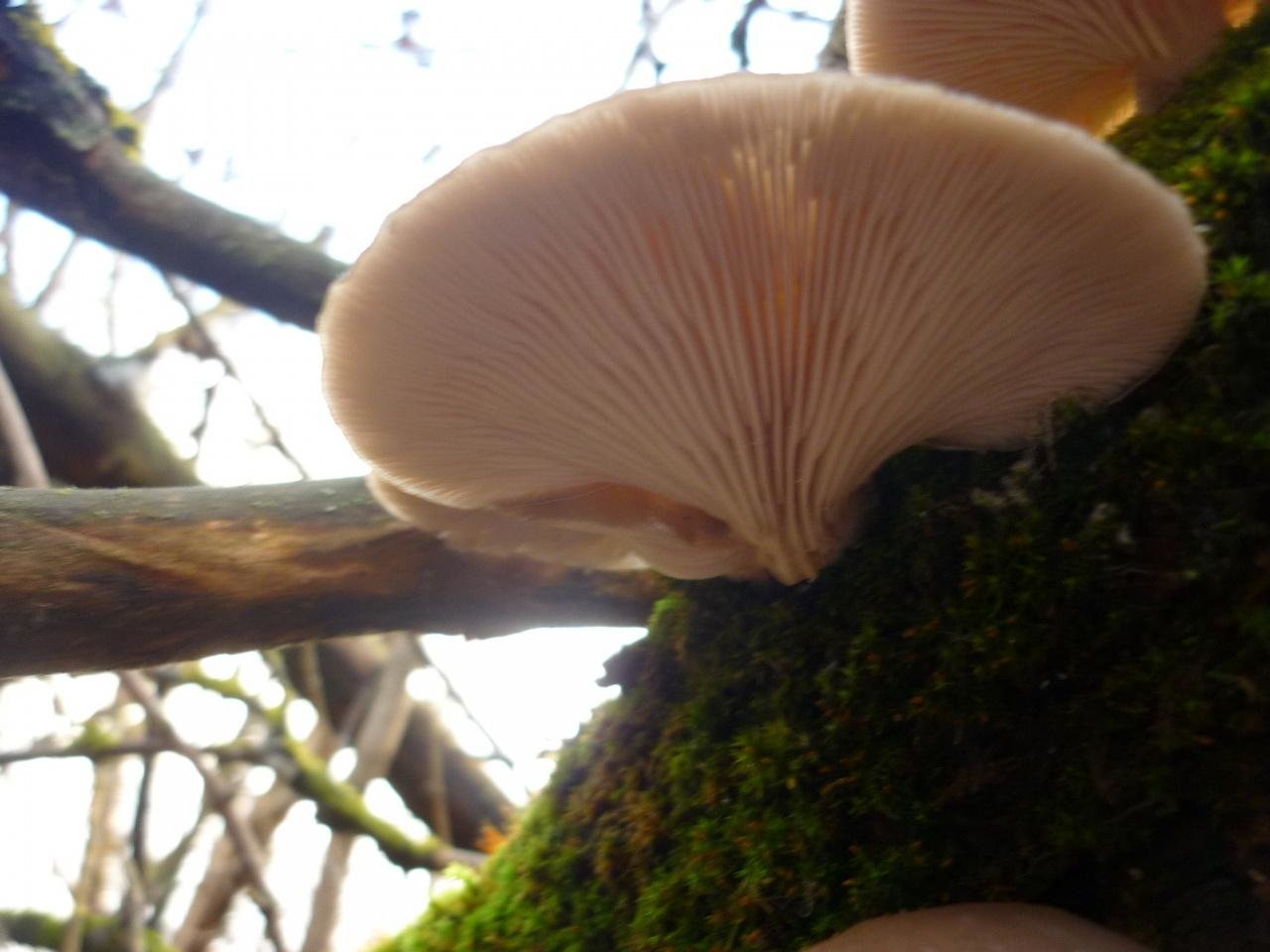
Oyster pulmonary plates are frequent, white. Several run down on the leg.

This is how the plates of oyster mushroom look like. A short leg is also visible
The flesh of the cap is white. It has a pleasant smell, but I don’t undertake to somehow associate and describe it, comparing it with something familiar.
The mushroom is not bitter at all. You can be convinced of this by licking the oyster mushroom on a cut or break.
What mushrooms does pulmonary oyster resemble? The most similar is common oyster mushroom (oyster). This is also an edible mushroom. But oyster mushroom has a denser and fleshy fruit body. The color of the cap is darker and brighter.
Oyster mushroom has no poisonous "doubles".
Oyster mushroom varieties, descriptions of varieties
What do oyster mushrooms look like? The color of the oyster mushroom cap can be yellow, grayish, lilac, white, even pink.All young mushrooms of this species have predominantly white juicy flesh, if it is young. Older specimens have a stiffer, fibrous consistency. At home, they can grow and bear fruit all year round. The main thing here is to competently maintain the required level of humidity, lighting, and air temperature. Let's look at the most popular types of oyster mushrooms, which are popular with home-based mushroom pickers.
Oyster mushroom
This is one of the most popular, valuable species due to its excellent taste. The hat can be slightly lilac or brown. This variety feels comfortable when grown at home, and with the proper approach to business, it pleases with a harvest all year round.
Oyster, photo
Oyster mushroom
It has a cone-shaped hat, which is why it bears that name. In artificial conditions, it is grown on stumps, mainly elm. The color of the cap ranges from light brown (sandy) to dark brown. Has firm pulp, pleasant, albeit slightly specific aroma.

Pink oyster mushroom
Pink oyster mushroom has another name - Pink Flamingo. It is a beautiful, fast growing mushroom with wavy edges of the cap, delicate pink color. This variety is thermophilic and requires an individual temperature approach (from + 16 ° C to + 30 ° C at different stages). Begins to bear fruit already 10 days after sowing the mycelium.
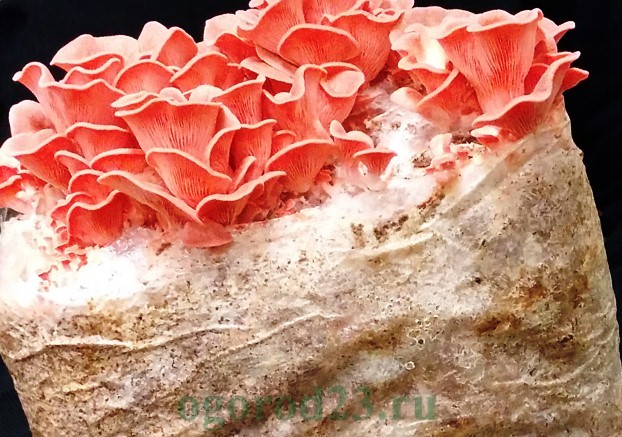 Pink or Pink flamingos, photo
Pink or Pink flamingos, photo
Lemon oyster mushroom
There is another name: Ilmovik. The mushroom has a bright conical cap. This variety is distinguished by its unpretentiousness to growing conditions, it is grown both on a substrate and on stumps. It is characterized by the closeness of fruiting bodies, graceful elongated legs. The diameter of the cap varies from 5 to 10 cm.

Steppe oyster mushroom
Steppe oyster mushroom (eringi) is also called Royal. This is the most delicious variety of oyster mushrooms, it has a fleshy dense pulp, a massive funnel-shaped leg. The mushroom cap (5-10 cm in diameter) changes. While the mushroom is growing: at first it is convex, then it becomes flat, and by the time of harvesting it is already concave. This species is grown in special large jars or cans (photo below).

Oyster mushroom
Common - the most popular variety, is grown on stumps or on various substrates. Yields a harvest from summer - until the very frost. Has a grayish yellow or brown cap.

Florida oyster mushroom
It is a light beige or grayish-white mushroom with a semicircular, slightly funnel-shaped cap (10-20 cm in diameter). Requires higher temperatures during the growing and fruiting stages.
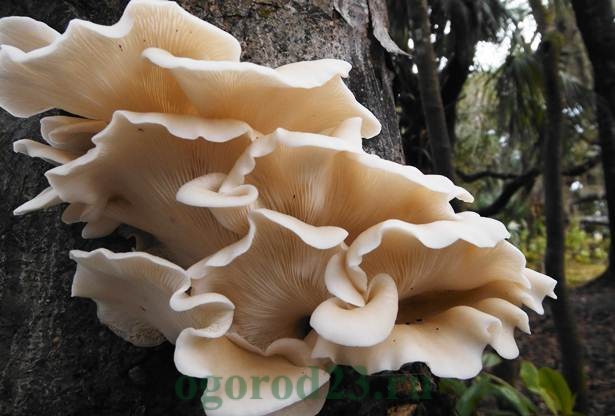

Pulmonary oyster mushroom
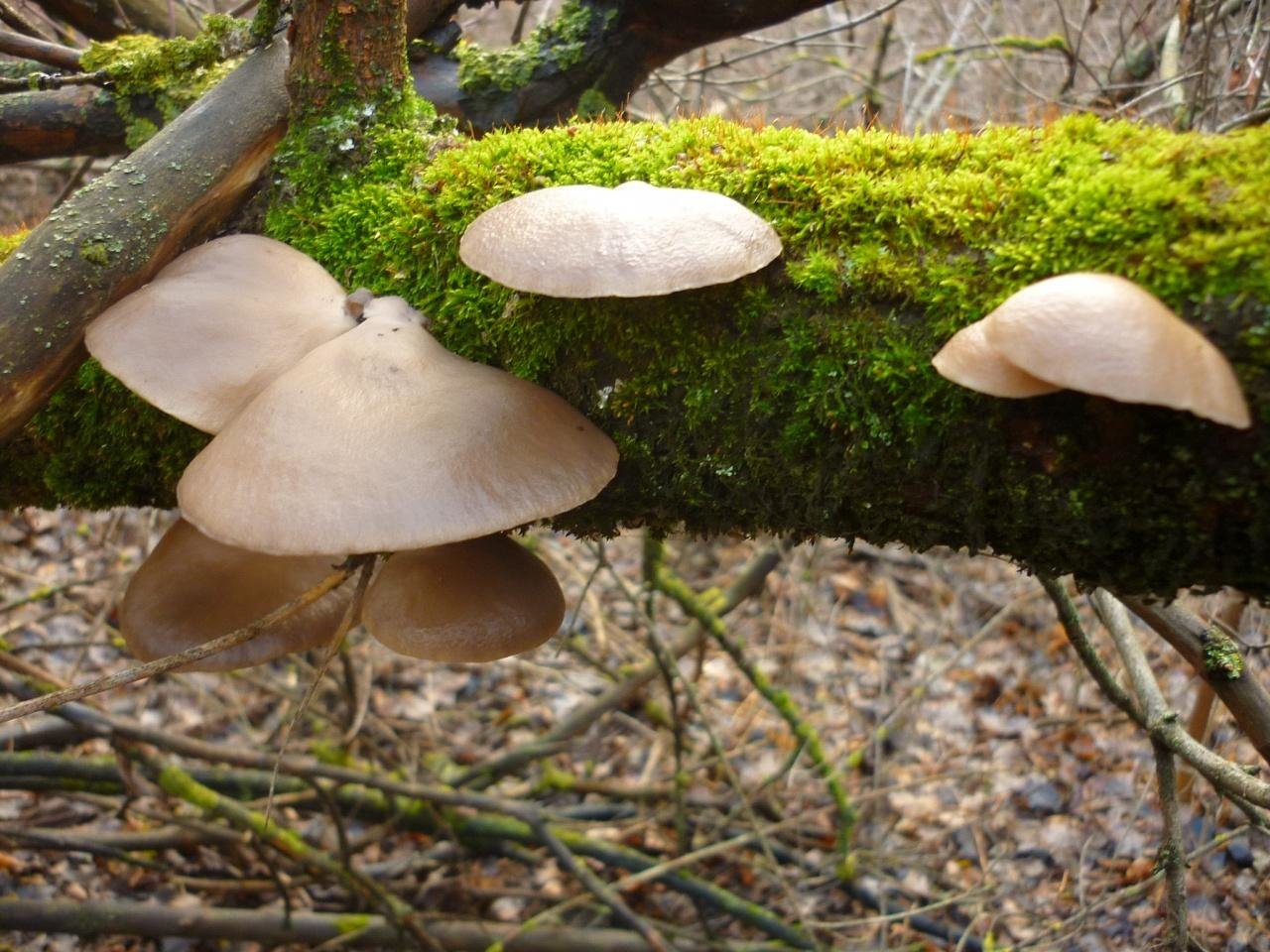
This species is eaten or processed only when young, as "old" mature mushrooms are characterized by increased rigidity. The cap of the mushroom has a tongue-like shape with slightly cracked edges, the color is white or brownish-cream. Fruiting from spring to the first cold weather.
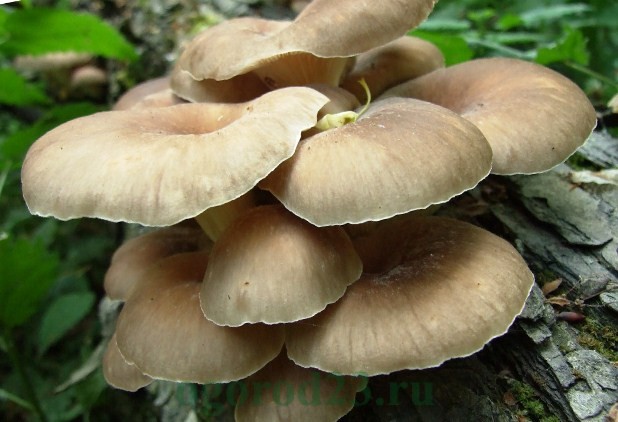

Oyster mushroom late
A mushroom with an exquisite, pronounced taste. It can be brown, gray or brown in color. It has an ear-shaped cap, which can reach large sizes (up to 25 cm in diameter), young mushrooms are darker in color, mature ones are lighter in color. It is grown on stumps or chocks (oak, poplar, aspen), as well as on substrates (straw, sunflower).
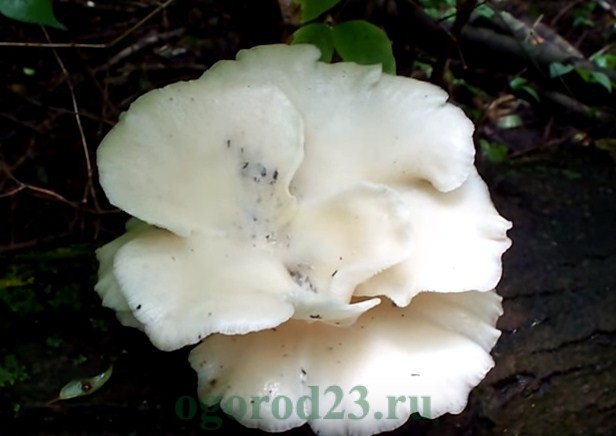

White Elf
A very tasty dietary grade. Has an elongated solid leg. The caps of this mushroom are white with slightly curly edges. The surface of the cap may be scaly. It is grown both on chocks or stumps, as well as on substrate blocks.

The above varieties of oyster mushrooms feel great when grown artificially. With proper care, they bear fruit abundantly. It is also worth mentioning hybrids, which are distinguished by high yields and unpretentiousness. The hybrids most preferred by mushroom pickers are: Dune NK-35, R-77, R-20, No. 420, No. 107.
Remember to unpack mycelium bags only with gloves. The material should be purchased from trusted sellers, the mycelium itself should be without black or green spots.
All of the above types of oyster mushrooms are adapted for growing at home.
The gastronomic and medicinal benefits of oyster mushrooms have been known to mankind for thousands of years. In Chinese medicine, these mushrooms have been used to strengthen the immune system for almost 30 centuries. With useful properties they resemble porcini mushrooms, and in terms of the content of vitamins they are not inferior to many vegetables and meat.
Who is the mushroom contraindicated
Eating the mushroom can be harmful in some cases. This is usually due to an individual intolerance to oyster mushrooms, an allergic reaction. If you get carried away with this food, you can earn bloating and heaviness in the stomach, diarrhea. Due to the difficult digestion, it is not advised to eat the mushroom for elderly people and small children. It is enough to use it twice a week.
Oyster mushrooms are contraindicated for people with diseases of the kidneys and liver, disorders of the pancreas. To avoid possible harm, it is worth listening to the following recommendations:
- Do not collect or buy oyster mushrooms that have yellow spots. They taste bad.
- Before pickling and salting, they must be processed in boiling water.
- Before eating mushrooms, you should consult with a specialist. This applies to pregnant and lactating women, as well as people with chronic gastrointestinal pathologies.
- You cannot store mushrooms for more than the prescribed period. They are kept in the refrigerator for up to 5 days.
In order for oyster mushrooms to be beneficial, you should use them in compliance with all the rules.
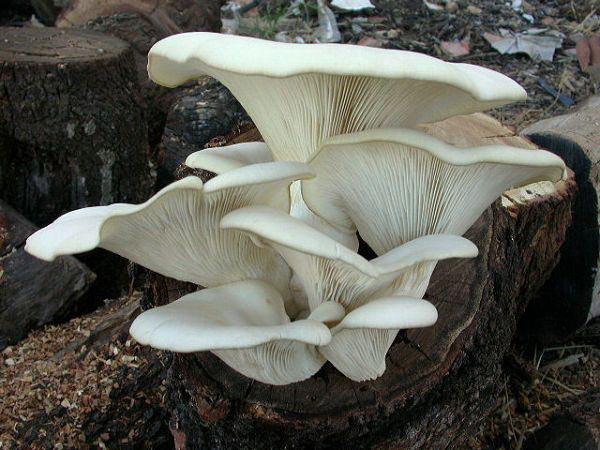
Oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus)
Synonyms:
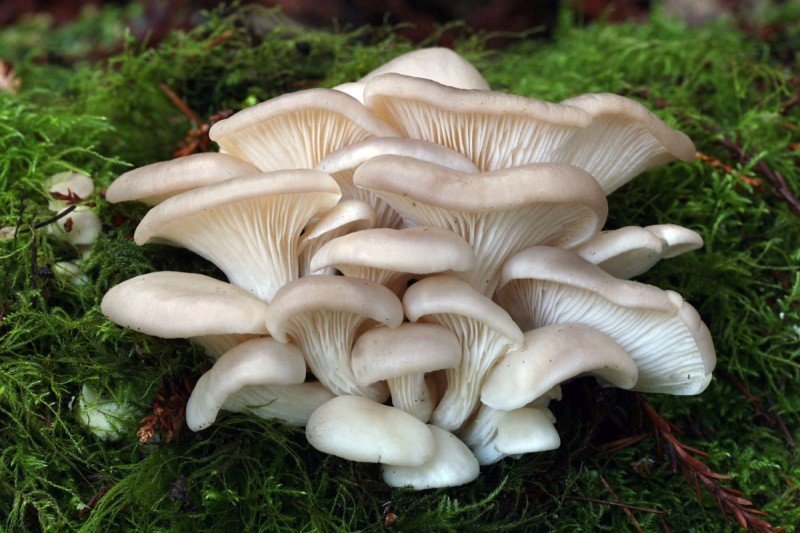

Oyster mushroom or common oyster mushroom is the most cultivated representative of the genus oyster mushroom. It is extremely convenient for cultivation due to its unpretentiousness to climatic conditions and tenacious mycelium, suitable for storage.
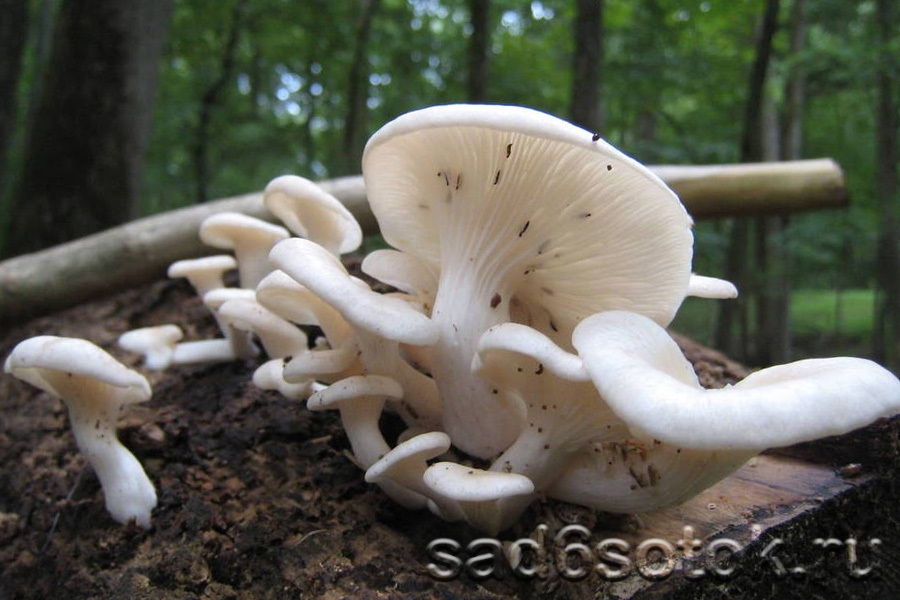
Oyster oyster mushroom cap: Rounded eccentric, funnel-shaped, ear-shaped, usually with rolled edges, matte, smooth, can take any shades in the range from light ash to dark gray (there are light, yellowish, and "metallic" options). Diameter 5-15 cm (up to 25). Several caps often form a fan-shaped, multi-tiered structure. The flesh is white, dense, becomes rather tough with age. The smell is weak, pleasant.
Oyster oyster mushroom plates: Descending along the stem (as a rule, do not reach the base of the stem), rare, wide, white in youth, then grayish or yellowish.
Spore powder: White.
Oyster leg of oyster mushroom: Lateral, eccentric, short (sometimes almost invisible), curved, up to 3 cm in length, light, hairy at the base. Older oyster mushrooms are very tough.
Distribution: Oyster mushroom grows on dead wood and weakened trees, preferring deciduous species. Mass fruiting, as a rule, is observed in September-October, although under favorable conditions it can appear in May. Oyster mushroom bravely fights frost, leaving behind almost all edible mushrooms, except for winter mushrooms (Flammulina velutipes). The "nesting" principle of the formation of fruit bodies actually guarantees a high yield.
Similar species: Oyster mushroom can, in principle, be confused with oyster mushroom (Pleurotus cornucopiae), from which it differs in a stronger constitution, a darker cap color (except for light varieties), a short stem and plates that do not reach its base. Oyster mushroom is also distinguished from whitish oyster mushroom (Pleurotus pulmonarius) by its dark color and more solid structure of the fruiting body; oak oyster mushroom (P. dryinus) - lack of a private bedspread. Inexperienced naturalists may also confuse oyster mushroom with the so-called autumn oyster mushroom (Panellus sirotinus), but this interesting mushroom has a special gelatinous layer under the skin of the cap that protects the fruiting body from hypothermia.

Edible: The mushroom is edible and even tasty when young. Artificially cultivated (whoever goes to the store saw it).Elderly oyster mushrooms become tough and tasteless.
Oyster mushroom video:
Author's notes: Surprisingly, but true: I first encountered the most common oyster mushroom only when I myself wanted it. Deliberately collided. I remembered in early September that I had never actually seen oyster mushroom in the field (shame!), And went in search of
I had to search for a long time: only on the way back, passing by a huge broken willow growing (or rather, rotting) at my gate, I noticed the strange gray "ears" defiantly bulging on the chopped trunk ...
Unlike its nondescript counterparts, oyster mushroom made a very serious impression on me. It does not look like a dried pig's ear, or a swollen overgrown chanterelle. Heavy "nests" that do not disintegrate during collection, large cozy burdocks of caps, dense white flesh, homerically huge worms ... all these signs set you up for a serious mood. Indeed, not every mushroom knows how to present itself in such a way that you want to grab a whole "nest" (with both hands, you can't drag it off with one) and carry it to show your neighbors - as I actually did.
And oyster mushroom nests can cleverly wriggle out from under the knife and fall with all their weight on the head of a hurried collector, without splitting at all.
Oyster mushroom varieties, descriptions of varieties
What do oyster mushrooms look like? The color of the oyster mushroom cap can be yellow, grayish, lilac, white, even pink. All young mushrooms of this species have predominantly white juicy flesh, if it is young. Older specimens have a stiffer, fibrous consistency. At home, they can grow and bear fruit all year round. The main thing here is to competently maintain the required level of humidity, lighting, and air temperature. Let's look at the most popular types of oyster mushrooms, which are popular with home-based mushroom pickers.
Oyster mushroom
This is one of the most popular, valuable species due to its excellent taste. The hat can be slightly lilac or brown. This variety feels comfortable when grown at home, and with the proper approach to business, it pleases with a harvest all year round.
Oyster, photo
Oyster mushroom
It has a cone-shaped hat, which is why it bears that name. In artificial conditions, it is grown on stumps, mainly elm. The color of the cap ranges from light brown (sandy) to dark brown. Has firm pulp, pleasant, albeit slightly specific aroma.
Pink oyster mushroom
Pink oyster mushroom has another name - Pink Flamingo. It is a beautiful, fast growing mushroom with wavy edges of the cap, delicate pink color. This variety is thermophilic and requires an individual temperature approach (from + 16 ° C to + 30 ° C at different stages). Begins to bear fruit already 10 days after sowing the mycelium.
 Pink or Pink flamingos, photo
Pink or Pink flamingos, photo
Lemon oyster mushroom
There is another name: Ilmovik. The mushroom has a bright conical cap. This variety is distinguished by its unpretentiousness to growing conditions, it is grown both on a substrate and on stumps. It is characterized by the closeness of fruiting bodies, graceful elongated legs. The diameter of the cap varies from 5 to 10 cm.

Steppe oyster mushroom
Steppe oyster mushroom (eringi) is also called Royal. This is the most delicious variety of oyster mushrooms, it has a fleshy dense pulp, a massive funnel-shaped leg. The mushroom cap (5-10 cm in diameter) changes. While the mushroom is growing: at first it is convex, then it becomes flat, and by the time of harvesting it is already concave. This species is grown in special large jars or cans (photo below).

Oyster mushroom
Common - the most popular variety, is grown on stumps or on various substrates. Yields a harvest from summer - until the very frost. Has a grayish yellow or brown cap.
Florida oyster mushroom
It is a light beige or grayish-white mushroom with a semicircular, slightly funnel-shaped cap (10-20 cm in diameter).Requires higher temperatures during the growing and fruiting stages.
Pulmonary oyster mushroom
This species is eaten or processed only when young, as "old" mature mushrooms are characterized by increased rigidity. The cap of the mushroom has a tongue-like shape with slightly cracked edges, the color is white or brownish-cream. Fruiting from spring to the first cold weather.

Oyster mushroom late
A mushroom with an exquisite, pronounced taste. It can be brown, gray or brown in color. It has an ear-shaped cap, which can reach large sizes (up to 25 cm in diameter), young mushrooms are darker in color, mature ones are lighter in color. It is grown on stumps or chocks (oak, poplar, aspen), as well as on substrates (straw, sunflower).

White Elf
A very tasty dietary grade. Has an elongated solid leg. The caps of this mushroom are white with slightly curly edges. The surface of the cap may be scaly. It is grown both on chocks or stumps, as well as on substrate blocks.

The above varieties of oyster mushrooms feel great when grown artificially. With proper care, they bear fruit abundantly. It is also worth mentioning hybrids, which are distinguished by high yields and unpretentiousness. The hybrids most preferred by mushroom pickers are: Dune NK-35, R-77, R-20, No. 420, No. 107.
Remember to unpack mycelium bags only with gloves. The material should be purchased from trusted sellers, the mycelium itself should be without black or green spots.
All of the above types of oyster mushrooms are adapted for growing at home.
The numerous advantages of some varieties of mushrooms contributed to the active development of their industrial cultivation.
Although initially attention was paid to truffles, today oyster mushrooms are also very popular. The reason for such popularity lies in the taste of this mushroom, which is not inferior to champignon
Oyster mushroom varieties are numerous and unpretentious, and their cultivation will require much less attention and care.
Beneficial features
Variety of varieties
Hybrids
Small Tips
Distribution and fruiting period
The species grows mainly in birch forests, aspen forests. It settles mainly on stumps, dry or rotting tree trunks, sometimes it is found on weakened trees. Prefers linden, aspen, birch. It is very rare to be found on dying wood and coniferous stumps (fir, spruce).
Usually the mushroom grows in large companies (sometimes there are more than 10 fruiting bodies in one group), while they grow together with their legs. The period of active fruiting begins in May and lasts until September-October.

Similar species
In nature, there are several species that have a certain similarity with this representative of the mushroom kingdom. For example, oyster mushroom (Pleurotus Ostreatus) looks very much like the heroine of our article, but differs from her in a stronger fruiting body, and her hat is darker. It is an edible tasty species but is only eaten at a young age.
There are also many similarities between pulmonary and plentiful or horn-shaped oyster mushrooms (Pleurotus Cornucopiae). But the second is more graceful in appearance and has a fluff on the edge of the cap. It is also edible.
Lemon oyster mushroom
Ilmak
Lemon oyster mushroom (Pleurotus citrinopileatus) is a cap mushroom from the Ryadovkov family, belongs to the Pleurotus genus (Pleurotus, Oyster mushroom).
External description
Lemon oyster mushroom (Pleurotus citrinopileatus) is a variety of decorative and edible mushrooms, the fruiting body of which consists of a stem and a cap. It grows in groups, and individual specimens grow together to form a beautiful lemon-colored mushroom cluster.
The mushroom pulp is white and has a flour smell. In young specimens, it is soft and tender, and in ripe mushrooms it becomes rough.
The stem of the mushroom is white (yellow in some specimens), comes from the central part of the cap. In mature mushrooms, it becomes lateral.
The diameter of the cap is 3-6 cm, but in some specimens it can reach 10 cm.In young mushrooms, the cap is thyroid, in ripe fruit bodies a large depression appears on it, and a little later the cap becomes funnel-shaped, and its edges are lobed. The bright lemon color of the cap of overripe, old mushrooms fades and becomes whitish.
The lamellar hymenophore consists of frequent and narrow plates, the width of which is 3-4 cm. They are slightly pinkish in color, descending to the pedicle in the form of lines. The spore powder is white in color, but in many specimens it has a pink-purple hue.
Season and habitat of the mushroom
Lemon oyster mushroom (Pleurotus citrinopileatus) grows in the southern part of Primorsky Krai, in mixed (with coniferous and broad-leaved trees) forests, on living or dead elms. This mushroom also develops well on elm deadwood, and in the northern regions and the middle vegetation zone it is also found on the trunks of birches. Lemon oyster mushrooms are widespread in the southern parts of the Far East; they are well known to the local population there and are used by them as edible mushrooms. Begins to bear fruit in May and ends in October.
Edibility
Lemon oyster mushroom (Pleurotus citrinopileatus) is an edible mushroom. Possesses good taste, it is used salted, boiled, fried and pickled. Lemon oyster can be dried. However, in ripe fruit bodies, only the cap is suitable for eating, since the stem of the fruit body becomes fibrous and rough. In some specimens, a part of the cap above the leg is also endowed with such qualities, so it also has to be cut out before cooking the mushrooms for food. Grown in artificial conditions for the purpose of implementation.
Other information about the mushroom
This oyster mushroom was named lemon yellow for its characteristic cap color, similar to the color of a ripe lemon. The mushroom retains its bright yellow color throughout its entire growth. Lemon oyster mushroom substrate mycelium is resistant to cold and frost. The mushroom itself is thermophilic, has a moderate taste properties, becomes a real decoration for the garden.
Mushroom photo Lemon oyster mushroom
from questions in recognition: