Root rot protection
To protect against root rot, it is recommended to carry out a set of preventive and extermination measures aimed at increasing the biological resistance of plantings and eliminating sources of infection:
conduct systematic supervision of the state of plantings, the appearance and spread of root rot;
create optimal conditions for the growth and development of woody plants (timely care, application of fertilizers and microelements, the use of growth stimulants, etc.), excluding their weakening and increasing biological resistance;
prevent trampling and compaction of the soil, which is accompanied by weakening of plants, exposure of root paws and mechanical damage to the roots and root collar of trunks, which are the gateway to infection;
when caring for plantings, the trunks and roots should be protected from mechanical damage through which pathogens of root rot penetrate;
to carry out raking of the litter, along which the rhizomorphs of the autumn mildew can spread and infect healthy plants;
remove from the plantations young drying and shriveled trees along with roots, which are sources of infection;
after cutting down older trees in order to eradicate sources of infection, it is necessary to uproot the stumps together with the roots, followed by their removal and destruction;
the pits formed after the removal of the affected stumps should be treated with a copper-containing fungicide - kartocide and covered with earth;
in the areas vacated after the uprooting of affected stumps, it is recommended to plant trees and shrubs no earlier than 2-3 years later.
Medicinal properties and contraindications in traditional medicine
Tinder fungus sulfur-yellow contains many bioactive substances - amino acids, glycosides, steroids, which are used to create drugs:
- an anti-thrombotic drug based on lecithin, which has a hemolytic effect;
- an aqueous extract of fresh mushrooms to inhibit the growth of sarcoma-180 and Ehrlich's carcinoma;
- methanol extract of mycelium to suppress the growth of cancer cells;
- drugs based on eburicoic acid for lowering blood sugar levels and treating endocrine diseases;
- dried and ground mushrooms can be used in place of tea daily as a cancer prevention agent.
Healing tincture of Letyporus
It is applied for:
- strengthening weakened immunity;
- prevention of bacterial and viral infections;
- treatment of tumors of the mammary and prostate glands and blood diseases;
- improving the well-being of women in menopause;
- enhancing sexual performance in men.
The tincture is easy to prepare at home:
- Take 40 grams of shredded mushroom.
- Pour 0.5 liters of 20% alcohol (or 250 g of vodka + 250 g of boiled water).
- Insist 3 days.
To strengthen immunity and prevent various diseases, take 1 tablespoon, 3 times a day before meals. The course of treatment is 10 days. You need to store the tincture in the refrigerator.
Contraindications for taking drugs based on sulfur-yellow tinder fungus:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, in particular, gastritis and gastric ulcer;
- pregnancy, breastfeeding;
- age under 18;
- individual intolerance.
Where does the tinder fungus grow, collection features
Tinder fungus is considered a perennial fungus, therefore, it can be found in nature all year round. Hardwoods are preferred for tinder fungi - alder, beech, larch, birch, cherry, willow, poplar, etc. On spruce, eucalyptus and yew, tinder fungi are rare guests. They like to "settle" at the bottom of infected trunks. Parks and forests, urban plantings, roadside trees are not bypassed.
Tinder fungi are found throughout Russia, with the exception of the Far North.They are harvested more often in August-November. If the mushroom is old, use only its cap, while the young are collected along with the body. Tinder fungi almost do not salt and do not dry, preferring to use them fresh.

If the fruit body is large, it is easier to knock it off the tree with an ax or a stick. At the same time, you need to collect mushrooms only from living trees, dead ones are not suitable for harvesting.
Store tinder fungi in the refrigerator. You can buy them in two types - tinder fungus, peeled from bark and tinder fungus, peeled from its own outer crust. The pulp of the mushroom is cut into small pieces, and decoctions and infusions are already made with them. There are 1,500 species of Trudoviks in total, most of which are considered conditionally edible mushrooms. You need to collect tinder fungi only knowing exactly how they look.
Methods for growing umbrella tinder fungus.
The cultivation of these mushrooms is carried out mainly in two ways:
Method one. Polypores can be grown in rooms in which special conditions are observed: the air humidity must exceed 80%, the temperature must be maintained around 20 degrees, in addition, it is necessary to provide natural light and constant air circulation.

A mixture of various solid residues is used as a substrate, for example, corn cobs, bark, shavings, small branches, sawdust, reeds, and so on. The substrate is poured with boiling water. When the mixture has cooled to room temperature, mycelium is added to it, at the rate of 100 grams per 35 kilograms. The mixture is placed in transparent plastic bags. Several holes are made in the bags to allow air ventilation.
Method two. Also, umbrella tinder fungi can be grown in natural conditions. In this case, the harvest is expected after 4 months. As a substrate, wooden blocks and hemp are used. The substrate is soaked in water for 4 days. The bars are filed and mycelium is poured into them. For 35 kilograms of substrate, there are 100 grams of mycelium. The bars are placed in shaded areas. Disembarkation can be carried out at any time of the year. Under optimal conditions, fruiting begins, which occurs about 5 times a year.

Similar species.
Tinder fungus is a similar species. It is also popularly called the ram mushroom. The ram mushroom is distinguished by a darker color of hats. This tinder fungus looks like a bushy growth. The fruiting body consists of distinct “legs” that turn into “caps”. The color of the fruiting body can be gray-pink or gray-green. The pulp is brittle, white. The pulp has a very pleasant smell and taste - nutty.

Tinder fungus, like its relative, the umbrella tinder fungus, is listed in the Red Book of the Russian Federation. These mushrooms are not found every year. They grow on the stumps of oaks and maples, and are also found at the bases of living trees. Fruiting occurs from August to September.
Useful properties and contraindications
Today, the medicinal properties of the species, used in ancient times by Indian shamans during various rituals, are not subject to the slightest doubt. So, the high content of nutrients in fruiting body of tinder fungus, allows you to use it for healing wounds and eliminating inflammatory processes in the body.
In addition, Chinese scientists, who have found a fairly wide application for this fungus in alternative medicine, argue that the inclusion of pomace of the fetus in complex therapy improves metabolic processes, ensures the removal of heavy toxins from the body and helps in the fight against tumor neoplasms.
On the basis of tinder fungus, supporters of traditional medicine prepare various universal healing infusions and decoctions for external use, using them in the treatment of various ailments.
Good to know! The absence of toxic substances in the pulp of this miracle mushroom, provided that it grows in good environmental conditions, far from highways and industrial enterprises, makes it as safe as possible.
However, it does not do without contraindications, the list of which includes:
- hemorrhagic diathesis;
- hemophilia;
- any internal and external bleeding;
- decreased blood clotting;
- pregnancy and lactation.
It is also not recommended to give such medicines to children under 7 years of age and the elderly. This is explained by the fact that the fungus expands the walls of blood vessels and thins the blood, which is fraught with hemorrhage and increased bleeding. In addition, side effects remain possible, including eating disorders, pain in the stomach and peritoneum, acute allergic manifestations, general weakness and dizziness, and sometimes hallucinations.
Description of larch tinder fungus
Fruit bodies are perennial, sessile, solitary, hoof-shaped or elongated upward, almost cylindrical, thick, dense and hard, brittle with age, 3-20 x 5-20 x 4-40 cm.The surface is rough, concentrically-ribbed, with pale , whitish, yellow and brownish-brown areas, sometimes knobby, with a thin, strongly cracking crust.
The edge is obtuse, rounded, of the same color as the upper surface. The pulp is soft when fresh, later hardening, crumbly and loose, light, white or yellowish, bitter, with a mealy odor. The tubules are indistinctly layered, the same color as the tissue, 0.5-1 cm long in each layer. The surface of the spore-bearing layer is white to brownish. The pores are rounded to angular, at first with solid edges that eventually become torn, on average 3-5 per 1 mm (sometimes up to 1 mm in diameter).
A forest species growing on conifers in old-growth forests. Usually found at the base of living trunks of larch (Larix) and Siberian cedar (Pinus sibirca), less often parasitizes on fir (Abies) and Scots pine (Pinus silvestris).
In Russia, the mushroom is found in the European part, in the Urals, Siberia and the Far East.
Polypores are mutable and sheep
Tinder fungus is changeable. The cap is 3–8 cm in diameter, regularly rounded or lingual, depressed at the point of attachment of the stem, often with an edge divided into lobes. The skin is golden yellow or light brown, with fine radial fibers at maturity. The tubular layer is descending, white or light cream in color. The pulp is tough, white or brown, the taste is soft, the smell of mushroom.
Leg. Diameter 0.5–1 cm, short, eccentric, lateral or central, light brown, almost black over time.
Spore powder. White.
Habitat. On dead hardwood.
Season. Spring - autumn.
Similarity. At a young age, the changeable tinder fungus looks like a scaly tinder fungus, but the cap of P. squamosus is covered with large scales.
Use. The mushroom is not poisonous, but due to its tough pulp, it is not eaten.
Sheep polypore, Sheep albatrellus, Sheep rudder. A hat with a diameter of up to 12 cm, convex or flat, smooth or fissured. The color is whitish or yellowish. Small tubes are white or yellowish, turn yellow when pressed. The flesh of young mushrooms is juicy, white, with a pleasant smell and taste, while the old ones are dry and bitter.
Leg. The height of the sheep tinder fungus is 2–7 cm, diameter is up to 4 cm, central or eccentric, solid, white.
Spore powder. White.
Habitat. In coniferous forests, it forms mycorrhiza with spruce.
Season. Summer autumn.
Similarity. With the confluent albatrellus (A. confluens), which has fawn or ocher caps and forms tight groups, and also grows under various conifers.
Use. All albatrellus species are edible but have a tough flesh.
Below you can find photos, descriptions and videos of other tinder fungi.
Scaly and varnished tinder fungi: photo and description
Scaly tinder fungus, motley, hare. The cap is 5-50 cm in diameter, 0.5-10 cm thick, whitish or creamy, with large pressed brown scales, making it variegated. The edge is usually more or less thin, often bent inward. Stem 4-8 × 1-4 cm, whitish-cream, almost black at the base. The tubular layer is white. The pulp is whitish, with a pleasant mealy smell and taste.Spore powder is white. Spores 10-14 × 4-5 (6) µm, oblong-ellipsoidal, smooth, colorless.
Growth. It grows on living and dead trunks and branches of fruit and broad-leaved trees.
Fruiting. June to September. Wound parasite. Having penetrated into the inner layers of the wood, the mycelium causes a yellowish-white internal rot.
Usage. Conditionally edible mushroom only at a young age (old mushrooms are tough).
Lacquered polypore. Basidiomas are annual or 2-3 years old with a cap and a leg. The cap is up to 25 cm in diameter and 1–3 cm thick, semicircular or kidney-shaped, covered with a shiny, lacquered, reddish, then reddish-purple, dark red or chestnut-brown and, finally, almost black crust. Leg up to 15 × 1–2 cm, sometimes short, eccentric, less often lateral, covered with the same crust as the cap, one color with the cap or almost black. The tubules are 0.5–2 cm long, ocher, with small and rounded pores.
As you can see in the photo, in the lacquered tinder fungus, the surface of the tubular layer is whitish, creamy, then turns brown, when pressed, it darkens:
The pulp is spongy-corky, hardening, white or light reddish. The hyphalous system is trimic. Spores 8-13x5.5-7.5 µm, ovoid or almost oval, truncated at the apex, warty.
The area where this tinder fungus grows in Russia is very wide. It is distributed in the Far East (Primorsky and Khabarovsk Territories, Jewish Autonomous, Amur, Sakhalin, Magadan and Kamchatka Regions), in the European part, in the Urals, in Siberia; outside Russia - in Europe, Asia, North Africa, North America.
Grows in deciduous, mixed and coniferous forests on stumps and deadwood of spruce, fir, larch, birch, in July - August, in small groups and singularly. The mushroom has medicinal properties. Grown in culture for food and medicinal purposes, maintained in pure culture in collections in many countries of the world, as well as in Russia.
Limiting factors. Human economic activity, leading to the removal of deadwood, deforestation, forest fires.
Below is another selection of photos of tinder fungi with a description.
Time and place of fruiting
The wood sponge inhabits the dead woods, stumps. Inhabits such woody coniferous and deciduous species of the territory of Russia and Europe:
- alder (Alnus);
- birch (Betula);
- hornbeam (Carpinus);
- beech (Fagus);
- spruce (Picea);
- pine (Pinus).
It is especially common in the European part, inhabits the North American continent. Bordered polypore is found on living diseased trees, more often lives on felled wood. Often it is brought into the house along with the building material. This is one of the representatives of the tinder fungus, capable of forming several fungi on the trunk.
The fruiting body of a bordered perennial tinder fungus, grows from the first ten days of May to November. The optimal conditions for harvesting are high humidity (up to 80%) and temperatures from 18 to 25 ° C. After being introduced into the nutrient medium, it bears fruit once.
Tinder beveled
Mowed polypore - Latin Inonotus obliquus
In another way, the mushroom is called Chaga, Tinderpot, Birch fungus, Black fungus, Wood fungus, Inonotus mowed or Black birch fungus.
Description of the mushroom
External characteristics
Young Chaga grows in the form of an uneven outgrowth on a tree trunk, reaching 5-20 cm. It is a semicircular cracked mass with black - brown or black colors, bumpy and rough to the touch. It is filled with hard brown or dark brown flesh with light veins. The pulp does not smell, after brewing it has an astringent tart aftertaste.
When the tree trunk dies off, the tinder fungus stops growing. On the other side of the fastening of the mushroom, a lobed, scarious, spreading outgrowth appears about thirty to forty centimeters wide and no more than 3 meters long.The bottom of the outgrowth is covered with tubes, the edges are tucked in and painted in a brownish-brown or woody shade. The fruit body is filled with a thin pulp that matches the color of wood, which darkens in old mushrooms, and is covered with skin.
Subsequently, when the bark of the tree collapses and the mushroom spores mature, the mushroom will darken and dry out.
Growing places
Tinder fungus, characterized by longevity, settles on birch, alder, mountain ash, willow and aspen trunks. The spores get caught in cracks in the bark and various depressions, and the fungus grows on the trees until they die and the trunk crumbles into dust. Due to the Black fungus, the wood is dominated by pith and white rot.
This fungus is rare, and the fact that we have a young chaga in front of us can be understood by the presence of sterile growths.
Cooking recipes
Young fruiting bodies of sulfur-yellow tinder fungus are tasty and are used in salads, fried, stewed (roast with potatoes), for making snacks and pie fillings. You can even make cutlets from them, dry them, cook salted, marinate them.
Primary processing
For safety reasons, a heat treatment of 40045 minutes is recommended. If there is complete confidence that the mushroom is real and not false, then 20-30 minutes is enough.
Cooking
Boiling mushrooms is one of the main operations before further cooking. The washed fruit bodies of the tinder fungus are placed in a saucepan with salted water and boiled for 40 minutes. After cooking, the water must be drained; it must not be used for food.
Frying
Fried mushrooms are one of the most delicious dishes. The sulfur-yellow tinder fungus must first be boiled, and then cut and fried.
Ingredients:
- 0.5 kg of boiled mushrooms;
- 2 onions;
- 4 tablespoons sunflower oil;
- 4 tablespoons tomato paste;
- salt and pepper to taste.
How to cook a sulfur-yellow tinder fungus:
- Cut the boiled tinder fungus into strips, the onion into half rings.
- Fry onions and mushrooms for 10 minutes in a skillet with sunflower oil.
- Add tomato paste, spices and simmer for another 5-10 minutes, stirring gently.
Pickling
Juicy pickled tinder fungi retain their useful and nutritious qualities and have a wonderful taste.
Ingredients: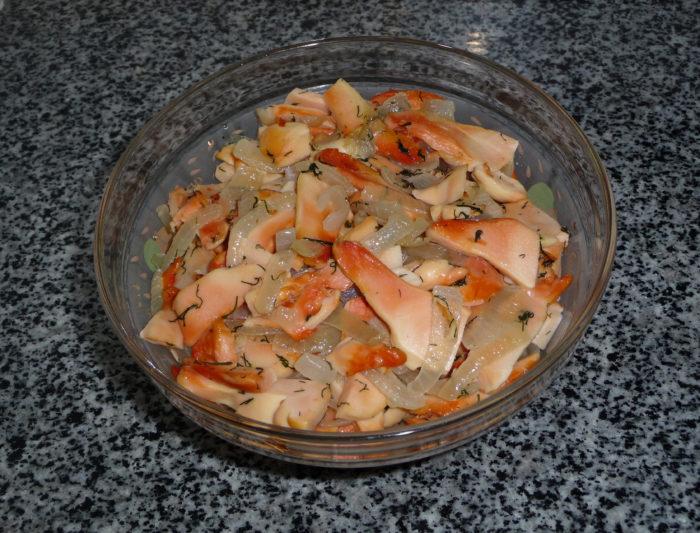
- 1 mushroom (about 2 kg);
- 300 g of water;
- 2 tbsp salt;
- 1 tbsp. l. Sahara;
- 100 ml of 9% vinegar;
- bay leaf - 3 pcs.;
- ground black pepper to taste.
How to pickle a chicken mushroom:
- Rinse the mushroom, cut into slices and place in a large saucepan.
- Add water, place over medium heat and bring to a boil.
- Add salt, sugar, spices (except vinegar) and simmer for 20 minutes.
- Add vinegar and leave for 10-12 hours at room temperature.
- When serving, sprinkle with unrefined sunflower oil, sprinkle with herbs.
- Store in the refrigerator for up to 2 weeks.
Canning for the winter
For long-term storage, put boiled hot pickled mushrooms according to the recipe described above in glass jars, add 1 tablespoon of 70% vinegar per 1 liter and close hermetically with an iron lid. If you have a large freezer, tinder fungi can be frozen.
Stewed mushroom
This method of cooking gives the mushroom pieces a more delicate soft consistency, the stewed tinder fungus can be used as a gravy for side dishes. Cooking will not take long:
- Take 0.5 kg of boiled tinder fungus and two onions, cut them into thin slices.
- Put chopped food in a frying pan with heated vegetable oil, add 3-4 tbsp. tablespoons of sour cream and sauté for 7-10 minutes, stirring occasionally.
- Close the lid and simmer over low heat for another 3-5 minutes.
Mushroom pate
It is easy to make a pate; such a dish can even be canned for the winter, but for this you need to slightly change the recipe by adding vinegar to the list of components.
Ingredients:
- 1 kg of mushrooms;
- 0.5 - 0.7 kg of onions;
- salt and pepper to taste.
Cooking step by step:
- Wash the mushrooms, cut into large pieces, put them in boiling water and cook for 40 minutes.
- Drain the water and leave the boiled tinder fungus to cool.
- Chop the onion and mix with the mushrooms, add salt and pepper.
- Fry in a large amount of sunflower oil, stirring regularly, until tender (10-15 minutes).
- Cover and simmer for another 5 minutes.
- The cooled mass must be ground in a blender until smooth.
Tinder fungus pate is perfect for making breakfast sandwiches. Spread the slices of bread with mayonnaise and put the pate on top.
- Peel 500 g of mushrooms, cut into large pieces and boil in salted water for 40 minutes. Drain the water, wait until it drains and the slices dry a little.
- Season with salt and pepper, squeeze out the juice of half a lemon, pour over with vegetable oil and stir.
- Place the mushrooms on a baking sheet and bake in the oven at 180 ° C for 15-20 minutes.
- Sprinkle with finely chopped parsley before serving.
Autumn honey agaric
Autumn honey fungus (Armillaria mellea) is the causative agent of white sapwood (peripheral) rot of roots and trunks. Currently, many researchers consider it not as a separate species of fungi, but as a complex of closely related species, differing in areas, morphological and biological features.
Many conifers and deciduous species, as well as fruit crops are affected. Often, honey fungus occurs as a saprotroph on dry, deadwood and stumps, but under certain conditions it turns into a parasitic way of life and infects living trees and shrubs, causing them to dry out.
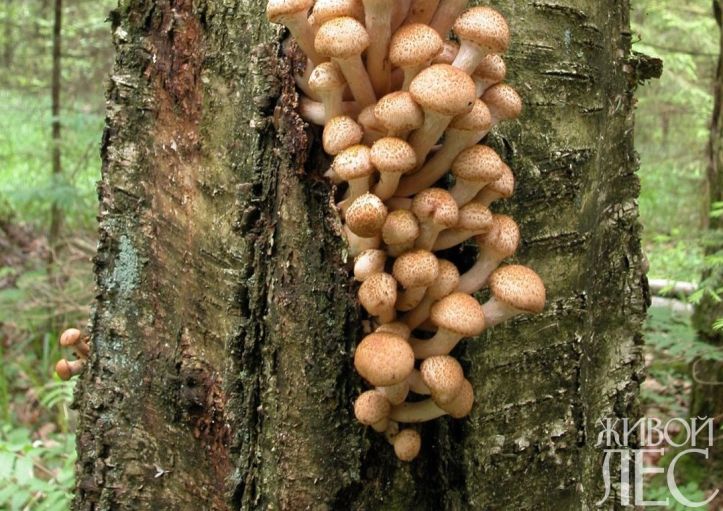

Mushroom on the trunk
Autumn honey agaric is widespread in different categories of forest and urban plantings.
- External signs of the disease in conifers are manifested in the thinning of the crown, yellow-green, yellow-brown or brown color of the needles, the presence of cracks and resinification in the butt of the trunks.
- When deciduous species are affected, the crowns of diseased trees become openwork due to crushing of leaf blades. Premature fall of foliage is often observed, cracks form in the butt of the trunks, from which a mucous liquid sometimes flows out.
The characteristic modifications of the mycelium (mycelium) in the form of films and rhizomorphs and fruiting bodies (basidiomas) are reliable signs of autumn honey fungus.
White fan-shaped films form under the bark of thick roots and trunks, covering a significant part of their surface. At first they are thin, but over time they thicken, turn yellow, partially split and transform into rhizomorphs.
- Rhizomorphs develop under the bark of roots and trunks and on the surface of the roots.
- Subcrustal rhizomorphs have the appearance of dark brown, flat, branching cords.
- The outer rhizomorphs are dark brown, almost black, rounded in cross section, similar to the roots of higher plants. They spread up to 30 m and infect healthy roots. Outside rhizomorphs can also move from infected roots to healthy ones through the litter.
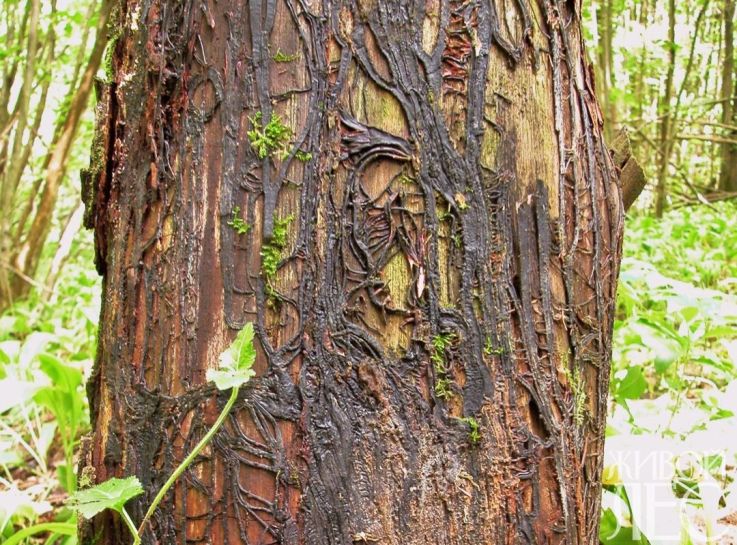

Rhizomorphs of the mushroom
The most active development and distribution of rhizomorphs occurs at high humidity and temperatures from +17 ° C to 25 ° C.
Fruiting bodies (basidiomas) of autumn honeydew have the appearance of annual caps on a central leg. Caps are convex or flat, often with a tubercle in the center, yellowish brown, grayish brown, covered with darker scales. The hymenophore is lamellar, white. Stem up to 10-15 cm long, slightly thickened at the base, light brown, fine-scaled, with a white fluffy ring under the cap. Fruiting bodies are formed in groups on old stumps, deadwood and dead wood trunks. In very rare cases, basidiomas can be found on the roots and at the base of the trunks of affected living trees.
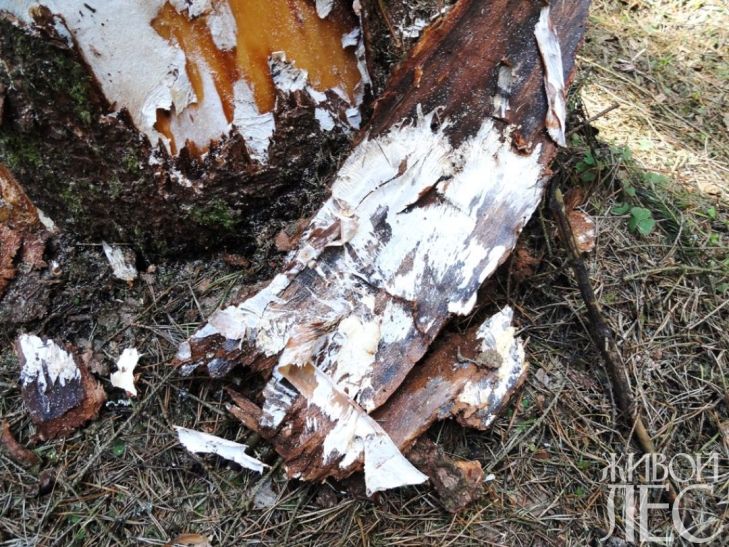

Honey mushroom films
The basidiospores formed on the hymenophore plates are spread by air currents, rainwater, animals and infect stumps and roots. The most active formation of basidiospores, their scattering and infection occurs at the end of summer - in autumn in humid warm weather.
Autumn honey fungus affects woody plants, as a rule, against the background of their preliminary weakening caused by various unfavorable factors (weather conditions, damage by other diseases, damage by pests, industrial air and soil pollution, etc.).
Difference from other types of tinder fungus
Despite the large number of varieties of the family, it is extremely difficult to confuse the fringed species with other tinder fungi, since it has a unique color. A similar variety is the oak tinder fungus, or, as it is also called, woody.
So, both species prefer to grow on trunks closer to the soil, choosing mainly a fresh log house, which is a potential victim of tinder fungus, getting into the risk zone. In addition, the oak mushroom also becomes covered with sticky drops in wet weather. But it does not do without significant differences, the main of which is the choice of the breed, because if the pine tinder fungus loves needles, then the oak tinder fungus grows exclusively on oaks.

(tree mushroom)
or burnt tinder fungus, false woody
✎ Affiliation and generic features
False tinder fungus (lat.Phellinus igniarius) and he is also a burnt tinder fungus, and among the people a tree fungus is a species of the genus fellinus (lat.Phellinus), an insignificant family of hymenochetes (lat.Hymenochaetaceae), of the same order, hymenochetes (lat.Hymenochaetales). In an exact and literal translation from Latin, its name means "cork". And it is this tinder fungus that is considered a false tinder fungus, that is: "a classic false tinder fungus" (or a false tree tinder fungus), although the same epithet (false) applies to many other species, for example, to: - false pine tinder fungus; - false tinder spruce; - false fir tinder fungus; - false aspen tinder fungus; - false oak tinder fungus; - a false plum tinder fungus, and, moreover, all these species are representatives of a single genus of fellinus. False tinder fungus, in adulthood, actually resembles something similar to a cork in the bark of a tree, but in fact it is a dangerous fungus-parasite (biotroph), which is related to the species of wood-destroying fungi that parasitize on rotten and rotten wood, or while still alive, climbing into damage to trees (cracks in the bark, broken branches or branches), causing colossal damage to forestry and parks. Recently, the false tinder fungus has been distributed into several special ranks (subspecies), slightly differing both in morphological characteristics and their confinement to parasitism on certain tree species, as well as in microscopic features. In appearance, the individual forms of the false tinder fungus practically do not differ from each other, but the original species of the false tinder fungus often affects either alder or birch, other varieties parasitize on aspen, ide, poplar, and other tree species. False tinder is a perennial creature, it does not belong to tubular mushrooms, because, unlike them, its tubules are inside the fetus itself, each year generating a "fresh" new layer, with the simultaneous overgrowing of the old one, while forming a hard, hoof-like outgrowth from rusty-brown to deep brown-chestnut color. False tinder fungus is related to inedible mushrooms due to the excessive rigidity of its pulp, which is not eliminated even by prolonged boiling and boiling, but it is used only for medical purposes.
✎ Healing properties
False tinder fungus (in the old days) in a crushed or ground form, was used as part of smoking mixtures. Well, in our time and in many regions of the planet, it is used in the guise of a medicinal resource. For example, in traditional Chinese medicine, it is used to prevent and treat cancer, diabetes, liver, heart and vascular diseases.And it is necessary to point out that despite the okay distribution of the false tinder fungus subspecies in almost all parts of the world, only one of them, which grows in Taiwan, has antitumor properties.
✎ Similar views
False tinder fungus has little resemblance to the species of its order, but sometimes it is confused with the present tinder fungus. And a distinctive feature of the present tinder fungus is its color and the peculiarity of fastening the fruit body to the tree, which manifests itself in the possibility of easy separation of the fruit from the trunk. And the main distinguishing feature of the false tinder fungus is already a powerful, monolithic and hoof-like fruit body, either dark brown or black, with a rusty-brown edging of a stiff tubular layer.
✎ Distribution in nature and seasonality
False tinder fungus is quite common in Europe and Russia, and is found in deciduous, mixed or coniferous forests, on trunks (more often birch), as well as on the roots of both living and dying, or already dead trees. Well, it can also be found in dead wood, on stumps and in dry wood, more often alone and less often in pairs. False tinder fungus forms fruits during the warmest period of the year, from May to December.
Removing toxins
The inhabitants of Ancient Rome and Greece believed in the healing effects of this mushroom family. In those days, a real tinder fungus cost a lot of money, so it was almost impossible for ordinary people to purchase it. But among the nobility, this mushroom became widespread, primarily due to the famous recipe of King Mithridates. This ruler made a tremendous discovery regarding the healing properties of tinder fungus and argued: if you constantly take a drug based on the mentioned mushroom, you can protect your body from toxins.
But the ability of the fungus to remove harmful substances without harm to health has already been established by modern scientists. Properly processed in tincture, the pulp is able to cope with even the strongest poisons like mercury dichloride, arsenic compounds and other dangerous variations that can accumulate in the human body for years. Later, the reason for such a unique function was revealed - the secret was in agaric acid, which has no natural analogues in modern science.






