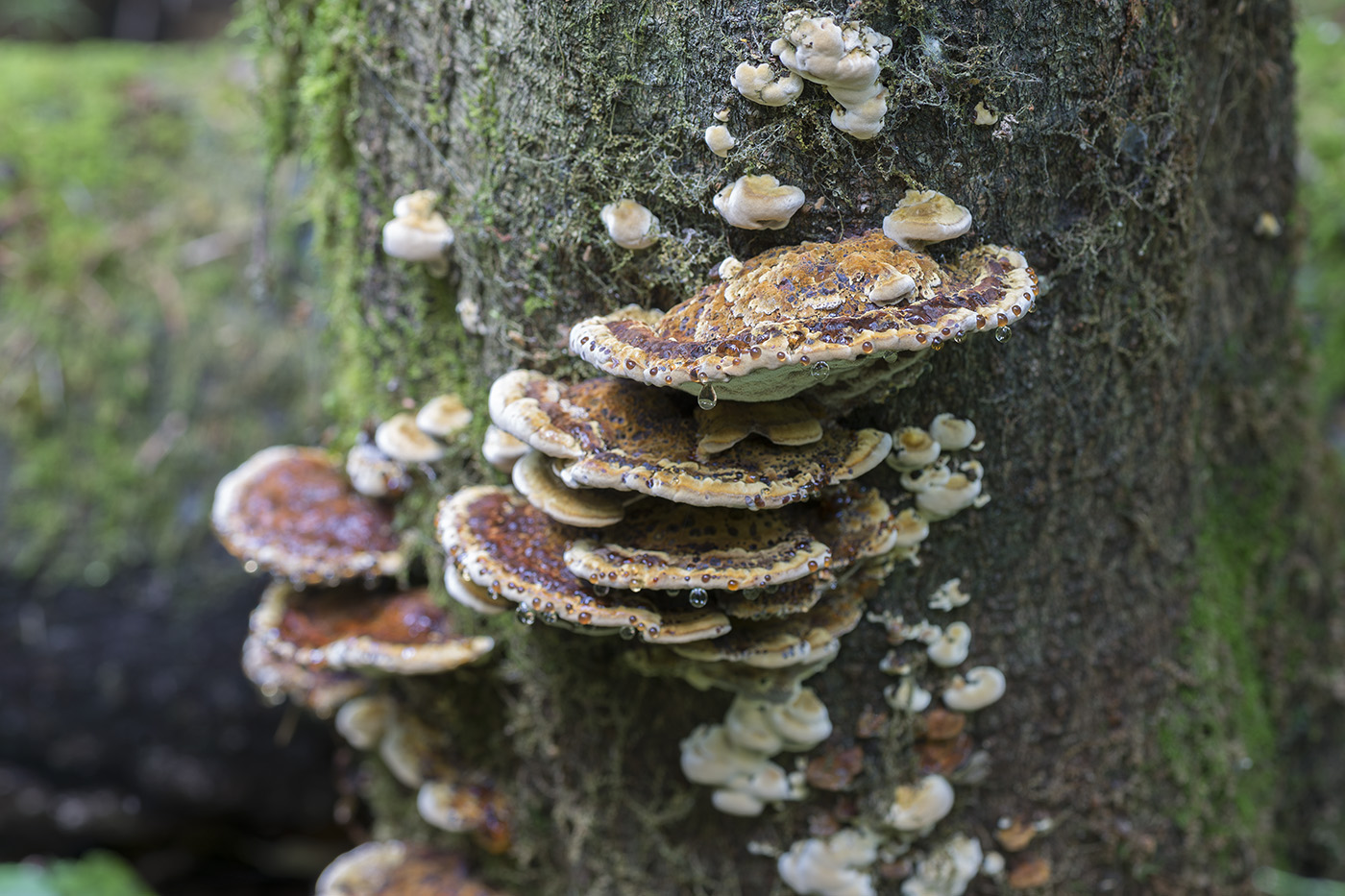
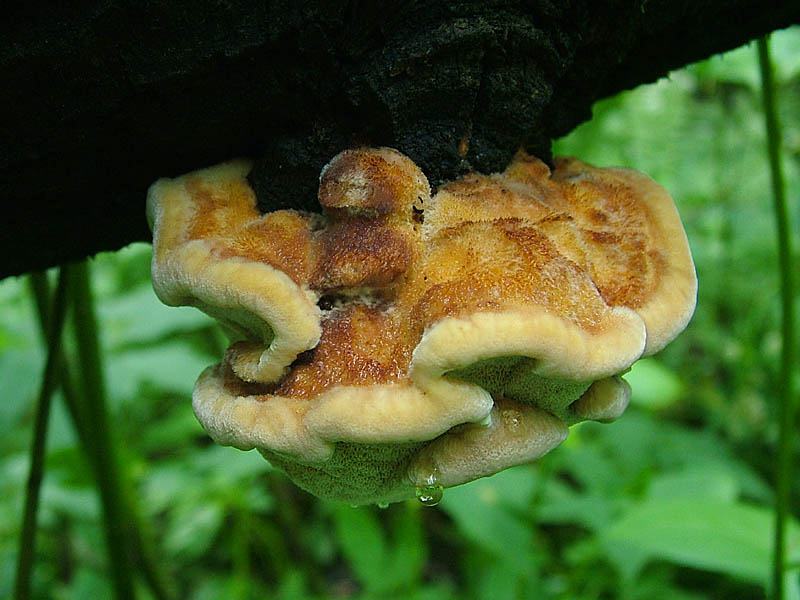
Edible chaga birch

Chaga birch is not an edible mushroom, but it is used in medicine as it has antimicrobial, antispasmodic and diuretic effects, normalizes the intestinal microflora, accelerates the healing of duodenal ulcers and stomach ulcers, normalizes the heart and respiratory system, increases immunity, accelerates metabolism, possesses antineoplastic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory action, lowers blood sugar levels. Chaga is used for gastritis, for the treatment of diseases of the skin, kidneys and liver, pancreas and gall bladder. Chaga-based remedies are also used for colds, bronchitis, tuberculosis. Decoctions and infusions are known as a laxative, styptic, and hypnotic. For prophylactic purposes, chaga is taken in the form of tea. Tea with birch chaga: Pour the dried chopped mushroom with boiling water (1: 5) and insist in a thermos. Take the infusion in half a glass half an hour before meals.
Indications and restrictions for use
Healing wood sponge is recommended for various diseases. The list of indications for internal use is quite long and includes diseases of many body systems. These include:
- oncology;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- leukopenia;
- viral diseases;
- inflammatory processes;
- diabetes mellitus and other disorders of the endocrine system;
- damage to the mucous membrane of the duodenum;
- gastritis;
- the transferred operation;
- insomnia, depression and other nervous disorders;
- obesity;
- cramping;
- tachycardia and hypertension.

Chaga birch mushroom In addition, the mushroom is used for general strengthening of the body and increasing immunity, to stimulate brain activity. Chaga is also used externally to treat diseases such as:
- dermatosis;
- rash;
- colds on the lips;
- keratinization of the integumentary epithelium;
- abscesses;
- burns;
- frostbite;
- scuffs, abrasions and wounds;
- acne;
- peeling of the skin;
- insect bites.
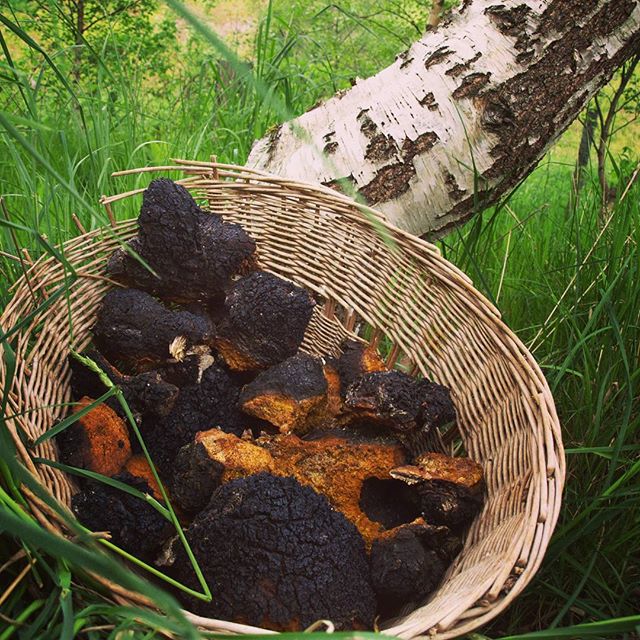

The use of the mushroom for the treatment of diseases In dentistry, it is used as an anti-inflammatory and analgesic agent for:
- deep damage to the periodontal tissue;
- inflammatory disease of periodontal tissues;
- damage to the oral mucosa;
- toothache.
However, it is not always possible to use tinder fungus for medicinal purposes. Contraindications to the use of the mushroom are:
- taking penicillin drugs;
- intravenous administration of glucose solution;
- insufficient bowel movements;
- inflammatory disease of the colon mucosa;
- shigellosis;
- pregnancy;
- lactation period;
- individual intolerance.
Advice!
During the treatment period, it is recommended to replace meat with vegetable and dairy sources of protein. You should not eat canned and smoked foods, spicy foods. In addition, you should give up bad habits such as smoking and alcohol abuse.
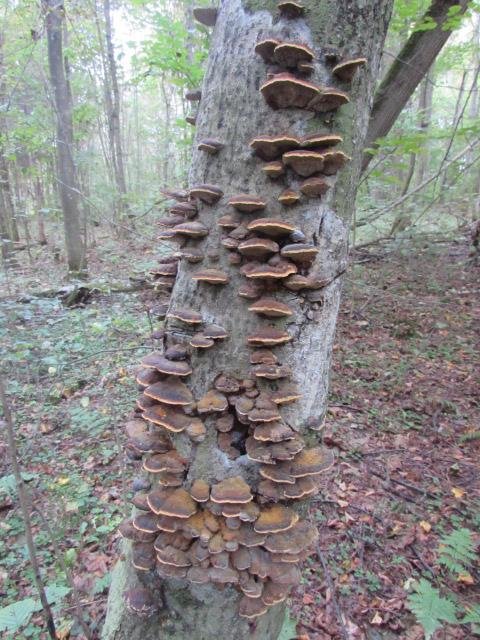
What is a tinder fungus
This is a large group of saprophytes that belong to the section Basidiomycetes. They parasitize on wood, leading to the death of the plant. But, unlike chaga, tinder fungi sometimes grow in soil.

You can find them in park areas, in pastures, along the roadside.
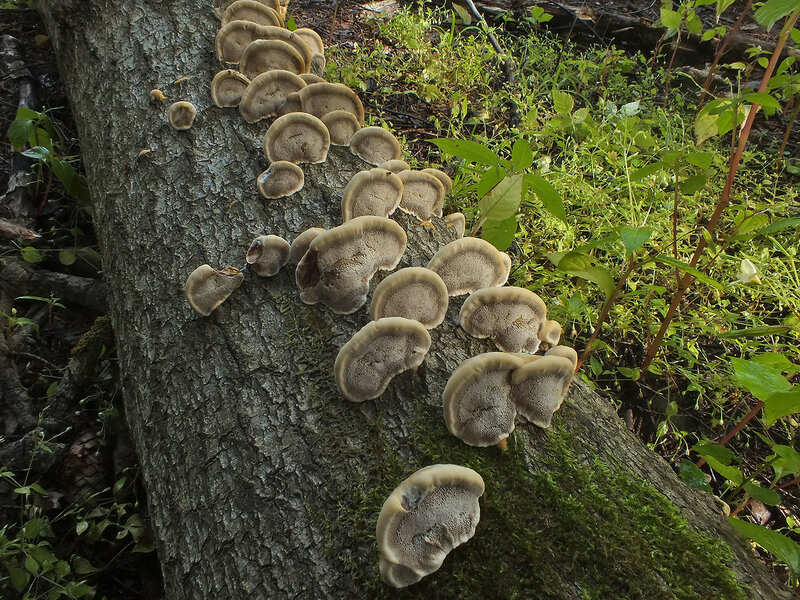
In contrast to the canted inonotus, tinder fungi have prostrate, sedentary bodies in the form of a semicircle, a flattened sponge or a large hoof. The consistency of their pulp is hard, woody, corky or spongy.
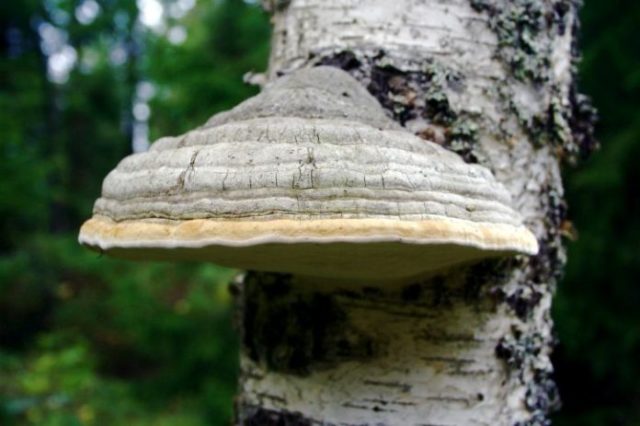

The stem of the fruiting body is often absent.
But there are known species in which this part of the sporocarp did not atrophy.
This group of basidiomycetes is characterized by a tubular hymenophore, but some representatives of the species are distinguished by a spongy structure. The shape and weight of different types of tinder mushrooms is strikingly different.Some specimens can be up to 1.5 m in size and weigh up to 2-3 kg.
External signs of raw materials
text_fieldstext_fieldsarrow_upward
External signs
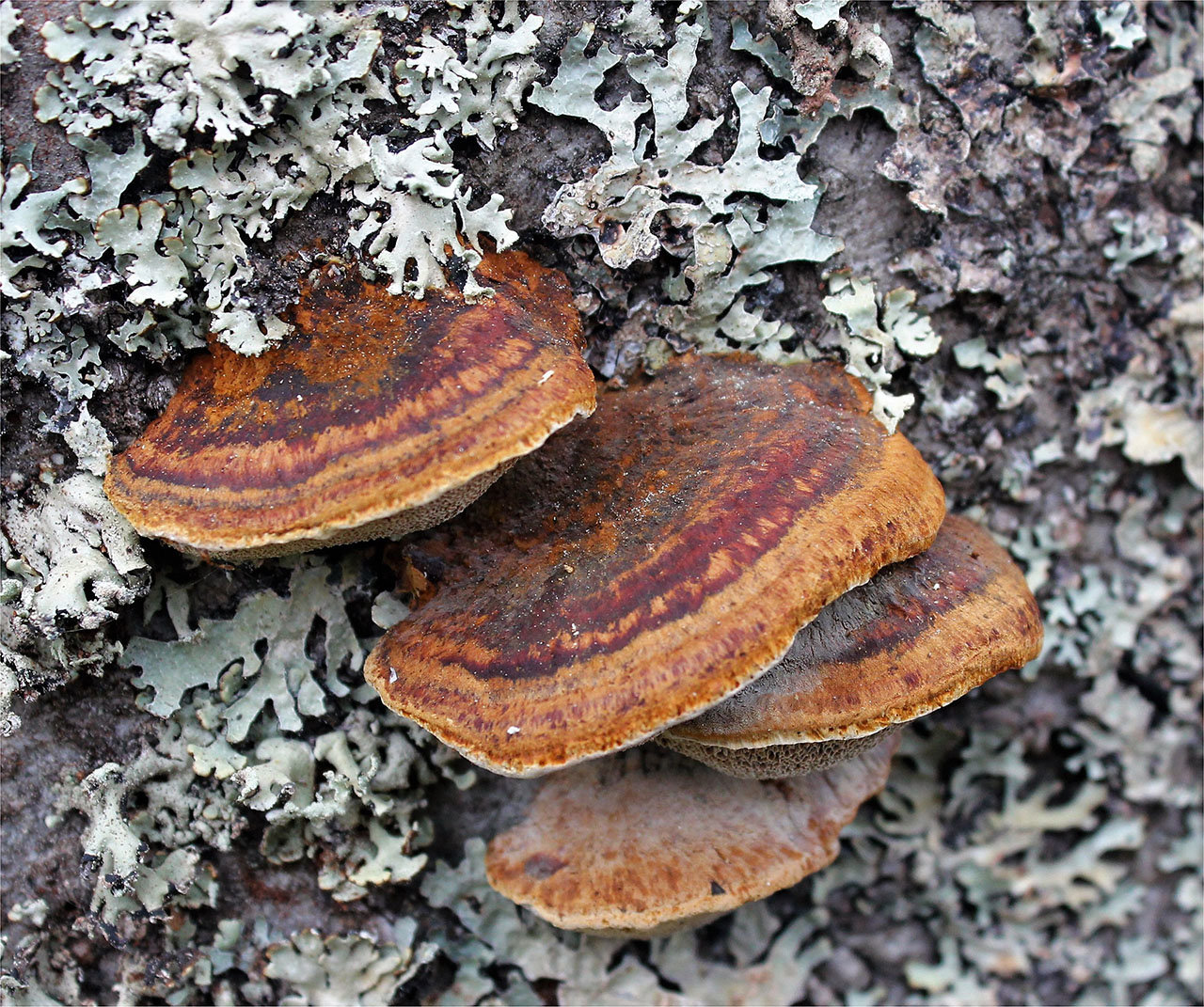
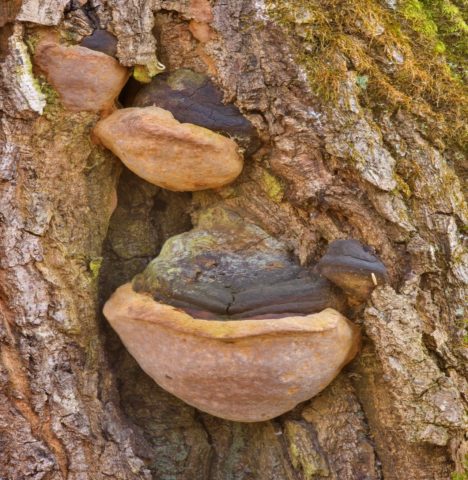
Rice. 11.17.2. Oblique tinder
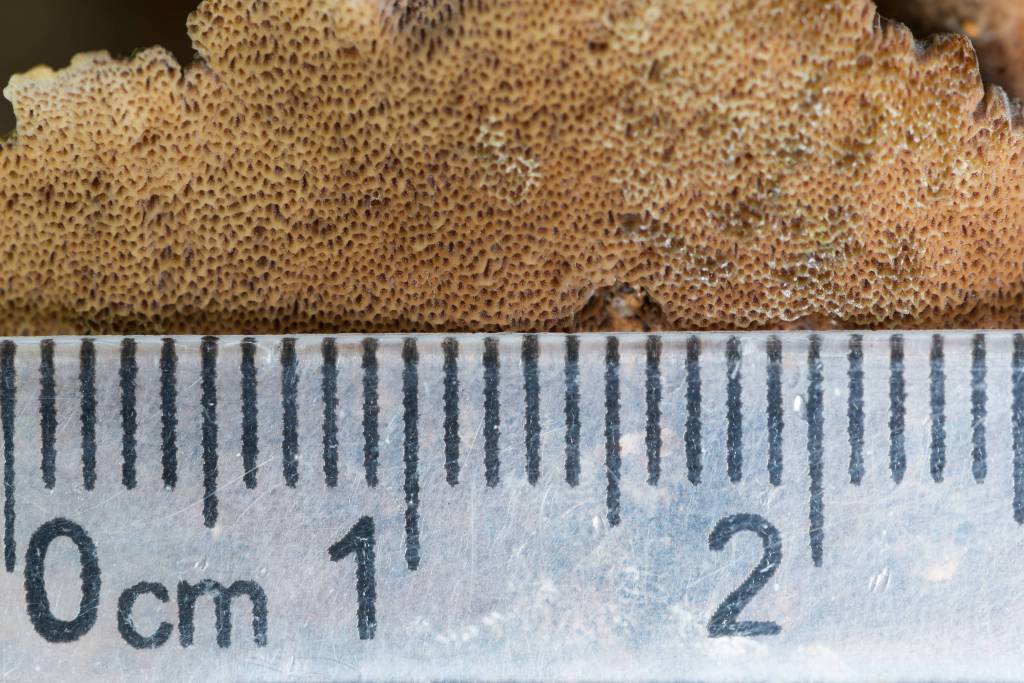
Whole raw material Pieces of various shapes up to 10 cm in size. The outer layer of the build-up is black, strongly cracking, the inner layer is dark or brown-brown with small yellow veins, the number of which increases towards the inner side. The tissue of the fungus is dense and hard. There is no smell. Bitter taste.
Chopped raw material Pieces of raw material passing through a sieve with holes with a diameter of 7 mm. Color dark brown. There is no smell. Bitter taste.
Impurities
Sometimes collectors mistakenly collect other fungi parasitizing on birch.
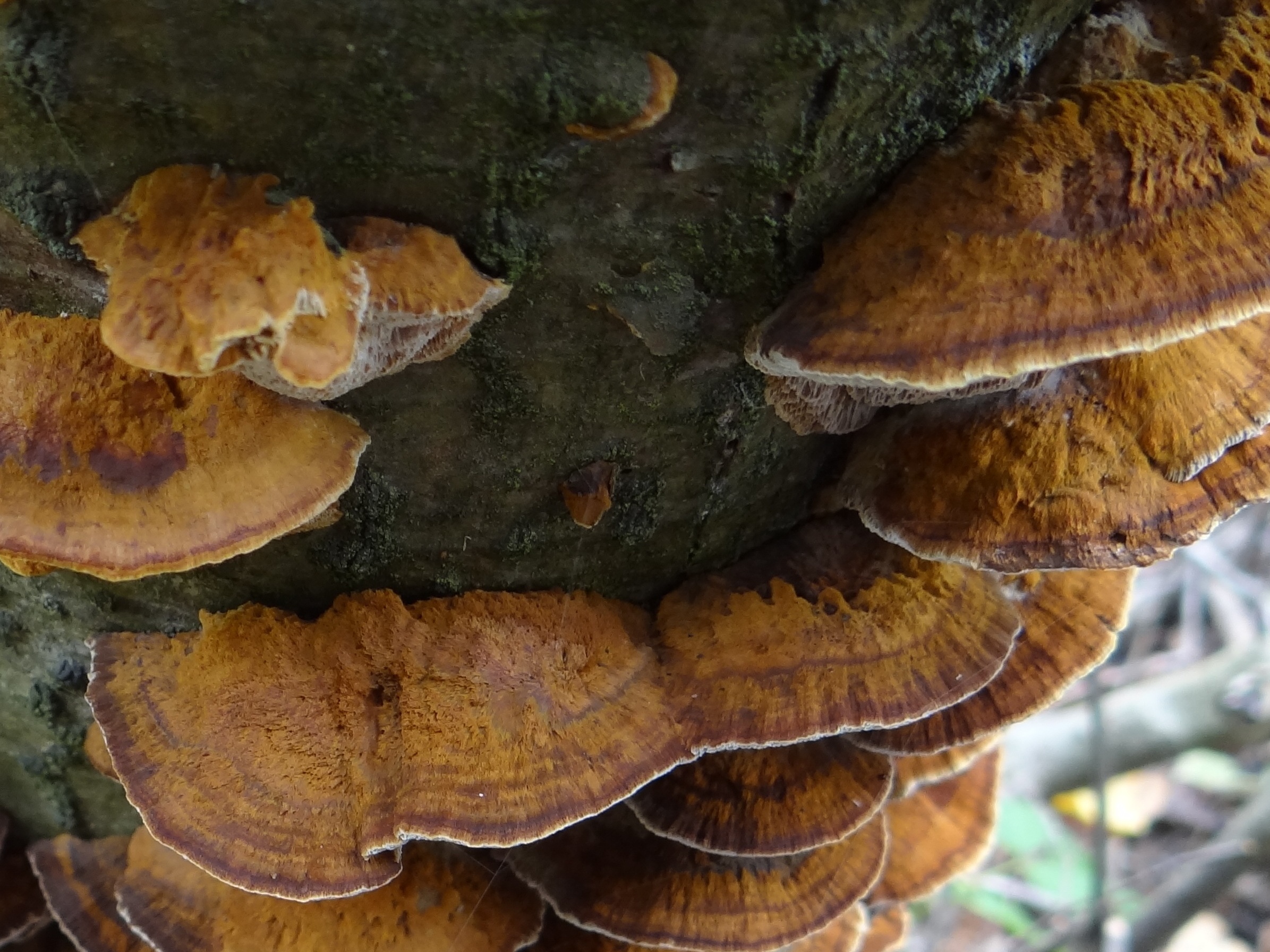
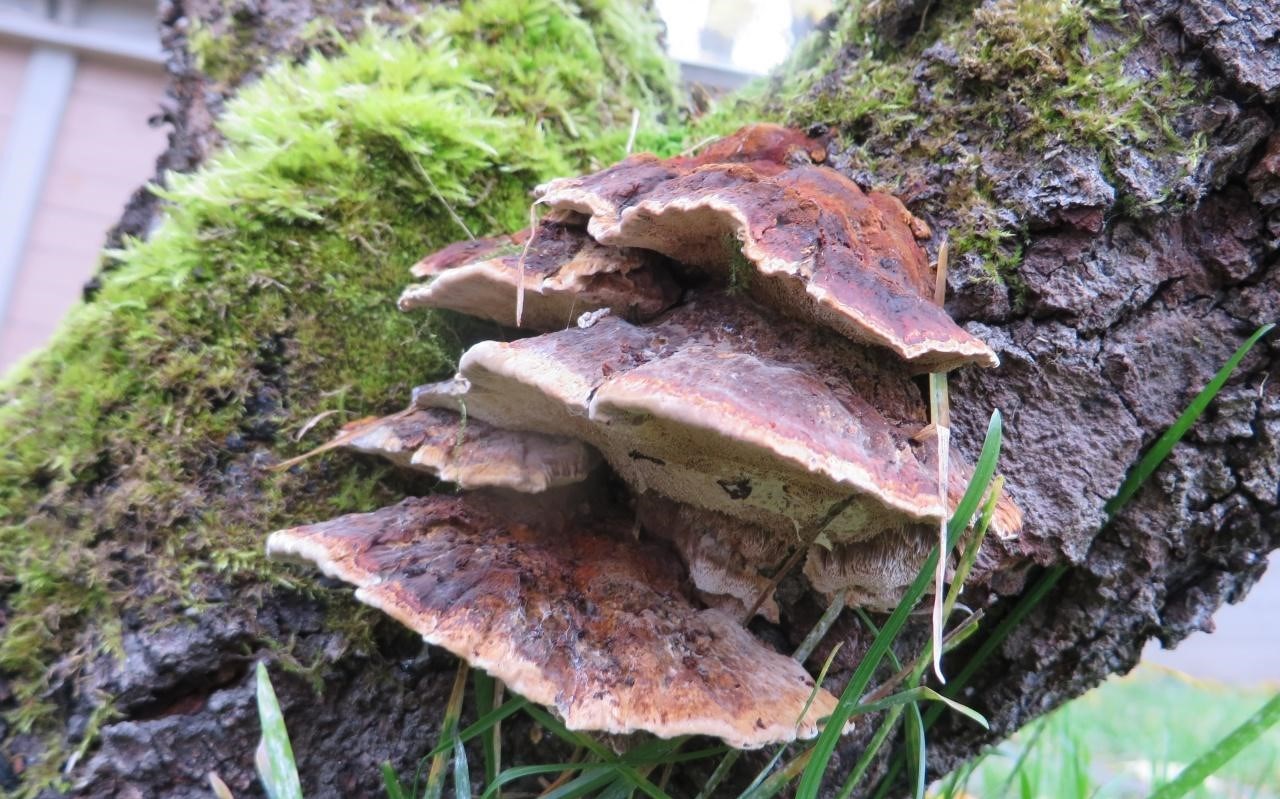
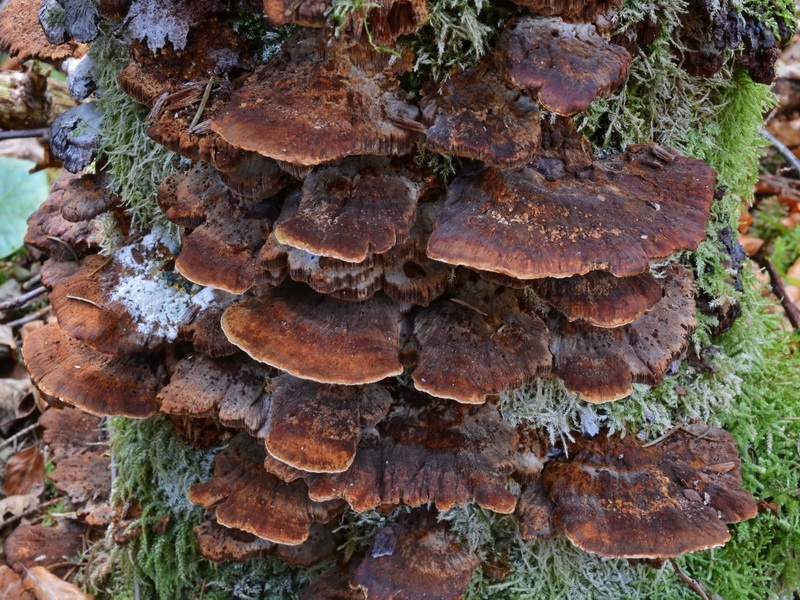
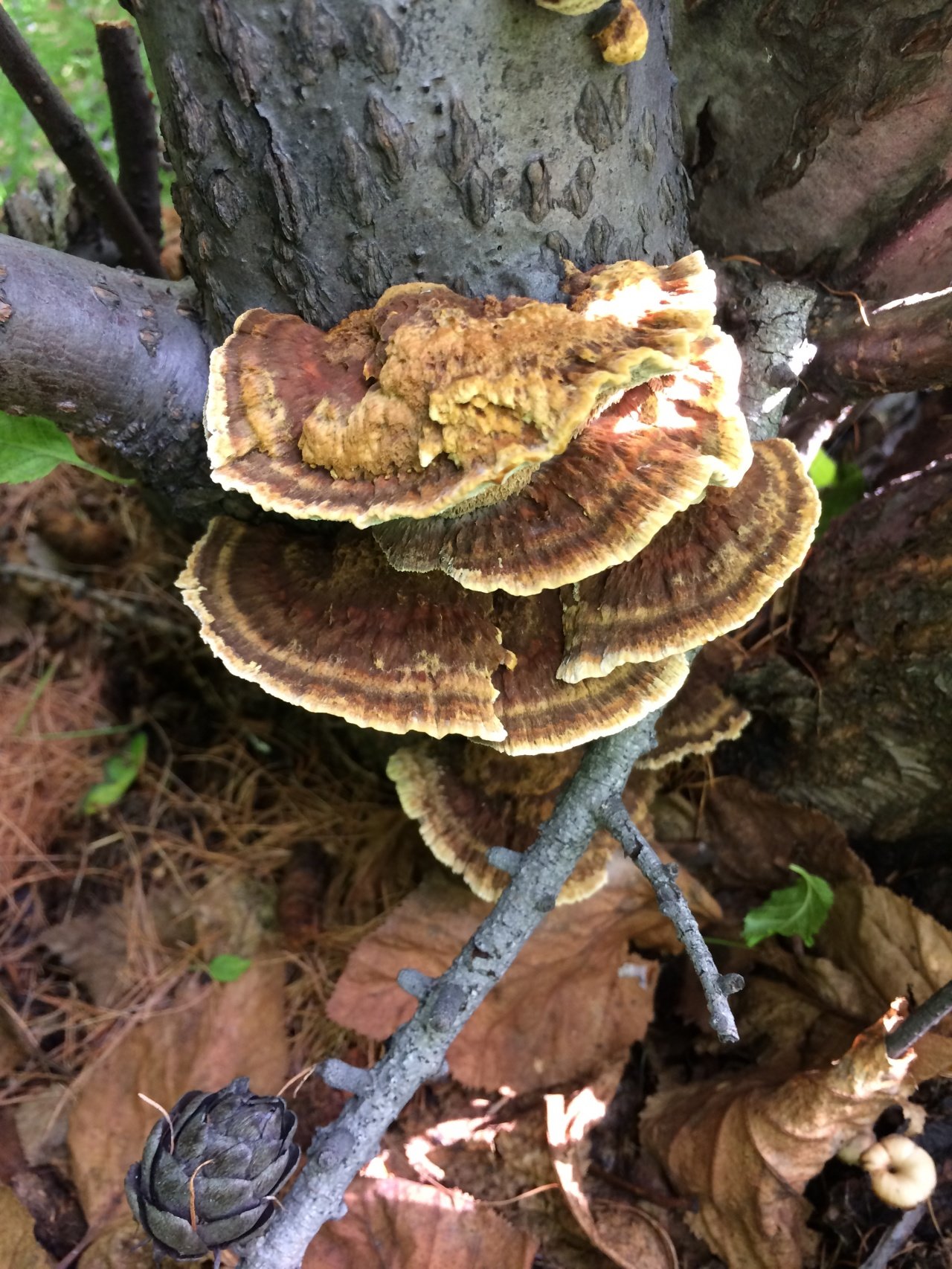
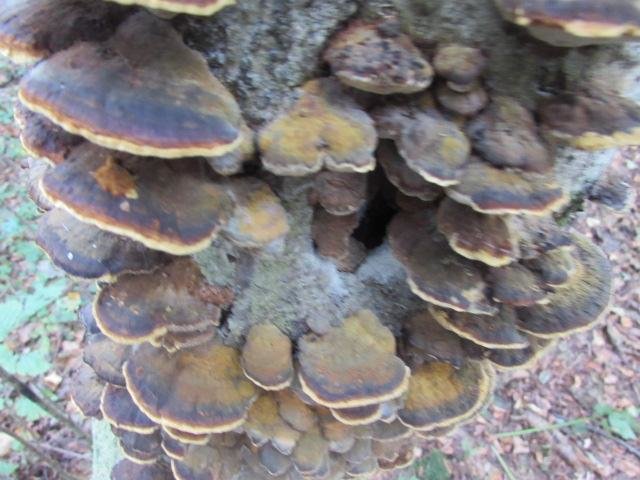
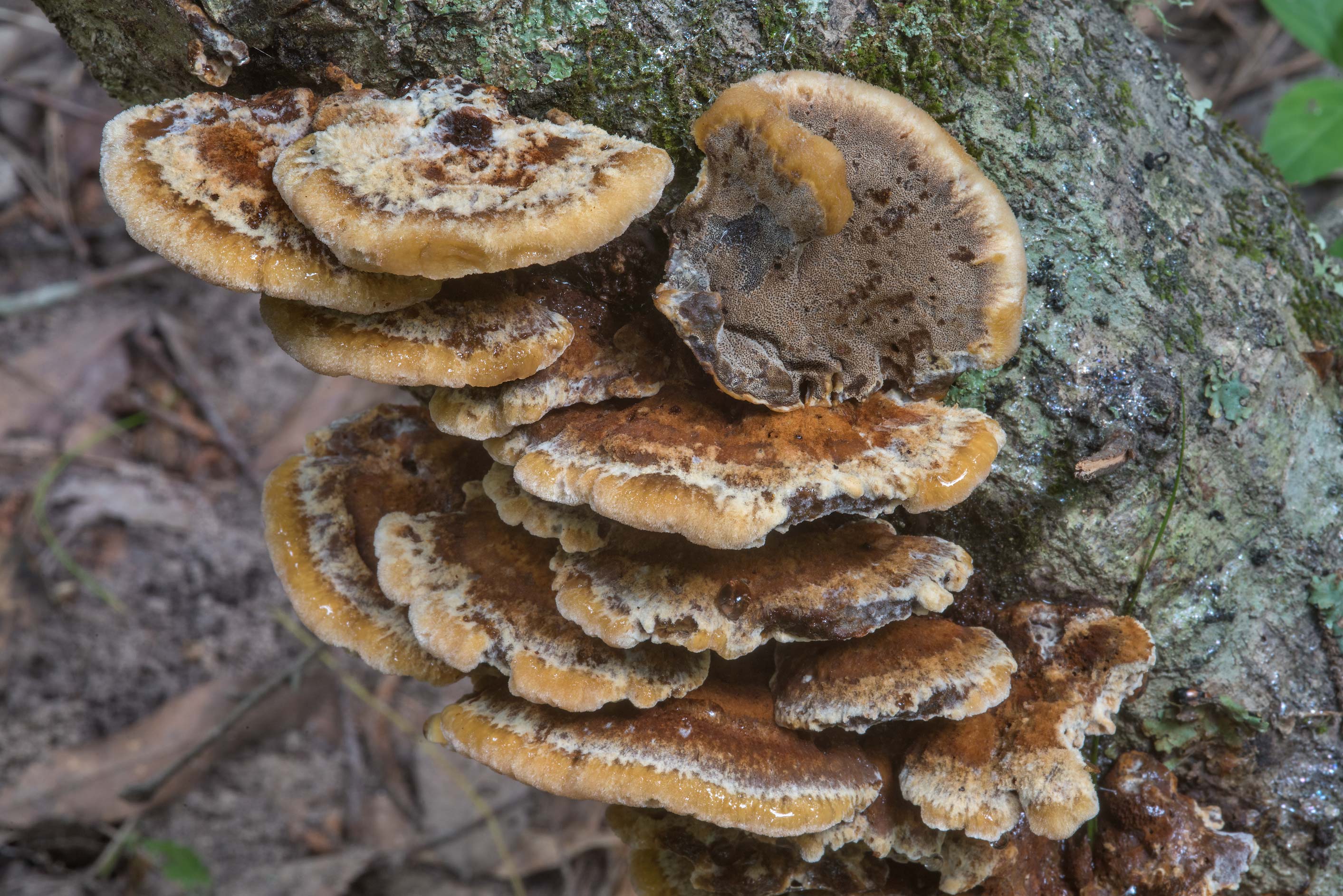
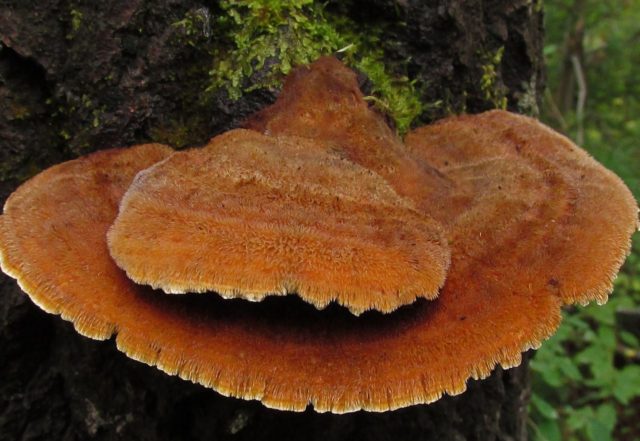
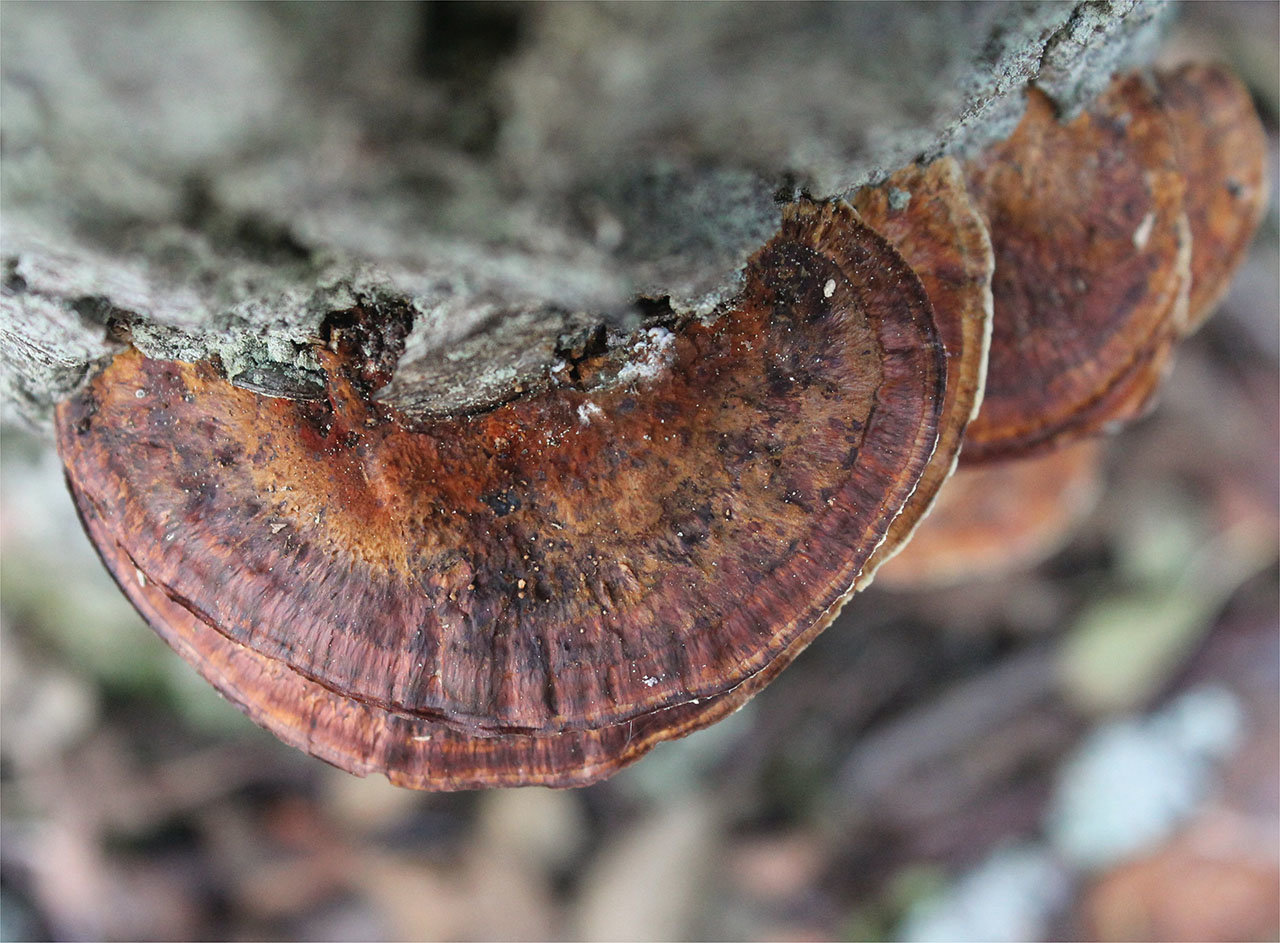
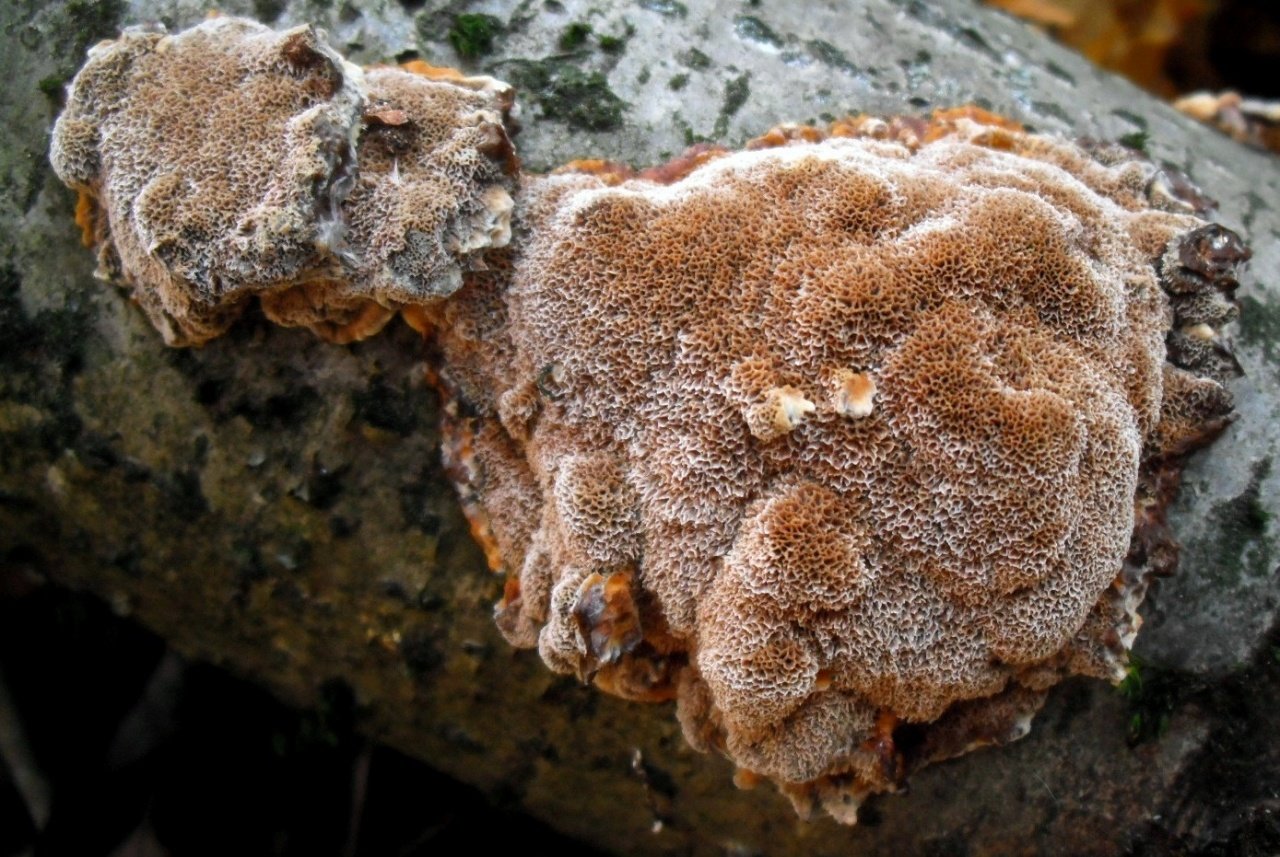
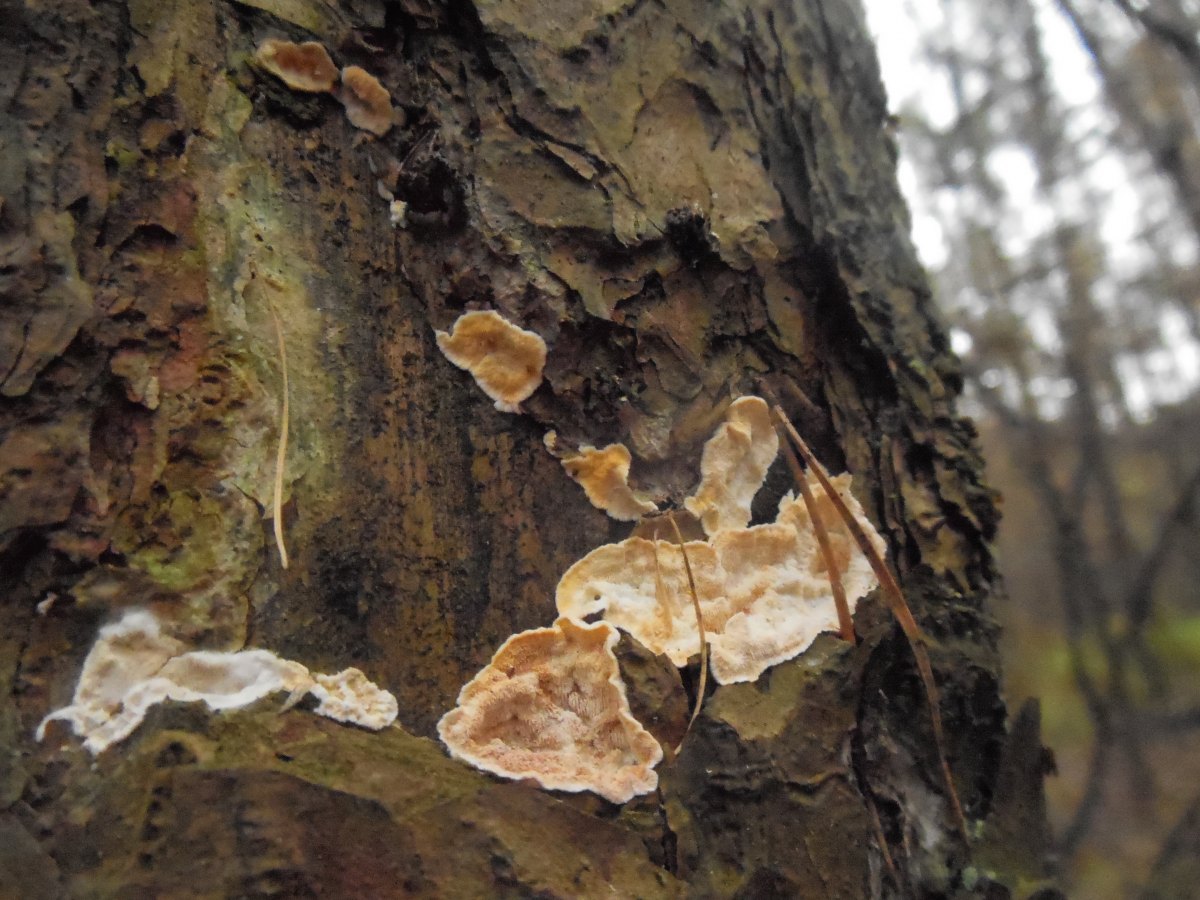
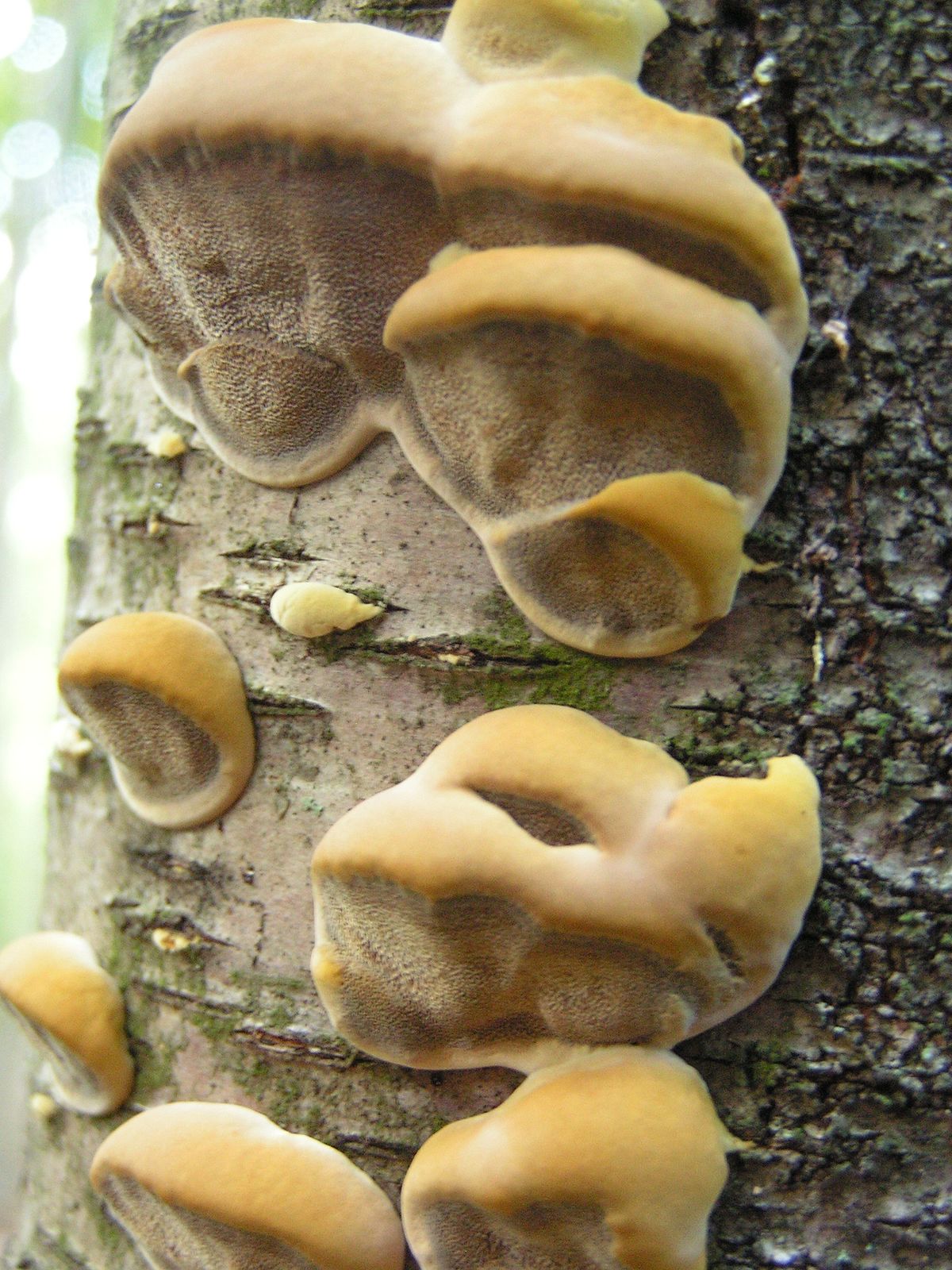
Most often, real and false tinder fungus come across. Both fungi develop a fruiting body, which has a hoof-like shape, convex above, flat below with a velvety surface (hymenial layer).
Distinctive features of a birch fungus from similar species
|
Mushroom name |
Diagnostic signs |
|
|
fruiting body shape |
surface |
|
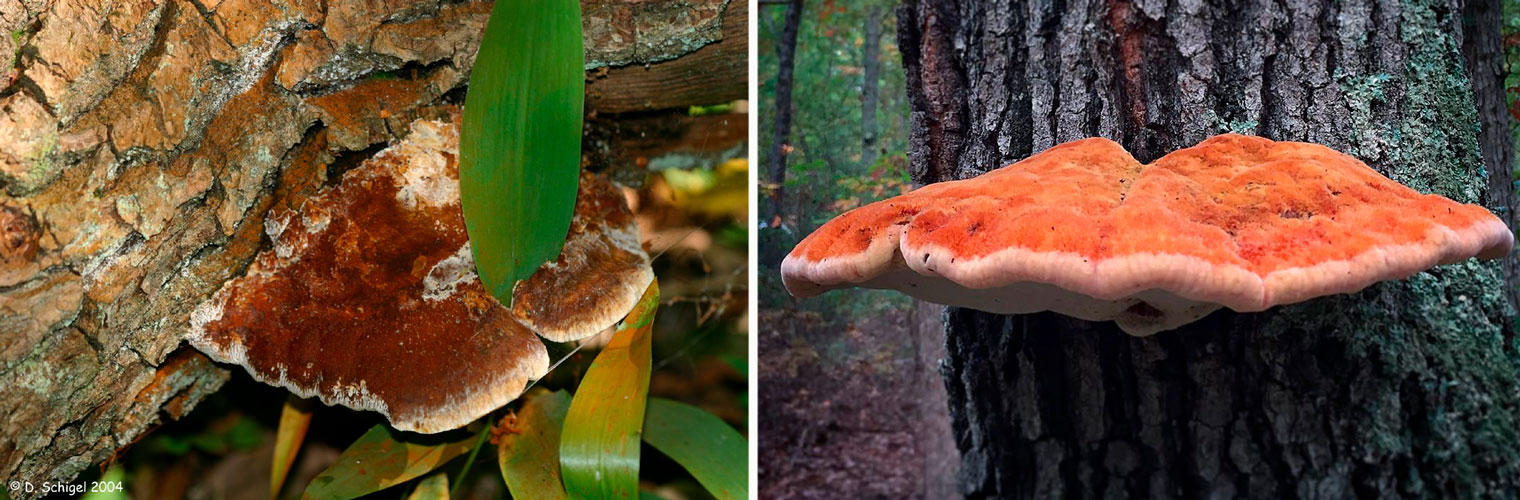
| Chaga | Oval or rounded | Dark brown, pitted or cracked, with many small bumps and fissures |
| False tinder fungus | Hoof-shaped, facing flat side down (top convex) or having the appearance of a hat | Velvety, with concentric circles, hard, with a grayish-black or black-brown crust |
| Real tinder | Hoof-shaped, semicircular in outline, flat on the underside, with a wide base | Smooth, with concentric grooves, hard, with a grayish or brownish crust. Wavy layers are noticeable |
Difference from false mushrooms
It is not difficult to distinguish chaga from other mushrooms; with the help of a photo, we will consider the features of the mown tinder fungus and other non-medicinal species.
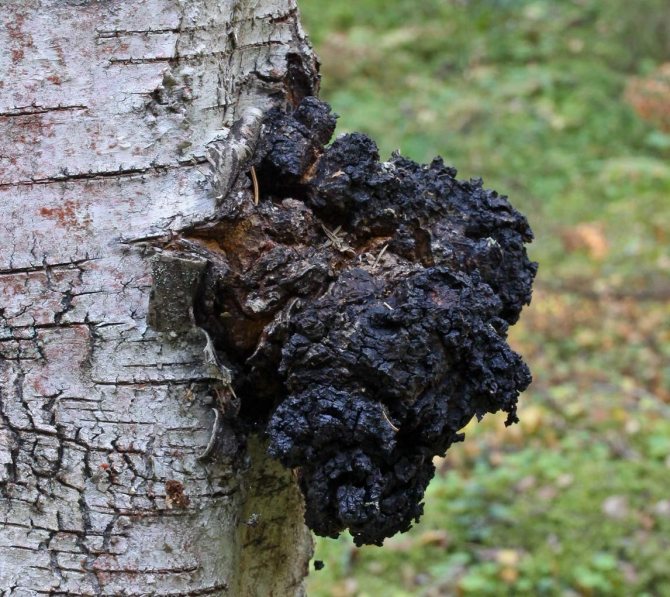

Chaga mushroom
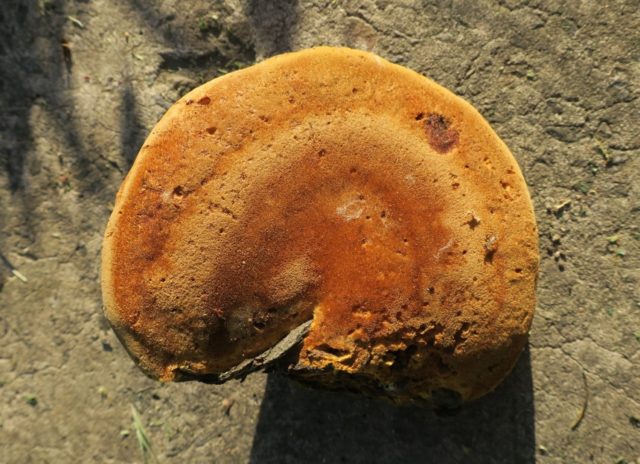
Chaga is not a fruiting body; its outer part resembles a knobby growth. It is hard to the touch, dark, cracked. The fungus can take a variety of forms, often stretching along a deep crack in the tree. Some growths can be up to 1 meter in length. The medicinal mushroom is very difficult to separate from the tree.
Chaga is most often confused with a false tinder fungus. Its fruiting body has a hard brownish surface covered with grooves and a light gray downy. Older mushrooms are brownish black or dark brown. The main difference between the false tinder fungus is its correct shape. Most often, false tinder fungi infect dead trees, which is not typical for chaga.
Real, but not medicinal, tinder fungi can be easily removed from the tree. Their fruiting bodies resemble a hoof, and they are soft and velvety to the touch. Outside, tinder fungi are gray-brown, below and inside - light and uniform.
Other types of tinder fungus are rarely mistaken for chaga, as they are too light and soft. An exception is the bordered tinder fungus. The old wood sponge is dark and hard to the touch, however, it is distinguished from chaga by its regular shape and orange edges.
Poisonous and inedible species of birch chaga
Poisonous similar species have not been described for birch chaga.
Growing birch chaga at home
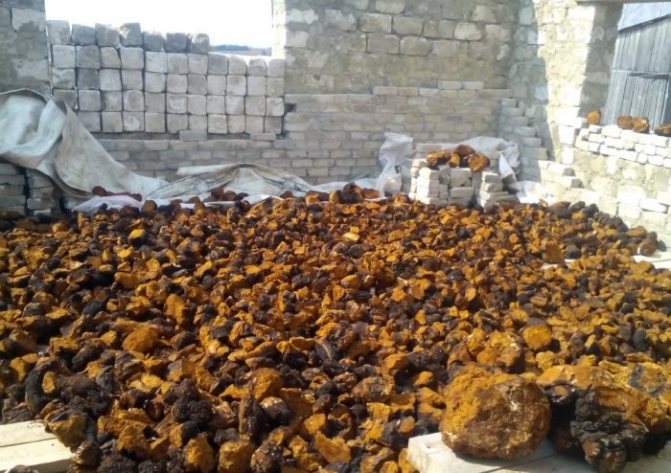

For the purpose of growing chaga, old birches are chosen. On their bark at a height of 1-1.5 m from the ground, horizontal notches with a depth of 10-15 cm are made with an ax, while the bark layer is lifted from top to bottom, exposing the wood. The notches are made in two or three rows. The vertical distance between such rows is 50-60 cm. At the places of the cuts, the wood is well moistened and the mycelium, or pieces of the ripe fruiting body of the fungus, or a spore suspension, or the loose inner part of the growths, are introduced into them. Then the bark is tied up with bandages, and the incisions are filled with wax or paraffin so that competing parasitic microflora does not get inside. Chaga birch outgrowths appear after 3-4 years.
Properties and uses of chaga
text_fieldstext_fieldsarrow_upward
Pharmacological properties of chaga
Chaga
- increases the body's defense reactions in the experiment,
- activates the metabolism in the brain tissue, which is manifested by an increase in the bioelectrical activity of the cerebral cortex.
- acts anti-inflammatory with
- internal and
- topical application.
In experimental studies of chaga
inhibits the growth of some tumors.
The use of chaga
enhances the cytostatic effects of cyclophosphamide.
Birch mushroom decoction
has a hypoglycemic effect: the maximum decrease in serum glucose levels is observed 1.5-3 hours after ingestion of the decoction. The sugar level drops by 15.8-29.9%.
It is noted that a decoction from the inner part of the mushroom gives a hypoglycemic effect, a decoction from the outer part does not possess this property.
The use of chaga
Chaga is used as
- fortifying and
- anti-inflammatory agent for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and
- as a symptomatic remedy for tumors of various localization.
Chaga infusion is prescribed to patients
peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum.
Chaga
- quickly relieves pain and dyspeptic symptoms,
- normalizes bowel function,
- increases overall tone.
The positive effect of chaga on patients with gastrointestinal diseases is confirmed by X-ray data.
Infusion and tincture of chaga, "Befungin" is used for
- psoriasis,
- eczema
- and other skin diseases,
the treatment is especially effective in cases of a combination of a skin disease with various inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, and biliary system.
When treating chaga, the patient is recommended to eat mainly dairy and vegetable food, to limit the intake of meat and fats, exclude canned food, smoked meats, hot spices. It is also impossible to inject glucose intravenously and use penicillin.
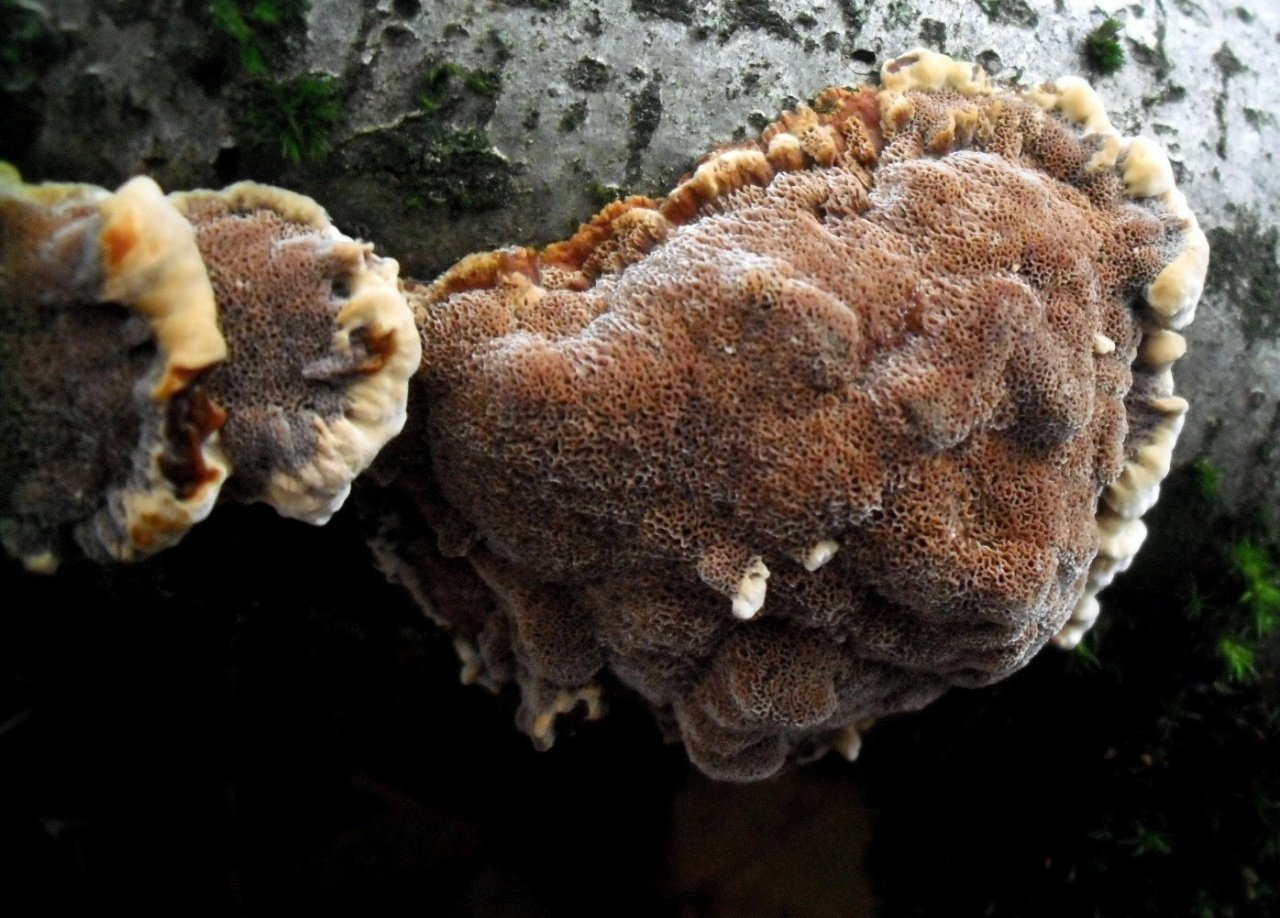
External description
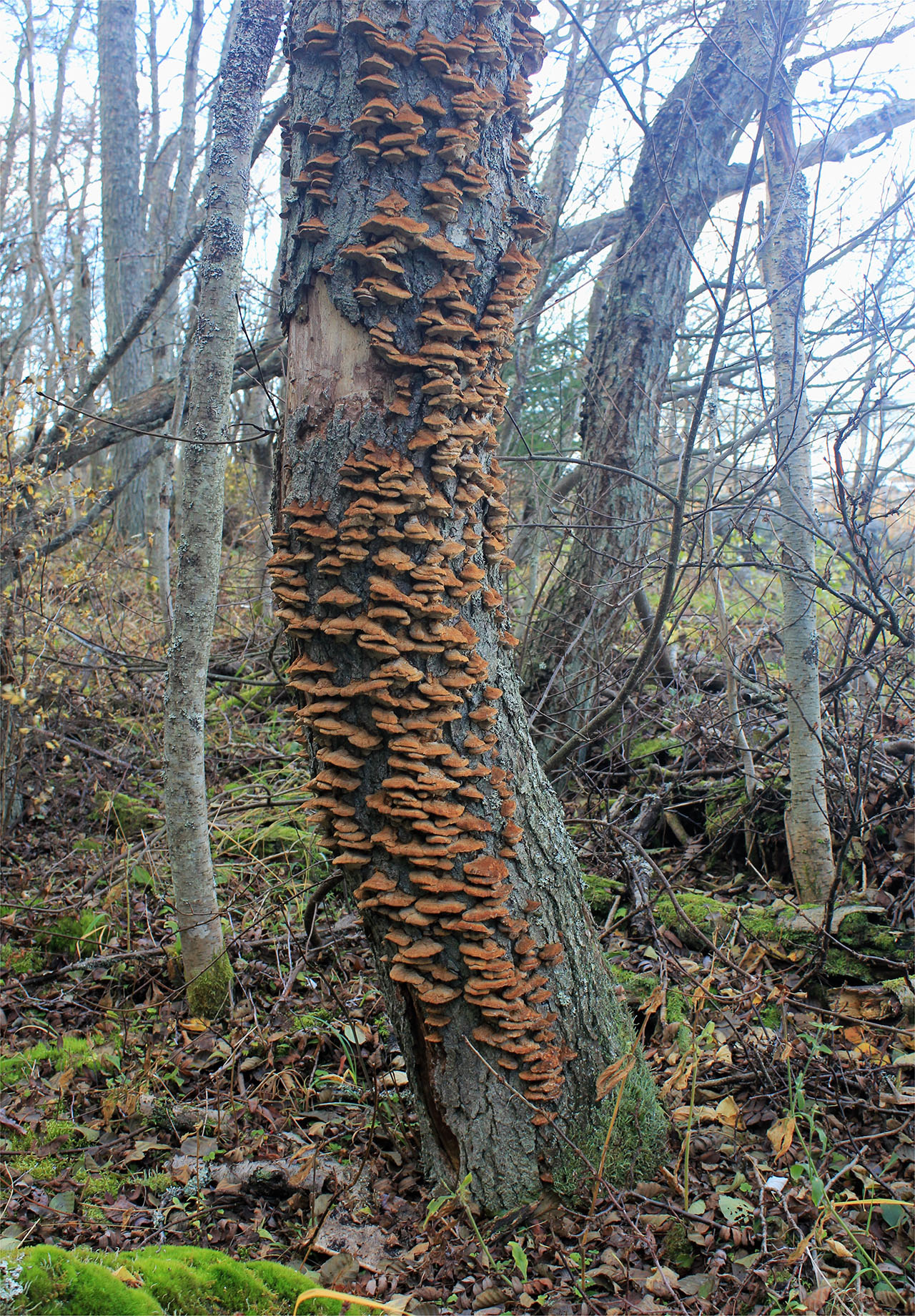
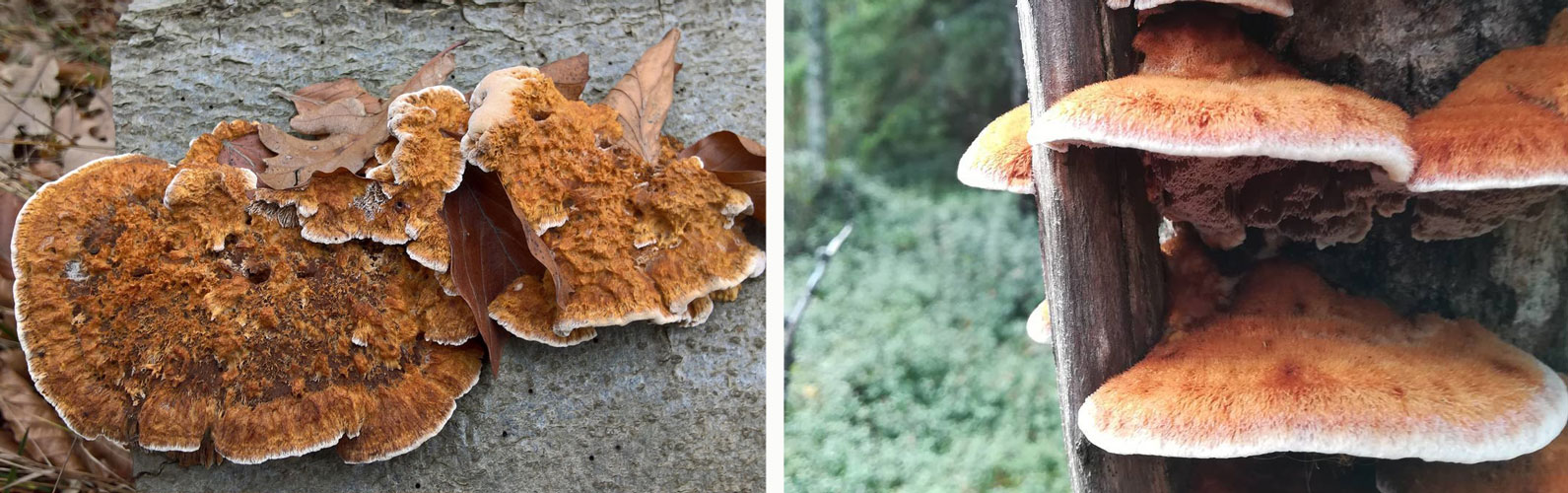
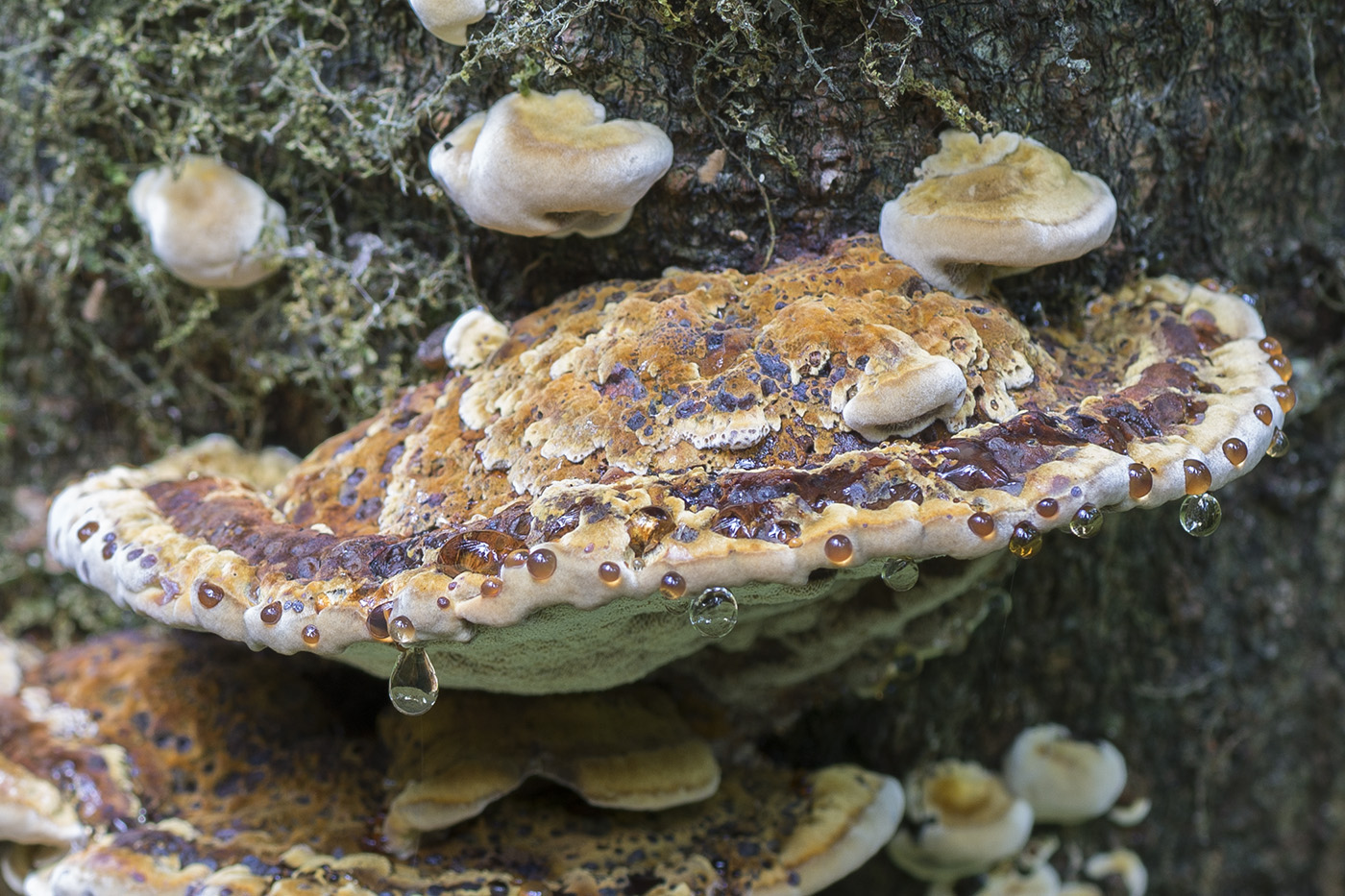
The fruit body of the mown tinder fungus goes through several stages of development. At the first stage of growth, the beveled tinder fungus is an outgrowth on a tree trunk, with sizes from 5 to 20 (sometimes up to 30) cm.The shape of the outgrowth is irregular, hemispherical, having a black-brown or black surface covered with cracks, tubercles and roughness. An interesting fact is that mown tinder fungi grow only on living, developing trees, but this fungus stops growing on dead tree trunks. From this moment, the second stage of development of the fruiting body begins. On the opposite side of the dead tree trunk, a prostrate fruit body begins its development, which initially has the appearance of a filmy and lobed mushroom, having a width of no more than 30-40 cm and a length of up to 3 m.The hymenophore of this fungus is tubular, the edges of the fruit body are characterized by brown-brown or woody, tucked up. The hymenophore tubes are inclined at an angle of about 30 ºC during their growth. As the tinder fungus ripens, it destroys the bark of a dead tree, and after the mushroom pores are sprayed, the fruit body becomes dark and gradually dries up.
The mushroom flesh of the cut tinder fungus is woody and very dense, characterized by a brownish or dark brown color. Whitish streaks are clearly visible on it, the pulp has no smell, but the taste when boiled is astringent, tart. Directly at the fruiting body, the pulp has a woody color and a small thickness, covered with a skin. In ripe mushrooms, it becomes dark.
The use of chaga in medicine
In official medicine, the following chaga medicines are used:
- Chaga, crushed dried raw materials - for the preparation of decoctions, infusions and tinctures.
- Alcohol tincture - as a general tonic for the treatment of depression, juvenile acne, spasms of internal organs.
- Broth - for diabetes mellitus to lower sugar levels, for chronic gastritis, intestinal atony. For a long time, the broth is used as an auxiliary therapy in the treatment of cancer.
- Infusion - for gastric diseases, to restore the body after infectious diseases and operations. Outwardly, the infusion is used for rinsing the mouth with tonsillitis, stomatitis, periodontal disease. Inhalations with infusion help to eliminate hoarseness, relieve inflammation in the airways.
- Befungin is a chaga extract combined with cobalt chloride. It is used to treat psoriasis, gastritis, gastrointestinal dyskinesia, intestinal atony, tumor pathologies.
Types of birch chaga
Related species of birch chaga are radiant and bristly-haired tinder fungi.
Radiant polypore, or inonotus radiant (Xanthopória radiáta)
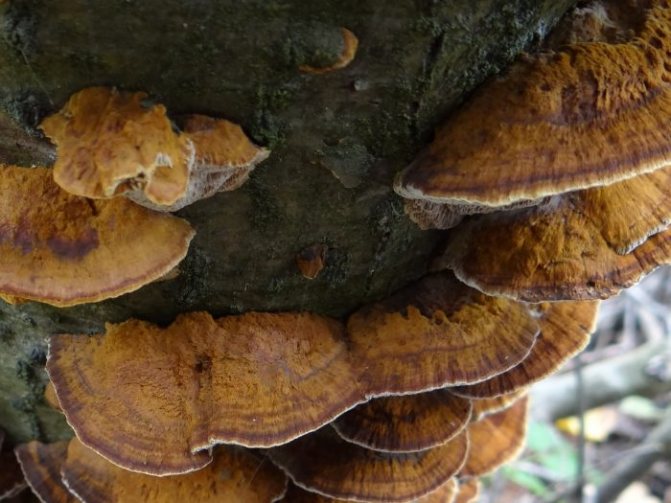

The fruiting body is annual, looks like a sessile, widely grown lateral cap, if there are several of them, then they form a kind of "tile". The length of the caps is about 5 cm, the width is 6-8 cm, and the thickness is 5-20 mm. The caps are flattened, the edge is sharp, in young mushrooms the surface is velvety, from yellow to reddish-brown, later becomes naked, shiny, rusty or dark brown, wrinkled. The pulp is shiny, fibrous, light brown or red-brown in color. The fungus infects the wood of deciduous trees, grows mainly on alder, rarely on birches. Found in the temperate zone of the Northern Hemisphere, in the Himalayas.
Bristly-haired polypore (Inonotus hispidus)
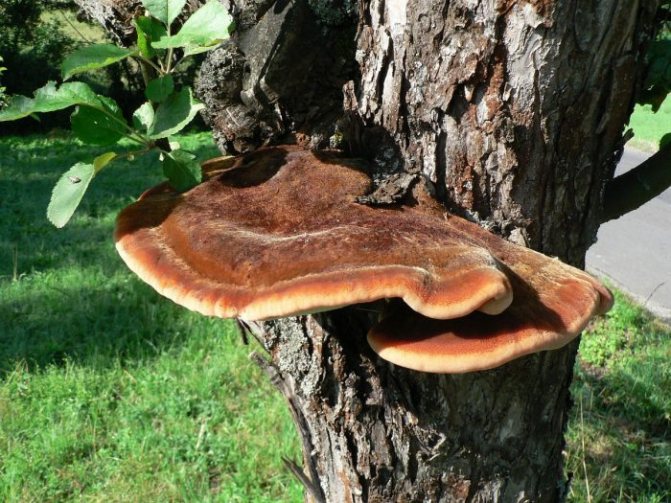

The fruiting body is annual, capped, sessile, solitary, or 2-3 caps form a "tile", widely growing to the substrate. The size of the cap is 10 × 16 × 8 cm. The surface of young mushrooms is colored red-orange, later red-brown or blackish, velvety-hairy. The pulp is brownish, light at the edge and surface of the caps, radially fibrous. The fungus is widespread in the temperate zone of the Northern Hemisphere, grows on broad-leaved trees, oaks, ash and apple trees, less often found on fir, maple, horse chestnut, alder, birch, hawthorn, beech, walnut, mulberry, pear, plane tree, poplar, plum.
Chaga - beneficial properties
Recent research has found that this mushroom has many benefits. Chaga, whose medicinal properties have already been proven, affects the body as follows:
- provides an antispasmodic effect;
- improves the functioning of the heart and brain;
- has a mild hypotensive effect;
- strengthens the body's defense system;
- participates in hematopoiesis;
- accelerates the process of scarring and subsequent restoration of injured tissues;
- relieves intoxication;
- normalizes blood glucose;
- prevents hyperpigmentation;
- enhances the work of anticancer drugs.
Porcini mushrooms on a birch. Mushrooms of Russian forests. White birch mushroom. The dream of any mushroom picker.
White birch mushroom (spikelet) (Latin Boletus betulicolus). This mushroom is a separate species or form of porcini mushroom. In some Russian regions, it acquired the local name spikelet. This was due to the fact that the first appearance of fruit bodies coincides with the earing of rye.
In the early summer time, I had to collect birch whites in the forests of various regions of Russia. And, almost always, I found them somewhere on hillocks, embankments, near old ditches, on abandoned roads and paths, lawns with dry white grass….
WHAT IT LOOKS LIKE:
Hat: up to 20 cm or more in diameter, up to 9 cm in thickness. At first, it is almost spherical, then hemispherical to cushion, smooth or somewhat wrinkled.
In dry weather, sometimes fissured, naked, dry, in wet weather, somewhat slimy, dull or shiny when dry. The color is whitish, sometimes buffy-yellowish or light brownish.
The tubular layer near the stem is deeply notched, easily separated from the pulp, white in youth, then turns yellow, then becomes olive green.
Leg: up to 15 cm in height, up to 6 cm or more in diameter. At a young age, usually tuberous or ovoid, then elongates, remaining more thickened downward.
It is solid, with a thin mesh pattern in the upper part of the leg, whitish, light brownish, often with the same shade as the cap, but more often lighter than the latter, especially at the top and at the very base.
The pulp is fleshy, strong, juicy, white. At a break or cut, the color does not change. The smell is pleasant, mushroom. Has no particular taste.
This mushroom grows exclusively under birch trees, it is found throughout the habitat, where there are birch forests and groves, as well as in forests mixed with birch. Fruiting from June to October. Often grows throughout Russia, as well as in Western Europe.
The pronounced taste and bright aroma of porcini mushrooms makes them an ideal product both for preparing independent dishes and for using as an additional ingredient in dishes with a complex composition.
What is not prepared from porcini mushrooms! Appetizers and salads, soups and main courses, pies and marinades. Porcini mushrooms are boiled, fried, stewed and baked, dried, pickled and salted ...
Just fried porcini mushrooms, stewed with sour cream, and good-quality nourishing buckwheat porridge cooked with boletus mushrooms, and stewed in the oven, and a refined puree soup with porcini mushrooms are equally tasty.
The aroma of porcini mushrooms, like no other, will be able to subtly emphasize the aroma of fried beef, baked chicken or stewed pork.
Interesting Facts

- The first documented case of the successful use of chaga in the treatment of cancer dates back to 1858.
- The earliest written references to the use of chaga as a medicine date back to the 12th century.
- Siberian peoples used a decoction of chaga for bathing children.
- Chaga preparations have been officially approved for use in the USSR since 1955, after extensive clinical trials.
- The Slavic tribes of the middle lane used chaga to make kvass.
Plants containing various groups of bioactive substances
Pharmacotherapeutic group. Antineoplastic, tonic agent. Reduces perspiration.
Composition and medicinal properties
Chaga contains elements that, in combination, provide a healing effect. The list of biologically active substances contained in a birch mushroom consists of:
- flavonoids;
- alkaloids;
- tannins;
- groups of organic acids.
Each of the elements in the composition of chaga has an individual effect of a therapeutic nature:
- organic acids control and normalize the acid-base balance of the human body;
- flavonoids have anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, diuretic and choleretic effect;
- phytoncides provide antimicrobial effect;
- alkaloids have a beneficial effect on the heart muscle;
- tannins strengthen and restore the mucous membrane and skin (used for bleeding and inflammation);
- melanin stimulates metabolic processes and restores the body.
Additionally, chaga contains minerals and trace elements. Of these, the most beneficial to human health are:
- magnesium - effective for diseases of bones, joints, teeth, heart, gastrointestinal tract, nerve tissues;
- potassium - helps to treat diseases of the blood, heart, kidneys, and has an antitoxic effect;
- iron - normalizes blood formation and tissue respiration, liver and spleen function, prevents anemia;
- manganese - strengthens bone tissue, improves the absorption of vitamins, relieves inflammation;
- copper - has a beneficial effect on hemoglobin, skin, hair, cellular respiration, oxygen supply, the construction of bone tissue, the work of the nervous system.
Also, the composition of chaga is filled with zinc, cobalt, nickel, silver and aluminum. Most of the elements contained in birch mushrooms are beneficial to human health. Therefore, chaga is used not only in medicine, but also in cosmetology.
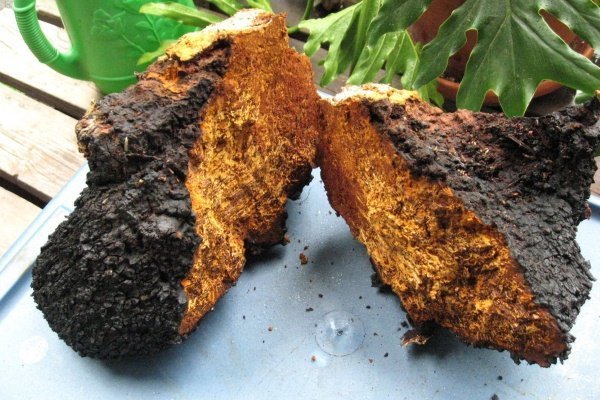

Other information about the mushroom
It is recommended to harvest chaga only on live trees, and preferably in spring. It is during this period of time that the trunks of the wood are best seen. In this case, the collected growth should not be loose, but very dense.You should cut off young mushrooms of the mown tinder fungus with a sharp knife, and the old fruiting bodies of the chaga are cut off with an ax. It is recommended to chop the mushroom into pieces of 5-6 cm in size. Before further use, they are dried in the oven at a temperature of about 60 degrees. Dried chaga should be stored for no more than 2 years.
LAT
Specifications:
| Group: | Tubular |
|---|---|
| Plates: | Beige, brown |
| Colour: | Dark brown or black |
| Info: | Woody pulp |
Systematics:
| Department: | Basidiomycota (Basidiomycetes) |
|---|---|
| Subdivision: | Agaricomycotina (Agaricomycetes) |
| Class: | Agaricomycetes (Agaricomycetes) |
| Subclass: | Incertae sedis (indefinite) |
| Order: | Hymenochaetales |
| Family: | Hymenochaetaceae |
| Genus: | Inonotus |
| View: | Inonotus obliquus (Tinder fungus) |
Among all the tinder mushrooms, the mown tinder fungus (hereinafter I will simply call it chaga) undoubtedly stands out. Probably none of the representatives of the kingdom of mushrooms has such a long "romance" with medicine. Here I will not even try to list all the ways of using chaga in classical and traditional medicine, because this is a topic for a separate and rather large article. I will only say that the first mentions of the use of chaga for medical purposes in Russia date back to pre-Christian times; this mushroom was also well known to the peoples of the Far East and Siberia.
Eleocharis mini
Eleocharis mini belongs to the dwarf varieties of the aquarium plant. It produces a large number of leaves and forms a bush, but its height does not exceed 5-7 cm.
Eleocharis mini is suitable for decorating the front edge of the aquarium, creating a depth effect. Under favorable conditions, it grows rapidly, filling the bottom surface. Prefers sandy soil, the thickness of which should be at least 5-7 cm.
The rhizome is developed, lobed. The plant is planted in bunches at a distance of 2 cm from each other. Eleocharis mini tolerates a water temperature of + 15 ... + 28 ° C. The recommended hardness is 4-15 dH, and the acidity is 5.5-8 pH. To accelerate growth, it is advisable to fertilize with CO2 at the rate of 5-10 mg / l once a month. Additionally, mineral fertilizers are applied.
To bookmarks
Interesting facts about the mushroom
The drug Brefulgin is made from chaga, which is indicated for peptic ulcer disease, chronic gastritis and oncological diseases. No wonder. The fungus has a positive effect on the human body, preventing the development of many diseases and eliminating existing ones.
This mushroom is also mentioned in Solzhenitsyn's novel Cancer Ward. In the work, he is presented in the form of a drug that treats cancer.
Another interesting fact that everyone should know. The best mushroom, which will be rich in vitamins and minerals, is in the highest place. The higher the chaga, the more beneficial properties.
All useful properties are preserved only during natural drying without the help of an oven. Of course, this requires more time, but all trace elements and substances will have a positive effect on the treatment and prevention of diseases.
The shelf life is approximately 2 years if stored properly. It is recommended to grind chaga into powder only before use.