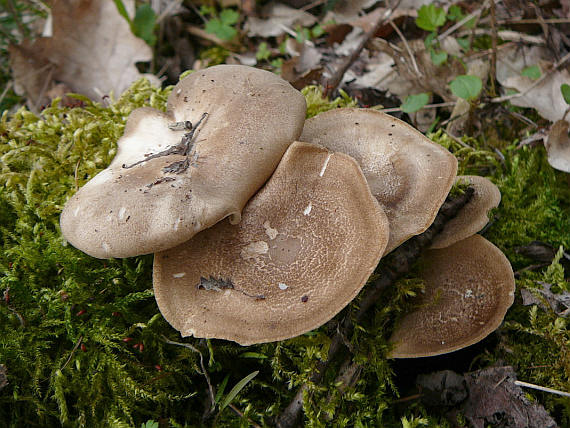
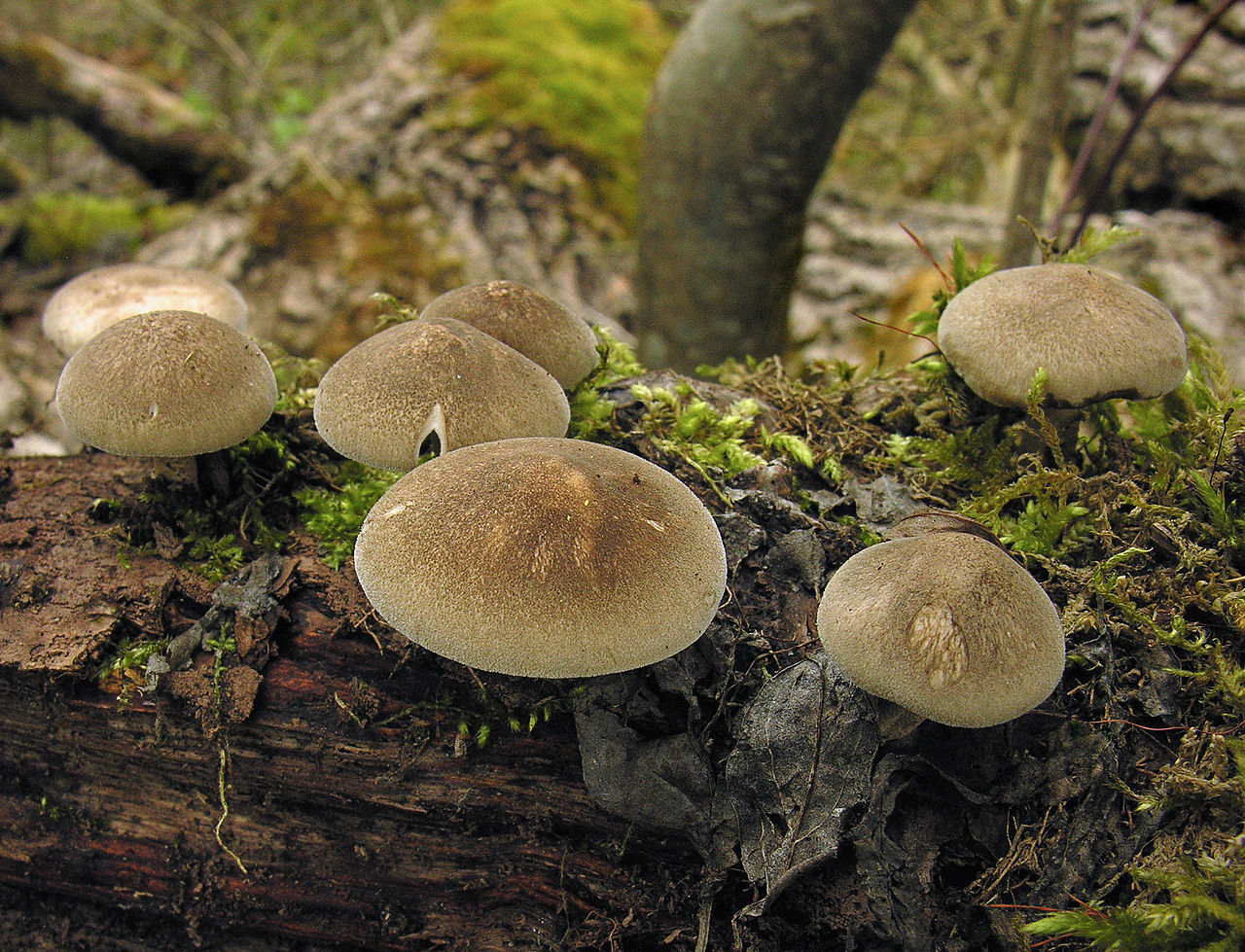
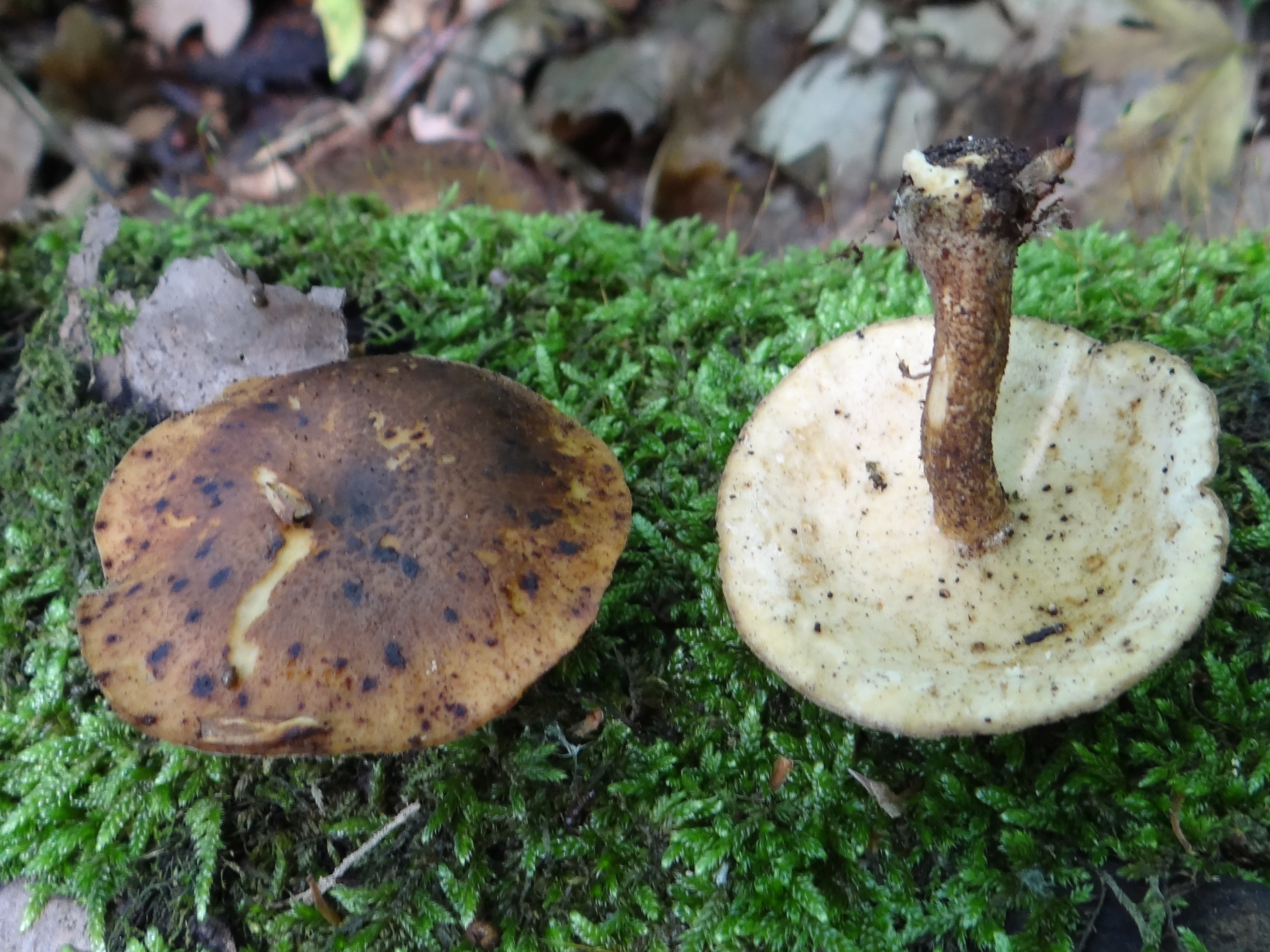
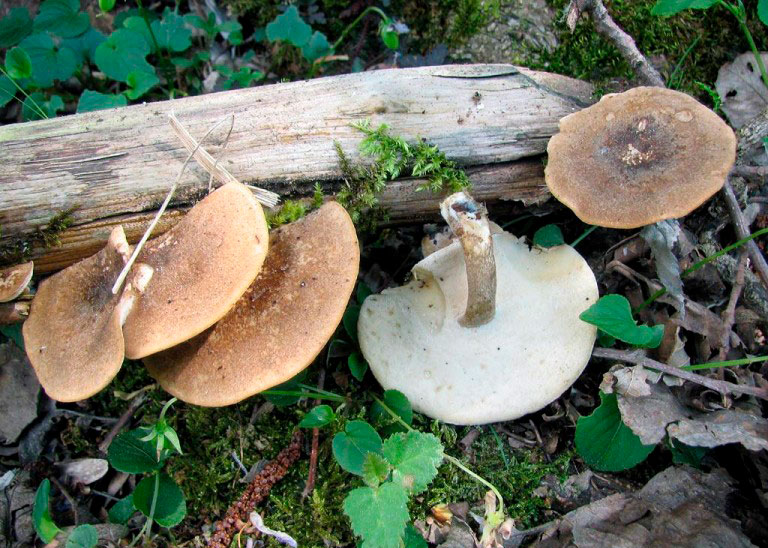
White mushroom. Borovik - white mushroom
The mushroom kingdom has its own king - the Borovik mushroom or the White mushroom. He received this title for a reason. Compared to other mushrooms, Borovik stands out due to its size and taste. It also contains many vitamins and nutrients. Every mushroom picker is happy to find such a mushroom "treasure" in the forest.
The Boletus mushroom grows in almost every forest on the planet, except Australia. He prefers the neighborhood of pines, fir trees, birches and oaks.
Description of the Borovik mushroom
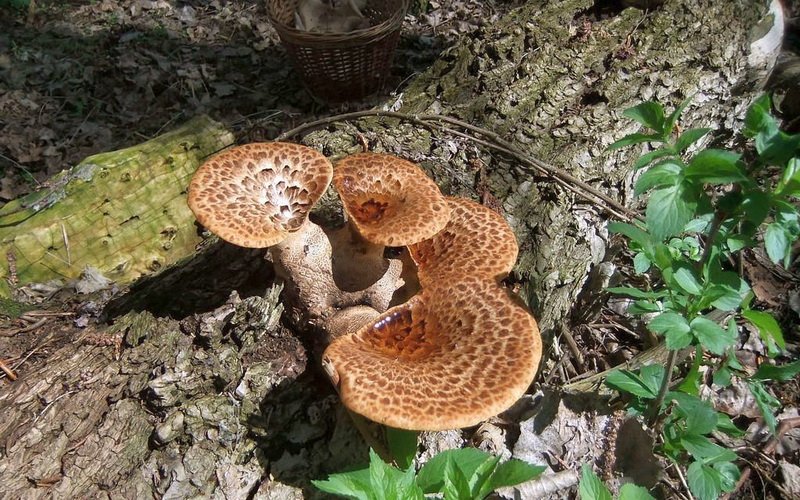
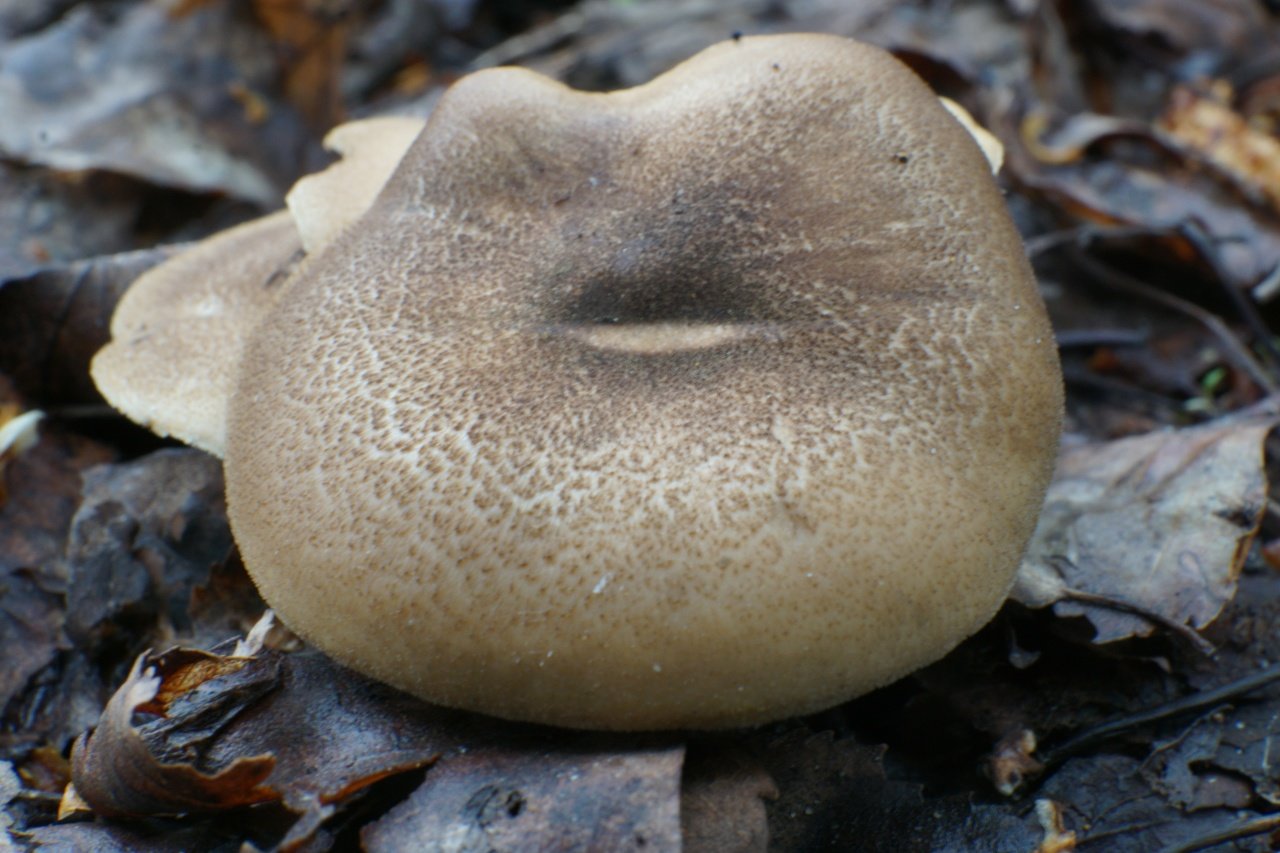
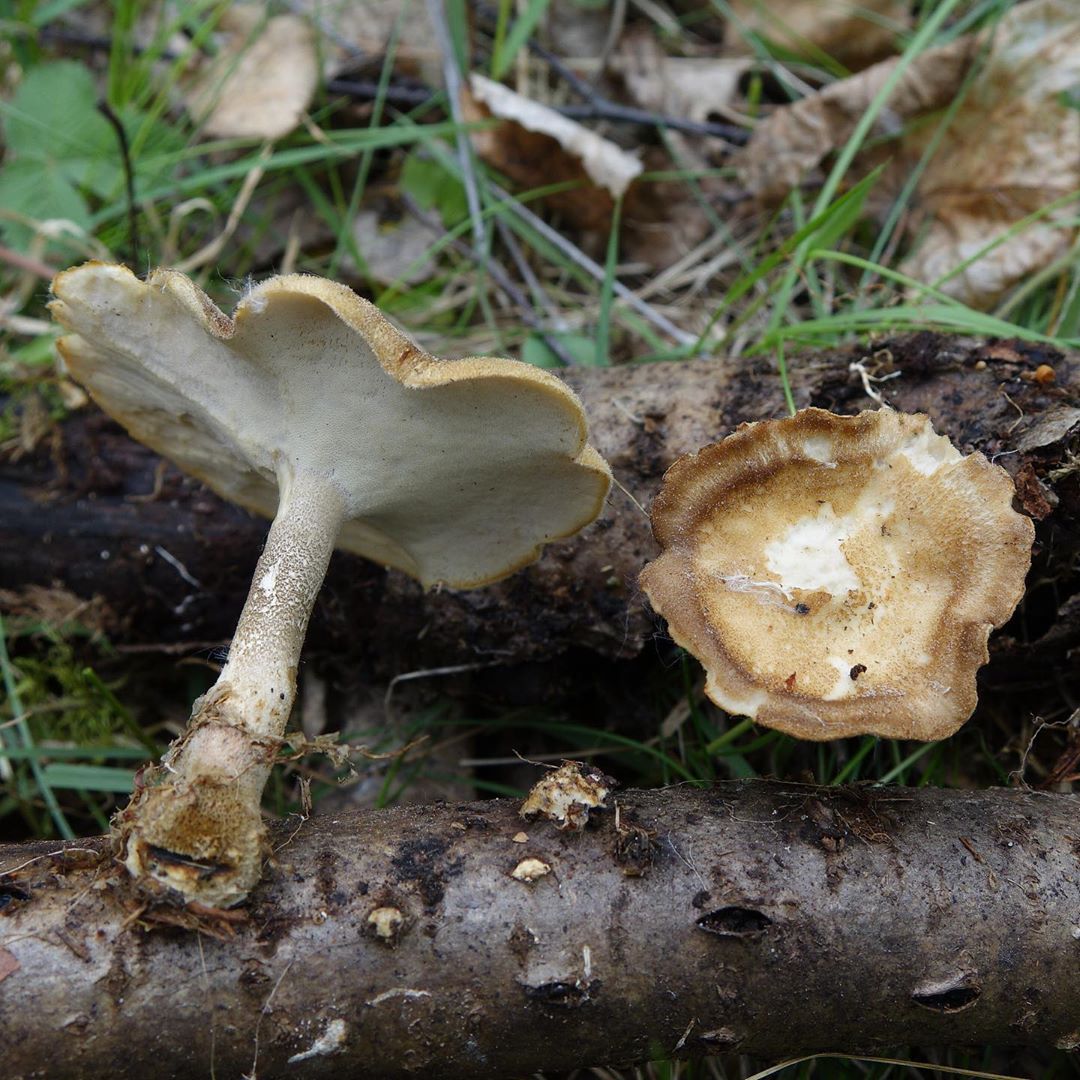
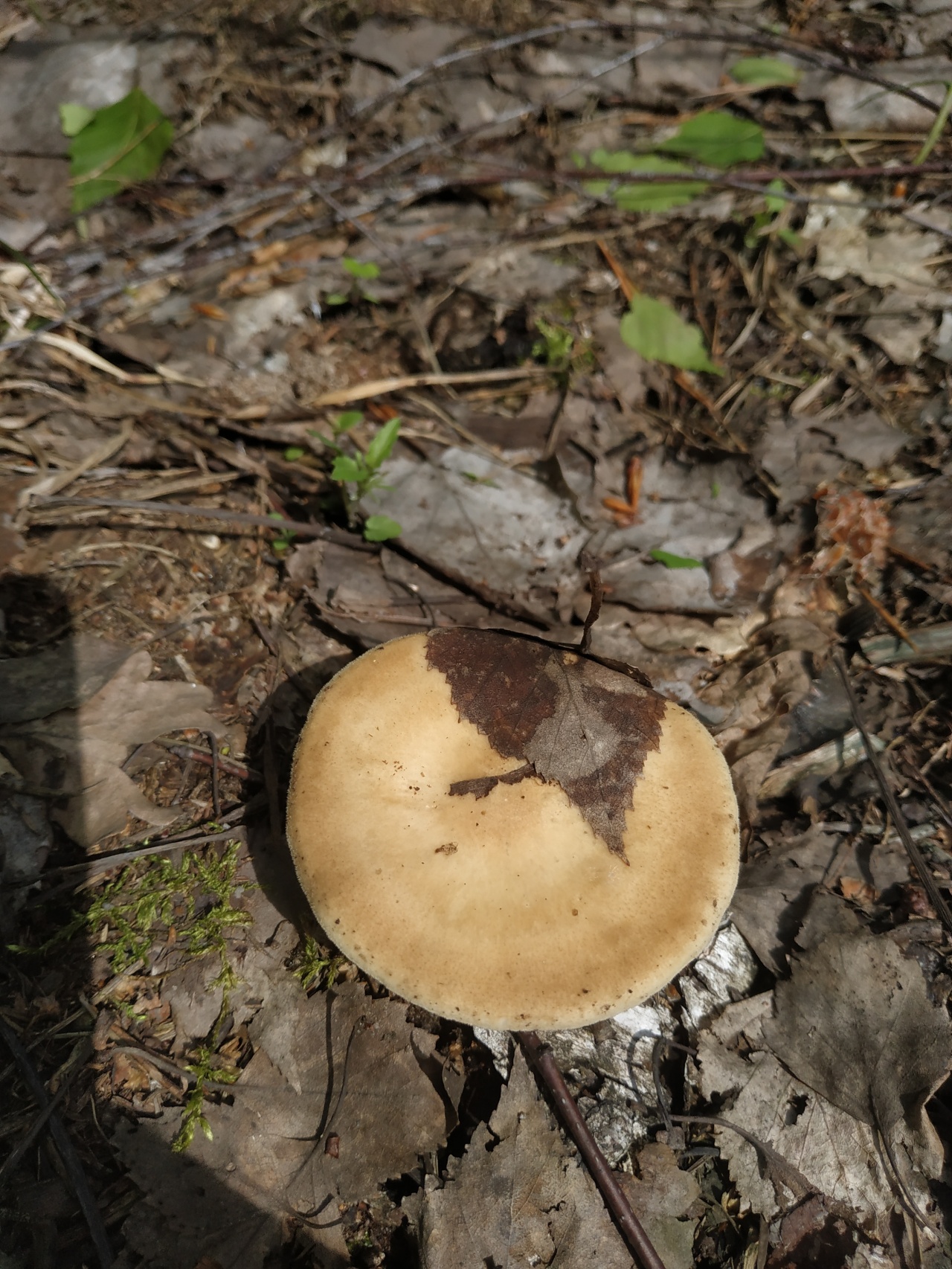
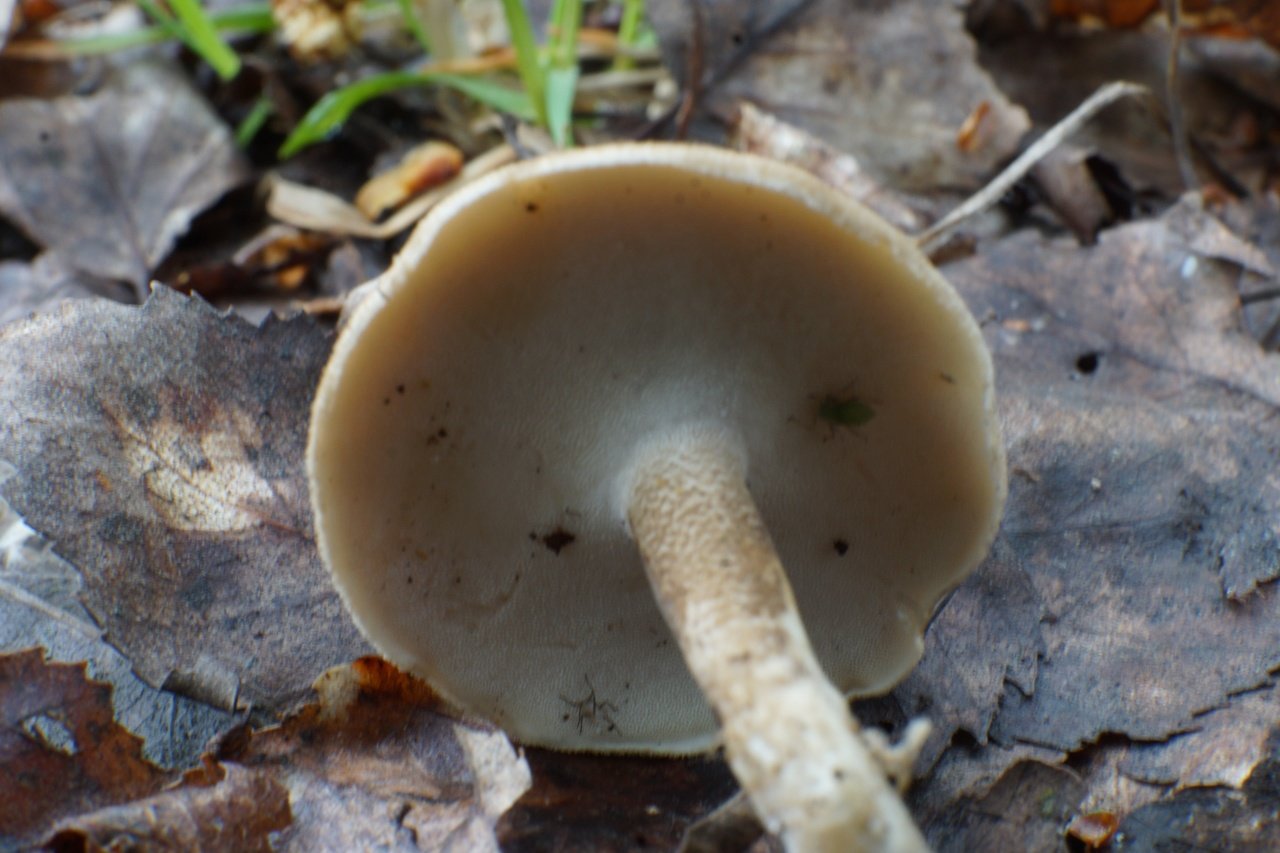
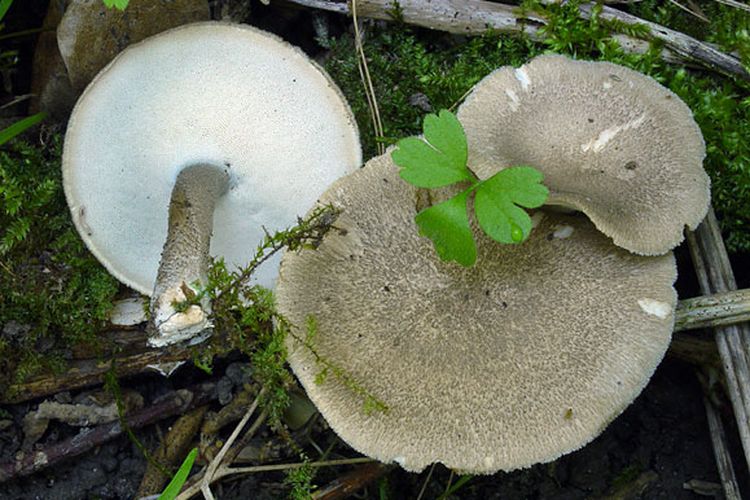
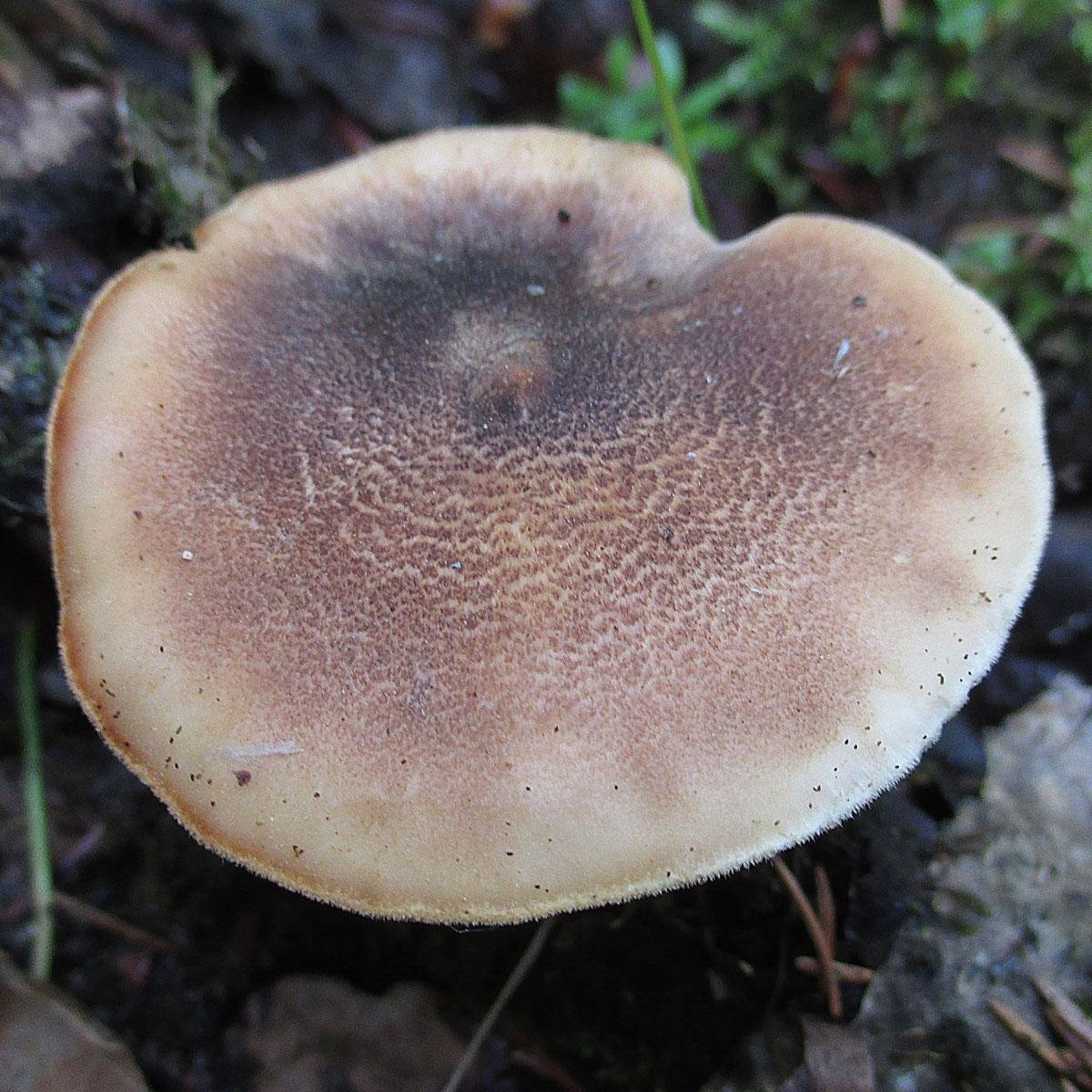
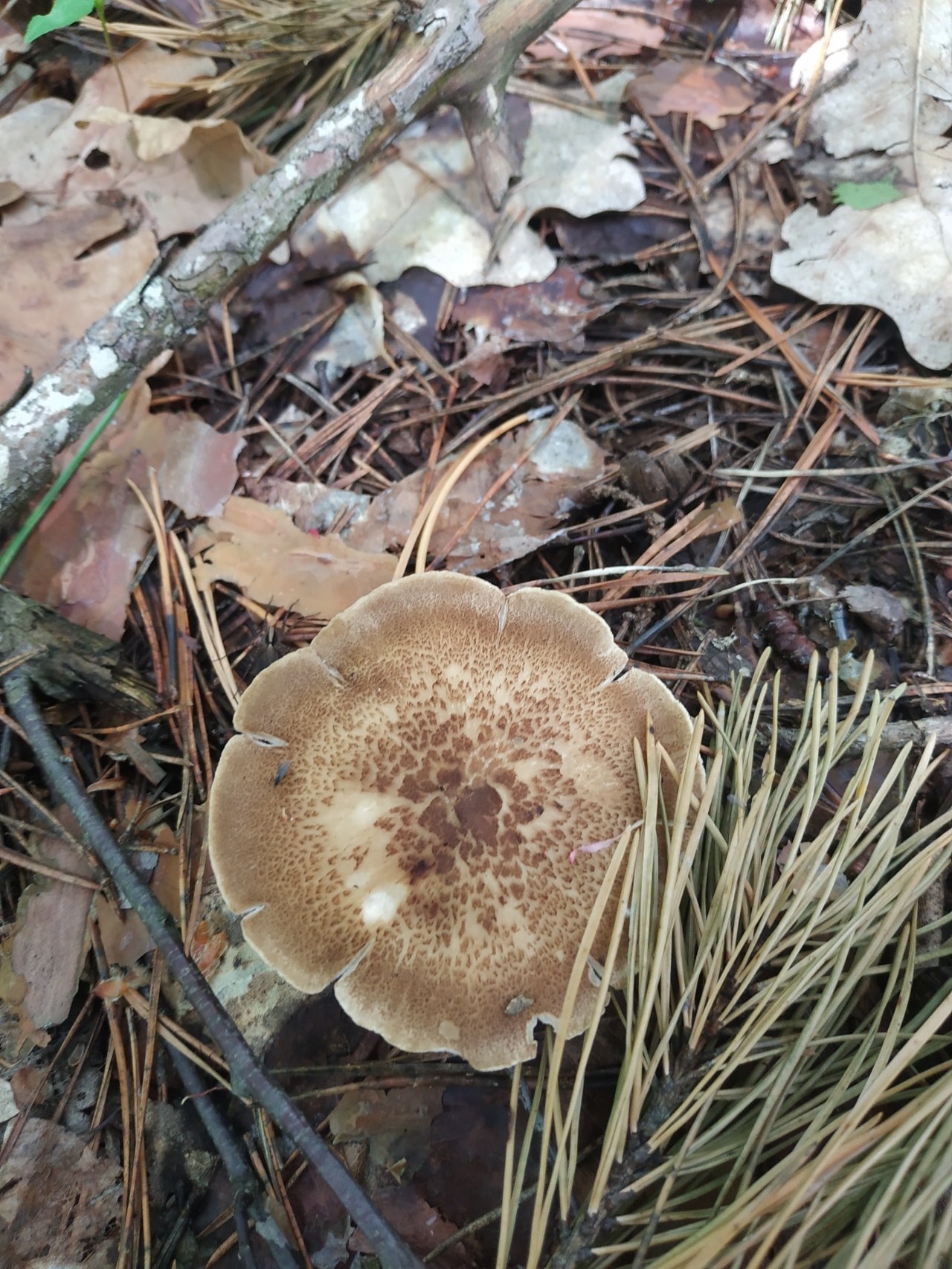
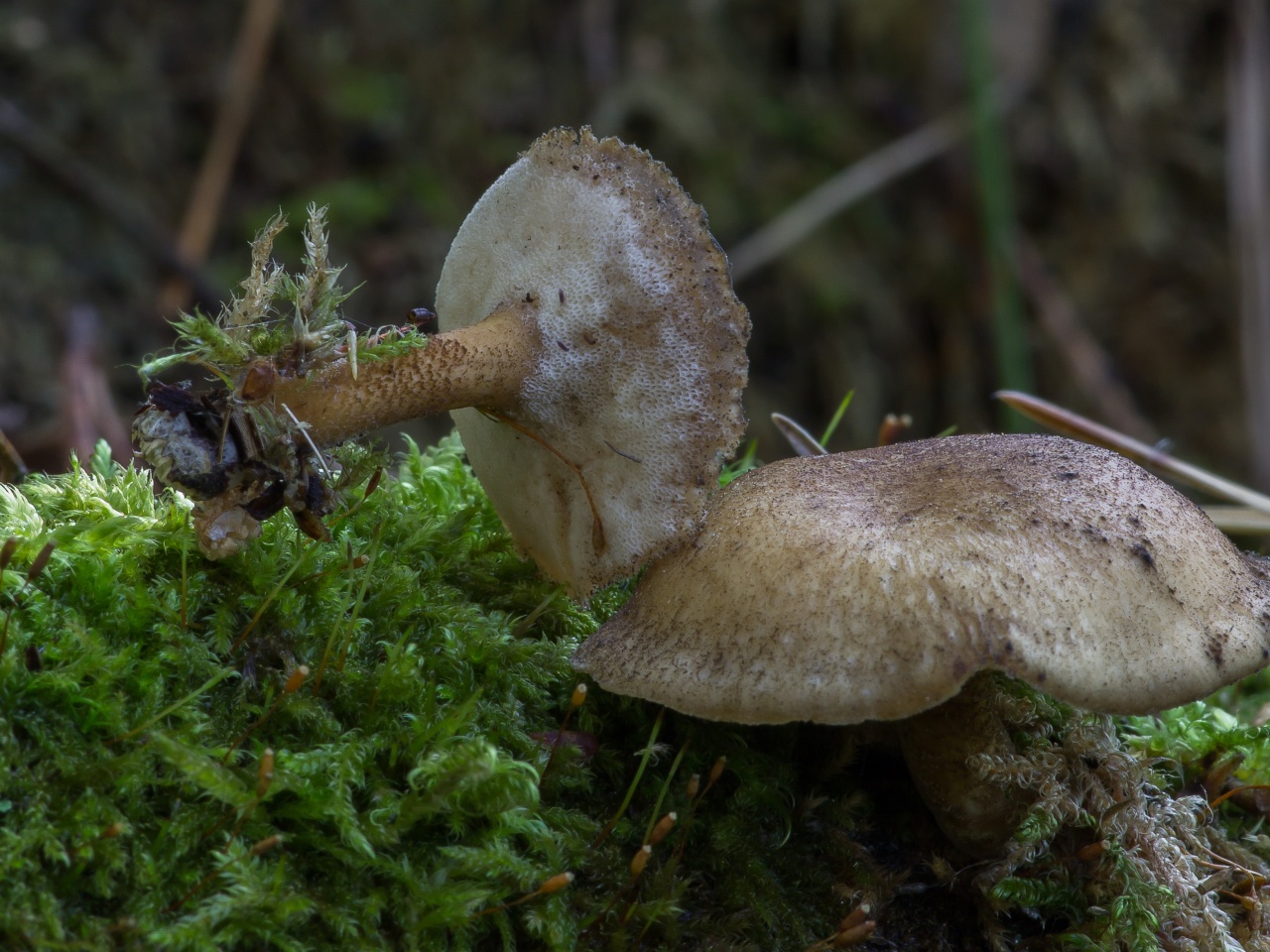
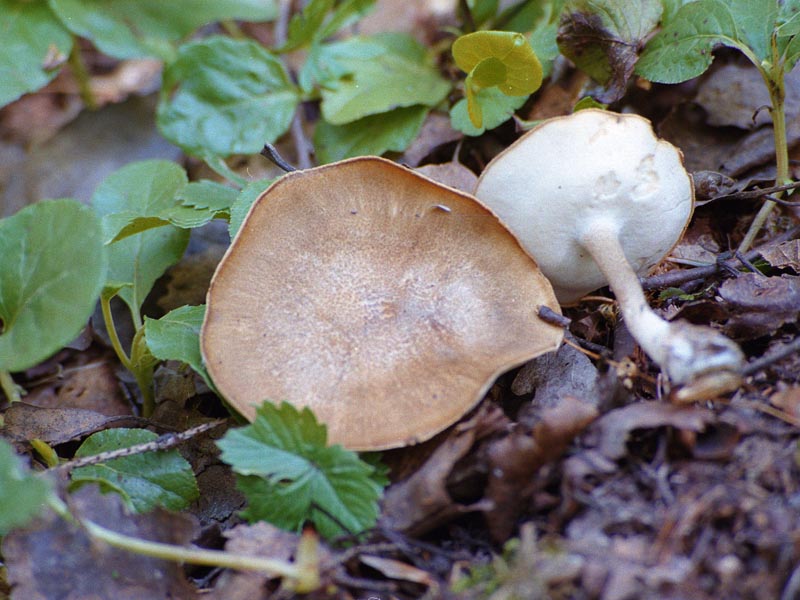
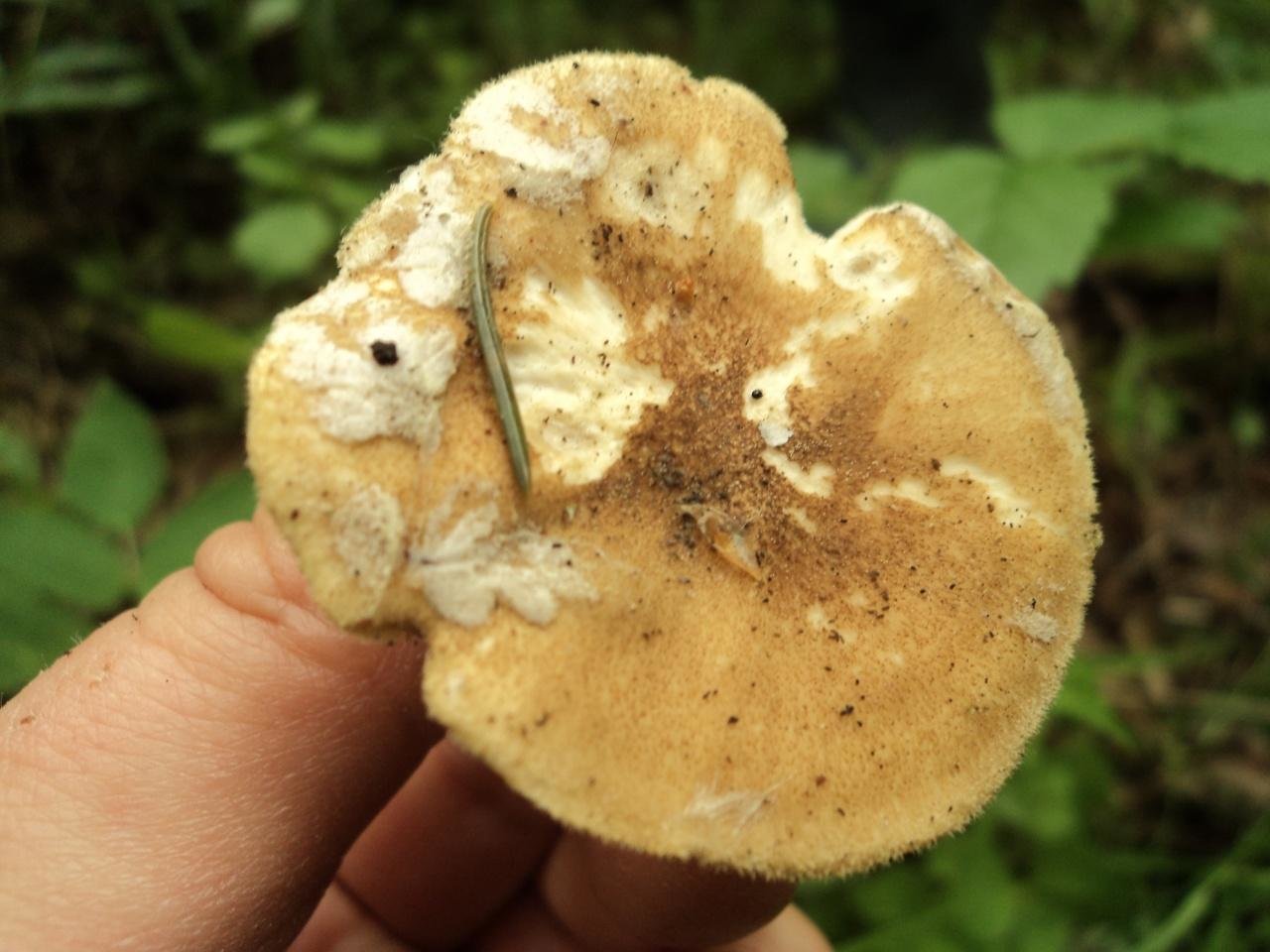
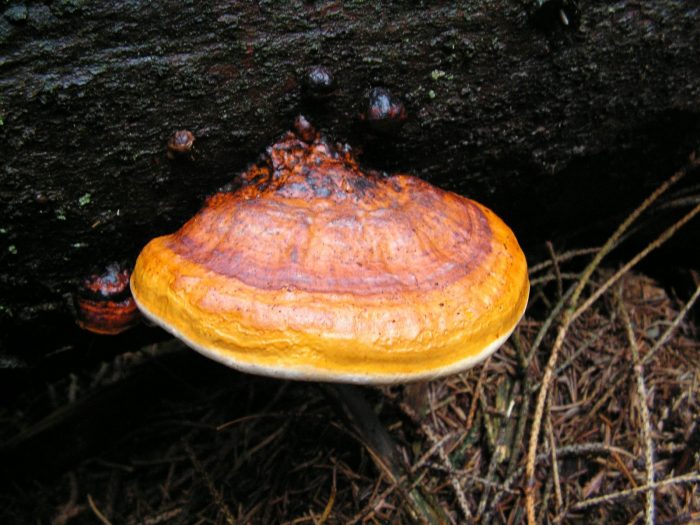
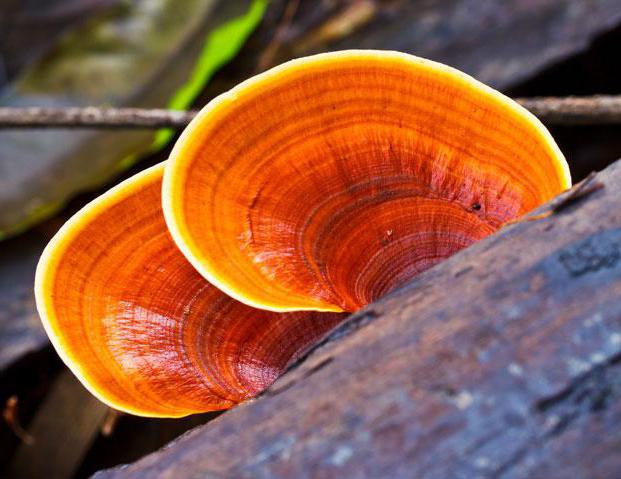
Boletus is difficult to confuse with other mushrooms due to its size. His hat grows in diameter from 7 to 30 cm, has a pillow shape, and is smooth or velvet to the touch. The color of the cap depends on the variety and the environment: lemon yellow, orange, reddish brown or purple. The leg reaches a length of 20 centimeters or more, has a thickening in the middle and below. Its fibrous surface is flat or scaly. The inside is white or lemon-colored, and on the cut it is blue, red or white.
There are several times more nutrients in Borovik than in meat and even more than in fish. The mushroom helps the digestive system and increases appetite. It also helps to fight many diseases, thanks to the presence of a large amount of vitamins.
What does it look like? Instructions for grade 3 children
Despite the fact that the Borovik mushroom most often has a yellow leg and a brownish cap, it is also called White. This is because if you break the mushroom, then inside it will be snow-white. It is worth remembering that the color of the fungus can vary depending on the age and species.
- Bronze Borovik grows in mixed forests in southern Russia, where there are pine trees. The mushroom is not large in height, about 12 cm. The leg is bronze in color, the cap is dark, almost black, up to 17 cm in diameter. It is rare and grows singly.
- Boletus reticulated or White oak mushroom may appear in May. You need to look for it in mountainous areas under an oak tree, less often under a beech or chestnut tree. Borovik got its name because of the hat, which cracks over time and becomes covered with a pattern similar to a grid. The hat is convex in a light brown shade.
- Girlish Borovik has a velvety brown-yellow or red-brown hat, then it becomes smooth. The leg is shaped like a mace and is covered with a net that disappears with growth.
- Maiden Boletus grows in mixed forests. Prefers the neighborhood of firs, calcareous soil and a moderately warm climate.
- Bicolor Boletus grows in North America. The hat and the bottom of the leg are pink, and the top is yellow.
- White mushroom is a famous and widespread type of Borovik. Grows under conifers and birches. The brown cap grows up to 30 cm. The leg is light up to 10 cm. In height. The surface of the mushroom is dry, but becomes shiny after rain.
Stages of development
False tinder fungus, like other species, grows not only in Russia, but also in Europe. It can be found both on living and already dead trees. In this case, the damage is foci. Infection of living trees occurs in places of damage to the bark and when spores of the fungus enter the cracks. When the decay process is just beginning, the wood takes on a brown color. After that, light yellow spots are formed. In subsequent stages, black lines appear on yellowish and off-white areas of rot.
Even someone who is not well versed in mushrooms knows that certain mushrooms can be eaten, and some of them are inedible. There are even representatives of the mushroom kingdom that are extremely harmful. When they grow on a tree, it rots. These types include the false tinder fungus, which can live up to 80 years. This mushroom is very widespread and can be seen quite often in the forests of our country.
general characteristics
This mushroom is long-lived and is found in areas where there are many trees. For them, this is a real mortal enemy. As it grows, it causes the formation of white rot. If a tree is infected with such a fungus, then it will die pretty quickly. This happens because a false tinderpop appeared on the tree, which, by the way, is not difficult to determine the age of. Each year, a new layer appears on the bottom of the mushroom. It is almost impossible to separate them, but they are easy to count.
Unlike the real tinder fungus, the surface of the false species is riddled with cracks. They are quite profound. This species belongs to polyporous fungi. Most of them are inedible. Such a representative belongs to the genus fellinus, which has several species, for example, the pine sponge, which includes the false pine tinder fungus.
False tinder fungi have many other names. They are also called burnt, and the people call them tree mushrooms. If you literally translate the name from Latin, you get a "cork". The variety of false tinder fungi fits into one genus, Fellinus. This name was given to these mushrooms for a reason. Indeed, in adulthood, it is somewhat reminiscent of a cork, the location of which is the bark of a tree.
Description
The surface of the mushroom is covered with a black crust. The mushroom is attached to the tree sideways. The body is round with blunt ends. The shape looks like a hemisphere or hoof. The diameter of the mushroom can be up to 25 millimeters, and in height with its growth it is 12 cm.
It is very difficult to distinguish different types of mushrooms by external signs, but you can do this by the type of tree on which it grows. Some of them prefer poplar, others - pine, other types of trees. The false tinder fungus belongs to perennial mushrooms, but it cannot be attributed to the tubular species, since the location of the tubes is the inner part of the fruit itself. One new layer is formed annually. It is represented by a hard hoof-like growth. It is characterized by significant color variability with different shades. The color can be chestnut or even cherry hues.
The mushroom is very tough, so it is not eaten. Its hardness cannot be eliminated even if it is boiled for a long time. But one should not assume that this representative is useless for people. It is widely used for medical purposes.
Characteristics of healing properties
If in the old days this mushroom, in crushed form, was used only as smoking mixtures, now it is used for medicinal purposes. Chinese folk medicine uses this mushroom for the prevention and treatment of cardiac pathology, conditions caused by liver pathology, and the prevention of oncology. But it should be said that only the mushroom that grows in Taiwan can be used to fight cancer. In addition, the mushroom can be used as a preventive measure against blood clots.
Natural prevalence
It is quite widespread in European countries and on the territory of our country. The place of its growth is deciduous and coniferous forests. Most often it can be seen on the trunk of a birch tree. It can appear not only on a sick, decaying tree. It is likely that it will appear on healthy trees as well. In addition, he prefers to grow on stumps, in dead wood. More often it is characterized by a single growth, but it is not uncommon to find couples. Fruit formation is observed during the warmest season. It starts in May and ends in December.
Interesting Facts
The tissue of the fruit tree is used in medicine as a hemostatic agent, therefore, the people call the mushroom a blood sponge.
The fungus is found in forests of any type, but the particular damage is caused to the vegetation of Siberia. He massively destroys wood not only in the forest, but also in warehouses.
Mushroom tincture is recommended for people with cancer. Long-term treatment is believed to help stop the process of cancer cell division.
In Russia, tinder mushrooms have long been used as fuel. Tinder fungus does not burn well, but after it begins to smolder, it retains heat well and keeps fire.
Bordered polypore is a permanent link in forest biocenoses. The fungus destroys organic residues, mineralizing them, and accelerates the circulation of mineral compounds. Woody, shrubby, herbaceous plants are fed.
The meaning of the tinder fungus is false
False polypore in nature has a meaning as a saprophyte that decomposes wood and turns it into substances available for assimilation by other plants.
False tinder fungus can cause significant damage to forestry, acting as a parasitic fungus and infecting living trees. Destroying cellulose and lignin, the fungus is able to quickly make the tree in which it settled, "lifeless".
At the same time, the false tinder fungus should be considered as a medicinal mushroom. Substances from its composition have antitumor, hepatoprotective (liver protection) action, help to strengthen the immune system.
It is necessary to collect only young fruiting bodies of a false, small-sized tinder fungus. They need to be cut into pieces and dried, like chaga, at a temperature not exceeding 60 °.
Of course, we are not talking about the use of the mushroom for food. A woody fruiting body is not the most suitable object for this. But here it is to dry the tinder fungus, and it is quite possible to brew pieces of the fruit body ground into powder as tea.
| Group: | Tubular |
|---|---|
| Plates: | Rusty brown to deep chestnut |
| Colour: | From gray to almost black with a brown tint |
| Info: | Woody pulp |
| Department: | Basidiomycota (Basidiomycetes) |
|---|---|
| Subdivision: | Agaricomycotina (Agaricomycetes) |
| Class: | Agaricomycetes (Agaricomycetes) |
| Subclass: | Incertae sedis (indefinite) |
| Order: | Hymenochaetales |
| Family: | Hymenochaetaceae |
| Genus: | Fomitiporia |
| View: | Fomitiporia robusta (Oak polypore) |
Thuja diseases
Young shoots and leaves, which turn yellow or acquire a reddish-brown color, are affected. Sporulation of the pathogen is formed on rounded dying areas of the bark and leaves, which looks like crowded black-brown rounded tubercles with a diameter of up to 0.3 mm protruding from the breaks of the integumentary tissues.
Pestalocyopsis necrosis (causative agent - fungus Pestalotiopsis funerea)
Pestalocyopsis necrosis
Young shoots and leaves, which acquire a light brown or reddish brown color, are affected. Leaf damage begins from the top of the shoots, spreading downward. On dying and dead leaves and bark, sporulation of the fungus is formed in the form of a few scattered black rounded tubercles with a diameter of up to 0.2 mm protruding from cracks in the integumentary tissues. Mature spores emerge on the surface of affected leaves and shoots in the form of dark brown, almost black drops and thin cords, which are a characteristic sign of the disease.
Phomopsis necrosis (causative agent - fungus Phomopsis juniperovora)
Affected shoots and leaves turn brown. On the dead bark and in the axils of the leaves, sporulation of the pathogen is formed in the form of black rounded tubercles. Mature spores emerge on the surface of the affected organs in the form of light droplets or strands.
Cytospore necrosis, or osteoporosis (caused by fungi from the genus Cytospora)
Mostly trunks and branches are affected, less often - leaves, which acquire a brown color. The disease is detected by the sporulation of pathogens, which look like numerous, very small conical tubercles with dark tops. Mature spores come to the surface in the form of well-visible golden-yellow, orange or reddish drops, thin flagella and spirals. (Read more about the disease in one of our articles).
Diplodious necrosis, or diplodiosis (causative agent - the fungus Diplodia thujae)
The bark of trunks, branches and leaves is affected. The color of the bark hardly changes, and the leaves turn brown or reddish-brown.In the dead areas, sporulation of the pathogen is formed, which looks like numerous scattered black rounded tubercles with a diameter of up to 0.5 mm.
Brown shute (causative agent - mushroom Herpotrichia juniperi)
The pathogen develops in winter under the snow, therefore, the leaves of only that part of the crown that is in the snow cover zone in winter are affected. After the snow melts, the infected leaves are covered with dense dark brown mycelium (mycelium), which, as it were, glues the affected shoots. On the mycelium, the fruiting bodies of the fungus are formed in the form of black spherical small tubercles, poorly distinguishable on the brown mycelium. Over time, the mycelium is destroyed, and dirty brown scraps remain on the affected leaves.
Mature thuja trees can become infected with wood-destroying fungi, of which root rot pathogens are the most dangerous: autumn honey fungus (Armillaria mellea), root sponge (Heterobasidion annosum), flat tinder fungus (Ganoderma lipsiense), Schweinitz tinder fungus (Phaeolus schweinitzii).
Honey fungus on the trunk Fruit bodies of the root sponge Fruit body of the tinder fungus
All these diseases occur, as a rule, against the background of a preliminary weakening of thuja caused by various unfavorable factors (weather conditions, imbalance of nutrients in the soil, damage by pests, etc.).
The benefits of tinder fungus
The medicinal properties of tinder fungus have long been known. It contains agaric, burikolic, ricinol, fumaric, malic and citric acids, lanophil polysaccharide, glucose, phytosterol, monosaccharide and a large amount of resins. In ancient times, tinder fungus was used as an external hemostatic property: due to its porous structure, it absorbed blood well, and resinous substances disinfected wounds. Infusion of tinder fungus was used for pulmonary and colds. But most often the dried mushroom (it was called tinder) was used to make a fire.
Nowadays, Japanese scientists have found that the lanophil contained in the tinder fungus stimulates the liver of the bladder. This clears the bile ducts and breaks down the fatty layer covering the liver. Polypore can be used for liver cirrhosis, hepatitis B and C, biliary dyskinesia. The tinder fungus is loaded with oncoprotective substances, so it is useful for cancer. Tinder fungus medications help to withstand severe chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Infusion of tinder fungus can be used to enhance immunity. Grind the tinder fungus, pour a tablespoon of powder with 2 cups of hot water and heat for 40 minutes. in a water bath. Let it brew in a thermos for 4 hours and strain. Take a tablespoon 3-4 times a day 30 minutes before meals. Drink the broth for 2 weeks, take a break and continue.
But tinder fungus gained particular popularity as a means. Thanks to the stimulation with lanophil, the liver breaks down fats better, and the enzymes that make up the tinder fungus reduce appetite. To improve liver function, pour 0.5 teaspoon of ground tinder fungus with a glass of boiling water and leave in a water bath for 15 minutes. Drink the infusion during the day in small sips. You can add a teaspoon of honey to improve the taste.
There is also a very simple one. Stir a levelless teaspoon of crushed tinder fungus in 1/2 cup of boiled water. Take 3 times a day 30-40 minutes before meals.
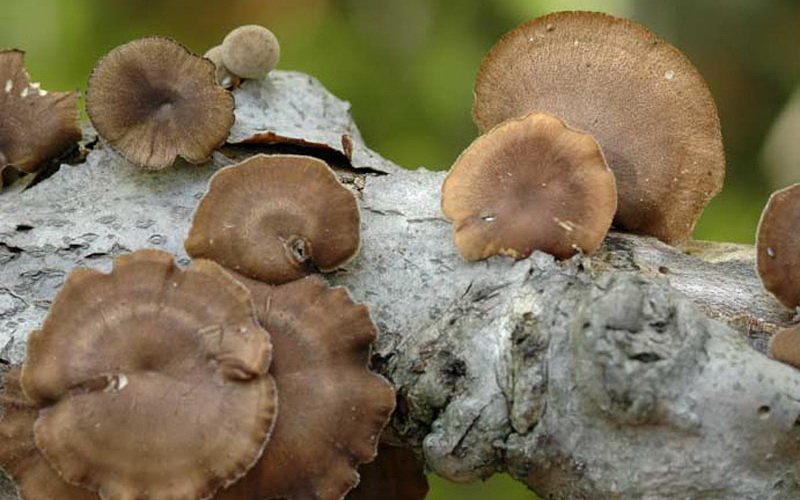
Among all the variety of tree fungi, tinder fungi are the most common in the middle lane.
These fruiting bodies can be found on both living and dead wood. The main harvesting season is from mid-spring to late autumn, sometimes winter varieties are also found.
As a rule, tinder fungi grow in groups, but there are also individual specimens.
Taste varies. But the most important thing that unites different species of tinder fungus is their high healing properties.
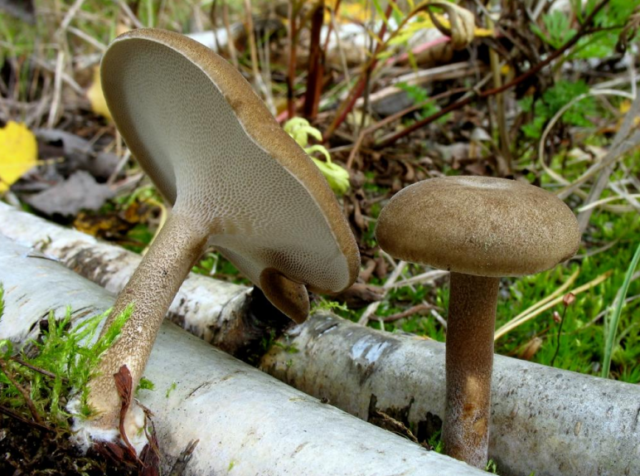
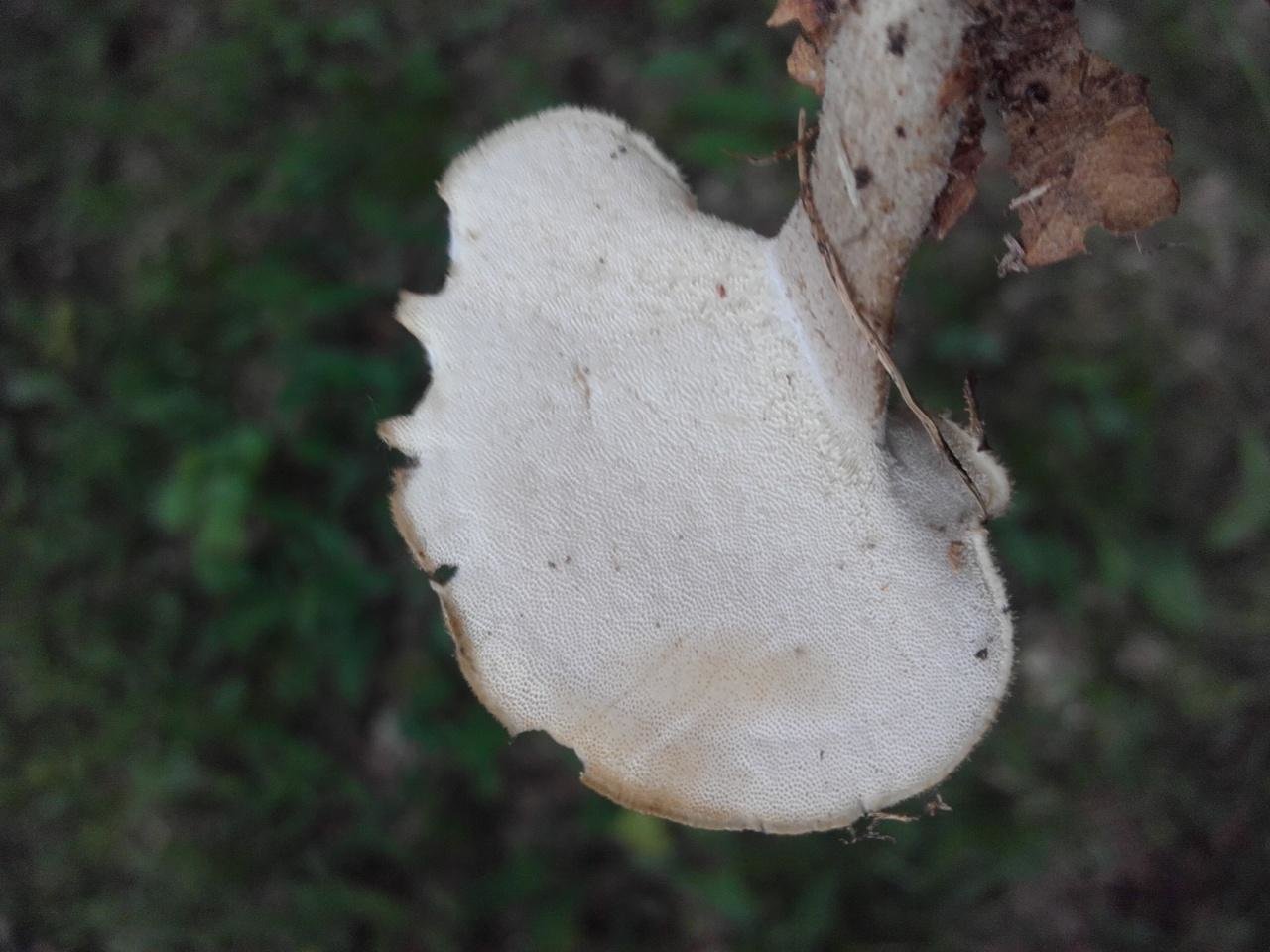
Birch polypores (Piptoporus betulinus)
can be observed all year round. In winter, they become harder, but do not change their properties. Young light tinder fungi are suitable for food.
Habitats of birch tinder fungi: in humid forests, on dead wood and dead birch trees.Season:
intensive growth - in May-November, in winter the growth slows down significantly, but the properties of the fungus do not change.
The appearance of the fruiting body of the birch tinder fungus is rounded, the mushroom has a small stem. A distinctive feature of the species is a cushion-shaped or flat-hoof-shaped, rounded, reniform fruiting body, slightly convex from above, with a blunt, rounded edge. The size of the fruiting body is from 3 to 20 cm, there are specimens up to 30 cm in size and 2-6 cm thick.
As you can see in the photo, the surface of the fruiting body of the tinder fungus is even, smooth, covered with a thin, easily peeling film, sometimes there is a cracking skin:
 The color of the caps of young mushrooms is whitish or cream, later yellowish, brown. At the junction with the stem, the color of the fruiting body is somewhat darker, with a brown tint.
The color of the caps of young mushrooms is whitish or cream, later yellowish, brown. At the junction with the stem, the color of the fruiting body is somewhat darker, with a brown tint.
The hymenophore is tubular up to 10 mm thick, the tubules are white, darken with age. The pores are white, small, rounded or slightly angular, there are 3-4 of them per 1 mm. Spore white powder.
The stem is either absent or small, no more than 10% of the length of the fruiting body.
The pulp of a young tinder fungus looks like a white, soft, homogeneous substance, has a pleasant sour smell. In mature specimens, the flesh is tough, crusty.
Variability: The color of the cap ranges from cream-white to brown.
Similar species. The description of the birch polypore is similar to the liverwort mushroom (Fistulina hepatica), which is distinguished by its bright red color.
Young and soft mushrooms of the 4th category are edible, when the color of the cap is still white or creamy, they are boiled and cutlets are made.
Medicinal properties:
- The study of the medicinal properties of the birch tinder fungus in the area of the central nervous system is being carried out.
- Research is underway on the analgesic properties of these mushrooms.
Next, you can familiarize yourself with a photo, a description of the appearance and medicinal properties of sulfur-yellow tinder fungi:


Views
There are more than 1.5 thousand species of polypores, here are some of them:
Larch (real)
Found on larch, cedar and fir. It is distinguished by a thick fruiting body up to 30 cm long, yellow or white, with a rough surface, rounded edges, furrows and brown areas. It is soft at first, but later becomes hard and crumbly. This mushroom tastes bitter. In the past, such a mushroom served as a raw material for obtaining tinder. Often grows on dead deciduous trees and dead. Larch tinder fungus is discussed in detail in another article.
Flat
Such a mushroom has flat caps up to 50 cm in diameter, on which there are uneven nodules and a brown matte crust. It is found mainly on birches (less often on conifers) - on dead wood and stumps.
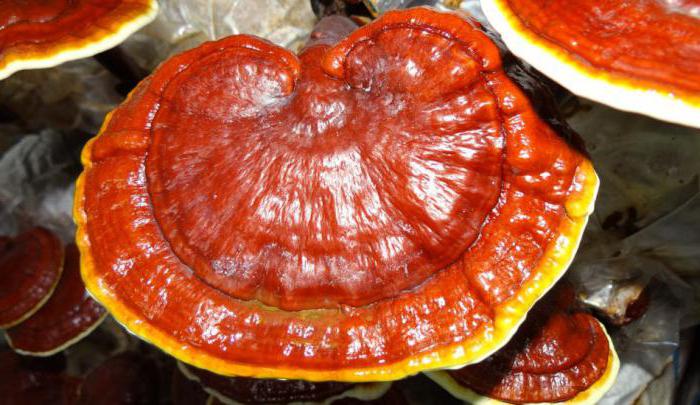
Lacquered (Reishi)
It is distinguished by a reddish-brown shiny cap, the presence of a leg and healing properties. Another name for this tinder fungus is reishi. Read more about it in another article.
Umbrella
It has flat, light, rounded caps, depressed in the center, collected in large fruiting bodies up to 40 cm in diameter and weighing up to 4 kg. This is a very rare tinder fungus, noted in the Red Book.

Sulfur yellow
The peculiarities of this type of tinder fungus is the yellow-orange color of its fruit chalk. The diameter of such a mushroom reaches 50 cm. It grows on weakened or dead trees in gardens, parks and forests.
Winter
Differs in flat-convex yellow-brown caps, firm gray-yellow legs, elastic flesh. Grows on roots, stumps and trunks of deciduous trees. Fruiting from May to December. Edible when young.
Bristly
A feature of such a tinder fungus is a triangular section of fruit chalk. The young fungus is spongy and moist, but later dries up and becomes hard. The diameter of the fruiting body of such a tinder fungus is up to 25 cm, the height is up to 35 cm.
Chestnut
Mushroom up to 10 cm high with funnel-shaped light caps with wavy edges and firm legs tapering towards the base.It grows on dead wood and stumps in damp places.
Haired
Such tinder fungi have semicircular sessile caps covered with hard gray hairs about 5 mm long, growing vertically in bunches. This species is found on deciduous trees - on trunks, deadwood, branches and stumps. Occasionally grows on wooden structures and fences.
Birch
A mushroom with a smooth whitish surface, spherical fruiting bodies and white pulp, which has a pronounced mushroom smell and a bitter taste. This tinder fungus grows only on birches. At an early age, it can be eaten. This tinder fungus contains polyporenic acid, which has anti-inflammatory activity.
Radiant
It is distinguished by annual semicircular flat bodies with a wrinkled surface of a yellow-orange hue (later brown), which grow in rows or tiers on dead and live hornbeams, aspens, lindens, birches and other trees.
Multicolored
A feature of such a tinder fungus is the velvety surface of fruit bodies with concentric zones of different colors - from yellow to brownish-blue. This mushroom grows in groups on stumps and dead trees (usually deciduous).
Scaly
Such a mushroom has spread light fleshy caps up to 30 cm in diameter, elastic dense flesh, as well as eccentrically located legs. Such tinder fungus grows in parks and forests on weakened and living trees (often on elms).
Cinnabar red
Differs in annual hoof-shaped fruiting bodies up to 10 cm in diameter with a bumpy red surface and red flesh. Found on decaying and weakened deciduous trees.
Odorous
The peculiarity of this tinder fungus is the aniseed aroma of its rusty-brown fruiting body. Such a mushroom often grows on deadwood and stumps of coniferous trees.
The Tinder fungus has certain medicinal properties. The scope of their application is different, but one follows from the other. Below are descriptions of the different types of tinder fungus and its healing effects.
Description and taxonomy of the inedible parasitic fungus
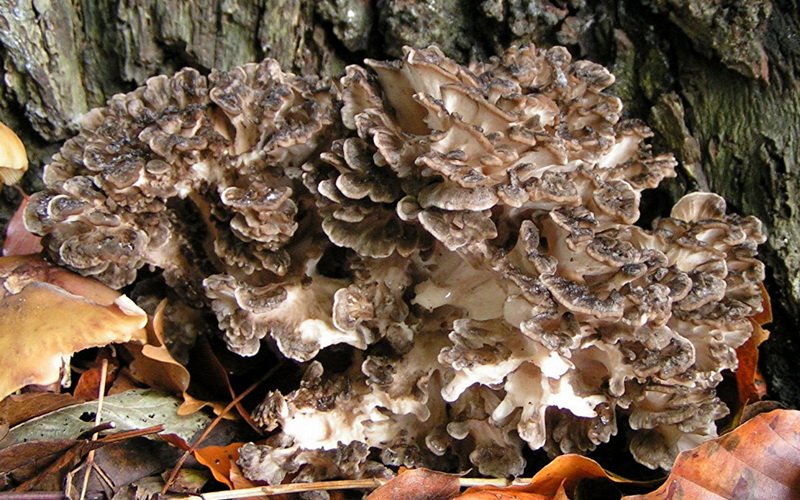
The wood sponge (in Latin Fomitopsis pinicola) belongs to the genus Fomitopsis, the Fomitopsis family. A feature of the structure of the fungus is the absence of a leg. The fruit body grows laterally to the tree.
Over the course of life, the shape of the tinder fungus changes. In young mushrooms, it is round or semicircular, then cushion-shaped. The diameter of the fruiting body at maturity reaches 20 cm, and in large representatives - 30 cm.The bordered polypore grows up to 10 cm.
The color of the cap is varied: from gray-gray to black. The outer part is orange or red. An uneven, dull skin covers the surface of the fruiting body. Concentric zones can be seen on the cap.
The lower part of the cap (hymenophore) is tubular. The beige or cream straws are arranged horizontally. When pressed, the surface of the hymenophore darkens, becoming brown or dark gray.
The spores are subtle, colorless, elliptical or ovoid. Powder of a creamy, whitish or yellowish tint.
On the cut, the pulp resembles a sponge, it is just as dense and elastic in structure. Flaky at the fracture. The color of the pulp changes with age. In young mushrooms, it is beige-yellow or light brown, chestnut by old age.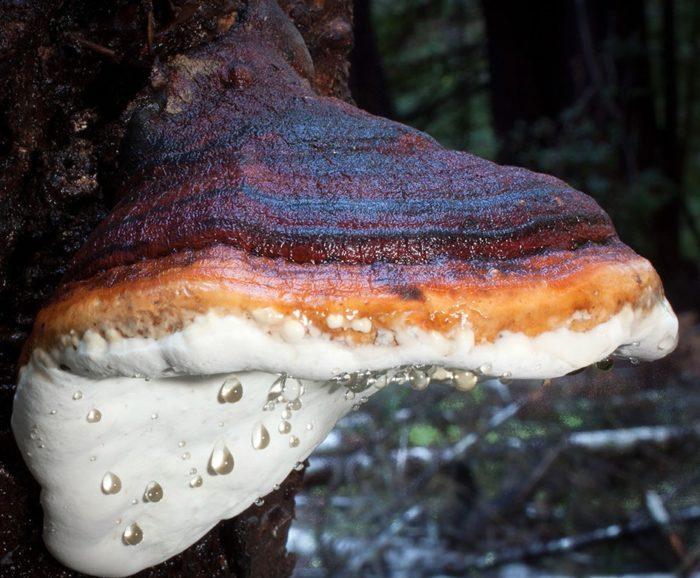
A bit of history
For a long time (until the middle of the 20th century), the tinder fungus group belonged to the Polyporaceae family. Then the concept of "tinder fungus" began to be considered from the point of view of morphological characteristics.
The author of the species is Peter Karsten, a Finnish mycologist-taxonomist, professor of botany.
REFERENCE! The ancient Indian tribes living in North America knew about the beneficial properties of tinder fungus. They used the mushroom as an additive to the tobacco mixture, made incense, spices.






















































